

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (7): 109-121.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022318
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
蒋晶晶1( ), 陈爱昌2, 魏周全2, 孙兴明2, 徐美蓉3(
), 陈爱昌2, 魏周全2, 孙兴明2, 徐美蓉3( ), 李雪萍1, 杜蕙1, 漆永红1(
), 李雪萍1, 杜蕙1, 漆永红1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-09
修回日期:2022-11-21
出版日期:2023-07-20
发布日期:2023-05-26
通讯作者:
徐美蓉,漆永红
作者简介:E-mail: xumeirong@gsagr.ac.cn基金资助:
Jing-jing JIANG1( ), Ai-chang CHEN2, Zhou-quan WEI2, Xing-ming SUN2, Mei-rong XU3(
), Ai-chang CHEN2, Zhou-quan WEI2, Xing-ming SUN2, Mei-rong XU3( ), Xue-ping LI1, Hui DU1, Yong-hong QI1(
), Xue-ping LI1, Hui DU1, Yong-hong QI1( )
)
Received:2022-08-09
Revised:2022-11-21
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-05-26
Contact:
Mei-rong XU,Yong-hong QI
摘要:
为明确甘肃省陇西县黄芩根腐病镰孢菌种类,采用组织分离法对2019-2021年采集的136份病株进行分离,通过病原菌形态学特征、结合镰孢菌属通用引物、特异性引物及TEF序列分析,对病原菌进行鉴定并完成柯赫氏法则验证。结果表明,从黄芩根腐病样本上共分离到83株镰孢菌,分别为尖孢镰孢菌(39.8%)、茄病镰孢菌(36.1%)、锐顶镰孢菌(16.9%)、芬芳镰孢菌(4.8%)、木贼镰孢菌(1.2%)和柔毛镰孢菌(1.2%),其中尖孢镰孢菌和茄病镰孢菌为优势病原菌;致病性测定结果表明,不同的镰孢菌致病力不同,且同一种内各菌株的致病力差异显著;尖孢镰孢菌的相对病情指数最高,为9.0,而芬芳镰孢菌的相对病情指数最低,为1.2,木贼镰孢菌和柔毛镰孢菌没有致病性;黄芩受到镰孢菌侵染后,根部主要营养元素含量变化不显著,而微量元素锌、锰和铁的含量显著升高(P<0.05)。本研究在国内首次报道了锐顶镰孢菌和芬芳镰孢菌是黄芩根腐病的新病原菌,为科学诊断该病害、研究根腐病菌对黄芩胁迫的响应提供理论依据。
蒋晶晶, 陈爱昌, 魏周全, 孙兴明, 徐美蓉, 李雪萍, 杜蕙, 漆永红. 甘肃陇西黄芩镰孢菌根腐病病原鉴定及其病株根部元素含量的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 109-121.
Jing-jing JIANG, Ai-chang CHEN, Zhou-quan WEI, Xing-ming SUN, Mei-rong XU, Xue-ping LI, Hui DU, Yong-hong QI. Identification of Fusarium species from Scutellaria baicalensis root rot in Longxi, Gansu Province and effects on element contents of root[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 109-121.
引物 Primer | 引物序列 Sequence(5'-3') | 片段大小 Size (bp) | 退火温度 Annealing temperature (℃) | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | ATTACTCCAGCATCCTTGC | 1000 | 50.0 | 镰孢菌通用引物Primer for Fusarium[ |
| F2 | TTTACAACTCCCAAACCCC | |||
| FS1 | CCGCCAGAGGACCCCTAACT | 300 | 57.0 | 茄病镰孢菌F. solani[ |
| FS2 | TGTGCCCACAGGGGGCTT | |||
| FO1 | AAGAAGTCGAAGAATACATCGCT | 700 | 59.0 | 尖孢镰孢菌Fusarium oxysporum[ |
| FO2 | CGAGGAGTGTATGAGACGGC | |||
| TEF-F | ATGGGTAAGGARGACAAGAC | 700 | 57.5 | 镰孢菌鉴定引物Primers for the identification of Fusarium[ |
| TEF-R | GGARGTACCAGTSATCATGTT |
表1 引物序列
Table 1 Primers sequence
引物 Primer | 引物序列 Sequence(5'-3') | 片段大小 Size (bp) | 退火温度 Annealing temperature (℃) | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | ATTACTCCAGCATCCTTGC | 1000 | 50.0 | 镰孢菌通用引物Primer for Fusarium[ |
| F2 | TTTACAACTCCCAAACCCC | |||
| FS1 | CCGCCAGAGGACCCCTAACT | 300 | 57.0 | 茄病镰孢菌F. solani[ |
| FS2 | TGTGCCCACAGGGGGCTT | |||
| FO1 | AAGAAGTCGAAGAATACATCGCT | 700 | 59.0 | 尖孢镰孢菌Fusarium oxysporum[ |
| FO2 | CGAGGAGTGTATGAGACGGC | |||
| TEF-F | ATGGGTAAGGARGACAAGAC | 700 | 57.5 | 镰孢菌鉴定引物Primers for the identification of Fusarium[ |
| TEF-R | GGARGTACCAGTSATCATGTT |

图1 黄芩根腐病田间发病症状A: 苗期发病植株Diseased plants at seedling stage; B: 成株期发病植株Diseased plants at adult stage; C: 轻度病根Diseased root at mild stage; D: 重度病根Diseased root at severe stage.
Fig.1 Symptoms of S. baicalensis root rot in the field
采样年份 Collection year | 镰孢菌株编号 Strain number of Fusarium | 采样地点 Collection site |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | HQ-1-2, HQ-1-6, HQ-1-9, HQ-1-12, HQ-1-17, HQ-1-23 | 通安驿镇马头川村Matouchuan Village,Tong’anyiTown |
| HQ-3-1, HQ-3-2, HQ-3-4, HQ-3-5, HQ-3-7, HQ-3-8, HQ-3-9, HQ-3-11 | 通安驿镇牛站村Niuzhan Village,Tong’anyi Town | |
| HQ-5-12, HQ-5-14, HQ-9-1 | 首阳镇李家营村Lijiaying Village,Shouyang Town | |
| HQ-8-10 | 福星镇庞家岔村Pangjiacha Village,Fuxing Town | |
| 2020 | 2A-HQ-1, 2A-HQ-3 | 菜子镇二十铺村Ershipu Village,Caizi Town |
| 8A-HQ-2 | 碧岩镇王庄村Wangzhuang Village,Biyan Town | |
| 12A-HQ-5 | 文峰镇黄家门村Huangjiamen Village,Wenfeng Town | |
| 17A-HQ-2 | 文峰镇汪家坡村Wangjiapo Village,Wenfeng Town | |
| 22A-HQ-4 | 首阳镇三十铺村Sanshipu Village,Shouyang Town | |
| 27A-HQ-1, 27A-HQ-4 | 双泉镇胡家门村Hujiamen Village,Shuangquan Town | |
| 29A-HQ-1, 30A-HQ-1, 30A-HQ-2 | 柯寨镇葡萄村Putao Village,Kezhai Town | |
| 31A-HQ-2, 31A-HQ-6, 31A-HQ-9, 31A-HQ-11 | 柯寨镇张家湾村Zhangjiawan Village,Kezhai Town | |
| 1-HQ-2 | 通安驿镇马头川村Matouchuan Village,Tong’anyi Town | |
| 2-HQ-L-1, 2-HQ-L-3, 2-HQ-L-6, 2-HQ-B-4 | 通安驿镇高阳村Gaoyang Village,Tong’anyi Town | |
| 3-HQ-4 | 通安驿镇牛站村Niuzhan Village,Tong’anyi Town | |
| 4-HQ-3 | 文峰镇火焰村Huoyan Village,Wenfeng Town | |
| 7-HQ-4 | 福星镇裴家湾村Peijiawan Village,Fuxing Town | |
| 10-HQ-3, 10-HQ-5 | 菜子镇元阁村Yuange Village,Caizi Town | |
| 12-HQ-1, 12-HQ-3, 12-HQ-6 | 菜子镇中川村Zhongchuan Village,Caizi Town | |
| 13-HQ-1, 13-HQ-2, 13-HQ-3, 13-HQ-4, 13-HQ-6 | 菜子镇四店村Sidian Village,Caizi Town | |
| 14-HQ-1, 14-HQ-2, 14-HQ-3, 14-HQ-5 | 菜子镇蔡家峪村Caijiayu Village,Caizi Town | |
| 2021 | HQ-R-1, HQ-R-2, HQ-R-4, HQ-R-5, HQ-R-6, HQ-R-7, HQ-R-9, HQ-R-10, HQ-R-11, HQ-R-12, HQ-R-13, HQ-R-15, HQ-R-16, HQ-R-17, HQ-R-18, HQ-R-19, HQ-R-20, HQ-R-24, HQ-R-26, HQ-R-27, HQ-R-28, HQ-R-30, HQ-R-42, HQ-R-44, HQ-R-45, HQ-R-46, HQ-R-47, HQ-X-7 | 福星镇李家湾村Lijiawan Village,Fuxing Town |
表2 陇西县不同地区镰孢菌的分离信息
Table 2 Isolation information of Fusarium in Longxi County
采样年份 Collection year | 镰孢菌株编号 Strain number of Fusarium | 采样地点 Collection site |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | HQ-1-2, HQ-1-6, HQ-1-9, HQ-1-12, HQ-1-17, HQ-1-23 | 通安驿镇马头川村Matouchuan Village,Tong’anyiTown |
| HQ-3-1, HQ-3-2, HQ-3-4, HQ-3-5, HQ-3-7, HQ-3-8, HQ-3-9, HQ-3-11 | 通安驿镇牛站村Niuzhan Village,Tong’anyi Town | |
| HQ-5-12, HQ-5-14, HQ-9-1 | 首阳镇李家营村Lijiaying Village,Shouyang Town | |
| HQ-8-10 | 福星镇庞家岔村Pangjiacha Village,Fuxing Town | |
| 2020 | 2A-HQ-1, 2A-HQ-3 | 菜子镇二十铺村Ershipu Village,Caizi Town |
| 8A-HQ-2 | 碧岩镇王庄村Wangzhuang Village,Biyan Town | |
| 12A-HQ-5 | 文峰镇黄家门村Huangjiamen Village,Wenfeng Town | |
| 17A-HQ-2 | 文峰镇汪家坡村Wangjiapo Village,Wenfeng Town | |
| 22A-HQ-4 | 首阳镇三十铺村Sanshipu Village,Shouyang Town | |
| 27A-HQ-1, 27A-HQ-4 | 双泉镇胡家门村Hujiamen Village,Shuangquan Town | |
| 29A-HQ-1, 30A-HQ-1, 30A-HQ-2 | 柯寨镇葡萄村Putao Village,Kezhai Town | |
| 31A-HQ-2, 31A-HQ-6, 31A-HQ-9, 31A-HQ-11 | 柯寨镇张家湾村Zhangjiawan Village,Kezhai Town | |
| 1-HQ-2 | 通安驿镇马头川村Matouchuan Village,Tong’anyi Town | |
| 2-HQ-L-1, 2-HQ-L-3, 2-HQ-L-6, 2-HQ-B-4 | 通安驿镇高阳村Gaoyang Village,Tong’anyi Town | |
| 3-HQ-4 | 通安驿镇牛站村Niuzhan Village,Tong’anyi Town | |
| 4-HQ-3 | 文峰镇火焰村Huoyan Village,Wenfeng Town | |
| 7-HQ-4 | 福星镇裴家湾村Peijiawan Village,Fuxing Town | |
| 10-HQ-3, 10-HQ-5 | 菜子镇元阁村Yuange Village,Caizi Town | |
| 12-HQ-1, 12-HQ-3, 12-HQ-6 | 菜子镇中川村Zhongchuan Village,Caizi Town | |
| 13-HQ-1, 13-HQ-2, 13-HQ-3, 13-HQ-4, 13-HQ-6 | 菜子镇四店村Sidian Village,Caizi Town | |
| 14-HQ-1, 14-HQ-2, 14-HQ-3, 14-HQ-5 | 菜子镇蔡家峪村Caijiayu Village,Caizi Town | |
| 2021 | HQ-R-1, HQ-R-2, HQ-R-4, HQ-R-5, HQ-R-6, HQ-R-7, HQ-R-9, HQ-R-10, HQ-R-11, HQ-R-12, HQ-R-13, HQ-R-15, HQ-R-16, HQ-R-17, HQ-R-18, HQ-R-19, HQ-R-20, HQ-R-24, HQ-R-26, HQ-R-27, HQ-R-28, HQ-R-30, HQ-R-42, HQ-R-44, HQ-R-45, HQ-R-46, HQ-R-47, HQ-X-7 | 福星镇李家湾村Lijiawan Village,Fuxing Town |
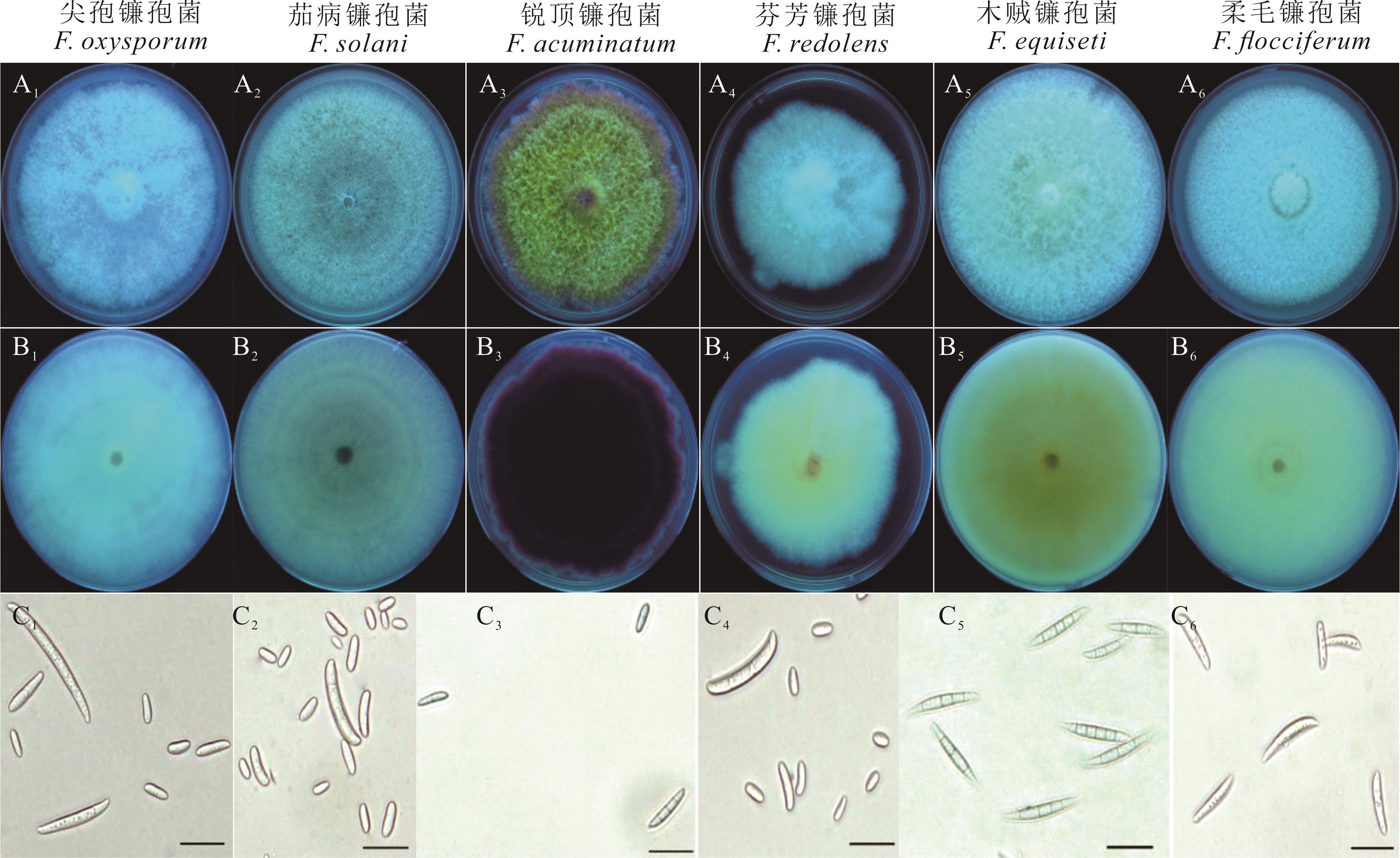
图2 不同镰孢菌在PSA (A、B) 和CLA (C) 培养基上的形态特征A1~A6: 菌落正面Colony obverse; B1~B6: 菌落背面Colony reverse; C1~C6: 分生孢子Conidium; 标尺为20 μm Scar bars=20 μm.
Fig.2 Morphological characteristics of different Fusarium on PSA (A, B) and CLA (C) medium
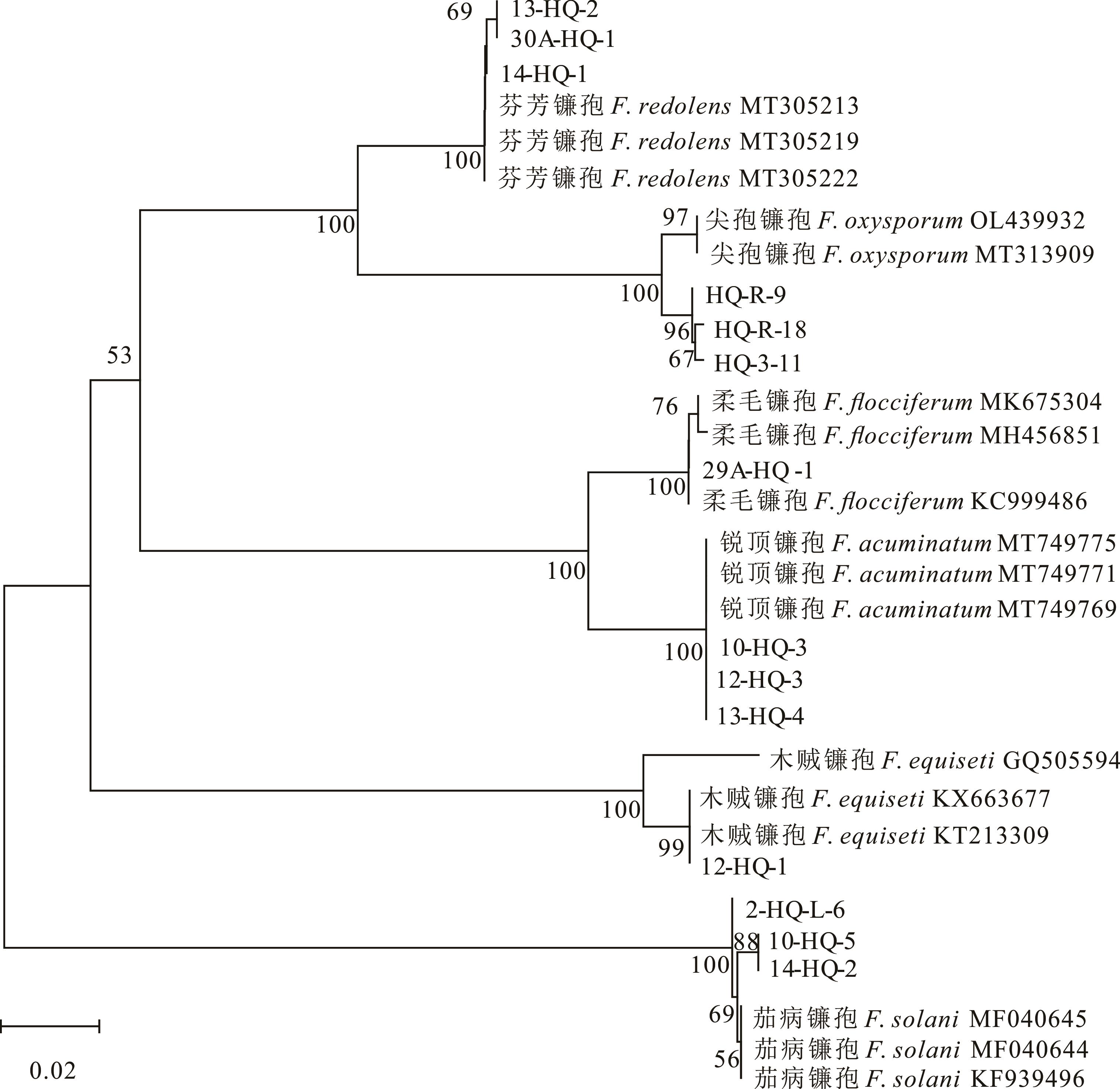
图3 基于TEF序列采用邻接法构建代表菌株及其相似菌株的系统发育树
Fig.3 Phylogenetic tree of representative strains and the related strains based on TEF gene sequences by using neighbor-joining method
病原菌种类 Species of pathogens | 分离率 Isolation rates (%) | 致病菌株比例 Ratio of pathogenic strains (%) | 菌株编号 Isolate code | 发病率 Incidence rate (%) | 相对发病率 Relative incidence rate (%) | 病情指数 Disease index | 相对病情指数 Relative disease index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
尖孢镰孢菌 F. oxysporum | 39.8 | 45.5 | HQ-3-1 | 55.6±11.1b | 27.6±2.2a | 38.9 | 9.0 |
| HQ-3-11 | 100.0±0.0a | 47.2 | |||||
| HQ-8-10 | 88.9±11.1a | 66.7 | |||||
| 2-HQ-B-4 | 100.0±0.0a | 75.0 | |||||
| 1-HQ-2 | 55.6±11.1b | 47.2 | |||||
| 3-HQ-4 | 100.0±0.0a | 100.0 | |||||
| 7-HQ-4 | 100.0±0.0a | 88.9 | |||||
| 2A-HQ-1 | 100.0±0.0a | 55.6 | |||||
| 2A-HQ-3 | 100.0±0.0a | 55.6 | |||||
| 12A-HQ-5 | 55.6±11.1b | 47.2 | |||||
| HQ-R-9 | 33.3±11.1bc | 33.3 | |||||
| HQ-R-13 | 22.2±11.1c | 16.7 | |||||
| HQ-R-24 | 100.0±0.0a | 50.0 | |||||
| HQ-R-30 | 11.1±11.1c | 11.1 | |||||
| HQ-R-45 | 11.1±11.1c | 11.1 | |||||
茄病镰孢菌 F. solani | 36.1 | 40.0 | HQ-1-6 | 100.0±0.0a | 27.4±10.2a | 66.7 | 7.8 |
| HQ-1-9 | 100.0±0.0a | 69.4 | |||||
| HQ-9-1 | 100.0±0.0a | 69.4 | |||||
| 10-HQ-5 | 100.0±0.0a | 69.4 | |||||
| 12-HQ-6 | 77.8±11.1ab | 63.9 | |||||
| 14-HQ-2 | 77.8±11.1ab | 61.1 | |||||
| 17A-HQ-2 | 66.7±0.0b | 55.6 | |||||
| 27A-HQ-4 | 66.7±19.3b | 47.2 | |||||
| 31A-HQ-6 | 66.7±0.0b | 41.7 | |||||
| HQ-R-4 | 33.3±0.0c | 25.0 | |||||
| HQ-R-28 | 22.2±11.1c | 11.1 | |||||
| 2-HQ-L-6 | 100.0±0.0a | 63.9 | |||||
锐顶镰孢菌 F. acuminatum | 16.9 | 50.0 | HQ-5-12 | 100.0±0.0a | 11.3±6.0b | 83.3 | 5.3 |
| HQ-5-14 | 100.0±0.0a | 100.0 | |||||
| 4-HQ-3 | 55.6±11.1b | 52.8 | |||||
| 10-HQ-3 | 100.0±0.0a | 100.0 | |||||
| 12-HQ-3 | 44.4±22.2bc | 44.4 | |||||
| 13-HQ-1 | 55.6±11.1b | 50.0 | |||||
| HQ-R-44 | 11.1±11.1c | 11.1 | |||||
| 芬芳镰孢菌F. redolens | 4.8 | 25.0 | 14-HQ-1 | 100.0±0.0a | 4.8±0.0c | 100.0 | 1.2 |
表3 致病镰孢菌的致病性测定
Table 3 Pathogenicity testing of pathogenic Fusarium
病原菌种类 Species of pathogens | 分离率 Isolation rates (%) | 致病菌株比例 Ratio of pathogenic strains (%) | 菌株编号 Isolate code | 发病率 Incidence rate (%) | 相对发病率 Relative incidence rate (%) | 病情指数 Disease index | 相对病情指数 Relative disease index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
尖孢镰孢菌 F. oxysporum | 39.8 | 45.5 | HQ-3-1 | 55.6±11.1b | 27.6±2.2a | 38.9 | 9.0 |
| HQ-3-11 | 100.0±0.0a | 47.2 | |||||
| HQ-8-10 | 88.9±11.1a | 66.7 | |||||
| 2-HQ-B-4 | 100.0±0.0a | 75.0 | |||||
| 1-HQ-2 | 55.6±11.1b | 47.2 | |||||
| 3-HQ-4 | 100.0±0.0a | 100.0 | |||||
| 7-HQ-4 | 100.0±0.0a | 88.9 | |||||
| 2A-HQ-1 | 100.0±0.0a | 55.6 | |||||
| 2A-HQ-3 | 100.0±0.0a | 55.6 | |||||
| 12A-HQ-5 | 55.6±11.1b | 47.2 | |||||
| HQ-R-9 | 33.3±11.1bc | 33.3 | |||||
| HQ-R-13 | 22.2±11.1c | 16.7 | |||||
| HQ-R-24 | 100.0±0.0a | 50.0 | |||||
| HQ-R-30 | 11.1±11.1c | 11.1 | |||||
| HQ-R-45 | 11.1±11.1c | 11.1 | |||||
茄病镰孢菌 F. solani | 36.1 | 40.0 | HQ-1-6 | 100.0±0.0a | 27.4±10.2a | 66.7 | 7.8 |
| HQ-1-9 | 100.0±0.0a | 69.4 | |||||
| HQ-9-1 | 100.0±0.0a | 69.4 | |||||
| 10-HQ-5 | 100.0±0.0a | 69.4 | |||||
| 12-HQ-6 | 77.8±11.1ab | 63.9 | |||||
| 14-HQ-2 | 77.8±11.1ab | 61.1 | |||||
| 17A-HQ-2 | 66.7±0.0b | 55.6 | |||||
| 27A-HQ-4 | 66.7±19.3b | 47.2 | |||||
| 31A-HQ-6 | 66.7±0.0b | 41.7 | |||||
| HQ-R-4 | 33.3±0.0c | 25.0 | |||||
| HQ-R-28 | 22.2±11.1c | 11.1 | |||||
| 2-HQ-L-6 | 100.0±0.0a | 63.9 | |||||
锐顶镰孢菌 F. acuminatum | 16.9 | 50.0 | HQ-5-12 | 100.0±0.0a | 11.3±6.0b | 83.3 | 5.3 |
| HQ-5-14 | 100.0±0.0a | 100.0 | |||||
| 4-HQ-3 | 55.6±11.1b | 52.8 | |||||
| 10-HQ-3 | 100.0±0.0a | 100.0 | |||||
| 12-HQ-3 | 44.4±22.2bc | 44.4 | |||||
| 13-HQ-1 | 55.6±11.1b | 50.0 | |||||
| HQ-R-44 | 11.1±11.1c | 11.1 | |||||
| 芬芳镰孢菌F. redolens | 4.8 | 25.0 | 14-HQ-1 | 100.0±0.0a | 4.8±0.0c | 100.0 | 1.2 |
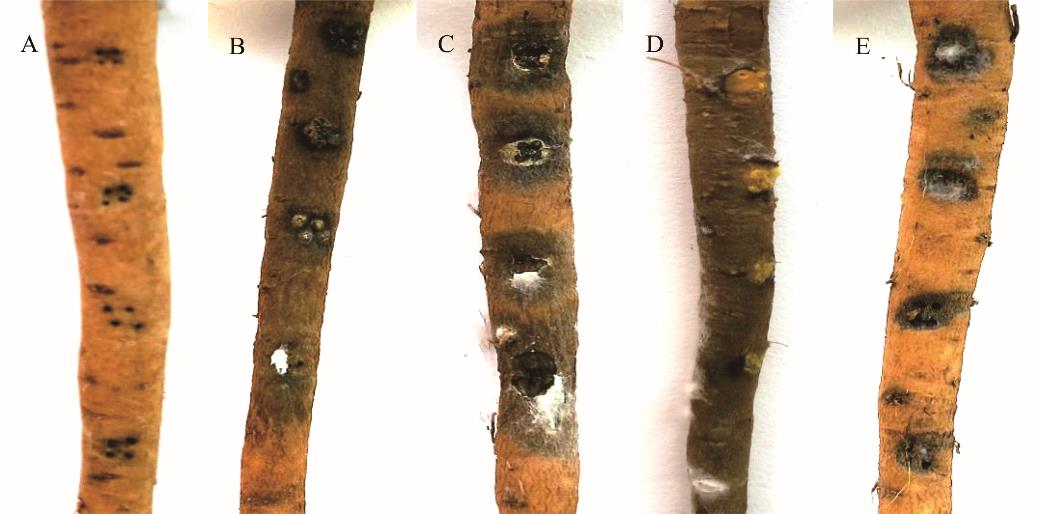

图4 镰孢菌接种离体根致病性测定A: 空白对照CK; B: 尖孢镰孢菌F. oxysporum; C: 茄病镰孢菌F. solani; D: 锐顶镰孢菌F. acuminatum; E: 芬芳镰孢菌F. redolens.
Fig.4 Pathogenicity testing inoculated roots with Fusariumin vitro
处理 Treatments | 总灰分 Total ash (%) | 蛋白质 Protein (g·100 g-1) | 总糖 Total sugar (g·100 g-1) | 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar (g·100 g-1) | N (g·kg-1) | P (g·kg-1) | K (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病根Diseased roots | 6.00±0.04a | 5.50±0.07a | 23.00±0.11b | 10.50±0.24a | 8.80±0.05a | 1.57±0.27a | 9.25±0.04a |
| 健根Healthy roots | 5.80±0.02a | 5.00±0.04a | 29.20±0.08a | 12.70±0.17a | 7.99±0.09a | 1.02±0.18a | 11.78±0.07a |
表4 根腐病菌对黄芩根部营养元素含量的影响
Table 4 Effect of Fusarium on nutrient elements of S. baicalensis roots
处理 Treatments | 总灰分 Total ash (%) | 蛋白质 Protein (g·100 g-1) | 总糖 Total sugar (g·100 g-1) | 可溶性糖 Soluble sugar (g·100 g-1) | N (g·kg-1) | P (g·kg-1) | K (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病根Diseased roots | 6.00±0.04a | 5.50±0.07a | 23.00±0.11b | 10.50±0.24a | 8.80±0.05a | 1.57±0.27a | 9.25±0.04a |
| 健根Healthy roots | 5.80±0.02a | 5.00±0.04a | 29.20±0.08a | 12.70±0.17a | 7.99±0.09a | 1.02±0.18a | 11.78±0.07a |
处理 Treatments | Zn (mg·kg-1) | Mn (mg·kg-1) | Cu (mg·kg-1) | Fe (mg·kg-1) | Ca (g·kg-1) | Mg (g·kg-1) | B (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病根Diseased roots | 19.00±0.18a | 24.80±0.24a | 9.30±0.13a | 496.00±0.09a | 4.72±0.27a | 3.07±0.09a | 10.50±0.15a |
| 健根Healthy roots | 12.30±0.09b | 19.50±0.14b | 7.60±0.11a | 384.00±0.10b | 3.66±0.16a | 3.27±0.12a | 12.90±0.15a |
表5 根腐病对黄芩根部微量元素含量的影响
Table 5 Effect of Fusarium on micro element of S. baicalensi roots
处理 Treatments | Zn (mg·kg-1) | Mn (mg·kg-1) | Cu (mg·kg-1) | Fe (mg·kg-1) | Ca (g·kg-1) | Mg (g·kg-1) | B (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病根Diseased roots | 19.00±0.18a | 24.80±0.24a | 9.30±0.13a | 496.00±0.09a | 4.72±0.27a | 3.07±0.09a | 10.50±0.15a |
| 健根Healthy roots | 12.30±0.09b | 19.50±0.14b | 7.60±0.11a | 384.00±0.10b | 3.66±0.16a | 3.27±0.12a | 12.90±0.15a |
| 1 | Zhao T T, Tang H L, Xie L, et al. Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. (Lamiaceae): a review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 2019, 71(9): 1353-1369. |
| 2 | She S F. Study on the medicinal value of Scutellaria baicalensis. Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2012, 29(3): 139-142. |
| 厍士芳. 黄芩属植物的药用价值研究. 中医药信息, 2012, 29(3): 139-142. | |
| 3 | Chang J, Yang Y X, Dan J Y, et al. Study on comprehensive control of the disease of Scutellaria baicalensis Geogi in Shaanxi Province. Journal of Xi’an University of Arts & Science (Natural Science Edition), 2007(2): 30-32. |
| 常瑾, 杨玉秀, 淡静雅, 等. 陕西黄芩主要病害及其综合防治技术研究. 西安文理学院学报(自然科学版), 2007(2): 30-32. | |
| 4 | Zhu G Q, Zeng Z H, Zhao J, et al. Isolation and identification of pathogens of Scutellaria baicalensis root rot in Shangluo city. Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 63(11): 63-64. |
| 朱广啟, 曾志海, 赵晋, 等. 商洛市黄芩根腐病病原菌分离与鉴定. 陕西农业科学, 2017, 63(11): 63-64. | |
| 5 | Zeng Z H, Zhao J, Sheng L, et al. Control of Scutellaria baicalensis Geogi root rot of different pesticides and microfertilizer. Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 63(2): 44-46. |
| 曾志海, 赵晋, 盛琳, 等. 不同农药、微肥组合防治黄芩根腐病试验. 陕西农业科学, 2017, 63(2): 44-46. | |
| 6 | Zeng Z H, Zhao J, Zhu G Q, et al. The inhibition effect of Trichoderma on Scutellaria baicalensis root rot pathogen. Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 64(3): 33-34. |
| 曾志海, 赵晋, 朱广啟, 等. 木霉菌对黄芩根腐病病原菌抑制作用初探. 陕西农业科学, 2018, 64(3): 33-34. | |
| 7 | Wang Z G, Cao S, Xu N, et al. Cultural characteristics of fungal endophyte from 3 locoweed species in China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(10): 158-169. |
| 汪治刚, 曹师, 徐娜, 等. 我国3种疯草的内生真菌培养特性研究. 草业学报, 2017, 26(10): 158-169. | |
| 8 | Li X P, Xu S Y, Wang X M, et al. Field survey and pathogen identification of naked barley root rot in Qinghai Province. Journal of Plant Protection, 2021, 48(4): 757-765. |
| 李雪萍, 许世洋, 汪学苗, 等. 青海省青稞根腐病调查及病原菌鉴定. 植物保护学报, 2021, 48(4): 757-765. | |
| 9 | Booth C. The genus Fusarium. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1988: 94-115. |
| Booth C. 镰刀菌属. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1988: 94-115. | |
| 10 | Li C Q, Li J Q, Wang X C, et al. Isolation, identification and biological characteristics of Fusarium perseae isolated from Potentilla anserina roots. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(4): 113-123. |
| 李晨芹, 李军乔, 王鑫慈, 等. 蕨麻根腐病病原菌的分离鉴定及其生物学特性研究. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 113-123. | |
| 11 | Zhang Y D, Liu J, Huang W K, et al. Molecular identification of Fusarium species from the wilt soybean lines in Langfang, Hebei Province. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2018, 48(6): 738-747. |
| 张亚朵, 刘佳, 黄文坤, 等. 河北廊坊大豆枯萎病病原镰刀菌的分子鉴定. 植物病理学报, 2018, 48(6): 738-747. | |
| 12 | Wang J S, Wang J M, Li X, et al. Rapid molecular detection of Fusarium oxysporum by PCR. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2013, 43(3): 318-322. |
| 王健生, 王佳妹, 李潇, 等. 尖镰孢菌(Fusarium oxysporum)的快速分子检测. 植物病理学报, 2013, 43(3): 318-322. | |
| 13 | Rahjoo V, Zad J, Javan-Nikkhah M, et al. Morphological and molecular identification of Fusarium isolated from maize ears in Iran. Journal of Plant Pathology, 2008, 90(3): 463-468. |
| 14 | Li X P. Naked barley root rot diseases and influence on its rhizosphere microecology in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2017. |
| 李雪萍. 青藏高原青稞根腐类病害及其对根际土壤微生态的影响. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2017. | |
| 15 | Huang Y P. Studies on the pathogens causing Angelica sinensis root rot. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2011. |
| 黄亚萍. 当归根腐病病原物研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2011. | |
| 16 | Huang S M, Wei S L, Wei L P, et al. Comparison and analysis of resistance of eight banana accessions to Fusarium wilt. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2019, 40(11): 2189-2196. |
| 黄素梅, 韦绍龙, 韦莉萍, 等. 8种香蕉种质对枯萎病的抗性比较与分析. 热带作物学报, 2019, 40(11): 2189-2196. | |
| 17 | Huang B Z, Xu L B, Yang H, et al. Preliminary results of field evaluation of banana germplasm resistant to Fusarium wilt disease. Guangdong Agricultural Science, 2005(6): 9-10. |
| 黄秉智, 许林兵, 杨护, 等. 香蕉种质资源枯萎病抗性田间评价初报. 广东农业科学, 2005(6): 9-10. | |
| 18 | Qi Y H, Cao S F, Li X P, et al. Effects of Fusarium avenaceum on the leaf cell structure and the physiological and biochemical characteristics of naked barley. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 32(9): 1839-1847. |
| 漆永红, 曹素芳, 李雪萍, 等. 燕麦镰孢菌对青稞叶片细胞结构及生理生化特性的影响. 核农学报, 2018, 32(9): 1839-1847. | |
| 19 | Qi Y H, Zhang X R, Cao S F, et al. Ditylenchus destructor: Effects on the cell structure and the physiological characteristics of Angelica sinensis. Journal of Agriculture, 2021, 11(6): 36-41. |
| 漆永红, 张新瑞, 曹素芳, 等. 腐烂茎线虫对当归细胞结构和生理特性的影响. 农学学报, 2021, 11(6): 36-41. | |
| 20 | Xu M R, Li M Q, Cao S F, et al. Effect of Fusarium oxysporiums on the cell structure and physiological characteristics of Codonopsis pilosula. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(4): 915-922. |
| 徐美蓉, 李敏权, 曹素芳, 等. 根腐病对党参细胞结构及生理生化特性的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(4): 915-922. | |
| 21 | Shen Q Q, Liu F, Hu Y. Research progress of pathogens of root rot disease on medicinal plants. Northern Horticulture, 2014(11): 187-190. |
| 沈清清, 刘芳, 胡彦. 药用植物根腐病病原菌研究进展. 北方园艺, 2014(11): 187-190. | |
| 22 | Gao F, Ren X X, Wang M L, et al. Research progress in root rot diseases of Chinese herbal medicine and control strategy by antagonistic microorganisms. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 40(21): 4122-4126. |
| 高芬, 任小霞, 王梦亮, 等. 中草药根腐病及其微生物防治研究进展. 中国中药杂志, 2015, 40(21): 4122-4126. | |
| 23 | Liao C H, Chen J W, Lv W W, et al. Progress on medicinal root rot in root and rhizome. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2017, 40(2): 492-497. |
| 廖长宏, 陈军文, 吕婉婉, 等. 根和根茎类药用植物根腐病研究进展. 中药材, 2017, 40(2): 492-497. | |
| 24 | Mu X R, Ma Y Y, Yang Z Z, et al. Research advance on the control of root rot disease of medical plants. Pharmacy and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica, 2014, 5(2): 5-8, 52. |
| 穆向荣, 马逾英, 杨枝中, 等. 药用植物根腐病防治的研究进展. 中药与临床, 2014, 5(2): 5-8, 52. | |
| 25 | Cao Z Y, Yang Y H, Shentu X P, et al. Identification of the pathogenic fungi of root rot of traditional medicinal Dendrobium officinale in Zhejiang Province. Journal of Plant Protection, 2020, 47(1): 178-186. |
| 曹瑱艳, 杨怡华, 申屠旭萍, 等. 浙江省铁皮石斛根腐病病原真菌的鉴定. 植物保护学报, 2020, 47(1): 178-186. | |
| 26 | Zarrin M, Ganj F, Faramarzi S. Development of a polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism method for identification of the Fusarium genus using the transcription elongation factor-1alpha gene. Biomedical Reports, 2016, 5(6): 705-708. |
| 27 | Wu Y L, Huang B Z, Zhang Z S, et al. Modification of in vitro bioassay for screening Musa species against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2020, 47(8): 1577-1584. |
| 吴元立, 黄秉智, 张智胜, 等. 香蕉枯萎病抗性离体接种鉴定方法的优化. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(8): 1577-1584. | |
| 28 | Xiao R F, Chen Y P, Chen M C, et al. Pathogen identification of root rot of Pseudostellaria heterophylla plant and fungicide screening for its efficient control. Journal of Plant Protection, 2020, 47(6): 1333-1342. |
| 肖荣凤, 陈燕萍, 陈梅春, 等. 太子参根腐病病原菌的鉴定及防治药剂筛选. 植物保护学报, 2020, 47(6): 1333-1342. | |
| 29 | Gao F, Zhao X X, Qin X M, et al. Analysis of dominant pathogen community causing Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus root rot in Shanxi Province. Journal of Plant Protection, 2018, 45(4): 878-885. |
| 高芬, 赵晓霞, 秦雪梅, 等. 山西省蒙古黄芪根腐病优势致病菌群分析. 植物保护学报, 2018, 45(4): 878-885. | |
| 30 | Moustafa B, Alejandro P D L, Diego R, et al. Physical and chemical barriers in root tissues contribute to quantitative resistance to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. pisi in pea. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 199-214. |
| [1] | 李彦忠, 喻军强, 李明. 48个苜蓿品种对3种病害抗性的初步评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 62-75. |
| [2] | 李雪萍, 刘梅金, 许世洋, 郭建炜, 漆永红, 李敏权. 青稞普通根腐病的调查与病原鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 190-198. |
| [3] | 孙林, 刘广华, 张欣昕, 薛艳林, 吴晓光, 肖燕子, 殷国梅, 刘思博, 张福金. 蒙药黄芩与制粒对紫花苜蓿维生素和化学成分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 99-108. |
| [4] | 王宝宝, 毕四刚, 肖明纲, 张冬英, 闫强, 张彦彦, 杨树龙, 朱振东, 段灿星. 黑龙江省玉米穗腐病致病镰孢菌分离鉴定及产毒基因型分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 163-174. |
| [5] | 方香玲, 张彩霞, 南志标. 紫花苜蓿镰刀菌根腐病研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 169-183. |
| [6] | 易铭, 梁嘉俊, 史建, 李洪建, 程积民, 焦锋. 采用EF-1α序列分析法对苜蓿根腐病病原菌——锐顶镰刀菌的鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(2): 61-68. |
| [7] | 柏玉晶, 姚玉玲, 张振粉, 杨成德, 薛莉. 紫花苜蓿根腐病原——厚垣镰刀菌的鉴定及其拮抗菌的筛选[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(2): 78-87. |
| [8] | 李彦忠, 徐娜, 汪治刚, 史敏. 沙打旺黄矮根腐病的研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(11): 196-204. |
| [9] | 孙广正, 姚拓, 赵桂琴, 李建宏, 陈龙, 刘欢. 植物根际促生菌对两种真菌病害病原的抑制作用及其鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(8): 154-163. |
| [10] | 李捷, 冯丽丹, 杨成德, 王有科, 何静, 张宝琳, 陈秀蓉. 接种尖镰孢菌对枸杞苯丙烷代谢关键酶及产物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(5): 87-94. |
| [11] | 伍文宪, 刘勇, 黄小琴, 张蕾, 周西全, 刘红雨. 尖孢镰刀菌分子检测技术的建立与应用[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(5): 109-115. |
| [12] | 韩文娇, 白林利, 李昌晓. 水淹胁迫对狗牙根光合、生长及营养元素含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(5): 49-59. |
| [13] | 刘莎莎,程园园,张丹,王晓丹,刘佳莉,郭长虹. 两株紫花苜蓿根际芽孢杆菌的筛选及生防效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(9): 96-103. |
| [14] | 李兴龙,李彦忠. 土传病害生物防治研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(3): 204-212. |
| [15] | 古丽君,徐秉良,李彬,梁巧兰. 草坪禾草根腐病病原菌生物学特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(3): 93-98. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||