

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 16-24.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023220
赵光华1( ), 高明龙2, 王朵3, 范世奇3, 唐健3, 孙阔4, 温玄烨3(
), 高明龙2, 王朵3, 范世奇3, 唐健3, 孙阔4, 温玄烨3( )
)
收稿日期:2023-06-28
修回日期:2023-09-19
出版日期:2024-05-20
发布日期:2024-02-03
通讯作者:
温玄烨
作者简介:E-mail: 397803265@qq.com基金资助:
Guang-hua ZHAO1( ), Ming-long GAO2, Duo WANG3, Shi-qi FAN3, Jian TANG3, Kuo SUN4, Xuan-ye WEN3(
), Ming-long GAO2, Duo WANG3, Shi-qi FAN3, Jian TANG3, Kuo SUN4, Xuan-ye WEN3( )
)
Received:2023-06-28
Revised:2023-09-19
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-02-03
Contact:
Xuan-ye WEN
摘要:
植物是入侵生物中种类和数量最多的类群,对入侵植物开展经济成本评估可为后续风险管理和相关政策的制定提供参考依据。本研究基于InvaCost数据库评估获得了1970-2017年全球入侵植物的经济成本,研究结果表明:1)入侵植物的保守经济成本为1943.65亿美元,年均40.49亿美元,其中,直接经济损失达1004.68亿美元,占比为51.69%;2)在64个国家和地区中,美国的经济成本最高,其次为澳大利亚,我国208.31亿美元(1407.07亿人民币)排名第三。凤眼莲是全球最昂贵的入侵植物种类,其危害所产生的成本高于排名5~10名的入侵植物成本之和;3)过去的近50年里,入侵植物的经济成本呈上升趋势,模型测算2017年入侵植物的可能成本为34.38亿~104.52亿美元,最高置信值为77.25亿美元。本研究有助于加深对入侵植物危害严重性的客观认识,可为我国开展更为积极的入侵植物治理提供科学依据。
赵光华, 高明龙, 王朵, 范世奇, 唐健, 孙阔, 温玄烨. 全球入侵植物的经济成本评估[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 16-24.
Guang-hua ZHAO, Ming-long GAO, Duo WANG, Shi-qi FAN, Jian TANG, Kuo SUN, Xuan-ye WEN. Economic cost assessment of global invasive plants[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(5): 16-24.
表1 1970-2017年植物入侵经济成本
Table 1 Economic costs of plants invasion for 1970-2017 (百万美元Millions USD)
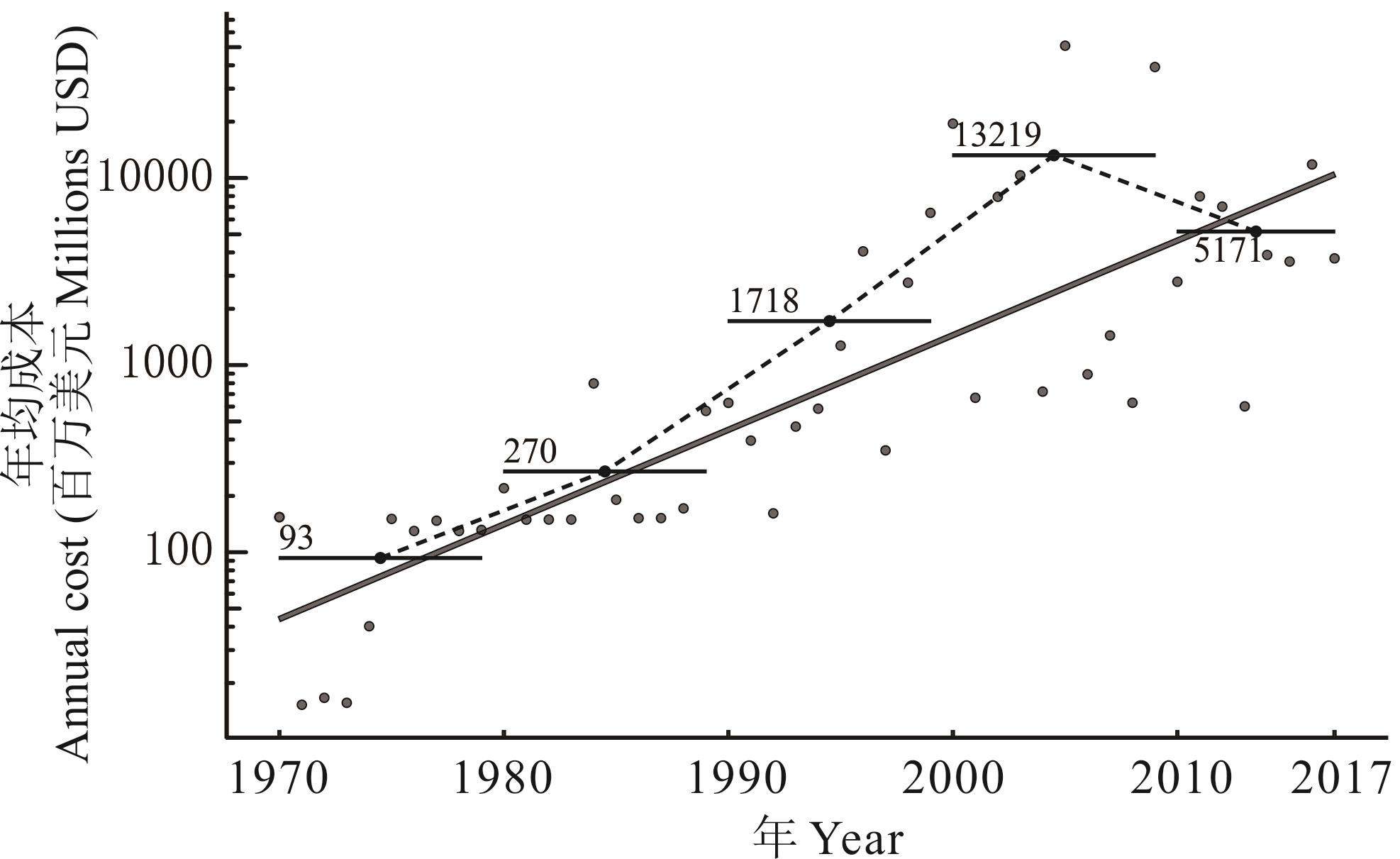
图1 入侵植物的保守经济成本图中实线表示基于线性回归的成本时间动态;虚线为每10年平均年成本连接线;水平条表示计算10年平均成本的总时间跨度。The solid line in Fig.1 represents the cost time dynamics based on linear regression; The dotted line is the connecting line of the average annual cost per decade; The horizontal bar represents the total time span for calculating the 10-year average cost.
Fig.1 Conservative economic cost of invasive plants
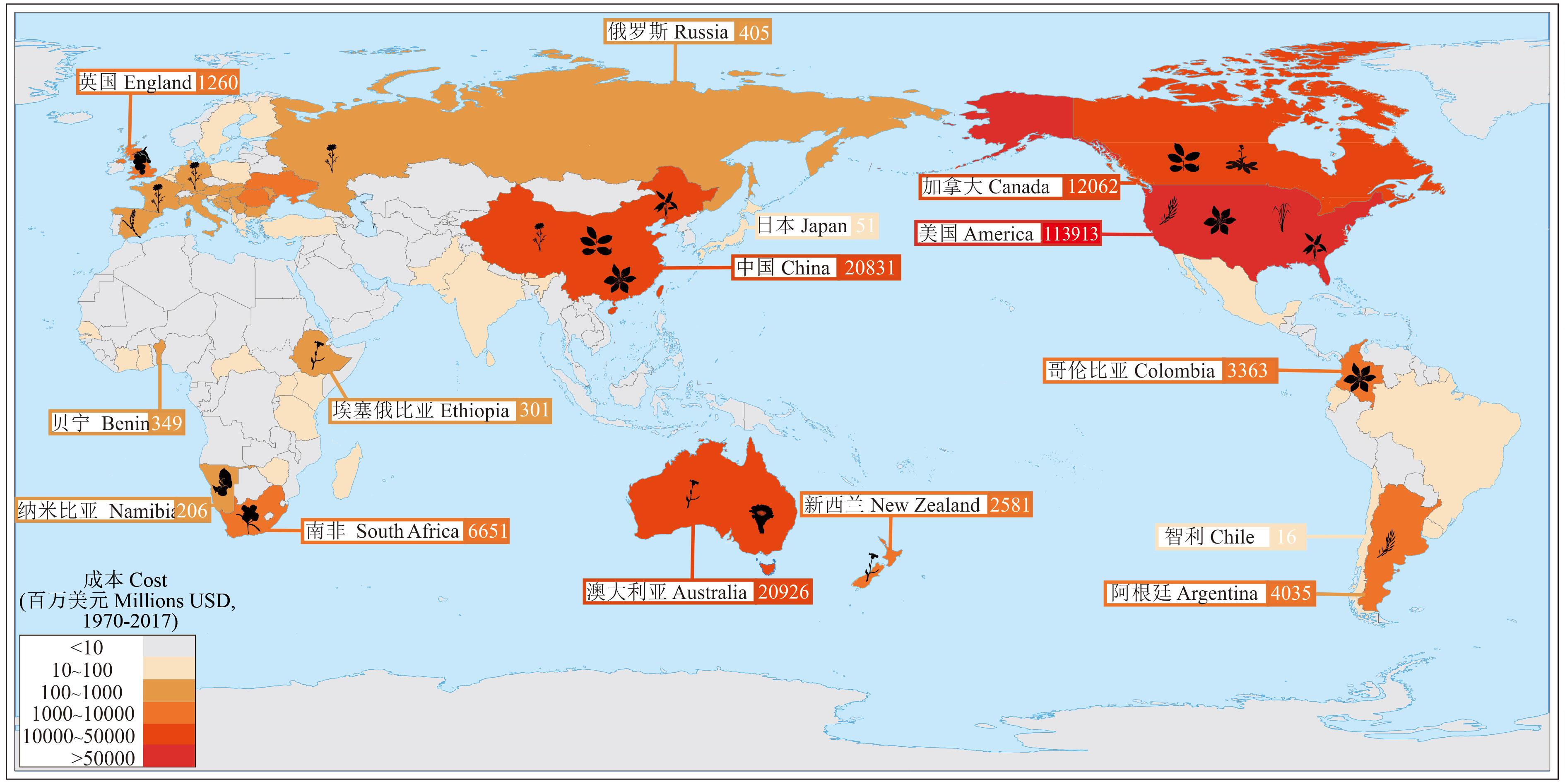
图2 各国入侵植物经济成本该图基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站下载的审图号为GS(2016)1665号的标准地图制作,底图无修改。The map is based on the standard map of GS(2016)1665 downloaded from the standard map service website of the Ministry of Natural Resources, and the base map is not modified.
Fig.2 Economic cost of invasive plants in various countries
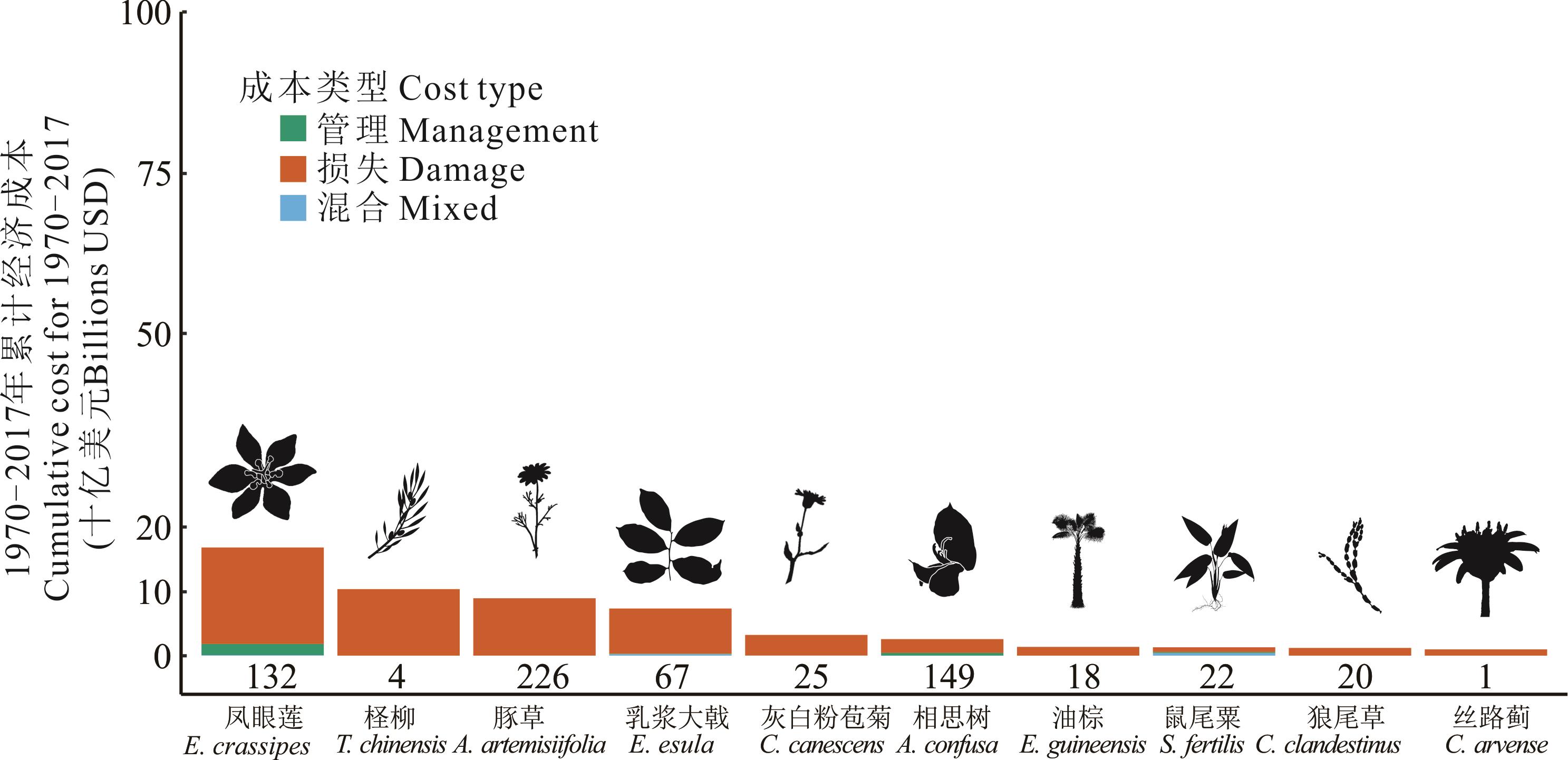
图3 经济成本较高的10种入侵植物条形图下面的数值表示成本估算的数量。Numbers below the bars indicate the number of cost estimates.
Fig.3 Invasive plants of the top ten with the higher economic costs
表2 模型测算结果
Table 2 Model measurement results
| 1 | Wan F H, Guo J Y, Wang D H. Alien invasive species in China: their damages and management strategies. Biodiversity Science, 2002, 10(1): 119-125. |
| 万方浩, 郭建英, 王德辉. 中国外来入侵生物的危害与管理对策. 生物多样性, 2002, 10(1): 119-125. | |
| 2 | Wang F N. Studies about the history, effects and measurements of alien invasive species. Studies in Dialectics of Nature, 2005, 21(1): 77-81. |
| 王丰年. 外来物种入侵的历史、影响及对策研究. 自然辩证法研究, 2005, 21(1): 77-81. | |
| 3 | Hu Y C, Song H M, Mu X D, et al. Invasion of exotic species and their control measures taken in China. Journal of Biosafety, 2012, 21(4): 256-261, 242. |
| 胡隐昌, 宋红梅, 牟希东, 等. 浅议我国外来物种入侵问题及其防治对策. 生物安全学报, 2012, 21(4): 256-261, 242. | |
| 4 | Shirley S M, Salit K. Amassing efforts against alien invasive species in Europe. PLoS Biology, 2006, 4(8): e279. |
| 5 | Westphal M I, Browne M, Mackinnon K. The link between international trade and the global distribution of invasive alien species. Biological Invasions, 2008, 10(4): 391-398. |
| 6 | Seebens H, Bacher S, Blackburn T M, et al. Projecting the continental accumulation of alien species through to 2050. Global Change Biology, 2021, 27(5): 970-982. |
| 7 | Chen B X, Sun Y F, Han Z H, et al. Challenges in preventing and controlling invasive alien species in China. Journal of Biosafety, 2020, 29(3): 157-163. |
| 陈宝雄, 孙玉芳, 韩智华, 等. 我国外来入侵生物防控现状、问题和对策. 生物安全学报, 2020, 29(3): 157-163. | |
| 8 | Park K J. Spatial structure and the control of invasive alien species. Animal Conservation, 2004, 7(3): 321-330. |
| 9 | Dextrase A J, Mandrak N E. Impacts of alien invasive species on freshwater fauna at risk in Canada. Biological Invasions, 2006, 8(1): 13-24. |
| 10 | Haubrock P J, Cuthbert R N, Ricciardi A, et al. Economic costs of invasive bivalves in freshwater ecosystems. Diversity and Distributions, 2022, 28(5): 1010-1021. |
| 11 | Kumschick S, Gaertner M, Vila M, et al. Ecological impacts of alien species: quantification, scope, caveats, and recommendations. Bioscience, 2015, 65(1): 55-63. |
| 12 | Richardson D M, Rejmanek M. Trees and shrubs as invasive alien species-a global review. Diversity and Distributions, 2011, 17(5): 788-809. |
| 13 | Ding H, Xu H G, Qiang S, et al. Status quo and trends of biological invasion into China. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2011, 27(3): 35-41. |
| 丁晖, 徐海根, 强胜, 等. 中国生物入侵的现状与趋势. 生态与农村环境学报, 2011, 27(3): 35-41. | |
| 14 | Yan X L, Shou H Y, Ma J S. The problem and status of the alien invasive plants in China. Plant Diversity and Resources, 2012, 34(3): 287-313. |
| 闫小玲, 寿海洋, 马金双. 中国外来入侵植物研究现状及存在的问题. 植物分类与资源学报, 2012, 34(3): 287-313. | |
| 15 | Tang T G, Zhang W J. A discussion of ecological engineering benefits of Spartina spp. and its ecological invasion. Strategic Study of CAE, 2003, 5(3): 15-20. |
| 唐廷贵, 张万钧. 论中国海岸带大米草生态工程效益与“生态入侵”. 中国工程科学, 2003, 5(3): 15-20. | |
| 16 | Gao L, Li B. The study of a specious invasive plant, water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes): achievements and challenges. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2004, 28(6): 735-752. |
| 高雷, 李博. 入侵植物凤眼莲研究现状及存在的问题. 植物生态学报, 2004, 28(6): 735-752. | |
| 17 | Yang R Y, Zan S T, Tang J J, et al. Invasion mechanisms of Solidago canadensis L.: a review. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(4): 1185-1196. |
| 杨如意, 昝树婷, 唐建军, 等. 加拿大一枝黄花的入侵机理研究进展. 生态学报, 2011, 31(4): 1185-1196. | |
| 18 | Chen Q, Ma K M. Research overview and trend on biological invasion in mangrove forests. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2015, 39(3): 283-299. |
| 陈权, 马克明. 红树林生物入侵研究概况与趋势. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(3): 283-299. | |
| 19 | Ewald W, Li B. Plant invasions in China: What is to be expected in the wake of economic development? Bioscience, 2008, 58(5): 437-444. |
| 20 | Follak S, Dullinger S, Kleinbauer I, et al. Invasion dynamics of three allergenic invasive Asteraceae (Ambrosia trifida, Artemisia annua, Iva xanthiifolia) in central and eastern Europe. Preslia, 2013, 85(1): 41-61. |
| 21 | Adkins S, Shabbir A. Biology, ecology and management of the invasive parthenium weed (Parthenium hysterophorus L.). Pest Management Science, 2014, 70(7): 1023-1029. |
| 22 | Xu H G, Ding H, Li M Y, et al. The distribution and economic losses of alien species invasion to China. Biological Invasions, 2006, 8(7): 1495-1500. |
| 23 | Wan F H, Liu W X, Guo J Y, et al. Invasive mechanism and control strategy of Ageratina adenophora (Sprengel). Scientia Sinica Vitae, 2011, 41(1): 13-21. |
| 万方浩, 刘万学, 郭建英, 等. 外来植物紫茎泽兰的入侵机理与控制策略研究进展. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2011, 41(1): 13-21. | |
| 24 | Liu T T, Zhang H J, Ma Z Y. Assessment of economic damage from biological invasion. Ecological Economy, 2010, 43(2): 173-175, 178. |
| 刘婷婷, 张洪军, 马忠玉. 生物入侵造成经济损失评估的研究进展. 生态经济, 2010, 43(2): 173-175, 178. | |
| 25 | Diagne C, Leroy B, Vaissiere A, et al. High and rising economic costs of biological invasions worldwide. Nature, 2021, 608(7924): 571-576. |
| 26 | Eiswerth M, Doanldson S, Johnson W. Potential environmental impacts and economic damages of Eurasian watermilfoil (Myriophyllum spicatum) in western Nevada and northeastern California. Weed Technology, 2000, 14(3): 511-518. |
| 27 | Diagne C, Leroy B, Gozlan R E, et al. InvaCost, a public database of the economic costs of biological invasions worldwide. Scientific Data, 2020, 7(1): 277. |
| 28 | Fantle-Lepczyk J E, Haubrock P J, Kramer A M, et al. Economic costs of biological invasions in the United States. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 806(3): 151318. |
| 29 | Zhang X, Zhao J J, Yan J, et al. Economic loss assessment of pine wilt disease in mainland China in 2017. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(10): 96-106. |
| 张旭, 赵京京, 闫峻, 等. 2017年中国大陆松材线虫病灾害经济损失评估. 北京林业大学学报, 2020, 42(10): 96-106. | |
| 30 | World Bank. World bank open data. https://data.worldbank.org.cn/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.CD. |
| 31 | Lin Q W, Xiao C, Ma J S. A dataset on catalogue of alien plants in China. Biodiversity Science, 2022, 30(5): 110-117. |
| 林秦文, 肖翠, 马金双. 中国外来植物数据集. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 110-117. | |
| 32 | He M Q, Zhang J E, Luo M Z, et al. Suggestions on reinforcing management and control of exotic pest species in China. Science and Technology Management Research, 2010, 30(14): 53-56. |
| 何铭谦, 章家恩, 罗明珠, 等. 关于加强我国外来有害物种入侵的管理与控制之思考. 科技管理研究, 2010, 30(14): 53-56. | |
| 33 | Wang S. Biosafety regulations and regulatory measures to cope with challenges of GM technology: Global experience and enlightenment. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2023, 21(20): 6746-6751. |
| 王素. 生物安全法规与监管措施应对转基因技术挑战: 全球经验与启示. 分子植物育种, 2023, 21(20): 6746-6751. | |
| 34 | Wang R, Huang H K, Zhang H B, et al. Analysis of gaps in regulations and management mechanisms for the prevention and control of invasive alien species in China. Plant Protection, 2022, 48(4): 2-9. |
| 王瑞, 黄宏坤, 张宏斌, 等. 中国外来入侵物种防控法规和管理机制空缺分析. 植物保护, 2022, 48(4): 2-9. | |
| 35 | Wan F H, Guo J Y. Advances in invasion biology and control strategy of alien species in agriculture and forestry in China. China Basic Science, 2007, 9(5): 8-14. |
| 万方浩, 郭建英. 农林危险生物入侵机理及控制基础研究. 中国基础科学, 2007, 9(5): 8-14. | |
| 36 | Essl F, Lenzner B, Bacher S, et al. Drivers of future alien species impacts: an expert-based assessment. Global Change Biology, 2020, 26(9): 4880-4893. |
| 37 | Yu X Q, Feng Y L, Li Q M. Review of research advances and prospects of invasive Chromolaena odorata. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2010, 34(5): 591-600. |
| 余香琴, 冯玉龙, 李巧明. 外来入侵植物飞机草的研究进展与展望. 植物生态学报, 2010, 34(5): 591-600. | |
| 38 | Jiang Z H, Li P C, Sun J W, et al. Effect of invasive plant Amaranthus spinosus L. on rice allelopathy and antioxidant system. Journal of China University of Metrology, 2017, 28(1): 68-75. |
| 蒋芝华, 李鹏程, 孙骏威, 等. 入侵植物刺苋对水稻化感效应及抗氧化系统的影响. 中国计量大学学报, 2017, 28(1): 68-75. | |
| 39 | Pimentel D, Zuniga R, Morrison D. Update on the environmental and economic costs associated with alien-invasive species in the United States. Ecological Economics, 2005, 52(3): 273-288. |
| 40 | Martin T G, Klinken R V. Value for money? Investment in weed management in Australian rangelands. Rangeland Journal, 2006, 28(1): 63-75. |
| [1] | 陈美杉, 陈鲜, 满晓珍, 刘闯, 佟佳林, 曲波. 入侵种瘤突苍耳细根解剖结构的可塑性与入侵性间的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 118-126. |
| [2] | 赵威, 王艳杰, 李亚鸽. 草地入侵植物对枝叶去除的生理生态响应:模式、机理与研究展望[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(6): 195-202. |
| [3] | 赵晓红, 杨殿林, 王慧, 刘红梅, 曲波, 皇甫超河. 黄顶菊入侵对不同地区土壤氮循环及微生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(2): 62-69. |
| [4] | 王瑞,万方浩. 外来入侵植物意大利苍耳在我国适生区预测[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(6): 222-230. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||