

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (7): 229-239.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022337
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
董佳琦1( ), 杨艳婷2, 范文强1, 王佳妮1, 石凤翎1(
), 杨艳婷2, 范文强1, 王佳妮1, 石凤翎1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-26
修回日期:2022-10-07
出版日期:2023-07-20
发布日期:2023-05-26
通讯作者:
石凤翎
作者简介:E-mail: sfl0000@126.com基金资助:
Jia-qi DONG1( ), Yan-ting YANG2, Wen-qiang FAN1, Jia-ni WANG1, Feng-ling SHI1(
), Yan-ting YANG2, Wen-qiang FAN1, Jia-ni WANG1, Feng-ling SHI1( )
)
Received:2022-08-26
Revised:2022-10-07
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-05-26
Contact:
Feng-ling SHI
摘要:
扁蓿豆是一种抗逆性强,遗传多样性丰富的豆科牧草,可作为同属牧草的杂交育种材料,为其提供丰富的基因资源。而如何获得真杂交种是开展杂交育种和杂种优势利用的重要基础。为获得遗传性状更加丰富的扁蓿豆新种质材料,以株型直立且高产的直立型扁蓿豆和抗逆性强的野生扁蓿豆(黄花变异材料,简称黄花扁蓿豆)为亲本,采取正反交配置了两个杂交组合。通过相关序列扩增多态性(SRAP)分子标记技术从118个杂交F1代中鉴定出85个真杂种。从直立型扁蓿豆♀×黄花扁蓿豆♂的杂种F1代中获得其F2代,进一步对表现优良的13株F1代和20株F2代的株高、株型指数、一级分枝数、近似叶面积、叶茎比和单株地上生物量等主要农艺性状进行杂种优势分析。结果表明:F1代各性状的表型值变异系数为18.82%~45.72%,其中单株地上生物量、叶茎比、一级分枝数变异较大。各性状中亲优势为-54.2%~26.9%,其中叶茎比(8.22%)表现出超亲优势。F2代各性状变异系数(19.66%~41.63%)较F1代减小,除近似叶面积(12.69%)、株型指数(17.46%)和叶茎比(35.38%)外其余性状中亲优势(-52.38%~-19.75%)均减弱。F1与F2代产量相关性状的中亲优势和超亲优势多为负向,种内杂种优势较弱。研究结果将为扁蓿豆及苜蓿属其余牧草的品种改良提供新种质。
董佳琦, 杨艳婷, 范文强, 王佳妮, 石凤翎. 扁蓿豆种内杂种鉴定及其F1和F2代主要农艺性状优势分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 229-239.
Jia-qi DONG, Yan-ting YANG, Wen-qiang FAN, Jia-ni WANG, Feng-ling SHI. Identification of Medicago ruthenica hybrids and heterosis analysis of main agronomic traits in F1 and F2[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 229-239.
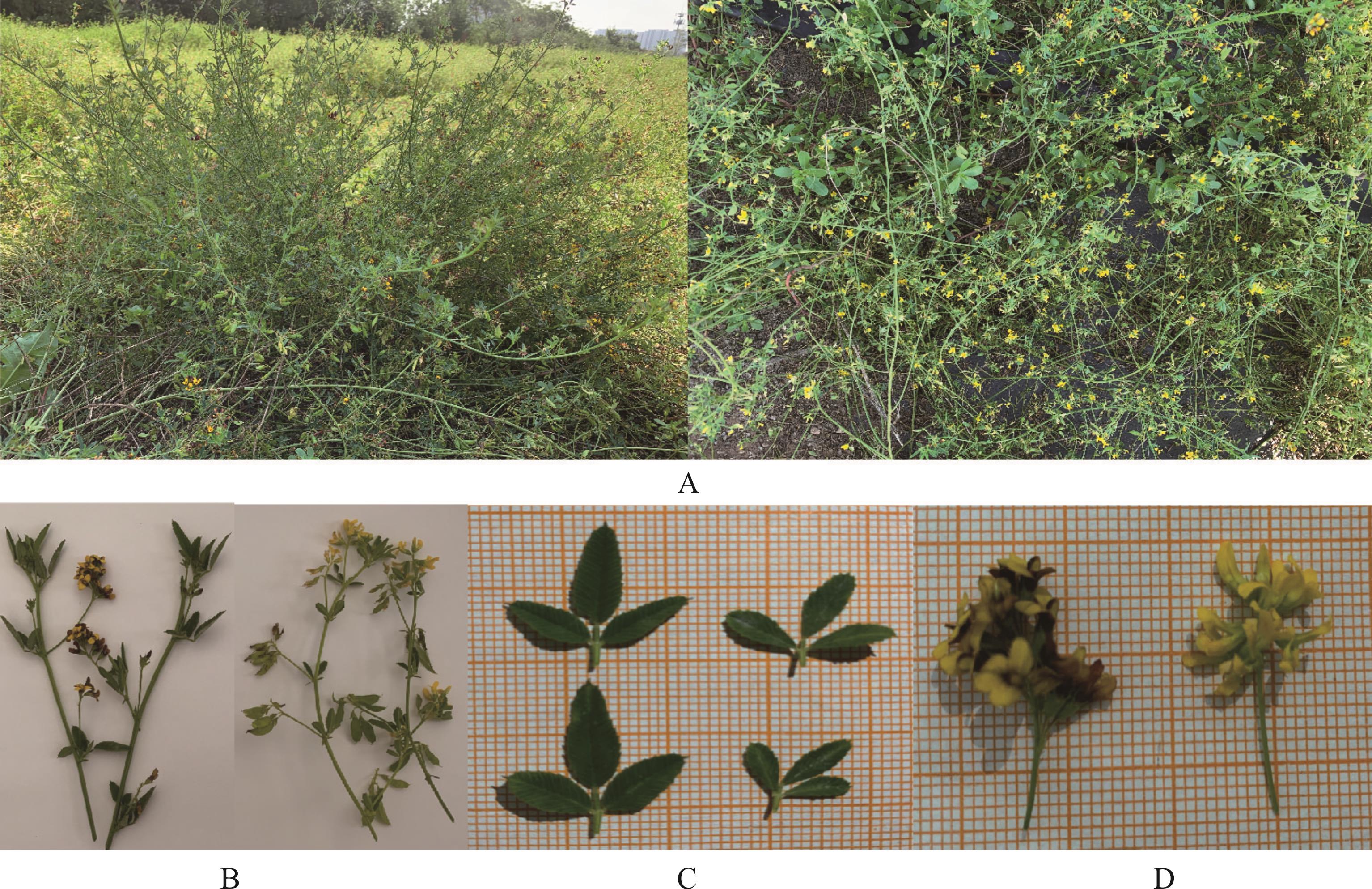

图1 杂交亲本A:株型;B:茎;C:叶;D:花。每图中左边为直立型扁蓿豆,右边为野生黄花扁蓿豆。 A: Plant type; B: Stem; C: Leaf; D: Flower. The left side of each picture is M. ruthenica ‘Zhilixing’ and the right is wild M. ruthenica.
Fig.1 The hybrid parents
| 正向引物Forward primer | 序列Sequence (5' -3') | 反向引物Reverse primer | 序列Sequence (5' -3') |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | TGAGTCCAAACCGGAGC | R1 | GACTGCGTACGAATTTGC |
| F2 | CGAATCTTAGCCGGCAC | R2 | GACTGCGTACGAATTAAC |
| F3 | CGAATCTTAGCCGGAAT | R3 | GACACCGTACGAATTGAC |
| F4 | GTAGCACAAGCCGGAGC | R4 | GACACCGTACGAATTTGA |
| F5 | CGAATCTTAGCCGGATA | R5 | CGCACGTCCGTAATTCCA |
| F6 | TGAGTCCAAACCGGATA | R6 | GACTGCGTACGAATTAAT |
表1 SRAP引物信息
Table 1 Information of SRAP primer
| 正向引物Forward primer | 序列Sequence (5' -3') | 反向引物Reverse primer | 序列Sequence (5' -3') |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | TGAGTCCAAACCGGAGC | R1 | GACTGCGTACGAATTTGC |
| F2 | CGAATCTTAGCCGGCAC | R2 | GACTGCGTACGAATTAAC |
| F3 | CGAATCTTAGCCGGAAT | R3 | GACACCGTACGAATTGAC |
| F4 | GTAGCACAAGCCGGAGC | R4 | GACACCGTACGAATTTGA |
| F5 | CGAATCTTAGCCGGATA | R5 | CGCACGTCCGTAATTCCA |
| F6 | TGAGTCCAAACCGGATA | R6 | GACTGCGTACGAATTAAT |
标记编号 Primer number | 引物组合 Primer combination | 标记编号 Primer number | 引物组合 Primer combination | 标记编号 Primer number | 引物组合 Primer combination |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR1 | F1R1 | FR13 | F1R5 | FR25 | F5R5 |
| FR2 | F1R2 | FR14 | F2R5 | FR26 | F6R1 |
| FR3 | F1R3 | FR15 | F3R5 | FR27 | F6R2 |
| FR4 | F1R4 | FR16 | F4R1 | FR28 | F6R3 |
| FR5 | F2R1 | FR17 | F4R2 | FR29 | F6R4 |
| FR6 | F2R2 | FR18 | F4R3 | FR30 | F6R5 |
| FR7 | F2R3 | FR19 | F4R4 | FR31 | F1R6 |
| FR8 | F2R4 | FR20 | F4R5 | FR32 | F2R6 |
| FR9 | F3R1 | FR21 | F5R1 | FR33 | F3R6 |
| FR10 | F3R2 | FR22 | F5R2 | FR34 | F4R6 |
| FR11 | F3R3 | FR23 | F5R3 | FR35 | F5R6 |
| FR12 | F3R4 | FR24 | F5R4 | FR36 | F6R6 |
表2 SRAP引物组合信息
Table 2 Information of SRAP combinations
标记编号 Primer number | 引物组合 Primer combination | 标记编号 Primer number | 引物组合 Primer combination | 标记编号 Primer number | 引物组合 Primer combination |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR1 | F1R1 | FR13 | F1R5 | FR25 | F5R5 |
| FR2 | F1R2 | FR14 | F2R5 | FR26 | F6R1 |
| FR3 | F1R3 | FR15 | F3R5 | FR27 | F6R2 |
| FR4 | F1R4 | FR16 | F4R1 | FR28 | F6R3 |
| FR5 | F2R1 | FR17 | F4R2 | FR29 | F6R4 |
| FR6 | F2R2 | FR18 | F4R3 | FR30 | F6R5 |
| FR7 | F2R3 | FR19 | F4R4 | FR31 | F1R6 |
| FR8 | F2R4 | FR20 | F4R5 | FR32 | F2R6 |
| FR9 | F3R1 | FR21 | F5R1 | FR33 | F3R6 |
| FR10 | F3R2 | FR22 | F5R2 | FR34 | F4R6 |
| FR11 | F3R3 | FR23 | F5R3 | FR35 | F5R6 |
| FR12 | F3R4 | FR24 | F5R4 | FR36 | F6R6 |
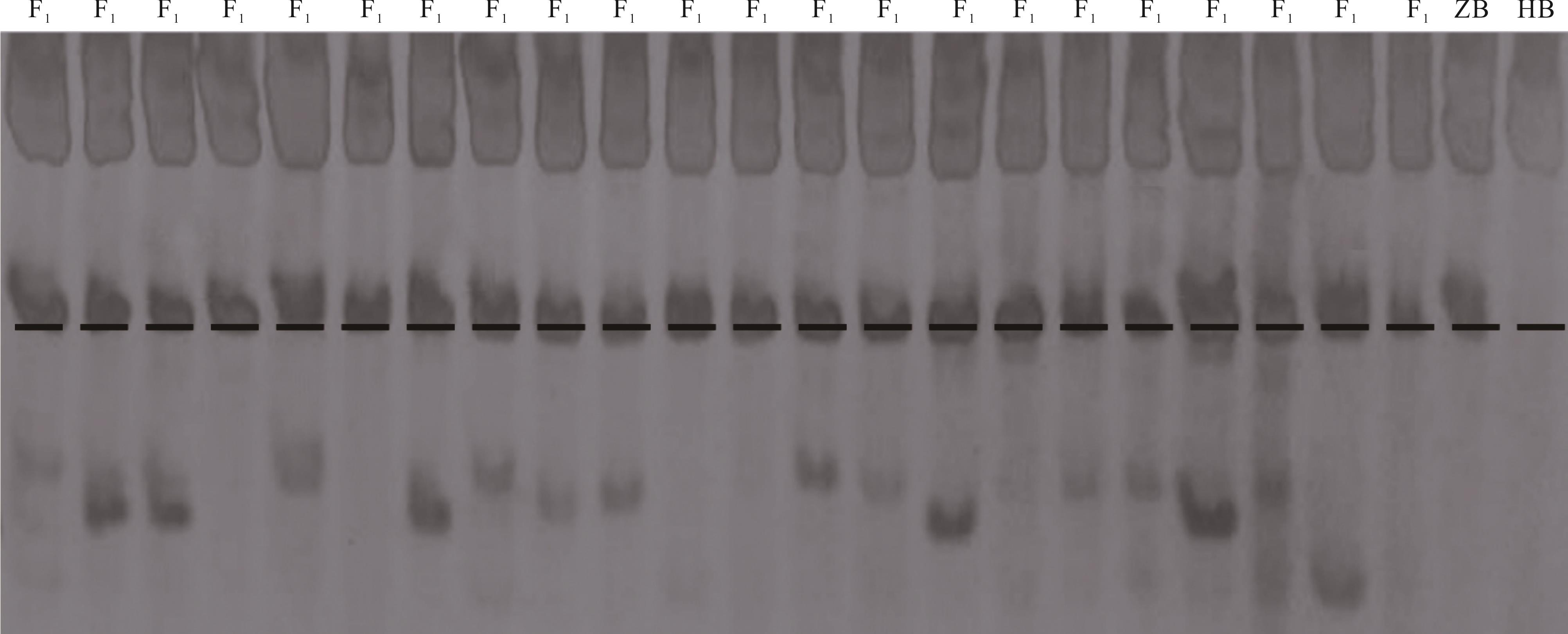
图2 FR9识别HZ F1群体的部分鉴定结果ZB为直立型扁蓿豆;HB为野生扁蓿豆;F1为以直立型扁蓿豆为母本的杂交第一代。ZB is the M. ruthenica ‘Zhilixing’;HB is the wild M. ruthenica;F1 is the first generation of cross with M. ruthenica ‘Zhilixing’ as female parent.
Fig.2 The part results of identification of HZ F1 population by FR9

图5 F2群体中ZH20在不同生长阶段的表现从左到右拍摄时间依次为5月15、5月30、6月13、7月15。From left to right, the shooting time is May 15, May 30, June 13 and July 15.
Fig.5 The performance of ZH20 at different growth stages in the F2 population
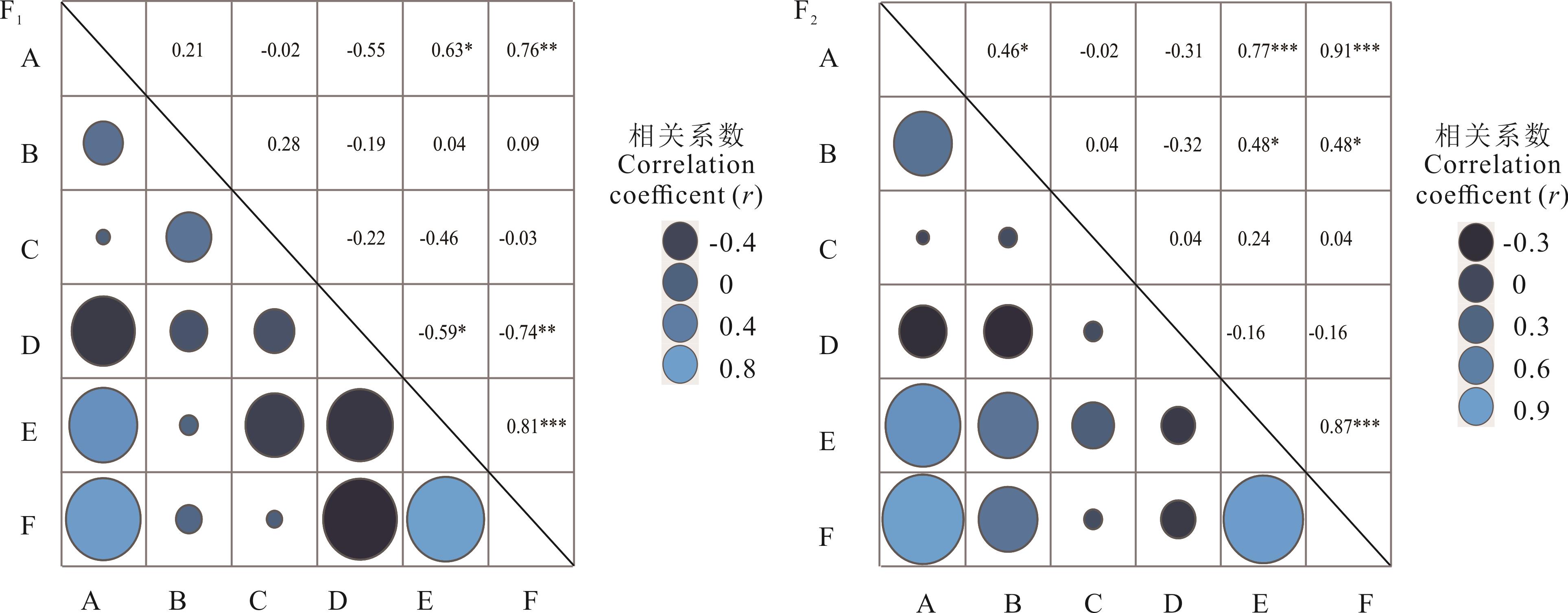
图6 杂交F1、F2群体不同农艺性状相关性*:P<0.05;**:P<0.01;***:P<0.001.A:一级分枝数Number of primary branches;B:近似叶面积Approximate leaf area;C:株型指数Plant type index;D:叶茎比Leaf stem ratio;E:植株绝对高度 Plant absolute height;F:单株地上生物量 Plant above-ground biomass
Fig.6 Correlation of different agronomic traits in F1 and F2 populations
群体 Population | 项目 Item | 一级分枝数 Number of primary branches | 近似叶面积 Approximate leaf area | 株型指数 Plant type index | 叶茎比 Leaf stem ratio | 植株绝对高度 Plant absolute height | 单株地上生物量 Plant above-ground biomass |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 中亲优势Hm | -16.15 | 26.90 | 11.11 | 21.54 | 5.57 | -54.20 |
| 超亲优势Hh | -20.95 | -9.42 | -7.89 | 8.22 | -8.99 | -68.90 | |
| F2 | 中亲优势Hm | -19.75 | 12.69 | 17.46 | 35.38 | -26.26 | -52.38 |
| 超亲优势Hh | -24.35 | -19.57 | -2.63 | 20.55 | -36.43 | -67.65 |
表3 扁蓿豆杂交后代群体各数量性状的杂种优势
Table 3 Heterosis for different agronomic traits in M. ruthenica hybrid population
群体 Population | 项目 Item | 一级分枝数 Number of primary branches | 近似叶面积 Approximate leaf area | 株型指数 Plant type index | 叶茎比 Leaf stem ratio | 植株绝对高度 Plant absolute height | 单株地上生物量 Plant above-ground biomass |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 中亲优势Hm | -16.15 | 26.90 | 11.11 | 21.54 | 5.57 | -54.20 |
| 超亲优势Hh | -20.95 | -9.42 | -7.89 | 8.22 | -8.99 | -68.90 | |
| F2 | 中亲优势Hm | -19.75 | 12.69 | 17.46 | 35.38 | -26.26 | -52.38 |
| 超亲优势Hh | -24.35 | -19.57 | -2.63 | 20.55 | -36.43 | -67.65 |
| 1 | Campbell T A, Bao G, Xia Z L. Agronomic evaluation of Medicago ruthenica collected in Inner Mongolia. Crop Science, 1997, 37(2): 599-604. |
| 2 | Wurina, Shi F L, Xu B, et al. Research progress and potential applications for the abiotic stress-resistant forage plant Medicago ruthenica. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(9): 1845-1854. |
| 乌日娜, 石凤翎, 徐舶, 等. 扁蓿豆适应非生物胁迫的研究进展及应用前景. 草业科学, 2020, 37(9): 1845-1854. | |
| 3 | Li H. Brief introduction of alfalfa varieties of ‘Longmu 801’ and ‘Longmu 803’. Modern Animal Husbandry Science & Technology, 2003(3): 18-19. |
| 李红. 龙牧801号, 龙牧803号苜蓿品种简介. 养殖技术顾问, 2003(3): 18-19. | |
| 4 | Li H Y, Li Z Y, Shi W G, et al. The genetic diversity of three ecological Medicago ruthenica germplasms revealed by ISSR and SSR. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(5): 107-113. |
| 李鸿雁, 李志勇, 师文贵, 等. 3种生态型野生扁蓿豆种质资源ISSR与SSR遗传多样性分析. 草业学报, 2012, 21(5): 107-113. | |
| 5 | Shi W G, Li Z Y, Li H Y, et al. Morphological diversity of wilding population in Medicago ruthenica from different origin. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2009, 29(5): 1001-1006. |
| 师文贵, 李志勇, 李鸿雁, 等. 扁蓿豆不同分布区野生居群形态多样性研究. 西北植物学报, 2009, 29(5): 1001-1006. | |
| 6 | Hasheml S H, Mirmohammadi-Maibody S A M, Nematzadeh G A, et al. Identification of rice hybrids using microsatellite and RAPD markers. African Journal of Biotechnology, 2009, 8(10): 2094-2101. |
| 7 | Saxena R K, Saxena K, Varshney R K. Application of SSR markers for molecular characterization of hybrid parents and purity assessment of ICPH 2438 hybrid of pigeonpea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millspaugh]. Molecular Breeding, 2010, 26(2): 371-380. |
| 8 | Li G, Quiros C F. Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: Its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2001, 103(2): 455-461. |
| 9 | Du Z Y, Yang C F, Chen J M, et al. Identification of hybrids in broad-leaved Potamogeton species (Potamogetonaceae) in China using nuclear and chloroplast DNA sequence data. Plant Systematics & Evolution, 2010, 287(1/2): 57-63. |
| 10 | Havelka M, Fujimoto T, Hagihara S, et al. Nuclear DNA markers for identification of Beluga and Sterlet sturgeon and their interspecific Bester hybrid. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 1694. |
| 11 | Ren X F, Deng Y B, Zang G Z, et al. SSR marker analysis of genetic diversity and population genetic structure of bermudagrass in Henan Province. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 60-70. |
| 任雪锋, 邓亚博, 臧国长, 等. 基于SSR标记的河南省狗牙根遗传多样性及群体遗传结构分析. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 60-70. | |
| 12 | Liang X Y, Ji Y, Bai S Q, et al. Construction of a genetic map for chicory using sequence-related amplified polymorphism markers. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(5): 153-158. |
| 梁小玉, 季杨, 白史且, 等. 基于SRAP分子标记构建的菊苣遗传连锁图谱.草业学报, 2015, 24(5): 153-158. | |
| 13 | Li J Q, Yu Z, Yang D S, et al. Construction of genetic linkage map for crested wheatgrass (Agropyron) based on SRAP molecular markers. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2019, 39(1): 76-83. |
| 李佳奇, 于卓, 杨东升, 等. 基于SRAP分子标记的冰草遗传连锁图谱构建. 西北植物学报, 2019, 39(1): 76-83. | |
| 14 | Shang X X, Zhang A S, Liu Y, et al. Genetic diversity and fingerprints of Muscat Hamburg grapevine series germplasm resource based on SRAP markers. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(6): 1916-1922. |
| 尚晓星, 张安世, 刘莹, 等. 玫瑰香系葡萄种质资源SRAP遗传多样性分析及指纹图谱构建. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(6): 1916-1922. | |
| 15 | Ye G, Zhang X X, Chen J B, et al. Morphological characteristics and identification of SRAP molecular markers in hybrid progeny of Zoysia. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(7): 1406-1415. |
| 叶刚, 张笑笑, 陈静波, 等. 结缕草属植物杂交后代形态特征和SRAP分子标记鉴定. 草地学报, 2021, 29(7): 1406-1415. | |
| 16 | Wu Y F, Yu Z, Shi F L. Breeding of Medicago ruthenica ‘Zhilixing’ and research on biological characteristics. Inner Mongolia Prataculture, 1993(Z1): 51-53. |
| 乌云飞, 玉柱, 石凤翎. 直立型扁蓿豆的选育及其生物学特性的研究. 内蒙古草业, 1993(Z1): 51-53. | |
| 17 | Zhao C Y, Zhao C X, Fang Z S, et al. Rapid determination method for leaf area of potato. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2010(13): 49-51. |
| 赵春燕, 赵春晓, 方子森, 等. 马铃薯叶面积速测方法的研讨. 湖南农业科学, 2010(13): 49-51. | |
| 18 | Xu Y B, Crouch J. Marker-assisted selection in plant breeding: From publications to practice. Crop Science, 2008, 48(2): 391-407. |
| 19 | Li H Y, Li Z Y, Mi F G, et al. Analysis of the genetic diversity of Medicago ruthenica by phenotype and SSR marker in China. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(9): 65-72, 80. |
| 李鸿雁, 李志勇, 米福贵, 等. 中国扁蓿豆遗传多样性的表型和SSR标记分析. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 39(9): 65-72, 80. | |
| 20 | Wurina, Xu B, Shi F L. Analysis of SSR characteristics for Medicago ruthenica ‘Zhilixing’ based on transcriptome data. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(5): 1-8. |
| 乌日娜, 徐舶, 石凤翎. 基于转录组数据的直立型扁蓿豆SSR序列特征分析. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 50(5): 1-8. | |
| 21 | Wang Y, Yi L M, Ban W T, et al. Identification of perennial ryegrass hybrid F1 hybrid based on SSR molecular markers. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(11): 10-17. |
| 汪阳, 易莉美, 班晚婷, 等. 基于SSR分子标记的多年生黑麦草杂交F1代杂种鉴定. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(11): 10-17. | |
| 22 | Su Y Y, Wang K C, Xue Q. Study of the pollen viability and stigma receptivity of Agastache rugosa from different areas. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(9): 189-196. |
| 苏芸芸, 王康才, 薛启. 不同产地藿香花粉活力与柱头可授性研究. 草业学报, 2016, 25(9): 189-196. | |
| 23 | Zhang H L, Chen F, Ma L, et al. The cross-compatibility of double-petaled Hemerocallis middendorfii and the phenotypic traits analysis of F1 generation. Journal of Northern Agriculture, 2021, 49(6): 103-113. |
| 张贺蕾, 陈芬, 马丽, 等. 重瓣大花萱草杂交亲和性及F1表型性状分析. 北方农业学报, 2021, 49(6): 103-113. | |
| 24 | Han H B, Shi W G, Wang X N, et al. Morphological properties of wild resources in Medicago ruthenica in Inner Mongolia. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2011, 12(5): 721-726. |
| 韩海波, 师文贵, 王晓娜, 等. 内蒙古扁蓿豆野生资源形态特征研究. 植物遗传资源学报, 2011, 12(5): 721-726. | |
| 25 | Wei W, Bi Y F, Zhang F X. Analysis of character variation of geographical distant hybridization progenies among alfalfa cultivars. Grassland and Turf, 2009(6): 1-4. |
| 魏微, 毕玉芬, 张凤仙. 地理远缘紫花苜蓿品种间杂交后代性状变异分析. 草原与草坪, 2009(6): 1-4. | |
| 26 | Fu B Z, Gao X Q, Gao Y F, et al. Correlation analysis and comprehensive evaluation of main agronomic characters of 21 alfalfa varieties. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(11): 174-182. |
| 伏兵哲, 高雪芹, 高永发, 等. 21个苜蓿品种主要农艺性状关联分析与综合评价. 草业学报, 2015, 24(11): 174-182. | |
| 27 | Geng H, Wang Z F, Liu Z, et al. Grey correlation analysis of main characters of alfalfa varieties at home and abroad. Pratacultural Science, 2009, 26(10): 85-88. |
| 耿慧, 王志锋, 刘卓, 等. 国内外苜蓿品种主要性状间的灰色关联度分析. 草业科学, 2009, 26(10): 85-88. | |
| 28 | Jin S J, Yang H. Analysis on yield and character performance of F2 generation of extra-early hybrid cotton. Liaoning Agricultural Sciences, 2003(5): 8-10. |
| 金世杰, 杨桦. 特早熟杂交棉F2代产量及性状表现分析. 辽宁农业科学, 2003(5): 8-10. | |
| 29 | Han H B. Identification and evaluation on germplasm resources of Medicago ruthenica L. in Inner Mongolia. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2011. |
| 韩海波. 内蒙古野生扁蓿豆种质资源的鉴定与评价. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2011. | |
| 30 | Chen L L, Yang X F, Wu Y H, et al. Evaluation of production performance of 35 introduced varieties of alfalfa in Chifeng area of Inner Mongolia. Pratacultural Science, 2012, 29(5): 790-797. |
| 陈玲玲, 杨秀芳, 乌艳红, 等. 35个紫花苜蓿品种在内蒙古赤峰地区的生产性能评价. 草业科学, 2012, 29(5): 790-797. | |
| 31 | Salek Z A, Fakhrevaezi A R. Effect of row spacing and seeding rate on forage yield local alfalfa, c.v. Gara Yonjeh (Medicago sativa). Journal of Crop and Weed Ecophysiology, 2011, 16(4): 71-82. |
| 32 | Pei G Y, Nan C M. Preliminary research of application value of cotton hybrid F2 in production. Agriculture of Henan, 2005(2): 34. |
| 裴桂英, 南翠梅. 棉花杂交种F2在生产上的应用价值研究初探. 河南农业, 2005(2): 34. | |
| 33 | Chen Y, Yuan D Y, Zou F, et al. Analysis on genetic variation of phenotypic traits of leaves of F1 progeny from interspecific hybridization of Camellia. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2020, 40(5): 47-56. |
| 陈雅, 袁德义, 邹锋, 等. 油茶种间杂交叶表型的遗传变异分析. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2020, 40(5): 47-56. | |
| 34 | Rajeev S, Patil S S, Manjula S M, et al. Studies on heterosis in cotton interspecific heterotic group hybrids (G. hirsutum×G. barbadense) for seed cotton yield and its components. Asian Journal of Bio Science, 2013, 7(10): 3437-3451. |
| 35 | Zhang B Q, Zhou S, Yang C F, et al. Biomass and root characters of intergeneric hybrid Erianthus arundinaceus×Saccharum spontaneum and its progeny. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2016, 21(4): 18-25. |
| 张保青, 周珊, 杨翠芳, 等. 斑割复合体及其杂交后代的生物量及根系性状. 中国农业大学学报, 2016, 21(4): 18-25. | |
| 36 | Lin J L, Zhu Z G, Gao J W. Heterosis in plant research. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2009, 24(Supple 1): 46-56. |
| 林建丽, 朱正歌, 高建伟. 植物杂种优势研究进展. 华北农学报, 2009, 24(增刊1): 46-56. |
| [1] | 王玉霞, 柴锦隆, 周洋洋, 徐长林, 王琳, 鱼小军. 种植方式对陇中干旱区扁蓿豆种子产量及构成因素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 60-72. |
| [2] | 赵小强, 方鹏, 彭云玲, 张金文, 曾文静, 任斌, 高巧红. 基于两个相关群体的玉米7个主要农艺性状遗传分析和QTL定位[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(9): 152-165. |
| [3] | 钟华,董洁,董宽虎. 盐胁迫对扁蓿豆幼苗脯氨酸积累及其代谢关键酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 189-194. |
| [4] | 肖红, 徐长林, 张德罡, 张建文, 杨海磊, 柴锦隆, 潘涛涛, 王艳, 鱼小军. 阴山扁蓿豆光合特性对模拟牦牛、藏羊践踏和降水的短期响应[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(2): 43-52. |
| [5] | 沈迎芳, 马超, 吴小培, 张业猛, 王海庆. 扁蓿豆SK2型脱水素基因MrDHN3的异源表达提高大肠杆菌对盐和高温胁迫的抗性[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(8): 118-127. |
| [6] | 姚佳, 刘信宝, 崔鑫, 李志华. 不同NaCl胁迫对苗期扁蓿豆渗透调节物质及光合生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(5): 91-99. |
| [7] | 梁小玉, 季杨, 白史且, 黄琳凯, 张新全. 基于SRAP分子标记构建的菊苣遗传连锁图谱[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(5): 153-158. |
| [8] | 崔秀妹,刘信宝,李志华,孙凯燕,李卉,张婷婷. 不同水分胁迫下水杨酸对分枝期扁蓿豆生长及光合生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(6): 82-93. |
| [9] | 李鸿雁,李志勇,师文贵,蔡丽艳,张静萍. 3种生态型野生扁蓿豆种质资源ISSR与SSR遗传多样性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(5): 107-113. |
| [10] | 张婧,黄琳凯,ZHAO Bing-yu,张新全,严海东,蒋晓阳. SRAP与SSR分子标记在柳枝稷杂种鉴定中的比较分析[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(5): 128-133. |
| [11] | 李鸿雁,李志勇,师文贵,蔡丽艳,刘磊 . 内蒙古扁蓿豆叶片解剖性状与抗旱性的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(3): 138-146. |
| [12] | 王颖,侯宇,李晓宇,蔺吉祥,杨光,穆春生. 扁蓿豆荚果和种子发育及硬实发生的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(3): 303-307. |
| [13] | 谢文刚, 张新全,陈永霞. 鸭茅杂交种的SSR分子标记鉴定及其遗传变异分析[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(2): 212-217. |
| [14] | 季杨,张新全,马啸,初秀娟,李芳,蒙宇. 多花黑麦草品种(系)间杂交及其杂种后代SRAP遗传分析[J]. 草业学报, 2009, 18(4): 260-265. |
| [15] | 陈宣,郭海林,薛丹丹,郑轶琦,刘建秀. 结缕草属植物耐盐性SRAP分子标记研究[J]. 草业学报, 2009, 18(2): 66-75. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||