

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (8): 129-140.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022389
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
徐蕊1( ), 王峥1, 王仪明2, 苏连泰1, 高鲤1, 周鹏1, 安渊1(
), 王峥1, 王仪明2, 苏连泰1, 高鲤1, 周鹏1, 安渊1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-10-05
修回日期:2022-12-06
出版日期:2023-08-20
发布日期:2023-06-16
通讯作者:
安渊
作者简介:E-mail: anyuan@sjtu.edu.cn基金资助:
Rui XU1( ), Zheng WANG1, Yi-ming WANG2, Lian-tai SU1, Li GAO1, Peng ZHOU1, Yuan AN1(
), Zheng WANG1, Yi-ming WANG2, Lian-tai SU1, Li GAO1, Peng ZHOU1, Yuan AN1( )
)
Received:2022-10-05
Revised:2022-12-06
Online:2023-08-20
Published:2023-06-16
Contact:
Yuan AN
摘要:
紫花苜蓿与水稻轮作具有改善稻田质量和增加水稻产量的作用,但苜蓿促进水稻增产的生理机制尚不清晰。试验设置种植黑麦草土+NPK基肥+尿素追肥(PRS)、种植苜蓿土+NPK基肥+尿素追肥(PAS)和苜蓿土+苜蓿绿肥+NPK基肥+尿素追肥(紫花苜蓿处理)3个处理。结果显示,与2个对照处理相比,紫花苜蓿处理显著提高了轮作水稻的分蘖数、生物量、籽实产量以及抽穗期叶片N、P、K含量;紫花苜蓿处理分蘖期、抽穗期和收获期的水稻净光合速率依次比PRS增加了16.99%、27.22%和40.99%,比PAS增加了16.88%、37.99%和33.51%;参与蔗糖代谢的关键基因OsAGPS1、OsAGPL1、OsMEX1、 OsSPS1和OsSUS5的相对表达量在叶片(白天和夜间)和根系中明显变化,与PRS相比,5个基因在分蘖期夜间的表达量分别上调2.45、2.96、1.29、1.66和6.04倍,而白天仅OsMEX1和OsSPS1的表达量明显上调,同时,OsMEX1在抽穗期夜间和收获期明显下调;在根系中,OsAGPL1、OsMEX1和OsAGPS1在分蘖期或抽穗期明显上调表达;与此相应,分蘖期叶片的蔗糖磷酸合成酶和可溶性淀粉合成酶活性,以及新叶和叶鞘的淀粉、蔗糖和可溶性糖含量显著增加,而老叶中蔗糖和可溶性糖含量显著下降。研究结果表明紫花苜蓿通过影响轮作水稻分蘖期叶片N、P、K含量和蔗糖代谢通路关键基因的昼夜表达格局而改变淀粉、蔗糖和可溶性糖在水稻叶片和叶鞘的分配,从而促进水稻增产。
徐蕊, 王峥, 王仪明, 苏连泰, 高鲤, 周鹏, 安渊. 紫花苜蓿对轮作水稻产量和蔗糖代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 129-140.
Rui XU, Zheng WANG, Yi-ming WANG, Lian-tai SU, Li GAO, Peng ZHOU, Yuan AN. Effect of alfalfa on the yield and sucrose metabolism of rice in an alfalfa-rice rotation system[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(8): 129-140.
土壤样品 Soil sample | 全氮 Total N (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total P (g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total K (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available N (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available P (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available K (mg·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRS | 0.13±0.00 | 0.68±0.05 | 10.78±1.19 | 88.43±0.70 | 5.56±0.43 | 165.55±12.02 | 16.75±0.28 |
| PAS | 0.14±0.00 | 0.77±0.05 | 10.89±1.68 | 98.03±1.20 | 9.74±1.03 | 171.17±21.55 | 17.82±1.79 |
表1 供试土壤基础养分
Table 1 Soil nutrients in the two experimental treatments
土壤样品 Soil sample | 全氮 Total N (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total P (g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total K (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available N (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available P (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available K (mg·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRS | 0.13±0.00 | 0.68±0.05 | 10.78±1.19 | 88.43±0.70 | 5.56±0.43 | 165.55±12.02 | 16.75±0.28 |
| PAS | 0.14±0.00 | 0.77±0.05 | 10.89±1.68 | 98.03±1.20 | 9.74±1.03 | 171.17±21.55 | 17.82±1.79 |

图2 水稻不同生育期地上生物量变化不同字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05) Different letters above the bars indicates significant difference among treatments (P<0.05); 下同The same below.
Fig. 2 Changes of aboveground biomass at different developmental stages of rice
处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicles (No.·pot-1) | 穗粒数 Grain number per panicle (No.) | 结实率 Seed setting rate (%) | 千粒重 Thousand-grain weight (g) | 籽粒重 Grain weight (g·pot-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRS | 12.67±1.69b | 115.12±7.52b | 70.91±5.00c | 23.22±0.42b | 27.77±2.65b |
| PAS | 11.69±0.47b | 115.55±3.64b | 77.26±0.98b | 24.10±0.74a | 28.07±1.59b |
| 紫花苜蓿Alfalfa (A) | 16.07±1.25a | 135.95±1.76a | 84.68±1.18a | 24.46±0.84a | 39.23±2.61a |
表2 不同处理水稻产量及产量构成因素
Table 2 Yield and yield components of rice under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 有效穗数 Effective panicles (No.·pot-1) | 穗粒数 Grain number per panicle (No.) | 结实率 Seed setting rate (%) | 千粒重 Thousand-grain weight (g) | 籽粒重 Grain weight (g·pot-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRS | 12.67±1.69b | 115.12±7.52b | 70.91±5.00c | 23.22±0.42b | 27.77±2.65b |
| PAS | 11.69±0.47b | 115.55±3.64b | 77.26±0.98b | 24.10±0.74a | 28.07±1.59b |
| 紫花苜蓿Alfalfa (A) | 16.07±1.25a | 135.95±1.76a | 84.68±1.18a | 24.46±0.84a | 39.23±2.61a |
处理 Treatment | 氮含量N content | 磷含量P content | 钾含量K content | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
分蘖期 Tillering stage | 抽穗期 Heading stage | 收获期 Harvesting stage | 分蘖期 Tillering stage | 抽穗期 Heading stage | 收获期 Harvesting stage | 分蘖期 Tillering stage | 抽穗期 Heading stage | 收获期 Harvesting stage | |
| PRS | 25.86±0.92b | 27.49±0.42b | 11.54±0.41ab | 4.47±0.26b | 3.06±0.47c | 0.83±0.48b | 45.30±2.63b | 18.53±0.29c | 9.54±0.55b |
| PAS | 29.72±1.72a | 28.47±0.46b | 10.57±0.61b | 4.65±0.07ab | 4.41±0.71b | 0.76±0.01b | 47.49±0.77ab | 24.77±0.40b | 9.31±0.75b |
| A | 29.40±0.45a | 33.47±2.26a | 12.52±0.19a | 4.93±0.08a | 5.87±0.39a | 1.14±0.02a | 52.26±3.53a | 37.14±2.51a | 13.22±0.89a |
表3 不同发育期水稻叶片的氮、磷、钾含量
Table 3 Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium contents in rice leaves at different developmental stages (g·kg-1)
处理 Treatment | 氮含量N content | 磷含量P content | 钾含量K content | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
分蘖期 Tillering stage | 抽穗期 Heading stage | 收获期 Harvesting stage | 分蘖期 Tillering stage | 抽穗期 Heading stage | 收获期 Harvesting stage | 分蘖期 Tillering stage | 抽穗期 Heading stage | 收获期 Harvesting stage | |
| PRS | 25.86±0.92b | 27.49±0.42b | 11.54±0.41ab | 4.47±0.26b | 3.06±0.47c | 0.83±0.48b | 45.30±2.63b | 18.53±0.29c | 9.54±0.55b |
| PAS | 29.72±1.72a | 28.47±0.46b | 10.57±0.61b | 4.65±0.07ab | 4.41±0.71b | 0.76±0.01b | 47.49±0.77ab | 24.77±0.40b | 9.31±0.75b |
| A | 29.40±0.45a | 33.47±2.26a | 12.52±0.19a | 4.93±0.08a | 5.87±0.39a | 1.14±0.02a | 52.26±3.53a | 37.14±2.51a | 13.22±0.89a |

图3 水稻分蘖期、抽穗期和收获期的叶片净光合速率、蒸腾速率、气孔导度和胞间CO2浓度
Fig.3 Leaf photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, stomatal conductance and intercellular CO2 concentration at tillering stage, heading stage and harvesting stage of rice
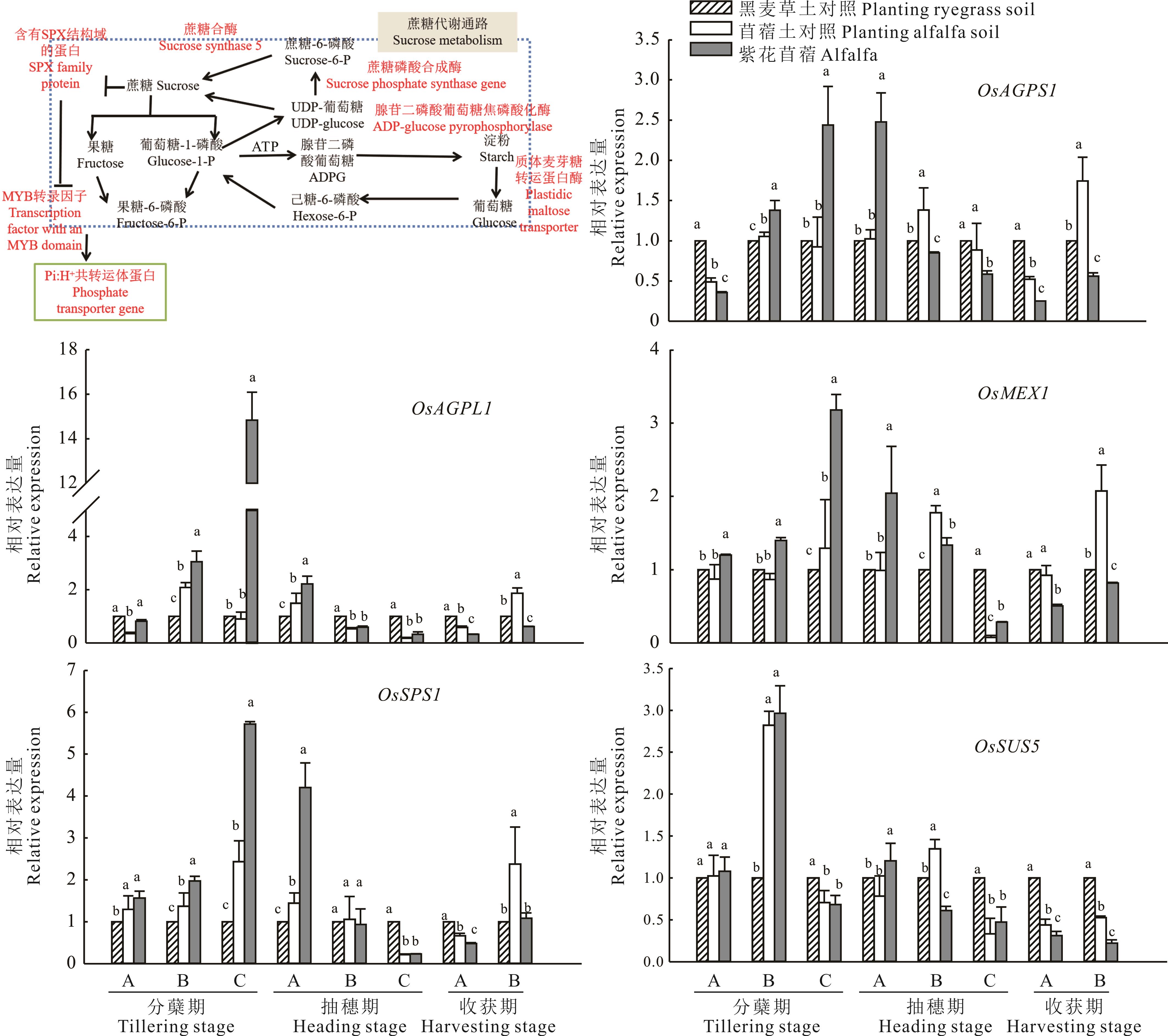
图5 水稻蔗糖代谢基因调控通路及关键基因相对表达量A: 白天叶Leaves at daytime; B: 晚间叶Leaves at night; C: 根Root.
Fig.5 Regulatory pathways of sucrose metabolism genes and relative expression of key genes in rice

图6 水稻分蘖末期蔗糖磷酸合成酶和可溶性淀粉合成酶活性及淀粉、蔗糖和可溶性糖含量
Fig.6 The activities of SPS and SSS in leaves and starch, sucrose and soluble sugar contents in different tissues of rice at tillering stage
| 1 | National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. China statistical yearbook. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2016. |
| 中华人民共和国国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2016. | |
| 2 | Ghassan J, Zakaria W, Shaari A. Application of mungbean residue as green manure Ⅱ. Effects on growth and yield of sweet potato. Agricultire Research, 2018, 18: 10-11. |
| 3 | Yang S. Effects of reducing the application of chemical fertilizers on the growth, yield, quality and soil fertility of maize. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2018. |
| 杨爽. 翻压光叶紫花苕减施化肥对玉米生长、产量、品质及土壤肥力的影响. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2018. | |
| 4 | Tian X, Zhang W, Wu Y P, et al. Effects of planting green manure and reduced nitrogen fertilizer application on soil fertility and fruit quality in citrus orchard. Soil and Fertilizer in China, 2020, 6: 197-204. |
| 田想, 张威, 伍玉鹏, 等. 绿肥种植配施减量氮肥对橘园土壤肥力及果实质量的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2020, 6: 197-204. | |
| 5 | Álvarez I L, Puig C, Revilla P, et al. Faba bean as green manure for field weed control in maize. Weed Research, 2018, 58(6): 437-449. |
| 6 | Kamran M, Huang L, Nie J, et al. Effect of reduced mineral fertilization (NPK) combined with green manure on aggregate stability and soil organic carbon fractions in a fluvo-aquic paddy soil. Soil and Tillage Research, 2021, 211: 105005. |
| 7 | Lal R. Soil carbon management and climate change. Carbon Management, 2013, 4(4): 439-462. |
| 8 | Ye X, Liu H, Li Z, et al. Effects of green manure continuous application on soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2014, 37(4): 498-508. |
| 9 | Wang L N, Jing C M, Zhang L, et al. Effects of different cultivation years alfalfa and rotation cotton on soil physical & chemical properties. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 54(8): 1523-1530. |
| 王林娜, 景春梅, 张玲, 等. 不同种植年限紫花苜蓿和棉花轮作对土壤理化性质的影响. 新疆农业科学, 2017, 54(8): 1523-1530. | |
| 10 | Goff B, Feng B C, Gao Q, et al. Benefit analysis of alfalfa and corn rotation in the United States. World Agriculture, 2017, 460(8): 199-201. |
| Goff B, 冯葆昌, 高秋, 等. 美国紫花苜蓿与玉米轮作的效益分析. 世界农业, 2017, 460(8): 199-201. | |
| 11 | Ma L L, Ma P J, Su S. Effects on wheat yield and soil organic matter of alfalfa-wheat rotation. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 46(18): 1-2. |
| 马伦兰, 马培杰, 苏生. 紫花苜蓿-小麦轮作对小麦产量与土壤有机质的影响. 现代农业科技, 2017, 46(18): 1-2. | |
| 12 | Ma L, Zhou P, Gao X Y, et al. Growth and nutrient dynamics of non-fall dormancy and semi-fall dormancy alfalfa cultivars in winter fallow land of South-east China. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2014, 36(5): 38-45. |
| 马力, 周鹏, 高小叶, 等. 非秋眠和半秋眠紫花苜蓿品种在华东冬闲田的生长规律和营养动态. 中国草地学报, 2014, 36(5): 38-45. | |
| 13 | Zhang J, Zhang Y H, Ma L, et al. Effect of sowing date and applying fertilizer on growth and quality of alfalfa in winter fallow land. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2015, 37(6): 35-41. |
| 张菁, 张于卉, 马力, 等. 播期和施肥对冬闲田紫花苜蓿生长和品质的影响. 中国草地学报, 2015, 37(6): 35-41. | |
| 14 | Zhao L, Shi D Y, Gao X Y, et al. Effect of alfalfa green manure on rice yield and soil fertilizer. Pratacultural Science, 2012, 29(7): 1142-1147. |
| 赵鲁, 史冬燕, 高小叶, 等. 紫花苜蓿绿肥对水稻产量和土壤肥力的影响. 草业科学, 2012, 29(7): 1142-1147. | |
| 15 | Qu H K, Gao Y H, Han J R. Research on the nitrogen fertilizer reduction effect of rice with green manure and alfalfa returned to the field. Agricultural Equipment and Technology, 2018, 44(1): 22-24. |
| 瞿怀康, 高月华, 韩九荣. 绿肥紫花苜蓿还田下水稻氮肥减量效应研究. 农业装备技术, 2018, 44(1): 22-24. | |
| 16 | Li F J, Yu C, Ma L, et al. Effects of fertilizer on alfalfa growth in winter fallow paddy fields and alfalfa green manure on rice yield. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(10): 2008-2018. |
| 李凤杰, 于晨, 马力, 等. 施肥对冬闲稻田紫花苜蓿生长及苜蓿绿肥对轮作水稻产量的影响. 草业科学, 2021, 38(10): 2008-2018. | |
| 17 | Yu C, Wang Y M, Ma L, et al. An annual rotation model of alfalfa and corn in Yangtze River area. Pratacultural Science, 2022, 39(5): 996-1005. |
| 于晨, 王仪明, 马力, 等. 长江中下游地区紫花苜蓿与玉米周年轮作栽培模式. 草业科学, 2022, 39(5): 996-1005. | |
| 18 | Li K, Li Z J. Agrochemical analysis method of soil. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2019. |
| 李科, 李志军. 土壤农化分析方法. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2019. | |
| 19 | Zheng B Z. Technical guidelines for soil analysis. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House, 2013. |
| 郑必昭. 土壤分析技术指南. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2013. | |
| 20 | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2- ΔΔ Ct method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| 21 | Cho Y G, Kang K K. Functional analysis of starch metabolism in plants. Plants, 2020, 9(9): 1152. |
| 22 | Gao X, Shi D, Lv A, et al. Increase phosphorus availability from the use of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) green manure in rice (Oryza sativa L.) agroecosystem. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 1-13. |
| 23 | Cheng H D, Lu Y H, Nie J, et al. Effects of different turning amounts of vetch on the yield and nutrient use efficiency of double-cropping rice under reduced fertilizer application. North China Agricultural Journal, 2020, 35(3): 143-152. |
| 程会丹, 鲁艳红, 聂军, 等. 化肥减施下紫云英不同翻压量对双季稻产量及养分利用效率的影响. 华北农学报, 2020, 35(3): 143-152. | |
| 24 | Zhou Z H, Liang Q, Quan Z M, et al. Effects of turning green manure Lathyrus sativus and reducing nitrogen application on growth, nutrient absorption and yield of rice. Northwest Botany, 2021, 41(11): 1962-1970. |
| 周泽弘, 梁琴, 全紫曼, 等. 翻压山黧豆绿肥与氮肥减施对水稻生长及其养分吸收与产量的影响. 西北植物学报, 2021,41(11): 1962-1970. | |
| 25 | Singh V K, Gautam P, Nanda G. Soil test based fertilizer application improves productivity, profitability and nutrient use efficiency of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under direct seeded condition. Agronomy, 2021, 11(9): 1756. |
| 26 | Li G, Hu Q, Shi Y, et al. Low nitrogen application enhances starch-metabolizing enzyme activity and improves accumulation and translocation of non-structural carbohydrates in rice stems. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 1128. |
| 27 | Meng Q, Zhang W, Hu X, et al. Two ADP glucose pyrophosphorylase subunits, OsAGPL1 and OsAGPS1, modulate phosphorus homeostasis in rice. The Plant Journal, 2020, 104(5): 1269-1284. |
| 28 | Qian W W, Guo P, Zhu H S, et al. Responses of leaf epidermis, anatomical structure and photosynthetic characteristics of Poa pratensis to different nitrogen application level. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(1): 141-153. |
| 钱文武, 郭鹏, 朱慧森, 等. 草地早熟禾叶片表皮特征、解剖结构及光合特性对不同施氮量的响应. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 141-153. | |
| 29 | Sun Y H, Zhao J W, Liu X S, et al. Effect of nitrogen application on photosynthetic daily variation, leaf morphology and dry matter yield of alfalfa at the early flowering growth stage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 63-75. |
| 孙延亮, 赵俊威, 刘选帅, 等. 施氮对苜蓿初花期光合日变化、叶片形态及干物质产量的影响. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 63-75. | |
| 30 | Xiong X, Liu J M, Wang J C, et al. Effects of phosphorus supply on photosynthesis-CO2 response of migao seedlings. Nanjing Agricultural Journal, 2017, 48(11): 1983-1988. |
| 熊雪, 刘济明, 王军才, 等. 磷素供给对米槁幼苗光合作用-CO2响应的影响. 南京农业学报, 2017, 48(11): 1983-1988. | |
| 31 | Thomas A, Beena R, Laksmi G, et al. Changes in sucrose metabolic enzymes to water stress in contrasting rice genotypes. Plant Stress, 2022, 5: 100088. |
| 32 | Li G H. Mechanism of accumulation and transport of non-structural carbohydrates in stem and sheath and unloading of caryopsis phloem in rice. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 李国辉. 水稻茎鞘非结构性碳水化合物积累转运和颖果韧皮部卸载机理. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2018. | |
| 33 | Hashida Y, Hirose T, Okamura M, et al. A reduction of sucrose phosphate synthase (SPS) activity affects sucrose/starch ratio in leaves but does not inhibit normal plant growth in rice. Plant Science, 2016, 253: 40-49. |
| 34 | Fan C, Wang G, Wang Y, et al. Sucrose synthase enhances hull size and grain weight by regulating cell division and starch accumulation in transgenic rice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(20): 4971. |
| 35 | He Y T, Wang G Y, Fan C F. Research progress in plant sucrose synthase. Chinese Journal of Plant Physiology, 2020, 56(6): 1165-1176. |
| 何艺涛, 王广亚, 范春芬. 植物蔗糖合酶研究进展. 植物生理学报, 2020, 56(6): 1165-1176. | |
| 36 | Bharali A, Baruah K K. Effects of integrated nutrient management on sucrose phosphate synthase enzyme activity and grain quality traits in rice. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2022, 28(2): 383-389. |
| 37 | Kato T, Morita R, Ootsuka S, et al. Evaluation of alleles at OsAGPS2, OsAGPL2, and OsSUT1 related to grain filling in rice in a common genetic background. Crop Science, 2021, 61(2): 1154-1167. |
| 38 | Okamura M, Hirose T, Hashida Y, et al. Starch reduction in rice stems due to a lack of OsAGPL1 or OsAPL3 decreases grain yield under low irradiance during ripening and modifies plant architecture. Functional Plant Biology, 2013, 40(11): 1137-1146. |
| 39 | Okamura M, Hirai M Y, Sawada Y, et al. Analysis of carbon flow at the metabolite level reveals that starch synthesis from hexose is a limiting factor in a high-yielding rice cultivar. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2021, 72(7): 2570-2583. |
| 40 | Ma B, Zhang L, Gao Q, et al. A plasma membrane transporter coordinates phosphate reallocation and grain filling in cereals. Nature Genetics, 2021, 53(6): 906-915. |
| [1] | 凌文卿, 张磊, 李珏, 冯启贤, 李妍, 周燚, 刘一佳, 阳伏林, 周晶. 布氏乳杆菌和不同糖类联用对紫花苜蓿青贮营养成分、发酵品质、瘤胃降解率及有氧稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 122-134. |
| [2] | 王少鹏, 刘佳, 洪军, 林积圳, 张义, 史昆, 王赞. 紫花苜蓿MsPPR1基因的克隆及抗旱功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 49-60. |
| [3] | 李超男, 王磊, 周继强, 赵长兴, 谢晓蓉, 刘金荣. 微塑料对紫花苜蓿生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 138-146. |
| [4] | 张振粉, 黄荣, 姚博, 张旺东, 杨成德, 陈秀蓉. 欧美进口紫花苜蓿可培养种带细菌及其对动植物的致病性[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 161-172. |
| [5] | 张士敏, 赵娇阳, 朱慧森, 卫凯, 王永新. 硒对不同品种紫花苜蓿发芽阶段物质转化和形态建成的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 79-90. |
| [6] | 王园, 王晶, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿MsBBX24基因的克隆及耐盐性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 107-117. |
| [7] | 田政, 杨正禹, 陆忠杰, 罗奔, 张茂, 董瑞. 44个紫花苜蓿品种的酸铝适应性与耐受性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 142-151. |
| [8] | 孙守江, 唐艺涵, 马馼, 李曼莉, 毛培胜. 紫花苜蓿种子吸胀期胚根线粒体AsA-GSH循环对低温胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 152-162. |
| [9] | 刘选帅, 孙延亮, 安晓霞, 马春晖, 张前兵. 施磷和接种解磷菌对紫花苜蓿光合特性及生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 189-199. |
| [10] | 王晓龙, 杨曌, 来永才, 李红, 钟鹏, 徐艳霞, 柴华, 李莎莎, 吴玥, 宋敏超, 周景明. 不同秋眠等级苜蓿根系性状对越冬的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 144-153. |
| [11] | 孙延亮, 赵俊威, 刘选帅, 李生仪, 马春晖, 王旭哲, 张前兵. 施氮对苜蓿初花期光合日变化、叶片形态及干物质产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 63-75. |
| [12] | 王星, 黄薇, 余淑艳, 李小云, 高雪芹, 伏兵哲. 宁夏地区地下滴灌水肥耦合对紫花苜蓿种子产量及构成因素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 76-85. |
| [13] | 吴永杰, 丁浩, 邵涛, 赵杰, 董东, 代童童, 尹雪敬, 宗成, 李君风. 酶制剂对水稻秸秆青贮发酵品质及体外消化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 167-177. |
| [14] | 赵建涛, 岳亚飞, 张前兵, 马春晖. 不同秋眠级紫花苜蓿品种抗寒性对新疆北疆地区覆雪厚度的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 24-34. |
| [15] | 刘彩婷, 毛丽萍, 阿依谢木, 于应文, 沈禹颖. 紫花苜蓿与垂穗披碱草混播比例对其抗寒生长生理特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 133-143. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||