

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (12): 183-194.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025047
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
王豫婉1,2( ), 刘凌云3, 郭一荻3, 范希峰3, 岳跃森3, 穆娜3, 肖国增1,2(
), 刘凌云3, 郭一荻3, 范希峰3, 岳跃森3, 穆娜3, 肖国增1,2( ), 滕珂3(
), 滕珂3( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-18
修回日期:2025-04-15
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-10-20
通讯作者:
肖国增,滕珂
作者简介:E-mail: tengke.123@163.com基金资助:
Yu-wan WANG1,2( ), Ling-yun LIU3, Yi-di GUO3, Xi-feng FAN3, Yue-sen YUE3, Na MU3, Guo-zeng XIAO1,2(
), Ling-yun LIU3, Yi-di GUO3, Xi-feng FAN3, Yue-sen YUE3, Na MU3, Guo-zeng XIAO1,2( ), Ke TENG3(
), Ke TENG3( )
)
Received:2025-02-18
Revised:2025-04-15
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-10-20
Contact:
Guo-zeng XIAO,Ke TENG
摘要:
近年来纳米磁珠介导的遗传转化体系克服了传统转基因方法需组织培养再生的问题,能够缩短转基因植物培育周期,适用范围广泛。目前狼尾草尚未建立纳米磁珠介导的转化体系,且现有遗传转化体系尚不成熟。为建立纳米磁珠介导的狼尾草花粉转化体系,本研究以‘丽秋’狼尾草为材料,分析了‘丽秋’狼尾草花粉转染的最适温度和处理时间、纳米磁珠负载能力、杂交授粉和转基因株系筛选等纳米磁珠介导转化的关键环节。结果表明:与12、16和25 ℃处理相比,4和8 ℃下狼尾草花粉的活力较高。开孔转染时间0.5~2.0 h的花粉开孔率无显著差异,不同开孔转染时间下的花粉活力无显著差异,故选择了0.5 h为转染开孔时间。用转染后的花粉对‘丽秋’狼尾草进行授粉,随机挑选了自然结实获得的150粒种子。播种后利用80 mg·L-1潮霉素进行筛选,之后经PCR检测和GFP荧光蛋白观察,获得了7株转基因植株。本研究建立了狼尾草纳米磁珠介导的花粉管通道转化法体系,5个月左右可以获得转基因苗,转化率达4.66%,为狼尾草遗传转化和分子改良提供了新的可行方案。
王豫婉, 刘凌云, 郭一荻, 范希峰, 岳跃森, 穆娜, 肖国增, 滕珂. 基于纳米磁珠介导的狼尾草花粉管通道转化法体系的建立[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(12): 183-194.
Yu-wan WANG, Ling-yun LIU, Yi-di GUO, Xi-feng FAN, Yue-sen YUE, Na MU, Guo-zeng XIAO, Ke TENG. Efficient transformation of Pennisetum alopecuroides using pollen transfected by DNA-coated magnetic nanoparticles[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(12): 183-194.

图1 ‘丽秋’狼尾草开花过程A: 雌蕊柱头露出Pistil stigma exposed; B: 雄蕊扬花散粉Stamens bloom and disperse powder; C: 扬花后雄蕊退化Stamen degeneration after flowering.
Fig.1 The flowering process of P. alopecuroides ‘Liqiu’
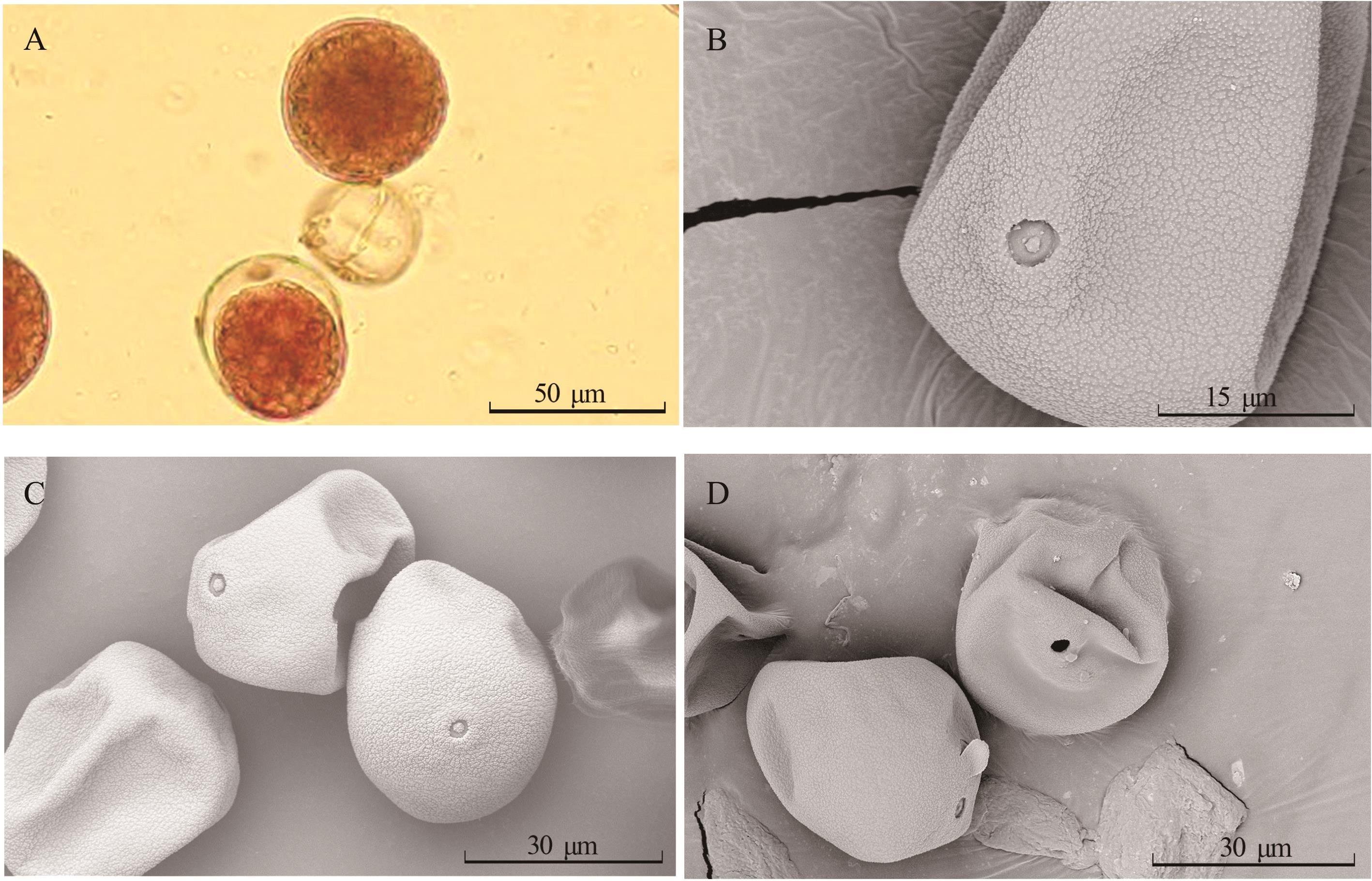
图2 ‘丽秋’狼尾草花粉形态观察A: 光学显微镜下花粉形态特征Pollen was observed under orthostatic optical microscope; B: 扫描电镜下花粉形态观察Pollen was observed under scanning electron microscope (SEM); C: 未经过花粉开孔液处理的花粉孔状态Pollen pore status that has not been treated with pollen pore-opening solution; D: 经过花粉开孔液处理的花粉孔状态Pollen pore status that has been treated with pollen pore-opening solution.
Fig.2 Pollen morphology observation of P. alopecuroides ‘Liqiu’
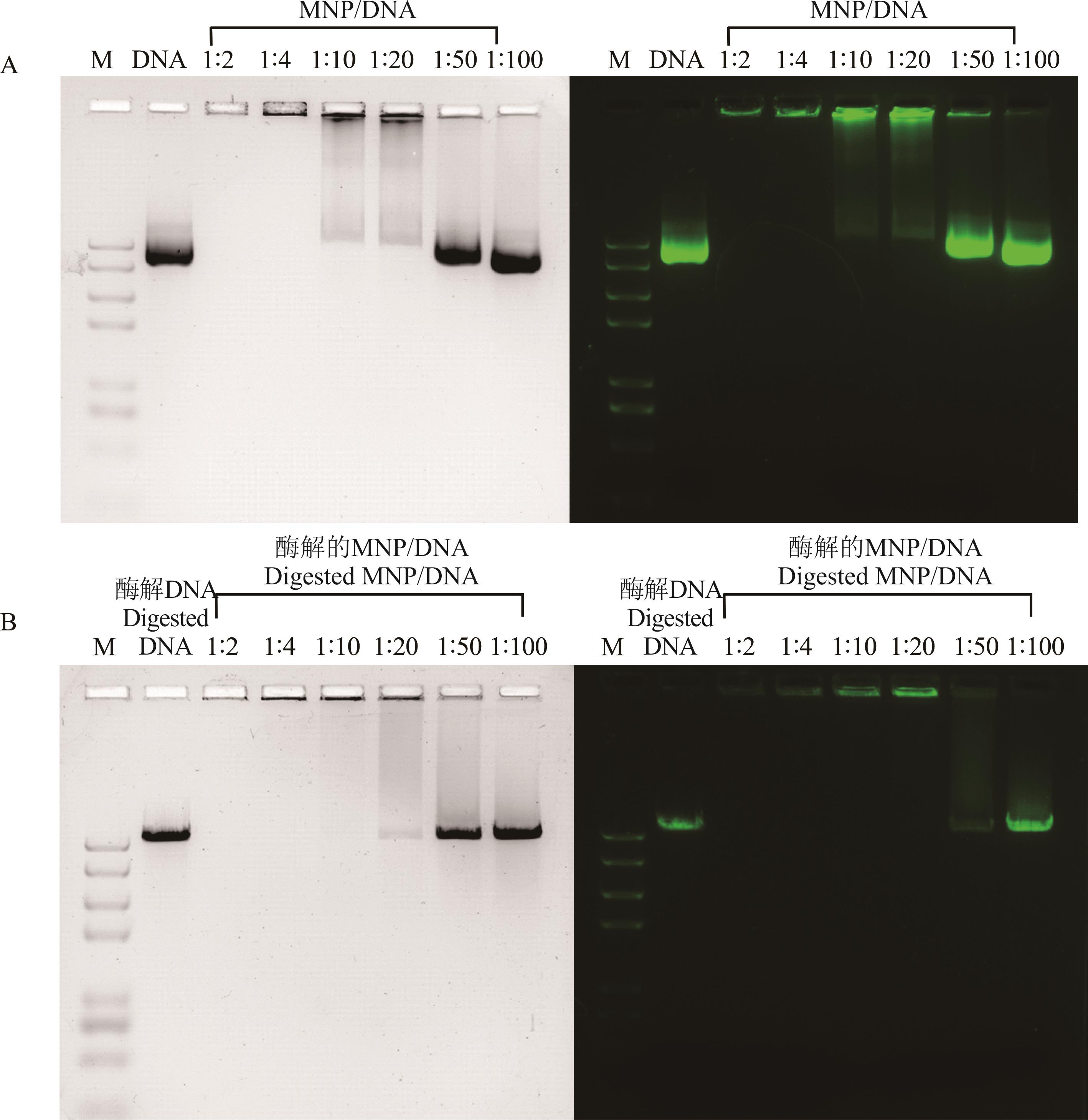
图3 纳米磁珠对质粒DNA的负载和保护能力A: MNP/DNA 复合物的琼脂糖凝胶电泳分析Agarose gel electrophoresis of plasmid DNA and MNPs/DNA; B: MNP/ DNA 复合物酶切产物的琼脂糖凝胶电泳分析Agarose gel electrophoresis of plasmid DNA and MNPs/DNA complexes digested with Xho Ⅰ; M: Trans 15K DNA Marker.
Fig.3 The loading and protective capabilities of magnetic nanoparticles for plasmid DNA
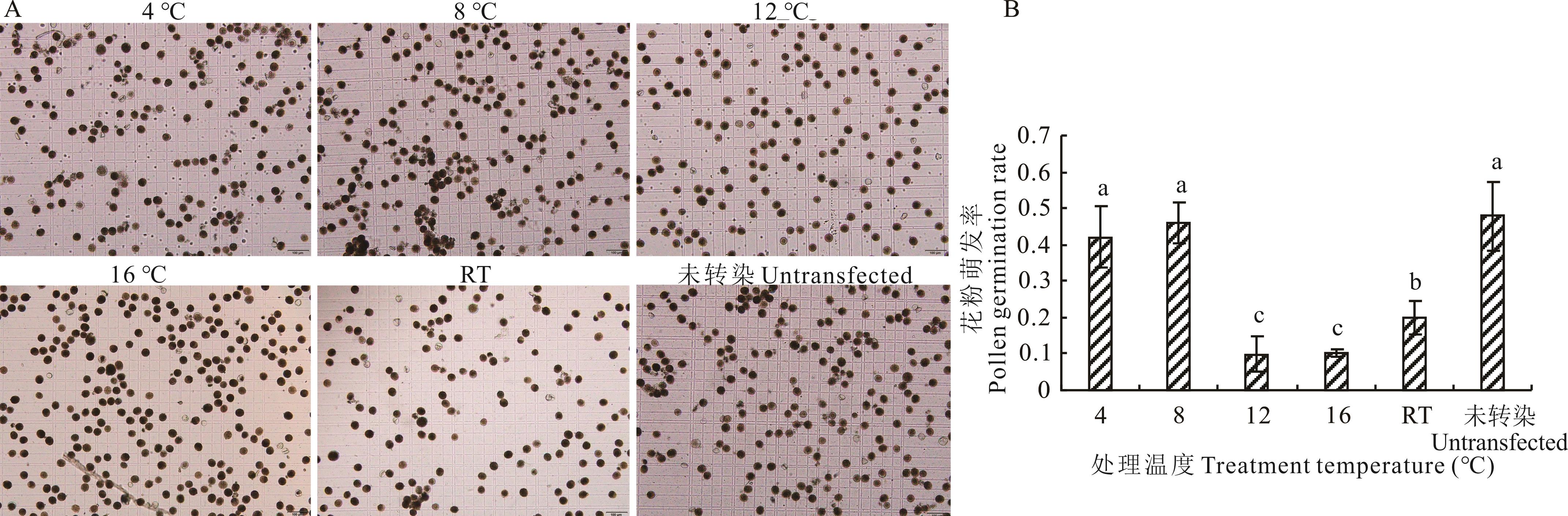
图4 ‘丽秋’狼尾草转染的最适温度A: 转染缓冲液预处理后,将花粉粒转入发芽液中,在室温下培养3 h After pretreatment with transfection buffer, pollen grains were transferred into germinating media and incubated 3 h under RT (直立光学显微镜下观察花粉萌发情况Pollen germination was observed under orthostatic optical microscope); B: 未经预处理或在指定温度下预处理的花粉发芽情况Germination of pollen without pretreatment with transfection or pretreated under indicated temperatures; RT: 室温Room temperature; 不同小写字母表示在P<0.05水平上差异显著,下同Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05 level, the same below.
Fig.4 Optimal temperature for transfection of P. alopecuroides ‘Liqiu’

图5 ‘丽秋’狼尾草开孔转染的最适时间A: 8 ℃下不同时间转染缓冲液预处理的花粉电镜图像Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of pollen pretreated with transfection buffer at 8 ℃ for different times; B: 不同转染时间的狼尾草花粉开孔率Pollen opening rate after pretreatment in transfection buffer at different times; C: 不同转染时间的狼尾草花粉活力Pollen viability after pretreatment in transfection buffer at different times.
Fig.5 Optimal time for transfection of P. alopecuroides ‘Liqiu’

图6 阳性植株验证A: 潮霉素筛选‘丽秋’狼尾草转染的种子Hygromycin screening seeds transfected with P. alopecuroides ‘Liqiu’; B: 阳性植物PCR检测结果PCR test results of positive plants; C: DNAMAN比对结果DNAMAN comparison results; M: Trans2K? Plus Ⅱ DNA Marker; WT:未转染植株Non-transfected plant.
Fig.6 Verification of positive plants
| [1] | Wu J Y, Teng W J, Wang Q H. Basic botanic characters, adaptabilities and applying in landscape architecture of Pennisetum alopecuroides. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 2005, 21(12): 57-59. |
| 武菊英, 滕文军, 王庆海. 狼尾草的生物学特性及在园林中的应用. 中国园林, 2005, 21(12): 57-59. | |
| [2] | Hou X C, Teng K, Guo Q, et al. Research advances in forage Pennisetum resource. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(6): 814-825. |
| 侯新村, 滕珂, 郭强, 等. 狼尾草属牧草研究进展. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 814-825. | |
| [3] | Tang J, Zhou H L, Wang W Q, et al. Advances in breeding and molecular biology research of Pennisetum. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2018, 39(11): 2313-2320. |
| 唐军, 周汉林, 王文强, 等. 狼尾草属牧草育种及分子生物学研究进展. 热带作物学报, 2018, 39(11): 2313-2320. | |
| [4] | Liu Z P, Liu W X, Yang Q C, et al. Progress and existing problems of forage breeding in China. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2023, 37(4): 528-536. |
| 刘志鹏, 刘文献, 杨青川, 等. 我国牧草育种进展及存在问题. 中国科学基金, 2023, 37(4): 528-536. | |
| [5] | Shahnam A D, Mahin P. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated plant transformation: A review. Molecular Biotechnology, 2024, 66(7): 1563-1580. |
| [6] | Zou Z, Lu C M. An overview of plant factors influencing Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2008(1): 1-9. |
| 邹智, 卢长明. 影响农杆菌介导遗传转化的植物因子研究进展. 生物技术通报, 2008(1): 1-9. | |
| [7] | Yang S K, Lai K, Low L Y, et al. Transgenic plants: Gene constructs, vector and transformation method. Rijeka: Intech Open, 2018. |
| [8] | Wang M, Sun R, Zhang B, et al. Pollen tube pathway-mediated cotton transformation. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2019, 1902: 67-73. |
| [9] | Maram G, Maretha M O, Anika M, et al. Transgenic and herbicide resistant pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum L.) R.Br. via microprojectile bombardment of scutellar tissue. Molecular Breeding, 2002, 10(4): 243-252. |
| [10] | Wang P Q, Duan C R, Wang B C, et al. Tissue culture with different organs of Pennisetum pureum. Journal of Chongqing University (Natural Science Edition), 2005, 28(6): 118-120. |
| 王凭青, 段传人, 王伯初, 等. 杂交狼尾草不同外植体材料组织培养实验. 重庆大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 28(6): 118-120. | |
| [11] | Mu T, Zhang X Y, Wang J G, et al. The optimization of Pennisetum agrobacterium-mediated transformation system and obtaining of transgenic plants. Crops, 2013(1): 45-48. |
| 牟彤, 张晓莹, 王金刚, 等. 狼尾草农杆菌转化体系的优化和转基因植株的获得. 作物杂志, 2013(1): 45-48. | |
| [12] | Ozyigit I I, Kuaybe Y K. Particle bombardment technology and its applications in plants. Molecular Biology Reports, 2020, 47(12): 9831-9847. |
| [13] | Rahman S U, Khan M O, Ullah R, et al. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation for the development of transgenic crops; present and future prospects. Molecular Biotechnology, 2024, 66(8): 1836-1852. |
| [14] | Su W, Xu M, Radani Y, et al. Technological development and application of plant genetic transformation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(13): 10646. |
| [15] | Wu K, Xu C, Li T, et al. Application of nanotechnology in plant genetic engineering. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(19): 14836. |
| [16] | Chang F P, Kuang L Y, Huang C A, et al. A simple plant gene delivery system using mesoporous silica nanoparticles as carriers. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2013, 1(39): 5279-5287. |
| [17] | Susana M O, Valenstein J S, Lin V S Y, et al. Gold functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticle mediated protein and DNA codelivery to plant cells via the biolistic method. Advanced Functional Materials, 2012, 22(17): 3576-3582. |
| [18] | Mykhaylyk O, Antequera Y S, Vlaskou D, et al. Generation of magnetic nonviral gene transfer agents and magnetofection in vitro. Nature Protocols, 2007, 2(10): 2391-2411. |
| [19] | Wang Z, Zhang Z B, Zheng D Y, et al. Efficient and genotype independent maize transformation using pollen transfected by DNA-coated magnetic nanoparticles. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2022, 64(6): 1145-1156. |
| [20] | Zhao X, Meng Z G, Wang Y, et al. Pollen magnetofection for genetic modification with magnetic nanoparticles as gene carriers. Nature Plants, 2017, 3(12): 956-964. |
| [21] | Zhang M F, Ma X, Jin G, et al. A modified method for transient transformation via pollen magnetofection in Lilium germplasm. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(20): 15304. |
| [22] | Xu Y, Liu L, Jia M, et al. Transcriptomic and physiological analysis provide new insight into seed shattering mechanism in Pennisetum alopecuroides ‘Liqiu’. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2024, 137(7): 157. |
| [23] | Teng K, Guo Q, Liu L, et al. Chromosome-level reference genome assembly provides insights into the evolution of Pennisetum alopecuroides. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 14(8): 1195479. |
| [24] | Kievit F M, Stephen Z R, Veiseh O, et al. Targeting of primary breast cancers and metastases in a transgenic mouse model using rationally designed multifunctional SPIONs. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(3): 2591-2601. |
| [25] | Park C W, Choi J Y, Son Y J, et al. Magnetofected pollen gene delivery system could generate genetically modified Cucumis sativus. Horticulture Research, 2024, 11(8): 179. |
| [26] | Zhang Y L, Zhang Q X, Xie S L. Pollen morphology of 8 species in Lilium from Qinba Mountain areas. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2010, 19(1): 144-146. |
| 张延龙, 张启翔, 谢松林. 秦巴山及其毗邻地区8种野生百合孢粉学研究. 西北农业学报, 2010, 19(1): 144-146. | |
| [27] | Xu W J, Zhang C, Wu Y, et al. The pollen morphological characteristics from five closely related medicinal plants of the genus Ligusticum. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2024, 52(11): 56-63. |
| 徐皖菁, 张超, 吴宇, 等. 5种藁本属近缘药用植物花粉的形态特征. 东北林业大学学报, 2024, 52(11): 56-63. | |
| [28] | Furness C A, Rudall P J. Pollen aperture evolution: A crucial factor for eudicot success? Trends in Plant Science, 2004, 9(3): 154-158. |
| [29] | Vejlupkova Z, Warman C, Sharma R, et al. No evidence for transient transformation via pollen magnetofection in several monocot species. Nature Plants, 2020, 6(11): 1323-1324. |
| [30] | Wang J X, Chen L B. Changes of vigor and respiratory rate of three kinds of grasses pollen stored under different gas conditions. Plant Physiology Communications, 2001, 37(2): 113-116. |
| 王金祥, 陈良碧. 不同气体下贮藏的3种禾本科植物花粉活力和呼吸速率变化. 植物生理学通讯, 2001, 37(2): 113-116. | |
| [31] | Li Y M, Chen L B. Vigor change of several grasses pollen stored in different temperature and humidity conditions. Plant Physiology Communications, 1998, 34(1): 35-37. |
| 李要民, 陈良碧. 不同温湿条件下贮藏的3种禾本科植物花粉活力变化. 植物生理学通讯, 1998, 34(1): 35-37. | |
| [32] | Lu Y M. Progress of magnetic nanoparticles as gene vector. Letters in Biotechnology, 2013, 24(5): 736-740. |
| 卢艳敏. 磁性纳米颗粒作为载体在基因转染中的研究进展. 生物技术通讯, 2013, 24(5): 736-740. | |
| [33] | Peng Z A, Li D D, Xia A Y, et al. Study on magnetic nanoparticle loading plasmid DNA. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2020, 41(1): 78-82. |
| 彭子艾, 李丹丹, 夏澳运, 等. 磁性纳米颗粒负载质粒DNA的研究. 华南农业大学学报, 2020, 41(1): 78-82. | |
| [34] | Hou X X, Zhang H, Zhang D S. Research progress of magnetic nanoparticles as gene vector. Journal of Medical Postgraduates, 2013, 26(2): 186-189. |
| 侯欣欣, 张皓, 张东生. 磁性纳米颗粒作为基因载体的研究进展. 医学研究生学报, 2013, 26(2): 186-189. | |
| [35] | Stephanie R, Hagen B, Helga R W, et al. Human serum albumin-polyethylenimine nanoparticles for gene delivery. Journal of Controlled Release, 2003, 92(1/2): 199-208. |
| [36] | He X, Wang K, Tan W, et al. Bioconjugated nanoparticles for DNA protection from cleavage. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(24): 7168-7169. |
| [37] | Sun H, Zhang J Y, Luo L J, et al. Development of transgenic hairy root induction and protoplast preparation systems for Stylosanthes leiocarpa. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(5): 1583-1591. |
| 孙昊, 张建禹, 罗丽娟, 等. 光果柱花草转基因毛状根及其原生质体制备体系的建立. 草地学报, 2024, 32(5): 1583-1591. | |
| [38] | Qin A G, Luo X F. Transformation of transcription factor DREB1C gene into the fast-growing black locust mediated with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2007, 29(6): 29-34. |
| 秦爱光, 罗晓芳. 农杆菌介导转录因子DREB1C基因转化速生型刺槐的研究. 北京林业大学学报, 2007, 29(6): 29-34. | |
| [39] | Elzen P J, Townsend J, Lee K Y, et al. A chimaeric hygromycin resistance gene as a selectable marker in plant cells. Plant Molecular Biology, 1985, 5(5): 299-302. |
| [40] | Oung H, Lin K, Wu T, et al. Hygromycin B-induced cell death is partly mediated by reactive oxygen species in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Molecular Biology, 2015, 89(6): 577-588. |
| [41] | Ge X, Xu J, Yang Z, et al. Efficient genotype-independent cotton genetic transformation and genome editing. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2023, 65(4): 907-917. |
| [42] | Nguyen T T, Hai-Vy V N, Hieu T V. Prokaryotic expression of chimeric GFP-hFc protein as a potential immune-based tool. Molecular Biology Research Communications, 2021, 10(3): 105-108. |
| [1] | 陆姣云, 田宏, 熊军波, 吴新江, 刘洋, 张鹤山. 14份乡土狼尾草材料幼苗的耐冷性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 98-111. |
| [2] | 姜凯, 吴雪莉, 刘奕君, 马越, 宋洋, 卢文杰, 王增裕. 海滨雀稗以hpt与bar基因为筛选标记的转化体系比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 165-177. |
| [3] | 李韦柳, 覃维治, 熊军, 韦民政, 唐秀桦, 闫海锋. 施氮对狼尾草在南方贫瘠旱坡地生长、能源品质及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 144-153. |
| [4] | 周香艳, 张宁, 刘柏林, 裴瑞芳, 司怀军, 王蒂. ARF基因干扰表达对不同发育阶段和贮藏条件马铃薯酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(4): 133-139. |
| [5] | 黄勤楼, 钟珍梅, 黄秀声, 陈钟佃, 冯德庆, 夏友国. 纤维素降解菌的筛选及在狼尾草青贮中使用效果评价[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(4): 197-203. |
| [6] | 裴瑞芳, 刘英, 刘柏林, 张宁, 司怀军, 王蒂. 马铃薯ARF基因RNAi载体的遗传转化及对其试管薯生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(2): 142-147. |
| [7] | 钟小仙,刘智微,刘伟国,崔莉莉,吴娟子,张建丽. 六倍体杂交狼尾草体细胞突变体特异性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(4): 107-113. |
| [8] | 吴娟子,张建丽,潘玉梅,刘智微,钟小仙. 象草和杂交狼尾草细胞壁组分及乙醇理论产量动态分析[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(4): 153-161. |
| [9] | 张怀山,赵桂琴,栗孟飞,夏曾润,王春梅. 中型狼尾草幼苗对PEG、低温和盐胁迫的生理应答[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(2): 180-188. |
| [10] | 黄秀声,黄勤楼,杨信,翁伯琦,陈钟佃,钟珍梅. 浇施沼液对狼尾草植株硝酸盐累积及其氮素利用效率研究[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(3): 61-68. |
| [11] | 冯德庆,黄勤楼,李春燕,黄秀声,钟珍梅. 28种牧草的脂肪酸组成分析研究[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(6): 214-218. |
| [12] | 陈志彤,黄勤楼,潘伟彬,黄毅斌. 狼尾草属牧草rDNA的ITS序列分析[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(4): 135-141. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||