

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 189-199.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020166
肖婉君1( ), 郭凤霞1(
), 郭凤霞1( ), 陈垣1,2(
), 陈垣1,2( ), 刘兰兰1, 陈永中1, 焦旭升1, 张碧全1, 白刚1, 金建琴1
), 刘兰兰1, 陈永中1, 焦旭升1, 张碧全1, 白刚1, 金建琴1
收稿日期:2020-04-08
修回日期:2020-04-27
出版日期:2021-03-20
发布日期:2021-03-09
通讯作者:
郭凤霞,陈垣
作者简介:Corresponding author. cygcx1963@163.com基金资助:
Wan-jun XIAO1( ), Feng-xia GUO1(
), Feng-xia GUO1( ), Yuan CHEN1,2(
), Yuan CHEN1,2( ), Lan-lan LIU1, Yong-zhong CHEN1, Xu-sheng JIAO1, Bi-quan ZHANG1, Gang BAI1, Jian-qin JIN1
), Lan-lan LIU1, Yong-zhong CHEN1, Xu-sheng JIAO1, Bi-quan ZHANG1, Gang BAI1, Jian-qin JIN1
Received:2020-04-08
Revised:2020-04-27
Online:2021-03-20
Published:2021-03-09
Contact:
Feng-xia GUO,Yuan CHEN
摘要:
为了探寻有机肥对当归成药栽培的影响,采用黑膜覆盖栽培,基施纯有机肥(O,2000 kg·hm-2)、纯化肥(C,磷酸二铵,420 kg·hm-2)、减半量化肥增施有机肥[1/2(O+C)],以不施肥为对照(CK),栽培期测定早期抽薹率、发病率、药材产量和性状指标。结果表明,纯有机肥栽培当归早期抽薹率为8.0%,分别较CK、1/2(O+C)和C降低19.4%、15.2%和7.1%。药材产量则相反,O、C和1/2(O+C)栽培当归药材产量相当,鲜产量分别较CK提高105.9%、84.6%和78.2%。纯有机肥栽培当归根最长,侧根最多,单根最重,药材产量最高。化肥对根的增粗作用最大,但含水量高,根病率高,发病重。不同施肥每hm2鲜药材产量与综合评价指数大小顺序一致,依次为O(9220.6 kg,0.926)>C(9038.5 kg,0.610)>1/2(O+C)(8728.4 kg,0.481)>CK(4897.4 kg,0.190)。每hm2干药材产量排序为O(3149.2 kg)>1/2(O+C)(3098.7 kg)>C(2909.2 kg)>CK(1707.0 kg),与经济收益一致。在岷县道地产区黑膜覆盖栽培,纯施有机肥对当归药材具有显著增效作用,可有效降低早薹率、根病率和发病程度,改善药材性状,提高药材产量和质量,在当归标准化栽培中可推广应用,以改变当归依赖化肥的生产现状,促进绿色有机栽培。
肖婉君, 郭凤霞, 陈垣, 刘兰兰, 陈永中, 焦旭升, 张碧全, 白刚, 金建琴. 施用有机肥对当归药材性状、产量及抗病性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 189-199.
Wan-jun XIAO, Feng-xia GUO, Yuan CHEN, Lan-lan LIU, Yong-zhong CHEN, Xu-sheng JIAO, Bi-quan ZHANG, Gang BAI, Jian-qin JIN. Effect of organic fertilizer application on the medicinal character, yield and disease resistance of Angelica sinensis[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 189-199.
施肥处理 Fertilizer application treatments | 有机肥用量 Amount of organic fertilizer | 磷酸二铵用量 Amount of diammonium phosphate | 总养分量 Amount of total nutrients | 有机质量 Amount of organic matter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | 2000 | 0 | ≥100.0 | >900 |
| C | 0 | 420 | >268.8 | 0 |
| 1/2(O+C) | 1000 | 210 | >184.4 | >450 |
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
表1 有机肥增量施肥方案
Table 1 Scheme of organic fertilizer increment (kg·hm-2)
施肥处理 Fertilizer application treatments | 有机肥用量 Amount of organic fertilizer | 磷酸二铵用量 Amount of diammonium phosphate | 总养分量 Amount of total nutrients | 有机质量 Amount of organic matter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | 2000 | 0 | ≥100.0 | >900 |
| C | 0 | 420 | >268.8 | 0 |
| 1/2(O+C) | 1000 | 210 | >184.4 | >450 |
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
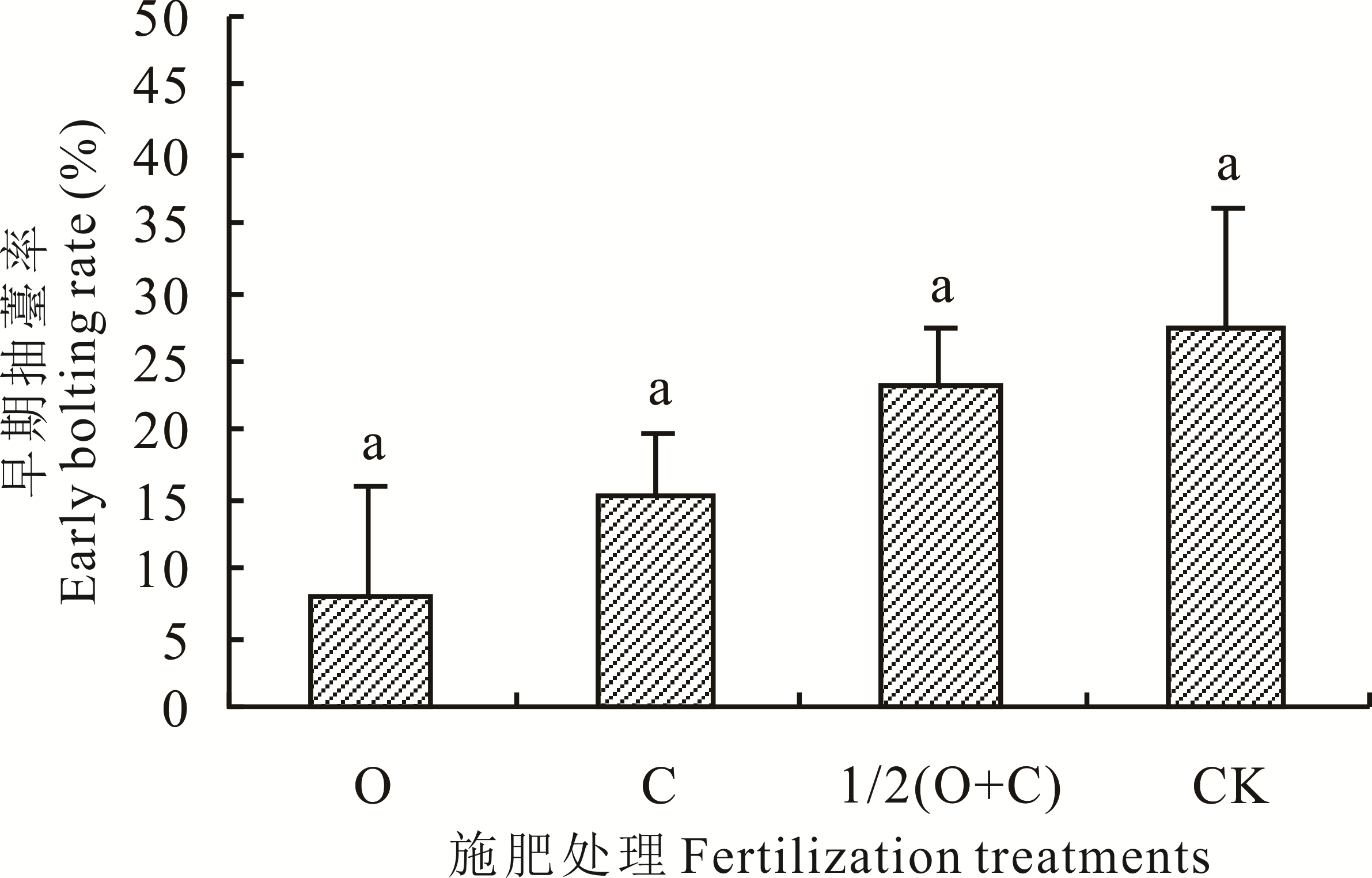
图1 有机肥与化肥施用量对当归早期抽薹率的影响不同小写字母表示P<0.05水平差异显著。下同。Different lowercase letters show significant difference in P<0.05. The same below.
Fig. 1 Effect of amount of fertilization on early bolting rate of A. sinensis
施肥处理 Fertilizer treatments | 主根长 Root length (cm) | 根粗 Root diameter(mm) | 侧根数 Lateral roots (No.) | 单根鲜重 Fresh weight of single root (g) | 单根干重 Dry weight of single root (g) | 根含水量 Water content in root (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | 27.5±1.0aA | 24.00±0.82bB | 9.0±0.9aA | 123.5±8.6aA | 41.95±3.0aA | 65.77±0.52aA |
| C | 26.0±0.8aA | 32.01±1.89aA | 6.4±0.6bAB | 105.6±10.9aA | 32.52±3.6bAB | 68.00±0.52aA |
| 1/2(O+C) | 25.8±1.5aA | 31.19±2.30aA | 7.0±0.8abAB | 97.0±10.9abAB | 29.70±2.8bcAB | 64.78±2.76aA |
| CK | 26.1±0.8aA | 20.02±0.68bB | 5.9±0.7bB | 61.2±7.6bB | 21.94±3.3cC | 65.02±1.14aA |
表2 不同处理对当归药材产量构成因素的影响
Table 2 Effects of different treatments on yield factors of A. sinensi
施肥处理 Fertilizer treatments | 主根长 Root length (cm) | 根粗 Root diameter(mm) | 侧根数 Lateral roots (No.) | 单根鲜重 Fresh weight of single root (g) | 单根干重 Dry weight of single root (g) | 根含水量 Water content in root (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | 27.5±1.0aA | 24.00±0.82bB | 9.0±0.9aA | 123.5±8.6aA | 41.95±3.0aA | 65.77±0.52aA |
| C | 26.0±0.8aA | 32.01±1.89aA | 6.4±0.6bAB | 105.6±10.9aA | 32.52±3.6bAB | 68.00±0.52aA |
| 1/2(O+C) | 25.8±1.5aA | 31.19±2.30aA | 7.0±0.8abAB | 97.0±10.9abAB | 29.70±2.8bcAB | 64.78±2.76aA |
| CK | 26.1±0.8aA | 20.02±0.68bB | 5.9±0.7bB | 61.2±7.6bB | 21.94±3.3cC | 65.02±1.14aA |
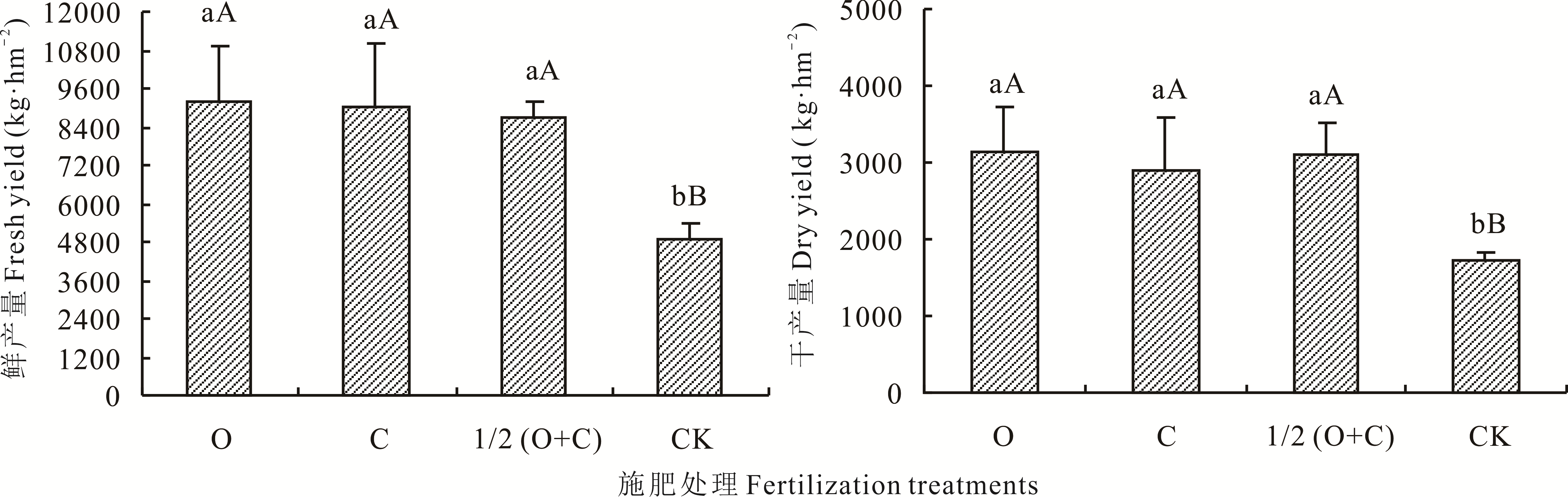
图2 施肥处理对当归鲜药材和干药材产量的影响不同大写字母表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。下同。Different uppercase letter indicate the most significant difference (P<0.01). The same below.
Fig. 2 Effect of fertilization on fresh and dry yield of A. sinensis
施肥处理 Fertilizer treatments | 药材毛收益 Medicinal income | 投入肥料成本 Input fertilizer cost | 肥料运费 Fertilizer carriage fee | 施肥成本 Cost of fertilization | 药材纯收益 Pure medicinal profit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | 94476.8 | 1200 | 500 | 1700 | 91076.8 |
| C | 87274.6 | 1512 | 108 | 1620 | 84034.6 |
| 1/2(O+C) | 92962.2 | 1356 | 304 | 1660 | 89642.2 |
| CK | 51210.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 51210.5 |
表3 不同施肥栽培当归效益分析
Table 3 Economic benefit analysis of Angelica under different fertilization cultivation (Yuan·hm-2)
施肥处理 Fertilizer treatments | 药材毛收益 Medicinal income | 投入肥料成本 Input fertilizer cost | 肥料运费 Fertilizer carriage fee | 施肥成本 Cost of fertilization | 药材纯收益 Pure medicinal profit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | 94476.8 | 1200 | 500 | 1700 | 91076.8 |
| C | 87274.6 | 1512 | 108 | 1620 | 84034.6 |
| 1/2(O+C) | 92962.2 | 1356 | 304 | 1660 | 89642.2 |
| CK | 51210.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 51210.5 |
处理 Treatments | 指标 Indicators | 根长 Root length | 根粗 Root diameter | 侧根数 Lateral roots | 单根鲜重 Fresh weight of single root | 单根干重 Dry weight of single root |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | 根粗Root diameter | 0.225 | ||||
| 侧根数Lateral roots | 0.686** | 0.244 | ||||
| 单根鲜重Fresh weight of single root | 0.757** | 0.267 | 0.772** | |||
| 单根干重Dry weight of single root | 0.618** | 0.283 | 0.655** | 0.921** | ||
| 含水量Water content | 0.273 | -0.022 | 0.254 | 0.154 | -0.234 | |
| C | 根粗Root diameter | -0.371 | ||||
| 侧根数Lateral roots | -0.565** | 0.496* | ||||
| 单根鲜重Fresh weight of single root | -0.314 | 0.786** | 0.638** | |||
| 单根干重Dry weight of single root | -0.301 | 0.612** | 0.454* | 0.840** | ||
| 含水量Water content | 0.114 | 0.182 | 0.267 | 0.210 | -0.322 | |
| 1/2(O+C) | 根粗Root diameter | 0.349 | ||||
| 侧根数Lateral roots | 0.190 | 0.354 | ||||
| 单根鲜重Fresh weight of single root | 0.394 | 0.672** | 0.722** | |||
| 单根干重Dry weight of single root | 0.359 | 0.470* | 0.675** | 0.852** | ||
| 含水量Water content | 0.366 | 0.524* | 0.418 | 0.613** | 0.226 | |
| CK | 根粗Root diameter | -0.113 | ||||
| 侧根数Lateral roots | 0.266 | 0.137 | ||||
| 单根鲜重Fresh weight of single root | -0.155 | -0.205 | 0.556* | |||
| 单根干重Dry weight of single root | -0.203 | -0.160 | 0.492* | 0.931** | ||
| 含水量Water content | 0.140 | 0.182 | 0.061 | -0.252 | -0.549* |
表4 各施肥栽培条件下当归产量构成因素的相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis of yield components of A. sinensis under different fertilization cultivated conditions
处理 Treatments | 指标 Indicators | 根长 Root length | 根粗 Root diameter | 侧根数 Lateral roots | 单根鲜重 Fresh weight of single root | 单根干重 Dry weight of single root |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | 根粗Root diameter | 0.225 | ||||
| 侧根数Lateral roots | 0.686** | 0.244 | ||||
| 单根鲜重Fresh weight of single root | 0.757** | 0.267 | 0.772** | |||
| 单根干重Dry weight of single root | 0.618** | 0.283 | 0.655** | 0.921** | ||
| 含水量Water content | 0.273 | -0.022 | 0.254 | 0.154 | -0.234 | |
| C | 根粗Root diameter | -0.371 | ||||
| 侧根数Lateral roots | -0.565** | 0.496* | ||||
| 单根鲜重Fresh weight of single root | -0.314 | 0.786** | 0.638** | |||
| 单根干重Dry weight of single root | -0.301 | 0.612** | 0.454* | 0.840** | ||
| 含水量Water content | 0.114 | 0.182 | 0.267 | 0.210 | -0.322 | |
| 1/2(O+C) | 根粗Root diameter | 0.349 | ||||
| 侧根数Lateral roots | 0.190 | 0.354 | ||||
| 单根鲜重Fresh weight of single root | 0.394 | 0.672** | 0.722** | |||
| 单根干重Dry weight of single root | 0.359 | 0.470* | 0.675** | 0.852** | ||
| 含水量Water content | 0.366 | 0.524* | 0.418 | 0.613** | 0.226 | |
| CK | 根粗Root diameter | -0.113 | ||||
| 侧根数Lateral roots | 0.266 | 0.137 | ||||
| 单根鲜重Fresh weight of single root | -0.155 | -0.205 | 0.556* | |||
| 单根干重Dry weight of single root | -0.203 | -0.160 | 0.492* | 0.931** | ||
| 含水量Water content | 0.140 | 0.182 | 0.061 | -0.252 | -0.549* |
主成分 Principal components | 特征根 Eigenvalue | 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) | 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.64 | 33.13 | 33.13 |
| 2 | 2.39 | 21.68 | 54.80 |
| 3 | 1.71 | 15.52 | 70.33 |
| 4 | 1.34 | 12.22 | 82.55 |
表5 当归产量及抗病性指标主成分分析结果
Table 5 The result of principal components analysis of yield and disease resistance indicators of A. sinensis
主成分 Principal components | 特征根 Eigenvalue | 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) | 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.64 | 33.13 | 33.13 |
| 2 | 2.39 | 21.68 | 54.80 |
| 3 | 1.71 | 15.52 | 70.33 |
| 4 | 1.34 | 12.22 | 82.55 |
性状指标 Indicators | 负荷量Load | 权重值 Weight value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| 根长Root length | 0.481 | -0.368 | -0.116 | 0.292 | 0.078 |
| 根粗Root diameter | 0.322 | 0.696 | -0.171 | 0.333 | 0.087 |
| 侧根数Lateral roots | 0.716 | -0.086 | 0.607 | -0.101 | 0.097 |
| 单根鲜重 Fresh weight of single root | 0.912 | 0.164 | 0.311 | 0.019 | 0.104 |
| 单根干重Dry weight of single root | 0.886 | 0.022 | 0.379 | -0.135 | 0.100 |
| 含水量Water content | -0.015 | -0.281 | -0.210 | 0.790 | 0.052 |
| 发病率Incidence | -0.392 | 0.826 | 0.292 | 0.237 | 0.102 |
| 病情指数Disease index | -0.304 | 0.778 | 0.368 | 0.170 | 0.093 |
| 早期抽薹率Early bolting rate | -0.415 | 0.212 | -0.118 | -0.598 | 0.073 |
| 鲜产量Fresh yield | 0.622 | 0.360 | -0.653 | -0.044 | 0.104 |
| 干产量Dry yield | 0.612 | 0.434 | -0.592 | -0.224 | 0.111 |
表6 当归产量及抗病性指标的负荷量和权重
Table 6 Capacity and weight of yield and disease resistance indicators of A. sinensis
性状指标 Indicators | 负荷量Load | 权重值 Weight value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| 根长Root length | 0.481 | -0.368 | -0.116 | 0.292 | 0.078 |
| 根粗Root diameter | 0.322 | 0.696 | -0.171 | 0.333 | 0.087 |
| 侧根数Lateral roots | 0.716 | -0.086 | 0.607 | -0.101 | 0.097 |
| 单根鲜重 Fresh weight of single root | 0.912 | 0.164 | 0.311 | 0.019 | 0.104 |
| 单根干重Dry weight of single root | 0.886 | 0.022 | 0.379 | -0.135 | 0.100 |
| 含水量Water content | -0.015 | -0.281 | -0.210 | 0.790 | 0.052 |
| 发病率Incidence | -0.392 | 0.826 | 0.292 | 0.237 | 0.102 |
| 病情指数Disease index | -0.304 | 0.778 | 0.368 | 0.170 | 0.093 |
| 早期抽薹率Early bolting rate | -0.415 | 0.212 | -0.118 | -0.598 | 0.073 |
| 鲜产量Fresh yield | 0.622 | 0.360 | -0.653 | -0.044 | 0.104 |
| 干产量Dry yield | 0.612 | 0.434 | -0.592 | -0.224 | 0.111 |
性状指标 Indicators | 施肥处理 Fertilization treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | C | 1/2(O+C) | CK | |
| 根长Root length | 1.000 | 0.086 | 0.000 | 0.026 |
| 根粗Root diameter | 0.325 | 1.000 | 0.990 | 0.000 |
| 侧根数Lateral roots | 1.000 | 0.150 | 0.330 | 0.000 |
| 单根鲜重 Fresh weight of single root | 1.000 | 0.731 | 0.572 | 0.000 |
| 单根干重Dry weight of single root | 1.000 | 0.546 | 0.370 | 0.000 |
| 含水量Water content | 0.693 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.925 |
| 发病率Incidence | 1.000 | 0.554 | 0.000 | 0.700 |
| 病情指数Disease index | 1.000 | 0.825 | 0.000 | 0.733 |
| 早期抽薹率Early bolting rate | 1.000 | 0.634 | 0.218 | 0.000 |
| 鲜产量Fresh yield | 1.000 | 0.958 | 0.886 | 0.000 |
| 干产量Dry yield | 1.000 | 0.834 | 0.965 | 0.000 |
| 综合评价指数 Comprehensive evaluation index | 0.926 | 0.610 | 0.481 | 0.190 |
| 综合排序Comprehensive sorting | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
表7 不同施肥栽培下当归产量及抗病性指标因子的隶属度值及综合评价指数
Table 7 Membership value and comprehensive evaluation index of yield and disease resistance factors of A. sinensis under different fertilization cultivation
性状指标 Indicators | 施肥处理 Fertilization treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | C | 1/2(O+C) | CK | |
| 根长Root length | 1.000 | 0.086 | 0.000 | 0.026 |
| 根粗Root diameter | 0.325 | 1.000 | 0.990 | 0.000 |
| 侧根数Lateral roots | 1.000 | 0.150 | 0.330 | 0.000 |
| 单根鲜重 Fresh weight of single root | 1.000 | 0.731 | 0.572 | 0.000 |
| 单根干重Dry weight of single root | 1.000 | 0.546 | 0.370 | 0.000 |
| 含水量Water content | 0.693 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.925 |
| 发病率Incidence | 1.000 | 0.554 | 0.000 | 0.700 |
| 病情指数Disease index | 1.000 | 0.825 | 0.000 | 0.733 |
| 早期抽薹率Early bolting rate | 1.000 | 0.634 | 0.218 | 0.000 |
| 鲜产量Fresh yield | 1.000 | 0.958 | 0.886 | 0.000 |
| 干产量Dry yield | 1.000 | 0.834 | 0.965 | 0.000 |
| 综合评价指数 Comprehensive evaluation index | 0.926 | 0.610 | 0.481 | 0.190 |
| 综合排序Comprehensive sorting | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 1 | Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. The Chinese Pharmacopoeia (a). Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2015: 133-134. |
| 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典(一部). 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2015: 133-134. | |
| 2 | Bai G, Guo F X, Chen Y, et al. Differences in physiological resistance traits of Angelica sinensis seedlings from uncultivated and cultivated fields in Min County. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(11): 86-95. |
| 白刚, 郭凤霞, 陈垣, 等. 岷县生荒地和熟地育成当归苗抗逆生理特性的差异. 草业学报, 2019, 28(11): 86-95. | |
| 3 | Zhu G Q. Angelica ecological climate analysis and being suitable to planting regionalization in Central Gansu. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2001, 19(1): 36-38. |
| 朱国庆. 甘肃中部当归生态气候分析及适生种植区划. 干旱气象, 2001, 19(1): 36-38. | |
| 4 | Wang Y Q, Frank S, An P K, et al. Effect of conjunctive application of Chinese medicine residue compost and mineral fertilizer on the yield and quality of Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels. Journal of Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, 2012, 29(5): 51-56. |
| 王引权, Frank S, 安培坤, 等. 中药渣堆肥与化肥配合施用对当归产量与品质的影响. 甘肃中医学院学报, 2012, 29(5): 51-56. | |
| 5 | Song X Z, Zhao C X, Wang X L, et al. Study of nitrate leaching and nitrogen fate under intensive vegetable production pattern in northern China. Comptes Rendus Biologies, 2009, 332(4): 385-392. |
| 6 | Zhang X D. Influencing mechanism of mulch planting and fertilization on the efficient utilization of resources and maize production sustainability in semi-arid areas. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2019. |
| 张旭东. 覆膜种植和施肥对半干旱地区资源高效利用及玉米生产持续性的影响机制. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2019. | |
| 7 | Ding Y, Wang F, Jia D Q, et al. Long-term located study of organic manure application effects on soil fertility. Xinjiang Agricultural Science, 2014, 51(10): 1857-1861. |
| 丁英, 王飞, 贾登泉, 等. 有机肥对土壤培肥作用长期定位研究. 新疆农业科学, 2014, 51(10): 1857-1861. | |
| 8 | Shen D L, Cao F M, Li L. Development status and prospect of bio organic fertilizer in China. Chinese Soil and Fertilizer, 2007(6): 1-5. |
| 沈德龙, 曹凤明, 李力. 我国生物有机肥的发展现状及展望. 中国土壤与肥料, 2007(6): 1-5. | |
| 9 | Dong C H, Gao J S, Zeng X B, et al. Effects of long-term organic manure and inorganic fertilizer combined application on rice yield and soil organic carbon content in reddish paddy fields. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2014, 20(2): 336-345. |
| 董春华, 高菊生, 曾希柏, 等. 长期有机无机肥配施下红壤性稻田水稻产量及土壤有机碳变化特征. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(2): 336-345. | |
| 10 | Xu M G, Li D C, Li J M, et al. Effects of organic manure application combined with chemical fertilizers on nutrients absorption and yield of rice. China Agricultural Science, 2008, 41(10): 3133-3139. |
| 徐明岗, 李冬初, 李菊梅, 等. 化肥有机肥配施对水稻养分吸收和产量的影响. 中国农业科学, 2008, 41(10): 3133-3139. | |
| 11 | Luo J, Zhao S, Yuan Y J, et al. Effects of a bio-organic fertilizer on the disease resistance-related enzymes activities of cotton. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2011, 34(3): 89-93. |
| 罗佳, 赵爽, 袁玉娟, 等. 施用微生物有机肥对棉花抗病性相关酶活性的影响. 南京农业大学学报, 2011, 34(3): 89-93. | |
| 12 | Li S H, Gu L P, Liu K X, et al. Effects of combined application of organic fertilizers on the control of soilborne diseases and the regulation of soil microbial diversity. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2009, 15(4): 965-969. |
| 李胜华, 谷丽萍, 刘可星, 等. 有机肥配施对番茄土传病害的防治及土壤微生物多样性的调控. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2009, 15(4): 965-969. | |
| 13 | Bai X C, Zhang J H, Feng K L, et al. Effects of chemical fertilizer reduction and application of organic manure on the yield and nutritive value of Zea mays and soil microbial activity. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(2): 348-354. |
| 白雪纯, 张君红, 冯魁亮, 等. 化肥减量配施有机肥对青贮玉米产量、营养价值及土壤微生物活性的影响. 草业科学, 2020, 37(2): 348-354. | |
| 14 | Wang B P, Cai C F, Xing Z X. Necessity of organic agriculture research in gap base of traditional Chinese medicine. Journal of Shanxi College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2003, 4(3): 45-47. |
| 王宝平, 蔡翠芳, 邢志雄. 中药材GAP基地进行有机农业研究的必要性. 山西中医学院学报, 2003, 4(3): 45-47. | |
| 15 | Ren L B, Li Z Z, Zhu Z L, et al. Effects of mulching different kinds of mulch on crop growth. Agricultural Engineering Technology, 2018, 38(16): 80-82. |
| 任领兵, 李中周, 朱珍丽, 等. 覆盖不同种类地膜对作物生长的影响. 农业工程技术, 2018, 38(16): 80-82. | |
| 16 | Chen Y, Zhu L, Guo F X, et al. Isolation and identification of the pathogens causing Astragalus membranaceus var mongholicus in Weiyuan of Gansu Province. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2011, 41(4): 428-431. |
| 陈垣, 朱蕾, 郭凤霞, 等. 甘肃渭源蒙古黄芪根腐病病原菌的分离与鉴定. 植物病理学报, 2011, 41(4): 428-431. | |
| 17 | Jin Y B, Guo F X, Chen Y, et al. Effect of various crop residues on growth and disease resistance of Angelica sinensis seedlings in Min County. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(4): 69-78. |
| 金彦博, 郭凤霞, 陈垣, 等. 岷县不同茬口对当归苗栽生长及抗病性的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 69-78. | |
| 18 | Wang F A. A brief analysis on the reasons for the increase of early bolting rate of Angelica sinensis in Min County in 2007. Agricultural Science-Technology and Information , 2008(7): 52. |
| 王冯爱. 浅析 2007 年岷县当归早期抽薹率上升原因. 农业科技与信息, 2008(7): 52. | |
| 19 | Yu G, Ma Y X, Duan J A, et al. Identification of differentially expressed genes involved in early bolting of Angelica sinensis (Apiaceae). Genetics & Molecular Research, 2012, 11(1): 494-502. |
| 20 | Qi J T, Lin H M, Liu X Z. Preliminary report on the effect of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer on bolting rate of angelica. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2004, 27(2): 82-83. |
| 漆琚涛, 蔺海明, 刘学洲. 氮磷肥对当归抽薹率的影响试验初报. 中药材, 2004, 27(2): 82-83. | |
| 21 | Wang J Y, Yan X Y, Gong W. Effect of long-term fertilization on soil productivity on the North China Plain. Pedosphere, 2015, 25(3): 450-458. |
| 22 | Wu X K, Jiang Z C, Lu Z X. Effects of the partial replacement of chemical fertilizer with manure on the yield and nitrogen emissions in leafy vegetable production. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2020, 28(3): 349-356. |
| 武星魁, 姜振萃, 陆志新. 有机肥部分替代化肥氮对叶菜产量和环境效应的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2020, 28(3): 349-356. | |
| 23 | Guo F X, Zhang M X, Chen Y, et al. Relation of several antioxidant enzymes to rapid freezing resistance in suspension cultured cells from alpine Chorispora bungeana. Cryobiology, 2006, 52(2): 241-250. |
| 24 | Xu L G. Effect of bio organic fertilizer on the growth, yield and quality of tomato. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2006. |
| 徐立功. 生物有机肥对番茄生长发育及产量品质的影响. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2006. | |
| 25 | Zhang G C, Ye J X, Zhang X M. Effect of organic manure on eggplant growth and disease resistance. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2003, 25(1): 66-70. |
| 张广臣, 叶景学, 张晓明. 有机肥对茄子生长发育及抗病性的影响. 吉林农业大学学报, 2003, 25(1): 66-70. | |
| 26 | Feng W L, Sun Y C, Sun B F. Research progress on bio-organic fertilizer control of replant disease in Chinese medicinal materials. Forest By-Product and Speciality in China, 2011(4): 88-90. |
| 封万里, 孙跃春, 孙丙富. 生物有机肥对药材连作病害的防治作用. 中国林副特产, 2011(4): 88-90. |
| [1] | 吴晓娟, 杨梅, 芦奕晓, 杨惠敏. 混播比例和施氮肥对箭筈豌豆/燕麦草地根系特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 106-116. |
| [2] | 张梨梨, 史敏, 李彦忠. 炭疽病对沙尔沁地区苜蓿产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 117-126. |
| [3] | 方香玲, 张彩霞, 南志标. 紫花苜蓿镰刀菌根腐病研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 169-183. |
| [4] | 白刚, 郭凤霞, 陈垣, 袁洪超, 肖婉君. 岷县生荒地和熟地育成当归苗抗逆生理特性的差异[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(11): 86-95. |
| [5] | 张建军, 樊廷录, 赵刚, 党翼, 王磊, 王勇, 李尚中, 程万莉. 耕作方式与长期定位施肥对雨养农田冬小麦产量的调控效应[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(7): 175-186. |
| [6] | 金彦博,郭凤霞,陈垣,白刚,袁洪超,梁伟. 岷县不同茬口对当归苗栽生长及抗病性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 69-78. |
| [7] | 袁洪超, 郭凤霞, 陈垣, 白刚, 梁伟. 高寒区轮作模式对当归田土壤特性及药材产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 183-193. |
| [8] | 杨成德, 卞静, 陈泰祥, 陈秀蓉, 王涵琦, 杨小利, 王艳. 当归炭疽病菌的生物学特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(6): 139-144. |
| [9] | 张咏梅, 马晖玲, 唐云智. 紫花苜蓿叶片受白粉病菌侵染后结构的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(2): 88-94. |
| [10] | 李春杰, 陈泰祥, 赵桂琴, 南志标. 燕麦病害研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(12): 203-222. |
| [11] | 梁伟, 郭凤霞, 陈垣, 白刚, 袁洪超, 金彦博. 高寒区农茬口对当归田杂草群落特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(11): 35-46. |
| [12] | 陈静, 黄有胜, 李廷轩. 猪粪有机肥施用下两种生态型粗齿冷水花磷积累特征变化[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(11): 139-146. |
| [13] | 李捷, 冯丽丹, 杨成德, 王有科, 何静, 张宝琳, 陈秀蓉. 接种尖镰孢菌对枸杞苯丙烷代谢关键酶及产物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(5): 87-94. |
| [14] | 黄杰, 杨发荣, 李敏权, 魏玉明, 顾娴, 漆永红. 13个藜麦材料在甘肃临夏旱作区适应性的初步评价[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 191-201. |
| [15] | 王瑜, 刘怡, 周彬彬, 袁庆华, 张丽, 潘龙其. 苜蓿对匍柄霉叶斑病与茎点霉叶斑病的抗性评价研究[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(7): 155-162. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||