

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (2): 76-87.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020530
杨春娇( ), 韩雨圳, 李忠馗, 张大才(
), 韩雨圳, 李忠馗, 张大才( ), 王洪斌, 栗宏林
), 王洪斌, 栗宏林
收稿日期:2020-12-01
修回日期:2021-04-06
出版日期:2022-02-20
发布日期:2021-12-22
通讯作者:
张大才
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: dczhang24@163.com基金资助:
Chun-jiao YANG( ), Yu-zhen HAN, Zhong-kui LI, Da-cai ZHANG(
), Yu-zhen HAN, Zhong-kui LI, Da-cai ZHANG( ), Hong-bin WANG, Hong-lin LI
), Hong-bin WANG, Hong-lin LI
Received:2020-12-01
Revised:2021-04-06
Online:2022-02-20
Published:2021-12-22
Contact:
Da-cai ZHANG
摘要:
导管是植物输导水分的通道,其结构的可塑性是植物适应生境的重要机制,也将决定水分输导的效率和安全性。矮生嵩草和大花嵩草是对水分依赖程度不同的生态类型,两者输导水分的效率和安全性是否存在差异?在藏东南高寒草甸沿土壤水分梯度设置6个样方,采集矮生嵩草和大花嵩草根系若干,采用石蜡切片和显微照相测量法,测量两种嵩草导管直径、管腔面积、管壁厚度等指标,利用相关性分析、单因素方差分析、主成分分析等方法,分析两种嵩草根系导管结构的动态变化及其对土壤水分的响应。结果表明:矮生嵩草管壁厚度与土壤含水率呈显著负相关,导管密度与土壤含水率呈显著正相关(P<0.01);大花嵩草管壁厚度和加固系数与土壤含水率呈显著负相关,管腔面积和导管平均直径与土壤含水率呈显著正相关(P<0.01)。矮生嵩草导管密度和加固系数显著高于大花嵩草,水分输导安全性得到很好的保护;大花嵩草管腔面积、导管平均直径、水力直径显著高于矮生嵩草(P<0.01),水分输导效率优势明显。矮生嵩草窄导管和中型导管比例相当,对水分输导效率和输导安全性的调节能力强;大花嵩草始终以中型导管占比最高,对水分输导效率和输导安全性的调节能力弱。不同生态类型植物对生境干旱化的适应策略不同,矮生嵩草属于耐旱型植物,对水分输导效率和输导安全性的调节能力强,对干旱生境适应能力强;大花嵩草属于湿润型植物,水分输导效率高,但输导安全性低,对干旱生境的适应能力弱。
杨春娇, 韩雨圳, 李忠馗, 张大才, 王洪斌, 栗宏林. 藏东南高寒草甸两种嵩草根系导管解剖结构对生境干旱化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 76-87.
Chun-jiao YANG, Yu-zhen HAN, Zhong-kui LI, Da-cai ZHANG, Hong-bin WANG, Hong-lin LI. Responses of root vessel anatomical structures to drought exposure for two Kobresia species in an alpine meadow habitat in Southeast Tibet[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(2): 76-87.
样方编号 No. of sample | 土壤含水率 Soil water content (%) | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 地形 Landform | 地理坐标 Longitude and latitude | 优势种 Dominant species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 22.4 | 4803 | 陡坡Steep slope | 29°71′94″ N, 98°04′53″ E | 矮生嵩草 K. humilis |
| S2 | 30.3 | 4773 | 陡坡Steep slope | 29°72′61″ N, 98°04′51″ E | 矮生嵩草 K. humilis |
| S3 | 37.6 | 4766 | 陡坡Steep slope | 29°71′08″ N, 98°04′48″ E | 矮生嵩草 K. humilis |
| S4 | 42.9 | 4762 | 缓坡Gentle slope | 29°71′58″ N, 98°04′24″ E | 矮生嵩草 K. humilis |
| S5 | 49.9 | 4759 | 平坦Flat | 29°72′95″ N, 98°04′08″ E | 矮生嵩草 K. humilis 大花嵩草 K. macrantha |
| S6 | 58.7 | 4758 | 溪边By the stream | 29°72′81″ N, 98°04′37″ E | 大花嵩草 K. macrantha |
表1 样方信息表
Table 1 Information of sample plots
样方编号 No. of sample | 土壤含水率 Soil water content (%) | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 地形 Landform | 地理坐标 Longitude and latitude | 优势种 Dominant species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 22.4 | 4803 | 陡坡Steep slope | 29°71′94″ N, 98°04′53″ E | 矮生嵩草 K. humilis |
| S2 | 30.3 | 4773 | 陡坡Steep slope | 29°72′61″ N, 98°04′51″ E | 矮生嵩草 K. humilis |
| S3 | 37.6 | 4766 | 陡坡Steep slope | 29°71′08″ N, 98°04′48″ E | 矮生嵩草 K. humilis |
| S4 | 42.9 | 4762 | 缓坡Gentle slope | 29°71′58″ N, 98°04′24″ E | 矮生嵩草 K. humilis |
| S5 | 49.9 | 4759 | 平坦Flat | 29°72′95″ N, 98°04′08″ E | 矮生嵩草 K. humilis 大花嵩草 K. macrantha |
| S6 | 58.7 | 4758 | 溪边By the stream | 29°72′81″ N, 98°04′37″ E | 大花嵩草 K. macrantha |
水分梯度 Water gradient | 土壤含水率 Soil water content(%) | 各实验对象及重复的样本量Sample sizes of each subjects and replicates | 合计样本量 Total sample size | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 矮生嵩草K. humilis | 大花嵩草K. macrantha | |||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| 1 | 22.4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 30 |
| 2 | 30.3 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 30 |
| 3 | 37.6 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 30 |
| 4 | 42.9 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 30 |
| 5 | 49.9 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 30 |
| 6 | 58.7 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 30 |
表2 实验设计
Table 2 Design of experiment
水分梯度 Water gradient | 土壤含水率 Soil water content(%) | 各实验对象及重复的样本量Sample sizes of each subjects and replicates | 合计样本量 Total sample size | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 矮生嵩草K. humilis | 大花嵩草K. macrantha | |||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| 1 | 22.4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 30 |
| 2 | 30.3 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 30 |
| 3 | 37.6 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 30 |
| 4 | 42.9 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 30 |
| 5 | 49.9 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 30 |
| 6 | 58.7 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 30 |
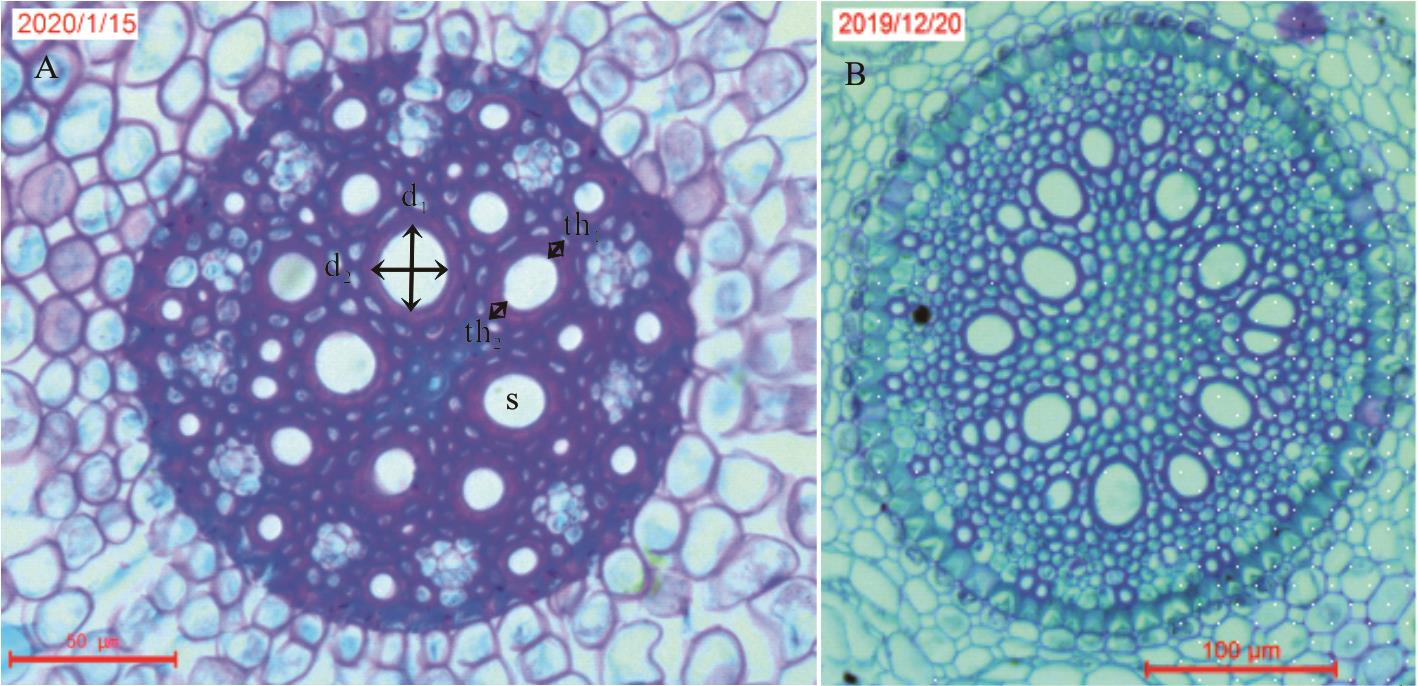
图1 矮生嵩草和大花嵩草根中柱横切面解剖图A.矮生嵩草根中柱横切面(10×40);B. 大花嵩草根中柱横切面(10×20)。A. Cross section of middle column of K. humilis under 40 times microscope; B. Cross section of middle column of K. macrantha under 20 times microscope.
Fig.1 Anatomic graph of the middle column, root cross section of K. humilis and K. macrantha
指标 Indices | 单位 Unit | 测量与计算方法 Methods of measurement and calculation | 每个生境数据量 Date volume per habitat | 总数据量 Total data |
|---|---|---|---|---|
管腔面积 Lumen area (s) | μm2 | 测量根横切面上每个导管的内腔面积。The lumen area of each vessel was measured. | 公式1 Formula 1 | 1055 |
导管平均直径 Average diameter of vessel ( | μm | 测量每个导管互相垂直方向上的两组直径(d1, d2),以平均值作为每个导管的直径。Two groups of diameters(d1, d2) of each vessel perpendicular to each other were measured, and the average value was calculated as the diameter of each vessel. | 公式1 Formula 1 | 1055 |
水力直径 Hydraulic diameter (dh) | μm | 同一条根所有导管计算1个水力直径,n代表每条根中导管数量,计算方法见 | 15 | 90 |
管壁厚度 Wall thickness (th) | μm | 每个导管随机测两组壁厚(th1, th2),以平均值作为该导管的管壁厚度。 The wall thickness(th1, th2) of each catheter was measured randomly, and the average value was calculated as the wall thickness of the vessel. | 公式1 Formula 1 | 1055 |
加固系数 Coefficient reinforcement (cwr) | 公式1 Formula 1 | 1055 | ||
导管密度 Vessel density (p) | n·mm-2 | 测量根横切面面积(a),计数根横切面上所有导管个数(n),根据 | 15 | 90 |
表 3 导管结构参数测量方法与数据量
Table 3 Measurement method and data quantity of vessel structures variables
指标 Indices | 单位 Unit | 测量与计算方法 Methods of measurement and calculation | 每个生境数据量 Date volume per habitat | 总数据量 Total data |
|---|---|---|---|---|
管腔面积 Lumen area (s) | μm2 | 测量根横切面上每个导管的内腔面积。The lumen area of each vessel was measured. | 公式1 Formula 1 | 1055 |
导管平均直径 Average diameter of vessel ( | μm | 测量每个导管互相垂直方向上的两组直径(d1, d2),以平均值作为每个导管的直径。Two groups of diameters(d1, d2) of each vessel perpendicular to each other were measured, and the average value was calculated as the diameter of each vessel. | 公式1 Formula 1 | 1055 |
水力直径 Hydraulic diameter (dh) | μm | 同一条根所有导管计算1个水力直径,n代表每条根中导管数量,计算方法见 | 15 | 90 |
管壁厚度 Wall thickness (th) | μm | 每个导管随机测两组壁厚(th1, th2),以平均值作为该导管的管壁厚度。 The wall thickness(th1, th2) of each catheter was measured randomly, and the average value was calculated as the wall thickness of the vessel. | 公式1 Formula 1 | 1055 |
加固系数 Coefficient reinforcement (cwr) | 公式1 Formula 1 | 1055 | ||
导管密度 Vessel density (p) | n·mm-2 | 测量根横切面面积(a),计数根横切面上所有导管个数(n),根据 | 15 | 90 |
指标 Indices | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient (R) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 矮生嵩草K. humilis | 大花嵩草K. macrantha | |||
| 土壤含水率Soil water content | 盖度Coverage | 土壤含水率Soil water content | 盖度Coverage | |
| 管壁厚度 Wall thickness | -0.131** | -0.218** | -0.185** | -0.170** |
| 加固系数 Coefficient reinforcement | -0.038 | -0.082** | -0.333** | -0.387** |
| 导管密度 Vessel density | 0.386** | 0.339** | -0.194 | -0.167 |
| 管腔面积 Lumen area | -0.053 | -0.061* | 0.162** | 0.167** |
| 导管平均直径 Average diameter | -0.053 | -0.051 | 0.180** | 0.208** |
| 水力直径 Hydraulic diameter | -0.008 | 0.021 | 0.153 | 0.174 |
表4 两种嵩草植物根系导管结构与土壤含水率及其群落盖度之间的相关关系
Table 4 Correlation between root vessel structure and community coverage or soil water content for two Kobresia species
指标 Indices | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient (R) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 矮生嵩草K. humilis | 大花嵩草K. macrantha | |||
| 土壤含水率Soil water content | 盖度Coverage | 土壤含水率Soil water content | 盖度Coverage | |
| 管壁厚度 Wall thickness | -0.131** | -0.218** | -0.185** | -0.170** |
| 加固系数 Coefficient reinforcement | -0.038 | -0.082** | -0.333** | -0.387** |
| 导管密度 Vessel density | 0.386** | 0.339** | -0.194 | -0.167 |
| 管腔面积 Lumen area | -0.053 | -0.061* | 0.162** | 0.167** |
| 导管平均直径 Average diameter | -0.053 | -0.051 | 0.180** | 0.208** |
| 水力直径 Hydraulic diameter | -0.008 | 0.021 | 0.153 | 0.174 |
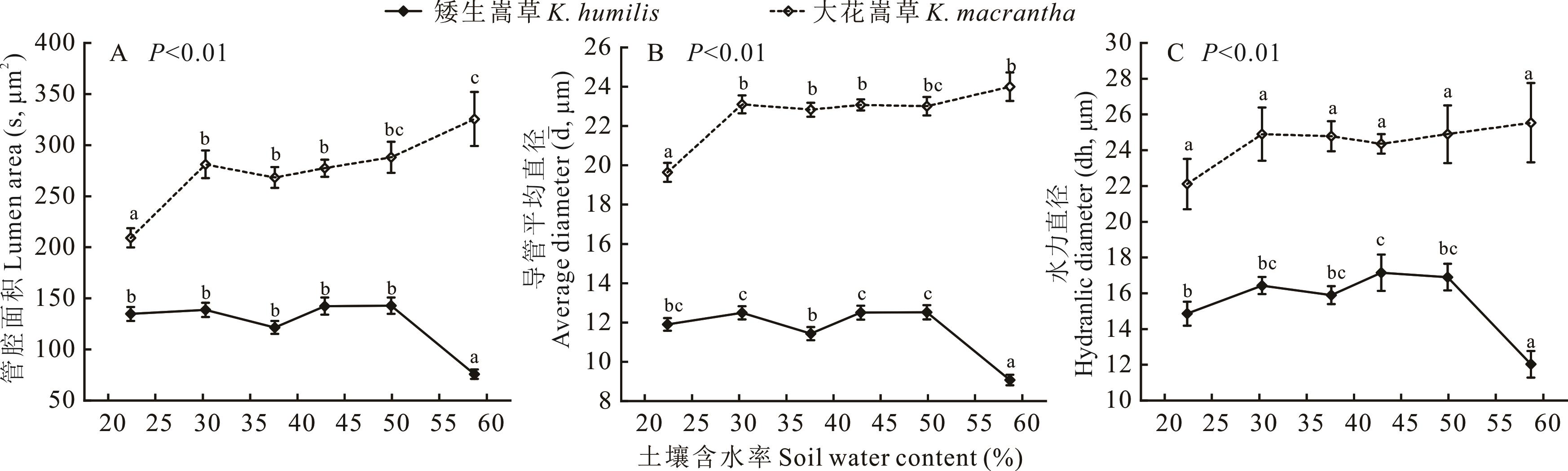
图3 矮生嵩草和大花嵩草管腔面积、导管平均直径、水力直径随土壤水分梯度的变化规律不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。Different letters indicate significant difference at P<0.05.
Fig.3 Variations of lumen area, average diameter of vessel and hydraulic diameter of K. humilis and K. macrantha with soil water gradient
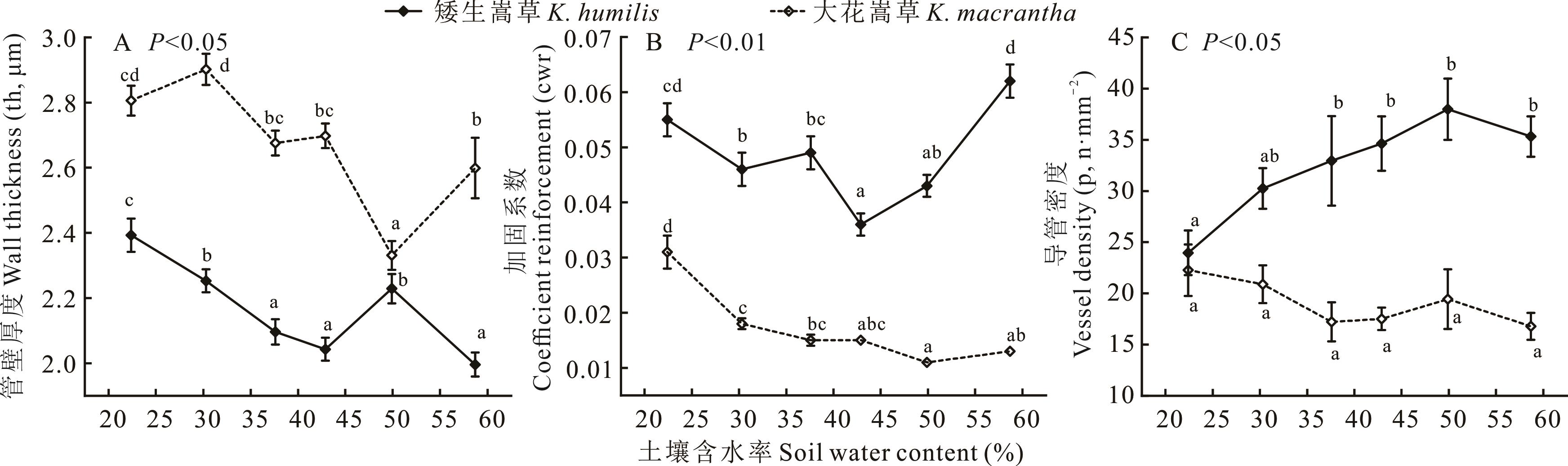
图4 矮生嵩草和大花嵩草管壁厚度、导管加固系数、导管密度随土壤水分梯度的变化规律
Fig.4 Variations of wall thickness, coefficient reinforcement and vessel density of K. humilis and K. macrantha with soil water gradient
指标 Indices | 矮生嵩草 K. humilis | 大花嵩草 K. macrantha | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 因子载荷 Factor loading | F | 排序 Rank | 因子载荷 Factor loading | F | 排序 Rank | ||||
| F1 | F2 | F1 | F2 | F3 | |||||
| 管腔面积Lumen area | -0.566 | 0.796 | -0.144 | 5 | 0.958 | -0.019 | -0.063 | 0.396 | 3 |
| 导管平均直径 Average diameter | 0.336 | 0.920 | 0.517 | 4 | 0.982 | 0.028 | 0.004 | 0.438 | 1 |
| 水力直径 Hydraulic diameter | -0.357 | 0.010 | -0.243 | 6 | -0.054 | -0.072 | -0.805 | -0.250 | 6 |
| 管壁厚度 Wall thickness | 0.986 | -0.022 | 0.674 | 2 | 0.306 | 0.933 | 0.051 | 0.437 | 2 |
| 加固系数 Coefficient reinforcement | 0.903 | 0.059 | 0.642 | 3 | -0.492 | 0.846 | 0.036 | 0.058 | 5 |
| 导管密度 Vessel density | 0.981 | 0.022 | 0.684 | 1 | -0.102 | -0.009 | 0.801 | 0.156 | 4 |
| 特征值 Characteristic value | 3.31 | 1.49 | 2.23 | 1.59 | 1.30 | ||||
| 方差贡献率 Variance contribution rate (%) | 55.17 | 24.76 | 37.18 | 26.56 | 21.61 | ||||
| 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 55.17 | 79.93 | 37.18 | 63.73 | 85.35 | ||||
表5 两种嵩草导管结构的主成分特征向量、贡献率及因子排序
Table 5 Eigenvectors and contribution rates of principal components in vessel structures of K. humilis and K. macrantha
指标 Indices | 矮生嵩草 K. humilis | 大花嵩草 K. macrantha | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 因子载荷 Factor loading | F | 排序 Rank | 因子载荷 Factor loading | F | 排序 Rank | ||||
| F1 | F2 | F1 | F2 | F3 | |||||
| 管腔面积Lumen area | -0.566 | 0.796 | -0.144 | 5 | 0.958 | -0.019 | -0.063 | 0.396 | 3 |
| 导管平均直径 Average diameter | 0.336 | 0.920 | 0.517 | 4 | 0.982 | 0.028 | 0.004 | 0.438 | 1 |
| 水力直径 Hydraulic diameter | -0.357 | 0.010 | -0.243 | 6 | -0.054 | -0.072 | -0.805 | -0.250 | 6 |
| 管壁厚度 Wall thickness | 0.986 | -0.022 | 0.674 | 2 | 0.306 | 0.933 | 0.051 | 0.437 | 2 |
| 加固系数 Coefficient reinforcement | 0.903 | 0.059 | 0.642 | 3 | -0.492 | 0.846 | 0.036 | 0.058 | 5 |
| 导管密度 Vessel density | 0.981 | 0.022 | 0.684 | 1 | -0.102 | -0.009 | 0.801 | 0.156 | 4 |
| 特征值 Characteristic value | 3.31 | 1.49 | 2.23 | 1.59 | 1.30 | ||||
| 方差贡献率 Variance contribution rate (%) | 55.17 | 24.76 | 37.18 | 26.56 | 21.61 | ||||
| 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 55.17 | 79.93 | 37.18 | 63.73 | 85.35 | ||||
| 1 | Guo X M, Xiao X, Xu X Y, et al. Observation on the vessel elements of secondary xylem in late-ripening peach trees. Journal of Fruit Science, 2008, 25(1): 22-26. |
| 郭学民, 肖啸, 徐兴友, 等. 21世纪桃树次生木质部导管分子特征的观察. 果树学报, 2008, 25(1): 22-26. | |
| 2 | Shen Q D. A study on xylem anatomy and drought resistance mechanism of different mulberry varieties. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, 2019. |
| 沈萩荻. 不同品种桑树木质部解剖特征及抗旱机理的研究. 镇江: 江苏科技大学, 2019. | |
| 3 | Lv L X. Relationships between vulnerability to xylem embolism and soil moisture in poplar cuttings. Xianyang: Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University, 2015. |
| 吕琳雪. 杨树木质部栓塞脆弱性与土壤水分的关系. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2015. | |
| 4 | Zhou H H, Li W H, Ayup M, et al. Xylem hydraulic conductivity and embolism properties of desert riparian forest plants and its response to drought stress. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2012, 36(1): 19-29. |
| 周洪华, 李卫红, 木巴热克·阿尤普, 等. 荒漠河岸林植物木质部导水与栓塞特征及其对干旱胁迫的响应. 植物生态学报, 2012, 36(1): 19-29. | |
| 5 | Chen Q. Hydrodynamics modeling and flow resistance characteristics of tissue structure of plant vessel and trachied. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2016. |
| 陈琦. 植物木质部导管与管胞微结构流场建模与流阻特性研究. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2016. | |
| 6 | Zhu G L, Chen X B, Ahmad I, et al. Mechanism of plasticity of root vessel structure of Ziziphus jujuba var. spinosa adapting ecotopes along a natural drought gradient. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2018, 55(3): 764-773. |
| 朱广龙, 陈许兵, Ahmad Irshad, 等. 酸枣根系导管结构的可塑性对自然梯度干旱生境的适应机制. 土壤学报, 2018, 55(3): 764-773. | |
| 7 | Liu G Z, Liu G H, Lan Q, et al. Comparative study on morphological characteristics and ecological adaptability of vessel elements of Salix gordejevii and S. microstachya var. bordensis. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2016, 36(2): 316-322. |
| 刘冠志, 刘果厚, 兰庆, 等. 黄柳与小红柳导管分子形态特征及其生态适应性比较研究. 西北植物学报, 2016, 36(2): 316-322. | |
| 8 | Helga L. Wood and leaf anatomy in Sessea corymbiflora from an ecological perspective. Iawa Journal, 1997, 18(2): 157-168. |
| 9 | Ding J J, Zhang X, Chu G M, et al. Vessel characteristics and their plasticity in three desert plants. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2016, 30(9): 171-177. |
| 丁俊杰, 张鑫, 楚光明, 等. 三种荒漠植物导管特征及其可塑性研究. 干旱区资源与环境, 2016, 30(9): 171-177. | |
| 10 | Ou Q M, Ni J F, Ma R J. Relation between roots xylem pipe and drought-resistance in spring wheat. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2005, 25(3): 27-31. |
| 欧巧明, 倪建福, 马瑞君. 春小麦根系木质部导管与其抗旱性的关系. 麦类作物学报, 2005, 25(3): 27-31. | |
| 11 | Wang D, Zhang X M, Gan X H, et al. A comparative observation on morphological characteristics of vessel elements in secondary xylem of two plants in Fagus. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2016, 32(4): 14-20. |
| 王东, 张雪梅, 甘小洪, 等. 2种水青冈属植物次生木质部导管分子形态特征比较观察. 中国农学通报, 2016, 32(4): 14-20. | |
| 12 | Sherwin C. How wood evolves: a new synthesis. Botany, 2012, 90(10): 901-940. |
| 13 | Wei W, Zhou J J, Baima G W, et al. Study of resource investigation of Kobresia in Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 2019, 38(3): 80-85. |
| 魏巍, 周娟娟, 白玛嘎翁, 等. 西藏高原嵩草属植物资源调查研究. 中国野生植物资源, 2019, 38(3): 80-85. | |
| 14 | Li J L, Li X L. Research progress on environmental adaptability of Kobresia humilis in alpine meadow. Ecological Science, 2016, 35(2): 156-165. |
| 李积兰, 李希来. 高寒草甸矮嵩草的环境适应性研究进展. 生态科学, 2016, 35(2): 156-165. | |
| 15 | Jia Z, Jian C X, Xiong P F, et al. Relationship between community coverage and aboveground biomass in farming-withdrawn grassland in loess hilly gully region. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 27(1): 319-327. |
| 贾昭, 简春霞, 熊沛枫, 等. 黄土丘陵区退耕草地群落盖度与地上生物量关系. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(1): 319-327. | |
| 16 | Lou Y J, Zhao K Y, Ma K P. Change in floristic composition and species diversity of plant community along environment gradient in Honghe National Nature Reserve, China. Acta Eoologica Sinica, 2007(9): 3883-3891. |
| 娄彦景, 赵魁义, 马克平. 洪河自然保护区典型湿地植物群落组成及物种多样性梯度变化. 生态学报, 2007(9): 3883-3891. | |
| 17 | Wu J G, Zhou Q F. Geographical distribution pattern and climate characteristics of adaptation for Kobresia in China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2012, 36(3): 199-221. |
| 吴建国, 周巧富. 中国嵩草属植物地理分布模式和适应的气候特征. 植物生态学报, 2012, 36(3): 199-221. | |
| 18 | Zhang D C, Zhu Y H, Li S Z. Variation in stomatal characteristics of eight plant species along a soil moisture gradient in alpine meadow of the Dongda Mountains in Southeast Tibet. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(7): 36-46. |
| 张大才, 朱玉怀, 李双智. 东达山高寒草甸8种植物气孔特征沿土壤水分梯度的变化. 草业学报, 2018, 27(7): 36-46. | |
| 19 | Yang C J, Chen D R, Zhang D C. Root morphology and distribution characteristics of plants in different habitats of alpine meadow in Southeast Tibet. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2020, 42(4): 79-84. |
| 杨春娇, 陈玳汝, 张大才. 藏东南高寒草甸不同生境植物根系形态及分布特征. 中国草地学报, 2020, 42(4): 79-84. | |
| 20 | Zhang X S. The microscopic observation and biological production technology. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2012. |
| 张学舒. 显微观察与生物制片技术. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2012. | |
| 21 | Hacke U G, Sperry J S, Feild T S, et al. Water transport in vesselless angiosperms: conducting efficiency and cavitation safety. International Journal of Plant Sciences, 2007, 168(8): 1113-1126. |
| 22 | Wu J. SPSS statistical analysis from scratch. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2014. |
| 吴骏. SPSS统计分析从零开始学. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2014. | |
| 23 | Li J H, Zhou M, Zhu J Y, et al. Adaptability response of root architecture of Cotinus coggygria seedings to soil nutrient stress. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(3): 65-77. |
| 李金航, 周玫, 朱济友, 等. 黄栌幼苗根系构型对土壤养分胁迫环境的适应性研究. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(3): 65-77. | |
| 24 | Li G X, Zheng B J. Comparative study on morphological characteristics and ecological adaptability of vessel elements of ten Ribes L.varieties. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2014, 34(1): 25-31. |
| 李国秀, 郑宝江. 10种茶藨子属植物导管分子形态特征及其生态适应性比较研究. 植物研究, 2014, 34(1): 25-31. | |
| 25 | Gu L W, Liu S H, Zhang D W. Morphology structure of vessel element of Spiraea in Heilongjiang Province. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2015, 34(1): 71-77. |
| 谷利伟, 刘树焕, 张大维. 黑龙江绣线菊属15种植物导管分子形态结构研究. 电子显微学报, 2015, 34(1): 71-77. | |
| 26 | Jordan G J, Brodribb T J, Blackman C J, et al. Climate drives vein anatomy in Proteaceae. American Journal of Botany, 2013, 100(8): 1483-1493. |
| 27 | Zhu G L, Deng R H, Ma Y, et al. Changes in the vessel morphology of Ziziphus jujuba var. spinosa plants in response to natural drought-gradient ecotopes. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(24): 8268-8275. |
| 朱广龙, 邓荣华, 马茵, 等. 酸枣茎导管对自然梯度干旱生境响应的结构特征. 生态学报, 2015, 35(24): 8268-8275. | |
| 28 | Xu Q, Chen Y N. Response of anatomy and hydraulic characteristics of xylem stem of Populus euphratica Oliv. to drought stress. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2012, 20(8): 1059-1065. |
| 徐茜, 陈亚宁. 胡杨茎木质部解剖结构与水力特性对干旱胁迫处理的响应. 中国生态农业学报, 2012, 20(8): 1059-1065. | |
| 29 | Xin G L, Zheng J M, Ye Z Y, et al. Ecological anatomical characteristics of secondary xylem in Kandelia obovata Sheue. Plant Science Journal, 2015, 33(6); 792-800. |
| 辛桂亮, 郑俊鸣, 叶志勇, 等. 秋茄次生木质部的生态解剖学研究. 植物科学学报, 2015, 33(6): 792-800. | |
| 30 | Han L J, Lin Y H, Wu S M. The effect of latitudes on the structure of secondary xylem in Liriodendron chinense Sarg. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2001, 18(3): 375-377. |
| 韩丽娟, 林月惠, 吴树明. 不同纬度对鹅掌楸次生木质部结构的影响. 植物学通报, 2001, 18(3): 375-377. | |
| 31 | Zimmermann M H. Functional xylem anatomy of angiosperm trees. Netherlands: Springer, 1982. |
| 32 | Zhao X, Dong K H, Zhang Y, et al. Drought resistance and root anatomy of Lespedeza davurica (Laxm.) Schindl. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2011, 19(1): 13-19. |
| 赵祥, 董宽虎, 张垚, 等. 达乌里胡枝子根解剖结构与其抗旱性的关系. 草地学报, 2011, 19(1): 13-19. | |
| 33 | Zhang C M, Shi S L, Liu Z, et al. Effects of drought stress on the root morphology and anatomical structure of alfalfa(Medicago sativa) varieties with differing drought-tolerance. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(5): 79-89. |
| 张翠梅, 师尚礼, 刘珍, 等. 干旱胁迫对不同抗旱性苜蓿品种根系形态及解剖结构的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(5): 79-89. | |
| 34 | Tulik M. The anatomical traits of trunk wood and their relevance to oak (Quercus robur L.) vitality. European Journal of Forest Research, 2014, 133(5): 845-855. |
| 35 | Li J H, Wang Y Y, Xia J, et al. Responses of root physiological characteristics of different drought-tolerant cotton varieties to drought. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(10): 3453-3460. |
| 李军宏, 王远远, 夏军, 等. 两个不同耐旱性棉花品种根系生理特性对干旱的响应. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(10): 3453-3460. | |
| 36 | Hajek P, Leuschner C, Hertel D, et al. Trade-offs between xylem hydraulic properties, wood anatomy and yield in Populus. Tree Physiology, 2014, 34(7): 744-756. |
| 37 | Chu G M, Liu N, Niu P X, et al. The anatomy characteristics of xylem vessel of three typical desert plants in Junggar basin. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2016, 30(2): 104-109. |
| 楚光明, 刘娜, 牛攀新, 等. 准噶尔盆地三种荒漠植物木质部导管解剖特征. 干旱区资源与环境, 2016, 30(2): 104-109. |
| [1] | 王传旗, 刘文辉, 张永超, 周青平. 野生老芒麦苗期耐旱性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 127-136. |
| [2] | 李州, 彭燕, 尹淑霞, 韩烈保. 甘露糖对白三叶抗旱性、糖及糖醇类代谢物积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 85-93. |
| [3] | 李跃, 万里强, 李向林. 内源脱落酸生理作用机制及其与苜蓿耐旱性关系研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(11): 195-205. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||