

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (9): 185-193.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024385
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
陈丹丹( ), 王垚, 郭田心, 梁秋雨, 张庆, 骈瑞琪(
), 王垚, 郭田心, 梁秋雨, 张庆, 骈瑞琪( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-10
修回日期:2024-11-28
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-07-02
通讯作者:
骈瑞琪
作者简介:E-mail: rqpian2003@scau.edu.cn基金资助:
Dan-dan CHEN( ), Yao WANG, Tian-xin GUO, Qiu-yu LIANG, Qing ZHANG, Rui-qi PIAN(
), Yao WANG, Tian-xin GUO, Qiu-yu LIANG, Qing ZHANG, Rui-qi PIAN( )
)
Received:2024-10-10
Revised:2024-11-28
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-07-02
Contact:
Rui-qi PIAN
摘要:
为提高秸秆的利用率,从白蚁肠道中通过刚果红初筛、滤纸降解复筛试验筛选到了两株纤维素降解菌,经NCBI同源序列比对百分比分别鉴定为沙福芽孢杆菌(BS)和伊朗纤维单胞菌(CE),其内切葡聚糖酶、外切葡聚糖酶、β-葡萄糖苷酶活力测定结果分别为0.102、0.321、0.112 U·mL-1和0.202、0.434、0.131 U·mL-1。两株菌的滤纸发酵差异代谢物主要是氨基酸及其代谢产物、苯及其衍生物、醛酮酯类、生物碱、有机酸及其衍生物和杂环化合物等物质。其差异代谢途径以苯丙氨酸、酪氨酸和色氨酸的生物合成和芳香族化合物的降解等为主。以水稻秸秆为唯一碳源培养沙福芽孢杆菌和伊朗纤维单胞菌14 d后,秸秆出现不同程度降解,与对照组相比,沙福芽孢杆菌和伊朗纤维单胞菌处理下秸秆的酸性洗涤纤维(48.80%、35.43% DM)和半纤维素含量(19.90%、17.53% DM)以及可溶性碳水化合物含量(0.11%、0.18% DM)均显著降低,伊朗纤维单胞菌处理下秸秆的失重率(43.12% DM)显著增加、中性洗涤纤维含量(52.95% DM)显著降低。
陈丹丹, 王垚, 郭田心, 梁秋雨, 张庆, 骈瑞琪. 纤维素降解菌的筛选以及对水稻秸秆的代谢利用[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 185-193.
Dan-dan CHEN, Yao WANG, Tian-xin GUO, Qiu-yu LIANG, Qing ZHANG, Rui-qi PIAN. Screening of cellulose-degrading bacteria involved in metabolic utilization of rice straw[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(9): 185-193.
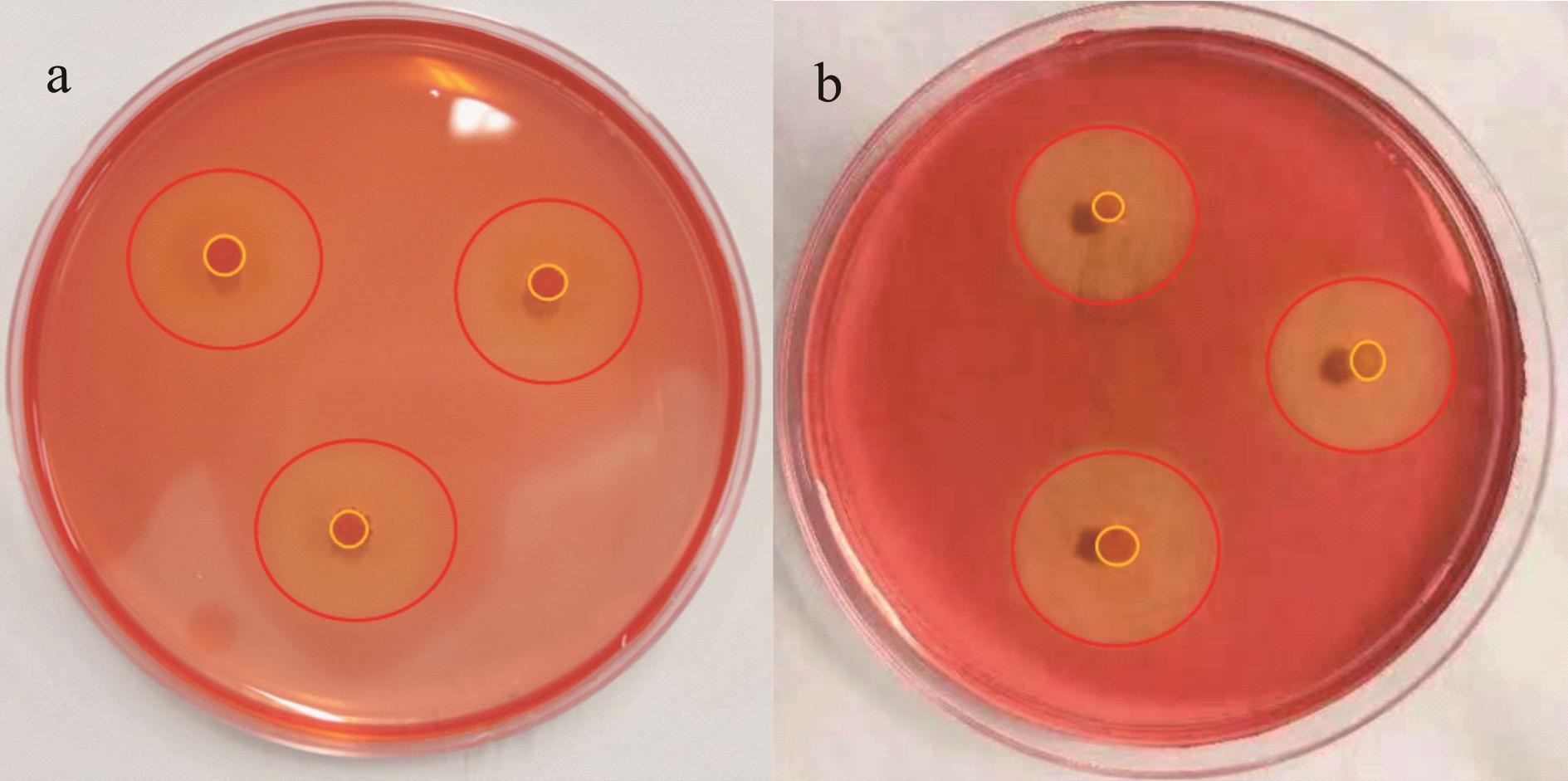
图1 纤维素降解菌的刚果红染色结果a: 1号菌No.1 bacterium; b: 2号菌No.2 bacterium. 黄色圈:菌落直径(d);红色圈:透明圈直径(D)。Yellow circle: Colony diameter (d); Red circle: Transparent circle diameter (D).
Fig.1 Congo red staining results of cellulose-degrading bacteria

图2 培养2 d后纤维素降解菌的滤纸降解情况a: 对照组Control group; b: 1号菌No.1 bacterium; c: 2号菌No.2 bacterium.
Fig.2 Filter paper degradation of cellulose-degrading bacteria after 2 days of cultivation
项目 Item | 沙福芽孢杆菌 B. safensis | 伊朗纤维单胞菌 C. iranensis | 项目 Item | 沙福芽孢杆菌 B. safensis | 伊朗纤维单胞菌 C. iranensis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 革兰氏Gram | + | + | D-水杨苷D-salicylic acid glycoside | + | - |
| 过氧化氢酶Catalase | + | + | 纤维二糖Cellobiose | + | + |
| 运动性Motile | + | + | 柠檬酸盐Citrate | + | - |
| 淀粉Starch | - | - | 麦芽糖Maltose | + | + |
| 甲基红试验Methylred test | + | + | 山梨醇Sorbitol | + | + |
| 明胶化Gelatinization | - | - | 海藻糖Trehalose | + | + |
| 硝酸盐还原Nitrate reduction | - | - | 葡萄糖Glucose | + | + |
| 棉子糖Raffinose | + | + | D-果糖D-fructose | + | - |
| 蔗糖Sucrose | + | + | L-鼠李糖L-rhamnose | - | + |
| 木聚糖Xylan | + | + | 松三糖Melezitose | + | + |
| 乳糖Lactose | + | + | 密二糖Melibiose | + | + |
| 菊糖Inulin | + | + | 壳聚糖Chitosan | - | - |
| 阿拉伯糖Arabinose | + | - | V-P试验V-P test | - | - |
表1 沙福芽孢杆菌和伊朗纤维单胞菌的生理生化结果
Table 1 Physiological and biochemical results of B. safensis and C. iranensis
项目 Item | 沙福芽孢杆菌 B. safensis | 伊朗纤维单胞菌 C. iranensis | 项目 Item | 沙福芽孢杆菌 B. safensis | 伊朗纤维单胞菌 C. iranensis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 革兰氏Gram | + | + | D-水杨苷D-salicylic acid glycoside | + | - |
| 过氧化氢酶Catalase | + | + | 纤维二糖Cellobiose | + | + |
| 运动性Motile | + | + | 柠檬酸盐Citrate | + | - |
| 淀粉Starch | - | - | 麦芽糖Maltose | + | + |
| 甲基红试验Methylred test | + | + | 山梨醇Sorbitol | + | + |
| 明胶化Gelatinization | - | - | 海藻糖Trehalose | + | + |
| 硝酸盐还原Nitrate reduction | - | - | 葡萄糖Glucose | + | + |
| 棉子糖Raffinose | + | + | D-果糖D-fructose | + | - |
| 蔗糖Sucrose | + | + | L-鼠李糖L-rhamnose | - | + |
| 木聚糖Xylan | + | + | 松三糖Melezitose | + | + |
| 乳糖Lactose | + | + | 密二糖Melibiose | + | + |
| 菊糖Inulin | + | + | 壳聚糖Chitosan | - | - |
| 阿拉伯糖Arabinose | + | - | V-P试验V-P test | - | - |
编号 Number | 菌种 Strains | 内切葡聚糖酶 Endoglucanase | 外切葡聚糖酶 Exoglucanase | β-葡萄糖苷酶 β-glucosidase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 沙福芽孢杆菌B. safensis | 0.102±0.003 | 0.321±0.002 | 0.112±0.004 |
| 2 | 伊朗纤维单胞菌C. iranensis | 0.202±0.003 | 0.434±0.001 | 0.131±0.002 |
表2 沙福芽孢杆菌和伊朗纤维单胞菌纤维素酶的活力
Table 2 Enzyme activities of cellulases from B. safensis and C. iranensis (n=3, U·mL-1)
编号 Number | 菌种 Strains | 内切葡聚糖酶 Endoglucanase | 外切葡聚糖酶 Exoglucanase | β-葡萄糖苷酶 β-glucosidase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 沙福芽孢杆菌B. safensis | 0.102±0.003 | 0.321±0.002 | 0.112±0.004 |
| 2 | 伊朗纤维单胞菌C. iranensis | 0.202±0.003 | 0.434±0.001 | 0.131±0.002 |

图5 沙福芽孢杆菌和伊朗纤维单胞菌的差异代谢物红色:伊朗纤维单胞菌相对沙福芽孢杆菌显著上调的代谢物;绿色:伊朗纤维单胞菌相对沙福芽孢杆菌显著下调的代谢物;灰色:两株菌无显著差异的代谢物;VIP:变量重要性投影;FC:差异倍数。Red: Metabolites significantly upregulated by C. iranensis relative to B. safensis; Green: Metabolites significantly downregulated by C. iranensis relative to B. safensis; Gray: No significant differences in metabolites between the two strains; VIP: Variable importance in the projection; FC: Fold change. VIP value>1; P<0.05; |log2FC|>3.
Fig.5 Differential metabolites between B. safensis and C. iranensis

图6 沙福芽孢杆菌和伊朗纤维单胞菌降解滤纸后差异显著重要代谢物热图
Fig.6 Thermogram of significant differences in important metabolites after degradation of filter paper by B. safensis and C. iranensis

图7 沙福芽孢杆菌和伊朗纤维单胞菌降解滤纸后代谢物富集分析横坐标表示每个通路对应的富集因子,纵坐标为通路名称(按照P值排序),点的颜色为P值大小,越红表示富集越显著。点的大小代表富集到差异代谢物的个数。The abscissa represents the rich factor to each pathway, the ordinate is the pathway name (sorted by P value), and the color of the point is the P-value, and the redder the point is, the more significant the enrichment. The size of the dot represents the number of differential metabolites enriched.
Fig.7 Enrichment analysis of metabolites after degradation of filter paper by B. safensis and C. iranensis
处理 Treatment | 失重率 Weight loss rate | 粗纤维 Crude fibre | 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fibre | 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fibre | 半纤维素 Hemicellulose | 可溶性碳水化合物 Water soluble carbohydrate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照Control | 29.18±0.91b | 45.34±0.84a | 69.50±0.45a | 51.41±0.43a | 26.81±0.03a | 0.99±0.01a |
| 沙福芽孢杆菌B. safensis | 32.30±0.52b | 45.68±0.79a | 70.91±0.31a | 48.80±0.30b | 19.90±0.52b | 0.11±0.03b |
| 伊朗纤维单胞菌C. iranensis | 43.12±0.19a | 36.72±0.65b | 52.95±0.45b | 35.43±0.34b | 17.53±0.49b | 0.18±0.01b |
| P值P value | <0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
表3 秸秆液态发酵14 d后纤维含量变化
Table 3 Changes in fiber content of straw after 14 days of liquid fermentation(n=3, % DM)
处理 Treatment | 失重率 Weight loss rate | 粗纤维 Crude fibre | 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fibre | 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fibre | 半纤维素 Hemicellulose | 可溶性碳水化合物 Water soluble carbohydrate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照Control | 29.18±0.91b | 45.34±0.84a | 69.50±0.45a | 51.41±0.43a | 26.81±0.03a | 0.99±0.01a |
| 沙福芽孢杆菌B. safensis | 32.30±0.52b | 45.68±0.79a | 70.91±0.31a | 48.80±0.30b | 19.90±0.52b | 0.11±0.03b |
| 伊朗纤维单胞菌C. iranensis | 43.12±0.19a | 36.72±0.65b | 52.95±0.45b | 35.43±0.34b | 17.53±0.49b | 0.18±0.01b |
| P值P value | <0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| [1] | Zhang X, Borjigin Q, Gao J L, et al. Community succession and straw degradation characteristics using a microbial decomposer at low temperature. PLoS One, 2022, 17(7): e270162. |
| [2] | Chen D Y, Cheng S, Guo Y F, et al. Advances in utilization of rice straw as feed. Chinese Animal Industry, 2024(15): 43-44. |
| 陈东颖, 程尚, 郭炎峰, 等. 水稻秸秆饲料化利用研究进展. 中国畜牧业, 2024(15): 43-44. | |
| [3] | Kou J T, Zhang J X. Effects of adding homo- and hetero-fermentative lactic acid bacteria on nutritional value of rice straw silage feed. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(12): 3980-3987. |
| 寇江涛, 张甲雄. 同/异型乳酸菌添加对水稻秸秆青贮饲料营养价值的影响. 草地学报, 2024, 32(12): 3980-3987. | |
| [4] | Wei X, Li W, Song Z, et al. Straw incorporation with exogenous degrading bacteria (ZJW-6): An integrated greener approach to enhance straw degradation and improve rice growth. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2024, 25(14): 7835. |
| [5] | Gong W B, Zeng Y Y, Li X R, et al. Molecular profiling of rice straw degradability discrepancy in Stropharia rugosoannulata core germplasm. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(45): 25379-25390. |
| [6] | Kumar A, Pandit S, Sharma K, et al. Microbial degradation of cellulose extracted from wheat bran for bioelectricity production using microbial fuel cell. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2024, 190(11): 574-585. |
| [7] | Ma Y N, Mongkolthanaruk W, Riddech N. Enhancing soil amendment for salt stress using pretreated rice straw and cellulolytic fungi. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1): 13903. |
| [8] | Chen X, Liang X, Shi N, et al. New wheat straw fermentation feed: recombinant Schizosaccharomyces pombe efficient degradation of lignocellulose and increase feed protein. Preparative Biochemistry & Biotechnology, 2024, 55(1): 36-44. |
| [9] | Gaizauskaite Z, Zvirdauskiene R, Svazas M, et al. Optimised degradation of lignocelluloses by edible filamentous fungi for the efficient biorefinery of sugar beet pulp. Polymers, 2024, 16(9): 1178. |
| [10] | Akhlaq M, Uroos M. Evaluating the impact of cellulose extraction via traditional and ionosolv pretreatments from domestic matchstick waste on the properties of carboxymethyl cellulose. ACS Omega, 2023, 8(9): 8722-8731. |
| [11] | Wilson D B. Microbial diversity of cellulose hydrolysis. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2011, 14(3): 259-263. |
| [12] | Chen H, Shi Z H, Wu C H, et al. Screening, identification and comparison of enzyme production capacity of cellulose-degrading bacteria from different sources. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(4): 1252-1258. |
| 陈欢, 史子浩, 吴春会, 等. 不同来源纤维素降解菌的筛选、鉴定及产酶能力的比较. 草地学报, 2024, 32(4): 1252-1258. | |
| [13] | Niu D Z, Zhu P, Pan T T, et al. Ensiling improved the colonization and degradation ability of Irpex lacteus in wheat straw. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2022, 19(20): 13668. |
| [14] | Tachaapaikoon C, Kosugi A, Pason P, et al. Isolation and characterization of a new cellulosome-producing Clostridium thermocellum strain. Biodegradation, 2012, 23(1): 57-68. |
| [15] | Song K L, Zhou Z C, Leng J H, et al. Effects of rumen microorganisms on the decomposition of recycled straw residue. Journal of Zhejiang University-Science Biomedicine Biotechnology, 2023, 24(4): 336-344. |
| [16] | Padhan K, Patra R K, Sethi D, et al. Exploitation of cellulose degrading bacteria in bioconversion of agro-wastes. Chemosphere, 2024, 347(1): 140654. |
| [17] | Qu F, Cheng H, Han Z, et al. Identification of driving factors of lignocellulose degrading enzyme genes in different microbial communities during rice straw composting. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 381(1): 129109. |
| [18] | Dar M A, Xie R, Pandit R S, et al. Exploring the region-wise diversity and functions of symbiotic bacteria in the gut system of wood-feeding termite, Coptotermes formosanus, toward the degradation of cellulose, hemicellulose, and organic dyes. Insect Science, 2022, 29(5): 1414-1432. |
| [19] | Thayer D W. Carboxymethylcellulase produced by facultative bacteria from the hind-gut of the termite Reticulitermes hesperus. Journal of General and Applied Microbiology, 1978, 106(1): 13-18. |
| [20] | Dröge S, Fröhlich J, Radek R, et al. Spirochaeta coccoides sp. nov., a novel coccoid spirochete from the hindgut of the termite Neotermes castaneus. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2006, 72(1): 392-397. |
| [21] | Cho M J, Kim Y H, Shin K, et al. Symbiotic adaptation of bacteria in the gut of Reticulitermes speratus: low endo-beta-1,4-glucanase activity. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2010, 395(3): 432-435. |
| [22] | Azhar S, Aihetasham A, Chaudhary A, et al. Cellulolytic and ethanologenic evaluation of Heterotermes indicola’s gut-associated bacterial isolates. ACS Omega, 2024, 9(10): 12084-12100. |
| [23] | Xiao Y, Li J, Wu P, et al. An alkaline thermostable laccase from termite gut associated strain of Bacillus stratosphericus. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2021, 179(5): 270-278. |
| [24] | Javaheri-Kermani M, Asoodeh A. A novel beta-1,4 glucanase produced by symbiotic Bacillus sp. CF96 isolated from termite (Anacanthotermes). International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2019, 131(6): 752-759. |
| [25] | Li H, Zhang M, Zhang Y, et al. Characterization of cellulose-degrading bacteria isolated from silkworm excrement and optimization of its cellulase production. Polymers (Basel), 2023, 15(20): 4142. |
| [26] | Zhang T, Wei S, Liu Y, et al. Screening and genome-wide analysis of lignocellulose-degrading bacteria from humic soil. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2023, 14(23): 1167293. |
| [27] | Li J F, Zhao J, Tang X Y, et al. Effect of a rumen cellulolytic microbial consortium on the degradation of structural carbohydrate in sterile rice straw silage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(7): 85-95. |
| 李君风, 赵杰, 唐小月, 等. 瘤胃纤维素降解菌系对灭菌水稻秸秆结构性碳水化合物降解的影响. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 85-95. | |
| [28] | Li J, Tang X, Zhao J, et al. Improvement of fermentation quality and cellulose convertibility of napier grass silage by inoculation of cellulolytic bacteria from Tibetan yak (Bos grunniens). Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2021, 130(6): 1857-1867. |
| [29] | Khosravi F, Khaleghi M, Naghavi H. Screening and identification of cellulose-degrading bacteria from soil and leaves at Kerman province, Iran. Archives of Microbiology, 2021, 204(1): 88. |
| [30] | Rettenmaier R, Gerbaulet M, Liebl W, et al. Hungateiclostridium mesophilum sp. nov., a mesophilic, cellulolytic and spore-forming bacterium isolated from a biogas fermenter fed with maize silage. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2019, 69(11): 3567-3573. |
| [31] | Lai J, Li C, Zhang Y, et al. Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses reveal the molecular and metabolic basis of flavonoids in Areca catechu L. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2023, 71(12): 4851-4862. |
| [32] | Sun L, Xue Y, Xiao Y, et al. Community synergy of lactic acid bacteria and cleaner fermentation of oat silage prepared with a multispecies microbial inoculant. Microbiology Spectrum, 2023, 11(3): 2165. |
| [33] | Hou D Y, Li T C, Diao Q P, et al. Analysis of flavor components in Anshan Laojiao liquor. Journal of Anshan Normal University, 2019, 21(6): 32-38. |
| 侯冬岩, 李铁纯, 刁全平, 等. 腾鳌老窖白酒风味成分组成的分析. 鞍山师范学院学报, 2019, 21(6): 32-38. | |
| [34] | Yuan M M, Zhang J, Sun Y X, et al. The influence of four different yeast strains on volatile aroma composition in hamimelon brandy. The Food Industry, 2017, 38(5): 309-314. |
| 原苗苗, 张将, 孙玉霞, 等. 4种商业酵母对哈密瓜白兰地挥发性香气成分的影响. 食品工业, 2017, 38(5): 309-314. | |
| [35] | Wang B D, Li W D, Yang K, et al. GC-MS analysis of volatile flavor components in Monascus purpureus Went fermentation broth. Light Industry Science and Technology, 2020, 36(10): 18-20. |
| 汪帮东, 李文达, 杨康, 等. 红曲霉发酵液可挥发性风味成分的GC-MS分析. 轻工科技, 2020, 36(10): 18-20. | |
| [36] | Zhu Y W, Lai P L, Wu X X, et al. Fluorescence spectroscopy was used to study the interaction of methylene blue with three aromatic amino acids. Chemical Research and Applications, 2015, 27(6): 815-821. |
| 朱燕舞, 赖彭亮, 吴笑笑, 等. 荧光光谱法研究亚甲蓝与三种芳香族氨基酸的相互作用. 化学研究与应用, 2015, 27(6): 815-821. | |
| [37] | Chen L, Hong F, Yang X X, et al. Biotransformation of wheat straw to bacterial cellulose and its mechanism. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 135(5): 464-468. |
| [1] | 吴永杰, 丁浩, 邵涛, 赵杰, 董东, 代童童, 尹雪敬, 宗成, 李君风. 酶制剂对水稻秸秆青贮发酵品质及体外消化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 167-177. |
| [2] | 李君风, 赵杰, 唐小月, 代童童, 董东, 宗成, 邵涛. 瘤胃纤维素降解菌系对灭菌水稻秸秆结构性碳水化合物降解的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 85-95. |
| [3] | 张帆, 杨茜. 紫云英与双季稻秸秆协同利用影响稻田土壤钾循环与平衡[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 72-80. |
| [4] | 罗颖洁, 陈桂华, 穆麟, 胡龙兴, 张志飞, 高帅, 魏仲珊. 不同稻秸添加比例对紫花苜蓿和麦麸混合青贮的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(5): 178-184. |
| [5] | 李君风, 原现军, 董志浩, Seare Tajebe Desta, 陈雷, 白晰, 白云峰, 邵涛. 西藏地区牦牛瘤胃中兼性厌氧纤维素降解菌的分离鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(6): 176-184. |
| [6] | 黄勤楼, 钟珍梅, 黄秀声, 陈钟佃, 冯德庆, 夏友国. 纤维素降解菌的筛选及在狼尾草青贮中使用效果评价[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(4): 197-203. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||