

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (10): 173-186.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022449
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
贾晶莹1,2( ), 刘宝宝1,2, 马云1,2, 段红娟1,2, 蔡小艳1,2(
), 刘宝宝1,2, 马云1,2, 段红娟1,2, 蔡小艳1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-11-14
修回日期:2023-02-21
出版日期:2023-10-20
发布日期:2023-07-26
通讯作者:
蔡小艳
作者简介:E-mail: caixiaoyan282@163.com基金资助:
Jing-ying JIA1,2( ), Bao-bao LIU1,2, Yun MA1,2, Hong-juan DUAN1,2, Xiao-yan CAI1,2(
), Bao-bao LIU1,2, Yun MA1,2, Hong-juan DUAN1,2, Xiao-yan CAI1,2( )
)
Received:2022-11-14
Revised:2023-02-21
Online:2023-10-20
Published:2023-07-26
Contact:
Xiao-yan CAI
摘要:
筛选出高乳脂奶牛和低乳脂奶牛血液和牛奶中显著差异表达的苜蓿来源miRNAs及其在奶牛体内的潜在靶基因,可为进一步探究苜蓿源miRNAs(mtr-miRNAs)在基因水平调节牛奶乳脂率奠定基础。试验首先对生产4胎,日粮水平一致的荷斯坦奶牛牛奶进行了奶牛生产性能(dairy herd improvement, DHI)检测,在高乳脂和低乳脂奶牛中各选3头作为重复。运用RT-qPCR对奶牛血液和牛奶中的苜蓿源miRNAs进行定量,筛选出差异表达miRNAs后对其进行靶基因预测和分析,并根据miRNA-mRNA结合位点和定量结果筛选出与乳脂代谢相关的靶基因。结果如下:1)DHI检测筛选出了3头高乳脂奶牛和3头低乳脂奶牛,高乳脂奶牛牛奶中脂肪含量>4.2%,低乳脂奶牛牛奶中脂肪含量<3.5%;2)苜蓿源novel-miR54、miR156f、miR166a、miR168b和miR168c-3p在奶牛血液和牛奶中均能检测到,其中mtr-miR168b在高乳脂奶牛血液中的表达量极显著低于在低乳脂奶牛中的表达量(P<0.01),在高乳脂奶牛牛奶中的表达量显著低于在低乳脂奶牛中的表达量(P<0.05);3)mtr-miR168b在乳腺上皮细胞中高表达抑制了其中脂代谢标志基因PPARγ,SCD1,CEBP/β和SREBP1的表达量;4)mtr-miR168b预测靶基因分别有1834和296个与GO和KEGG数据库比对成功,靶基因主要与N-聚糖生物合成(3.72%)、cGMP-PKG信号通路(2.37%)和血管平滑肌收缩(2.37%)密切相关,甘油磷脂代谢(1.69%)通路也被显著富集;5)筛选出CPT1A和STARD7两个与脂代谢密切相关的基因,并通过双荧光素酶报告确认了miR-168b和CPT1A与STARD7的靶向关系。由此可见,mtr-miR168b可抑制乳腺上皮细胞中的成脂标志基因的表达,试验为后续验证苜蓿源miRNAs调控奶牛乳脂率提供了可进一步验证的靶基因。
贾晶莹, 刘宝宝, 马云, 段红娟, 蔡小艳. 苜蓿源miR168b跨界调控奶牛体内乳脂相关靶基因的筛选[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 173-186.
Jing-ying JIA, Bao-bao LIU, Yun MA, Hong-juan DUAN, Xiao-yan CAI. Screening of target genes related to milk fat in dairy cows regulated by alfalfa miR168b[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(10): 173-186.
牛号 ID | 产犊日期 Calving date (year/month/day) | 胎次 Parity | 产犊间隔 Calving interval (d) | 泌乳天数 Lactation days (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0001 | 2021/7/19 | 4 | 371 | 120 |
| 0002 | 2021/7/12 | 4 | 340 | 127 |
| 0003 | 2021/5/13 | 4 | 364 | 187 |
| 0004 | 2021/7/12 | 4 | 426 | 127 |
| 0005 | 2021/5/15 | 4 | 381 | 185 |
| 0006 | 2021/7/31 | 4 | 364 | 108 |
表1 采样牛基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of sampling cattle
牛号 ID | 产犊日期 Calving date (year/month/day) | 胎次 Parity | 产犊间隔 Calving interval (d) | 泌乳天数 Lactation days (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0001 | 2021/7/19 | 4 | 371 | 120 |
| 0002 | 2021/7/12 | 4 | 340 | 127 |
| 0003 | 2021/5/13 | 4 | 364 | 187 |
| 0004 | 2021/7/12 | 4 | 426 | 127 |
| 0005 | 2021/5/15 | 4 | 381 | 185 |
| 0006 | 2021/7/31 | 4 | 364 | 108 |
| 项目 Item | 含量 Content | 营养水平 Nutritient level | 含量 Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| 苜蓿 Alfalfa (%) | 6.00 | 干物质采食量 Dry matter feed intake(kg·d-1) | 24.4 |
| 玉米青贮 Corn silage (%) | 50.00 | 粗蛋白 Crude protein (CP, %) | 17.2 |
| 全棉籽 Cottonseed (%) | 1.00 | 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fiber (NDF, %) | 27.5 |
| 甜菜颗粒 Beet granules (%) | 1.60 | 粗脂肪 Fat (%) | 3.9 |
| 湿啤酒糟 Wet beer lees (%) | 10.00 | 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fiber (ADF, %) | 21.7 |
| 压片玉米 Tablet corn (%) | 4.00 | 牛奶净能Milk net energy production (NEL, MJ·kg-1) | 7.78 |
| 预混料 Premix (%) | 26.96 | 淀粉 Starch (%) | 27.5 |
| 水 H2O (%) | 1.20 | 钙 Ca (%) | 0.53 |
| 合计 Total (%) | 100.00 | 磷 P (%) | 0.36 |
表2 日粮组成及营养水平(干物质基础)
Table 2 The dietary composition and nutrient level (DM basis)
| 项目 Item | 含量 Content | 营养水平 Nutritient level | 含量 Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| 苜蓿 Alfalfa (%) | 6.00 | 干物质采食量 Dry matter feed intake(kg·d-1) | 24.4 |
| 玉米青贮 Corn silage (%) | 50.00 | 粗蛋白 Crude protein (CP, %) | 17.2 |
| 全棉籽 Cottonseed (%) | 1.00 | 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fiber (NDF, %) | 27.5 |
| 甜菜颗粒 Beet granules (%) | 1.60 | 粗脂肪 Fat (%) | 3.9 |
| 湿啤酒糟 Wet beer lees (%) | 10.00 | 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fiber (ADF, %) | 21.7 |
| 压片玉米 Tablet corn (%) | 4.00 | 牛奶净能Milk net energy production (NEL, MJ·kg-1) | 7.78 |
| 预混料 Premix (%) | 26.96 | 淀粉 Starch (%) | 27.5 |
| 水 H2O (%) | 1.20 | 钙 Ca (%) | 0.53 |
| 合计 Total (%) | 100.00 | 磷 P (%) | 0.36 |
| miRNAs名称miRNAs name | 引物序列Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| U6 | F:GCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAAT |
| R:CGCTTCACGAATTTGCGTGTCAT | |
| mtr-miR168b | F:CATGTGTCGCTTGGTGCAG |
| R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACTTCCCGAC | |
| mtr-miR166a | F: CACAGTTCGGACCAGGCTT |
| R: AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGGGGAATG | |
| mtr-miR168c-3p | F: CATAGACCCGCCTTGCATC |
| R: AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACATTCAGTT | |
| mtr-miR156f | F: CCGTTGACAGAAGATAGAGAGCAC |
| R: ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGTGCTC | |
| mtr-novel-miR54 | F: CCAAGTCCTTGTGTTGCATCTC |
| R: ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGAGATG | |
| bta-miR-16a | F: GCCCGTAGCAGCACGTAAAT |
| R: TGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAAT | |
| RT: CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGCACCAA |
表3 miRNAs引物信息
Table 3 Primer information of miRNAs
| miRNAs名称miRNAs name | 引物序列Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| U6 | F:GCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAAT |
| R:CGCTTCACGAATTTGCGTGTCAT | |
| mtr-miR168b | F:CATGTGTCGCTTGGTGCAG |
| R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| RT:GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACTTCCCGAC | |
| mtr-miR166a | F: CACAGTTCGGACCAGGCTT |
| R: AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGGGGAATG | |
| mtr-miR168c-3p | F: CATAGACCCGCCTTGCATC |
| R: AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACATTCAGTT | |
| mtr-miR156f | F: CCGTTGACAGAAGATAGAGAGCAC |
| R: ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGTGCTC | |
| mtr-novel-miR54 | F: CCAAGTCCTTGTGTTGCATCTC |
| R: ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACGAGATG | |
| bta-miR-16a | F: GCCCGTAGCAGCACGTAAAT |
| R: TGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAAT | |
| RT: CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGCACCAA |
基因名称 Gene name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| GAPDH | F: GGCATCGTGGAGGGACTTATG |
| R: GCCAGTGAGCTTCCCGTTGAG | |
| PPARγ | F: AAAGGAGAGCCTGAACTTGGAG |
| R: TCTGAACTGTGCTGTGGCAA | |
| SCD1 | F: ACATTGATCCCCACCTGCAA |
| R: AAACGTCATTCTGGAACGGC | |
| CEBP/β | F: TGGTGAATAGTGCTGCCCAT |
| R: GGTGGTAGTTGTGGAAGCCC | |
| SREBP1 | F: CAATGTGTGAGAAGGCCAGT |
| R:ACAAGGAGCAGGTCACACAG | |
| SERINC1 | F: TTGCGGCCGC CAAGCCAAGCGCATAAGT |
| R: CCTCGAGCCTGTAGGACAAGGCATC | |
| STARD7 | F: TTGCGGCCGC CGTTCTCGGTCCAAGCGTT |
| R: CCTCGAGATGGGAGGCGGAGACTGA | |
| CPT1A | F: TTGCGGCCGC CTTAAGGGACAAGCGATT |
| R: CCTCGAGCAGTCTGATGGAAGGGAA |
表4 引物信息
Table 4 Primer information
基因名称 Gene name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| GAPDH | F: GGCATCGTGGAGGGACTTATG |
| R: GCCAGTGAGCTTCCCGTTGAG | |
| PPARγ | F: AAAGGAGAGCCTGAACTTGGAG |
| R: TCTGAACTGTGCTGTGGCAA | |
| SCD1 | F: ACATTGATCCCCACCTGCAA |
| R: AAACGTCATTCTGGAACGGC | |
| CEBP/β | F: TGGTGAATAGTGCTGCCCAT |
| R: GGTGGTAGTTGTGGAAGCCC | |
| SREBP1 | F: CAATGTGTGAGAAGGCCAGT |
| R:ACAAGGAGCAGGTCACACAG | |
| SERINC1 | F: TTGCGGCCGC CAAGCCAAGCGCATAAGT |
| R: CCTCGAGCCTGTAGGACAAGGCATC | |
| STARD7 | F: TTGCGGCCGC CGTTCTCGGTCCAAGCGTT |
| R: CCTCGAGATGGGAGGCGGAGACTGA | |
| CPT1A | F: TTGCGGCCGC CTTAAGGGACAAGCGATT |
| R: CCTCGAGCAGTCTGATGGAAGGGAA |
项目 Item | 牛号 ID | 产奶量 DMY (kg·cow-1) | 乳脂率 MFP (%) | 乳蛋白率 MPP (%) | 乳糖率 MLP (%) | 总固形物 Total solids (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高乳脂组High-milk fat group | 0001 | 44.7 | 4.66 | 2.77 | 5.78 | 14.62 |
| 0002 | 43.8 | 4.50 | 3.30 | 4.32 | 13.44 | |
| 0003 | 34.9 | 4.27 | 4.21 | 5.21 | 15.21 | |
| 低乳脂组Low-milk fat group | 0004 | 33.0 | 3.42 | 3.23 | 5.38 | 13.32 |
| 0005 | 31.2 | 3.32 | 3.78 | 5.59 | 13.88 | |
| 0006 | 29.8 | 3.27 | 3.72 | 4.79 | 13.19 |
表5 基于DHI检测的高乳脂与低乳脂奶牛的奶产量及奶品质
Table 5 Milk yield and quality of high-fat and low-fat dairy cows based on DHI detection
项目 Item | 牛号 ID | 产奶量 DMY (kg·cow-1) | 乳脂率 MFP (%) | 乳蛋白率 MPP (%) | 乳糖率 MLP (%) | 总固形物 Total solids (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高乳脂组High-milk fat group | 0001 | 44.7 | 4.66 | 2.77 | 5.78 | 14.62 |
| 0002 | 43.8 | 4.50 | 3.30 | 4.32 | 13.44 | |
| 0003 | 34.9 | 4.27 | 4.21 | 5.21 | 15.21 | |
| 低乳脂组Low-milk fat group | 0004 | 33.0 | 3.42 | 3.23 | 5.38 | 13.32 |
| 0005 | 31.2 | 3.32 | 3.78 | 5.59 | 13.88 | |
| 0006 | 29.8 | 3.27 | 3.72 | 4.79 | 13.19 |

图1 苜蓿源miRNAs在奶牛血液中相对表达量a:苜蓿源miRNAs在牛血液中的表达量;b: 苜蓿源miRNAs在高乳脂和低乳脂奶牛血液中的表达差异。ID: 0001~ID:0006为牛号,下同。**P<0.01为显著性。a: Alfalfa miRNAs expression level in blood, b: Expression difference of alfalfa miRNAs in blood of high-milk fat and low-milk fat dairy cows. ID: 0001-ID:0006 indicate cows numbers, the same below. **P<0.01 was considered statistically significant.
Fig.1 Relative expression level of alfalfa miRNAs in bovine blood

图2 苜蓿源miRNAs在奶牛牛奶的相对表达量a: 苜蓿源miRNAs在牛奶中的表达量;b: 苜蓿源miRNAs在高乳脂和低乳脂奶牛牛奶中的表达差异。*P<0.05为显著性。a: Alfalfa miRNAs expression level in milk, b: Expression difference of alfalfa miRNAs in milk of high-milk fat and low-milk fat dairy cows. *P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Fig.2 Relative expression level of alfalfa miRNAs in milk
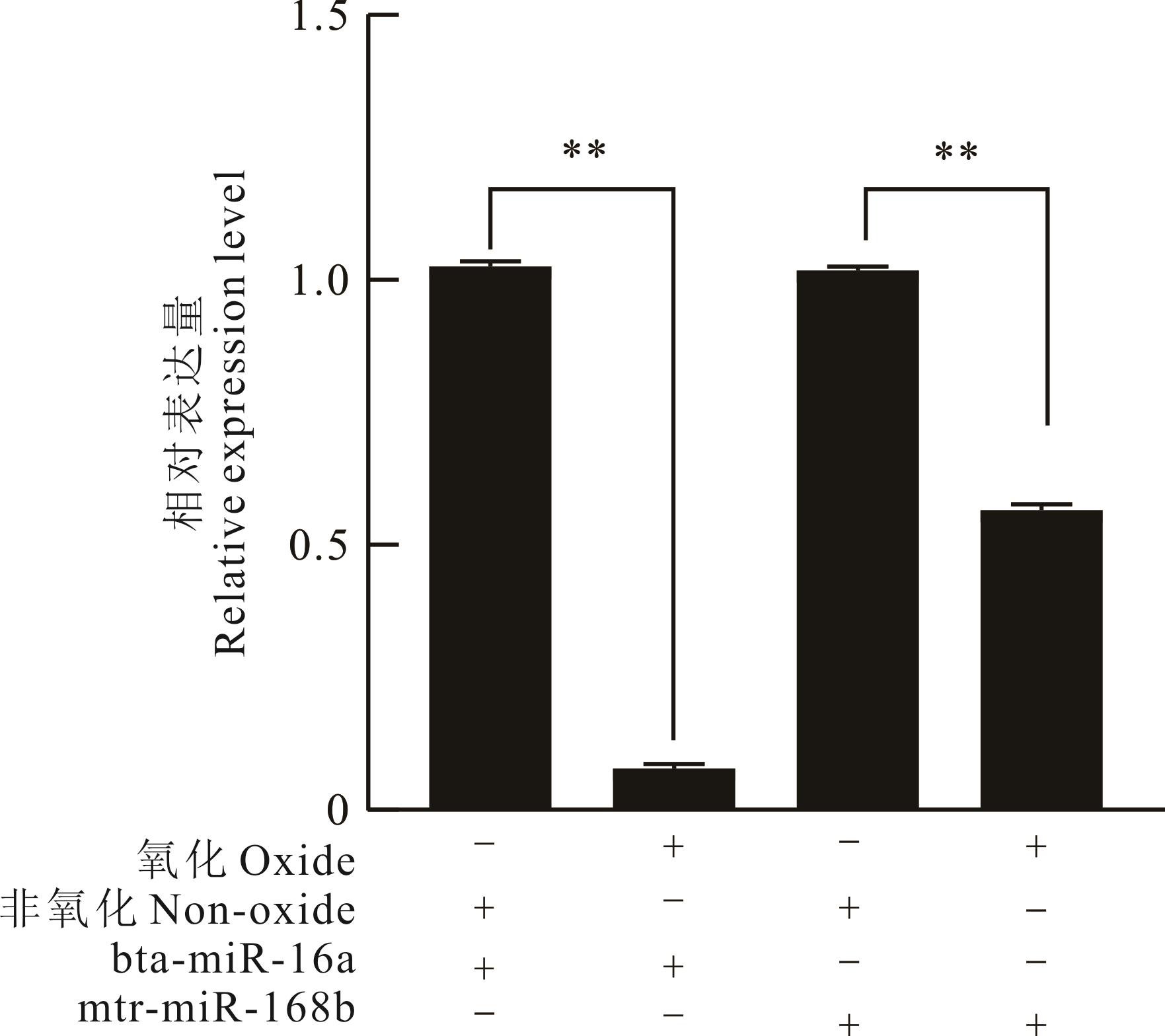
图3 氧化前后牛血液中内源性miRNA与外源性miRNA表达量检测+代表经过该处理或检测miRNA表达水平,-代表未经过该处理或未检测此种miRNA,**P<0.01为显著性。+ stands for the expression level of the treated or detected miRNA, - stands for the untreated or detected miRNA. **P<0.01 was considered statistically significant.
Fig.3 The expression levels of endogenous and exogenous miRNA in bovine blood before and after oxidation

图4 mtr-miR168b高表达抑制奶牛BMEC乳脂的合成a: miR168b过表达后在不同诱导时间的相对表达量;b~e: miR168b高表达后BMEC中脂代谢相关基因定量。**P<0.01和*P<0.05为显著性。NC是mtr-miR168b mimics的阴性对照,是一段无义序列。 mimics为 mtr-miR168b mimics的序列模拟物,与mtr-miR168b的序列相同。a: Relative expression level of miR168b at different induction time after overexpression; b-e: Quantification of genes related to lipid metabolism in BMEC after high expression of mtr-miR168b. **P<0.01 and *P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. NC is negative control, which is the negative control of mtr-miR168b mimics, and it is a meaningless sequence. mimics is the sequence analog of mtr-miR168b mimics, which has the same sequence as mtr-miR168b.
Fig.4 High expression of mtr-miR168b inhibits the synthesis of milk fat in cow mammary epithelial cells
靶基因 Target gene | 与mtr-miR168b种子区域结合位点 Combine site with seed region of mtr-miR168b | 表达组织(表达评分) Expression organization (expression score) |
|---|---|---|
| CLN8 | 结合位点 Position: 1296 靶基因 Target gene --GCAAGCGG-- miRNA AAGGGCTGGACGTGGTTCGCT | 牛奶 Milk(61.92) 乳腺脂肪 Breast fat(73.63) |
| CLN8 | 结合位点 Position: 1482 靶基因 Target gene --CCAAGCGA-- miRNA AAGGGCTGGACGTGGTTCGCT | 牛奶 Milk(61.92) 乳腺脂肪 Breast fat(73.63) |
| SERINC1 | 结合位点 Position: 1559 靶基因 Target gene --CCAAGCGC-- miRNA AAGGGCTGGACGTGGTTCGCT | 牛奶 Milk(96.08) 乳腺脂肪 Breast fat(97.83) |
| CPTP | 结合位点 Position: 933 靶基因 Target gene --CCAAGCGT-- miRNA AAGGGCTGGACGTGGTTCGCT | 牛奶 Milk(73.02) 乳腺脂肪 Breast fat(85.06) 乳腺Mammary gland(88.71) |
| STARD7 | 结合位点 Position: 1206 靶基因 Target gene --CCAAGCGT-- miRNA AAGGGCTGGACGTGGTTCGCT | 牛奶 Milk(80.79) 乳腺脂肪 Breast fat(88.08) 乳腺 Mammary gland(90.56) |
| CPT1A | 结合位点 Position: 2716 靶基因 Target gene --ACAAGCGA-- miRNA AAGGGCTGGACGTGGTTCGCT | 牛奶 Milk(85.82) 乳腺脂肪 Breast fat(91.13) 乳腺 Mammary gland(75.98) |
表6 mtr-miR168b脂质代谢靶基因与组织表达评分
Table 6 mtr-miR168b lipid metabolism target gene and tissue expression score
靶基因 Target gene | 与mtr-miR168b种子区域结合位点 Combine site with seed region of mtr-miR168b | 表达组织(表达评分) Expression organization (expression score) |
|---|---|---|
| CLN8 | 结合位点 Position: 1296 靶基因 Target gene --GCAAGCGG-- miRNA AAGGGCTGGACGTGGTTCGCT | 牛奶 Milk(61.92) 乳腺脂肪 Breast fat(73.63) |
| CLN8 | 结合位点 Position: 1482 靶基因 Target gene --CCAAGCGA-- miRNA AAGGGCTGGACGTGGTTCGCT | 牛奶 Milk(61.92) 乳腺脂肪 Breast fat(73.63) |
| SERINC1 | 结合位点 Position: 1559 靶基因 Target gene --CCAAGCGC-- miRNA AAGGGCTGGACGTGGTTCGCT | 牛奶 Milk(96.08) 乳腺脂肪 Breast fat(97.83) |
| CPTP | 结合位点 Position: 933 靶基因 Target gene --CCAAGCGT-- miRNA AAGGGCTGGACGTGGTTCGCT | 牛奶 Milk(73.02) 乳腺脂肪 Breast fat(85.06) 乳腺Mammary gland(88.71) |
| STARD7 | 结合位点 Position: 1206 靶基因 Target gene --CCAAGCGT-- miRNA AAGGGCTGGACGTGGTTCGCT | 牛奶 Milk(80.79) 乳腺脂肪 Breast fat(88.08) 乳腺 Mammary gland(90.56) |
| CPT1A | 结合位点 Position: 2716 靶基因 Target gene --ACAAGCGA-- miRNA AAGGGCTGGACGTGGTTCGCT | 牛奶 Milk(85.82) 乳腺脂肪 Breast fat(91.13) 乳腺 Mammary gland(75.98) |

图7 转染后乳腺上皮细胞预测靶基因表达量a:mtr-miR168b表达量,b:预测脂代谢相关靶基因SERINC1、CPT1A和STARD7的表达量。**P<0.01为显著性。a: mtr-miR168b expression level, b: Predicting target gene SERINC1, CPT1A and STARD7 expression level which related to lipid metabolism. **P<0.01 was considered statistically significant.
Fig.7 Predicting target gene expression level of breast epithelial cells after transfection

图8 相对荧光素酶活性a,b为mtr-miR168b与构建的靶基因载体序列比对;c,d为相对荧光素酶活性。ns为无显著差异。**P<0.01为显著性。a, b is sequence comparison between mtr-miR168b and the constructed target gene vector; c, d is relative luciferase activity.ns indicate no difference. **P<0.01 was considered statistically significant.
Fig.8 Relative luciferase activity
| 1 | Bartel D P. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell, 2004, 116(2): 281-297. |
| 2 | Ambros V, Bartel B, Bartel D P, et al. A uniform system for microRNA annotation. RNA, 2003, 9(3): 277-279. |
| 3 | Hwang H W, Mendell J T. MicroRNAs in cell proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. British Journal of Cancer, 2006, 94(6): 776-780. |
| 4 | Wahid F, Shehzad A, Khan T, et al. MicroRNAs: synthesis, mechanism, function, and recent clinical trials. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2010, 1803(11): 1231-1243. |
| 5 | Li H Q, Jiang H G, Shen X N, et al. Effects of upregulated LncRNA TUG1 targeted miRNA-194-5p promoting expression of KIAA1199 on proliferation, invasion and EMT of colorectal cancer cells. Chongqing Medicine, 2022, 51(15): 2532-2538. |
| 李海强, 蒋红钢, 沈徐宁, 等. 上调LncRNA TUG1靶向miRNA-194-5p促进KIAA1199表达对结直肠癌细胞增殖侵袭和EMT的影响. 重庆医学, 2022, 51(15) : 2532-2538. | |
| 6 | Franczyk B, Gluba-Brzozka A, Olszewski R, et al. miRNA biomarkers in renal disease. International Urology and Nephrology, 2022, 54(3): 575-588. |
| 7 | Fries J. MicroRNAs as markers to monitor endothelin-1 signalling and potential treatment in renal disease: Carcinoma-proteinuric damage-toxicity. Biology of the Cell, 2019, 111(7): 169-186. |
| 8 | Yang Y, Wang T, Wang M, et al. Recent Advances in microRNAs related to plant nutrient stress. Molecular Plant Breeding, [2023-05-08].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20210906.1425.008.html. |
| 杨阳, 王婷, 王明, 等. 植物养分胁迫相关microRNA研究进展. 分子植物育种, [2023-05-08].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20210906.1425.008.html. | |
| 9 | Zhou Y K, Zhang J H, Zhang W, et al. Value of prenatal ultrasound parameters offetal ductus venosus combined with maternal serum miR-19b indiagnosis of fetal congenitalheart disease. Clinical Misdiagnosis & Mistherapy, 2022, 35(4): 74-78. |
| 周钰昆, 张金辉, 张伟, 等. 胎儿静脉导管产前超声参数联合母体血清miR-19b对胎儿先天性心脏病的诊断价值. 临床误诊误治, 2022, 35(4): 74-78. | |
| 10 | Zhang L, Hou D, Chen X, et al. Exogenous plant MIR168a specifically targets mammalian LDLRAP1: evidence of cross-kingdom regulation by microRNA. Cell Research, 2012, 22(1): 107-126. |
| 11 | Zhou Z, Li X, Liu J, et al. Honeysuckle-encoded atypical microRNA2911 directly targets influenza a viruses. Cell Research, 2015, 25(1): 39-49. |
| 12 | Zhou Z, Zhou Y, Jiang X M, et al. Decreased HD-MIR2911 absorption in human subjects with the SIDT1 polymorphism fails to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication. Cell Discovery, 2020, 6: 63. |
| 13 | Zhou L K, Zhou Z, Jiang X M, et al. Absorbed plant MIR2911 in honeysuckle decoction inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication and accelerates the negative conversion of infected patients. Cell Discovery, 2020, 6(1): 54. |
| 14 | Liu J, Wang F, Song H, et al. Soybean-derived gma-miR159a alleviates colon tumorigenesis by suppressing TCF7/MYC in mice. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 2021, 92: 108627. |
| 15 | Yu W Y, Cai W, Ying H Z, et al. Exogenous plant gma-miR-159a, identified by miRNA library functional screening, ameliorated hepatic stellate cell activation and inflammation via inhibiting GSK-3beta-mediated pathways. Journal of Inflammation Research, 2021, 14: 2157-2172. |
| 16 | Zhang Z Y. China feed science. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2000. |
| 张子仪. 中国饲料学. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 17 | He F, Li X L, Tong Z Y, et al. Case study of lamb fattening by rotational grazing technique on alfalfa mixtures grassland. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(1): 273-278. |
| 何峰, 李向林, 仝宗永, 等. 基于紫花苜蓿混播草地的全草型肉羊放牧育肥模式案例研究. 草地学报, 2020, 28(1):273-278. | |
| 18 | Wang Z, Chen Y, Luo H, et al. Influence of restricted grazing time systems on productive performance and fatty acid composition of longissimus dorsi in growing lambs. Asian-Australas Journal of Animnal Science, 2015, 28(8): 1105-1115. |
| 19 | Laroche J P, Gervais R, Lapierre H, et al. Milk production and efficiency of utilization of nitrogen, metabolizable protein, and amino acids are affected by protein and energy supplies in dairy cows fed alfalfa-based diets. Journal of Dairy Science, 2022, 105(1): 329-346. |
| 20 | Dai Q, Hou Z, Gao S, et al. Substitution of fresh forage ramie for alfalfa hay in diets affects production performance, milk composition, and serum parameters of dairy cows. Tropical Animal Health and Production, 2019, 51(2): 469-472. |
| 21 | Luo Y, Wang P, Wang X, et al. Detection of dietetically absorbed maize-derived microRNAs in pigs. Science Reporter, 2017, 7(1): 645. |
| 22 | Wang Y H. Study on three kinds of maize miRNAs absorption: in vivo and in vitro in pig. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2016. |
| 王宇豪. 三种玉米miRNAs在猪体内、外的吸收规律研究. 成都: 四川农业大学, 2016. | |
| 23 | Li M, Wei L M, Chen T, et al. Effects of maize RNA on fat deposition of mice. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2021, 33(2): 1091-1099. |
| 黎梦, 魏立民, 陈婷, 等. 玉米RNA对小鼠脂肪沉积的影响. 动物营养学报, 2021, 33(2): 1091-1099. | |
| 24 | Chen T, Ma F, Peng Y, et al. Plant miR167e-5p promotes 3T3-L1 adipocyte adipogenesis by targeting beta-catenin. In Vitro Cellular and Developmental Biology Animal, 2022, 58(6): 471-479. |
| 25 | Aquilano K, Ceci V, Gismondi A, et al. Adipocyte metabolism is improved by TNF receptor-targeting small RNAs identified from dried nuts. Communications Biology, 2019, 2: 317. |
| 26 | Xu K, Ji M, Huang X, et al. Differential regulatory roles of microRNAs in porcine intramuscular and subcutaneous adipocytes. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2020, 68(13): 3954-3962. |
| 27 | Liang J J, Lin Y Q, Yu Y Y, et al. Cloning and expression of goat CPT1A gene and its correlation with intramuscular fat content. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2019, 34(5): 231-238. |
| 梁计峻, 林亚秋, 俞雨阳, 等. 山羊CPT1A基因的克隆表达及肌内脂肪含量的相关性分析. 华北农学报, 2019, 34(5): 231-238. | |
| 28 | Weber M, Mera P, Casas J, et al. Liver CPT1A gene therapy reduces diet-induced hepatic steatosis in mice and highlights potential lipid biomarkers for human NAFLD. The FASEB Journal, 2020, 34(9): 11816-11837. |
| 29 | Zhao X W, Yang Y X, Huang D W, et al. Comparison of milk fat globule membrane proteins in milk samples of dairy cow and goat. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2016, 43(11): 2963-2969. |
| 赵小伟, 杨永新, 黄冬维, 等. 牛奶和山羊奶中乳脂球膜蛋白的比较研究. 中国畜牧兽医, 2016, 43(11): 2963-2969. | |
| 30 | Ji X X, Ma Y. Compositons and properties of milk fat globule membrane from five different species milk. China Dairy Industry, 2017, 45(6): 19-23. |
| 姬晓曦, 马莺. 5种乳源乳脂肪球膜的组成和性质. 中国乳品工业, 2017, 45(6): 19-23. | |
| 31 | Manoni M, Di Lorenzo C, Ottoboni M, et al. Comparative proteomics of milk fat globule membrane (MFGM) proteome across species and lactation stages and the potentials of MFGM fractions in infant formula preparation. Foods, 2020, 9(9): 1251. |
| 32 | Mohri S, Takahashi H, Sakai M, et al. Integration of bioassay and non-target metabolite analysis of tomato reveals that beta-carotene and lycopene activate the adiponectin signaling pathway, including AMPK phosphorylation. PLoS One, 2022, 17(7): e267248. |
| 33 | Viollet B, Mounier R, Leclerc J, et al. Targeting AMP-activated protein kinase as a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of metabolic disorders. Diabetes Metabolism, 2007, 33(6): 395-402. |
| 34 | Graziosi A, Sita G, Corrieri C, et al. Effects of subtoxic concentrations of atrazine, cypermethrin, and vinclozolin on microRNA-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in SH-SY5Y cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(23): 14538. |
| 35 | Zhou Y, Liu F. Coordination of the AMPK, Akt, mTOR, and p53 pathways under glucose starvation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(23): 14945. |
| [1] | 任伟忠, 高艳霞, 李秋凤, 曹玉凤, 李建国. 全株玉米青贮、谷草和羊草组合全混合日粮饲喂干奶前期奶牛对其围产期生产性能和血液生化及免疫指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 124-136. |
| [2] | 罗佳捷,彭瑛,罗锐,张彬,李丽立,吴力专,占今舜,邢月腾. 中国荷斯坦奶牛铁蛋白基因3′端克隆及序列分析[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(5): 96-103. |
| [3] | 吴力专,罗佳捷,张彬,李丽立,罗锐,占今舜. 外源性金属硫蛋白对中国荷斯坦奶牛血淋巴细胞凋亡/坏死及线粒体膜电位的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(4): 205-211. |
| [4] | 王聪,刘强,张延利,张拴林,裴彩霞,白元生,师周戈,刘晓妮. 甘油对围产期奶牛能量平衡和肝脏糖原合成的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(1): 252-259. |
| [5] | 吴力专,陈海燕,张彬,李丽立,陈宇光,肖定福,罗佳捷,吴宗明. 外源性金属硫蛋白对中国荷斯坦奶牛产能性能和内分泌的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(1): 183-188. |
| [6] | 李红玉,刘强,王聪,杨效民,贺东昌,郭刚. 丙酸镁对泌乳早期奶牛体况、泌乳性能和代谢参数的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2009, 18(4): 187-194. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||