

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (12): 34-44.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024054
韩雨轩1,2,3( ), 王瑞3, 郝丽芬2, 袁海滨1(
), 王瑞3, 郝丽芬2, 袁海滨1( ), 林克剑2(
), 林克剑2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-02-05
修回日期:2024-03-25
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2024-10-09
通讯作者:
袁海滨,林克剑
作者简介:yuanhaibin@jlau.edu.cn基金资助:
Yu-xuan HAN1,2,3( ), Rui WANG3, Li-fen HAO2, Hai-bin YUAN1(
), Rui WANG3, Li-fen HAO2, Hai-bin YUAN1( ), Ke-jian LIN2(
), Ke-jian LIN2( )
)
Received:2024-02-05
Revised:2024-03-25
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-10-09
Contact:
Hai-bin YUAN,Ke-jian LIN
摘要:
外来植物长刺蒺藜草的入侵已对我国北方草原和农牧交错带造成了极大危害。已开展的研究主要集中在长刺蒺藜草生物学特性、防治措施等,但是其在我国发生的入侵和扩散蔓延规律、地理分布格局及其影响因素并不清楚。基于此,以标本、文献、实地调查等数据重建长刺蒺藜草在我国的入侵历史过程;通过空间分析等方法揭示其空间分布格局和扩散蔓延的时空异质性;基于主成分分析对8种环境因子进行筛选,识别影响分布和扩散格局的关键因素。长刺蒺藜草最早于1963年入侵辽宁省锦州市,此后扩散至邻近的内蒙古东南部和吉林西部,目前在这里已经形成了入侵聚集区且还处在扩散蔓延阶段,同时于2010年扩散至内蒙古西部并形成了新的聚集区。长刺蒺藜草在辽宁省的扩散呈各向异性,主要向北向西扩散,而基本没有向西南方向扩散。长刺蒺藜草于20世纪70年代在北京市朝阳区和河北省秦皇岛有分布记录,但此后基本没有扩散。长刺蒺藜草传入辽宁和北京后扩散方向和范围的异质性可能是由于传入后不能定殖导致的。传入和定殖区间的因子分析结果表明土壤碳酸钙含量、年平均降水量、表层土壤沙子含量以及表层土壤碳氮比是影响传入后能否定殖的关键因子。未来进行风险评估时应该考虑长刺蒺藜草种群在不同土壤环境中的适应性和繁殖能力,全面解析不同环境中的繁殖生长特性和入侵能力,为精准识别定殖风险区、制定高效监测与防控措施,抑制进一步扩散蔓延提供科学支撑。
韩雨轩, 王瑞, 郝丽芬, 袁海滨, 林克剑. 外来入侵植物长刺蒺藜草在我国的地理分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 34-44.
Yu-xuan HAN, Rui WANG, Li-fen HAO, Hai-bin YUAN, Ke-jian LIN. The geographic distribution pattern and factors influencing the spread in China of the invasive alien plant Cenchrus longispinus[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(12): 34-44.
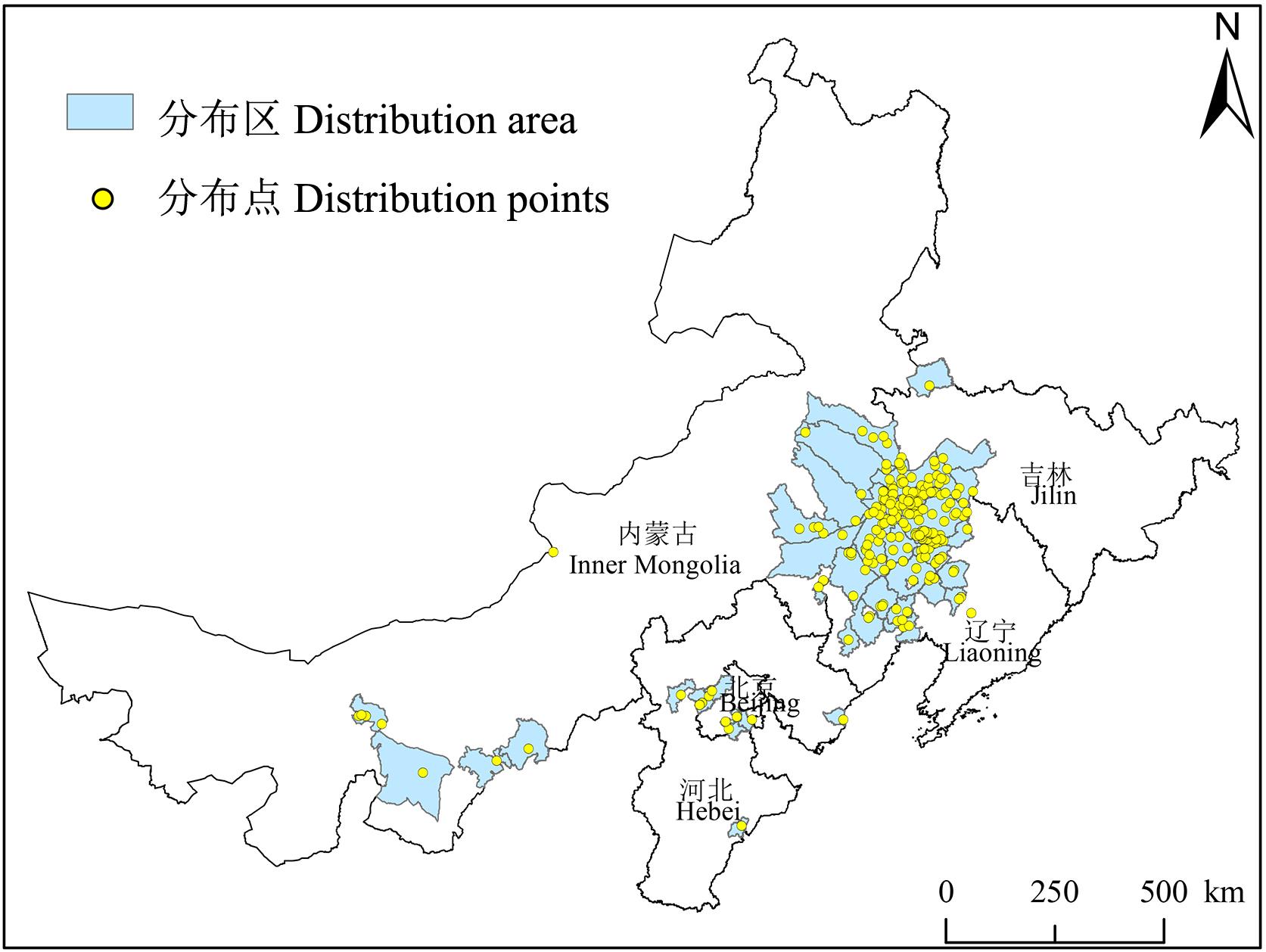
图1 长刺蒺藜草在我国的分布该图基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2019)1822号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改,下同。The map is based on the standard map of GS(2019)1822, the standard map service website of the Ministry of Natural Resources, and the boundary of the bottom map is not modified, the same below.
Fig.1 Distribution of C. longispinus in China
环境因子 Environmental factors | 因子载荷 Factor loading | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | |
| 年均地表温度AAST | 0.589 | 0.005 | -0.584 |
| 归一化植被指数NDVI | -0.559 | 0.162 | 0.571 |
| 年均降水量Annual average precipitation | -0.844 | 0.135 | 0.237 |
| 表层土壤沙子含量SSSC | 0.162 | -0.906 | 0.170 |
| 碳酸钙含量Soil calcium carbonate content | 0.824 | 0.074 | 0.427 |
| 土壤类型Soil type | 0.652 | -0.233 | 0.171 |
| 表层土壤碳氮比Surface soil C/N | 0.350 | 0.869 | -0.052 |
| 土壤pH值Soil pH value | 0.791 | 0.172 | 0.493 |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 3.250 | 1.711 | 1.210 |
| 百分比方差Percentage variance (%) | 40.631 | 21.383 | 15.122 |
| 累积百分比方差CPV (%) | 40.631 | 62.014 | 77.136 |
表1 各环境因子主成分的特征值及累积方差
Table 1 Eigenvalues and cumulative variance of principal components of various environmental factors
环境因子 Environmental factors | 因子载荷 Factor loading | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | |
| 年均地表温度AAST | 0.589 | 0.005 | -0.584 |
| 归一化植被指数NDVI | -0.559 | 0.162 | 0.571 |
| 年均降水量Annual average precipitation | -0.844 | 0.135 | 0.237 |
| 表层土壤沙子含量SSSC | 0.162 | -0.906 | 0.170 |
| 碳酸钙含量Soil calcium carbonate content | 0.824 | 0.074 | 0.427 |
| 土壤类型Soil type | 0.652 | -0.233 | 0.171 |
| 表层土壤碳氮比Surface soil C/N | 0.350 | 0.869 | -0.052 |
| 土壤pH值Soil pH value | 0.791 | 0.172 | 0.493 |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 3.250 | 1.711 | 1.210 |
| 百分比方差Percentage variance (%) | 40.631 | 21.383 | 15.122 |
| 累积百分比方差CPV (%) | 40.631 | 62.014 | 77.136 |
| 1 | Seebens H, Essl F, Dawson W, et al. Global trade will accelerate plant invasions in emerging economies under climate change. Global Change Biology, 2015, 21(11): 4128-4140. |
| 2 | Benning J, Clar E, Hufbauer R, et al. Environmental gradients mediate dispersal evolution during biological invasions. BioRxiv, 2023, 9: 570855. |
| 3 | Wan F H, Guo J Y, Wang D H. Alien invasive species in China: Their damages and management strategies. Biodiversity Science, 2002, 10(1): 119-125. |
| 万方浩, 郭建英, 王德辉. 中国外来入侵生物的危害与管理对策. 生物多样性, 2002, 10(1): 119-125. | |
| 4 | Ding H, Xu H G, Qiang S, et al. Status quo and trends of biological invasion into China. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2011, 27(3): 35-41. |
| 丁晖, 徐海根, 强胜, 等. 中国生物入侵的现状与趋势. 生态与农村环境学报, 2011, 27(3): 35-41. | |
| 5 | Buchadas A, Vaz A S, Honrado J P, et al. Dynamic models in research and management of biological invasions. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 196: 594-606. |
| 6 | Wang R, Huang H K, Zhang H B, et al. Analysis of gaps in regulations and management mechanisms for the prevention and control of invasive alien species in China. Plant Protection, 2022, 48(4): 2-9. |
| 王瑞, 黄宏坤, 张宏斌, 等. 中国外来入侵物种防控法规和管理机制空缺分析. 植物保护, 2022, 48(4): 2-9. | |
| 7 | Theoharides K A, Dukes J S. Plant invasion across space and time: Factors affecting nonindigenous species success during four stages of invasion. New Phytologist, 2007, 176(2): 256-273. |
| 8 | Hou Q C, Feng Y L, Zhou Y J, et al. Main hypotheses on mechanisms underlying plant invasion: A review. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(11): 3105-3115. |
| 侯清晨, 冯燕楼, 周玉洁, 等. 植物入侵机制的主要假说.应用生态学报, 2022, 33(11): 3105-3115. | |
| 9 | Varpe, Øystein. Life history adaptations to seasonality. Integrative and Comparative Biology, 2017, 57(5): 943-960. |
| 10 | Hertling U M, Lubke R A. Assessing the potential for biological invasion-the case of Ammophila arenaria in South Africa. South African Journal of Science, 2000, 96: 520-527. |
| 11 | Meng W, Feagin R A, Innocenti R A, et al. Invasion and ecological effects of exotic smooth cordgrass Spartina alterniflora in China. Ecological Engineering, 2020, 143: 105670. |
| 12 | Park J S, Lee H. Predicting the spatio-temporal distribution of the invasive alien plant Andropogon virginicus, in the South Korean peninsula considering long-distance dispersal capacities. PLoS One, 2023, 18(11): 291365. |
| 13 | Essl F, Dullinger S, Rabitsch W, et al. Historical legacies accumulate to shape future biodiversity in an era of rapid global change. Diversity and Distributions, 2015, 21: 534-547. |
| 14 | Ma Y, Shen Z Y. Exotic plant invasion and its ecological risk assessment. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2006, 25(8): 983-988. |
| 马晔, 沈珍瑶. 外来植物的入侵机制及其生态风险评价. 生态学杂志, 2006, 25(8): 983-988. | |
| 15 | Seebens H, Blackburn T M, Dyer E E, et al. No saturation in the accumulation of alien species worldwide. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 14435. |
| 16 | Buckland-Nicks M, Heim A, Lundholm J. Spatial environmental heterogeneity affects plant growth and thermal performance on a green roof. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 553: 20-31. |
| 17 | Hua M Y, Sun Z L, Gao K. Plastic response of life history traits and material allocation to heterotopia of life history of Cenchrus spinifex Cav. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023(10): 30-35. |
| 华明阳, 孙忠林, 高凯. 少花蒺藜草生活史性状和物质分配对生活史异位的可塑响应. 黑龙江农业科学, 2023(10): 30-35.. | |
| 18 | Dong W X, Zhao G L, Li X H. Investigation on the biological characteristics of Cenchrus pauciflorus. Inner Mongolia Forestry, 2010, 1(1): 22. |
| 董文信, 赵桂玲, 李秀华. 光梗蒺藜草生物学特性调查. 内蒙古林业, 2010, 1(1): 22. | |
| 19 | Jia X Y, Li Q F, Xu J. Flowering and seeding characteristics of invasive plant on Cenchrus pauciflorus. Journal of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 33(2): 83-88. |
| 贾鲜艳, 李青丰, 徐军. 外来入侵植物光梗蒺藜草开花与结实特性研究. 内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 33(2): 83-88. | |
| 20 | Du G M, Cao F Q, Liu W B, et al. The distribution and harmfulness of Cenchrus pauciflorus Benth. in Liaoning Province. Grassland of China, 1995(3): 71-73. |
| 杜广明, 曹凤琴, 刘文斌, 等. 辽宁省草场的少花蒺藜草及其危害. 中国草地, 1995(3): 71-73. | |
| 21 | Wang W, Han Z S. The harm and distribution of Cenchrus pauciflorus, an alien invasive species, in Liaoning Province. Pratacultural Science, 2005(7): 63-64. |
| 王巍, 韩志松. 外来入侵生物-少花蒺藜草在辽宁地区的危害与分布. 草业科学, 2005(7): 63-64. | |
| 22 | Zhou Q L, Wang Z W, Qi F L, et al. Biological and ecological characteristics of Cenchrus pauciflorus and the integrated control strategies. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(8): 2593-2600. |
| 周全来, 王正文, 齐凤林, 等. 少花蒺藜草生物生态学特征与综合防除策略. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(8): 2593-2600. | |
| 23 | Zhang Y L, Zhang R H, Fu W D, et al. Effects of different cultivation practices on the amount of seeds in the soils and seed production of Cenchrus pauciflorus Benth. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2015, 32(3): 312-320. |
| 张衍雷, 张瑞海, 付卫东, 等. 不同农作措施对少花蒺藜草(Cenchrus pauciflorus Benth)种子库及其繁殖能力的影响. 农业资源与环境学报, 2015, 32(3): 312-320. | |
| 24 | Guo Q X. Risk analysis of import of Cenchrus longispinus into China. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2011, 23(12): 68-70. |
| 郭琼霞. 长刺蒺藜草(Cenchrus longispinus)传入中国的风险性研究. 江西农业学报, 2011, 23(12): 68-70. | |
| 25 | Wang J J, He L L.The geographical distribution and main environmental impact factors of Cenchrus longispinus in Liaoning Province. Xin Nongye, 2022, 24: 10-12. |
| 王晶晶, 何莉莉. 少花蒺藜草在辽宁省的地理分布与主要环境影响因子. 新农业, 2022, 24: 10-12. | |
| 26 | Zhang X L, Chen Z N, Wu Z J. Distribution area changes of Cenchrus spinifex in China under climate change scenarios. Guihaia, 2023, 43(4): 658-669. |
| 张小丽, 陈泽柠, 武正军. 气候变化情景下少花蒺藜草在中国的分布区变化. 广西植物, 2023, 43(4): 658-669. | |
| 27 | Zhang Q P, Wang J, Wang Q. Effects of abiotic factors on plant diversity and species distribution of alpine meadow plants. Ecological Informatics, 2021, 61: 101210-101218. |
| 28 | Catford J A, Bode M, Tilman D. Introduced species that overcome life history tradeoffs can cause native extinctions. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 2131. |
| 29 | Zheng Z X, Wang R, Zhang F J, et al. The geographic distribution pattern and spatiotemporal dynamic of the invasive alien plant Flaveria bidentis (Asteraceae) in China. Journal of Biosafety, 2018, 27(4): 295-299. |
| 郑志鑫, 王瑞, 张风娟, 等. 外来入侵植物黄顶菊在我国的地理分布格局及其时空动态. 生物安全学报, 2018, 27(4): 295-299. | |
| 30 | He L L, Liu J C, Luan Y S. Distribution pattern and early monitoring and warning of two invasive plants in Liaoning Province. Liaoning Agricultural Sciences, 2022(6): 13-18. |
| 何莉莉, 刘金昌, 栾云松. 两种入侵植物在辽宁省的分布格局与早期监测预警. 辽宁农业科学, 2022(6): 13-18. | |
| 31 | Bellard C, Thuiller W, Leroy B, et al. Will climate change promote future invasions? Global Change Biology, 2013, 19(12): 3740-3748. |
| 32 | Lin H M, Zhang W L. Differences and similarities between principal component analysis and factor analysis, and SPSS Software: Discussion with comrades Liu Yumei, Lu Wendai, and others. Statistical Research, 2005, 3: 65-69. |
| 林海明, 张文霖. 主成分分析与因子分析的异同和SPSS软件——兼与刘玉玫、卢纹岱等同志商榷. 统计研究, 2005, 3: 65-69. | |
| 33 | Greenacre M, Groenen P J F, Hastie T, et al. Principal component analysis. Nature Reviews Methods Primers, 2002, 2: 100. |
| 34 | Twentyman J D. Control of vegetative and reproductive growth in sand burr (Cenchrus longispinus). Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture, 1974, 14(71): 764-770. |
| 35 | Twentyman J. Environmental control of dormancy and germination in the seeds of Cenchrus longispinus (Hack.) Fern. Weed Research, 1974, 14(1): 1-11. |
| 36 | Fagaraş M. Cenchrus longispinus (Hack) Fernald, one of the most aggressive alien plants on the Romanian black sea coast. Diversity in Coastal Marine Sciences: Historical Perspectives and Contemporary Research of Geology, Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and Remote Sensing, 2018, 24: 383-395. |
| 37 | An R J, Wang Y Z, Tian X. Research progress of the invasive plant-Cenchrus pauciflorus. Weed Science, 2015, 33(1): 27-31. |
| 安瑞军, 王永忠, 田迅. 外来入侵植物-少花蒺藜草研究进展. 杂草科学, 2015, 33(1): 27-31. | |
| 38 | Bertelsmeier C, Ollier S, Liebhold A, et al. Recent human history governs global ant invasion dynamics. Nature Ecology and Evolution, 2017, 1: 184. |
| 39 | Wang R, Wang Y Z, Wan F H. Spatiotemporal expansion pattern and potential spread of invasive alien plant Erigeron annuus (Asteraceae) in China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2010, 29(6): 1068-1074. |
| 王瑞, 王印政, 万方浩. 外来入侵植物一年蓬在中国的时空扩散动态及其潜在分布区预测. 生态学杂志, 2010, 29(6): 1068-1074. | |
| 40 | Banks N C, Paini D R, Bayliss K L, et al. The role of global trade and transport network topology in the human-mediated dispersal of alien species. Ecology Letters, 2015, 18: 188-199. |
| 41 | Li P P, He X N, Zuo R L, et al. Prediction of potential habitability of four Cenchrus weeds in China. Journal of Weed Science, 2022, 40(2): 15-23. |
| 李盼畔, 何旭诺, 左然玲, 等. 4种蒺藜草属杂草在中国的潜在适生性预测. 杂草学报, 2022, 40(2): 15-23. | |
| 42 | Omer A, Fristoe T, Yang Q, et al. The role of phylogenetic relatedness on alien plant success depends on the stage of invasion. Nature Plants, 2022, 8: 906-914. |
| 43 | Vila J C C, Jones M L, Patel M, et al. Uncovering the rules of microbial community invasions. Nature Ecology and Evolution, 2019, 3: 1162-1171. |
| 44 | Wan F H, Yang N W. Invasion and management of agricultural alien insects in China. Annual Review Entomology, 2016, 61: 77-98. |
| 45 | Li H R, Yan J, Du C, et al. Current status and suggestions of research on invasive risk assessment of alien plants in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(16): 6451-6463. |
| 李惠茹, 严靖, 杜诚, 等. 中国外来植物入侵风险评估研究. 生态学报, 2022, 42(16): 6451-6463. | |
| 46 | Wang K F. Study on habitat conditions and spread laws of Cenchrus pauciflorus. Modern Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2019(10): 31-35. |
| 王坤芳. 少花蒺藜草生境条件及扩散规律研究. 现代畜牧兽医, 2019(10): 31-35. | |
| 47 | Zhang Y, Ma Y, Zhang H, et al. Environmental factors coordinate circadian clock function and rhythm to regulate plant development. Plant Signaling and Behavior, 2023, 18(1): 2231202. |
| 48 | Chen J N, Feng H X, Su H, et al. Physiological response and drought resistance evaluation of invasive plants Cenchrus pauciflorus to drought. Grassland and Turf, 2023, 43(3): 77-83, 91. |
| 陈佳宁, 冯海旭, 苏慧, 等. 入侵植物少花蒺藜草对干旱胁迫的生理响应及抗旱性评价. 草原与草坪, 2023, 43(3): 77-83, 91. | |
| 49 | Zhang C B, Liu Y T, Li D R, et al. Influence of soil moisture content on pullout properties of Hippophae rhamnoides Linn. roots. Journal of Mountain Science, 2020, 17: 2816-2826. |
| 50 | Bao Q S, Hai L, Wang B, et al. Research progress of soil respiration studies in sandy ecosystems. Northern Horticulture, 2023(22): 125-131. |
| 鲍青松, 海龙, 王冰, 等. 沙地生态系统土壤呼吸研究进展. 北方园艺, 2023(22): 125-131. | |
| 51 | Jing D W, Xing S J, Ma B Y, et al. Research advances on calcium nutrition in soil and plant. Biological Disaster Science, 2012, 35(4): 447-451. |
| 井大炜, 邢尚军, 马丙尧, 等. 土壤与植物中钙营养研究进展. 生物灾害科学, 2012, 35(4): 447-451. | |
| 52 | Shao F F, Chen Y H, Cui Y, et al. Plant community characteristics under low and high soil moisture conditions in typical marsh wetlands in Northern China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(21): 8692-8703.. |
| 邵非凡, 陈禹含, 崔圆, 等. 北方典型沼泽湿地高低土壤水分下植物群落特征.生态学报, 2023, 43(21): 8692-8703. | |
| 53 | Wang M J, Bai Z Y, Jia A M, et al. Research progress on effects of nitrogen deposition,warming and precipitation pattern changes on grassland carbon sequestration. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2023, 54(6): 89-96. |
| 王明君, 白朕银, 贾傲梅, 等. 氮沉降、增温和降水变化对草地碳固存的影响研究进展. 东北农业大学学报, 2023, 54(6): 89-96. |
| [1] | 赵光华, 高明龙, 王朵, 范世奇, 唐健, 孙阔, 温玄烨. 全球入侵植物的经济成本评估[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 16-24. |
| [2] | 刘晶, 杨艺涵, 钱永强, 陈雨峰, 刘丹, 解孝满, 刘岳含, 柳鑫, 邹博坤. 尼山-峄山区外来入侵草本植物风险评估[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 1-14. |
| [3] | 陈美杉, 陈鲜, 满晓珍, 刘闯, 佟佳林, 曲波. 入侵种瘤突苍耳细根解剖结构的可塑性与入侵性间的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 118-126. |
| [4] | 蒙仲举, 陈颜洁, 包斯琴. 苏尼特右旗荒漠草原三种放牧方式下群落斑块特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 13-23. |
| [5] | 方昭, 张少康, 刘海威, 焦峰, 张军. 黄土丘陵区草本群落生物量空间分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 26-35. |
| [6] | 赵威, 王艳杰, 李亚鸽. 草地入侵植物对枝叶去除的生理生态响应:模式、机理与研究展望[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(6): 195-202. |
| [7] | 刘任涛, 郗伟华, 朱凡. 宁夏荒漠草原地面节肢动物群落组成及季节动态特征[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(6): 126-135. |
| [8] | 赵晓红, 杨殿林, 王慧, 刘红梅, 曲波, 皇甫超河. 黄顶菊入侵对不同地区土壤氮循环及微生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(2): 62-69. |
| [9] | 王桃,徐长林,张丽静,周志宇. 5个燕麦品种和品系不同生育期不同部位养分分布格局[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(4): 70-81. |
| [10] | 李武斌,何丙辉,王力,申建红,黄治清,张兴华,文基坚,代万贵. 九寨沟马脑壳金矿矿山土壤养分空间分布格局[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(3): 1-9. |
| [11] | 王瑞,万方浩. 外来入侵植物意大利苍耳在我国适生区预测[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(6): 222-230. |
| [12] | 柴永青,曹致中,蔡卓山,万丽霞,李学玲. 肃北地区稀有植物裸果木种群的空间分布格局[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(5): 239-249. |
| [13] | 鲁为华,朱进忠,王东江,靳瑰丽,余博. 天山北坡围栏封育条件下伊犁绢蒿幼苗分布格局及数量动态变化规律研究[J]. 草业学报, 2009, 18(4): 17-26. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||