

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 189-199.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021071
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
王晓佳1,2( ), 邹瑾1, 曹兵1(
), 邹瑾1, 曹兵1( ), 刘佳欣1, 冯学瑞1, 李运毛1, 李尚玉1
), 刘佳欣1, 冯学瑞1, 李运毛1, 李尚玉1
收稿日期:2021-02-25
修回日期:2021-06-16
出版日期:2022-04-20
发布日期:2022-01-25
通讯作者:
曹兵
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: bingcao2006@126.com基金资助:
Xiao-jia WANG1,2( ), Jin ZOU1, Bing CAO1(
), Jin ZOU1, Bing CAO1( ), Jia-xin LIU1, Xue-rui FENG1, Yun-mao LI1, Shang-yu LI1
), Jia-xin LIU1, Xue-rui FENG1, Yun-mao LI1, Shang-yu LI1
Received:2021-02-25
Revised:2021-06-16
Online:2022-04-20
Published:2022-01-25
Contact:
Bing CAO
摘要:
根系分泌物是植物与土壤之间物质交换和信息传递的重要载体。为深入了解植物根系分泌物研究的现状和发展趋势,本研究采用Web of Science核心合集数据库中1998-2020年间有关植物根系分泌物研究的相关文献4047篇,基于CiteSpace软件进行可视化文献计量学分析。结果表明:1)有关植物根系分泌物的发文量、篇均被引次数呈典型线性增长;2)中国、美国、德国、日本、澳大利亚和法国等是发文量居前的国家;3)中国科学院、南京农业大学、西班牙国家研究委员会、西澳大学等机构在发文总量、被引次数等方面优势明显。有关植物根系分泌物的研究涉及植物科学、土壤科学、农学、环境科学、微生物学和生态学等领域,最具代表性的是荷兰期刊《Plant and Soil》,发表文章最多(256篇),h指数最高;4)植物根系分泌物的研究主要集中在根际、植物、土壤、有机酸、化感作用等方面。根据植物根系分泌物的研究现状,提出深入系统地研究根系分泌物介导下植物-土壤-微生物相互作用的方式与机理,揭示土壤微生态系统功能,定向调控植物根际生物学过程是近年来新兴的研究热点。
王晓佳, 邹瑾, 曹兵, 刘佳欣, 冯学瑞, 李运毛, 李尚玉. 基于CiteSpace的植物根系分泌物研究现状和趋势[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 189-199.
Xiao-jia WANG, Jin ZOU, Bing CAO, Jia-xin LIU, Xue-rui FENG, Yun-mao LI, Shang-yu LI. The knowledge domain and emerging trends in plant root exudates: a bibliometric analysis based on CiteSpace[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(4): 189-199.

图4 植物根系分泌物研究的国家知识图谱PEOPLES R CHINA: 中国; USA: 美国; GERMANY: 德国; JAPAN: 日本; AUSTRALIA: 澳大利亚; FRANCE: 法国; ENGLAND: 英国; SPAIN: 西班牙; ITALY: 意大利; INDIA: 印度; CANADA: 加拿大; BRAZIL: 巴西; NETHERLANDS: 荷兰; SWITZERLAND: 瑞士; RUSSIA: 俄罗斯; SCOTLAND: 苏格兰; SOUTH KOREA: 韩国; AUSTRIA: 奥地利; ARGENTINA: 阿根廷; SWEDEN: 瑞典; PAKISTAN: 巴基斯坦; BELGIUM: 比利时; DENMARK: 丹麦; CZECH REPUBLIC: 捷克; MEXICO: 墨西哥; POLAND: 波兰; ISRAEL: 以色列; IRAN: 伊朗;WALES:威尔士.
Fig.4 Visualization knowledge map of countries of plant root exudates
机构 Institution | 国家 Country | 文章总数 Total article | 总引文次数 Total citation | 篇均被引次数 Average citation | h指数 h-index | 中介中心性 Centrality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中国科学院Chinese Academic of Sciences | 中国China | 250 | 5812 | 23.25 | 39 | 0.14 |
| 南京农业大学Nanjing Agricultural University | 中国China | 95 | 2793 | 29.40 | 30 | 0.02 |
| 西班牙国家研究委员会Spanish National Research Council | 西班牙Spain | 91 | 2969 | 32.63 | 29 | 0.12 |
| 西澳大学University of Western Australia | 澳大利亚Australia | 70 | 4208 | 60.11 | 33 | 0.05 |
| 浙江大学Zhejiang University | 中国China | 69 | 2650 | 38.41 | 32 | 0.06 |
| 科罗拉多州立大学Colorado State University | 美国USA | 67 | 7757 | 115.78 | 36 | 0.33 |
| 霍恩海姆大学University of Hohenheim | 德国Germany | 60 | 5033 | 83.88 | 32 | 0.06 |
| 中国农业大学China Agricultural University | 中国China | 56 | 1640 | 29.29 | 19 | 0.02 |
美国农业部农业研究所Agricultural Research Service of United States Department of Agriculture | 美国USA | 55 | 3142 | 57.13 | 27 | 0.12 |
| 哥廷根大学Gottingen University | 德国Germany | 54 | 2101 | 38.91 | 25 | 0.08 |
表1 1998-2020年文献发表量前10的机构
Table 1 The performance of the top 10 most productive institutions from 1998 to 2020
机构 Institution | 国家 Country | 文章总数 Total article | 总引文次数 Total citation | 篇均被引次数 Average citation | h指数 h-index | 中介中心性 Centrality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中国科学院Chinese Academic of Sciences | 中国China | 250 | 5812 | 23.25 | 39 | 0.14 |
| 南京农业大学Nanjing Agricultural University | 中国China | 95 | 2793 | 29.40 | 30 | 0.02 |
| 西班牙国家研究委员会Spanish National Research Council | 西班牙Spain | 91 | 2969 | 32.63 | 29 | 0.12 |
| 西澳大学University of Western Australia | 澳大利亚Australia | 70 | 4208 | 60.11 | 33 | 0.05 |
| 浙江大学Zhejiang University | 中国China | 69 | 2650 | 38.41 | 32 | 0.06 |
| 科罗拉多州立大学Colorado State University | 美国USA | 67 | 7757 | 115.78 | 36 | 0.33 |
| 霍恩海姆大学University of Hohenheim | 德国Germany | 60 | 5033 | 83.88 | 32 | 0.06 |
| 中国农业大学China Agricultural University | 中国China | 56 | 1640 | 29.29 | 19 | 0.02 |
美国农业部农业研究所Agricultural Research Service of United States Department of Agriculture | 美国USA | 55 | 3142 | 57.13 | 27 | 0.12 |
| 哥廷根大学Gottingen University | 德国Germany | 54 | 2101 | 38.91 | 25 | 0.08 |
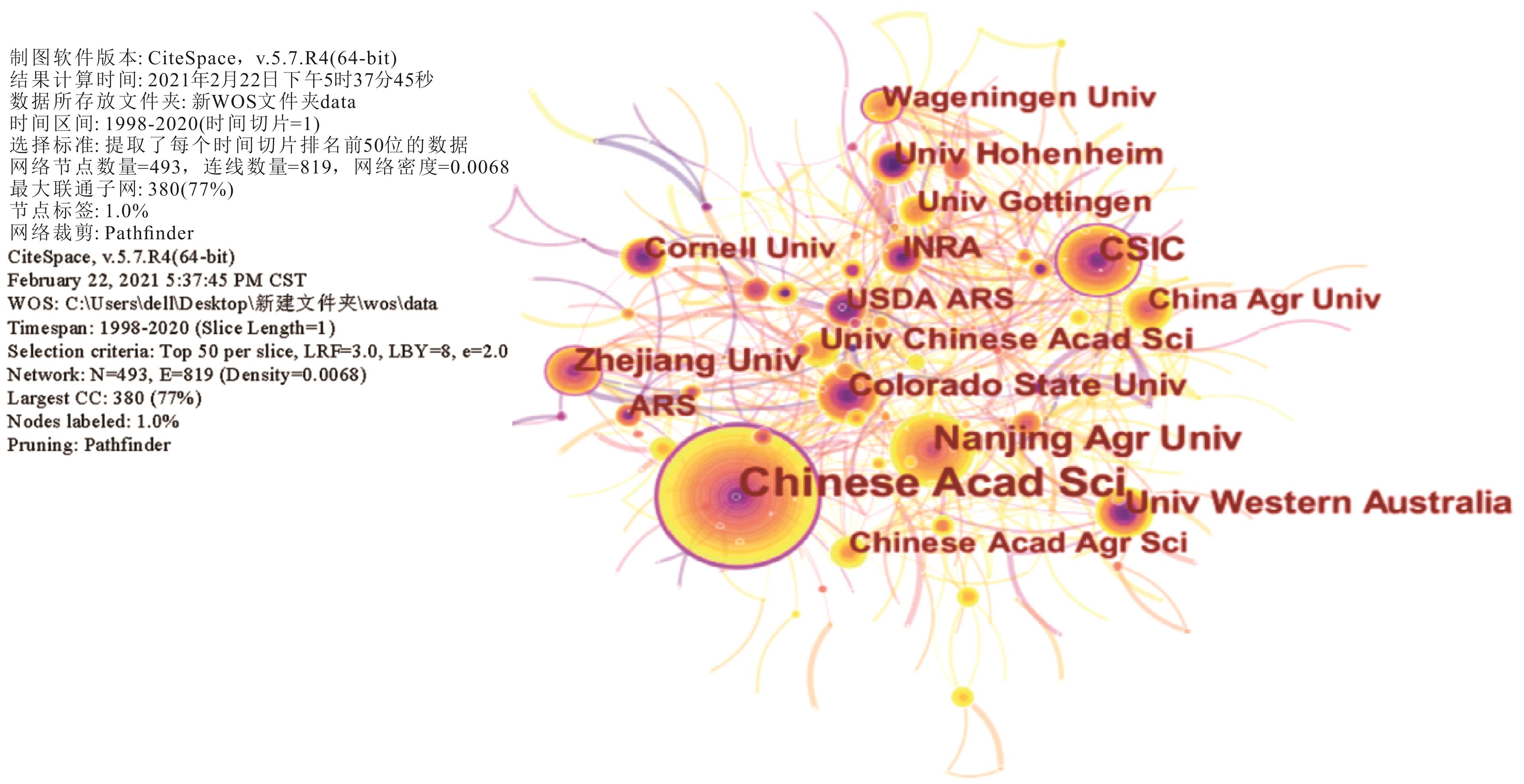
图5 植物根系分泌物研究的机构知识图谱Chinese Acad Sci: 中国科学院; Nanjing Agr Univ: 南京农业大学; CSIC: 西班牙国家研究委员会; Univ Western Australia: 西澳大学; Zhejiang Univ: 浙江大学; Colorado State Univ: 科罗拉多州立大学; Univ Hohenheim: 霍恩海姆大学; China Agr Univ: 中国农业大学; USDA ARS: 美国农业部农业研究所; Univ Gottingen: 哥廷根大学; INRA: 法国国家农业科学院; Univ Chinese Acad Science: 中国科学院大学; Cornell Univ: 康奈尔大学; Chinese Acad Agr Sci: 中国农业科学院; ARS: 美国农业研究院; Wageningen Univ: 瓦格宁根大学.
Fig.5 Visualization knowledge map of institutions of plant root exudates
期刊 Journal | 国家 Country | 文章总数 Total article | 总引文次数 Total citation | 篇均被引次数 Average citation | h指数 h index | 影响因子 IF (2019) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植物和土壤Plant and Soil | 荷兰Netherlands | 256 | 17292 | 67.55 | 62 | 3.299 |
| 土壤生物与生物化学Soil Biology & Biochemistry | 英国United Kingdom | 181 | 9362 | 51.72 | 55 | 5.795 |
| 化感作用杂志Allelopathy Journal | 印度India | 113 | 908 | 8.04 | 17 | 1.275 |
| 新植物学家New Phytologist | 英国United Kingdom | 73 | 5368 | 73.53 | 38 | 8.512 |
| 科学公共图书馆PLoS One | 美国USA | 67 | 2085 | 31.12 | 24 | 2.740 |
| 植物科学前沿Frontiers in Plant Science | 瑞士Switzerland | 62 | 1047 | 16.89 | 16 | 4.402 |
| 化学生态学杂志Journal of Chemical Ecology | 美国USA | 51 | 2231 | 43.75 | 27 | 2.117 |
| 微生物学前沿Frontiers in Microbiology | 瑞士Switzerland | 47 | 921 | 19.60 | 16 | 4.236 |
应用环境微生物学Applied and Environmental Microbiology | 美国USA | 45 | 2641 | 58.69 | 29 | 4.016 |
分子植物-微生物相互作用 Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions | 美国USA | 45 | 3005 | 66.78 | 25 | 3.696 |
表2 1998-2020年文献发表量前10的期刊
Table 2 The performance of the top 10 most productive journals from 1998 to 2020
期刊 Journal | 国家 Country | 文章总数 Total article | 总引文次数 Total citation | 篇均被引次数 Average citation | h指数 h index | 影响因子 IF (2019) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植物和土壤Plant and Soil | 荷兰Netherlands | 256 | 17292 | 67.55 | 62 | 3.299 |
| 土壤生物与生物化学Soil Biology & Biochemistry | 英国United Kingdom | 181 | 9362 | 51.72 | 55 | 5.795 |
| 化感作用杂志Allelopathy Journal | 印度India | 113 | 908 | 8.04 | 17 | 1.275 |
| 新植物学家New Phytologist | 英国United Kingdom | 73 | 5368 | 73.53 | 38 | 8.512 |
| 科学公共图书馆PLoS One | 美国USA | 67 | 2085 | 31.12 | 24 | 2.740 |
| 植物科学前沿Frontiers in Plant Science | 瑞士Switzerland | 62 | 1047 | 16.89 | 16 | 4.402 |
| 化学生态学杂志Journal of Chemical Ecology | 美国USA | 51 | 2231 | 43.75 | 27 | 2.117 |
| 微生物学前沿Frontiers in Microbiology | 瑞士Switzerland | 47 | 921 | 19.60 | 16 | 4.236 |
应用环境微生物学Applied and Environmental Microbiology | 美国USA | 45 | 2641 | 58.69 | 29 | 4.016 |
分子植物-微生物相互作用 Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions | 美国USA | 45 | 3005 | 66.78 | 25 | 3.696 |
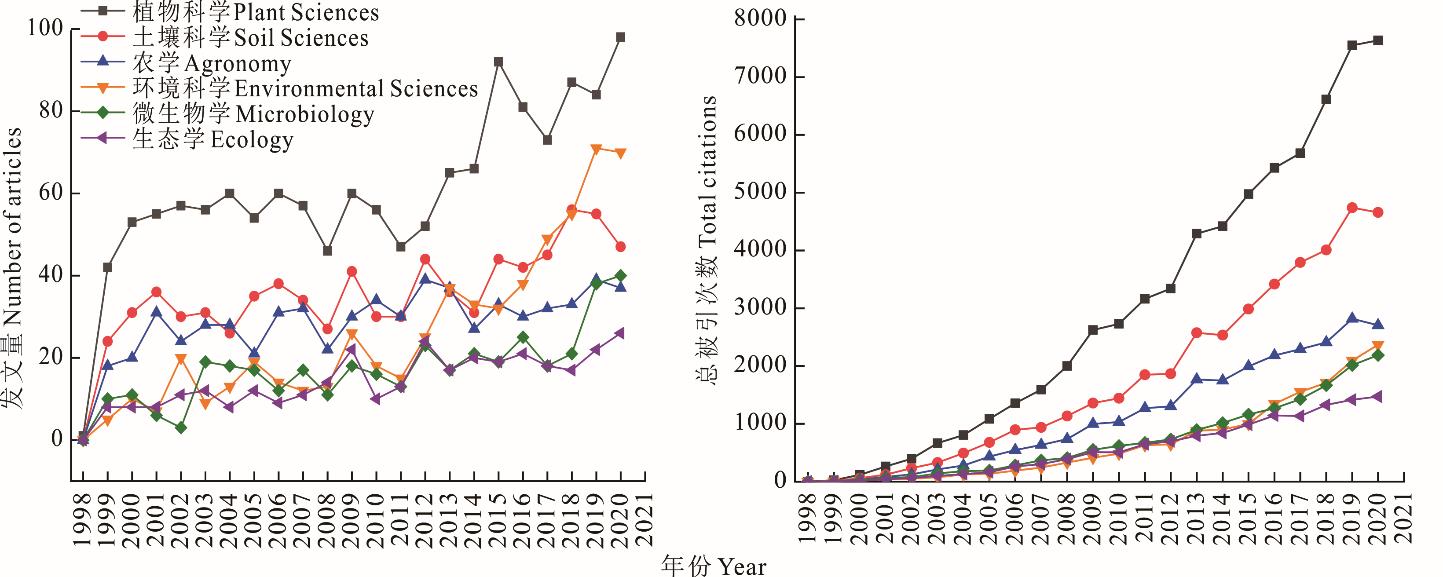
图6 1998-2020年文献发表量前6的学科类别年发表论文量和年总引用量
Fig.6 Tendency of publishing articles per year and total citations per year of top 6 subject categories from 1998 to 2020
| 排序Rank | 关键词Key words | 总数Count | 中介中心性Centrality | 群集编号Cluster ID | 大小Size | 轮廓值Silhouette |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 根系分泌物Root exudate | 1121 | 0.01 | #0 | 51 | 0.910 |
| 2 | 根际Rhizosphere | 1013 | 0.04 | #1 | 49 | 0.845 |
| 3 | 植物Plant | 692 | 0.03 | #2 | 40 | 0.893 |
| 4 | 土壤Soil | 605 | 0 | #3 | 40 | 0.839 |
| 5 | 生长Growth | 531 | 0.01 | #4 | 39 | 0.940 |
| 6 | 根系Root | 387 | 0.03 | #5 | 38 | 0.924 |
| 7 | 有机酸Organic acid | 316 | 0.27 | #6 | 38 | 0.812 |
| 8 | 化感作用Allelopathy | 305 | 0.25 | #7 | 35 | 0.894 |
| 9 | 氮Nitrogen | 263 | 0.07 | #8 | 35 | 0.848 |
| 10 | 拟南芥Arabidopsis thaliana | 241 | 0.14 | #9 | 34 | 0.927 |
表3 1998-2020年排名前10的高频关键词及集群表现
Table 3 The performance of the top 10 high-frequency key words and clusters from 1998 to 2020
| 排序Rank | 关键词Key words | 总数Count | 中介中心性Centrality | 群集编号Cluster ID | 大小Size | 轮廓值Silhouette |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 根系分泌物Root exudate | 1121 | 0.01 | #0 | 51 | 0.910 |
| 2 | 根际Rhizosphere | 1013 | 0.04 | #1 | 49 | 0.845 |
| 3 | 植物Plant | 692 | 0.03 | #2 | 40 | 0.893 |
| 4 | 土壤Soil | 605 | 0 | #3 | 40 | 0.839 |
| 5 | 生长Growth | 531 | 0.01 | #4 | 39 | 0.940 |
| 6 | 根系Root | 387 | 0.03 | #5 | 38 | 0.924 |
| 7 | 有机酸Organic acid | 316 | 0.27 | #6 | 38 | 0.812 |
| 8 | 化感作用Allelopathy | 305 | 0.25 | #7 | 35 | 0.894 |
| 9 | 氮Nitrogen | 263 | 0.07 | #8 | 35 | 0.848 |
| 10 | 拟南芥Arabidopsis thaliana | 241 | 0.14 | #9 | 34 | 0.927 |
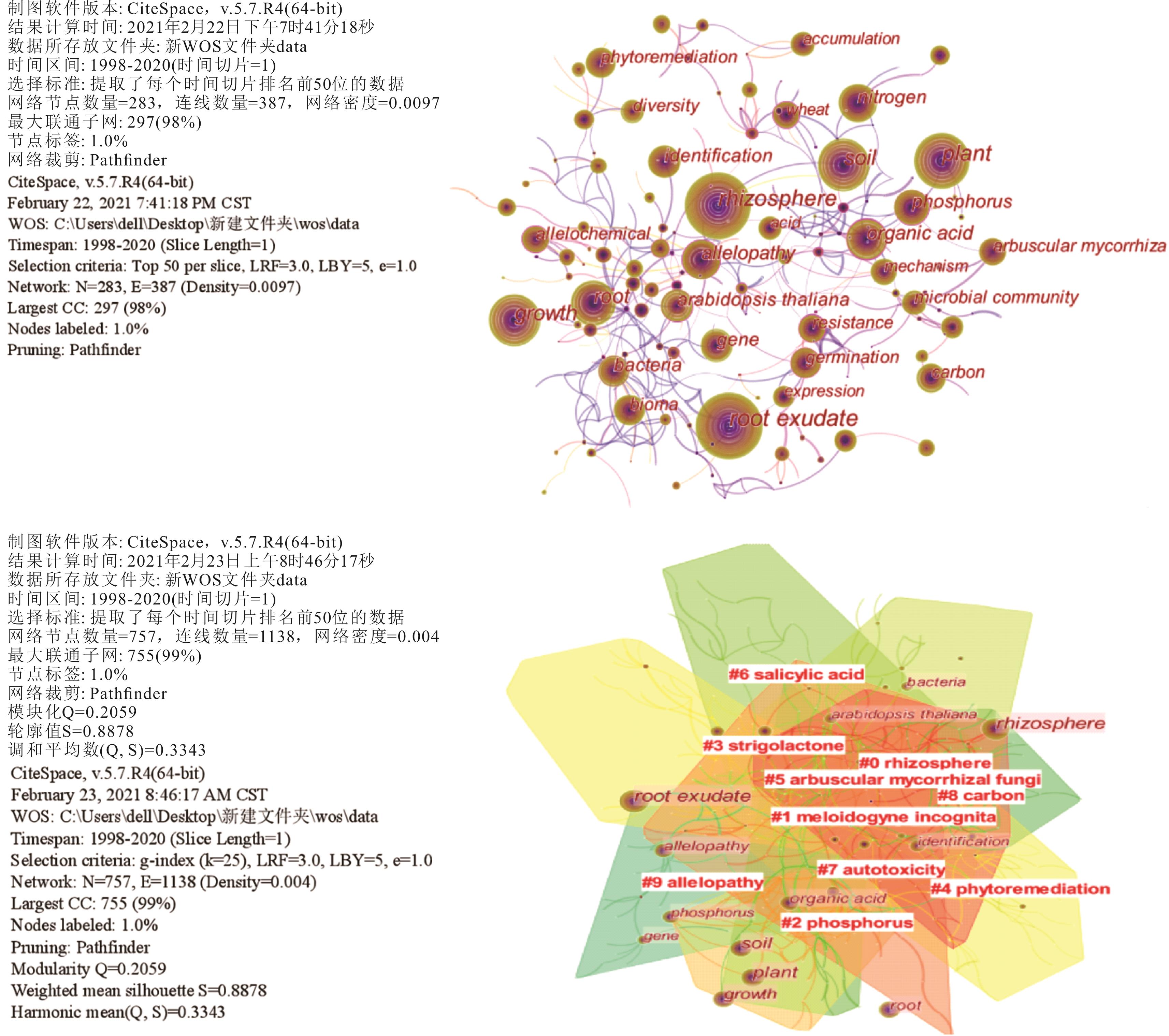
图7 植物根系分泌物研究的关键词共现与聚类知识图谱root exudate: 根系分泌物; rhizosphere: 根际; plant: 植物; soil: 土壤; growth: 生长; root: 根系; organic acid: 有机酸; allelopathy: 化感作用; nitrogen: 氮; arabidopsis thaliana: 拟南芥; identification: 识别; phosphorus: 磷; bacteria: 细菌; gene: 基因; bioma: 生物; phytoremediation: 植物修复; diversity: 多样性; arbuscular mycorrhiza: 丛枝菌根; carbon: 碳; resistance: 抗性; allelochemical: 化感物质; germination: 发芽; microbial community: 微生物群落; wheat: 小麦; mechanism: 机制; accumulation: 积累; acid: 酸; #0 rhizosphere: 集群0根际; #1 meloidogyne incognita: 根结线虫; #2 phosphorus: 磷; #3 strigolactone: 独脚金内酯; #4 phytoremediation: 植物修复; #5 arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: 丛枝菌根真菌; #6 salicylic acid: 水杨酸; #7 autotoxicity: 自毒; #8 carbon: 碳; #9 allelopathy: 化感作用.
Fig.7 The co-occurrence and cluster knowledge map of keywords of plant root exudates
| 关键词Key words | 强度Strength | 起始年Begin | 终止年End | 时间Time (1998-2020) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 影响Impact | 14.7678 | 2013 | 2018 |  |
| 玉米Zea mays | 14.0052 | 2000 | 2008 |  |
| 独脚金内酯Strigolactone | 13.6757 | 2007 | 2015 |  |
| 独脚金属Striga | 13.5086 | 2006 | 2011 |  |
| 细菌群落Bacterial community | 12.7206 | 2014 | 2020 |  |
| 黑麦草属Lolium | 12.4001 | 1999 | 2005 |  |
| 运输Transport | 11.9371 | 1999 | 2008 |  |
| 白羽扇豆Lupinus albus | 11.8370 | 1999 | 2009 |  |
| 种子萌发Seed germination | 11.7596 | 2007 | 2014 |  |
| 有机质Organic matter | 11.1297 | 2015 | 2018 |  |
| 群落结构Community structure | 9.8155 | 2014 | 2020 |  |
| 氧化应激Oxidative stress | 9.4790 | 2015 | 2016 |  |
| 蛋白质根Proteoid root | 9.3772 | 1999 | 2006 |  |
| 结瘤Nodulation | 9.3318 | 1999 | 2002 |  |
| 大麦Barley | 9.3235 | 1999 | 2003 |  |
| 土壤污染Contaminated soil | 9.2443 | 2014 | 2017 |  |
| 酚酸Phenolic acid | 9.0579 | 2013 | 2016 |  |
| 植物生长Plant growth | 8.9138 | 2015 | 2018 |  |
| 重金属Heavy metal | 8.6078 | 2016 | 2020 |  |
| 真菌Fungi | 8.2168 | 2007 | 2015 |  |
表4 1998-2020年排名前20的关键词共现网络突现词
Table 4 The top 20 key words with the strongest citation bursts in the co-occurrence network from 1998 to 2020
| 关键词Key words | 强度Strength | 起始年Begin | 终止年End | 时间Time (1998-2020) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 影响Impact | 14.7678 | 2013 | 2018 |  |
| 玉米Zea mays | 14.0052 | 2000 | 2008 |  |
| 独脚金内酯Strigolactone | 13.6757 | 2007 | 2015 |  |
| 独脚金属Striga | 13.5086 | 2006 | 2011 |  |
| 细菌群落Bacterial community | 12.7206 | 2014 | 2020 |  |
| 黑麦草属Lolium | 12.4001 | 1999 | 2005 |  |
| 运输Transport | 11.9371 | 1999 | 2008 |  |
| 白羽扇豆Lupinus albus | 11.8370 | 1999 | 2009 |  |
| 种子萌发Seed germination | 11.7596 | 2007 | 2014 |  |
| 有机质Organic matter | 11.1297 | 2015 | 2018 |  |
| 群落结构Community structure | 9.8155 | 2014 | 2020 |  |
| 氧化应激Oxidative stress | 9.4790 | 2015 | 2016 |  |
| 蛋白质根Proteoid root | 9.3772 | 1999 | 2006 |  |
| 结瘤Nodulation | 9.3318 | 1999 | 2002 |  |
| 大麦Barley | 9.3235 | 1999 | 2003 |  |
| 土壤污染Contaminated soil | 9.2443 | 2014 | 2017 |  |
| 酚酸Phenolic acid | 9.0579 | 2013 | 2016 |  |
| 植物生长Plant growth | 8.9138 | 2015 | 2018 |  |
| 重金属Heavy metal | 8.6078 | 2016 | 2020 |  |
| 真菌Fungi | 8.2168 | 2007 | 2015 |  |
| 1 | Li X, Duan Z Q. Progress on the research methods for root exudates. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2013, 32(4): 540-547. |
| 李汛, 段增强. 植物根系分泌物的研究方法. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2013, 32(4): 540-547. | |
| 2 | Van Dam N M, Bouwmeester H J. Metabolomics in the rhizosphere: Tapping into belowground chemical communication. Trends in Plant Science, 2016, 21(3): 256-265. |
| 3 | Dakora F D, Phillips D A. Root exudates as mediators of mineral acquisition in low-nutrient environments. Plant and Soil, 2002, 245: 35-47. |
| 4 | Farrar J, Hawes M, Jones D, et al. How roots control the flux of carbon to the rhizosphere. Ecology, 2003, 84(4): 827-837. |
| 5 | Jakoby G, Rog I, Megidish S, et al. Enhanced root exudation of mature broadleaf and conifer trees in a mediterranean forest during the dry season. Plant & Environmental Sciences, 2020, 40(11): 1595-1605. |
| 6 | Bertin C, Yang X, Weston L A. The role of root exudates and allelochemicals in the rhizosphere. Plant and Soil, 2003, 256: 67-83. |
| 7 | Badri D V, Vivanco J M. Regulation and function of root exudates. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2009, 32(6): 666-681. |
| 8 | Bais H P, Weir T L, Perry L G, et al. The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interactions with plants and other organisms. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2006, 57(1): 233-266. |
| 9 | Bais H P, Park S W, Weir T L, et al. How plants communicate using the underground information superhighway. Trends in Plant Science, 2004, 9(1): 26-32. |
| 10 | Delory B M, Delaplace P, Fauconnier M-L, et al. Root-emitted volatile organic compounds: Can they mediate belowground plant-plant interactions? Plant and Soil, 2016, 402: 1-26. |
| 11 | Wu L K, Lin X M, Lin W X. Advances and perspective in research on plant-soil-microbe interactions mediated by root exudates. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38(3): 298-310. |
| 吴林坤, 林向民, 林文雄. 根系分泌物介导下植物-土壤-微生物互作关系研究进展与展望. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(3): 298-310. | |
| 12 | Tu S X, Wu J. A review on research methods of root exudates. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010, 19(9): 2493-2500. |
| 涂书新, 吴佳. 植物根系分泌物研究方法评述. 生态环境学报, 2010, 19(9): 2493-2500. | |
| 13 | Chen Z Y, Ma J, Lai H Y, et al. Research advances in the mechanisms of plant root systems disturbance in rhizosphere micro-environment. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(2): 524-529. |
| 陈智裕, 马静, 赖华燕, 等. 植物根系对根际微环境扰动机制研究进展. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(2): 524-529. | |
| 14 | Xiao J X, Zheng Y, Tang L, et al. Effect of wheat and faba bean intercropping on sugar and amino acid exuded by roots. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(11): 1825-1830. |
| 肖靖秀, 郑毅, 汤利, 等. 小麦-蚕豆间作对根系分泌糖和氨基酸的影响. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(11): 1825-1830. | |
| 15 | Hu K, Tao J P, Huang K, et al. Effects of simulated root exudate carbon inputs on dynamics in microbial community during litter decomposition. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2020, 26(2): 417-424. |
| 胡凯, 陶建平, 黄科, 等. 模拟根系分泌物碳输入对凋落叶分解中微生物群落动态的影响. 应用与环境生物学报, 2020, 26(2): 417-424. | |
| 16 | Sun Y Z. Crop rhizosphere microbial community composition. Journal of Agricultural Catastrophology, 2019, 9(4): 120-121. |
| 孙跃志. 农作物根际微生物群落组成研究概述. 农业灾害研究, 2019, 9(4): 120-121. | |
| 17 | Ma N, Shen Q R, Zhang C, et al. Analysis of international development trend of soil microbial community research based on bibliometrics. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2021, 29(4): 813-824. |
| 马宁, 沈其荣, 张超, 等. 基于文献计量的土壤微生物群落研究国际发展态势. 农业生物技术学报, 2021, 29(4): 813-824. | |
| 18 | Fu L, Xie Y Z, Ma H B. The research status quo of rural households in China and abroad: A bibliometric analysis. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(8): 142-154. |
| 傅理, 谢应忠, 马红彬. 基于文献计量分析的家庭牧场国内外研究进展. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 142-154. | |
| 19 | Zhao J M, Qiu J P, Huang K, et al. A new scientometric indicator -review on h index and its applications. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2008, 2(3): 24-32. |
| 赵基明, 邱均平, 黄凯, 等. 一种新的科学计量指标——h指数及其应用述评. 中国科学基金, 2008, 2(3): 24-32. | |
| 20 | Ma L L, Du L T, Dan Y, et al. Research status and trend of carbon water coupling in terrestrial ecosystem based on Cite Space. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(15): 5441-5449. |
| 马龙龙, 杜灵通, 丹杨, 等. 基于CiteSpace的陆地生态系统碳水耦合研究现状及趋势. 生态学报, 2020, 40(15): 5441-5449. | |
| 21 | Wu J, Wang M, Jin Z, et al. Review and prospect of research on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil environment: A bibliometric analysis based on megadata of Web of Science. Acta Pedolohica Sinica, 2016, 53(5): 1086-1096. |
| 22 | Ouyang W, Wang Y, Lin C, et al. Heavy metal loss from agricultural watershed to aquatic system: A scientometrics review. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 637/638: 208-220. |
| 23 | Ye N, Kueh T, Hou L, et al. A bibliometric analysis of corporate social responsibility in sustainable development. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 272(1): 122679-122717. |
| 24 | Umehara M, Hanada A, Yoshida S, et al. Inhibition of shoot branching by new terpenoid plant hormones. Nature, 2008, 455: 195-200. |
| 25 | Hanson P J, Edwards N T, Garten C T, et al. Separating root and soil microbial contributions to soil respiration: A review of methods and observations. Biogeochemistry, 2000, 48: 115-146. |
| 26 | Finch-Savage W E, Leubner-Metzger G. Seed dormancy and the control of germination. New Phytologist, 2006, 171(3): 501-523. |
| 27 | FernÁndez-Aparicio M, GarcÍa-Garrido J M, Ocampo J A, et al. Colonisation of field pea roots by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi reduces Orobanche and Phelipanche species seed germination. Weed Research, 2010, 50(3): 262-268. |
| 28 | Weston L A, Mathesius U. Flavonoids: Their structure, biosynthesis and role in the rhizosphere, including allelopathy. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 2013, 39(2): 283-297. |
| 29 | Saxena D, Stotzky G. Bacillus thuringiensis (bt) toxin released from root exudates and biomass of bt corn has no apparent effect on earthworms, nematodes, protozoa, bacteria, and fungi in soil. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2001, 33(9): 1225-1230. |
| 30 | Jones D L, Nguyen C, Finlay R D. Carbon flow in the rhizosphere: Carbon trading at the soil–root interface. Plant and Soil, 2009, 321(1/2): 5-33. |
| 31 | Inderjit, Duke S O. Ecophysiological aspects of allelopathy. Planta, 2003, 217(4): 529-539. |
| 32 | Berg G, Smalla K. Plant species and soil type cooperatively shape the structure and function of microbial communities in the rhizosphere. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2009, 68(1): 1-13. |
| 33 | Wang S, Li H, Lin C. Physiological, biochemical and growth responses of Italian ryegrass to butachlor exposure. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 2013, 106(1/2): 21-27. |
| 34 | Zhao L, Huang Y, Hu J, et al. 1h nmr and gc-ms based metabolomics reveal defense and detoxification mechanism of cucumber plant under nano-cu stress. Environment Science Technology, 2016, 50(4): 2000-2010. |
| 35 | Shinano T. Research on ways to improve crop productivity through the regulation of rhizosphere environments. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2019, 66(1): 10-14. |
| 36 | Lai J L, Liu Z W, Luo X G. A metabolomic, transcriptomic profiling, and mineral nutrient metabolism study of the phytotoxicity mechanism of uranium. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 386: 121437-121461. |
| 37 | Hinsinger P. Bioavailability of soil inorganic P in the rhizosphere as affected by root-induced chemical changes: A review. Plant and Soil, 2001, 237: 173-195. |
| 38 | Forieri I, Sticht C, Reichelt M, et al. System analysis of metabolism and the transcriptome in Arabidopsis thaliana roots reveals differential co-regulation upon iron, sulfur and potassium deficiency. Plant Cell Environment, 2017, 40(1): 95-107. |
| 39 | Gallardo F, Borie F, Alvear M, et al. Evaluation of aluminum tolerance of three barley cultivars by two short-term screening methods and field experiments. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 1999, 45(3): 713-719. |
| 40 | Sun Y, Liang Z Y, Wang G B, et al. Research hotspots and frontier analysis for agroforestry management. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University, 2020, 44(6): 228-234. |
| 孙圆, 梁子瑜, 汪贵斌, 等. 农林复合经营工程领域研究热点与前沿分析. 南京林业大学学报, 2020, 44(6): 228-234. | |
| 41 | Callaway R M, Aschehoug E T. Invasive plants versus their new and old neighbors: A mechanism for exotic invasion. Science, 2000, 290(5491): 521-523. |
| 42 | Bronick C J, Lal R. Soil structure and management: A review. Geoderma, 2005, 124(1/2): 3-22. |
| 43 | Hall J L. Cellular mechanisms for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2002, 53(366): 1-11. |
| 44 | Akiyama K, Matsuzaki K, Hayashi H. Plant sesquiterpenes induce hyphal branching in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Nature, 2005, 435(7043): 824-827. |
| [1] | 王瑞永,乔江,袁清. 锡林郭勒盟草原三维数字模型的建立[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(3): 62-69. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||