

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (12): 122-133.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024048
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
陈莺宇1( ), 邱亚娟1, 邵晓龄1, 黄钰芳1,2,3(
), 邱亚娟1, 邵晓龄1, 黄钰芳1,2,3( ), 杨扶德1, 陈林杰1, 陈红刚1,2, 谢田朋1,2
), 杨扶德1, 陈林杰1, 陈红刚1,2, 谢田朋1,2
收稿日期:2024-02-02
修回日期:2024-03-07
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2024-10-09
通讯作者:
黄钰芳
作者简介:. E-mail: 1049395950@qq.com基金资助:
Ying-yu CHEN1( ), Ya-juan QIU1, Xiao-ling SHAO1, Yu-fang HUANG1,2,3(
), Ya-juan QIU1, Xiao-ling SHAO1, Yu-fang HUANG1,2,3( ), Fu-de YANG1, Lin-jie CHEN1, Hong-gang CHEN1,2, Tian-peng XIE1,2
), Fu-de YANG1, Lin-jie CHEN1, Hong-gang CHEN1,2, Tian-peng XIE1,2
Received:2024-02-02
Revised:2024-03-07
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-10-09
Contact:
Yu-fang HUANG
摘要:
为探究纹党连作土壤浸提液对其种子萌发及幼苗生长的自毒效应,并筛选出其中潜在的化感自毒物质,选取连作1、2和3年的纹党根际土壤,利用种子发芽试验及幼苗生长试验研究其浸提液对纹党种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响,并利用气质联用技术(GC-MS)对根际土壤中的自毒物质进行鉴定。结果表明,各连作年限土壤浸提液对纹党种子的萌发及幼苗的生长均表现出“低促高抑”的影响趋势;在同等抑制浓度条件下,连作3年的抑制作用最强,连作1年的最弱。纹党幼苗叶片叶绿素的含量以及过氧化氢酶、过氧化物酶、超氧化物歧化酶的活性随土壤浸提液浓度的增大先升高后降低,丙二醛、脯氨酸的含量随土壤浸提液浓度的增大而上升,且连作3年的影响效应最强。GC-MS结果显示,连作1、2和3年土壤浸提液中分别检测出12、18和8种化学物质,包括烃类、醇类、酮类及脂肪酸类等多种化合物。纹党连作土壤浸提液对其种子萌发和幼苗生长具有自毒效应;自毒作用是纹党连作障碍发生的原因之一。
陈莺宇, 邱亚娟, 邵晓龄, 黄钰芳, 杨扶德, 陈林杰, 陈红刚, 谢田朋. 纹党连作土壤浸提液对其种子萌发及幼苗生长的自毒效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 122-133.
Ying-yu CHEN, Ya-juan QIU, Xiao-ling SHAO, Yu-fang HUANG, Fu-de YANG, Lin-jie CHEN, Hong-gang CHEN, Tian-peng XIE. A study of autotoxic effects of soil extract from continuously cropped Codonopsis pilosula var. modesta on seed germination and seedling growth[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(12): 122-133.
年限 Years | 浓度Content (g·L-1) | 测定指标Determination index | 化感效应指数Allelopathic response index | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GR (%) | GP (%) | GI | RL (cm) | GR | GP | GI | RL | SE | ||
| 1 | CK | 0.77±0.00bc | 0.37±0.02bcde | 13.32±0.04bc | 7.47±0.18c | |||||
| 15 | 0.85±0.04a | 0.44±0.01ab | 14.82±0.52a | 7.55±0.06c | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.0875 | |
| 25 | 0.86±0.01a | 0.50±0.03a | 15.10±0.47a | 10.48±0.22a | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.29 | 0.1925 | |
| 50 | 0.84±0.01a | 0.40±0.05bc | 14.41±0.09ab | 10.31±0.43a | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.28 | 0.1250 | |
| 100 | 0.81±0.06ab | 0.38±0.03bcd | 14.15±0.98ab | 9.50±0.52b | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.21 | 0.0875 | |
| 150 | 0.76±0.01bcd | 0.36±0.04bcde | 13.23±0.18bc | 6.79±0.30d | -0.02 | -0.01 | -0.04 | -0.08 | -0.0375 | |
| 200 | 0.75±0.05bcd | 0.34±0.01cde | 12.53±0.93cd | 5.29±0.15e | -0.03 | -0.06 | -0.08 | -0.29 | -0.1150 | |
| 300 | 0.73±0.01cd | 0.31±0.02de | 12.22±0.06cd | 4.82±0.30ef | -0.06 | -0.08 | -0.18 | -0.35 | -0.1675 | |
| 500 | 0.70±0.01d | 0.29±0.07e | 11.82±0.21d | 4.42±0.37f | -0.10 | -0.11 | -0.22 | -0.40 | -0.2075 | |
| 2 | CK | 0.77±0.00abc | 0.37±0.02bc | 13.32±0.04abc | 7.47±0.18c | |||||
| 15 | 0.83±0.09ab | 0.41±0.02b | 14.30±1.53ab | 7.50±0.39c | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.0575 | |
| 25 | 0.85±0.00a | 0.47±0.01a | 14.82±0.01a | 10.15±0.22a | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.1650 | |
| 50 | 0.81±0.07abc | 0.37±0.05bc | 13.58±1.41abc | 9.20±0.38b | 0.05 | 0.02 | -0.01 | 0.19 | 0.0625 | |
| 100 | 0.77±0.02abc | 0.32±0.03cd | 13.02±0.25bc | 6.73±0.21d | -0.01 | -0.02 | -0.14 | -0.09 | -0.0650 | |
| 150 | 0.73±0.04bcd | 0.31±0.02cd | 12.58±0.50bcd | 4.59±0.06e | -0.06 | -0.06 | -0.18 | -0.38 | -0.1700 | |
| 200 | 0.72±0.01cd | 0.28±0.02de | 12.31±0.06cd | 4.50±0.29e | -0.06 | -0.08 | -0.26 | -0.39 | -0.1975 | |
| 300 | 0.71±0.01cd | 0.26±0.01de | 11.92±0.08cd | 3.92±0.43f | -0.08 | -0.11 | -0.30 | -0.47 | -0.2400 | |
| 500 | 0.64±0.01d | 0.22±0.03e | 10.90±0.08d | 3.42±0.08g | -0.17 | -0.18 | -0.41 | -0.54 | -0.3250 | |
| 3 | CK | 0.77±0.00a | 0.37±0.02ab | 13.32±0.04abc | 7.47±0.18b | |||||
| 15 | 0.79±0.02a | 0.40±0.02a | 13.39±0.62ab | 7.48±0.18b | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.0225 | |
| 25 | 0.82±0.05a | 0.43±0.08a | 14.14±0.94a | 10.12±0.10a | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.26 | 0.1275 | |
| 50 | 0.74±0.00ab | 0.36±0.01ab | 12.74±0.08bcd | 6.82±0.25c | -0.04 | -0.04 | -0.04 | -0.08 | -0.0500 | |
| 100 | 0.69±0.03bc | 0.34±0.01abc | 12.12±0.44cde | 6.03±0.11d | -0.10 | -0.09 | -0.09 | -0.19 | -0.1175 | |
| 150 | 0.66±0.04c | 0.30±0.03bc | 11.56±0.80de | 4.32±0.54e | -0.15 | -0.13 | -0.19 | -0.42 | -0.2225 | |
| 200 | 0.65±0.00c | 0.27±0.20cd | 11.47±0.05e | 3.75±0.10f | -0.16 | -0.14 | -0.28 | -0.49 | -0.2675 | |
| 300 | 0.64±0.04c | 0.20±0.06de | 10.22±0.08f | 3.22±0.21g | -0.17 | -0.23 | -0.47 | -0.57 | -0.3600 | |
| 500 | 0.54±0.06d | 0.13±0.10e | 8.07±0.59g | 3.08±0.08g | -0.30 | -0.39 | -0.66 | -0.58 | -0.4825 | |
表1 纹党不同连作年限根际土壤浸提液对其种子萌发的影响
Table 1 Effect of soil water extracts in different continuous cropping years on seeds germination of C. pilosula var. modesta
年限 Years | 浓度Content (g·L-1) | 测定指标Determination index | 化感效应指数Allelopathic response index | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GR (%) | GP (%) | GI | RL (cm) | GR | GP | GI | RL | SE | ||
| 1 | CK | 0.77±0.00bc | 0.37±0.02bcde | 13.32±0.04bc | 7.47±0.18c | |||||
| 15 | 0.85±0.04a | 0.44±0.01ab | 14.82±0.52a | 7.55±0.06c | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.0875 | |
| 25 | 0.86±0.01a | 0.50±0.03a | 15.10±0.47a | 10.48±0.22a | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.29 | 0.1925 | |
| 50 | 0.84±0.01a | 0.40±0.05bc | 14.41±0.09ab | 10.31±0.43a | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.28 | 0.1250 | |
| 100 | 0.81±0.06ab | 0.38±0.03bcd | 14.15±0.98ab | 9.50±0.52b | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.21 | 0.0875 | |
| 150 | 0.76±0.01bcd | 0.36±0.04bcde | 13.23±0.18bc | 6.79±0.30d | -0.02 | -0.01 | -0.04 | -0.08 | -0.0375 | |
| 200 | 0.75±0.05bcd | 0.34±0.01cde | 12.53±0.93cd | 5.29±0.15e | -0.03 | -0.06 | -0.08 | -0.29 | -0.1150 | |
| 300 | 0.73±0.01cd | 0.31±0.02de | 12.22±0.06cd | 4.82±0.30ef | -0.06 | -0.08 | -0.18 | -0.35 | -0.1675 | |
| 500 | 0.70±0.01d | 0.29±0.07e | 11.82±0.21d | 4.42±0.37f | -0.10 | -0.11 | -0.22 | -0.40 | -0.2075 | |
| 2 | CK | 0.77±0.00abc | 0.37±0.02bc | 13.32±0.04abc | 7.47±0.18c | |||||
| 15 | 0.83±0.09ab | 0.41±0.02b | 14.30±1.53ab | 7.50±0.39c | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.0575 | |
| 25 | 0.85±0.00a | 0.47±0.01a | 14.82±0.01a | 10.15±0.22a | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.1650 | |
| 50 | 0.81±0.07abc | 0.37±0.05bc | 13.58±1.41abc | 9.20±0.38b | 0.05 | 0.02 | -0.01 | 0.19 | 0.0625 | |
| 100 | 0.77±0.02abc | 0.32±0.03cd | 13.02±0.25bc | 6.73±0.21d | -0.01 | -0.02 | -0.14 | -0.09 | -0.0650 | |
| 150 | 0.73±0.04bcd | 0.31±0.02cd | 12.58±0.50bcd | 4.59±0.06e | -0.06 | -0.06 | -0.18 | -0.38 | -0.1700 | |
| 200 | 0.72±0.01cd | 0.28±0.02de | 12.31±0.06cd | 4.50±0.29e | -0.06 | -0.08 | -0.26 | -0.39 | -0.1975 | |
| 300 | 0.71±0.01cd | 0.26±0.01de | 11.92±0.08cd | 3.92±0.43f | -0.08 | -0.11 | -0.30 | -0.47 | -0.2400 | |
| 500 | 0.64±0.01d | 0.22±0.03e | 10.90±0.08d | 3.42±0.08g | -0.17 | -0.18 | -0.41 | -0.54 | -0.3250 | |
| 3 | CK | 0.77±0.00a | 0.37±0.02ab | 13.32±0.04abc | 7.47±0.18b | |||||
| 15 | 0.79±0.02a | 0.40±0.02a | 13.39±0.62ab | 7.48±0.18b | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.0225 | |
| 25 | 0.82±0.05a | 0.43±0.08a | 14.14±0.94a | 10.12±0.10a | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.26 | 0.1275 | |
| 50 | 0.74±0.00ab | 0.36±0.01ab | 12.74±0.08bcd | 6.82±0.25c | -0.04 | -0.04 | -0.04 | -0.08 | -0.0500 | |
| 100 | 0.69±0.03bc | 0.34±0.01abc | 12.12±0.44cde | 6.03±0.11d | -0.10 | -0.09 | -0.09 | -0.19 | -0.1175 | |
| 150 | 0.66±0.04c | 0.30±0.03bc | 11.56±0.80de | 4.32±0.54e | -0.15 | -0.13 | -0.19 | -0.42 | -0.2225 | |
| 200 | 0.65±0.00c | 0.27±0.20cd | 11.47±0.05e | 3.75±0.10f | -0.16 | -0.14 | -0.28 | -0.49 | -0.2675 | |
| 300 | 0.64±0.04c | 0.20±0.06de | 10.22±0.08f | 3.22±0.21g | -0.17 | -0.23 | -0.47 | -0.57 | -0.3600 | |
| 500 | 0.54±0.06d | 0.13±0.10e | 8.07±0.59g | 3.08±0.08g | -0.30 | -0.39 | -0.66 | -0.58 | -0.4825 | |
年限 Year | 浓度Content (g·L-1) | 测定指标Determination index | 化感效应指数Allelopathic response index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RL (cm) | SL (cm) | FW (g·10 plants-1) | RL | SL | FW | SE | ||
| 1 | CK | 6.24±0.05c | 4.16±0.10c | 0.1918±0.02b | ||||
| 100 | 7.54±0.23ab | 5.39±0.17a | 0.2259±0.01a | 0.17 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.1839 | |
| 150 | 8.02±0.19a | 5.48±0.31a | 0.2361±0.01a | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.2170 | |
| 250 | 7.08±0.05b | 4.74±0.23b | 0.2048±0.03ab | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.1014 | |
| 350 | 6.48±0.27c | 4.31±0.17bc | 0.1759±0.01b | 0.04 | 0.03 | -0.08 | -0.0039 | |
| 550 | 5.27±0.59d | 3.97±0.38cd | 0.1371±0.01c | -0.14 | -0.04 | -0.29 | -0.1573 | |
| 750 | 4.49±0.43e | 3.68±0.34d | 0.1293±0.00c | -0.27 | -0.12 | -0.33 | -0.2367 | |
| 2 | CK | 6.24±0.05b | 4.16±0.10cd | 0.1918±0.02ab | ||||
| 100 | 7.26±0.12a | 4.81±0.15b | 0.2069±0.07a | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.1161 | |
| 150 | 6.55±0.32b | 5.24±0.27a | 0.2093±0.03a | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.1124 | |
| 250 | 5.79±0.48c | 4.46±0.24c | 0.1427±0.02bc | -0.06 | 0.07 | -0.26 | -0.0817 | |
| 350 | 5.20±0.09d | 3.91±0.04de | 0.1319±0.00c | -0.15 | -0.06 | -0.31 | -0.1755 | |
| 550 | 4.61±0.22e | 3.76±0.25e | 0.1295±0.02c | -0.25 | -0.10 | -0.32 | -0.2232 | |
| 750 | 4.31±0.20e | 2.47 ±0.07f | 0.1089±0.00c | -0.30 | -0.41 | -0.43 | -0.3792 | |
| 3 | CK | 6.24±0.05b | 4.16±0.10a | 0.1918±0.02a | ||||
| 100 | 7.17±0.33a | 4.50±0.11a | 0.2067±0.01a | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.0926 | |
| 150 | 5.24±0.87c | 4.35±0.29a | 0.1931±0.01a | -0.15 | 0.04 | 0.01 | -0.0319 | |
| 250 | 5.08±0.19cd | 4.10±0.66b | 0.1375±0.03b | -0.17 | -0.02 | -0.28 | -0.1570 | |
| 350 | 4.50±0.28d | 3.53±0.09c | 0.1125±0.01bc | -0.27 | -0.15 | -0.41 | -0.2773 | |
| 550 | 3.63±0.20e | 2.42±0.31c | 0.1085±0.00c | -0.41 | -0.42 | -0.43 | -0.4209 | |
| 750 | 3.21±0.10e | 2.25±0.10c | 0.0848±0.00c | -0.48 | -0.46 | -0.56 | -0.4984 | |
表2 纹党不同连作年限根际土壤浸提液对其幼苗生长的影响
Table 2 Effect of soil water extracts in different continuous cropping years on seedlings of C. pilosula var. modesta
年限 Year | 浓度Content (g·L-1) | 测定指标Determination index | 化感效应指数Allelopathic response index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RL (cm) | SL (cm) | FW (g·10 plants-1) | RL | SL | FW | SE | ||
| 1 | CK | 6.24±0.05c | 4.16±0.10c | 0.1918±0.02b | ||||
| 100 | 7.54±0.23ab | 5.39±0.17a | 0.2259±0.01a | 0.17 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.1839 | |
| 150 | 8.02±0.19a | 5.48±0.31a | 0.2361±0.01a | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.2170 | |
| 250 | 7.08±0.05b | 4.74±0.23b | 0.2048±0.03ab | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.1014 | |
| 350 | 6.48±0.27c | 4.31±0.17bc | 0.1759±0.01b | 0.04 | 0.03 | -0.08 | -0.0039 | |
| 550 | 5.27±0.59d | 3.97±0.38cd | 0.1371±0.01c | -0.14 | -0.04 | -0.29 | -0.1573 | |
| 750 | 4.49±0.43e | 3.68±0.34d | 0.1293±0.00c | -0.27 | -0.12 | -0.33 | -0.2367 | |
| 2 | CK | 6.24±0.05b | 4.16±0.10cd | 0.1918±0.02ab | ||||
| 100 | 7.26±0.12a | 4.81±0.15b | 0.2069±0.07a | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.1161 | |
| 150 | 6.55±0.32b | 5.24±0.27a | 0.2093±0.03a | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.1124 | |
| 250 | 5.79±0.48c | 4.46±0.24c | 0.1427±0.02bc | -0.06 | 0.07 | -0.26 | -0.0817 | |
| 350 | 5.20±0.09d | 3.91±0.04de | 0.1319±0.00c | -0.15 | -0.06 | -0.31 | -0.1755 | |
| 550 | 4.61±0.22e | 3.76±0.25e | 0.1295±0.02c | -0.25 | -0.10 | -0.32 | -0.2232 | |
| 750 | 4.31±0.20e | 2.47 ±0.07f | 0.1089±0.00c | -0.30 | -0.41 | -0.43 | -0.3792 | |
| 3 | CK | 6.24±0.05b | 4.16±0.10a | 0.1918±0.02a | ||||
| 100 | 7.17±0.33a | 4.50±0.11a | 0.2067±0.01a | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.0926 | |
| 150 | 5.24±0.87c | 4.35±0.29a | 0.1931±0.01a | -0.15 | 0.04 | 0.01 | -0.0319 | |
| 250 | 5.08±0.19cd | 4.10±0.66b | 0.1375±0.03b | -0.17 | -0.02 | -0.28 | -0.1570 | |
| 350 | 4.50±0.28d | 3.53±0.09c | 0.1125±0.01bc | -0.27 | -0.15 | -0.41 | -0.2773 | |
| 550 | 3.63±0.20e | 2.42±0.31c | 0.1085±0.00c | -0.41 | -0.42 | -0.43 | -0.4209 | |
| 750 | 3.21±0.10e | 2.25±0.10c | 0.0848±0.00c | -0.48 | -0.46 | -0.56 | -0.4984 | |
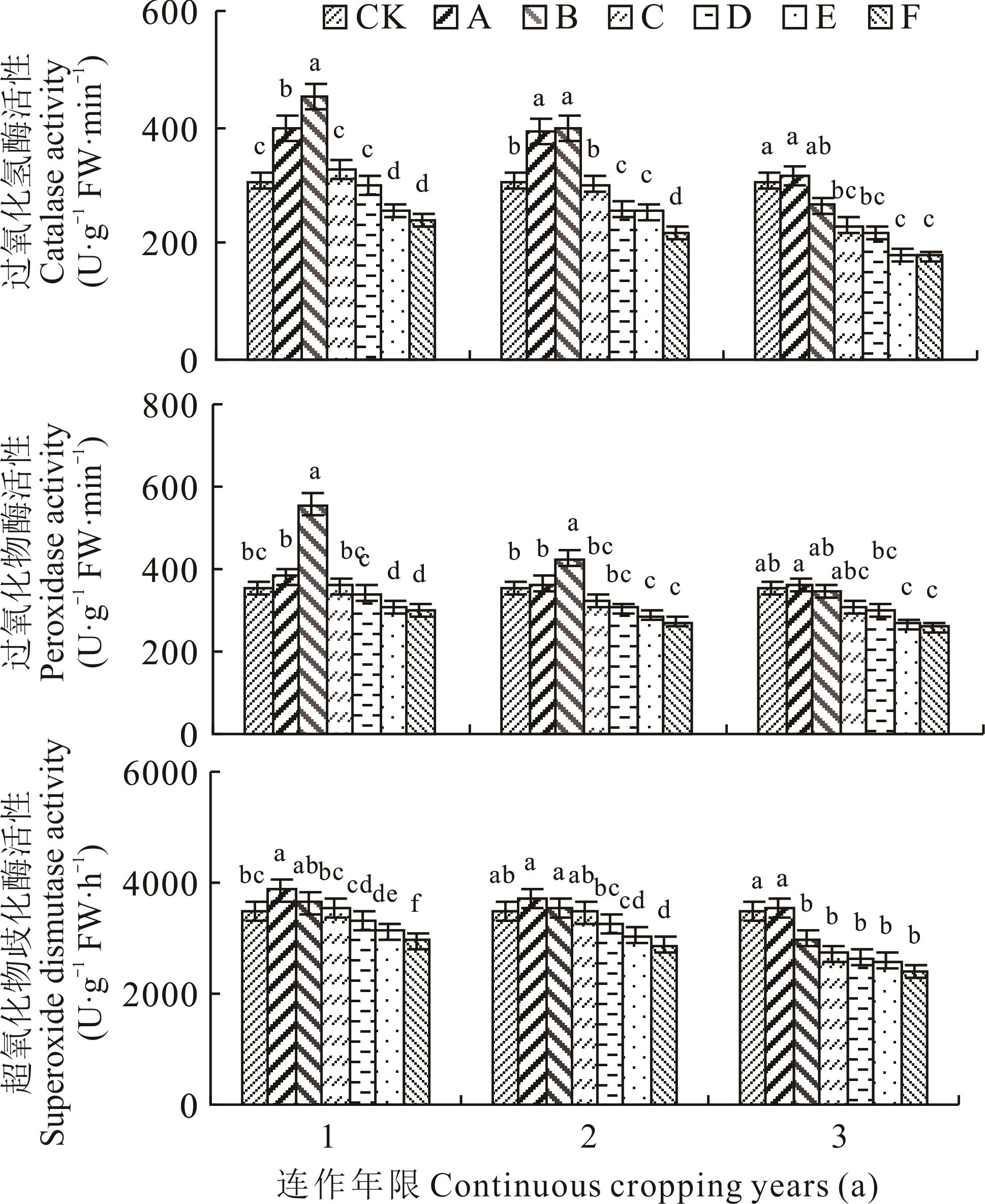
图1 不同连作年限土壤浸提液对纹党幼苗过氧化氢酶、过氧化物酶、超氧化物歧化酶活性的影响A、B、C、D、E、F分别表示浸提液浓度为100、150、250、350、550和750 g·L-1,小写字母表示同一连作年限不同浓度间有显著性差异(P<0.05),下同。 The A, B, C, D, E and F indicate that the concentration of the extract is 100, 150, 250, 350, 550 and 750 g·L-1, respectively, and the lowercase letters indicate that there are significant differences among different concentrations in the same continuous cultivation years(P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.1 Effects of soil extracts on catalase, peroxidase and superoxide dismutase activities of seedlings with different continuous cropping years
保留时间 Retention time (min) | 化合物 Compound | 分子式 Molecular formula | 连作年限 Continuous cropping years | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| 4.678 | 对二甲苯Paraxylene | C8H10 | 3.07 | 5.02 | 3.33 |
| 4.981 | 2-苯乙基异烟酸酯Isonicotinic acid, 2-phenylethyl ester | C14H13NO2 | 4.01 | 7.01 | 4.52 |
| 6.286 | 五氯乙烷Ethane, pentachloro- | C2HCl5 | 0.39 | 0.65 | - |
| 7.814 | 六氯乙烷Ethane, hexachloro- | C2Cl6 | - | 0.52 | - |
| 8.987 | 3-丁基吡啶Pyridine, 3-butyl- | C9H13N | - | 0.45 | - |
| 14.840 | 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯Dimethyl phthalate | C10H10O4 | 1.31 | 1.17 | 0.68 |
| 18.491 | 正十六烷Hexadecane | C16H34 | 0.51 | - | - |
| 20.190 | 1-十六烷醇1-Hexadecanol | C16H34O | 0.43 | - | - |
| 21.981 | 4, 8a-二甲基-6-异丙烯基-3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 8a-六氢萘-2-酮2(1H)Naphthalenone, 3,5,6,7,8,8a-hexahydro-4,8a-dimethyl-6-(1-methylethenyl)- | C15H22O | - | 1.00 | - |
| 22.725 | 3-吲哚乙醇Tryptophol | C10H11NO | - | 1.26 | - |
| 25.535 | 3, 6-二甲基-7-异丙烯基-6-乙烯基八氢环己并[1, 2-b]呋喃-2-酮2(3H)-Benzofuranone, 6-ethenylhexahydro-3,6-dimethyl-7-(1-methylethenyl)-, [3S-(3.alpha.,3a.alpha.,6.alpha.,7.beta.,7a.beta.)]- | C15H22O2 | - | 0.85 | - |
| 27.606 | (-)-异长叶醇Isolongifolol | C15H26O | - | 0.50 | - |
| 29.237 | (4S,4αR,6R,8αR)-4α-羟基-4,8α-二甲基-6-(2-丙烯基)-3,4,5,6,7,8-六氢-2H-萘-1-酮 (4S,4αR,6R,8αR)-4α-hydroxy-4,8α-dimethyl-6-prop-1-en-2-yl-3,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-2H-naphthalen-1-one | C15H24O2 | - | 1.30 | - |
| 29.649 | 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯Dibutyl phthalate | C16H22O4 | 14.72 | 1.94 | 6.79 |
| 30.038 | 棕榈酸n-Hexadecanoic acid | C16H32O2 | - | 4.23 | - |
| 31.320 | 喘诺木烯内酯Reynosin | C15H20O3 | - | 7.33 | - |
| 37.236 | 十六碳酰胺Hexadecanamide | C16H33NO | 13.29 | 13.55 | - |
| 41.745 | E, E, Z-1, 3, 12-十九碳三烯-5, 14-二醇E,E,Z-1,3,12-Nonadecatriene-5,14-diolE,E,Z-1,3,12-Nonadecatriene-5,14-diol | C19H34O2 | - | - | 2.17 |
| 41.751 | 2-油烯基-外消旋甘油E,E,Z-1,3,12-Nonadecatriene-5,14-diol | C19H34O2 | 3.47 | - | - |
| 41.957 | 油酸酰胺9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | C18H35NO | 37.29 | 40.03 | 20.33 |
| 42.913 | 2,2'-亚甲基双-(4-甲基-6-叔丁基苯酚)Phenol, 2, 2'-methylenebis-6-(1, 1-dimethylethyl)-4-methyl- | C23H32O2 | 13.38 | 5.47 | 6.79 |
| 45.402 | 邻苯二甲酸二辛酯Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate | C24H38O4 | 8.13 | 7.71 | 55.40 |
表3 纹党不同连作年限根际土壤浸提液中的化学成分相对含量
Table 3 Chemical components relative content of rhizosphere soil leaching solution in different years of continuous cropping (%)
保留时间 Retention time (min) | 化合物 Compound | 分子式 Molecular formula | 连作年限 Continuous cropping years | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| 4.678 | 对二甲苯Paraxylene | C8H10 | 3.07 | 5.02 | 3.33 |
| 4.981 | 2-苯乙基异烟酸酯Isonicotinic acid, 2-phenylethyl ester | C14H13NO2 | 4.01 | 7.01 | 4.52 |
| 6.286 | 五氯乙烷Ethane, pentachloro- | C2HCl5 | 0.39 | 0.65 | - |
| 7.814 | 六氯乙烷Ethane, hexachloro- | C2Cl6 | - | 0.52 | - |
| 8.987 | 3-丁基吡啶Pyridine, 3-butyl- | C9H13N | - | 0.45 | - |
| 14.840 | 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯Dimethyl phthalate | C10H10O4 | 1.31 | 1.17 | 0.68 |
| 18.491 | 正十六烷Hexadecane | C16H34 | 0.51 | - | - |
| 20.190 | 1-十六烷醇1-Hexadecanol | C16H34O | 0.43 | - | - |
| 21.981 | 4, 8a-二甲基-6-异丙烯基-3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 8a-六氢萘-2-酮2(1H)Naphthalenone, 3,5,6,7,8,8a-hexahydro-4,8a-dimethyl-6-(1-methylethenyl)- | C15H22O | - | 1.00 | - |
| 22.725 | 3-吲哚乙醇Tryptophol | C10H11NO | - | 1.26 | - |
| 25.535 | 3, 6-二甲基-7-异丙烯基-6-乙烯基八氢环己并[1, 2-b]呋喃-2-酮2(3H)-Benzofuranone, 6-ethenylhexahydro-3,6-dimethyl-7-(1-methylethenyl)-, [3S-(3.alpha.,3a.alpha.,6.alpha.,7.beta.,7a.beta.)]- | C15H22O2 | - | 0.85 | - |
| 27.606 | (-)-异长叶醇Isolongifolol | C15H26O | - | 0.50 | - |
| 29.237 | (4S,4αR,6R,8αR)-4α-羟基-4,8α-二甲基-6-(2-丙烯基)-3,4,5,6,7,8-六氢-2H-萘-1-酮 (4S,4αR,6R,8αR)-4α-hydroxy-4,8α-dimethyl-6-prop-1-en-2-yl-3,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-2H-naphthalen-1-one | C15H24O2 | - | 1.30 | - |
| 29.649 | 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯Dibutyl phthalate | C16H22O4 | 14.72 | 1.94 | 6.79 |
| 30.038 | 棕榈酸n-Hexadecanoic acid | C16H32O2 | - | 4.23 | - |
| 31.320 | 喘诺木烯内酯Reynosin | C15H20O3 | - | 7.33 | - |
| 37.236 | 十六碳酰胺Hexadecanamide | C16H33NO | 13.29 | 13.55 | - |
| 41.745 | E, E, Z-1, 3, 12-十九碳三烯-5, 14-二醇E,E,Z-1,3,12-Nonadecatriene-5,14-diolE,E,Z-1,3,12-Nonadecatriene-5,14-diol | C19H34O2 | - | - | 2.17 |
| 41.751 | 2-油烯基-外消旋甘油E,E,Z-1,3,12-Nonadecatriene-5,14-diol | C19H34O2 | 3.47 | - | - |
| 41.957 | 油酸酰胺9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | C18H35NO | 37.29 | 40.03 | 20.33 |
| 42.913 | 2,2'-亚甲基双-(4-甲基-6-叔丁基苯酚)Phenol, 2, 2'-methylenebis-6-(1, 1-dimethylethyl)-4-methyl- | C23H32O2 | 13.38 | 5.47 | 6.79 |
| 45.402 | 邻苯二甲酸二辛酯Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate | C24H38O4 | 8.13 | 7.71 | 55.40 |
| 1 | Yang Y. The alleviating effect of microbial fertilizer on replant problem of Astragalus. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2022. |
| 杨焱. 微生物肥料对黄芪连作障碍的缓解作用. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2022. | |
| 2 | Lu H, Li M, Li L M. Allelotoxic effect of aqueous extract solution from Pogostemon cablin. Northern Horticulture, 2021, 487(16): 108-115. |
| 卢红, 李明, 李龙明. 广藿香植株水提液的化感自毒作用. 北方园艺, 2021, 487(16): 108-115. | |
| 3 | Zou P, Guo Y, Ding S, et al. Autotoxicity of endogenous organic acid stress in two Ganoderma lucidum cultivars. Molecules, 2022, 27(19): 6734. |
| 4 | Li M, Yan X F, Ma L, et al. Allelopathic inhibition of phenolic acids on germination of wolfberry (Lycium barbarum Linn.). Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(6): 2072-2079. |
| 李敏, 闫兴富, 马丽, 等. 酚酸类化感自毒物质对枸杞种子萌发的抑制作用. 生态学报, 2020, 40(6): 2072-2079. | |
| 5 | Yan Z H, He X F, Guo K, et al. Allelochemicals from the rhizosphere of Lanzhou lily: Discovery of the autotoxic compounds of a bulb crop. Scientia Horticulturae, 2019, 250(2): 121-126. |
| 6 | Bao L M, Ding Y F, Wei Y L, et al. Analysis on the composition and diversity of fungi community in the continuous cropping and fallow soil of Panax notoginseng. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2021, 44(1): 7-12. |
| 保丽美, 丁亚芳, 魏云林, 等. 三七连作与休闲土壤真菌群落组成与多样性分析.中药材, 2021, 44(1): 7-12. | |
| 7 | Ma H Y, Li J J, Luo A H, et al. Vanillin, a newly discovered autotoxic substance in long-term potato continuous cropping soil, inhibits plant growth by decreasing the root auxin content and reducing adventitious root numbers. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2023, 71(45): 16993-17004. |
| 8 | Liu S B, Li C Y, Zhang Y S, et al. Evaluating quality of Gansu merchandise wen codonopsis radix with fuzzy matter-element model based on variation coefficient weight. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2016, 22(9): 16-20. |
| 刘书斌, 李成义, 张樱山, 等. 基于变异系数权重的模糊物元模型评价甘肃商品纹党的质量. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2016, 22(9): 16-20. | |
| 9 | Tie X Y, Zhang Y H, Zhang W G, et al. Comparative study on effects of Codonopsis radix before and after stir-baking with rice on anti-oxidation in vitro and regulation of immune function and digestive absorption in diarrhea rats with spleen deficiency. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2021, 52(22): 6871-6880. |
| 帖晓燕, 张云鹤, 张文广, 等. 纹党米炒前后体外抗氧化活性及干预脾虚泄泻大鼠的药效对比研究. 中草药, 2021, 52(22): 6871-6880. | |
| 10 | Liu S B, Li C Y, Chang Y C, et al. Comprehensive quality evaluation of Gansu Wen radix codonopsis of different regions. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 2017, 28(3): 707-708. |
| 刘书斌, 李成义, 常耀成, 等. 甘肃不同产地商品纹党的质量比较研究. 时珍国医国药, 2017, 28(3): 707-708. | |
| 11 | Xie T P, Cui Z J, Huang Y F, et al. Allelopathic effects of Lamiophlomis rotata on seed and seedlings of itself and two crops in alpine areas. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2023, 45(7): 30-40. |
| 谢田朋, 崔治家, 黄钰芳, 等. 独一味对自身及两种高寒地区作物种子和幼苗的化感作用. 中国草地学报, 2023, 45(7): 30-40. | |
| 12 | Lin J Z. Preliminary study on the occurrence mechanism of continuous cropping obstacle in Curcuma kwangsiensis S. G-Lee et C-F. Liang. Nanning: Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023. |
| 林敬祯. 广西莪术连作障碍发生机制初步研究. 南宁: 广西中医药大学, 2023. | |
| 13 | Ma S Y, Chen G P, Wang N, et al. Identification of potential autotoxic substances in pea soil and analysis of their autotoxic effects. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(6): 134-145. |
| 马绍英, 陈桂平, 王娜, 等. 豌豆土壤中潜在自毒物质的鉴定及自毒效应研究. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 134-145. | |
| 14 | Liu P, Li M J, Ding Y F. Experiment of plant physiology. Beijing: Science Press, 2016. |
| 刘萍, 李明军, 丁义峰. 植物生理学实验. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016. | |
| 15 | Bruce W G, Richardson D. Bioassays for allelopathy: Measuring treatment responses with independent controls. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 1988, 14(1): 181-187. |
| 16 | Huang Y F, Zhang E H, Zhang X H, et al. Identification of soil allelochemicals and autotoxicity of Lilium davidii var. unicolor salisb in different continuous cropping years. Agricultural Research in Arid Areas, 2021, 39(2): 62-68, 94. |
| 黄钰芳, 张恩和, 张新慧, 等. 兰州百合不同连作年限土壤中化感物质的检测及其自毒效应的研究. 干旱地区农业研究, 2021, 39(2): 62-68, 94. | |
| 17 | Rice E L. Allelopathy. Orlando, Florida: Academic Press, 1984. |
| 18 | Yang K X, Wu X H, Zheng F P, et al. Allelopathic effects of aqueous extracts of the invasive plant Acmella radicans on seed germination and seedling growth of four weeds. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(12): 3759-3767. |
| 杨轲欣, 吴晓涵, 郑凤萍, 等. 白花金钮扣水提液对4种杂草种子萌发和幼苗生长的化感作用研究. 草地学报, 2023, 31(12): 3759-3767. | |
| 19 | Luo Q, Ma Z Y, Niu Q M, et al. Allelopathic effect and physiological mechanism of extracts from different parts of Euphorbia jolkinii on growth of perennial ryegrass seedlings. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(10): 3212-3219. |
| 罗钦, 马祖艳, 牛琼梅, 等. 大狼毒不同部位浸提液对多年生黑麦草幼苗生长的化感效应及生理机制. 草地学报, 2023, 31(10): 3212-3219. | |
| 20 | Tang Z Y, Chen J Z, Liu J M, et al. Effects of litter autotoxicity on the growth of Cinnamomum migao seedlings. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2022, 42(2): 65-74. |
| 唐子燕, 陈敬忠, 刘济明, 等. 凋落物自毒作用对米槁幼苗生长的影响. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2022, 42(2): 65-74. | |
| 21 | Wang K, Dou P, Miao Z, et al. Seed germination and seedling growth response of Leymus chinensis to the allelopathic influence of grassland plants. Oecologia, 2024, 204(4): 899-913. |
| 22 | Zeng R S. Review on bioassay methods for allelopathy research. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 1999, 10(1): 125-128. |
| 曾任森. 化感作用研究中的生物测定方法综述. 应用生态学报, 1999, 10(1): 125-128. | |
| 23 | Zhang Y B. Effects of litter extract of Phoebe bournei on seed germination, seedling growth and physiological index. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2023. |
| 张艺博.闽楠凋落物浸提液对其种子萌发和幼苗生长及生理的影响. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2023. | |
| 24 | Huang Y F, Zhang E H, Zhang X H, et al. Autotoxicity of water extracts from continuous cropping soil of Lilium davidii var. unicolor salisb. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(7): 84-93. |
| 黄钰芳, 张恩和, 张新慧, 等. 兰州百合连作土壤水浸液自毒作用研究. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 48(7): 84-93. | |
| 25 | Ruan K F, Wang T Q, Hou L N, et al. Allelopathic effects of Koelreuteria paniculata fallen leaves on seed germination and seedling growth of three medicinal plants. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(6): 1-10. |
| 阮坤非, 王天琪, 侯立娜, 等. 栾树凋落叶对3种中药材种子萌发及幼苗生长的化感效应. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52(6): 1-10. | |
| 26 | Zhou W X, Xiong L K, Zhang Y J, et al. Effects of allelopathy on seed germination and seedling growth of Codonopsis tangshen Oliv. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 54(11): 76-85. |
| 周武先, 熊琳珂, 张雅娟, 等. 化感作用对川党参种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响. 山东农业科学, 2022, 54(11): 76-85. | |
| 27 | Jiao H R, Meng Y, Zhou B Q, et al. Identification of allelochemicals and allelopathic effects in rhizosphere soil of continuous cropping Salvia miltiorrhiza. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2022, 45(7): 1538-1544. |
| 焦焕然, 孟缘, 周冰谦, 等. 连作丹参根际土壤化感物质鉴定及化感效应研究. 中药材, 2022, 45(7): 1538-1544. | |
| 28 | Tang K, Li M, Zhao P, et al. Allelopathy of effect volatile oil from Pogostemon cabin to its tissue culture seedlings. Northern Horticulture, 2014(19): 128-131. |
| 唐堃, 李明, 赵盼, 等. 广藿香挥发油对其组织培养幼苗化感自毒作用的研究. 北方园艺, 2014(19): 128-131. | |
| 29 | Cui J J. Effects of two typical allelochemicals on growth and microorganism of Lanzhou lily. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2022. |
| 崔佳佳. 两种典型化感自毒物质对兰州百合生长及微生物作用研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2022. | |
| 30 | Wang X Y. Effects of autotoxic substance on the growth of pepper seedlings and physiological mechanism of MT alleviating DEP stress. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2020. |
| 王馨悦. 自毒物质对辣椒幼苗生长的影响和MT缓解DEP胁迫的生理机制研究. 南昌: 江西农业大学, 2020. |
| [1] | 马绍英, 陈桂平, 王娜, 马蕾, 连荣芳, 李胜, 张绪成. 豌豆土壤中潜在自毒物质的鉴定及自毒效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 134-145. |
| [2] | 彭彤, 马少兰, 马彩霞, 宋燕芳, 高娜, 李凯乐, 张传继, 李静雯, 纳小凡, 王立光. 长期单作对枸杞园不同土层土壤微生物代谢活性和多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 89-98. |
| [3] | 尹国丽, 蔡卓山, 陶茸, 吴芳, 陈建纲, 师尚礼. 不同草田轮作方式对土壤肥力、微生物数量及自毒物质含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 42-50. |
| [4] | 黄钰芳, 张恩和, 张新慧, 王惠珍, 王琦, 刘青林, 石雨仟. 兰州百合连作障碍效应及机制研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 146-155. |
| [5] | 赵新梅, 王军, 莫静静, 杨水平, 温明霞, 张雪, 赵建, 陈大霞, 蒋卫. 三种作物茎叶枯落物水浸液对烟草幼苗生长的化感效应[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(9): 37-45. |
| [6] | 王田涛,王琦,王惠珍,张恩和. 连作条件下间作模式对当归生长特性和产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(2): 54-61. |
| [7] | 林茂兹,张志兴,林争春,尤垂怀,曾令杰,林文雄. 太子参连作障碍蛋白差异表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(6): 197-207. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||