

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (7): 130-141.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023316
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2023-09-01
修回日期:2023-09-28
出版日期:2024-07-20
发布日期:2024-04-08
通讯作者:
方香玲
作者简介:方香玲 (1984-), 女, 河南平顶山人, 教授, 博士。E-mail: xlf@lzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Xiang-ling FANG( ), Shi-yang XU, Zhi-biao NAN
), Shi-yang XU, Zhi-biao NAN
Received:2023-09-01
Revised:2023-09-28
Online:2024-07-20
Published:2024-04-08
Contact:
Xiang-ling FANG
摘要:
厚垣孢子是尖孢镰刀菌在土壤中的主要存活结构,土壤中厚垣孢子的数量及萌发状况,直接影响着病害的发生及其严重度。首先通过研究合成低营养琼脂(SNA)和SNA加滤纸片(SNAF)培养基以及不同浓度葡萄糖和碳酸镁的双盐溶液(KH2PO4和MgSO4·7H2O)中厚垣孢子的形成,建立苜蓿专化型菌株厚垣孢子的诱导形成方法并进行验证,然后研究不同碳源和氮源对厚垣孢子萌发的影响。菌株T6和T9在2 mg·L-1葡萄糖的双盐溶液中静置培养7 d时形成大量的厚垣孢子,分别为4.2×105和5.1×105个·mL -1;且静置培养时的厚垣孢子数量均高于振荡培养时的数量,分别为4.2和2.8倍。不同苜蓿专化型菌株经双盐溶液诱导后,都在培养7 d时形成大量厚垣孢子,且培养前7 d时数量都快速增加,7 d时的均值为3 d时的2.3倍;而培养14和21 d时数量增加较慢,21 d时的均值仅为7 d时的1.2倍。对厚垣孢子萌发及芽管生长促进作用较大的碳源和氮源分别为葡萄糖和氯化铵,促进作用较小的碳源和氮源分别为乳糖和尿素。结果表明尖孢镰刀菌苜蓿专化型菌株厚垣孢子的形成需要微量的碳源和低氧环境,且厚垣孢子的萌发及生长需要适宜的碳源和氮源,可从控制病原菌初侵染源角度为苜蓿土传病害的绿色防控提供新思路。
方香玲, 许世洋, 南志标. 尖孢镰刀菌苜蓿专化型厚垣孢子的诱导形成方法及萌发特性[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 130-141.
Xiang-ling FANG, Shi-yang XU, Zhi-biao NAN. Induced formation method and germination characteristics of chlamydospores by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. medicaginis[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(7): 130-141.
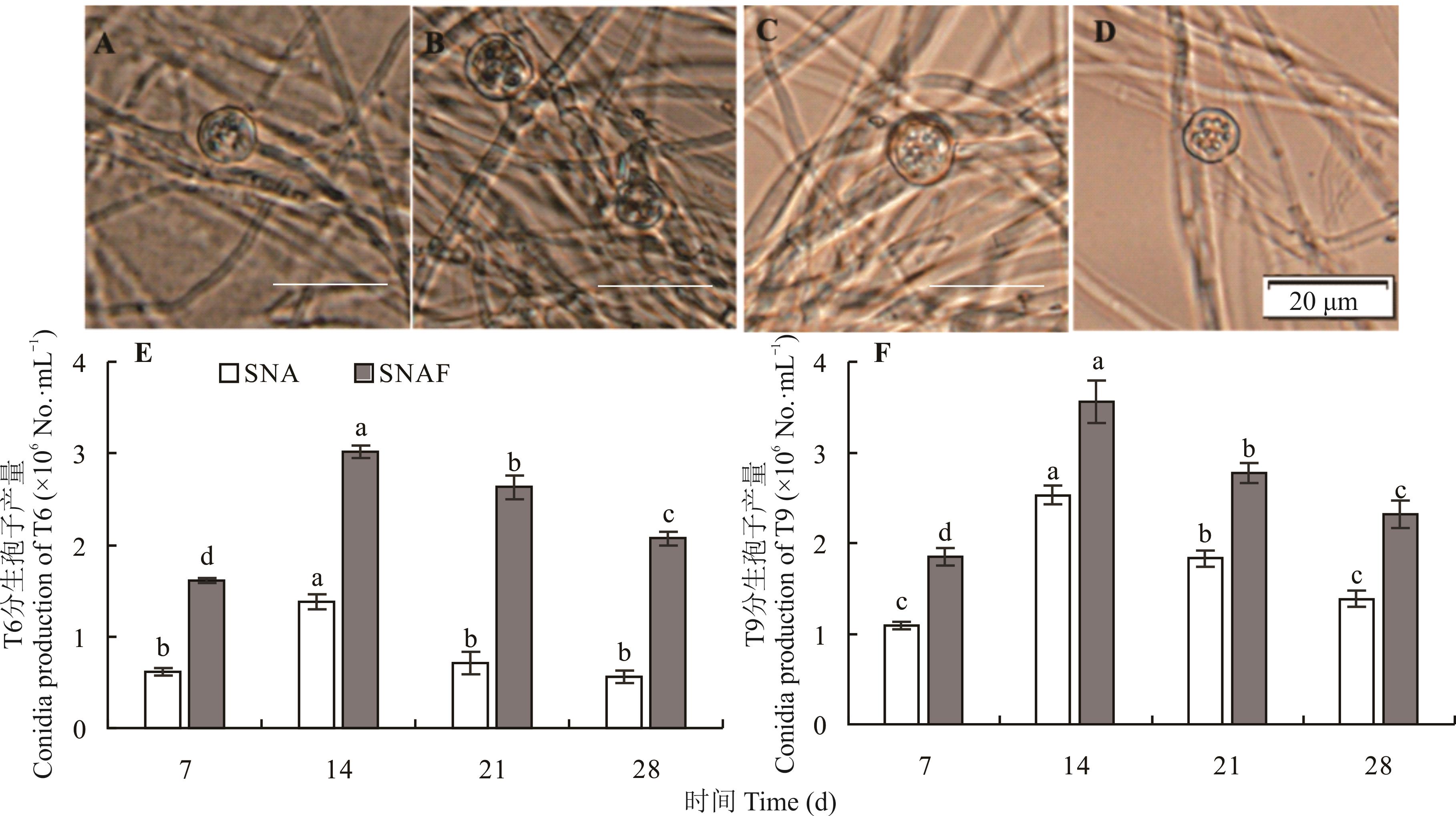
图1 菌株T6和T9在SNA和SNAF培养基上产生的孢子A,B:菌株T6在SNA培养基上培养28 d时产生的厚垣孢子Chlamydospore production of strain T6 on SNA at 28 days; C,D:T6在SNAF培养基上培养28 d时产生的厚垣孢子Chlamydospore production of T6 on SNAF at 28 days. 标尺长度为20 μm, 柱形图上不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05) ,下同。Scale bars represent 20 μm, and different lowercase above the bars indicate significant differences (P<0.05) among treatments, the same below.
Fig.1 Spore production of strains T6 and T9 on SNA and SNAF medium

图2 菌株T6和T9在葡萄糖双盐溶液中产生的厚垣孢子A,B:菌株T6培养3 d时Strain T6 at 3 days; C,D:T9培养3 d时T9 at 3 days; E:T6培养7 d时T6 at 7 days; F:T9培养7 d时T9 at 7 days; B~D:菌丝体用0.1%苯胺蓝水溶液染色Mycelia stained with 0.1% aniline blue in water solution.
Fig. 2 Chlamydospore production of strains T6 and T9 in two-salt solution with glucose
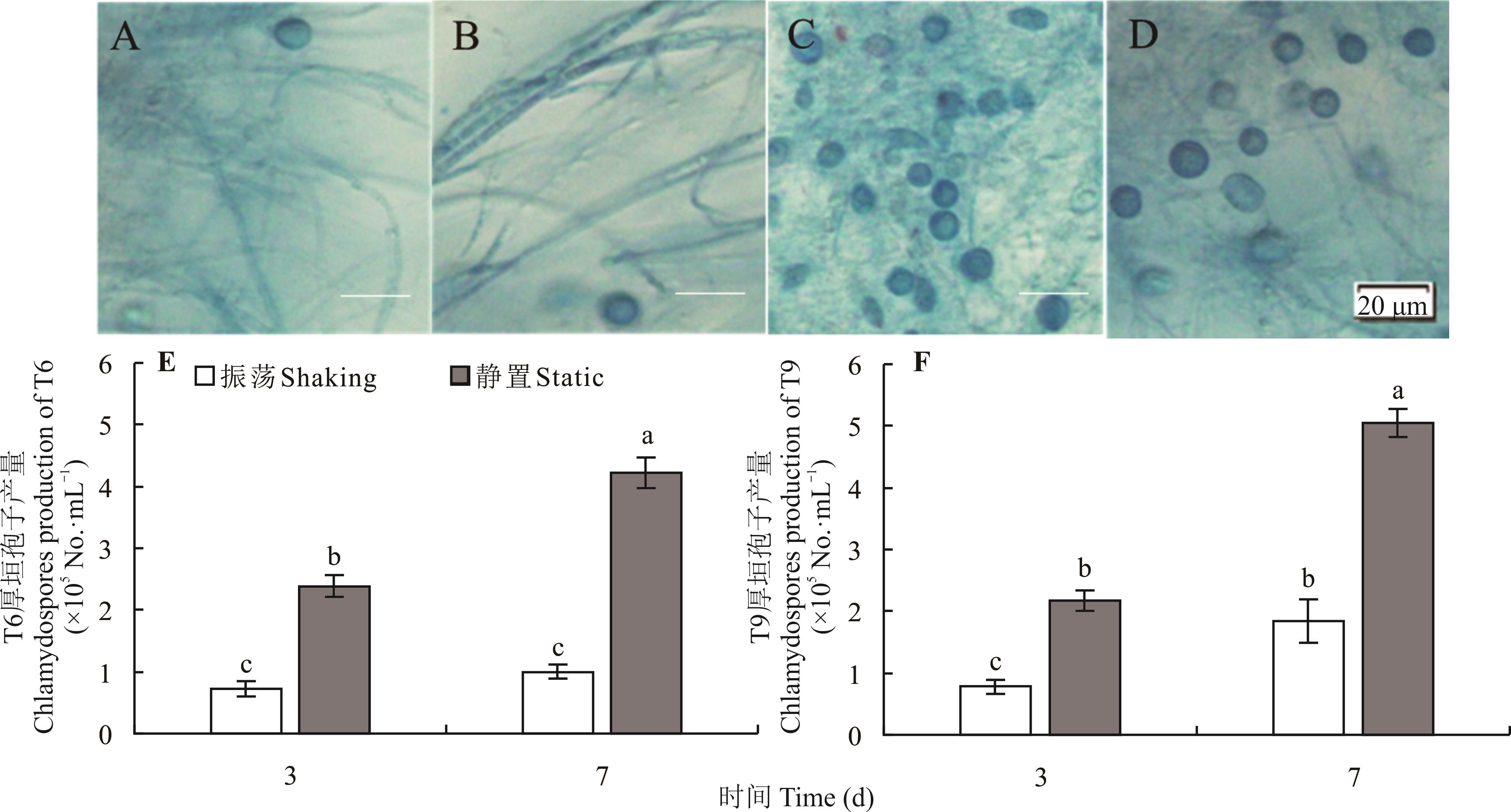
图3 菌株T6和T9在葡萄糖双盐溶液中振荡和静置培养条件下产生的厚垣孢子A,B:分别为菌株T6和T9振荡培养7 d时Strain T6 and T9 under shaking culture at 7 days, respectively; C,D:分别为菌株T6和T9静置培养7 d时Strain T6 and T9 under static culture at 7 days, respectively; E:T6在振荡和静置培养条件下厚垣孢子的产量Chlamydospore production of T6 under shaking culture and static culture; F:T9在振荡和静置培养条件下厚垣孢子的产量Chlamydospore production of T9 under shaking culture and static culture. A~D:0.1%苯胺蓝水溶液染色Stained with 0.1% aniline blue in water solution.
Fig.3 Chlamydospore production of strains T6 and T9 in two-salt solution with glucose under shaking culture and static culture
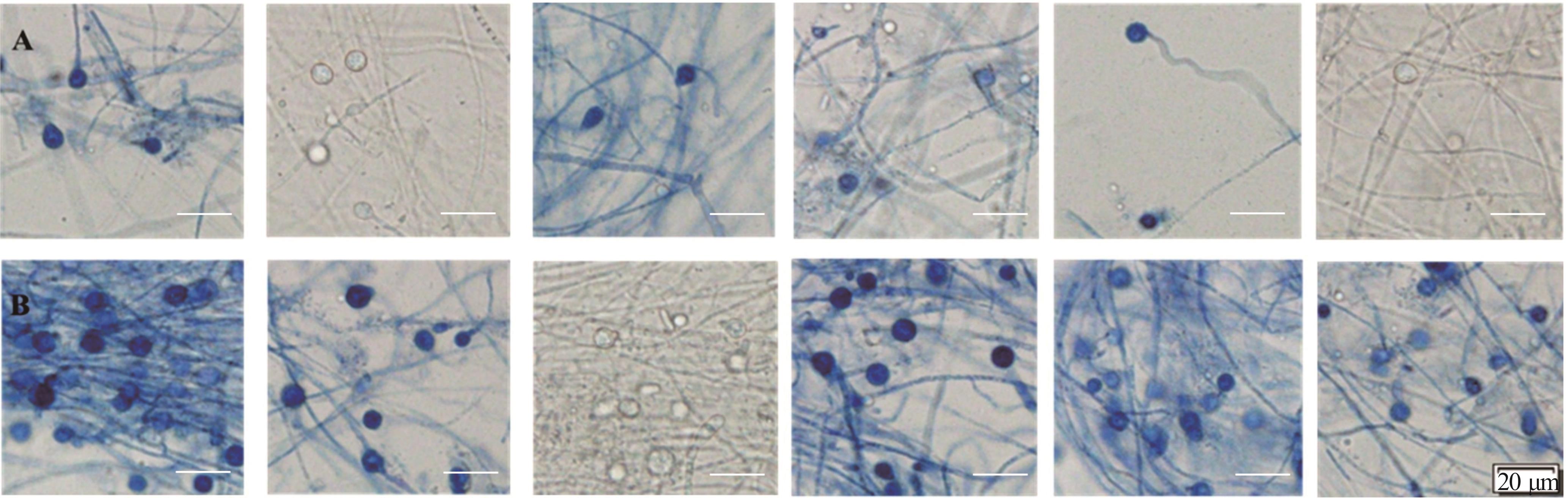
图4 不同菌株在葡萄糖双盐溶液中静置培养3和7 d时厚垣孢子的产生A,B:分别为菌株HT11、HX56、LT25、LZ21、QY28和QY57培养3和7 d时HT11, HX56, LT25, LZ21, QY28 and QY57 at 3 and 7 days, respectively.
Fig.4 Chlamydospore production of different strains in two-salt solution with glucose under static culture at 3 and 7 days
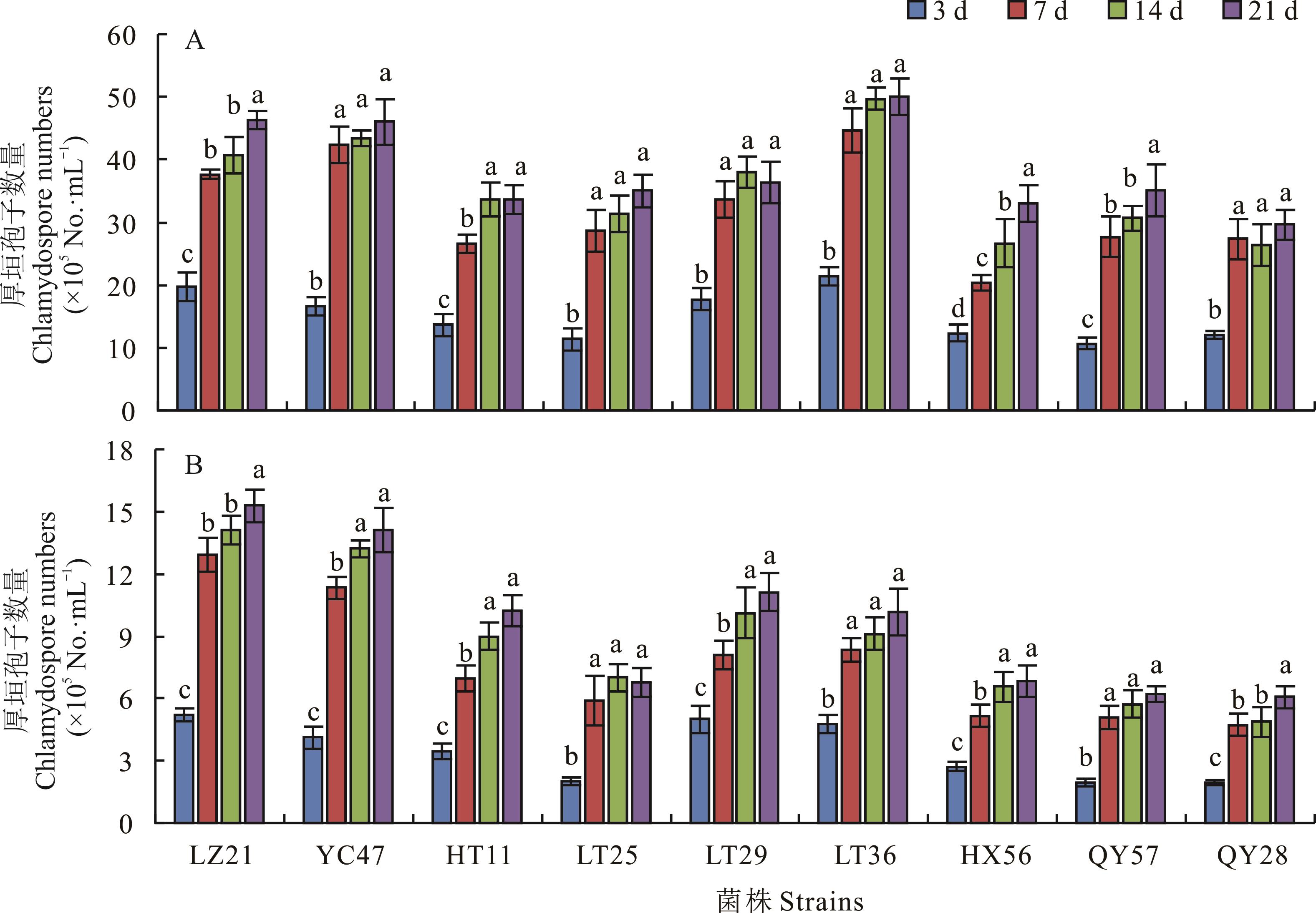
图5 不同菌株在葡萄糖双盐溶液中静置培养条件下厚垣孢子随时间的产生A:通过载玻片上不同视野统计不同时间点的厚垣孢子数量Chlamydospore numbers observed by different visual fields on glass slide; B:通过血球计数板统计不同时间点的厚垣孢子数量Chlamydospore numbers observed by hemocytometer.
Fig.5 Chlamydospore production of different strains in two-salt solution with glucose under static culture with times

图6 菌株T6和T9厚垣孢子在不同碳源培养基中的萌发率和芽管长度C0~C5分别代表无菌水、蔗糖、葡萄糖、麦芽糖、乳糖和淀粉。C0-C5 indicates sterile water, sucrose, glucose, maltose, lactose and starch, respectively.
Fig.6 Germination rate and germ tube length of strains T6 and T9 chlamydospores in medium with different carbon source
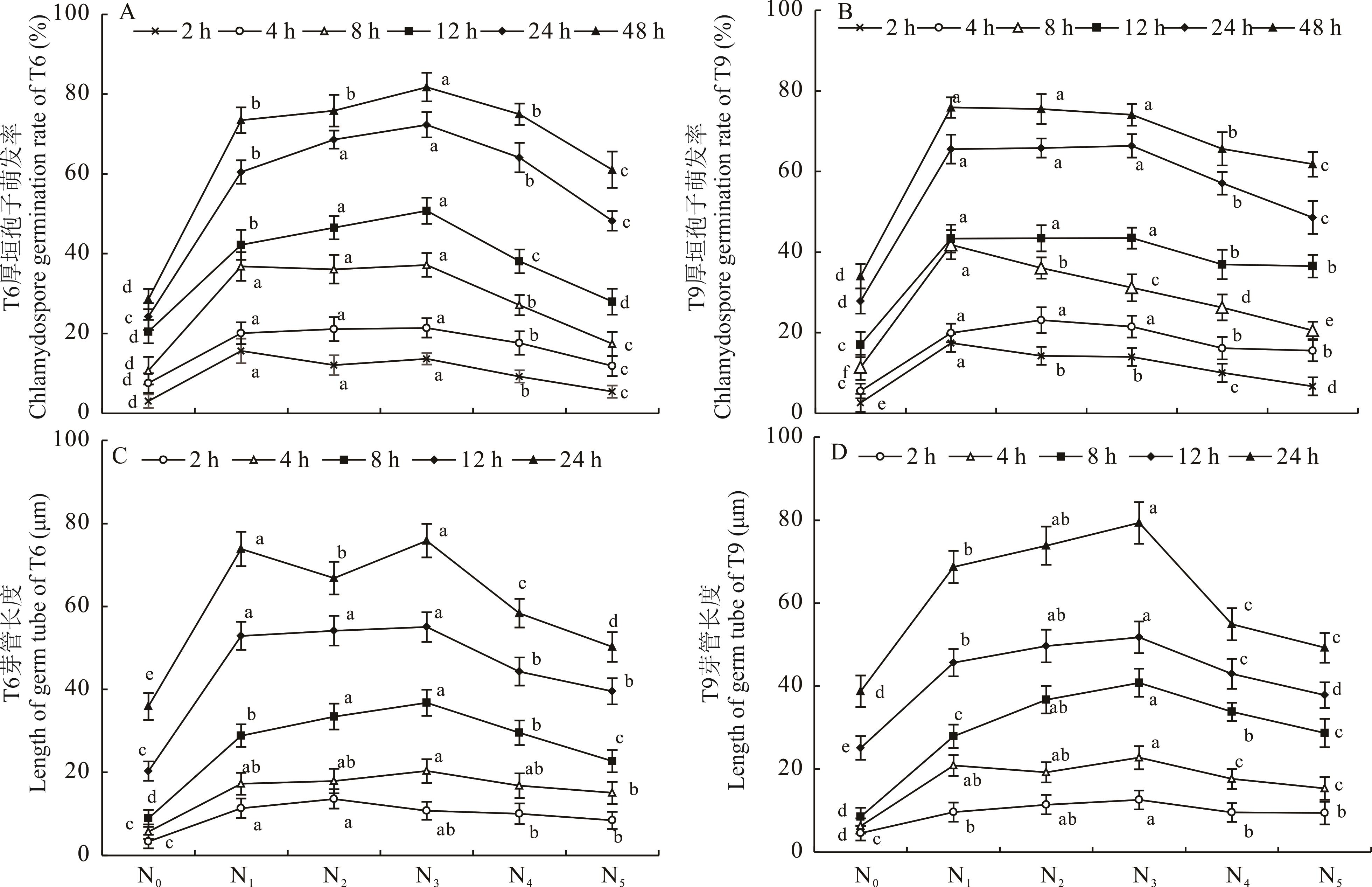
图7 菌株T6和T9厚垣孢子在不同氮源培养基中的萌发率和芽管长度N0~N5分别代表无菌水、硝酸钠、硝酸钾、氯化铵、磷酸氢二铵和尿素。N0-N5 indicates sterile water, sodium nitrate, potassium nitrate, ammonium chloride, diammonium hydrogen phosphate and urea, respectively.
Fig.7 Germination rate and germ tube length of strains T6 and T9 chlamydospores in medium with different nitrogen source
| 1 | Berrocal-Lobo M, Molina A. Arabidopsis defense response against Fusarium oxysporum. Trends in Plant Science,2008, 13(3): 145-150. |
| 2 | Dean R, Van Kan J A L, Pretorius Z A, et al. The top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Molecular Plant Pathology,2012, 13(4): 414-430. |
| 3 | Fravel D, Olivain C, Alabouvette C. Fusarium oxysporum and its biocontrol. New Phytologist,2003, 157(3): 493-502. |
| 4 | Gordon T R. Fusarium oxysporum and the Fusarium wilt syndrome. Annual Review of Phytopathology,2017, 55: 23-39. |
| 5 | Ma L J, Van Der Does H C, Borkovich K A, et al. Comparative genomics reveals mobile pathogenicity chromosomes in Fusarium. Nature,2010, 464(7287): 367-373. |
| 6 | Michielse C B, Rep M. Pathogen profile update: Fusarium oxysporum. Molecular Plant Pathology,2009, 10(3): 311-324. |
| 7 | Wang Z H, Fang X L. The research on genetic diversity of Fusarium oxysporum. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(5): 106-114. |
| 王泽华, 方香玲. 尖孢镰刀菌遗传多样性研究进展. 中国草地学报,2021, 43(5): 106-114. | |
| 8 | Edel-Hermann V, Lecomte C. Current status of Fusarium oxysporum formae speciales and races. Phytopathology,2019, 109(4): 512-530. |
| 9 | Fang X L, Zhang C X, Wang Z, et al. Co-infection by soil-borne fungal pathogens alters disease responses among diverse alfalfa varieties. Frontiers in Microbiology,2021, 12: 1-15. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.664385. |
| 10 | Ohara T, Tsuge T. FoSTUA, encoding a basic helix-loop-helix protein, differentially regulates development of three kinds of asexual spores, macroconidia, microconidia, and chlamydospores, in the fungal plant pathogen Fusarium oxysporum. Eukaryotic Cell, 2004, 3(6): 1412-1422. |
| 11 | Nan Z B. Establishing sustainable management system for diseases of pasture crops in China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2000, 9(2): 1-9. |
| 南志标. 建立中国的牧草病害可持续管理体系. 草业学报, 2000, 9(2): 1-9. | |
| 12 | Nan Z B. Alfalfa diseases and their comprehensive control system in China. Animal Science & Veterinary Medicine, 2001, 18(4): 81-84. |
| 南志标. 我国的苜蓿病害及其综合防治体系. 动物科学与动物医学,2001, 18(4): 81-84. | |
| 13 | Peterson J J, Samac D A, Grau C R. First report of Fusarium wilt of alfalfa caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. medicaginis in Wisconsin. Plant Disease,2018, 102(2): 447. |
| 14 | Rispail N, Rubiales D. Identification of sources of quantitative resistance to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. medicaginis in Medicago truncatula. Plant Disease,2014, 98(5): 667-673. |
| 15 | Williams A H, Sharma M, Thatcher L F, et al. Comparative genomics and prediction of conditionally dispensable sequences in legume-infecting Fusarium oxysporum formae speciales facilitates identification of candidate effectors. BMC Genomics,2016, 17(1): 1-24. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.664385. |
| 16 | Fang X L, Zhang C X, Nan Z B. Research advances in Fusarium root rot of alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(12): 169-183. |
| 方香玲, 张彩霞, 南志标. 紫花苜蓿镰刀菌根腐病研究进展. 草业学报,2019, 28(12): 169-183. | |
| 17 | Wille L, Messmer M M, Studer B, et al. Insights to plant-microbe interactions provide opportunities to improve resistance breeding against root diseases in grain legumes. Plant, Cell & Environment,2019, 42(1): 20-40. |
| 18 | Spraker J E, Sanchez L M, Lowe T M, et al. Ralstonia solanacearum lipopeptide induces chlamydospore development in fungi and facilitates bacterial entry into fungal tissues. The ISME Journal,2016, 10(9): 2317-2330. |
| 19 | Wang F, Sethiya P, Hu X, et al. Transcription in fungal conidia before dormancy produces phenotypically variable conidia that maximize survival in different environments. Nature Microbiology,2021, 6(8): 1066-1081. |
| 20 | Xu S, Liu Y X, Cernava T, et al. Fusarium fruiting body microbiome member Pantoea agglomerans inhibits fungal pathogenesis by targeting lipid rafts. Nature Microbiology, 2022, 7(6): 831-843. |
| 21 | Ma C, Yang X R, Jiang G F, et al. Research progresses on key factors affecting survival of Ralstonia solanacearum in soils. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2021, 58(6): 1359-1367. |
| 马超, 杨欣润, 江高飞,等. 病原青枯菌土壤存活的影响因素研究进展. 土壤学报,2021, 58(6): 1359-1367. | |
| 22 | Fang X L, Barbetti M J. Differential protein accumulations in isolates of the strawberry wilt pathogen Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. fragariae differing in virulence. Journal of Proteomics,2014, 108(2014): 223-237. |
| 23 | Henry P M, Pincot D D, Jenner B N, et al. Horizontal chromosome transfer and independent evolution drive diversification in Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. fragariae. New Phytologist,2021, 230(1): 327-340. |
| 24 | Liu S, Li J, Zhang Y, et al. Fusaric acid instigates the invasion of banana by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense TR 4. New Phytologist, 2020, 225(2): 913-929. |
| 25 | Masachis S, Segorbe D, Turrà D, et al. A fungal pathogen secretes plant alkalinizing peptides to increase infection. Nature Microbiology,2016, 1(6): 1-9. |
| 26 | Wang C, Guo H, He X, et al. Scaffold protein GhMORG1 enhances the resistance of cotton to Fusarium oxysporum by facilitating the MKK6‐MPK4 cascade. Plant Biotechnology Journal,2020, 18(6): 1421-1433. |
| 27 | Zuriegat Q, Zheng Y, Liu H, et al. Current progress on pathogenicity-related transcription factors in Fusarium oxysporum. Molecular Plant Pathology,2021, 22(7): 882-895. |
| 28 | Akhter A, Hage-Ahmed K, Soja G, et al. Potential of Fusarium wilt-inducing chlamydospores, in vitro behaviour in root exudates and physiology of tomato in biochar and compost amended soil. Plant and Soil,2016, 406: 425-440. |
| 29 | De Cal A, Pascual S, Melgarejo P. Infectivity of chlamydospores vs microconidia of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici on tomato. Journal of Phytopathology,1997, 145(5/6): 231-233. |
| 30 | Yun Y, Zhou X, Yang S, et al. Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici C2H2 transcription factor FolCzf1 is required for conidiation, fusaric acid production, and early host infection. Current Genetics,2019, 65(3): 773-783. |
| 31 | Sun L, Chu X J, Hao Y, et al. FoPLC4, encoding phospholipase C4, is involved in sporulation and pathogenicity in Fusarium oxysporum. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2014, 47(12): 2357-2364. |
| 孙玲, 褚小静, 郝宇, 等. 尖孢镰刀菌 FoPLC4 参与调控孢子形成和致病性. 中国农业科学,2014, 47(12): 2357-2364. | |
| 32 | Qu J X, Fang X L. Research progress on the spore formation and germination mechanism of plant pathogenic fungus Fusarium. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(8): 106-113. |
| 屈佳欣, 方香玲. 植物病原真菌镰刀菌孢子形成与萌发机理研究进展. 中国草地学报,2021, 43(8): 106-113. | |
| 33 | Ding Z J, Qi Y X, Zeng F Y, et al. Amino sugar metabolism pathway involved in chlamydospore formation of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense. Mycosystema, 2019, 38(4): 485-493. |
| 丁兆建, 漆艳香, 曾凡云, 等. 氨基糖代谢通路影响尖孢镰刀菌古巴专化型厚垣孢子的形成. 菌物学报,2019, 38(4): 485-493. | |
| 34 | Ding Z J, Qi Y X, Zeng F Y, et al. Amino acid involved in chlamydospore formation of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense. Mycosystema, 2021, 40(6): 1413-1426. |
| 丁兆建, 漆艳香, 曾凡云,等. 氨基酸影响尖孢镰孢菌古巴专化型厚垣孢子的形成. 菌物学报,2021, 40(6): 1413-1426. | |
| 35 | Yang X Y, Li M, Zhang L, et al. Transcriptome analysis of Trichoderma harzianum Th-33 in chlamydospore formation. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2015, 31(1): 85-95. |
| 杨晓燕, 李梅, 张林,等. 哈茨木霉 Th-33 厚垣孢子形成过程的转录组变化分析. 中国生物防治学报,2015, 31(1): 85-95. | |
| 36 | Qureshi A, Page O. Observations on chlamydospore production by Fusarium in a two-salt solution. Canadian Journal of Microbiology,1970, 16(1): 29-32. |
| 37 | Schippers B, Old K. Factors affecting chlamydospore formation by Fusarium solani f. sp. cucurbitae in pure culture. Soil Biology and Biochemistry,1974, 6(3): 153-160. |
| 38 | Zhang L, Jiang X L, Yang X Y, et al. Inhibition of chlamydospore germination and mycelial growth of Trichoderma spp. by chemical fungicides. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2014, 30(33): 150-155. |
| 张林, 蒋细良, 杨晓燕, 等. 化学杀菌剂对木霉菌厚垣孢子萌发及菌丝生长的抑制作用. 中国农学通报,2014, 30(33): 150-155. | |
| 39 | Du Y X, Shi N N, Ruan H C, et al. Conditions for germination of Mycogone perniciosa chlamydospores. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 35(1): 67-73. |
| 杜宜新, 石妞妞, 阮宏椿,等. 有害疣孢霉厚垣孢子萌发特性研究. 福建农业学报,2020, 35(1): 67-73. | |
| 40 | Griffin G J. Roles of low pH, carbon and inorganic nitrogen source use in chlamydospore formation by Fusarium solani. Canadian Journal of Microbiology,1976, 22(9): 1381-1389. |
| 41 | Smith S N, Snyder W. Germination of Fusarium oxysporum chlamydospores in soils favorable and unfavorable to wilt establishment. Phytopathology,1972, 62: 273-277. |
| 42 | Leslie J F, Summerell B A. The Fusarium laboratory manual. USA: Blackwell Publishing, 2006. |
| 43 | Peng H X, Sivasithamparam K, Turner D W. Chlamydospore germination and Fusarium wilt of banana plantlets in suppressive and conducive soils are affected by physical and chemical factors. Soil Biology and Biochemistry,1999, 31(10): 1363-1374. |
| 44 | Fang X L, Kuo J, Finnegan P M, et al. Comparative root colonisation of strawberry cultivars Camarosa and Festival by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. fragariae. Plant and Soil,2012, 358(1/2): 75-89. |
| 45 | Steinkellner S, Mammerler R, Vierheilig H. Germination of Fusarium oxysporum in root exudates from tomato plants challenged with different Fusarium oxysporum strains. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2008, 122(3): 395-401. |
| 46 | Bennett R S, Davis R M. Method for rapid production of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vasinfectum chlamydospores. Journal of Cotton Science,2013, 17(1): 52-59. |
| 47 | Goyal J, Maraite H, Meyer J. Abundant production of chlamydospores by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. melonis in soil extract with glucose. Netherlands Journal of Plant Pathology,1973, 79: 162-164. |
| 48 | Zhang D F, Liu M T, Zhu S A. Study on inducing conditions of the chlamydospores from Fusarium oxyporium f. sp. cucumarinum. Journal of Henan Institute of Science and Technology, 2010, 38(1): 30-32. |
| 张定法, 刘鸣韬, 朱盛安. 黄瓜枯萎病菌产生厚垣孢子诱导条件的研究. 河南科技学院学报,2010, 38(1): 30-32. | |
| 49 | Böttcher B, Pöllath C, Staib P, et al. Candida species rewired hyphae developmental programs for chlamydospore formation. Frontiers in Microbiology,2016, 7: 1-17. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01697. |
| 50 | Gordon T, Martyn R. The evolutionary biology of Fusarium oxysporum. Annual Review of Phytopathology,1997, 35(1): 111-128. |
| 51 | Sephton-Clark P C, Voelz K. Spore germination of pathogenic filamentous fungi. Advances in Applied Microbiology, 2018, 102: 117-157. |
| [1] | 王晓瑜, 丁婷婷, 李彦忠, 段廷玉. AM真菌与根瘤菌对紫花苜蓿镰刀菌萎蔫和根腐病的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 139-149. |
| [2] | 伍文宪, 刘勇, 黄小琴, 张蕾, 周西全, 刘红雨. 尖孢镰刀菌分子检测技术的建立与应用[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(5): 109-115. |
| [3] | 刘莎莎,程园园,张丹,王晓丹,刘佳莉,郭长虹. 两株紫花苜蓿根际芽孢杆菌的筛选及生防效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(9): 96-103. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||