

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 183-195.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023232
• 研究简报 • 上一篇
潘斯瑶( ), 宋渝川, 袁如薏, 候圣彤, 蔡俊歌, 陈冰, 程军回(
), 宋渝川, 袁如薏, 候圣彤, 蔡俊歌, 陈冰, 程军回( )
)
收稿日期:2023-07-05
修回日期:2023-08-04
出版日期:2024-05-20
发布日期:2024-02-03
通讯作者:
程军回
作者简介:E-mail: cjhgraymice@126.com基金资助:
Si-yao PAN( ), Yu-chuan SONG, Ru-yi YUAN, Sheng-tong HOU, Jun-ge CAI, Bing CHEN, Jun-hui CHENG(
), Yu-chuan SONG, Ru-yi YUAN, Sheng-tong HOU, Jun-ge CAI, Bing CHEN, Jun-hui CHENG( )
)
Received:2023-07-05
Revised:2023-08-04
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-02-03
Contact:
Jun-hui CHENG
摘要:
土壤无机氮作为植物可直接吸收和利用的氮源,其含量变化反映了土壤供氮能力。大量研究表明荒漠生态系统中土壤无机氮含量受到灌木种类和空间位置的影响。然而,有关采样方向对土壤无机氮含量的影响,目前仍所知甚少。基于此,本研究以准噶尔荒漠西北缘两种广泛分布的优势灌木为对象-梭梭和里海盐爪爪,通过测定和计算两物种个体大小(大、中、小和较小个体)在4个空间位置(主根周围、冠幅中央、冠幅边缘和株间空地)和4个采样方向(东、南、西和北)上0~10 cm和10~20 cm土层中土壤铵态氮、硝态氮含量和铵硝比,分析了灌木个体大小、空间位置和采样方向主效应及其交互效应对各土层无机氮含量的影响。研究结果发现:1)梭梭和里海盐爪爪冠下土壤无机氮含量均受到个体大小主效应的影响。两物种大个体冠下硝态氮含量均显著高于较小个体,梭梭大个体冠下铵态氮含量和铵硝比最低,而里海盐爪爪大个体冠下则拥有最高的铵态氮含量和铵硝比,表明土壤无机氮含量变化存在灌木个体大小依赖性。2)两物种冠下0~10 cm土层中硝态氮和铵态氮含量都显著高于10~20 cm,意味着灌木对表层土壤无机氮的影响幅度更大。3)梭梭冠下土壤无机氮含量还受到个体大小与采样方向交互作用的影响,且在冠幅东侧和南侧存在无机氮富集特征。4)空间位置和采样方向对里海盐爪爪冠下土壤无机氮存在显著交互作用,在里海盐爪爪冠下东侧和南侧,主根周围无机氮含量普遍高于其他3个空间位置。这些结果表明荒漠生态系统中土壤无机氮的变化特征因物种而异,同时受到个体大小、空间位置和采样方向等多种因素的影响。
潘斯瑶, 宋渝川, 袁如薏, 候圣彤, 蔡俊歌, 陈冰, 程军回. 准噶尔荒漠两种灌木冠下土壤无机氮含量变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 183-195.
Si-yao PAN, Yu-chuan SONG, Ru-yi YUAN, Sheng-tong HOU, Jun-ge CAI, Bing CHEN, Jun-hui CHENG. Variations in soil inorganic nitrogen content under canopies of two shrubs in the Junggar Desert[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(5): 183-195.
| 物种Species | 大个体Large individual | 中个体Middle individual | 小个体Small individual | 较小个体Smaller individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 梭梭H. ammodendron | 5.60~17.28 | 1.66~5.50 | 0.50~1.65 | 0.21~0.49 |
| 里海盐爪爪K. caspicum | 1.06~12.69 | 0.63~1.05 | 0.33~0.62 | 0.05~0.32 |
表1 梭梭和里海盐爪爪个体大小划分标准
Table 1 Classification criterion of individual sizes of H. ammodendron and K. caspicum (m2)
| 物种Species | 大个体Large individual | 中个体Middle individual | 小个体Small individual | 较小个体Smaller individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 梭梭H. ammodendron | 5.60~17.28 | 1.66~5.50 | 0.50~1.65 | 0.21~0.49 |
| 里海盐爪爪K. caspicum | 1.06~12.69 | 0.63~1.05 | 0.33~0.62 | 0.05~0.32 |
物种 Species | 影响因素 Influencing factors | df | 硝态氮 log10 NO3--N (mg·g-1) | 铵态氮 log10 NH4+-N (mg·g-1) | 铵态氮/硝态氮 log10(NH4+-N/NO3--N) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | |||
梭梭 H. ammodendron | 个体大小Individual sizes (I) | 3 | 68.95 | <0.001 | 47.81 | <0.001 | 76.06 | <0.001 |
| 空间位置Spatial positions (P) | 3 | - | - | 3.80 | 0.010 | 2.93 | 0.034 | |
| 采样方向Sampling directions (D) | 3 | 4.26 | 0.006 | 0.91 | 0.435 | - | - | |
| 土层深度Soil depths (S) | 1 | 23.72 | <0.001 | 27.85 | <0.001 | 7.88 | 0.005 | |
| I×D | 9 | 2.87 | 0.003 | 1.84 | 0.060 | - | - | |
| I×S | 3 | - | - | 3.69 | 0.012 | - | - | |
里海盐爪爪 K. caspicum | I | 3 | 106.29 | <0.001 | 105.35 | <0.001 | 75.49 | <0.001 |
| P | 3 | 11.19 | <0.001 | 11.09 | <0.001 | 7.97 | <0.001 | |
| D | 3 | 2.09 | 0.101 | 2.10 | 0.100 | 2.36 | 0.071 | |
| S | 1 | 168.66 | <0.001 | 167.41 | <0.001 | 126.42 | <0.001 | |
| D×P | 9 | 2.87 | 0.003 | 2.11 | 0.029 | 2.26 | 0.018 | |
| I×S | 3 | 5.62 | 0.001 | 5.45 | 0.001 | 2.44 | 0.064 | |
| D×S | 3 | 2.40 | 0.068 | 2.40 | 0.068 | - | - | |
表2 个体大小、空间位置、采样方向和土层深度对梭梭和里海盐爪爪冠下土壤NO3--N、NH4+-N和NH4+-N/NO3--N的影响
Table 2 Effects of individual sizes, spatial positions, sampling directions and soil depths on NO3--N, NH4+-N and NH4+-N/NO3--N under canopies of H. ammodendron and K. caspicum
物种 Species | 影响因素 Influencing factors | df | 硝态氮 log10 NO3--N (mg·g-1) | 铵态氮 log10 NH4+-N (mg·g-1) | 铵态氮/硝态氮 log10(NH4+-N/NO3--N) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | |||
梭梭 H. ammodendron | 个体大小Individual sizes (I) | 3 | 68.95 | <0.001 | 47.81 | <0.001 | 76.06 | <0.001 |
| 空间位置Spatial positions (P) | 3 | - | - | 3.80 | 0.010 | 2.93 | 0.034 | |
| 采样方向Sampling directions (D) | 3 | 4.26 | 0.006 | 0.91 | 0.435 | - | - | |
| 土层深度Soil depths (S) | 1 | 23.72 | <0.001 | 27.85 | <0.001 | 7.88 | 0.005 | |
| I×D | 9 | 2.87 | 0.003 | 1.84 | 0.060 | - | - | |
| I×S | 3 | - | - | 3.69 | 0.012 | - | - | |
里海盐爪爪 K. caspicum | I | 3 | 106.29 | <0.001 | 105.35 | <0.001 | 75.49 | <0.001 |
| P | 3 | 11.19 | <0.001 | 11.09 | <0.001 | 7.97 | <0.001 | |
| D | 3 | 2.09 | 0.101 | 2.10 | 0.100 | 2.36 | 0.071 | |
| S | 1 | 168.66 | <0.001 | 167.41 | <0.001 | 126.42 | <0.001 | |
| D×P | 9 | 2.87 | 0.003 | 2.11 | 0.029 | 2.26 | 0.018 | |
| I×S | 3 | 5.62 | 0.001 | 5.45 | 0.001 | 2.44 | 0.064 | |
| D×S | 3 | 2.40 | 0.068 | 2.40 | 0.068 | - | - | |
物种 Species | 无机氮组分 Inorganic nitrogen components | 大个体 Large individual | 中个体 Middle individual | 小个体 Small individual | 较小个体 Smaller individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
梭梭 H. ammodendron | 硝态氮log10 NO3--N (mg·g-1) | 1.71±0.01a | 1.55±0.02b | 1.54±0.01b | 1.48±0.01c |
| 铵态氮log10 NH4+-N (mg·g-1) | 0.47±0.04c | 0.82±0.03b | 0.90±0.04a | 0.84±0.02b | |
| 铵态氮/硝态氮log10(NH4+-N/NO3--N) | -1.24±0.03b | -0.73±0.04a | -0.65±0.04a | -0.66±0.02a | |
里海盐爪爪 K. caspicum | 硝态氮log10 NO3--N (mg·g-1) | 1.75±0.01a | 1.69±0.01b | 1.65±0.01c | 1.60±0.01d |
| 铵态氮log10 NH4+-N (mg·g-1) | 0.74±0.01a | 0.68±0.01b | 0.63±0.01c | 0.59±0.01d | |
| 铵态氮/硝态氮log10(NH4+-N/NO3--N) | -1.01±0.01a | -1.02±0.01a | -1.02±0.01a | -1.02±0.01a |
表3 不同个体大小梭梭和里海盐爪爪冠下土壤NO3--N、NH4+-N的含量和NH4+-N/NO3--N
Table 3 Content of NO3--N, NH4+-N and NH4+-N/NO3--N in different individual sizes under canopies of H. ammodendron and K. caspicum
物种 Species | 无机氮组分 Inorganic nitrogen components | 大个体 Large individual | 中个体 Middle individual | 小个体 Small individual | 较小个体 Smaller individual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
梭梭 H. ammodendron | 硝态氮log10 NO3--N (mg·g-1) | 1.71±0.01a | 1.55±0.02b | 1.54±0.01b | 1.48±0.01c |
| 铵态氮log10 NH4+-N (mg·g-1) | 0.47±0.04c | 0.82±0.03b | 0.90±0.04a | 0.84±0.02b | |
| 铵态氮/硝态氮log10(NH4+-N/NO3--N) | -1.24±0.03b | -0.73±0.04a | -0.65±0.04a | -0.66±0.02a | |
里海盐爪爪 K. caspicum | 硝态氮log10 NO3--N (mg·g-1) | 1.75±0.01a | 1.69±0.01b | 1.65±0.01c | 1.60±0.01d |
| 铵态氮log10 NH4+-N (mg·g-1) | 0.74±0.01a | 0.68±0.01b | 0.63±0.01c | 0.59±0.01d | |
| 铵态氮/硝态氮log10(NH4+-N/NO3--N) | -1.01±0.01a | -1.02±0.01a | -1.02±0.01a | -1.02±0.01a |
物种 Species | 土层深度 Soil depths (cm) | 硝态氮 log10 NO3--N (mg·g-1) | 铵态氮 log10 NH4+-N (mg·g-1) | 铵态氮/硝态氮 log10(NH4+-N/NO3--N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
梭梭 H. ammodendron | 0~10 | 1.60±0.01a | 0.83±0.01a | -0.78±0.03a |
| 10~20 | 1.54±0.01b | 0.68±0.03b | -0.86±0.03b | |
里海盐爪爪 K. caspicum | 0~10 | 1.71±0.01a | 0.70±0.01a | -1.01±0.01a |
| 10~20 | 1.63±0.01b | 0.62±0.01b | -1.02±0.01a |
表4 不同土层深度梭梭和里海盐爪爪冠下土壤NO3--N、NH4+-N的含量和NH4+-N/NO3--N
Table 4 Content of NO3--N, NH4+-N and NH4+-N/NO3--N in different soil depths under canopies of H. ammodendron and K. caspicum
物种 Species | 土层深度 Soil depths (cm) | 硝态氮 log10 NO3--N (mg·g-1) | 铵态氮 log10 NH4+-N (mg·g-1) | 铵态氮/硝态氮 log10(NH4+-N/NO3--N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
梭梭 H. ammodendron | 0~10 | 1.60±0.01a | 0.83±0.01a | -0.78±0.03a |
| 10~20 | 1.54±0.01b | 0.68±0.03b | -0.86±0.03b | |
里海盐爪爪 K. caspicum | 0~10 | 1.71±0.01a | 0.70±0.01a | -1.01±0.01a |
| 10~20 | 1.63±0.01b | 0.62±0.01b | -1.02±0.01a |
| 无机氮组分Inorganic nitrogen components | 东部East | 南部South | 西部West | 北部North |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 硝态氮log10 NO3--N (mg·g-1) | 1.56±0.02ab | 1.60±0.01a | 1.57±0.01ab | 1.54±0.02b |
| 铵态氮log10 NH4+-N (mg·g-1) | 0.79±0.03a | 0.74±0.03a | 0.73±0.04a | 0.76±0.04a |
| 铵态氮/硝态氮log10(NH4+-N/NO3--N) | -0.78±0.04a | -0.86±0.04a | -0.84±0.05a | -0.78±0.05a |
表5 不同采样方向梭梭冠下土壤NO3--N、NH4+-N的含量和NH4+-N/NO3--N
Table 5 Content of NO3--N, NH4+-N and NH4+-N/NO3--N in different sampling directions under canopies of H. ammodendron
| 无机氮组分Inorganic nitrogen components | 东部East | 南部South | 西部West | 北部North |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 硝态氮log10 NO3--N (mg·g-1) | 1.56±0.02ab | 1.60±0.01a | 1.57±0.01ab | 1.54±0.02b |
| 铵态氮log10 NH4+-N (mg·g-1) | 0.79±0.03a | 0.74±0.03a | 0.73±0.04a | 0.76±0.04a |
| 铵态氮/硝态氮log10(NH4+-N/NO3--N) | -0.78±0.04a | -0.86±0.04a | -0.84±0.05a | -0.78±0.05a |
物种 Species | 无机氮组分 Inorganic nitrogen components | 主根周围 Shrub center | 冠幅中央 Shrub middle | 冠幅边缘 Shrub edge | 株间空地 Shrub outside |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
梭梭 H. ammodendron | 硝态氮log10 NO3--N (mg·g-1) | 1.57±0.02a | 1.57±0.02a | 1.56±0.01a | 1.58±0.01a |
| 铵态氮log10 NH4+-N (mg·g-1) | 0.82±0.03a | 0.78±0.03a | 0.72±0.04a | 0.71±0.04a | |
| 铵态氮/硝态氮log10(NH4+-N/NO3--N) | -0.75±0.04a | -0.80±0.04ab | -0.84±0.04ab | -0.88±0.04b | |
里海盐爪爪 K. caspicum | 硝态氮log10 NO3--N (mg·g-1) | 1.70±0.01a | 1.68±0.01ab | 1.66±0.01b | 1.66±0.01b |
| 铵态氮log10 NH4+-N (mg·g-1) | 0.69±0.01a | 0.66±0.01b | 0.64±0.01b | 0.65±0.01b | |
| 铵态氮/硝态氮log10(NH4+-N/NO3--N) | -1.01±0.01a | -1.01±0.01a | -1.01±0.01a | -1.01±0.01a |
表6 不同空间位置梭梭和里海盐爪爪冠下土壤NO3--N、NH4+-N的含量和NH4+-N/NO3--N
Table 6 Content of NO3--N, NH4+-N and NH4+-N/NO3--N in different spatial positions under canopies of H. ammodendron and K. caspicum
物种 Species | 无机氮组分 Inorganic nitrogen components | 主根周围 Shrub center | 冠幅中央 Shrub middle | 冠幅边缘 Shrub edge | 株间空地 Shrub outside |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
梭梭 H. ammodendron | 硝态氮log10 NO3--N (mg·g-1) | 1.57±0.02a | 1.57±0.02a | 1.56±0.01a | 1.58±0.01a |
| 铵态氮log10 NH4+-N (mg·g-1) | 0.82±0.03a | 0.78±0.03a | 0.72±0.04a | 0.71±0.04a | |
| 铵态氮/硝态氮log10(NH4+-N/NO3--N) | -0.75±0.04a | -0.80±0.04ab | -0.84±0.04ab | -0.88±0.04b | |
里海盐爪爪 K. caspicum | 硝态氮log10 NO3--N (mg·g-1) | 1.70±0.01a | 1.68±0.01ab | 1.66±0.01b | 1.66±0.01b |
| 铵态氮log10 NH4+-N (mg·g-1) | 0.69±0.01a | 0.66±0.01b | 0.64±0.01b | 0.65±0.01b | |
| 铵态氮/硝态氮log10(NH4+-N/NO3--N) | -1.01±0.01a | -1.01±0.01a | -1.01±0.01a | -1.01±0.01a |
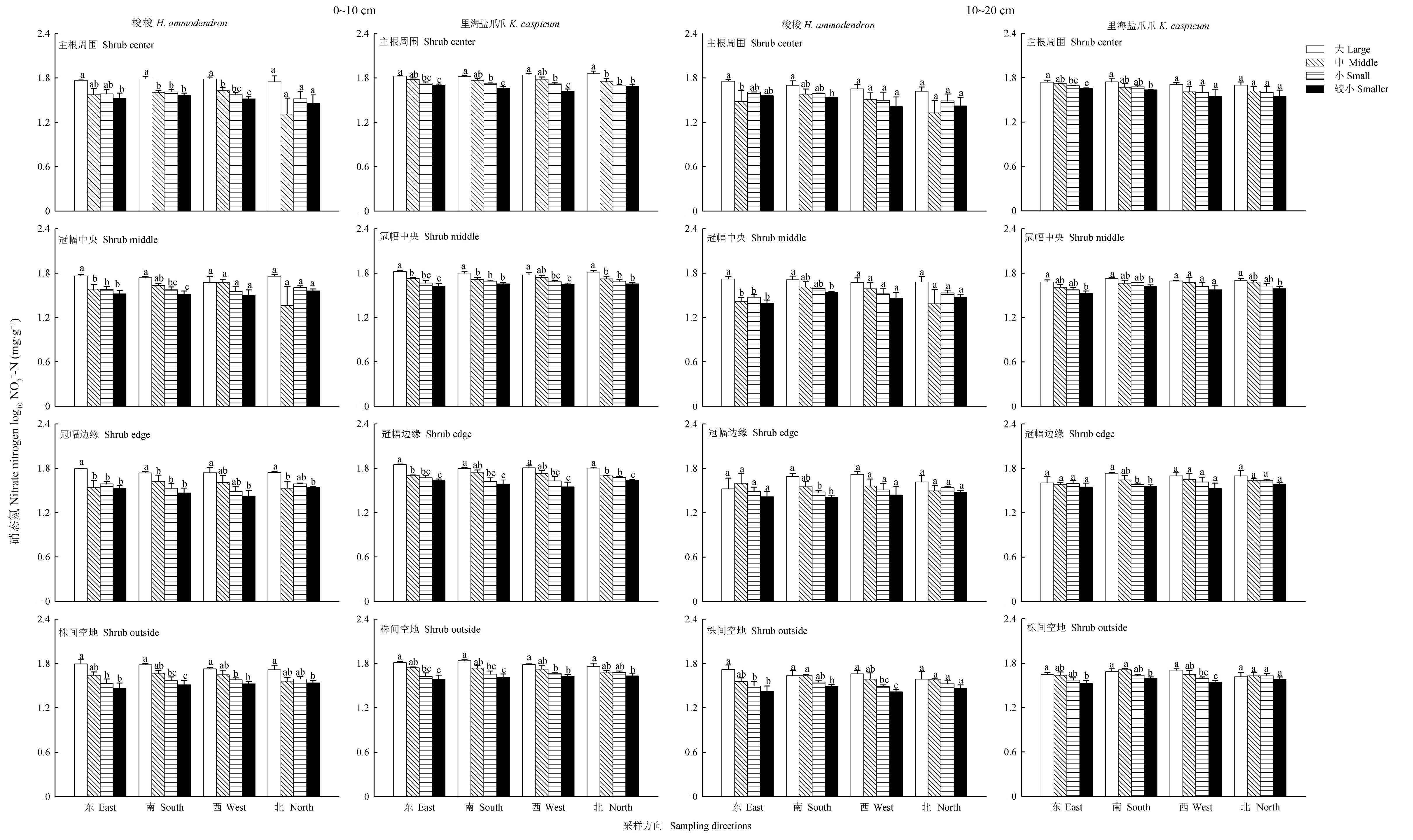
图1 梭梭和里海盐爪爪冠下硝态氮含量变化特征不同小写字母表示同一空间位置及采样方向灌木大小个体之间存在显著差异(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in different individual sizes of shrubs at the same spatial positions and sampling directions (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.1 Variation character of NO3--N content under canopies of H. ammodendron and K. caspicum
| 1 | Whitford W G. Ecology of desert systems. New York: Academic Press, 2002. |
| 2 | Friedel M H, Cellier K M, Nicolson K P. Nutrient deficiencies in central Australian semi-desert rangelands, with reference to decline in range condition. The Rangeland Journal, 1980, 2(2): 151-161. |
| 3 | Wang S P, Zhou G S, Gao S H, et al. Gradient distribution of soil nitrogen and its response to climate change along the Northeast China Transect. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2005, 16(2): 279-283. |
| 王淑平, 周广胜, 高素华, 等. 中国东北样带土壤氮的分布特征及其对气候变化的响应. 应用生态学报, 2005, 16(2): 279-283. | |
| 4 | Zhu Z L, Wen Q X. Nitrogen in soils of China. Nanjing: Jiangsu Science and Technology Publishing House, 1992. |
| 朱兆良, 文启孝. 中国土壤氮素. 南京: 江苏科学技术出版社, 1992. | |
| 5 | Zhao H M, Cheng J H, Zhang W T, et al. Litters decomposition characteristics of five species in the Gurbantunggut Desert. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(2): 165-176. |
| 赵红梅, 程军回, 张文太, 等. 古尔班通古特沙漠5种植物凋落物分解特征. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 165-176. | |
| 6 | Erdenebileg E, Wang C W, Yu W Y, et al. Carbon versus nitrogen release from root and leaf litter is modulated by litter position and plant functional type. Journal of Ecology, 2023, 111(1): 198-213. |
| 7 | Lajtha K, Schlesinger W H. Plant response to variations in nitrogen availability in a desert shrubland community. Biogeochemistry, 1986, 2(1): 29-37. |
| 8 | Yang Z P, Li X Y, Yi W J. Review on stemflow of desert shrubs-research methods and eco-hydrological effects. Journal of Desert Research, 2010, 30(2): 303-311. |
| 杨志鹏, 李小雁, 伊万娟. 荒漠灌木树干茎流及其生态水文效应研究进展. 中国沙漠, 2010, 30(2): 303-311. | |
| 9 | Whitfrod W G, Anderson J, Rice P M. Stemflow contribution to the fertile island effect in creosote bush, Larrea tridentata. Journal of Arid Environments, 1997, 35(3): 451-457. |
| 10 | Liu Y H, Yang Y L, Sheng J D, et al. ‘Fertile island’ characteristics of soil nutrients in Haloxylon ammodendron land in north Xinjiang. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2010, 47(3): 545-554. |
| 刘耘华, 杨玉玲, 盛建东, 等. 北疆荒漠植被梭梭立地土壤养分“肥岛”特征研究. 土壤学报, 2010, 47(3): 545-554. | |
| 11 | Stevenson F J, Cole M A. Cycles of soils: carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, micronutrients (second edition). USA: John Wiley & Sons, 1999. |
| 12 | Yao Y F, Zhao Z N, Wei X R, et al. Effects of shrub species on soil nitrogen mineralization in the desert-loess transition zone. Catena, 2019, 173: 330-338. |
| 13 | Zhan Y Y. Characteristics of nitrogen content of rhizosphere and xerophilous shrubs. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2009. |
| 詹媛媛. 旱生灌木根际及灌丛土壤氮素含量特征研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2009. | |
| 14 | Zhou Z Y, Yu M H, Ding G D, et al. Effects of Hedysarum leguminous plants on soil bacterial communities in the Mu Us Desert, northwest China. Ecology and Evolution, 2020, 10(20): 11423-11439. |
| 15 | Navarro-Cano J A, Verdu M, Garcia C, et al. What nurse shrubs can do for barren soils: rapid productivity shifts associated with a 40 years ontogenetic gradient. Plant and soil, 2015, 388(1/2):197-209. |
| 16 | Bo Z, Dang X H, Liu X J, et al. Fertile island effect in the sedimentary process of Tetraena mongolica Maxim neck has in steppe-desert ecotones on the Inner Mongolia Plateau, China. Journal of Mountain Science, 2022, 19(10): 2791-2805. |
| 17 | Tao Y, Liu Y B, Wu G L, et al. Regional-scale stoichiometric characteristics and spatial distribution patterns of key elements in surface soils in the Junggar desert, China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(7): 13-23. |
| 陶冶, 刘耀斌, 吴甘霖, 等. 准噶尔荒漠区域尺度浅层土壤化学计量特征及其空间分布格局. 草业学报, 2016, 25(7): 13-23. | |
| 18 | Wei W S. Response and feedback of modern desert to climate change: A case study of Gurbantunggut. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(6): 636-641. |
| 魏文寿. 现代沙漠对气候变化的响应与反馈:以古尔班通古特沙漠为例. 科学通报, 2000, 45(6): 636-641. | |
| 19 | Liang M, Mi X J, Li C H, et al. Salinity characteristics and halophytic vegetation diversity of uncultivated saline-alkali soil in Junggar Basin, Xinjiang. Arid Land Geography, 2022, 45(1): 185-196. |
| 梁萌, 米晓军, 李晨华, 等. 新疆准噶尔盆地未开垦盐碱土盐分与盐生植被多样性分析. 干旱区地理, 2022, 45(1): 185-196. | |
| 20 | Wang X Q, Jiang J, Lei J Q, et al. The distribution of ephemeral vegetation on the longitudinal dune surface and its stabilization significance in the Gurbantunggut Desert. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2003, 58(4): 598-605. |
| 王雪芹, 蒋进, 雷加强, 等. 古尔班通古特沙漠短命植物分布及其沙面稳定意义. 地理学报, 2003, 58(4): 598-605. | |
| 21 | Zhang L Y, Chen C D. On the general characteristics of plant diversity of Gurbantunggut sandy desert. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2002, 22(11): 1923-1932. |
| 张立运, 陈昌笃. 论古尔班通古特沙漠植物多样性的一般特点. 生态学报, 2002, 22(11): 1923-1932. | |
| 22 | Zhang S H, Tao Y, Chen Y S, et al. Spatial pattern of soil multifunctionality and its correlation with environmental and vegetation factors in the Junggar Desert, China. Biodiversity Science, 2022, 30(8): 140-150. |
| 张世航, 陶冶, 陈玉森, 等. 准噶尔荒漠土壤多功能性的空间变异特征及其驱动因素. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 140-150. | |
| 23 | Cao Y F, Ding J X, Yu Y J, et al. Preliminary studies on Haloxylon ammodendron ‘Fertile Islands’ in desert soils different in texture. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016, 53(1): 261-270. |
| 曹艳峰, 丁俊祥, 于亚军, 等. 不同质地土壤中荒漠灌木梭梭“肥岛”的初步探讨. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(1): 261-270. | |
| 24 | Ren X, Chu G X, Wang G D, et al. Fractal dimension characteristics of soil particles in oasis desert ecotone in southern edge of Junggar Basin. Journal of Desert Research, 2009, 29(2): 298-304. |
| 任雪, 褚贵新, 王国栋, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘绿洲-沙漠过渡带“肥岛”形成过程中土壤颗粒的分形研究. 中国沙漠, 2009, 29(2): 298-304. | |
| 25 | Lu F H, Shayiban·W, Liu S S, et al. Rooting depth determined physiological response of Haloxylon ammodendron to summer drought. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(8): 3178-3189. |
| 卢福浩, 沙衣班·吾布力, 刘深思, 等. 根深决定不同个体大小梭梭对夏季干旱生理响应的差异. 生态学报, 2021, 41(8): 3178-3189. | |
| 26 | Hao M Y, Zhao W L, Qin L J, et al. A methodology to determine the optimal quadrat size for desert vegetation surveying based on unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) RGB photography. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 42(1): 84-105. |
| 27 | Wang Z H, Fang J Y, Tang Z Y, et al. Geographical patterns in the beta diversity of China’s woody plants: the influence of space, environment and range size. Ecography, 2012, 35(12): 1092-1102. |
| 28 | Chen J, Cui X X, Ding Y L, et al. Exploring the temporal and spatial evolution trend of soil nutrients of different plantation ages based on the fertile island. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 26(6): 71-79. |
| 陈婧, 崔向新, 丁延龙, 等. 基于“肥岛”效应探讨人工梭梭土壤养分时空演变趋势. 水土保持研究, 2019, 26(6): 71-79. | |
| 29 | Bao S D. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis (The third edition). Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 30 | Han X, Yuan C Y, Li J H, et al. Effects of tree species and soil layers on soil extractable nitrogen content. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2022, 31(11): 2143-2151. |
| 韩鑫, 袁春阳, 李济宏, 等. 树种和土层对土壤无机氮的影响. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2143-2151. | |
| 31 | De V F T, Manning P, Tallowin J R, et al. Abiotic drivers and plant traits explain landscape-scale patterns in soil microbial communities. Ecology Letters, 2012, 15(11): 1230-1239. |
| 32 | Li C J, Li Y, Ma J. Spatial heterogeneity of soil chemical properties at fine scales induced by Haloxylon ammodendron (Chenopodiaceae) plants in a sandy desert. Ecological Research, 2011, 26(2): 385-394. |
| 33 | Wang G H, Chen Y L, Gou Q Q. Responses of Haloxylon ammodendron with different plantation ages to changes of soil moisture in a desert-oasis ecotone. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(14): 5658-5668. |
| 王国华, 陈蕴琳, 缑倩倩. 荒漠绿洲过渡带不同年限雨养梭梭(Haloxylon ammodendron)对土壤水分变化的响应. 生态学报, 2021, 41(14): 5658-5668. | |
| 34 | Alusihude, Wang S S, Wen Q, et al. Studies on soil physical properties of typical plant communities in Bayinwenduer desert. Journal of Inner Mongolia Forestry Science and Technology, 2021, 47(1): 1-7. |
| 阿路斯呼德, 王树森, 温泉, 等. 巴音温都尔沙漠典型植物群落土壤物理性质研究. 内蒙古林业科技, 2021, 47(1): 1-7. | |
| 35 | Chen Y Z, Tang Q Y, Gu M Y, et al. Microbial distribution characteristics around the roots of Kalidium foliatum and the effect of salt concentrations on microbial metabolism analysis. Microbiology China, 2019, 46(11): 2900-2908. |
| 陈禹竹, 唐琦勇, 顾美英, 等. 盐爪爪根部微生物分布特征及盐浓度对碳源代谢分析的影响. 微生物学通报, 2019, 46(11): 2900-2908. | |
| 36 | Li Y, Yang X D, Qin L, et al. The bacterial diversity and community structures in rhizosphere soil of two halophytes, Lycium ruthenium and Kalidium caspicum. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(9): 3118-3131. |
| 李岩, 杨晓东, 秦璐, 等. 两种盐生植物根际土壤细菌多样性和群落结构. 生态学报, 2018, 38(9): 3118-3131. | |
| 37 | Cai W T, Lai L M, Li H Y, et al. Progress of research on shrub encroachment in grassland. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2016, 22(4): 531-537. |
| 蔡文涛, 来利明, 李贺祎, 等. 草地灌丛化研究进展. 应用与环境生物学报, 2016, 22(4): 531-537. | |
| 38 | Qu W L, Yang X P, Zhang C T, et al. Shrub-mediated “fertile island” effects in arid and semi-arid grassland. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(4): 201-207. |
| 瞿王龙, 杨小鹏, 张存涛, 等. 干旱、半干旱地区天然草原灌木及其肥岛效应研究进展. 草业学报, 2015, 24(4): 201-207. | |
| 39 | Shu X Y, Hu Y F, He J, et al. Effect of Salix cupularis shrubs on soil nitrogen in the alpine sandy land of Northwest Sichuan. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(7): 55-61. |
| 舒向阳, 胡玉福, 何佳, 等. 川西北高寒沙地不同大小高山柳对土壤氮素的影响. 草业学报, 2017, 26(7): 55-61. | |
| 40 | Liu X D, Chen L, Yang X G, et al. ‘Fertile island’ effect of soil nutrients occurring in Caragana korshinskii and Artemisia ordosica shrubs in desert steppe. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2016, 31(4): 26-32, 92. |
| 刘学东, 陈林, 杨新国, 等. 荒漠草原2种柠条(Caragana korshinskii)和油蒿(Artemisia ordosica)灌丛土壤养分“肥岛”效应. 西北林学院学报, 2016, 31(4): 26-32, 92. | |
| 41 | McClaran M P, Moore-Kucera J, Martens D A, et al. Soil carbon and nitrogen in relation to shrub size and death in a semi-arid grassland. Geoderma, 2008, 145(1): 60-68. |
| 42 | Gross K L, Burton P A J. Spatial variation in nitrogen availability in three successional plant communities. Journal of Ecology, 1995, 83(3): 357-367. |
| 43 | Li X L, Wei Y J, Dang X H, et al. Soil mechanical composition and soil nutrient content of Reaumuria soongorica nebkhas. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(3): 933-942. |
| 李小乐, 魏亚娟, 党晓宏, 等. 红砂灌丛沙堆土壤粒度组成及养分积累特征. 干旱区研究, 2022, 39(3): 933-942. | |
| 44 | Zhang Y D, Bai S B. Effects of nitrogen forms on nutrient uptake and growth of trees. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2003, 14(11): 2044-2048. |
| 张彦东, 白尚斌. 氮素形态对树木养分吸收和生长的影响. 应用生态学报, 2003, 14(11): 2044-2048. | |
| 45 | Li J, Zhao C Y, Zhu H, et al. Species effect of Tamarix spp. and Haloxylon ammodendron on shrub ‘fertile island’. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(12): 5138-5147. |
| 李君, 赵成义, 朱宏, 等. 柽柳(Tamarix spp.)和梭梭(Haloxylon ammodendron)的“肥岛”效应. 生态学报, 2007, 27(12): 5138-5147. | |
| 46 | Li R, He X D, Zhang N, et al. Temporal-spatial variation of soil NH4 +-N and NO3 --N in sand dune fixing process. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2010, 47(2): 295-302. |
| 李荣, 何兴东, 张宁, 等. 沙丘固定过程中土壤铵态氮和硝态氮的时空变化. 土壤学报, 2010, 47(2): 295-302. | |
| 47 | Zhao X, Li J J, Li H J. Effects of vegetation restoration type on soil carbon, nitrogen, and microbial quantity in Guandi Mountain. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2010, 29(11): 2102-2110. |
| 赵溪, 李君剑, 李洪建. 关帝山不同植被恢复类型对土壤碳、氮含量及微生物数量的影响. 生态学杂志, 2010, 29(11): 2102-2110. | |
| 48 | Guan L J, Mei X F, Zhang Y Y, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution of soil moisture content and fertility of Caragana stenophylla shrub nabkhas in different habitats. Arid Zone Research, 2016, 33(2): 253-259. |
| 关林婧, 梅续芳, 张媛媛, 等. 狭叶锦鸡儿灌丛沙堆土壤水分和肥力的时空分布. 干旱区研究, 2016, 33(2): 253-259. | |
| 49 | Su Y Z, Zhao H L, Zhang T H. Influencing mechanism of several shrubs and subshrubs on soil fertility in Keerqin sandy land. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002, 13(7): 802-806. |
| 苏永中, 赵哈林, 张铜会. 几种灌木、半灌木对沙地土壤肥力影响机制的研究. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(7): 802-806. | |
| 50 | Gao L J, Lv G H, Wang Y, et al. Vertical distribution of soil nitrogen under halophyte community in the Ebinur Lake Area. Arid Zone Research, 2014, 31(1): 51-56. |
| 高丽娟, 吕光辉, 王芸, 等. 艾比湖地区盐生植物群落土壤氮素的垂直分布特征. 干旱区研究, 2014, 31(1): 51-56. | |
| 51 | Wang L X, Macko S A. Constrained preferences in nitrogen uptake across plant species and environments. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2011, 34(3): 525-534. |
| 52 | Hilde V, Bernard M, Pascal B, et al. Use of principal component analysis to assess factors controlling net N mineralization in deciduous and coniferous forest soils. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2002, 36(2): 93-101. |
| [1] | 金欣悦, 龚莉, 王梦亭, 陶冶, 周多奇. 紫草科2种短命植物功能性状的差异化协变特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 58-70. |
| [2] | 李亚娟, 刘静, 徐长林, 曹文侠. 不同退化程度对高寒草甸土壤无机氮及脲酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 45-53. |
| [3] | 刘继亮, 李锋瑞,刘七军,牛瑞雪. 黑河中游干旱荒漠地面节肢动物群落季节变异规律[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(5): 161-169. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||