

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (12): 104-114.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023060
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
李云昊1( ), 李仲贤2, 伏帅1, 张忠雪1, 茆士琴1, 冯琦胜1, 梁天刚1(
), 李仲贤2, 伏帅1, 张忠雪1, 茆士琴1, 冯琦胜1, 梁天刚1( ), 李彦忠1
), 李彦忠1
收稿日期:2023-03-02
修回日期:2023-05-26
出版日期:2023-12-20
发布日期:2023-10-18
通讯作者:
梁天刚
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: tgliang@lzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Yun-hao LI1( ), Zhong-xian LI2, Shuai FU1, Zhong-xue ZHANG1, Shi-qin MAO1, Qi-sheng FENG1, Tian-gang LIANG1(
), Zhong-xian LI2, Shuai FU1, Zhong-xue ZHANG1, Shi-qin MAO1, Qi-sheng FENG1, Tian-gang LIANG1( ), Yan-zhong LI1
), Yan-zhong LI1
Received:2023-03-02
Revised:2023-05-26
Online:2023-12-20
Published:2023-10-18
Contact:
Tian-gang LIANG
摘要:
苜蓿病害的准确快速识别是栽培苜蓿草地病害防治的关键。苜蓿病害鉴别对专业知识和识别工具及检测环境要求较高,传统的苜蓿病害识别往往需要采用显微观察等手段对叶片病害部位进行镜检,存在时效性差、成本高,难以实现大范围多点位的快速识别等弊端。近年来在图像识别领域的计算机视觉和深度学习得到快速发展,为苜蓿病害智能化识别提供了新途径。本研究利用13种常见苜蓿病害图像数据集,基于改进的AlexNet深度学习卷积神经网络,经过300次迭代训练,构建了苜蓿病害识别模型,并对比分析了不同图像输入分辨率的苜蓿病害识别精度。结果表明:13种苜蓿病害最优模型识别总体精度达到72%,最优图像输入尺寸为512像素×512像素;剔除识别精度过低的苜蓿病害样本图片后,褐斑病、霜霉病、炭疽病、黑茎叶斑病和小光壳叶斑病5类苜蓿病害的识别总体精度提高到92%,最优输入尺寸为1200像素×1200像素。这2种模型均能够实现对苜蓿主要病害的快速识别,研究结果可以为苜蓿病害智能检测系统的研发提供图像识别方面的技术支持。
李云昊, 李仲贤, 伏帅, 张忠雪, 茆士琴, 冯琦胜, 梁天刚, 李彦忠. 基于AlexNet的栽培苜蓿病害识别[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 104-114.
Yun-hao LI, Zhong-xian LI, Shuai FU, Zhong-xue ZHANG, Shi-qin MAO, Qi-sheng FENG, Tian-gang LIANG, Yan-zhong LI. Identification of cultivated alfalfa diseases based on AlexNet[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(12): 104-114.
| 分组Group | 苜蓿病害 Alfalfa disease | 样本 Samples (No.) | 清洗后样本 Samples after cleaning (No.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 锈病U. striatus | 98 | 80 |
| 2 | 霜霉病P. cubensis | 200 | 163 |
| 3 | 白粉病P. fusca | 148 | 95 |
| 4 | 黑茎叶斑病P. medicaginis | 197 | 174 |
| 5 | 尾孢黑茎叶斑病C. medicaginis | 225 | 203 |
| 6 | 褐斑病C. beticola | 405 | 361 |
| 7 | 黄斑病L. medicaginis | 78 | 65 |
| 8 | 葡柄霉叶斑病S. botryosum | 71 | 64 |
| 9 | 小光壳叶斑病L. briosiana | 302 | 260 |
| 10 | 壳针孢叶斑病S. medicaginis | 173 | 155 |
| 11 | 炭疽病B. anthracis | 284 | 213 |
| 12 | 黄萎病Cyanosis | 131 | 89 |
| 13 | 病毒病Mosaicvirus | 118 | 92 |
| 14 | 健康苜蓿Healthy alfalfa | 1020 | 908 |
表1 苜蓿病害数据集
Table 1 Alfalfa disease dataset
| 分组Group | 苜蓿病害 Alfalfa disease | 样本 Samples (No.) | 清洗后样本 Samples after cleaning (No.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 锈病U. striatus | 98 | 80 |
| 2 | 霜霉病P. cubensis | 200 | 163 |
| 3 | 白粉病P. fusca | 148 | 95 |
| 4 | 黑茎叶斑病P. medicaginis | 197 | 174 |
| 5 | 尾孢黑茎叶斑病C. medicaginis | 225 | 203 |
| 6 | 褐斑病C. beticola | 405 | 361 |
| 7 | 黄斑病L. medicaginis | 78 | 65 |
| 8 | 葡柄霉叶斑病S. botryosum | 71 | 64 |
| 9 | 小光壳叶斑病L. briosiana | 302 | 260 |
| 10 | 壳针孢叶斑病S. medicaginis | 173 | 155 |
| 11 | 炭疽病B. anthracis | 284 | 213 |
| 12 | 黄萎病Cyanosis | 131 | 89 |
| 13 | 病毒病Mosaicvirus | 118 | 92 |
| 14 | 健康苜蓿Healthy alfalfa | 1020 | 908 |
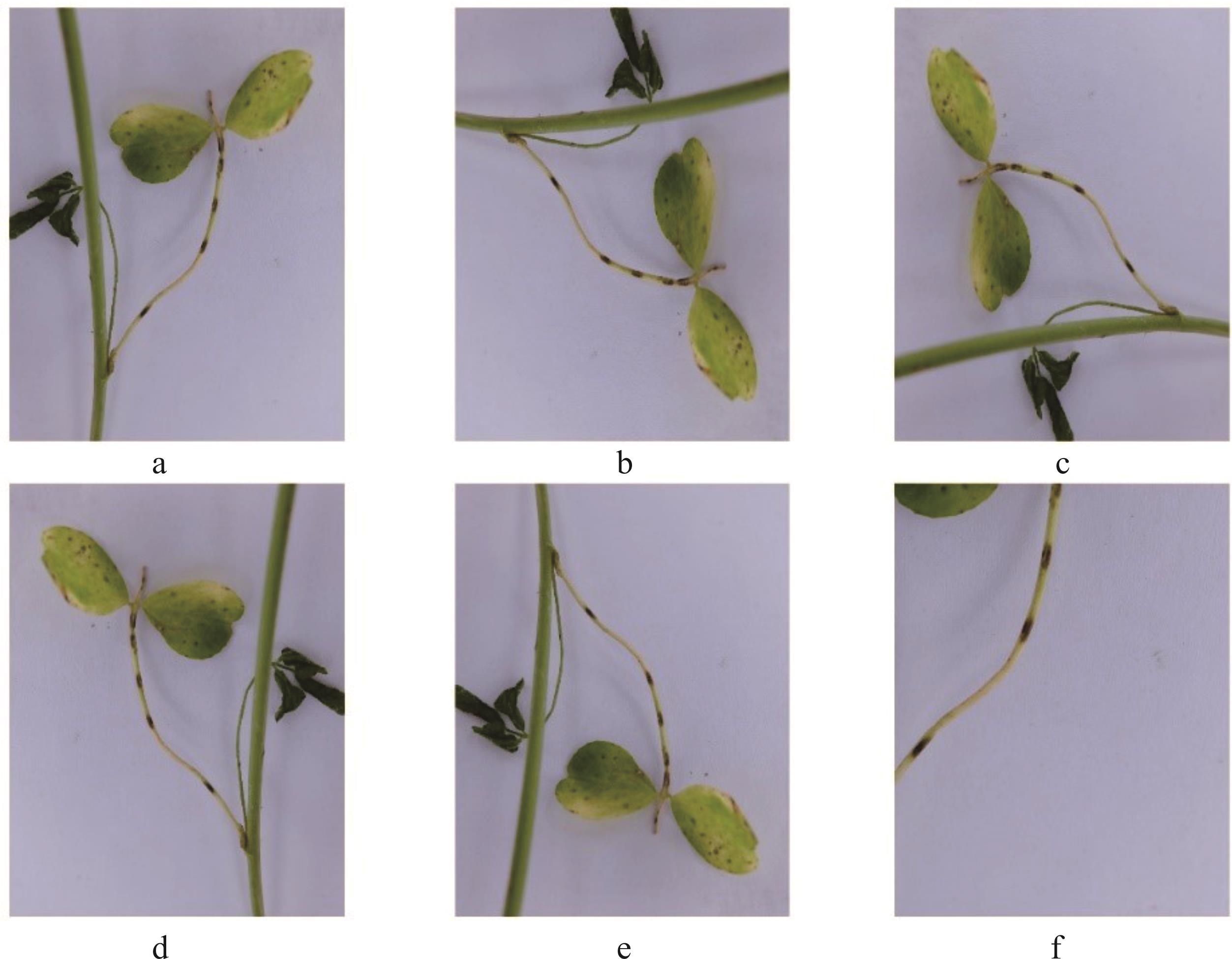

图2 数据增强a: 原图Original image; b: 顺时针旋转90°Rotate 90° clockwise; c: 顺时针旋转270°Rotate 270° clockwise; d: 水平经镜像翻转Flip horizontally through a mirror image; e: 处置镜像翻转Dispose of mirror flipping; f: 随机剪裁Randomly cut.
Fig.2 Examples of enhancing data
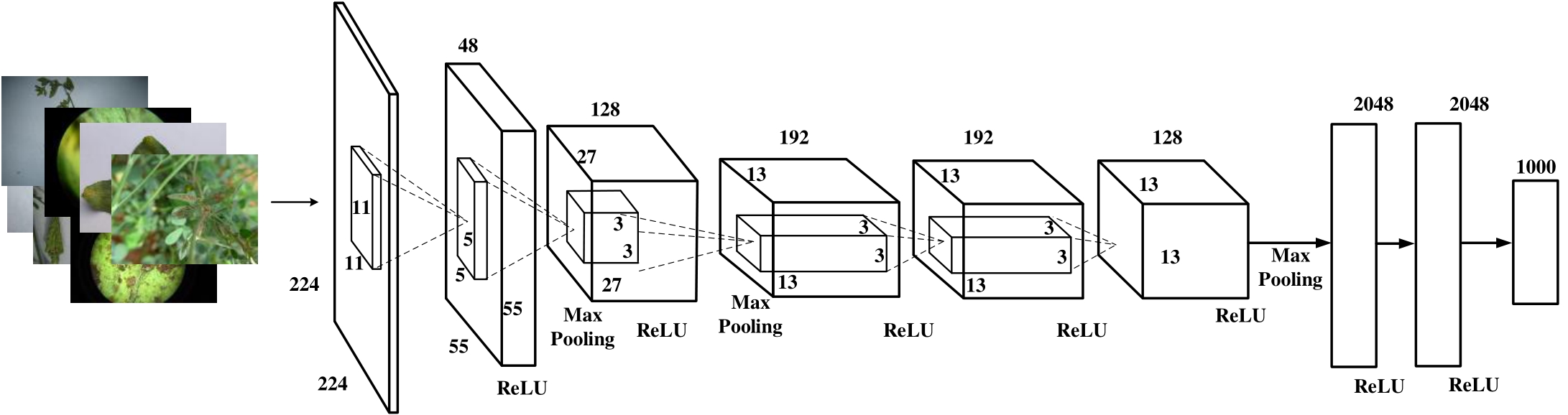
图3 简化型AlexNet网络结构图中数字以像素为单位,ReLU为网络所使用的激活函数,MaxPooling为最大池化。Numbers in the Figure are in pixels, ReLU (rectified linear unit) is the activation function used by the network, and MaxPooling is the maximum pooling.
Fig.3 Simplified structure of AlexNet model
项目 Item | 分组Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 训练输入尺寸Training input size (pixels) | 128×128 | 224×224 | 256×256 | 512×512 |
| 总体识别精度Overall recognition accuracy (%) | 68.2 | 71.3 | 70.2 | 72.5 |
表2 13类病害分组训练总体识别精度
Table 2 Overall recognition accuracy of group training for 13 kinds of diseases
项目 Item | 分组Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 训练输入尺寸Training input size (pixels) | 128×128 | 224×224 | 256×256 | 512×512 |
| 总体识别精度Overall recognition accuracy (%) | 68.2 | 71.3 | 70.2 | 72.5 |
项目 Item | 分组Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 训练输入尺寸Training input size (pixels) | 128×128 | 224×224 | 256×256 | 512×512 |
| 总体识别精度Overall recognition accuracy (%) | 81.6 | 82.5 | 83.3 | 83.7 |
表3 5类病害分组训练总体识别精度(低分辨率组)
Table 3 Overall recognition accuracy of group training for five kinds of diseases (low resolution group)
项目 Item | 分组Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 训练输入尺寸Training input size (pixels) | 128×128 | 224×224 | 256×256 | 512×512 |
| 总体识别精度Overall recognition accuracy (%) | 81.6 | 82.5 | 83.3 | 83.7 |
项目 Item | 分组Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 训练输入尺寸Training input size (pixels) | 768×768 | 1200×1200 | 1500×1500 |
| 总体识别精度Overall recognition accuracy (%) | 80.6 | 92.3 | 87.2 |
表4 5类病害分组训练总体识别精度(高分辨率组)
Table 4 Overall recognition accuracy of group training for five kinds of diseases (high resolution group)
项目 Item | 分组Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 训练输入尺寸Training input size (pixels) | 768×768 | 1200×1200 | 1500×1500 |
| 总体识别精度Overall recognition accuracy (%) | 80.6 | 92.3 | 87.2 |
评价指标 Evaluating indicator | 识别Recognize | |
|---|---|---|
| 正确Correct | 错误Incorrect | |
| 健康苜蓿Healthy alfalfa | 101 | 0 |
| 褐斑病C. beticola | 30 | 5 |
| 霜霉病P.cubensis | 17 | 1 |
| 炭疽病B. anthracis | 22 | 2 |
| 黑茎叶斑病P. medicaginis | 19 | 3 |
| 小光壳叶斑病L.briosiana | 25 | 4 |
表5 最优模型测试集识别精度
Table 5 Identification accuracy of the optimal model on the test set
评价指标 Evaluating indicator | 识别Recognize | |
|---|---|---|
| 正确Correct | 错误Incorrect | |
| 健康苜蓿Healthy alfalfa | 101 | 0 |
| 褐斑病C. beticola | 30 | 5 |
| 霜霉病P.cubensis | 17 | 1 |
| 炭疽病B. anthracis | 22 | 2 |
| 黑茎叶斑病P. medicaginis | 19 | 3 |
| 小光壳叶斑病L.briosiana | 25 | 4 |
| 1 | Wang X, Ma Y X, Li J. Fat-breeding effects of full-grazing turkey on regressed grassland. Pratacultural Science, 2003, 20(10): 39-41. |
| 王鑫, 马永祥, 李娟. 紫花苜蓿营养成分及主要生物学特性. 草业科学, 2003, 20(10): 39-41. | |
| 2 | Pan X, Gao Y, Liu B, et al. Current situation and prospect of alfalfa industry. Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2017(13): 104-107. |
| 潘霞, 高永, 刘博, 等. 苜蓿产业发展现状及前景展望. 绿色科技, 2017(13): 104-107. | |
| 3 | Chen S K, Zhou Z X, Chen P, et al. Study on incidence of diseases in varieties of alfalfa grown in Hulunbuir City. Journal of Inner Mongolia Minzu University (Natural Sciences), 2017, 32(6): 521-525. |
| 陈申宽, 周忠学, 陈鹏, 等. 呼伦贝尔市岭东苜蓿品种主要苜蓿病害研究. 内蒙古民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 32(6): 521-525. | |
| 4 | Chen J, Guo Z W, Pan C Q, et al. Research status of alfalfa diseases, insect pests and weeds. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science, 2022(1): 1-14. |
| 陈婧, 郭子雯, 潘春清, 等. 苜蓿病虫草害研究现状. 草学, 2022(1): 1-14. | |
| 5 | Nan Z B. Diseases of alfalfa in my country and their integrated control system. Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2001, 18(4): 81-84. |
| 南志标. 我国的苜蓿病害及其综合防治体系. 动物科学与动物医学, 2001, 18(4): 81-84. | |
| 6 | Wei H A. Alfalfa disease summary. Grassland and Turf, 1986(2): 37. |
| 魏宏安. 苜蓿病害概要. 草原与牧草, 1986(2): 37. | |
| 7 | Yuan Q H. Advances in alfalfa diseases in China. Plant Protection, 2007, 33(1): 6-10. |
| 袁庆华. 我国苜蓿病害研究进展. 植物保护, 2007, 33(1): 6-10. | |
| 8 | Han Y J, Liu X P, Du G M, et al. Leaf disease investigation and pathogen identification of alfalfa in Daqing area. Contemporary Animal Husbandry, 2013(4): 53-55. |
| 韩玉静, 刘香萍, 杜广明, 等. 大庆地区紫花苜蓿叶部病害调查和病原菌鉴定. 当代畜牧, 2013(4): 53-55. | |
| 9 | Hou T J. Occurrence status and control strategies of alfalfa diseases in China. Inner Mongolia Prataculture, 1994(Z2): 4-8. |
| 侯天爵. 我国苜蓿病害发生现状及防治对策. 内蒙古草业, 1994(Z2): 4-8. | |
| 10 | Lv X L, Ai L, Yin Q F, et al. Investigation and research on alfalfa downy mildew. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 1976(3): 39-42. |
| 吕新龙, 艾里, 殷启夫, 等. 苜蓿霜霉病的调查研究. 甘肃农业大学学报, 1976(3): 39-42. | |
| 11 | Lu H T, Zhang Q C. Applications of deep convolutional neural network in computer vision. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 2016, 31(1): 1-17. |
| 卢宏涛, 张秦川. 深度卷积神经网络在计算机视觉中的应用研究综述. 数据采集与处理, 2016, 31(1): 1-17. | |
| 12 | Gu Y L, Zong X X. Survey of object detection based on deep learning. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 48(6): 1230-1239. |
| 谷永立, 宗欣欣. 基于深度学习的目标检测研究综述. 现代信息科技, 2022, 48(6): 1230-1239. | |
| 13 | Zhang H, Wang K F, Wang F Y. Advances and perspectives on applications of deep learning in visual object detection. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(8): 1289-1305. |
| 张慧, 王坤峰, 王飞跃. 深度学习在目标视觉检测中的应用进展与展望. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(8): 1289-1305. | |
| 14 | LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G, et al. Deep learning. Nature, 2015, 521: 436-444. |
| 15 | Rumelhart D, Hinton G E, Williams R J, et al. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature, 1986, 323: 533-536. |
| 16 | Hinton G E, Osindero S, The Y W, et al. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Computation, 2006, 18(7): 1527-1554. |
| 17 | Hinton G E, Salakhutdinov R R, Hinton G E, et al. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science, 2006, 313: 504-507. |
| 18 | Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E.Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2012, 25: 1097-1105. |
| 19 | Schroff F, Kalenichenko D, Philbin J, et al. Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2015: 815-823. |
| 20 | Fawaz H I, Forestier G, Weber J, et al. Deep learning for time series classification: A review. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2019, 33(4): 917-963. |
| 21 | Qiang M J. Research of deep learning in crop image recognition. Journal of Fujian Computer, 2021, 37(2): 1-5. |
| 强敏杰. 深度学习在农作物图像识别中的应用研究. 福建电脑, 2021, 37(2): 1-5. | |
| 22 | Liu W X, Kuai N Y, Han S, et al. The intelligent identification system of alien invasive plants based on Android and deep learning. Plant Protection, 2021, 47(4): 174-179, 233. |
| 刘万学, 蒯乃阳, 韩爽, 等. 基于Android和深度学习的外来入侵植物智能识别系统. 植物保护, 2021, 47(4): 174-179, 233. | |
| 23 | Yang W Q, Liu T X, Tang X P, et al. Research progress on plant phenomics in the context of smart agriculture. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 51(7): 1-12. |
| 杨文庆, 刘天霞, 唐兴萍, 等. 智慧农业背景下的植物表型组学研究进展. 河南农业科学, 2022, 51(7): 1-12. | |
| 24 | Gao H Y, Gao X H, Feng Q S, et al. Approach to plant species identification in natural grasslands based on deep learning. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(9): 1931-1939. |
| 高宏元, 高新华, 冯琦胜, 等. 基于深度学习的天然草地植物物种识别方法. 草业科学, 2020, 37(9): 1931-1939. | |
| 25 | Li M, Wang J X, Li H L, et al. Method for identifying crop disease based on CNN and transfer learning. Smart Agriculture, 2019, 1(3): 46-55. |
| 李淼, 王敬贤, 李华龙, 等. 基于CNN和迁移学习的农作物病害识别方法研究. 智慧农业, 2019, 1(3): 46-55. | |
| 26 | Xu J H, Shao M Y, Wang Y C, et al. Recognition of corn leaf spot and rust based on transfer learning with convolutional neural network. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(2): 230-236, 253. |
| 许景辉, 邵明烨, 王一琛, 等. 基于迁移学习的卷积神经网络玉米病害图像识别. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(2): 230-236, 253. | |
| 27 | Qin F, Ruan L, Ma Z H, et al. Image recognition of alfalfa brown spot and rust based on Logistic regression model//Green prevention and control of pests and diseases and the quality and safety of agricultural products-Proceedings of the 2015 Academic Annual Conference of the Chinese Society for Plant Protection. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2015: 465. |
| 秦丰, 阮柳, 马占鸿, 等. 基于Logistic回归模型的苜蓿褐斑病和锈病的图像识别//病虫害绿色防控与农产品质量安全-中国植物保护学会2015年学术年会论文集. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2015: 465. | |
| 28 | Li Y Z, Yu B H, Xu L B. Alfalfa disease atlas. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2016: 10. |
| 李彦忠, 俞斌华, 徐林波. 紫花苜蓿病害图谱. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2016: 10. | |
| 29 | Xiao W, Feng Q, Zhang J H, et al. Research on plant disease identification based on few-shot learning. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2021, 42(11): 138-143. |
| 肖伟, 冯全, 张建华, 等. 基于小样本学习的植物病害识别研究. 中国农机化学报, 2021, 42(11): 138-143. | |
| 30 | Ren S N, Sun Y, Zhang H Y, et al. Plant disease identification for small sample based on one-shot learning. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 35(5): 1061-1067. |
| 任胜男, 孙钰, 张海燕, 等. 基于one-shot学习的小样本植物病害识别. 江苏农业学报, 2019, 35(5): 1061-1067. | |
| 31 | Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection// IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 779-788. |
| 32 | Girshick R. Fast r-cnn// Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV). Boston, MA, USA, 2015: 1440-1448. |
| [1] | 王晓瑜, 丁婷婷, 李彦忠, 段廷玉. AM真菌与根瘤菌对紫花苜蓿镰刀菌萎蔫和根腐病的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 139-149. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||