

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (1): 145-163.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020486
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2020-10-28
修回日期:2020-12-14
出版日期:2021-12-01
发布日期:2021-12-01
通讯作者:
庄黎丽
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: nauzll@njau.edu.cn基金资助:
Zhi-min YANG( ), Rui XING, Yun-jia DING, Li-li ZHUANG(
), Rui XING, Yun-jia DING, Li-li ZHUANG( )
)
Received:2020-10-28
Revised:2020-12-14
Online:2021-12-01
Published:2021-12-01
Contact:
Li-li ZHUANG
摘要:
分蘖与株高是禾本科草类植物重要的农艺性状,明确参与调控分蘖与株高的基因类型对牧草和草坪草分子辅助育种具有重要意义。以表型差异明显的两个高羊茅品种“Kentucky-31”(K31)和“Regenerate”为材料,旨在构建高羊茅分蘖节转录组图谱,挖掘在分蘖节部位调控生长发育相关的差异表达基因(differentially expressed genes,DEGs)。基于高通量测序技术平台Illumina HiSeq 2500×Miseq 300进行转录组测序,并将得到的数据进行de novo组装,结果共获得77872条单基因簇(unigene)。将获得的unigenes与非冗余蛋白数据库(non-redundant protein database,NR)、蛋白质数据库(universal protein,Uniprot)、基因本体数据库(gene ontology,GO)、东京基因与基因组数据库(kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes,KEGG)以及直系同源蛋白簇(clusters of orthologous groups,COG)数据库进行比对,结果显示:分别有59927、40213、44447、15146和13767条unigenes成功获得注释。“Regenerate”与“K31”对比有1573个上调DEGs和1441个下调DEGs。GO富集分析发现,DEGs主要富集在细胞、细胞组分、大分子复合物组装等生物过程。DEGs中共注释到42个差异表达转录因子,主要包括TCP、WRKY和ARF等19种类型。还注释到与8类植物激素相关的DEGs,包括生长素、细胞分裂素、脱落酸、赤霉素、乙烯、油菜素甾醇、水杨酸和茉莉酸。利用实时荧光定量PCR对DEGs进行表达模式验证,发现其与RNA-Seq测序结果一致,证实了测序结果的准确性。研究结果丰富了高羊茅的转录组序列资源,初步获得控制株高及分蘖发育的候选因子,为进一步开展基因功能及分子育种研究提供了理论支持。
杨志民, 邢瑞, 丁鋆嘉, 庄黎丽. 基于转录组测序的高羊茅分蘖与株高相关差异表达基因分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 145-163.
Zhi-min YANG, Rui XING, Yun-jia DING, Li-li ZHUANG. Analysis of differentially expressed genes in relation to tiller development and plant height based on transcriptomic sequencing of two tall fescue cultivars[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 145-163.
| 基因编号Unigene ID | 正向引物 (5′-3′)Forward primers (5′-3′) | 反向引物 (5′-3′)Reverse primers (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Unigene003394 | GGTGGACGAGAAGCAGTACT | CGGGTAGTAGTTGCAGGTGA |
| Unigene054336 | CTCAAGGGCAAGGAATCTGC | ATTCGATCGGGGAGAAAGCA |
| Unigene005703/4/5 | AGAGTGTGATGGCGTTGAGA | GCAGATTCCTTGGCCTTGAG |
| Unigene005713 | TGTCTCAACACCGTCACACT | ATGTTGAGGGAGATGGTGGC |
| Unigene074113 | CAGAACTGGCAGAGCAACTC | GGGAGGAGGAAGACGACTAC |
| Unigene031989 | CATCGTGCCAGTCAACTACAG | AGGTTGAAGTAGGAGTGGCC |
| Unigene055976 | TCCCTCGTCAACTACCCCTA | TTGGGGAGCAGATGACACAT |
| Unigene063823 | GCAAGCACCGATCCAGTATG | CGGACTTGTAGGATTTGGCG |
| Unigene036563 | CTCAACTCCAACCGCTTCTG | GTTGTTGCTGAGGTCGAGC |
| Unigene067511 | CTGCTCCTGTCCACCTGTAA | AGTCAGCGAAGAAGTCACCA |
| Unigene056675 | GCGTCGTCACTGCTTTCTAT | CGTCGATGTACAGGTTGGTC |
| Unigene031117 | CTCTCACTTGCCGTCTTTGG | GACGAGGCAGTGTCCATCT |
| Unigene059338 | GAGCTGCCTTTCATCGCTAC | CTCTGGGATGGCAGAAAGGA |
| Unigene033181 | GCTTACTCTCAGCCTCCACT | GGCCTGCAGAAATTGGGAAT |
| Unigene023003 | TTGCTTTAGAAGGCAGGCAC | AGCAGCAAACACACCACTTT |
| Unigene033817 | TGAAGCAGATGTGGAGCAGA | GCCTCCGCTTTATTGCTTGA |
| Unigene061235 | AAGAACTGCATGCCGTTGTT | ATTCTTGGAGGCGTTCATGC |
| Unigene074427 | CAACAAGGGTGCTGAGATCG | GGCGATGCTACCTTGTTCAG |
| Unigene037483 | CTCGATAAGCTGTGGGACGA | CTAGTGCTGTGTTGATGGCC |
| Unigene003016 | ATGGCATGTTCAACGGTGTC | GAGTATCTGTCCGTGGCTGA |
| Unigene066660 | TCATCCCAGGTGAACACTCC | GCGCTGTACAAGTTCGGTAG |
| Unigene074432 | ATCCGTCTCAGGTCCAAGTG | GCGAAATACTGTCCGCCAAT |
| Unigene022674 | GACGGACGGAATCAAGAGGA | CATACCATTCGAAGTGCCGG |
| Unigene054725 | GTAGCACCTCCGTCCCTATC | GGACTTGATCGAGCTGAGGA |
表1 PCR验证引物
Table 1 PCR validation primers
| 基因编号Unigene ID | 正向引物 (5′-3′)Forward primers (5′-3′) | 反向引物 (5′-3′)Reverse primers (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Unigene003394 | GGTGGACGAGAAGCAGTACT | CGGGTAGTAGTTGCAGGTGA |
| Unigene054336 | CTCAAGGGCAAGGAATCTGC | ATTCGATCGGGGAGAAAGCA |
| Unigene005703/4/5 | AGAGTGTGATGGCGTTGAGA | GCAGATTCCTTGGCCTTGAG |
| Unigene005713 | TGTCTCAACACCGTCACACT | ATGTTGAGGGAGATGGTGGC |
| Unigene074113 | CAGAACTGGCAGAGCAACTC | GGGAGGAGGAAGACGACTAC |
| Unigene031989 | CATCGTGCCAGTCAACTACAG | AGGTTGAAGTAGGAGTGGCC |
| Unigene055976 | TCCCTCGTCAACTACCCCTA | TTGGGGAGCAGATGACACAT |
| Unigene063823 | GCAAGCACCGATCCAGTATG | CGGACTTGTAGGATTTGGCG |
| Unigene036563 | CTCAACTCCAACCGCTTCTG | GTTGTTGCTGAGGTCGAGC |
| Unigene067511 | CTGCTCCTGTCCACCTGTAA | AGTCAGCGAAGAAGTCACCA |
| Unigene056675 | GCGTCGTCACTGCTTTCTAT | CGTCGATGTACAGGTTGGTC |
| Unigene031117 | CTCTCACTTGCCGTCTTTGG | GACGAGGCAGTGTCCATCT |
| Unigene059338 | GAGCTGCCTTTCATCGCTAC | CTCTGGGATGGCAGAAAGGA |
| Unigene033181 | GCTTACTCTCAGCCTCCACT | GGCCTGCAGAAATTGGGAAT |
| Unigene023003 | TTGCTTTAGAAGGCAGGCAC | AGCAGCAAACACACCACTTT |
| Unigene033817 | TGAAGCAGATGTGGAGCAGA | GCCTCCGCTTTATTGCTTGA |
| Unigene061235 | AAGAACTGCATGCCGTTGTT | ATTCTTGGAGGCGTTCATGC |
| Unigene074427 | CAACAAGGGTGCTGAGATCG | GGCGATGCTACCTTGTTCAG |
| Unigene037483 | CTCGATAAGCTGTGGGACGA | CTAGTGCTGTGTTGATGGCC |
| Unigene003016 | ATGGCATGTTCAACGGTGTC | GAGTATCTGTCCGTGGCTGA |
| Unigene066660 | TCATCCCAGGTGAACACTCC | GCGCTGTACAAGTTCGGTAG |
| Unigene074432 | ATCCGTCTCAGGTCCAAGTG | GCGAAATACTGTCCGCCAAT |
| Unigene022674 | GACGGACGGAATCAAGAGGA | CATACCATTCGAAGTGCCGG |
| Unigene054725 | GTAGCACCTCCGTCCCTATC | GGACTTGATCGAGCTGAGGA |

图1 “Regenerate”和“K31”植株的表型差异比较A~B:45 d苗龄时“K31”和“Regenerate”的表型;C:两个品种分蘖数统计(萌发后第4周至第7周);D:两个品种株高测量(萌发后4周至7周);E:茎秆直径(萌发后4周及6周);F:完全展开的成熟叶片表皮细胞面积,每个品种取9片叶,每片叶取3个细胞。显著水平:*表示P<0.05,**表示P<0.01,下同。A-B: Phenotype of 45-d-old seedlings of “K31”and “Regenerate”; C: Tillers number calculated from 4-week-old to 7-week-old plants; D: Plants height measured from 4-7 weeks after germination; E: Diameter of the main clum of “K31” and “Regenerate” at 4 weeks and 6 weeks respectively; F: Cell size on the lower surface of the fully expanded leaves in “K31” and “Regenerate”, 9 leaves for each cultivar, three cells for each leaf. Significance level: * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, the same below.
Fig.1 Comparison of phenotypic difference between “K31” and “ Regenerate” plants
| 样品Sample | 原始数据Raw reads | 测序数据Clean reads | 原始下机数据Raw bases | 测序下机数据Clean bases | 测序数据比率 Clean data rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regenerate | 88475512 | 88345910 | 11834878498 | 11576251799 | 97.81 |
| K31 | 76673214 | 76533900 | 10284187805 | 10037407880 | 97.60 |
表2 de novo RNA-seq详细序列信息
Table 2 Detail sequence information for de novo RNA-seq
| 样品Sample | 原始数据Raw reads | 测序数据Clean reads | 原始下机数据Raw bases | 测序下机数据Clean bases | 测序数据比率 Clean data rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regenerate | 88475512 | 88345910 | 11834878498 | 11576251799 | 97.81 |
| K31 | 76673214 | 76533900 | 10284187805 | 10037407880 | 97.60 |
| RNA-Seq信息 RNA-Seq information | 数据 Data |
|---|---|
| Unigene 数目 Unigene number | 77872 |
| 最大unigene bases Max unigene bases (bp) | 13402 |
| 最小unigene bases Min unigene bases (bp) | 200 |
| 全部数据长度 Whole dataset lengths (bp) | 47586469 |
| 平均unigene长度 Average unigene lengths (bp) | 611.086 |
| (G+C)/(A+T+G+C) (%) | 53.2 |
| N50 (bp) | 920 |
| N90 (bp) | 262 |
表3 样品RNA-Seq数据汇总
Table 3 Summary of sample based on the RNA-Seq data
| RNA-Seq信息 RNA-Seq information | 数据 Data |
|---|---|
| Unigene 数目 Unigene number | 77872 |
| 最大unigene bases Max unigene bases (bp) | 13402 |
| 最小unigene bases Min unigene bases (bp) | 200 |
| 全部数据长度 Whole dataset lengths (bp) | 47586469 |
| 平均unigene长度 Average unigene lengths (bp) | 611.086 |
| (G+C)/(A+T+G+C) (%) | 53.2 |
| N50 (bp) | 920 |
| N90 (bp) | 262 |
数据库 Database | 获得注释unigenes数目 Annotated unigenes number | 百分比 Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| NR | 59927 | 76.96 |
| GO | 44447 | 57.08 |
| COG | 13767 | 17.68 |
| Uniprot | 40213 | 51.64 |
| KEGG | 15146 | 19.45 |
表4 数据库BLAST分析结果
Table 4 BLAST analysis results against important public databases
数据库 Database | 获得注释unigenes数目 Annotated unigenes number | 百分比 Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| NR | 59927 | 76.96 |
| GO | 44447 | 57.08 |
| COG | 13767 | 17.68 |
| Uniprot | 40213 | 51.64 |
| KEGG | 15146 | 19.45 |

图4 高羊茅unigenes COG注释分类1: RNA加工和修饰 RNA processing and modification; 2: 染色质结构和动力学 Chromatin structure and dynamics; 3: 能量生产与转化 Energy production and conversion; 4: 细胞周期调控, 细胞分裂, 染色体分区 Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning; 5: 氨基酸转运和代谢 Amino acid transport and metabolism; 6: 核苷酸转运与代谢 Nucleotide transport and metabolism; 7: 碳水化合物运输与代谢 Carbohydrate transport and metabolism; 8: 辅酶转运和代谢 Coenzyme transport and metabolism; 9: 脂质运输与代谢 Lipid transport and metabolism; 10: 翻译,核糖体结构和生物发生 Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis; 11: 转录 Transcription; 12: 复制,重组和修复 Replication, recombination and repair; 13: 细胞壁/膜/被膜生物发生 Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis; 14: 细胞能动性 Cell motility; 15: 蛋白质翻译后修饰-蛋白质周转-分子伴侣 Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones; 16: 无机离子运输与代谢 Inorganic ion transport and metabolism; 17: 次生代谢产物的生物合成, 转运和分解代谢 Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism; 18: 一般功能预测蛋白 General function prediction only; 19: 未知功能 Unknown function; 20: 信号转导机制 Signal transduction mechanisms; 21: 胞内运输, 分泌与囊泡运输 Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport; 22: 防御机制 Defense mechanisms; 23: 核结构 Nuclear structure; 24: 细胞骨架 Cytoskeleton.
Fig.4 Cluster of orthologous group (COG) classi?cation of unigenes in F. arundinacea
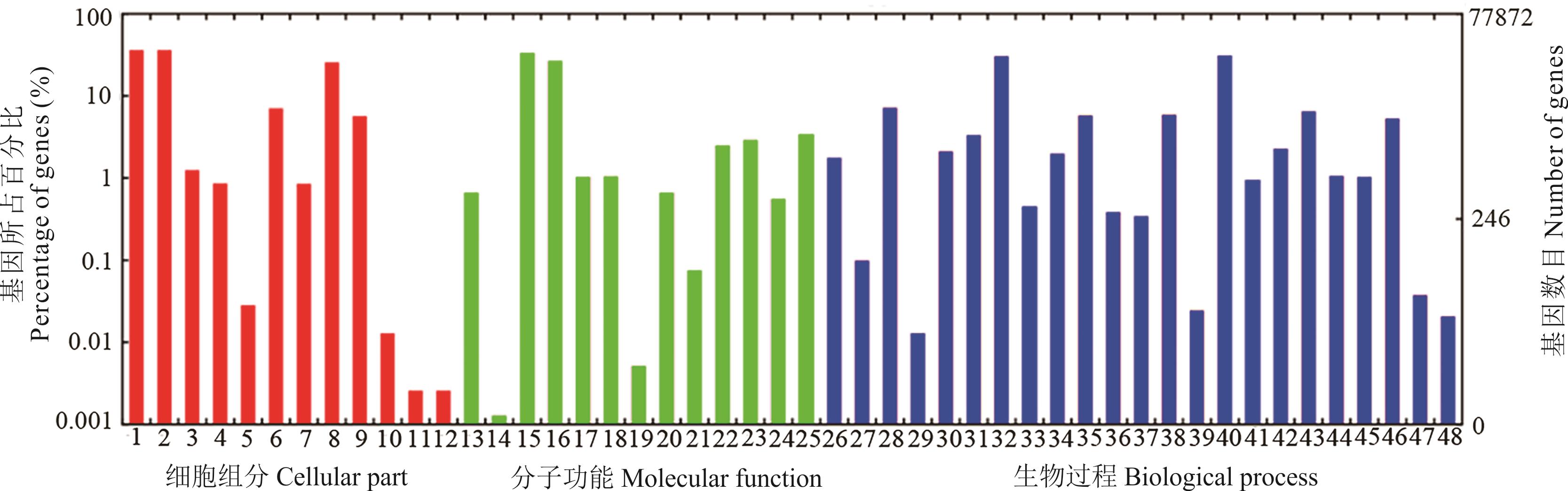
图5 高羊茅unigenes GO注释分类1: 细胞 Cell; 2: 细胞组分 Cell part; 3: 被膜 Envelope; 4: 胞外区域 Extracellular region; 5: 胞外区域部分 Extracellular region part; 6: 大分子复合物 Macromolecular complex; 7: 膜封闭腔 Membrane-enclosed lumen; 8: 细胞器 Organelle; 9: 细胞器组分 Organelle part; 10: 共生体 Symplast; 11: 病毒体 Virion; 12: 病毒体组分 Virion part; 13: 抗氧化剂活性 Antioxidant activity; 14: 辅助转运蛋白活性 Auxiliary transport protein activity; 15: 捆绑 Binding; 16: 催化活性 Catalytic activity; 17: 电子载体活性 Electron carrier activity; 18: 酶调节器活性 Enzyme regulator activity; 19: 金属伴侣活性 Metallochaperone activity; 20: 分子换能器活性 Molecular transducer activity; 21: 养分库活性 Nutrient reservoir activity; 22: 结构分子活性 Structural molecule activity; 23: 转录调节器活性 Transcription regulator activity; 24: 翻译调节器活性 Translation regulator activity; 25: 转运体活性 Transporter activity; 26: 解剖结构形成 Anatomical structure formation; 27: 生物粘附 Biological adhesion; 28: 生物调节 Biological regulation; 29: 细胞杀伤 Cell killing; 30: 细胞成分生物发生 Cellular component biogenesis; 31: 细胞成分组织 Cellular component organization; 32: 细胞过程 Cellular process; 33: 死亡 Death; 34: 发展过程 Developmental process; 35: 定位建立 Establishment of localization; 36: 生长 Growth; 37: 免疫系统过程 Immune system process; 38: 定位 Localization; 39: 运动 Locomotion; 40: 代谢过程 Metabolic process; 41: 多元生物过程 Multi\-organism process; 42: 多细胞生物过程 Multicellular organismal process; 43: 色素沉着 Pigmentation; 44: 再生产 Reproduction; 45: 生殖过程 Reproductive process; 46: 刺激响应 Response to stimulus; 47: 节律过程 Rhythmic process; 48: 病毒增殖 Viral reproduction.
Fig.5 Gene ontology (GO) classification of unigenes in F. arundinacea

图6 高羊茅unigenes KEGG注释分类1: 感觉系统 Sensory system; 2: 神经系统 Nervous system; 3: 免疫系统 Immune system; 4: 排泄系统 Excretory system; 5: 环境适应 Environmental adaption; 6: 内分泌系统 Endocrine system; 7: 消化系统 Digestive system; 8: 发育 Development; 9: 循环系统 Circulatory system; 10: 外源性物质的生物降解和代谢 Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism; 11: 核苷酸代谢 Nucleotide metabolism; 12: 萜类化合物和聚酮化合物代谢 Metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides; 13: 其他氨基酸的代谢 Metabolism of other amino acids; 14: 辅助因子和维生素的代谢 Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins; 15: 脂质代谢 Lipid metabolism; 16: 多糖的生物合成与代谢 Glycan biosynthesis and metabolism; 17: 能量代谢 Energy metabolism; 18: 碳水化合物代谢 Carbohydrate metabolism; 19: 次生代谢产物生物合成 Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites; 20: 氨基酸代谢 Amino acid metabolism; 21: 翻译 Translation; 22: 转录 Transcription; 23: 复制和修复 Replication and repair; 24: 折叠,分类和降解 Folding, sorting and degradation; 25: 信号分子与互作 Signaling molecules and interaction; 26: 信号转导 Signal transduction; 27: 膜运输 Membrane transport; 28: 运输和分解代谢 Transport and catabolism; 29: 细胞能动性 Cell motility; 30: 细胞生长与死亡 Cell growth and death; 31: 细胞免疫 Cellular immunity.
Fig.6 KEGG classi?cation of unigenes in F. arundinacea
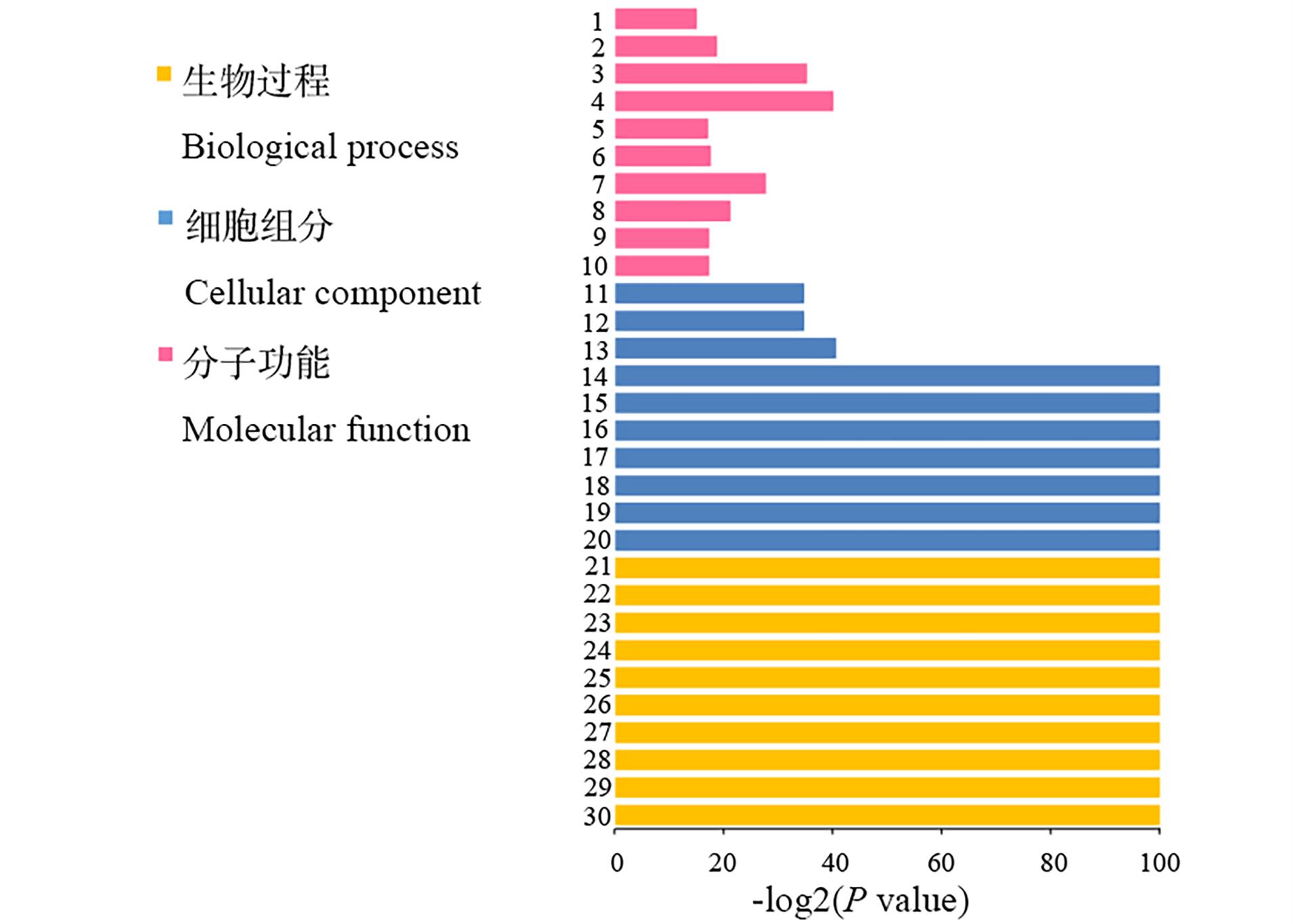
图7 高羊茅DEGs的GO功能分析1: 核苷二磷酸激酶活性 Nucleoside diphosphate kinase activity; 2: 水解酶活性, 作用于醚键 Hydrolase activity, acting on ether bonds; 3: 酶抑制剂活性 Enzyme inhibitor activity; 4: 肽链内切酶抑制剂活性 Endopeptidase inhibitor activity; 5: 天冬氨酸型肽酶活性 Aspartic-type peptidase activity; 6: 天冬氨酸型肽链内切酶活性Aspartic-type endopeptidase activity; 7: 天冬酰胺酶活性 Asparaginase activity; 8: 腺苷半胱氨酸酶活性Adenosylhomocysteinase activity; 9: 5-甲基四氢蝶酰基三-L-谷氨酸依赖性甲基转移酶活性 5-Methyletrahydropteroyltri-l-glutamate-dependent methyltransferase activity; 10: 5-甲基四蝶酰基三谷氨酸-高半胱氨酸S-甲基转移酶活性5-methyltetrahydropteroyltriglutamate-homocysteine S-methyltransferase activity; 11: 细胞组分 Cell part; 12: 细胞 Cell; 13: 大分子复合物 Macromolecular complex; 14: 蛋白质-DNA复合物 Protein-DNA complex; 15: 核小体 Nucleosome; 16: 非膜细胞器 Non-membrane-bounded organelle; 17: 细胞内非膜细胞器 Intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle; 18: 染色体 Chromosome; 19: 染色体组分 Chromosomal part; 20: 染色质Chromatin; 21: 大分子复合物组装 Macromolecular complex assembly; 22: DNA包装 DNA packaging; 23: 染色体组织 Chromosome organization; 24: 染色质组织 Chromatin organization; 25: 染色质组装或拆卸 Chromatin assembly or disassembly; 26: 染色质组装 Chromatin assembly; 27: 细胞大分子复合物亚基组织 Cellular macromolecular complex subunit organization; 28: 细胞大分子复合物组装 Cellular macromolecular complex assembly; 29: 细胞组分生物发生 Cellular component biogenesis; 30: 细胞组分组装 Cellular component assembly.
Fig.7 Functional categorization of assembled unigenes based on gene ontology (GO) classification in crowns of F. arundinacea
基因编号 Unigene ID | 转录因子 Transcription factor | 水稻中功能释义 Functional description in rice | 差异倍数 Log2 fold change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unigene038874 | AP2 | AP2-like乙烯响应转录因子TOE3同源异构体X2 AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor TOE3 isoform X2 | -1.64 |
| Unigene003016 | ARF | 生长素响应转录因子25同源异构体X2 Auxin response factor 25 isoform X2 | 2.64 |
| Unigene027288 | ARF | 生长素响应因子15,推测,表达 Auxin response factor 15, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene003404 | ARF | 生长素响应转录因子12同源异构体X2 Auxin response factor 12 isoform X2 | -10.00 |
| Unigene067511 | bHLH | bHLH96转录因子 Transcription factor bHLH96 | 1.51 |
| Unigene067617 | bHLH | bHLH96转录因子 Transcription factor bHLH96 | 1.24 |
| Unigene017047 | bHLH | 花青素调节R-S蛋白Anthocyanin regulatory R-S protein | -2.04 |
| Unigene043455 | bZIP | bZIP转录因子RF2b bZIP transcription factor RF2b | -10.00 |
| Unigene054725 | C2H2 | C2H2锌指蛋白,PROSTRATE GROWTH 1 (PROG1) C2H2 zinc finger protein, PROSTRATE GROWTH 1 (PROG1) | 1.53 |
| Unigene028588 | C3H | 锌指蛋白CCCH保守结构域蛋白33 Zinc finger protein CCCH domain-containing protein 33 | -10.00 |
| Unigene018078 | C3H | 锌指蛋白家族,推测,表达 Zinc finger family protein, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene016356 | Dof | 锌指蛋白MNB1A Zinc finger protein MNB1A | 10.00 |
| Unigene016424 | ERF | 乙烯响应转录因子ERF118 Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF118 | -1.44 |
| Unigene077012 | ERF | 乙烯响应转录因子ERF073 Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF073 | 1.34 |
| Unigene066363 | ERF | 假定蛋白OsJ_05447 Hypothetical protein OsJ_05447 | 10.00 |
| Unigene000226 | ERF | 乙烯响应转录因子7 Ethylene-responsive transcription factor 7 | 1.77 |
| Unigene059623 | ERF | 脱水反应元件结合蛋白,推测,表达 Dehydration-responsive element-binding protein, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene051413 | ERF | 乙烯响应转录因子8 Ethylene-responsive transcription factor 8 | 1.89 |
| Unigene058012 | FAR1 | 远红受损响应蛋白-like Far-red impaired response protein-like | -1.36 |
| Unigene012666 | G2-like | 可能是转录因子GLK2同源异构体X2 Probable transcription factor GLK2 isoform X2 | 1.26 |
| Unigene072964 | G2-like | 转录因子PCL1-like Transcription factor PCL1-like | -10.00 |
| Unigene039377 | GATA | GATA转录因子2 GATA transcription factor 2 | -10.00 |
| Unigene072410 | GATA | GATA转录因子16 GATA transcription factor 16 | -1.88 |
| Unigene011395 | GATA | GATA转录因子5 GATA transcription factor 5 | 1.47 |
| Unigene070942 | GRAS | 几丁质诱导赤霉素响应蛋白2 Chitin-inducible gibberellin-responsive protein 2 | -10.00 |
| Unigene023454 | HD-ZIP | 同源框-亮氨酸拉链蛋白ROC5 Homeobox-leucine zipper protein ROC5 | 10.00 |
| Unigene012030 | LSD | LSD1蛋白同源异构体X1 Protein LSD1 isoform X1 | -2.69 |
| Unigene003445 | MADS | MADS-box转录因子22 MADS-box transcription factor 22 | 10.00 |
| Unigene008312 | MADS | MADS-box转录因子51 MADS-box transcription factor 51 | 1.90 |
| Unigene032888 | MADS | 转录因子MADS37 Transcription factor MADS37 | 1.30 |
| Unigene016122 | MADS | MADS-box转录因子50 MADS-box transcription factor 50 | -2.01 |
| Unigene067434 | MADS | Agamous-like MADS-box蛋白AGL3同源异构体X2 Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL3 isoform X2 | 1.45 |
| Unigene049455 | MADS | MADS-box转录因子51 MADS-box transcription factor 51 | 1.31 |
| Unigene075408 | MYB_related | 蛋白REVEILLE 6 Protein REVEILLE 6 | 10.00 |
| Unigene051158 | SBP | 鳞状细胞启动子结合样蛋白15 Squamosa promoter-binding-like protein 15 | -10.00 |
| Unigene032517 | TCP | 转录因子PCF6 Transcription factor PCF6 | -2.55 |
| Unigene063740 | TCP | 转录因子TCP13 Transcription factor TCP13 | -1.03 |
| Unigene010687 | TCP | 转录因子TCP7-like Transcription factor TCP7-like | -1.77 |
| Unigene022674 | TCP | 转录因子TCP21 Transcription factor TCP21 | -5.50 |
| Unigene010684 | TCP | 转录因子PCF1 Transcription factor PCF1 | -1.52 |
| Unigene021636 | WRKY | 可能是WRKY转录因子70 Probable WRKY transcription factor 70 | 2.34 |
| Unigene036266 | WRKY | 可能是WRKY转录因子19同源异构体X1 Probable WRKY transcription factor 19 isoform X1 | 10.00 |
表5 差异表达转录因子
Table 5 Differentially expressed transcription factors
基因编号 Unigene ID | 转录因子 Transcription factor | 水稻中功能释义 Functional description in rice | 差异倍数 Log2 fold change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unigene038874 | AP2 | AP2-like乙烯响应转录因子TOE3同源异构体X2 AP2-like ethylene-responsive transcription factor TOE3 isoform X2 | -1.64 |
| Unigene003016 | ARF | 生长素响应转录因子25同源异构体X2 Auxin response factor 25 isoform X2 | 2.64 |
| Unigene027288 | ARF | 生长素响应因子15,推测,表达 Auxin response factor 15, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene003404 | ARF | 生长素响应转录因子12同源异构体X2 Auxin response factor 12 isoform X2 | -10.00 |
| Unigene067511 | bHLH | bHLH96转录因子 Transcription factor bHLH96 | 1.51 |
| Unigene067617 | bHLH | bHLH96转录因子 Transcription factor bHLH96 | 1.24 |
| Unigene017047 | bHLH | 花青素调节R-S蛋白Anthocyanin regulatory R-S protein | -2.04 |
| Unigene043455 | bZIP | bZIP转录因子RF2b bZIP transcription factor RF2b | -10.00 |
| Unigene054725 | C2H2 | C2H2锌指蛋白,PROSTRATE GROWTH 1 (PROG1) C2H2 zinc finger protein, PROSTRATE GROWTH 1 (PROG1) | 1.53 |
| Unigene028588 | C3H | 锌指蛋白CCCH保守结构域蛋白33 Zinc finger protein CCCH domain-containing protein 33 | -10.00 |
| Unigene018078 | C3H | 锌指蛋白家族,推测,表达 Zinc finger family protein, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene016356 | Dof | 锌指蛋白MNB1A Zinc finger protein MNB1A | 10.00 |
| Unigene016424 | ERF | 乙烯响应转录因子ERF118 Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF118 | -1.44 |
| Unigene077012 | ERF | 乙烯响应转录因子ERF073 Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF073 | 1.34 |
| Unigene066363 | ERF | 假定蛋白OsJ_05447 Hypothetical protein OsJ_05447 | 10.00 |
| Unigene000226 | ERF | 乙烯响应转录因子7 Ethylene-responsive transcription factor 7 | 1.77 |
| Unigene059623 | ERF | 脱水反应元件结合蛋白,推测,表达 Dehydration-responsive element-binding protein, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene051413 | ERF | 乙烯响应转录因子8 Ethylene-responsive transcription factor 8 | 1.89 |
| Unigene058012 | FAR1 | 远红受损响应蛋白-like Far-red impaired response protein-like | -1.36 |
| Unigene012666 | G2-like | 可能是转录因子GLK2同源异构体X2 Probable transcription factor GLK2 isoform X2 | 1.26 |
| Unigene072964 | G2-like | 转录因子PCL1-like Transcription factor PCL1-like | -10.00 |
| Unigene039377 | GATA | GATA转录因子2 GATA transcription factor 2 | -10.00 |
| Unigene072410 | GATA | GATA转录因子16 GATA transcription factor 16 | -1.88 |
| Unigene011395 | GATA | GATA转录因子5 GATA transcription factor 5 | 1.47 |
| Unigene070942 | GRAS | 几丁质诱导赤霉素响应蛋白2 Chitin-inducible gibberellin-responsive protein 2 | -10.00 |
| Unigene023454 | HD-ZIP | 同源框-亮氨酸拉链蛋白ROC5 Homeobox-leucine zipper protein ROC5 | 10.00 |
| Unigene012030 | LSD | LSD1蛋白同源异构体X1 Protein LSD1 isoform X1 | -2.69 |
| Unigene003445 | MADS | MADS-box转录因子22 MADS-box transcription factor 22 | 10.00 |
| Unigene008312 | MADS | MADS-box转录因子51 MADS-box transcription factor 51 | 1.90 |
| Unigene032888 | MADS | 转录因子MADS37 Transcription factor MADS37 | 1.30 |
| Unigene016122 | MADS | MADS-box转录因子50 MADS-box transcription factor 50 | -2.01 |
| Unigene067434 | MADS | Agamous-like MADS-box蛋白AGL3同源异构体X2 Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL3 isoform X2 | 1.45 |
| Unigene049455 | MADS | MADS-box转录因子51 MADS-box transcription factor 51 | 1.31 |
| Unigene075408 | MYB_related | 蛋白REVEILLE 6 Protein REVEILLE 6 | 10.00 |
| Unigene051158 | SBP | 鳞状细胞启动子结合样蛋白15 Squamosa promoter-binding-like protein 15 | -10.00 |
| Unigene032517 | TCP | 转录因子PCF6 Transcription factor PCF6 | -2.55 |
| Unigene063740 | TCP | 转录因子TCP13 Transcription factor TCP13 | -1.03 |
| Unigene010687 | TCP | 转录因子TCP7-like Transcription factor TCP7-like | -1.77 |
| Unigene022674 | TCP | 转录因子TCP21 Transcription factor TCP21 | -5.50 |
| Unigene010684 | TCP | 转录因子PCF1 Transcription factor PCF1 | -1.52 |
| Unigene021636 | WRKY | 可能是WRKY转录因子70 Probable WRKY transcription factor 70 | 2.34 |
| Unigene036266 | WRKY | 可能是WRKY转录因子19同源异构体X1 Probable WRKY transcription factor 19 isoform X1 | 10.00 |
基因编号 Unigene ID | 水稻中功能释义 Functional description in rice | 差异倍数 Log2 fold change |
|---|---|---|
| Unigene046376 | 磷脂酶D,推测,表达Phospholipase D, putative, expressed | 2.90 |
| Unigene060586 | 多药耐药相关蛋白,推测,表达Multidrug resistance-associated protein, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene028345 | 含WD重复序列蛋白,推测,表达WD repeat-containing protein, putative, expressed | 2.00 |
| Unigene012266 | 半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂前体蛋白,推测,表达Cysteine proteinase inhibitor precursor protein, putative, expressed | 1.87 |
| Unigene072636 | 醛氧化酶,推测Aldehyde oxidase, putative | -1.73 |
| Unigene030806 | 醛氧化酶,推测Aldehyde oxidase, putative | -10.00 |
| Unigene000154 | 转录抑制因子,推测,表达Transcriptional repressor, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene017481 | 脂肪酶蛋白,推测,表达Lipozygenase protein, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene061983 | 脂氧合酶,推测,表达Lipoxygenase, putative, expressed | -1.14 |
| Unigene061978 | 脂肪酶蛋白,推测,表达Lipozygenase protein, putative, expressed | -1.49 |
| Unigene039361 | 烯醇酶,推测,表达Enolase, putative, expressed | -2.13 |
| Unigene073044 | 氨基酸激酶,推测,表达Amino acid kinase, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene066363 | 含AP2结构域的蛋白,推测AP2 domain containing protein, putative | 10.00 |
| Unigene000226 | 含AP2结构域的蛋白,推测AP2 domain containing protein, putative | 1.77 |
| Unigene005128 | DEAD-盒ATP-依赖的RNA解旋酶,推测,表达DEAD-box ATP-dependent RNA helicase, putative, expressed | 1.71 |
| Unigene031676 | RNA结合蛋白,推测,表达RNA binding protein, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene013478 | 泛素连接酶,推测,表达Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, putative, expressed | -2.51 |
| Unigene011796 | 晚期胚胎发生丰富蛋白,推测Late embryogenesis abundant protein, putative | 1.94 |
| Unigene070085 | 细胞色素P450,推测,表达Cytochrome P450, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene060943 | 富含半胱氨酸类受体蛋白激酶7前体,推测,表达Cysteine-rich receptor-like protein kinase 7 precursor, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene034794 | 富含半胱氨酸类受体蛋白激酶7前体,推测,表达Cysteine-rich receptor-like protein kinase 7 precursor, putative, expressed | 1.42 |
| Unigene074427 | 醛氧化酶,推测Aldehyde oxidase, putative | -1.24 |
| Unigene024549 | 含LSM结构域蛋白,表达LSM domain containing protein, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene044589 | LTPL11蛋白酶抑制剂/种子储藏/LTP家族蛋白前体,表达LTPL11-protease inhibitor/seed storage/LTP family protein precursor, expressed | 3.32 |
| Unigene029300 | LTPL11蛋白酶抑制剂/种子储藏/LTP家族蛋白前体,表达LTPL11-protease inhibitor/seed storage/LTP family protein precursor, expressed | 1.83 |
| Unigene036441 | LTPL11蛋白酶抑制剂/种子储藏/LTP家族蛋白前体,表达LTPL11-protease inhibitor/seed storage/LTP family protein precursor, expressed | 1.42 |
| Unigene003016 | 生长素响应因子,推测,表达Auxin response factor, putative, expressed | 2.64 |
| Unigene003404 | 生长素响应因子,推测,表达Auxin response factor, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene010610 | 泛素融合蛋白,推测,表达Ubiquitin fusion protein, putative, expressed | -1.71 |
| Unigene016356 | 含dof锌指结构的蛋白,推测,表达Dof zinc finger domain containing protein, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene016424 | 含AP2结构域蛋白,表达AP2 domain containing protein, expressed | -1.44 |
| Unigene021698 | EF手性家族蛋白,推测,表达EF hand family protein, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene027288 | 生长素响应因子15,推测,表达Auxin response factor 15, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene029798 | COP9信号体复合体亚基5b,推测,表达COP9 signalosome complex subunit 5b, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene035367 | OsSAUR21-生长素响应SAUR基因家族成员,表达OsSAUR21-auxin-responsive SAUR gene family member, expressed | 1.43 |
| Unigene037483 | 生长素响应蛋白,推测,表达Auxin-repressed protein, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene038997 | 促后期复合物亚基11,推测,表达Anaphase-promoting complex subunit 11, putative, expressed | 2.04 |
| Unigene040618 | 含PAZ结构域蛋白,推测,表达PAZ domain containing protein, putative, expressed | 1.06 |
| Unigene046724 | OsIAA30-生长素响应 Aux/IAA基因家族成员,表达OsIAA30-auxin-responsive Aux/IAA gene family member, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene046971 | 核糖体蛋白L24,推测,表达Ribosomal protein L24, putative, expressed | -1.58 |
| Unigene054539 | PINHEAD,推测,表达PINHEAD, putative, expressed | 1.32 |
| Unigene058662 | 邻氨基苯甲酸合成酶组分I-1,叶绿体前体,推测,表达Anthranilate synthase component I-1, chloroplast precursor, putative, expressed | -1.01 |
| Unigene059108 | 多药耐药性蛋白,推测,表达Multidrug resistance protein, putative, expressed | -1.48 |
| Unigene073724 | 多药耐药性蛋白,推测,表达Multidrug resistance protein, putative, expressed | 2.69 |
| Unigene074290 | 糖基水解酶家族16,推测,表达Glycosyl hydrolases family 16, putative, expressed | 1.10 |
| Unigene045370 | 组氨酸激酶,推测,表达Histidine kinase, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene016424 | 含AP2结构域蛋白,推测AP2 domain containing protein, putative | -1.44 |
| Unigene066660 | 内切葡聚糖酶,推测,表达Endoglucanase, putative, expressed | 4.06 |
| Unigene000226 | 含AP2结构域蛋白,推测AP2 domain containing protein, putative | 1.77 |
| Unigene003249 | 脱氢酶,推测,表达Dehydrogenase, putative, expressed | 1.04 |
| Unigene003404 | 生长素响应因子,推测,表达Auxin response factor, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene004616 | 网格蛋白组装蛋白,推测,表达Clathrin assembly protein, putative, expressed | 1.86 |
| Unigene004990 | 剪接因子,富含精氨酸/丝氨酸,推测,表达Splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich, putative, expressed | 2.03 |
| Unigene004991 | 剪接因子,富含精氨酸/丝氨酸,推测,表达Splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich, putative, expressed | -2.60 |
| Unigene004995 | 剪接因子,富含精氨酸/丝氨酸,推测,表达Splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich, putative, expressed | -1.78 |
| Unigene013048 | Vignain前体,推测,表达Vignain precursor, putative, expressed | -4.34 |
| Unigene013756 | MBTB11-Bric-a-Brac结构域,表达MBTB11-Bric-a-Brac domain, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene026080 | 含tubulin/FtsZ结构域蛋白,推测,表达Tubulin/FtsZ domain containing protein, putative, expressed | 3.96 |
| Unigene037362 | 热激蛋白,推测,表达Heat shock protein, putative, expressed | -3.44 |
| Unigene038349 | 含RNA识别基序蛋白,表达RNA recognition motif containing protein, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene050603 | CHIT14-几丁质酶家族蛋白前体,表达CHIT14-Chitinase family protein precursor, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene051413 | 含AP2结构域蛋白,表达AP2 domain containing protein, expressed | 1.89 |
| Unigene055349 | 原叶绿素还原酶A,叶绿体前体,推测,表达Protochlorophyllide reductase A, chloroplast precursor, putative, expressed | -1.40 |
| Unigene064634 | 1-氨基环丙烷-1-羧酸氧化酶蛋白,推测,表达1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase protein, putative, expressed | 1.56 |
| Unigene066363 | 含AP2结构域蛋白,表达AP2 domain containing protein, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene066897 | 含KH结构域蛋白,推测,表达KH domain containing protein, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene071207 | 脱氢酶,推测,表达Dehydrogenase, putative, expressed | 1.51 |
| Unigene071208 | 脱氢酶,推测,表达Dehydrogenase, putative, expressed | 1.71 |
| Unigene073772 | 氧化还原酶,含短链脱氢/还原酶家族结构域蛋白,表达Oxidoreductase, short chain dehydrogenase/reductase family domain containing family, expressed | -2.07 |
| Unigene074432 | 糖基水解酶家族16,推测,表达Glycosyl hydrolases family 16, putative, expressed | 2.51 |
| Unigene037534 | 扩展蛋白前体,推测,表达Expansin precursor, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene031989 | 扩展蛋白前体,推测,表达Expansin precursor, putative, expressed | 1.90 |
| Unigene074120 | 扩展蛋白前体,推测,表达Expansin precursor, putative, expressed | 1.62 |
| Unigene026443 | 类促开花因子,推测,表达Flowering promoting factor-like 1, putative, expressed | 1.17 |
| Unigene012266 | 半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂前体蛋白,推测,表达Cysteine proteinase inhibitor precursor protein, putative, expressed | 1.87 |
| Unigene058662 | 邻氨基苯甲酸合成酶-组分I-1,叶绿体前体,推测,表达Anthranilate synthase component I-1, chloroplast precursor, putative, expressed | -1.01 |
| Unigene046376 | 磷脂酶D,推测,表达Phospholipase D, putative, expressed | 2.90 |
| Unigene008565 | 脂氧合酶,推测,表达Lipoxygenase, putative, expressed | 1.47 |
| Unigene045105 | 脂氧合酶,推测,表达Lipoxygenase, putative, expressed | -1.40 |
| Unigene071224 | 3-羟酰基-辅酶A脱氢酶,推测,表达3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene023000 | CESA5-纤维素合成酶,表达CESA5-cellulose synthase, expressed | 1.88 |
| Unigene017047 | 花青素调节蛋白,推测,表达Anthocyanin regulatory Lc protein, putative, expressed | -2.04 |
| Unigene059623 | 脱水反应元件结合蛋白,推测,表达Dehydration-responsive element-binding protein, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene056424 | 胺氧化酶,推测,表达Amine oxidase, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene016424 | 含AP2结构域蛋白,表达AP2 domain containing protein, expressed | -1.44 |
表6 植物激素相关差异表达基因
Table 6 Plants hormone related DEGs
基因编号 Unigene ID | 水稻中功能释义 Functional description in rice | 差异倍数 Log2 fold change |
|---|---|---|
| Unigene046376 | 磷脂酶D,推测,表达Phospholipase D, putative, expressed | 2.90 |
| Unigene060586 | 多药耐药相关蛋白,推测,表达Multidrug resistance-associated protein, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene028345 | 含WD重复序列蛋白,推测,表达WD repeat-containing protein, putative, expressed | 2.00 |
| Unigene012266 | 半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂前体蛋白,推测,表达Cysteine proteinase inhibitor precursor protein, putative, expressed | 1.87 |
| Unigene072636 | 醛氧化酶,推测Aldehyde oxidase, putative | -1.73 |
| Unigene030806 | 醛氧化酶,推测Aldehyde oxidase, putative | -10.00 |
| Unigene000154 | 转录抑制因子,推测,表达Transcriptional repressor, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene017481 | 脂肪酶蛋白,推测,表达Lipozygenase protein, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene061983 | 脂氧合酶,推测,表达Lipoxygenase, putative, expressed | -1.14 |
| Unigene061978 | 脂肪酶蛋白,推测,表达Lipozygenase protein, putative, expressed | -1.49 |
| Unigene039361 | 烯醇酶,推测,表达Enolase, putative, expressed | -2.13 |
| Unigene073044 | 氨基酸激酶,推测,表达Amino acid kinase, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene066363 | 含AP2结构域的蛋白,推测AP2 domain containing protein, putative | 10.00 |
| Unigene000226 | 含AP2结构域的蛋白,推测AP2 domain containing protein, putative | 1.77 |
| Unigene005128 | DEAD-盒ATP-依赖的RNA解旋酶,推测,表达DEAD-box ATP-dependent RNA helicase, putative, expressed | 1.71 |
| Unigene031676 | RNA结合蛋白,推测,表达RNA binding protein, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene013478 | 泛素连接酶,推测,表达Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, putative, expressed | -2.51 |
| Unigene011796 | 晚期胚胎发生丰富蛋白,推测Late embryogenesis abundant protein, putative | 1.94 |
| Unigene070085 | 细胞色素P450,推测,表达Cytochrome P450, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene060943 | 富含半胱氨酸类受体蛋白激酶7前体,推测,表达Cysteine-rich receptor-like protein kinase 7 precursor, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene034794 | 富含半胱氨酸类受体蛋白激酶7前体,推测,表达Cysteine-rich receptor-like protein kinase 7 precursor, putative, expressed | 1.42 |
| Unigene074427 | 醛氧化酶,推测Aldehyde oxidase, putative | -1.24 |
| Unigene024549 | 含LSM结构域蛋白,表达LSM domain containing protein, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene044589 | LTPL11蛋白酶抑制剂/种子储藏/LTP家族蛋白前体,表达LTPL11-protease inhibitor/seed storage/LTP family protein precursor, expressed | 3.32 |
| Unigene029300 | LTPL11蛋白酶抑制剂/种子储藏/LTP家族蛋白前体,表达LTPL11-protease inhibitor/seed storage/LTP family protein precursor, expressed | 1.83 |
| Unigene036441 | LTPL11蛋白酶抑制剂/种子储藏/LTP家族蛋白前体,表达LTPL11-protease inhibitor/seed storage/LTP family protein precursor, expressed | 1.42 |
| Unigene003016 | 生长素响应因子,推测,表达Auxin response factor, putative, expressed | 2.64 |
| Unigene003404 | 生长素响应因子,推测,表达Auxin response factor, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene010610 | 泛素融合蛋白,推测,表达Ubiquitin fusion protein, putative, expressed | -1.71 |
| Unigene016356 | 含dof锌指结构的蛋白,推测,表达Dof zinc finger domain containing protein, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene016424 | 含AP2结构域蛋白,表达AP2 domain containing protein, expressed | -1.44 |
| Unigene021698 | EF手性家族蛋白,推测,表达EF hand family protein, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene027288 | 生长素响应因子15,推测,表达Auxin response factor 15, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene029798 | COP9信号体复合体亚基5b,推测,表达COP9 signalosome complex subunit 5b, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene035367 | OsSAUR21-生长素响应SAUR基因家族成员,表达OsSAUR21-auxin-responsive SAUR gene family member, expressed | 1.43 |
| Unigene037483 | 生长素响应蛋白,推测,表达Auxin-repressed protein, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene038997 | 促后期复合物亚基11,推测,表达Anaphase-promoting complex subunit 11, putative, expressed | 2.04 |
| Unigene040618 | 含PAZ结构域蛋白,推测,表达PAZ domain containing protein, putative, expressed | 1.06 |
| Unigene046724 | OsIAA30-生长素响应 Aux/IAA基因家族成员,表达OsIAA30-auxin-responsive Aux/IAA gene family member, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene046971 | 核糖体蛋白L24,推测,表达Ribosomal protein L24, putative, expressed | -1.58 |
| Unigene054539 | PINHEAD,推测,表达PINHEAD, putative, expressed | 1.32 |
| Unigene058662 | 邻氨基苯甲酸合成酶组分I-1,叶绿体前体,推测,表达Anthranilate synthase component I-1, chloroplast precursor, putative, expressed | -1.01 |
| Unigene059108 | 多药耐药性蛋白,推测,表达Multidrug resistance protein, putative, expressed | -1.48 |
| Unigene073724 | 多药耐药性蛋白,推测,表达Multidrug resistance protein, putative, expressed | 2.69 |
| Unigene074290 | 糖基水解酶家族16,推测,表达Glycosyl hydrolases family 16, putative, expressed | 1.10 |
| Unigene045370 | 组氨酸激酶,推测,表达Histidine kinase, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene016424 | 含AP2结构域蛋白,推测AP2 domain containing protein, putative | -1.44 |
| Unigene066660 | 内切葡聚糖酶,推测,表达Endoglucanase, putative, expressed | 4.06 |
| Unigene000226 | 含AP2结构域蛋白,推测AP2 domain containing protein, putative | 1.77 |
| Unigene003249 | 脱氢酶,推测,表达Dehydrogenase, putative, expressed | 1.04 |
| Unigene003404 | 生长素响应因子,推测,表达Auxin response factor, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene004616 | 网格蛋白组装蛋白,推测,表达Clathrin assembly protein, putative, expressed | 1.86 |
| Unigene004990 | 剪接因子,富含精氨酸/丝氨酸,推测,表达Splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich, putative, expressed | 2.03 |
| Unigene004991 | 剪接因子,富含精氨酸/丝氨酸,推测,表达Splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich, putative, expressed | -2.60 |
| Unigene004995 | 剪接因子,富含精氨酸/丝氨酸,推测,表达Splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich, putative, expressed | -1.78 |
| Unigene013048 | Vignain前体,推测,表达Vignain precursor, putative, expressed | -4.34 |
| Unigene013756 | MBTB11-Bric-a-Brac结构域,表达MBTB11-Bric-a-Brac domain, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene026080 | 含tubulin/FtsZ结构域蛋白,推测,表达Tubulin/FtsZ domain containing protein, putative, expressed | 3.96 |
| Unigene037362 | 热激蛋白,推测,表达Heat shock protein, putative, expressed | -3.44 |
| Unigene038349 | 含RNA识别基序蛋白,表达RNA recognition motif containing protein, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene050603 | CHIT14-几丁质酶家族蛋白前体,表达CHIT14-Chitinase family protein precursor, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene051413 | 含AP2结构域蛋白,表达AP2 domain containing protein, expressed | 1.89 |
| Unigene055349 | 原叶绿素还原酶A,叶绿体前体,推测,表达Protochlorophyllide reductase A, chloroplast precursor, putative, expressed | -1.40 |
| Unigene064634 | 1-氨基环丙烷-1-羧酸氧化酶蛋白,推测,表达1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase protein, putative, expressed | 1.56 |
| Unigene066363 | 含AP2结构域蛋白,表达AP2 domain containing protein, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene066897 | 含KH结构域蛋白,推测,表达KH domain containing protein, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene071207 | 脱氢酶,推测,表达Dehydrogenase, putative, expressed | 1.51 |
| Unigene071208 | 脱氢酶,推测,表达Dehydrogenase, putative, expressed | 1.71 |
| Unigene073772 | 氧化还原酶,含短链脱氢/还原酶家族结构域蛋白,表达Oxidoreductase, short chain dehydrogenase/reductase family domain containing family, expressed | -2.07 |
| Unigene074432 | 糖基水解酶家族16,推测,表达Glycosyl hydrolases family 16, putative, expressed | 2.51 |
| Unigene037534 | 扩展蛋白前体,推测,表达Expansin precursor, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene031989 | 扩展蛋白前体,推测,表达Expansin precursor, putative, expressed | 1.90 |
| Unigene074120 | 扩展蛋白前体,推测,表达Expansin precursor, putative, expressed | 1.62 |
| Unigene026443 | 类促开花因子,推测,表达Flowering promoting factor-like 1, putative, expressed | 1.17 |
| Unigene012266 | 半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂前体蛋白,推测,表达Cysteine proteinase inhibitor precursor protein, putative, expressed | 1.87 |
| Unigene058662 | 邻氨基苯甲酸合成酶-组分I-1,叶绿体前体,推测,表达Anthranilate synthase component I-1, chloroplast precursor, putative, expressed | -1.01 |
| Unigene046376 | 磷脂酶D,推测,表达Phospholipase D, putative, expressed | 2.90 |
| Unigene008565 | 脂氧合酶,推测,表达Lipoxygenase, putative, expressed | 1.47 |
| Unigene045105 | 脂氧合酶,推测,表达Lipoxygenase, putative, expressed | -1.40 |
| Unigene071224 | 3-羟酰基-辅酶A脱氢酶,推测,表达3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene023000 | CESA5-纤维素合成酶,表达CESA5-cellulose synthase, expressed | 1.88 |
| Unigene017047 | 花青素调节蛋白,推测,表达Anthocyanin regulatory Lc protein, putative, expressed | -2.04 |
| Unigene059623 | 脱水反应元件结合蛋白,推测,表达Dehydration-responsive element-binding protein, putative, expressed | 10.00 |
| Unigene056424 | 胺氧化酶,推测,表达Amine oxidase, putative, expressed | -10.00 |
| Unigene016424 | 含AP2结构域蛋白,表达AP2 domain containing protein, expressed | -1.44 |
| 1 | Janssen B J, Drummond R S, Snowden K C. Regulation of axillary shoot development. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2014, 17: 28-35. |
| 2 | Teo Z W N, Song S, Wang Y Q, et al. New insights into the regulation of inflorescence architecture. Trends in Plant Science, 2014, 19(3): 158-165. |
| 3 | Rameau C, Bertheloot J, Leduc N, et al. Multiple pathways regulate shoot branching. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2015, 5: 741. |
| 4 | Karin S, Thomas S, Mathias R, et al. The Lateral suppressor (Ls) gene of tomato encodes a new member of the VHIID protein family. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1999, 96(1): 290-295. |
| 5 | Li X Y, Qian Q, Fu Z M, et al. Control of tillering in rice. Nature, 2003, 422(6932): 618. |
| 6 | Thomas G, Oliver C, Elisabeth S, et al. Molecular analysis of the LATERAL SUPPRESSOR gene in Arabidopsis reveals a conserved control mechanism for axillary meristem formation. Genes & Development, 2003, 17(9): 1175-1187. |
| 7 | Raman S, Greb T, Peaucelle A, et al. Interplay of miR164, CUP-SHAPED COTYLEDON genes and LATERAL SUPPRESSOR controls axillary meristem formation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Journal, 2008, 55(1): 65-76. |
| 8 | Thomas K, Jessica A, Thomas M, et al. Arabidopsis regulator of axillary meristems1 controls a leaf axil stem cell niche and modulates vegetative development. The Plant Cell, 2006, 18(3): 598-611. |
| 9 | Aguilar-Martínez J A, Poza-Carrión C, Cubas P. Arabidopsis BRANCHED1 acts as an integrator of branching signals within axillary buds. The Plant Cell, 2007, 19(2): 458-472. |
| 10 | Minakuchi K, Kameoka H, Yasuno N, et al. FINE CULM1 (FC1) works downstream of strigolactones to inhibit the outgrowth of axillary buds in rice. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2010, 51(7): 1127-1135. |
| 11 | Nils B, Alexandre de S G, Jean-Paul P, et al. The pea TCP transcription factor PsBRC1 acts downstream of strigolactones to control shoot branching. Plant Physiology, 2012, 158(1): 225-238. |
| 12 | Shi P B, Guy K M, Wu W F, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the ClTCP transcription factors in Citrullus lanatus. BMC Plant Biology, 2016, 16: 85-97. |
| 13 | Lee D J, Zeevaart J A. Molecular cloning of GA 2-oxidase3 from spinach and its ectopic expression in Nicotiana sylvestris. Plant Physiology, 2005, 138(1): 243-254. |
| 14 | Schomburg F M. Overexpression of a novel class of gibberellin 2-oxidases decreases gibberellin levels and creates dwarf plants. Plant Cell, 2003, 15(1): 151-163. |
| 15 | Guo Y L, Zou S H, Wang H P, et al. Cloning and preliminary functional analysis of three gibberellin 2-oxidase genes in petunia (Petunia hybrida). Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2013, 21(8): 940-948. |
| 郭余龙, 邹世慧, 王会平, 等. 矮牵牛3个赤霉素2-氧化酶基因的克隆及初步功能分析. 农业生物技术学报, 2013, 21(8): 940-948. | |
| 16 | Wang Y, Deng D. Molecular basis and evolutionary pattern of GA-GID1-DELLA regulatory module. Molecular Genetics & Genomics, 2014, 289(1): 1-9. |
| 17 | Woodward A W, Bartel B. Auxin: Regulation, action, and interaction. Annals of Botany, 2005, 95(5): 707-735. |
| 18 | Chung Y, Maharjan P M, Lee O, et al. Auxin stimulates DWARF4 expression and brassinosteroid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Journal for Cell & Molecular Biology, 2011, 66(4): 564-578. |
| 19 | Salchert K, Bhalerao R, Koncz-Kalman Z, et al. Control of cell elongation and stress responses by steroid hormones and carbon catabolic repression in plants. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 1998, 353(1374): 1517-1520. |
| 20 | Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Shimizu-Sato S, et al. Loss-of-function of a rice brassinosteriod biosynthetic enzyme, C-6 oxidase, prevents the organized arrangement and polar elongation of cells in the leaves and stem. Plant Journal, 2002, 32(4): 495-508. |
| 21 | Mian M A R, Zhang Y, Wang Z Y, et al. Analysis of tall fescue ESTs representing different abiotic stresses, tissue types and developmental stages. BMC Plant Biology, 2008, 8(1): 27. |
| 22 | Hu T, Sun X, Zhang X, et al. An RNA sequencing transcriptome analysis of the high-temperature stressed tall fescue reveals novel insights into plant thermotolerance. BMC Genomics, 2014, 15(1): 1147. |
| 23 | Su Y L, Liu M J, Li H F. Research progress on MADS-box gene in rice (Oryza sativa). Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 45(9): 1-7. |
| 苏亚丽, 刘梦佳, 李海峰. 水稻MADS-box基因研究进展. 河南农业科学, 2016, 45(9): 1-7. | |
| 24 | Guo S Y, Xu Y Y, Liu H H, et al. The interaction between OsMADS57 and OsTB1 modulates rice tillering via DWARF14. Nature Communications, 2013, 4(1): 1566. |
| 25 | Fabio F, Veronica G, Nilla P, et al. The rice StMADS11-like genes OsMADS22 and OsMADS47 cause floral reversions in Arabidopsis without complementing the svp and agl24 mutants. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2008, 59(8): 2181-2190. |
| 26 | Sakurai A, Yokota T, Clouse S D. Brassinosteroids: Steroidal plant hormones. Tokyo: Springer-Verlag, 1999: 21-45. |
| 27 | Kamuro Y, Takatsuto S. Capability for and problems of practical uses of brassinosteroids. Acs Symposium Series, 1991, 474: 292-297. |
| 28 | Cano-Delgado A, Yin Y H, Yu C, et al. BRL1 and BRL3 are novel brassinosteroid receptors that function in vascular differentiation in Arabidopsis. Development, 2004, 131(21): 5341-5351. |
| 29 | Martín-Trillo M, Cubas P. TCP genes: A family snapshot ten years later. Trends in Plant Science, 2010, 15(1): 31-39. |
| 30 | Li C X, Potuschak T, Colón-Carmona A, et al. Arabidopsis TCP20 links regulation of growth and cell division control pathways. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2005, 102(36): 12978-12983. |
| 31 | Steiner E, Efroni I, Gopalraj M, et al. The ArabidopsisO-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase SPINDLY interacts with class I TCPs to facilitate cytokinin responses in leaves and flowers. Plant Cell, 2012, 24(1): 96-108. |
| 32 | Daviere J M, Wild M, Regnault T, et al. Class I TCP-DELLA interactions in inflorescence shoot apex determine plant height. Current Biology, 2014, 24(16): 1923-1928. |
| 33 | Luo X, Sun X L, Liu B H, et al. Ectopic expression of a WRKY homolog from Glycine soja alters flowering time in Arabidopsis. PLoS One, 2013, 8(8): e73295. |
| 34 | Tian X J, Li X F, Zhou W J, et al. Transcription factor OsWRKY53 positively regulates brassinosteroid signaling and plant architecture. Plant Physiology, 2017, 175(3): 1337-1349. |
| 35 | Zhang C Q, Xu Y, Lu Y, et al. The WRKY transcription factor OsWRKY78 regulates stem elongation and seed development in rice. Planta, 2011, 234(3): 541-554. |
| 36 | Song Y, Chen L G, Zhang L P, et al. Overexpression of OsWRKY72 gene interferes in the abscisic acid signal and auxin transport pathway of Arabidopsis. Journal of Biosciences, 2010, 35(3): 459-471. |
| 37 | Yu Y C. The molecular mechanism of WRKY71 transcription factor in regulating flower and branch development of Arabidopsis thialiana. Jinan: Shandong University, 2011. |
| 于延冲. 拟南芥转录因子WRKY71对花和分枝发育的调控机制研究. 济南: 山东大学, 2011. | |
| 38 | Vanderauwera S, Vandenbroucke K, Inze A, et al. AtWRKY15 perturbation abolishes the mitochondrial stress response that steers osmotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2012, 109(49): 20113-20118. |
| 39 | Yu F, Huaxia Y, Lu W, et al. GhWRKY15, a member of the WRKY transcription factor family identified from cotton (Gossypium hirsutum), is involved in disease resistance and plant development. BMC Plant Biology, 2012, 12(1): 144. |
| 40 | Cai Y H, Chen X J, Xie K, et al. Dlf1, a WRKY transcription factor, is involved in the control of flowering time and plant height in rice. PLoS One, 2014, 9(7): e102529. |
| 41 | Qiu D Y, Xiao J, Xie W B, et al. Rice gene network inferred from expression profiling of plants overexpressing OsWRKY13, a positive regulator of disease resistance. Molecular Plant, 2008, 1(3): 538-551. |
| 42 | Wang H H, Hao J J, Chen X J, et al. Overexpression of rice WRKY89 enhances ultraviolet B tolerance and disease resistance in rice plants. Plant Molecular Biology, 2007, 65(6): 799-815. |
| 43 | Yao C, Finlayson S A. Abscisic acid is a general negative regulator of Arabidopsis axillary bud growth. Plant Physiology, 2015, 169(1): 611-626. |
| 44 | Arney S E, Mitchell D L. The effect of abscisic acid on stem elongation and correlative inhibition. New Phytologist, 1969, 68(4): 1001-1015. |
| 45 | Chatfield S P, Stirnberg P, Forde B G, et al. The hormonal regulation of axillary bud growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Journal, 2000, 24(2): 159-169. |
| 46 | Cline M G, Choonseok O. Reappraisal of the role of abscisic acid and its interaction with auxin in apical dominance. Annals of Botany, 2006, 98(4): 891-897. |
| 47 | Bris M L, Nicole M F, Jacob Y, et al. Regulation of bud dormancy by manipulation of ABA in isolated buds of Rosa hybrida cultured invitro. Functional Plant Biology, 1999, 26(3): 273-281. |
| 48 | Wang R F, Zhang J W, Lv P, et al. Effects of endogenous hormones on tiller development process of different maize varieties. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2012, 45(5): 840-847. |
| 王如芳, 张吉旺, 吕鹏, 等. 不同类型玉米品种分蘖发生过程中内源激素的作用. 中国农业科学, 2012, 45(5): 840-847. | |
| 49 | Domagalska M A, Leyser O. Signal integration in the control of shoot branching. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2011, 12(4): 211-221. |
| 50 | Reddy S K, Finlayson S A. Phytochrome B promotes branching in Arabidopsis by suppressing auxin signaling. Plant Physiology, 2014, 164(3): 1542-1550. |
| 51 | Song Y L, You J, Xiong L Z. Characterization of OsIAA1 gene, a member of rice Aux/IAA family involved in auxin and brassinosteroid hormone responses and plant morphogenesis. Plant Molecular Biology, 2009, 70(3): 297-309. |
| 52 | Fukaki H, Nakao Y, Okushima Y, et al. Tissue-specific expression of stabilized SOLITARY-ROOT/IAA14 alters lateral root development in Arabidopsis. Plant Journal, 2005, 44(3): 382-395. |
| 53 | Sakamoto T, Morinaka Y, Ishiyama K, et al. Genetic manipulation of gibberellin metabolism in transgenic rice. Nature Biotechnology, 2003, 21(8): 909-913. |
| 54 | Shan C, Mei Z L, Duan J L, et al. OsGA2ox5, a gibberellin metabolism enzyme, is involved in plant growth, the root gravity response and salt stress. PLoS One, 2014, 9(1): e87110. |
| 55 | Huang J, Tang D, Shen Y, et al. Activation of gibberellin 2-oxidase 6 decreases active gibberellin levels and creates a dominant semi-dwarf phenotype in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2010, 37(1): 23-36. |
| 56 | Hong X F, Jiang P Y, Zheng Z S, et al. Effects of gibberellin (GA3) on tillering control and tillering rate improvement in rice (Oryza sativa L.) tillering stage. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 1998(1): 3-5. |
| 洪晓富, 蒋鹏炎, 郑寨生, 等. 水稻分蘖期喷施赤霉素(GA3)对控制分蘖和提高成穗率的效果. 浙江农业科学, 1998(1): 3-5. | |
| 57 | Barleben L, Ma X Y, Koepke J, et al. Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of strictosidine glucosidase, an enzyme initiating biosynthetic pathways to a unique diversity of indole alkaloid skeletons. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2005, 1747(1): 89-92. |
| 58 | Kovi M R, Zhang Y, Yu S, et al. Candidacy of a chitin-inducible gibberellin-responsive gene for a major locus affecting plant height in rice that is closely linked to green revolution gene sd1. Theoretical & Applied Genetics, 2011, 123(5): 705-714. |
| [1] | 周晶, 陈思齐, 史文娇, 阳伏林, 林辉, 林占熺. 巨菌草幼叶及根转录组功能基因测序及分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 143-155. |
| [2] | 王如月, 文武武, 赵恩华, 周鹏, 安渊. 紫花苜蓿MsWRKY11基因的克隆及其耐盐功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 157-169. |
| [3] | 汪芳珍, 杨成行, 何子华, 林子茹, 曾浩源, 马清. 盐处理下旱生植物沙芥蛋白激酶相关基因的差异表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 116-124. |
| [4] | 罗维, 舒健虹, 刘晓霞, 王子苑, 牟琼, 王小利, 吴佳海. 高羊茅FaRVE8基因的克隆、亚细胞定位及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 60-69. |
| [5] | 王晓瑜, 丁婷婷, 李彦忠, 段廷玉. AM真菌与根瘤菌对紫花苜蓿镰刀菌萎蔫和根腐病的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 139-149. |
| [6] | 滕珂, 张蕊, 檀鹏辉, 岳跃森, 范希峰, 武菊英. 日本结缕草ZjERF1的克隆、转录激活活性、亚细胞定位及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(6): 56-65. |
| [7] | 钱晨, 刘智微, 钟小仙, 吴娟子, 张建丽, 潘玉梅. 海滨雀稗自交结实突变体及野生型幼穗组织的转录组分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(5): 132-142. |
| [8] | 闵学阳, 韦兴燚, 刘文献, 张正社, 金小煜, NDAYAMBAZABoniface, 吴洪林, 李昱, 王彦荣. 箭筈豌豆品种间遗传差异的SSR分析及指纹图谱构建[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(4): 116-128. |
| [9] | 姜红岩, 滕珂, 檀鹏辉, 尹淑霞. 日本结缕草ZjZFN1基因对拟南芥的转化及其耐旱性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(4): 129-138. |
| [10] | 成启明, 格根图, 撒多文, 王志军, 范文强, 卜振鲲, 司强, 李俊峰, 卢娟, 贾玉山. 不同品种紫花苜蓿转录组分析及营养品质差异的探讨[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(10): 199-208. |
| [11] | 李孟湛, 尹红菊, 李丁丁, 刘亚琪, 王锁民. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术敲除拟南芥转录因子MYB 40的两种可变剪接体[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 120-127. |
| [12] | 柯丹霞, 彭昆鹏, 夏远君, 朱玉莹, 张丹丹. 盐胁迫应答基因GmWRKY6的克隆及转基因百脉根的抗盐分析[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 95-106. |
| [13] | 庄黎丽, 王剑, 杨志民. 基于转录组数据库的高羊茅HD-Zip I转录因子的鉴定及表达模式解析[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 67-77. |
| [14] | 刘慧霞, 林丽果, 武文莉, 林选栋, 宋锐. 硅对不同抗性高羊茅耐盐性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 84-92. |
| [15] | 李小冬, 吴佳海, 孙方, 陈光吉, 王小利. 过量表达Fa14-3-3C促进拟南芥对低氮胁迫耐受性的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(9): 104-112. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||