

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (11): 172-185.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024013
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
侯铭辉1( ), 孙延亮1, 杨开鑫1, 齐军仓2, 张前兵1(
), 孙延亮1, 杨开鑫1, 齐军仓2, 张前兵1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-04
修回日期:2024-03-15
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-09-09
通讯作者:
张前兵
作者简介:E-mail: qbz102@163.com基金资助:
Ming-hui HOU1( ), Yan-liang SUN1, Kai-xin YANG1, Jun-cang QI2, Qian-bing ZHANG1(
), Yan-liang SUN1, Kai-xin YANG1, Jun-cang QI2, Qian-bing ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2024-01-04
Revised:2024-03-15
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-09-09
Contact:
Qian-bing ZHANG
摘要:
通过分析不同氮磷钾水平对大麦饲草鲜草产量和粗蛋白的影响,筛选适合水培大麦饲草的最优氮磷钾水平,以期为该资源的合理利用提供理论依据及数据参考。通过单因素试验确定氮添加量A、磷添加量B和钾添加量C的取值范围,并采用响应曲面优化法构建一个二次多项式回归模型,通过中心复合旋转设计在水培过程中添加不同水平的氮磷钾,其中氮添加量是3.30、5.00、7.50、10.00和11.70 mmol·L-1,磷添加量是0.66、1.00、1.50、2.00和2.34 mmol·L-1,钾添加量是1.98、3.00、4.50、6.00和7.02 mmol·L-1,选择鲜草产量和粗蛋白含量为优化目标。结果表明:鲜草产量和粗蛋白含量之间的二次多项式影响均极显著(P<0.01),决定系数都为0.97。其中,钾对鲜草产量的曲面效应影响极显著(P<0.01),氮和钾的交互作用对鲜草产量的曲面效应影响极显著(P<0.01),磷和钾的交互作用对鲜草产量的曲面效应影响显著(P<0.05)。氮钾和磷钾对粗蛋白的曲面效应影响极显著(P<0.01)。在氮添加量为9.19 mmol·L-1,磷添加量为1.08 mmol·L-1,钾添加量为3.99 mmol·L-1时,响应曲面优化结果最好,鲜草产量预测值可达到12.07 kg·plate-1,粗蛋白含量预测值可达到19.35%DM,在此条件下,水培大麦饲草鲜草产量和粗蛋白含量均达到最优。
侯铭辉, 孙延亮, 杨开鑫, 齐军仓, 张前兵. 基于响应曲面法确定水培大麦饲草高产优质的氮磷钾养分投入量[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 172-185.
Ming-hui HOU, Yan-liang SUN, Kai-xin YANG, Jun-cang QI, Qian-bing ZHANG. Determination of optimal input levels of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium for high yield and quality of hydroponic barley forage based on response surface methodology[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(11): 172-185.
试验变量 Experiment variables | 代码 Codes | 符号 Symbols | 编码变量水平Levels of coded variables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -1.68 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 1.68 | |||
| 氮Nitrogen | A | N | 3.30 | 5 | 7.5 | 10 | 11.70 |
| 磷Phosphorus | B | P | 0.66 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.34 |
| 钾Potassium | C | K | 1.98 | 3 | 4.5 | 6 | 7.02 |
表1 中心复合旋转设计(CCD)中的试验变量、代码和编码水平
Table 1 Experimental variables, codes and coding levels in central composite design (CCD)
试验变量 Experiment variables | 代码 Codes | 符号 Symbols | 编码变量水平Levels of coded variables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -1.68 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 1.68 | |||
| 氮Nitrogen | A | N | 3.30 | 5 | 7.5 | 10 | 11.70 |
| 磷Phosphorus | B | P | 0.66 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.34 |
| 钾Potassium | C | K | 1.98 | 3 | 4.5 | 6 | 7.02 |
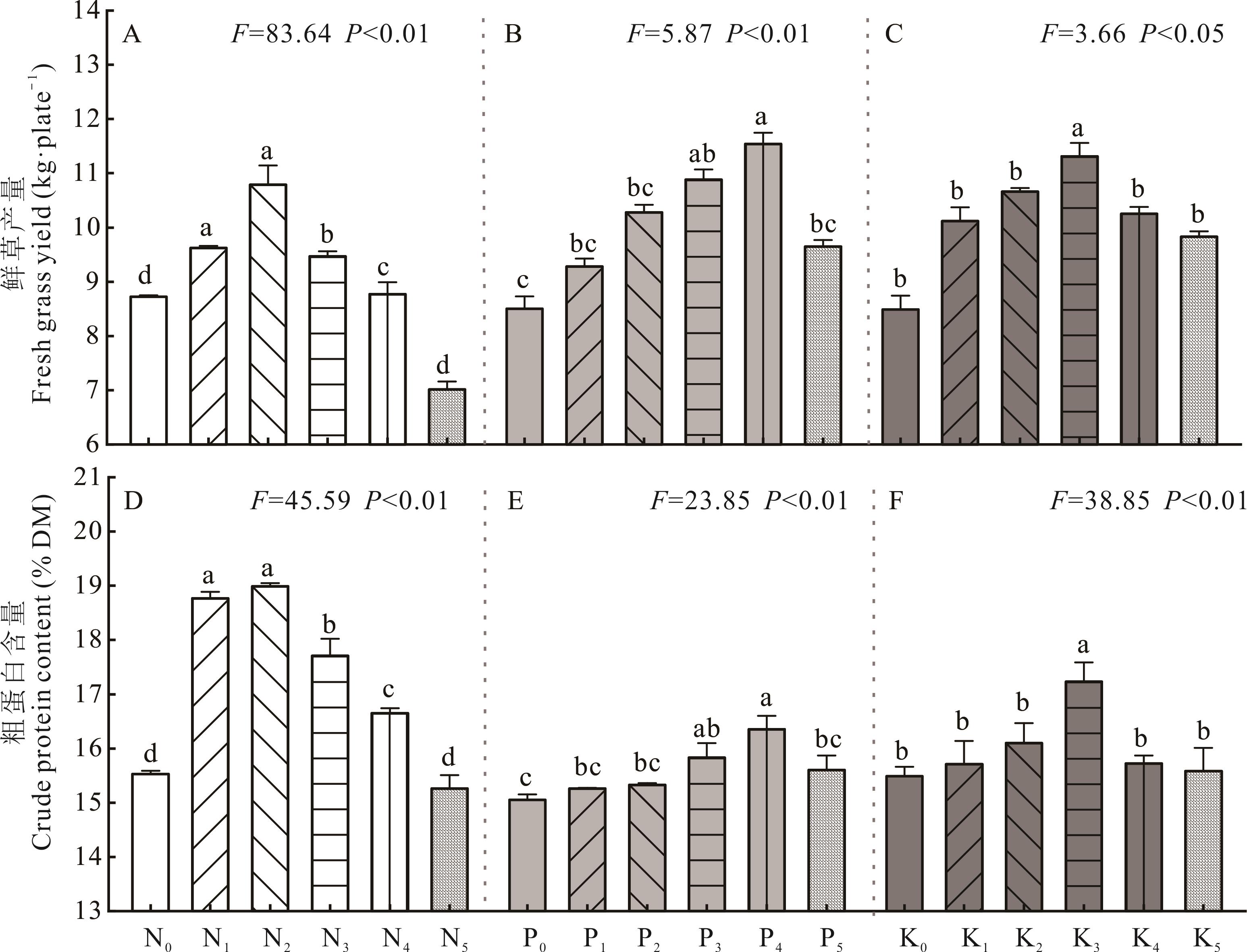
图1 不同氮磷钾水平对大麦饲草鲜草产量和粗蛋白含量的影响不同字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different letters indicate significant differences among treatments (P<0.05). N0~N5依次代表施氮0、5、10、20、40和80 mmol·L-1;P0~P5依次代表施磷0、0.25、0.50、1.00、2.00和4.00 mmol·L-1;K0~K5依次代表施钾0、1.5、3.0、6.0、12.0和24.0 mmol·L-1。N0-N5 represented nitrogen application rates of 0, 5, 10, 20, 40 and 80 mmol·L-1, respectively; P0-P5 represented phosphorus application rates of 0, 0.25, 0.50, 1.00, 2.00 and 4.00 mmol·L-1, respectively; K0-K5 represented potassium application rates of 0, 1.5, 3.0, 6.0, 12.0 and 24.0 mmol·L-1, respectively.
Fig.1 Effects of different levels of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium on fresh grass yield and crude protein content of barley forage
处理 Treatments | 变量代码Variables code | 鲜草产量 Fresh grass yield (kg·plate-1) | 粗蛋白含量 Crude protein content (%DM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | |||
| 1 | 5.00(-1) | 1.00(-1) | 3.00(-1) | 12.01 | 18.93 |
| 2 | 10.00(1) | 1.00(-1) | 3.00(-1) | 12.03 | 19.93 |
| 3 | 5.00(-1) | 2.00(1) | 3.00(-1) | 11.68 | 17.47 |
| 4 | 10.00(1) | 2.00(1) | 3.00(-1) | 12.17 | 17.56 |
| 5 | 5.00(-1) | 1.00(-1) | 6.00(1) | 11.60 | 15.60 |
| 6 | 10.00(1) | 1.00(-1) | 6.00(1) | 10.66 | 16.58 |
| 7 | 5.00(-1) | 2.00(1) | 6.00(1) | 11.45 | 17.12 |
| 8 | 10.00(1) | 2.00(1) | 6.00(1) | 11.03 | 17.98 |
| 9 | 3.30(-1.682) | 1.50(0) | 4.50(0) | 10.77 | 16.50 |
| 10 | 11.70(1.682) | 1.50(0) | 4.50(0) | 11.03 | 18.73 |
| 11 | 7.50(0) | 0.66(-1.682) | 4.50(0) | 12.11 | 17.74 |
| 12 | 7.50(0) | 2.34(1.682) | 4.50(0) | 12.37 | 17.97 |
| 13 | 7.50(0) | 1.50(0) | 1.98(-1.682) | 12.16 | 18.54 |
| 14 | 7.50(0) | 1.50(0) | 7.02(1.682) | 10.95 | 16.05 |
| 15 | 7.50(0) | 1.50(0) | 4.50(0) | 12.22 | 18.78 |
| 16 | 7.50(0) | 1.50(0) | 4.50(0) | 12.10 | 19.19 |
| 17 | 7.50(0) | 1.50(0) | 4.50(0) | 12.27 | 19.26 |
| 18 | 7.50(0) | 1.50(0) | 4.50(0) | 12.16 | 18.83 |
| 19 | 7.50(0) | 1.50(0) | 4.50(0) | 12.17 | 18.76 |
| 20 | 7.50(0) | 1.50(0) | 4.50(0) | 11.96 | 18.81 |
表2 3个变量及其观测响应的中心复合设计
Table 2 Central composite design of three variables and their observed responses
处理 Treatments | 变量代码Variables code | 鲜草产量 Fresh grass yield (kg·plate-1) | 粗蛋白含量 Crude protein content (%DM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | |||
| 1 | 5.00(-1) | 1.00(-1) | 3.00(-1) | 12.01 | 18.93 |
| 2 | 10.00(1) | 1.00(-1) | 3.00(-1) | 12.03 | 19.93 |
| 3 | 5.00(-1) | 2.00(1) | 3.00(-1) | 11.68 | 17.47 |
| 4 | 10.00(1) | 2.00(1) | 3.00(-1) | 12.17 | 17.56 |
| 5 | 5.00(-1) | 1.00(-1) | 6.00(1) | 11.60 | 15.60 |
| 6 | 10.00(1) | 1.00(-1) | 6.00(1) | 10.66 | 16.58 |
| 7 | 5.00(-1) | 2.00(1) | 6.00(1) | 11.45 | 17.12 |
| 8 | 10.00(1) | 2.00(1) | 6.00(1) | 11.03 | 17.98 |
| 9 | 3.30(-1.682) | 1.50(0) | 4.50(0) | 10.77 | 16.50 |
| 10 | 11.70(1.682) | 1.50(0) | 4.50(0) | 11.03 | 18.73 |
| 11 | 7.50(0) | 0.66(-1.682) | 4.50(0) | 12.11 | 17.74 |
| 12 | 7.50(0) | 2.34(1.682) | 4.50(0) | 12.37 | 17.97 |
| 13 | 7.50(0) | 1.50(0) | 1.98(-1.682) | 12.16 | 18.54 |
| 14 | 7.50(0) | 1.50(0) | 7.02(1.682) | 10.95 | 16.05 |
| 15 | 7.50(0) | 1.50(0) | 4.50(0) | 12.22 | 18.78 |
| 16 | 7.50(0) | 1.50(0) | 4.50(0) | 12.10 | 19.19 |
| 17 | 7.50(0) | 1.50(0) | 4.50(0) | 12.27 | 19.26 |
| 18 | 7.50(0) | 1.50(0) | 4.50(0) | 12.16 | 18.83 |
| 19 | 7.50(0) | 1.50(0) | 4.50(0) | 12.17 | 18.76 |
| 20 | 7.50(0) | 1.50(0) | 4.50(0) | 11.96 | 18.81 |
| 模型评价指标Model evaluation indicators | 鲜草产量Fresh grass yield | 粗蛋白含量Crude protein content |
|---|---|---|
| 标准偏差 Standard deviation (SD) | 0.13 | 0.29 |
| 均值 Mean value | 11.72 kg·plate-1 | 18.02%DM |
| 变异系数 Coefficient of variation (CV, %) | 1.11 | 1.59 |
| 模型相关系数 Model correlation coefficient (r) | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| 校正决定系数 Correction determination coefficient (R2adj) | 0.95 | 0.94 |
| 预测决定系数 Prediction determination coefficient (R2) | 0.85 | 0.82 |
| 相对准确度 Relative accuracy | 18.09 | 22.27 |
表3 试验模型相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis of experimental model
| 模型评价指标Model evaluation indicators | 鲜草产量Fresh grass yield | 粗蛋白含量Crude protein content |
|---|---|---|
| 标准偏差 Standard deviation (SD) | 0.13 | 0.29 |
| 均值 Mean value | 11.72 kg·plate-1 | 18.02%DM |
| 变异系数 Coefficient of variation (CV, %) | 1.11 | 1.59 |
| 模型相关系数 Model correlation coefficient (r) | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| 校正决定系数 Correction determination coefficient (R2adj) | 0.95 | 0.94 |
| 预测决定系数 Prediction determination coefficient (R2) | 0.85 | 0.82 |
| 相对准确度 Relative accuracy | 18.09 | 22.27 |
| 鲜草产量 Fresh grass yield (Y1) | 粗蛋白含量 Crude protein content (Y2) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
来源 Source | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 df | 均方 Mean square | F | P | 来源 Source | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 df | 均方 Mean square | F | P |
| 模型Model | 6.21 | 9 | 0.69 | 41.02 | <0.0001 | 模型Model | 25.27 | 9 | 2.81 | 34.31 | <0.0001 |
| A-N | 0.00 | 1 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.7961 | A-N | 3.27 | 1 | 3.27 | 39.92 | <0.0001 |
| B-P | 0.07 | 1 | 0.07 | 4.41 | 0.0620 | B-P | 0.02 | 1 | 0.02 | 0.24 | 0.6314 |
| C-K | 2.40 | 1 | 2.40 | 142.57 | <0.0001 | C-K | 8.54 | 1 | 8.54 | 104.30 | <0.0001 |
| AB | 0.03 | 1 | 0.03 | 1.50 | 0.2482 | AB | 0.13 | 1 | 0.13 | 1.62 | 0.2319 |
| AC | 0.22 | 1 | 0.22 | 13.14 | 0.0047 | AC | 0.07 | 1 | 0.07 | 0.86 | 0.3758 |
| BC | 0.11 | 1 | 0.11 | 6.70 | 0.0270 | BC | 5.70 | 1 | 5.70 | 69.58 | <0.0001 |
| A2 | 2.85 | 1 | 2.85 | 169.28 | <0.0001 | A2 | 2.77 | 1 | 2.77 | 33.83 | 0.0002 |
| B2 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.73 | 0.4144 | B2 | 1.80 | 1 | 1.80 | 22.00 | 0.0009 |
| C2 | 0.65 | 1 | 0.65 | 38.87 | <0.0001 | C2 | 4.38 | 1 | 4.38 | 53.55 | <0.0001 |
| 残差Residual | 0.17 | 10 | 0.02 | 残差Residual | 0.82 | 10 | 0.08 | ||||
| 缺失拟合项Lack of fit | 0.11 | 5 | 0.02 | 1.89 | 0.2516 | 缺失拟合项Lack of fit | 0.57 | 5 | 0.11 | 2.25 | 0.1972 |
| 纯误差Pure error | 0.06 | 5 | 0.01 | 纯误差Pure error | 0.25 | 5 | 0.05 | ||||
| 总计Total | 6.38 | 19 | 总计Total | 26.09 | 19 | ||||||
表4 鲜草产量和粗蛋白的二次多项式拟合模型的方差分析
Table 4 Analysis of variance for quadratic polynomial fitting models of fresh grass yield and crude protein
| 鲜草产量 Fresh grass yield (Y1) | 粗蛋白含量 Crude protein content (Y2) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
来源 Source | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 df | 均方 Mean square | F | P | 来源 Source | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 df | 均方 Mean square | F | P |
| 模型Model | 6.21 | 9 | 0.69 | 41.02 | <0.0001 | 模型Model | 25.27 | 9 | 2.81 | 34.31 | <0.0001 |
| A-N | 0.00 | 1 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.7961 | A-N | 3.27 | 1 | 3.27 | 39.92 | <0.0001 |
| B-P | 0.07 | 1 | 0.07 | 4.41 | 0.0620 | B-P | 0.02 | 1 | 0.02 | 0.24 | 0.6314 |
| C-K | 2.40 | 1 | 2.40 | 142.57 | <0.0001 | C-K | 8.54 | 1 | 8.54 | 104.30 | <0.0001 |
| AB | 0.03 | 1 | 0.03 | 1.50 | 0.2482 | AB | 0.13 | 1 | 0.13 | 1.62 | 0.2319 |
| AC | 0.22 | 1 | 0.22 | 13.14 | 0.0047 | AC | 0.07 | 1 | 0.07 | 0.86 | 0.3758 |
| BC | 0.11 | 1 | 0.11 | 6.70 | 0.0270 | BC | 5.70 | 1 | 5.70 | 69.58 | <0.0001 |
| A2 | 2.85 | 1 | 2.85 | 169.28 | <0.0001 | A2 | 2.77 | 1 | 2.77 | 33.83 | 0.0002 |
| B2 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.73 | 0.4144 | B2 | 1.80 | 1 | 1.80 | 22.00 | 0.0009 |
| C2 | 0.65 | 1 | 0.65 | 38.87 | <0.0001 | C2 | 4.38 | 1 | 4.38 | 53.55 | <0.0001 |
| 残差Residual | 0.17 | 10 | 0.02 | 残差Residual | 0.82 | 10 | 0.08 | ||||
| 缺失拟合项Lack of fit | 0.11 | 5 | 0.02 | 1.89 | 0.2516 | 缺失拟合项Lack of fit | 0.57 | 5 | 0.11 | 2.25 | 0.1972 |
| 纯误差Pure error | 0.06 | 5 | 0.01 | 纯误差Pure error | 0.25 | 5 | 0.05 | ||||
| 总计Total | 6.38 | 19 | 总计Total | 26.09 | 19 | ||||||
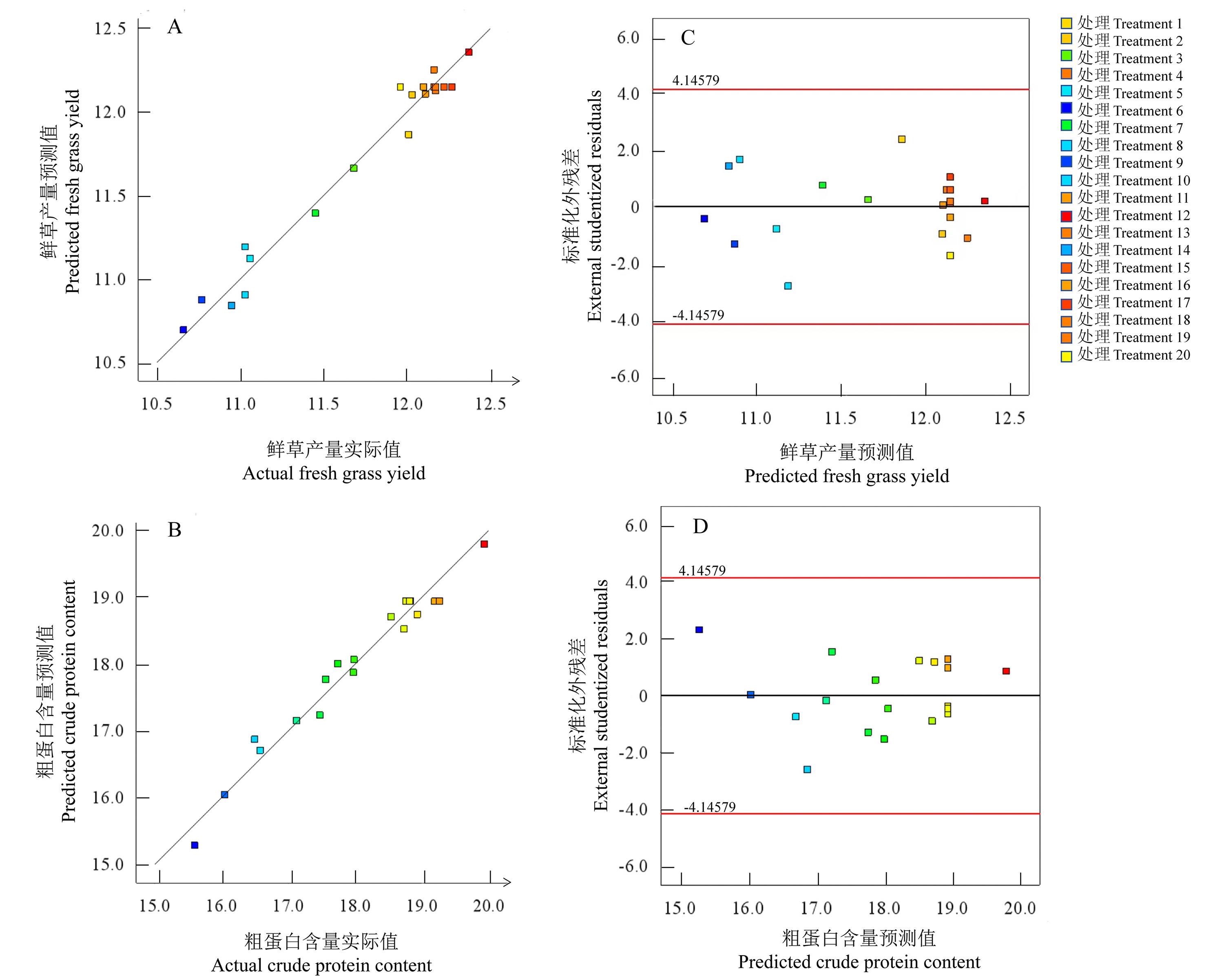
图2 鲜草产量和粗蛋白含量预测值与实际值对比(A, B)及残差与预测值的正态概率图(C, D)
Fig.2 Comparison of the prodicted fresh grass yield and crude protein content with the actual values (A, B) and the normal probability plots of the residuals and the prodicted values (C, D)
| 1 | Sturchio M A, Kannenberg S A, Knapp A K. Agrivoltaic arrays can maintain semi-arid grassland productivity and extend the seasonality of forage quality. Applied Energy, 2024, 356: 122418. |
| 2 | Wang W X, Ru Z, Guo H J, et al. Analysis of American market power in China’s forage imported market. Agricultural Economics and Management, 2022, 6: 78-87. |
| 王文信, 茹卓, 郭豪杰, 等. 中国牧草进口市场的美国市场势力分析. 农业经济与管理, 2022, 6: 78-87. | |
| 3 | Jia Y S, Du S, Wang Z J, et al. A review of herbage storage in pastoral areas of China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(9): 189-196. |
| 贾玉山, 都帅, 王志军, 等. 中国牧区饲草储备展望. 草业学报, 2015, 24(9): 189-196. | |
| 4 | Zhang C H, Zhao L, Zhao X Q. Theoretical basis, technical principles and realization of grassland multifunctional objective management. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 212-223. |
| 张春辉, 赵亮, 赵新全. 草地多功能目标管理的理论基础、技术原理及实现途径. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 212-223. | |
| 5 | Ireen D, Sven M, Christian P, et al. Annual cumulative ambient precipitation determines the effects of climate change on biomass and yield of three important field crops. Field Crops Research, 2023, 290: 108766. |
| 6 | Rajput V, Minkina T, Fedorenko A, et al. Toxicity of copper oxide nanoparticles on spring barley (Hordeum sativum distichum). Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 645: 1103-1113. |
| 7 | Long C Y, Qin S R, Qing Y L, et al. Experimental methods for bulbil storage and hydroponic cultivation of Polygonum viviparum. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(11): 2263-2273. |
| 龙成燕, 秦少容, 卿玉玲, 等. 珠芽蓼珠芽的贮藏及水培技术. 草业科学, 2020, 37(11): 2263-2273. | |
| 8 | Sharma N, Acharya S, Kumar K, et al. Hydroponics as an advanced technique for vegetable production: An overview. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 17(4): 364-371. |
| 9 | Zheng H M, Wang J, Wang M Z. The nutritive value and use of barley grass. Barley and Cereal Science, 2017, 34(2): 20-22, 27. |
| 郑慧敏, 王军, 王梦竹. 大麦苗的营养价值及应用. 大麦与谷类科学, 2017, 34(2): 20-22, 27. | |
| 10 | Nikkhah A. Barley forages for modern global ruminant agriculture: A review. Russian Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 39(3): 206-213. |
| 11 | Dong J Q, Jiang W, Huang Y X, et al. Nutritional value of hydroponic barley seedling and its application in livestock and poultry breeding. Modern Animal Husbandry Science & Technology, 2023, 100(9): 53-56. |
| 董佳强, 蒋微, 黄宇翔, 等. 水培大麦苗的营养价值及在畜禽养殖中的应用. 现代畜牧科技, 2023, 100(9): 53-56. | |
| 12 | Oliver G, Emma S H, Saskia B, et al. In-depth observation on the microbial and fungal community structure of four contrasting tomato cultivation systems in soil based and soilless culture systems. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 520834. |
| 13 | Geng G, Wang G, Stevanato P, et al. Physiological and proteomic analysis of different molecular mechanisms of sugar beet response to acidic and alkaline pH environment. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 682799. |
| 14 | Yang Z J, Wu X H, Grossnickle S C, et al. Formula fertilization promotes Phoebe bournei robust seedling cultivation. Forests, 2020, 11(7): 781. |
| 15 | Renata K, Dominika S, Marcin B, et al. The effect of different fertilization regimes on yield, selected nutrients, and bioactive compounds profiles of onion. Agronomy, 2021, 11(5): 883. |
| 16 | Wang X, Nie S H, Zhang J S, et al. Effects of combined application of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer on agronomic traits and yield of barley in dryland. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 54(11): 2028-2035. |
| 王仙, 聂石辉, 张金汕, 等. 氮磷钾肥配施对旱田大麦农艺性状和产量的影响. 新疆农业科学, 2017, 54(11): 2028-2035. | |
| 17 | Qiao J L, Guo M L, Dou Y W, et al. Optimization of nutrient solution formula and its effect on growth and production efficiency of hydroponic lettuce. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 54(2): 166-172. |
| 乔佳乐, 郭美玲, 窦煜炜, 等. 营养液配方优化及其对水培生菜生长和生产效率的影响. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 54(2): 166-172. | |
| 18 | Jang S, Lee Y A, Lee R A, et al. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of glycyrrhizic acid from licorice using response surface methodology. Integrative Medicine Research, 2017, 6(4): 388-394. |
| 19 | Liu Y, Wei S, Liao M. Optimization of ultrasonic extraction of phenolic compounds from Euryale ferox seed shells using response surface methodology. Industrial Crops and Products, 2013, 49: 837-843. |
| 20 | Zou T B, Wang M, Gan R Y, et al. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of anthocyanins from mulberry, using response surface methodology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2011, 12(5): 3006-3017. |
| 21 | General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. Determination of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in fertilizer by automatic analyzer, GB/T 22923-2008. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008: 1-3. |
| 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 肥料中氮、磷、钾的自动分析仪测定法, GB/T 22923-2008. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008: 1-3. | |
| 22 | Siewe B F, Kudre G T, Narayan B. Optimisation of ultrasound-assisted enzymatic extraction conditions of umami compounds from fish by-products using the combination of fractional factorial design and central composite design. Food Chemistry, 2021, 334: 127498. |
| 23 | Castagliola P. Response surfaces, mixtures, and ridge analyses. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series A: Statistics in Society, 2008, 171(1): 313. |
| 24 | Luo T, Kang H M, Yang W Z, et al. Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilization on the growth of Schima superba seedlings under hydroponic conditions. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2021, 50(4): 88-94, 112. |
| 罗婷, 康洪梅, 杨文忠, 等. 水培条件下氮磷钾配比施肥对木荷幼苗生长的影响. 西部林业科学, 2021, 50(4): 88-94, 112. | |
| 25 | Chen K, Liu S Q, Zhang Z K, et al. Effects of potassium nutrition on growth, photosynthetic characteristics and quality of garlic seedlings. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2011, 17(2): 506-512. |
| 陈昆, 刘世琦, 张自坤, 等. 钾素营养对大蒜生长、光合特性及品质的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(2): 506-512. | |
| 26 | Rhodes R, Miles N, Hughes C J. Interactions between potassium, calcium and magnesium in sugarcane grown on two contrasting soils in South Africa. Field Crops Research, 2018, 223: 1-11. |
| 27 | Qiao Y, Hu X T, Wang R, et al. Certification in optimum of potassium concentration applied to hydroponic celery based on principal component analysis. Northern Horticulture, 2016, 22: 5-10. |
| 乔源, 胡笑涛, 王瑞, 等. 基于主成分分析的水培芹菜最佳钾浓度筛选. 北方园艺, 2016, 22: 5-10. | |
| 28 | Su Y J, Hu X T, Wang W E, et al. Effects of potassium concentration on growth and dynamic absorption of mineral elements of hydroponic lettuce. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(8): 191-196, 204. |
| 苏苑君, 胡笑涛, 王文娥, 等. 钾浓度对水培生菜生长及矿质元素动态吸收的影响. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 44(8): 191-196, 204. | |
| 29 | Yu T F, Liu X J, Wu Y, et al. Fertilization effect of alfalfa high yield field and its recommended fertilizer application in Northwest drought irrigated area. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(8): 15-27. |
| 于铁峰, 刘晓静, 吴勇, 等. 西北干旱灌区紫花苜蓿高产田施肥效应及推荐施肥量研究. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 15-27. | |
| 30 | Du S P, Ma Z M, Tang C N, et al. Interactive effects of water, nitrogen, and potassium on yield and quality of grafted watermelon in gravel-mulched field. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(8): 1535-1544. |
| 杜少平, 马忠明, 唐超男, 等. 水、氮、钾互作对砂田嫁接西瓜产量和品质的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(8): 1535-1544. | |
| 31 | Ni K, Wang X, Lu Y, et al. Exploring the silage quality of alfalfa ensiled with the residues of astragalus and hawthorn. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 297: 122249. |
| 32 | Yang J Y. Responses of seedling growth and feed nutrient metabolism of hydroponic barley in different light formulas and nitrogen level. Urumchi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2023. |
| 杨金钰. 水培大麦苗生长及饲用营养物质代谢对不同光配方和氮素的响应. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2023. | |
| 33 | Yang L B. Effects of combined application of nitrogen and potassium on accumulation and transport of dry matter, and quality of rice. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2023. |
| 杨柳斌. 氮钾配合施用对水稻干物质积累转运及稻米品质的影响. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2023. | |
| 34 | Sun Y L, Zhao J W, Liu X S, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on photosynthetic daily variation, leaf morphology and dry matter yield of alfalfa at the early flowering growth stage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 63-75. |
| 孙延亮, 赵俊威, 刘选帅, 等. 施氮对苜蓿初花期光合日变化、叶片形态及干物质产量的影响. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 63-75. | |
| 35 | Welschmeyer N A, Lorenzen C J. Chlorophyll-specific photosynthesis and quantum efficiency at subsaturating light intensities. Journal of Phycology, 2010, 17(4): 283-293. |
| 36 | Zhao J T, Yang K X, Ma C H, et al. Photosynthetic physiological parameters and antioxidant capacity of alfalfa leaves in response to nitrogen application. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2023, 45(2): 46-55. |
| 赵建涛, 杨开鑫, 马春晖, 等. 苜蓿叶片光合生理参数及抗氧化能力对施氮的响应. 中国草地学报, 2023, 45(2): 46-55. | |
| 37 | Bai Y T, Wei Z J, Yan R R, et al. Effects of fertilization application on the yield of forage and nutrient content in Leymus chinensis mowing meadow. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2017, 39(4): 60-66. |
| 白玉婷, 卫智军, 闫瑞瑞, 等. 施肥对羊草割草地牧草产量及品质的影响. 中国草地学报, 2017, 39(4): 60-66. | |
| 38 | Chen S. Effects of different nitrogen-potassium ratios and irrigation and fertilization methods on potted citrus tree growth and soil. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2023. |
| 陈爽. 不同氮钾比例和灌溉施肥方式对盆栽柑橘树体生长及土壤的影响. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2023. | |
| 39 | Wang Y, Li D B, Qi X N, et al. Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus levels on grain yield and qualities of compact corn. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2006, 28(2): 184-188. |
| 王洋, 李东波, 齐晓宁, 等. 不同氮、磷水平对耐密型玉米籽粒产量和营养品质的影响. 吉林农业大学学报, 2006, 28(2): 184-188. | |
| 40 | Wang B. Effects of mixed cropping ratio and NPK fertilizers on the production performance and soil physical and chemical properties of Sorghum bicolor/Dolichos lablab grassland. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2023. |
| 王斌. 混播比例与氮磷钾肥配施对甜高粱/拉巴豆草地生产性能和土壤理化性质的影响. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2023. |
| [1] | 王飞, 刘彩玲, 何春梅, 李清华, 刘玉洁, 黄毅斌. 适宜磷、钾肥配比及稻秆半量还田提高紫云英产量与养分截获[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 81-89. |
| [2] | 方美烟, 王贤东, 于全平, 陈勇. 不同消化能、粗蛋白质水平饲粮对泌乳前期伊犁马营养物质消化代谢、血液生理生化指标和激素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 129-138. |
| [3] | 田秀娥, 万美娇, 王永军, 张阳. 水煮和提取处理对中草药干物质消化率和小肠可消化蛋白质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 207-215. |
| [4] | 娄珊宁, 侯扶江, 任继周. 用食物当量评价草地农业的生产力[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 1-16. |
| [5] | 王茜, 李志坚, 李晶, 周帮伟. 不同类型燕麦农艺和饲草品质性状分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 149-158. |
| [6] | 王亚麒, 袁玲. 甜高粱、高丹草和拉巴豆对难溶性磷的活化与吸收[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(10): 33-43. |
| [7] | 任晓利, 崔纪菡, 刘猛, 赵宇, 艾月鹏, 刘斐, 南春梅, 夏雪岩, 李顺国. 夏播饲用谷子农艺性状与品质评价[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 15-26. |
| [8] | 胡安, 康颖, 陈先江, 侯扶江. 刈割时间对黄土高原紫花苜蓿产量与营养品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(9): 57-65. |
| [9] | 张昌吉, 李成, 张勇, 郭武君, 张利平, 滚双宝. 甘肃高山细毛羊妊娠母羊营养需要量估测[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(6): 168-175. |
| [10] | 王文石, 田雨, 娄玉杰. 施用鸡粪对特高多花黑麦草SPAD值,干草产量和蛋白质含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 240-244. |
| [11] | 姬奇武,韩汝旦,董宽虎,马雪豪. 山西不同居群白羊草的营养成分及瘤胃降解规律[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(9): 53-62. |
| [12] | 吕小东,王建光,孙启忠,姚贵平,高凤芹. 苜蓿人工草地高光谱遥感估产模型的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(1): 84-91. |
| [13] | 惠文森,王康英,申晓蓉,刘慧霞. 酵母菌发酵玉米秸秆试验研究[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(6): 180-185. |
| [14] | 王齐,王有国,师春娟,孙吉雄,谭一凡. 中水水培对4种绿地植物生长及光合生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(6): 106-113. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||