

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 116-124.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020368
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
汪芳珍( ), 杨成行(
), 杨成行( ), 何子华, 林子茹, 曾浩源, 马清(
), 何子华, 林子茹, 曾浩源, 马清( )
)
收稿日期:2020-07-29
修回日期:2020-10-19
出版日期:2021-09-16
发布日期:2021-09-16
通讯作者:
马清
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: maq@lzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Fang-zhen WANG( ), Cheng-hang YANG(
), Cheng-hang YANG( ), Zi-hua HE, Zi-ru LIN, Hao-yuan ZENG, Qing MA(
), Zi-hua HE, Zi-ru LIN, Hao-yuan ZENG, Qing MA( )
)
Received:2020-07-29
Revised:2020-10-19
Online:2021-09-16
Published:2021-09-16
Contact:
Qing MA
摘要:
旱生植物沙芥具有极强的耐盐能力,对其耐盐相关分子基础的研究将为农作物和牧草抗逆性遗传改良提供重要的基因资源。前期研究已采用转录组学研究方法分析了盐胁迫下沙芥功能基因的差异表达情况,并筛选了一批与沙芥耐盐性相关的重要候选功能基因,而盐胁迫下沙芥体内调控基因的表达变化情况未见报道。为进一步揭示沙芥耐盐分子机制,本研究利用已获得的50 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理6和24 h后沙芥根和叶组织的转录组数据,分析了盐胁迫下沙芥体内蛋白激酶相关基因的差异表达情况。结果表明,50 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理下沙芥体内大量蛋白激酶相关基因表达发生显著变化。其中,根和地上部中大量富亮氨酸重复类受体蛋白激酶(LRR-RLKs)编码基因的表达在50 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理6和24 h后均显著上调;50 mmol·L-1 NaCl短期处理(6 h)后,根和地上部中众多促分裂原活化蛋白激酶级联途径(MAPK/MAPKK/MAPKKK)相关基因的表达被显著诱导,而一些乙烯信号转导途径中重要负调控因子CTR1编码基因在对照处理下均有表达,但在50 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理6 h后的根中均不表达。上述结果表明,LRR-RLK家族蛋白在沙芥适应盐胁迫过程中可能发挥着重要的调控作用,MAPK/MAPKK/MAPKKK可能参与调控沙芥对短期盐胁迫的响应,CTR1可能在沙芥根系响应盐胁迫过程中发挥负调控功能。
汪芳珍, 杨成行, 何子华, 林子茹, 曾浩源, 马清. 盐处理下旱生植物沙芥蛋白激酶相关基因的差异表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 116-124.
Fang-zhen WANG, Cheng-hang YANG, Zi-hua HE, Zi-ru LIN, Hao-yuan ZENG, Qing MA. Analysis of differentially expressed protein kinase related genes in the xerophyte Pugionium cornutum under salt treatment[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(10): 116-124.
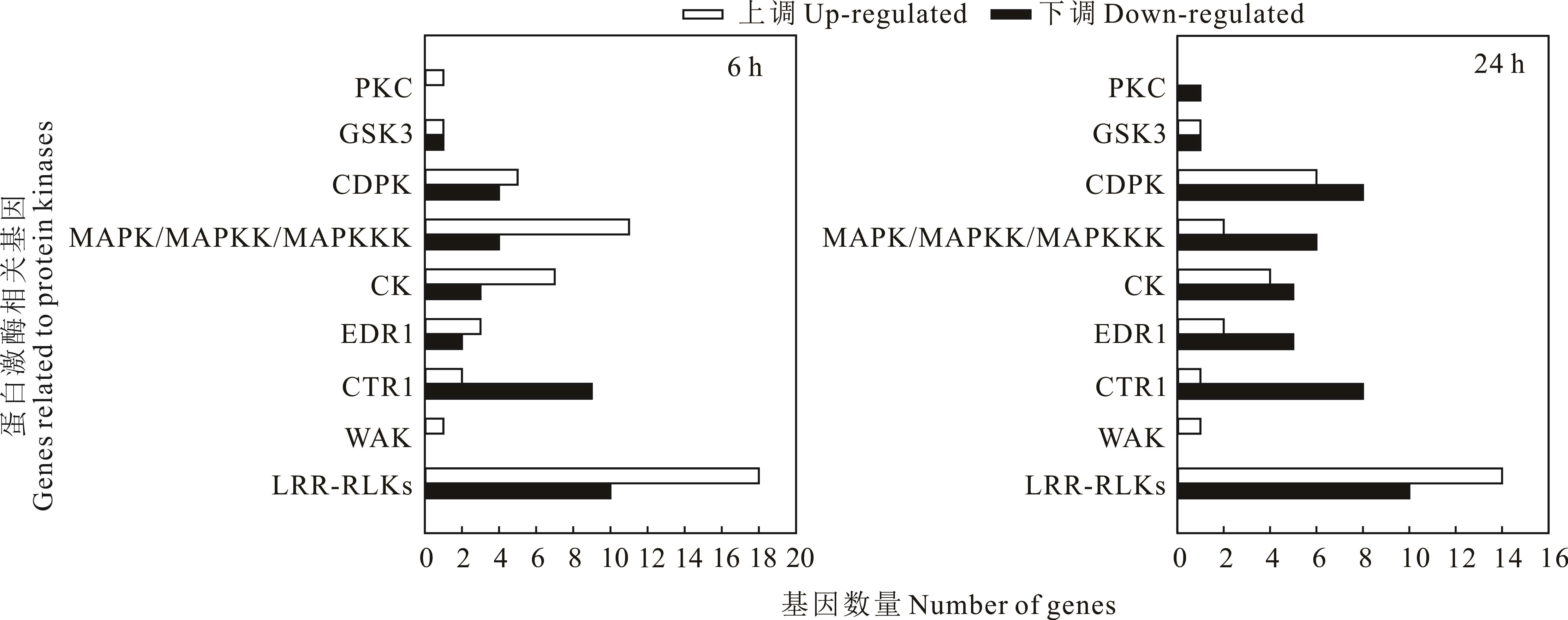
图1 50 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理6和24 h后沙芥根中蛋白激酶相关DEGsPKC为蛋白激酶C;GSK3为糖原合成酶激酶;CDPK为钙依赖性蛋白激酶;MAPK/MAPKK/MAPKKK为促分裂原活化蛋白激酶级联途径;CK为酪蛋白激酶;EDR1为增强抗病性因子;CTR1为组成型三重反应;WAK为细胞壁连接的类受体激酶;LRR-RLKs为富亮氨酸重复类受体蛋白激酶。下同。PKC: protein kinase C; GSK3: glycose synthase kinase 3; CDPK: calcium-dependent protein kinase; MAPK/MAPKK/MAPKKK: mitogen-activated protein kinase/MAP kinase kinase/MAP kinase kinase kinase; CK: casein kinase; EDR1: enhanced disease resistance 1; CTR1: constitutive triple response 1; WAK: wall associated kinase-like; LRR-RLKs: leucine rich repeat receptor-like kinases. The same below.
Fig. 1 Protein kinase-associated DEGs in root of P. cornutum under 50 mmol·L-1 NaCl for 6 and 24 h
| 基因Gene | 基因编号Gene ID | 同源基因Homologous gene | 同源物种Homologous species |
|---|---|---|---|
| LRR-RLKs | CL2242.Contig2_All | LRR-RLK (AT5G10020) | 拟南芥Arabidopsis thaliana |
| CL797.Contig29_All | LRR-RLK (AT3G49670) | 亚麻荠Camelina sativa | |
| CL6717.Contig2_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G29720) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CL7990.Contig5_All | LRR-RLK (AT3G14350 ) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| Unigene29560_All | LRR-RLK (AT5G07150) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CL1136.Contig10_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G07560) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| WAK | CL807.Contig2_All | WAK 4 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| EDR1 | CL4341.Contig2_All | EDR1 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CK | CL1663.Contig1_All | CK II | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| MAPK/MAPKK/MAPKKK | CL2088.Contig2_All | MAPK 5 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL1291.Contig1_All | MAPK18 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
表1 沙芥根中对照处理下不表达而50 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理6 h后表达的蛋白激酶相关基因
Table 1 Genes related to protein kinase expressed in root of P. cornutum under 50 mmol·L-1 NaCl for 6 h but not expressed in root under control condition
| 基因Gene | 基因编号Gene ID | 同源基因Homologous gene | 同源物种Homologous species |
|---|---|---|---|
| LRR-RLKs | CL2242.Contig2_All | LRR-RLK (AT5G10020) | 拟南芥Arabidopsis thaliana |
| CL797.Contig29_All | LRR-RLK (AT3G49670) | 亚麻荠Camelina sativa | |
| CL6717.Contig2_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G29720) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CL7990.Contig5_All | LRR-RLK (AT3G14350 ) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| Unigene29560_All | LRR-RLK (AT5G07150) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CL1136.Contig10_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G07560) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| WAK | CL807.Contig2_All | WAK 4 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| EDR1 | CL4341.Contig2_All | EDR1 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CK | CL1663.Contig1_All | CK II | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| MAPK/MAPKK/MAPKKK | CL2088.Contig2_All | MAPK 5 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL1291.Contig1_All | MAPK18 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| 处理时间Treatments time (h) | 基因编号Gene ID | 同源基因Homologous gene | 同源物种Homologous species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | CL3516.Contig2_All | CTR1 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL2980.Contig2_All | CTR1 | 琴叶拟南芥Arabidopsis lyrata | |
| 24 | CL2548.Contig11_All | CTR1 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL2980.Contig4_All | CTR1 | 琴叶拟南芥A. lyrata | |
| CL3385.Contig7_All | CTR1 | 琴叶拟南芥A. lyrata |
表2 沙芥根中对照处理下表达而50 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理下不表达的CTR1编码基因
Table 2 Genes encoding CTR1 expressed in root of P. cornutum under control but not expressed under 50 mmol·L-1 NaCl treatment
| 处理时间Treatments time (h) | 基因编号Gene ID | 同源基因Homologous gene | 同源物种Homologous species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | CL3516.Contig2_All | CTR1 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL2980.Contig2_All | CTR1 | 琴叶拟南芥Arabidopsis lyrata | |
| 24 | CL2548.Contig11_All | CTR1 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL2980.Contig4_All | CTR1 | 琴叶拟南芥A. lyrata | |
| CL3385.Contig7_All | CTR1 | 琴叶拟南芥A. lyrata |
| 基因Gene | 基因编号Gene ID | 同源基因Homologous gene | 同源物种Homologous species |
|---|---|---|---|
| LRR-RLKs | CL797.Contig15_All | LRR-RLK (AT3G49670) | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL2242.Contig1_All | LRR-RLK (AT5G10020) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CL217.Contig3_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G07650) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CDPK | CL5176.Contig7_All | CDPK5 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| Unigene12783_All | CDPK6 | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CK | Unigene2819_All | CKI | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
表3 沙芥根中对照处理下不表达而50 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理24 h后表达的蛋白激酶相关基因
Table 3 Genes related to protein kinase expressed in root of P. cornutum under 50 mmol·L-1 NaCl for 24 h but not expressed in root under control condition
| 基因Gene | 基因编号Gene ID | 同源基因Homologous gene | 同源物种Homologous species |
|---|---|---|---|
| LRR-RLKs | CL797.Contig15_All | LRR-RLK (AT3G49670) | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL2242.Contig1_All | LRR-RLK (AT5G10020) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CL217.Contig3_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G07650) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CDPK | CL5176.Contig7_All | CDPK5 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| Unigene12783_All | CDPK6 | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CK | Unigene2819_All | CKI | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
基因编号 Gene ID | 同源基因 Homologous gene | 上调/下调 Up/down-regulated |
|---|---|---|
| CL2548.Contig6_All | CTR1 | down |
| CL101.Contig3_All | CTR1 | down |
| CL4149.Contig6_All | CTR1 | down |
| CL70.Contig23_All | CTR1 | down |
| CL3225.Contig5_All | CTR1 | down |
| CL7357.Contig2_All | CTR1 | down |
| Unigene29671_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G79620) | up |
表4 50 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理6和24 h后沙芥根中均上调或下调表达的蛋白激酶相关DEGs
Table 4 Protein kinase-associated DEGs that were up-regulated or down-regulated in root of P. cornutum under 50 mmol·L-1 NaCl for both 6 and 24 h
基因编号 Gene ID | 同源基因 Homologous gene | 上调/下调 Up/down-regulated |
|---|---|---|
| CL2548.Contig6_All | CTR1 | down |
| CL101.Contig3_All | CTR1 | down |
| CL4149.Contig6_All | CTR1 | down |
| CL70.Contig23_All | CTR1 | down |
| CL3225.Contig5_All | CTR1 | down |
| CL7357.Contig2_All | CTR1 | down |
| Unigene29671_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G79620) | up |
| 基因Gene | 基因编号Gene ID | 同源基因Homologous gene | 同源物种Homologous species |
|---|---|---|---|
| LRR-RLKs | CL8787.Contig2_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G04210) | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL8721.Contig3_All | LRR-RLK (AT2G35620) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CL7704.Contig2_All | LRR-RLK (AT2G17440) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CL4552.Contig2_All | LRR-RLK (AT4G26050) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| WAK | CL807.Contig2_All | WAK 4 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CDPK | CL707.Contig1_All | CDPK 5 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL5176.Contig7_All | CDPK 6 | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CL1773.Contig18_All | CDPK 32 | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CL4470.Contig2_All | CDPK 2 | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| MAPK/MAPKK/MAPKKK | CL10.Contig5_All | MAP4K 2 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL3832.Contig4_All | MAPKK 1 | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| Unigene7805_All | MAPK 16 | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| EDR1 | CL5872.Contig4_All | EDR1 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL4341.Contig2_All | EDR1 | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CK | CL1663.Contig1_All | CK II | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| Unigene16644_All | CK I | 琴叶拟南芥A. lyrata | |
| Unigene9975_All | CK I | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
表5 沙芥地上部对照处理下不表达而在50 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理6 h后表达的蛋白激酶相关基因
Table 5 Genes related to protein kinase expressed in shoot of P. cornutum under 50 mmol·L-1 NaCl for 6 h but not expressed in shoot under control condition
| 基因Gene | 基因编号Gene ID | 同源基因Homologous gene | 同源物种Homologous species |
|---|---|---|---|
| LRR-RLKs | CL8787.Contig2_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G04210) | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL8721.Contig3_All | LRR-RLK (AT2G35620) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CL7704.Contig2_All | LRR-RLK (AT2G17440) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CL4552.Contig2_All | LRR-RLK (AT4G26050) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| WAK | CL807.Contig2_All | WAK 4 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CDPK | CL707.Contig1_All | CDPK 5 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL5176.Contig7_All | CDPK 6 | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CL1773.Contig18_All | CDPK 32 | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CL4470.Contig2_All | CDPK 2 | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| MAPK/MAPKK/MAPKKK | CL10.Contig5_All | MAP4K 2 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL3832.Contig4_All | MAPKK 1 | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| Unigene7805_All | MAPK 16 | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| EDR1 | CL5872.Contig4_All | EDR1 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL4341.Contig2_All | EDR1 | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CK | CL1663.Contig1_All | CK II | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| Unigene16644_All | CK I | 琴叶拟南芥A. lyrata | |
| Unigene9975_All | CK I | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| 基因Gene | 基因编号Gene ID | 同源基因Homologous gene | 同源物种Homologous species |
|---|---|---|---|
| LRR-RLKs | CL3884.Contig5_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G51800) | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL4661.Contig4_All | LRR-RLK (AT5G01720) | 亚麻荠C. sativa | |
| CL3235.Contig3_All | LRR-RLK (AT3G11330) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CL4047.Contig1_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G29720) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| EDR1 | CL1578.Contig1_All | EDR1 | 琴叶拟南芥A. lyrata |
| CDPK | CL707.Contig1_All | CDPK5 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL1773.Contig18_All | CDPK32 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
表6 沙芥地上部对照处理下不表达而50 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理24 h后表达的蛋白激酶相关基因
Table 6 Genes related to protein kinase expressed in shoot of P. cornutum under 50 mmol·L-1 NaCl for 24 h but not expressed in shoot under control condition
| 基因Gene | 基因编号Gene ID | 同源基因Homologous gene | 同源物种Homologous species |
|---|---|---|---|
| LRR-RLKs | CL3884.Contig5_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G51800) | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL4661.Contig4_All | LRR-RLK (AT5G01720) | 亚麻荠C. sativa | |
| CL3235.Contig3_All | LRR-RLK (AT3G11330) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| CL4047.Contig1_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G29720) | 拟南芥A. thaliana | |
| EDR1 | CL1578.Contig1_All | EDR1 | 琴叶拟南芥A. lyrata |
| CDPK | CL707.Contig1_All | CDPK5 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
| CL1773.Contig18_All | CDPK32 | 拟南芥A. thaliana |
基因编号 Gene ID | 同源基因 Homologous gene | 上调/下调 Up/down-regulated |
|---|---|---|
| CL797.Contig29_All | LRR-RLK (BAM2) | up |
| CL8787.Contig2_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G04210) | up |
| CL4552.Contig2_All | LRR-RLK (AT4G26050) | up |
| CL3884.Contig6_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G51800) | up |
| CL8721.Contig3_All | LRR-RLK (AT2G35620) | up |
| CL1773.Contig18_All | CDPK32 | up |
| CL5415.Contig8_All | CKII | up |
| CL1578.Contig8_All | EDR1 | up |
| CL3385.Contig7_All | CTR1 | down |
表7 50 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理6和24 h后沙芥地上部中均上调或下调表达的蛋白激酶相关DEGs
Table 7 Protein kinase-related DEGs that were up-regulated or down-regulated in shoot of P. cornutum under 50 mmol·L-1 NaCl for both 6 and 24 h
基因编号 Gene ID | 同源基因 Homologous gene | 上调/下调 Up/down-regulated |
|---|---|---|
| CL797.Contig29_All | LRR-RLK (BAM2) | up |
| CL8787.Contig2_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G04210) | up |
| CL4552.Contig2_All | LRR-RLK (AT4G26050) | up |
| CL3884.Contig6_All | LRR-RLK (AT1G51800) | up |
| CL8721.Contig3_All | LRR-RLK (AT2G35620) | up |
| CL1773.Contig18_All | CDPK32 | up |
| CL5415.Contig8_All | CKII | up |
| CL1578.Contig8_All | EDR1 | up |
| CL3385.Contig7_All | CTR1 | down |
| 1 | Lu J H, Lv X, Wu L, et al. Germination responses of three medicinal licorices to saline environments and their suitable ecological regions. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(2): 195-202. |
| 陆嘉惠, 吕新, 吴玲, 等. 三种药用甘草种子对盐渍环境的萌发响应及其适宜生态种植区. 草业学报, 2013, 22(2): 195-202. | |
| 2 | Liu H L, Yang G H, Zhang S J. Impact of the irrigation diverted water from the Huanghe River on land salinification in Mongolia Hetao Regions. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2006, 34(5): 948-950. |
| 刘和林, 杨改河, 张生军. 内蒙古河套灌区引黄灌溉对盐渍化的影响分析. 安徽农业科学, 2006, 34(5): 948-950. | |
| 3 | Tai S X, He Q, Bi J. Study on appraisal and conservation measures of environment in West Inner Mongolia. Arid Zone Research, 2007, 24(3): 364-368. |
| 邰生霞, 何桥, 毕佳. 内蒙古西部区环境评价. 干旱区研究, 2007, 24(3): 364-368. | |
| 4 | Rozema J, Flowers T. Crops for a salinized world. Science, 2008, 322(5907): 1478-1480. |
| 5 | Yue L J, Cui Y N, Yuan K, et al. The osmotic adjustment in Pugionium cornutum subjected to salt stress. Plant Physiology Journal, 2016, 52(4): 569-574. |
| 岳利军, 崔彦农, 袁坤, 等. NaCl胁迫下沙芥的渗透调节作用. 植物生理学报, 2016, 52(4): 569-574. | |
| 6 | Yue L J, Yuan K, Li H W, et al. Adaptive responses of eremophyte Pugionium cornutum seedlings to different concentrations of NaCl. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(1): 144-152. |
| 岳利军, 袁坤, 李海伟, 等. 荒漠植物沙芥苗期对不同浓度NaCl的适应机制. 草业学报, 2016, 25(1): 144-152. | |
| 7 | Flowers T J, Colmer T D. Plant salt tolerance: Adaptations in halophytes. Annals Botany, 2015, 115(3): 327-331. |
| 8 | Munns R, Gilliham M. Salinity tolerance of crops-what is the cost. New Phytologist, 2015, 208(3): 668-673. |
| 9 | Zhao Y Z. A tax ological revision and floristic analysis of the Genus Pugionium. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Neimongol, 1999, 30(2): 197-199. |
| 赵一之. 沙芥属的分类校正及其区系分析. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 1999, 30(2): 197-199. | |
| 10 | He X, Zhou S Q, Yan J, et al. Anatomical observation on nutrituve organs of Pugionium cornutum and P. dolabratum. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 1998, 12(2): 96-100. |
| 贺晓, 周世权, 闫洁, 等. 沙芥和斧形沙芥营养器官的解剖学观察. 干旱区资源与环境, 1998, 12(2): 96-100. | |
| 11 | Hao L Z, Zhai S, Jia J, et al. A study on vegetative growth law and leaf anatomy of Pugionium cornutum (L.) Gaertn. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2004, 19(4): 66-69. |
| 郝丽珍, 翟胜, 贾晋, 等. 沙芥营养生长规律及叶片解剖结构的研究. 华北农学报, 2004, 19(4): 66-69. | |
| 12 | He Y P. NaCl coercion to Pugionium Gaertn.plant seedling different vegetal period physiology foundation influence. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2009. |
| 贺勇鹏. NaCl胁迫对沙芥属植物幼苗不同生长期生理基础的影响. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2009. | |
| 13 | Cui Y N, Li X T, Yuan J Z, et al. Chloride is beneficial for growth of the xerophyte Pugionium cornutum by enhancing osmotic adjustment capacity under salt and drought stresses. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2020, 71(14): 4215-4231. |
| 14 | Cui Y N, Wang F Z, Yang C H, et al. Transcriptomic profiling identifies candidate genes involved in the salt tolerance of the xerophyte Pugionium cornutum. Genes, 2019, 10(12): 1039. |
| 15 | Osakabe Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K, et al. Sensing the environment: Key roles of membrane-localized kinases in plant perception and response to abiotic stress. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2013, 64(2): 445-458. |
| 16 | Kazan K. Diverse roles of jasmonates and ethylene in abiotic stress tolerance. Trends in Plant Science, 2015, 20(4): 219-229. |
| 17 | Pei L L, Guo Y H, Xu Z S, et al. Research progress on stress-related protein kinases in plants. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2012, 32(5): 1052-1061. |
| 裴丽丽, 郭玉华, 徐兆师, 等. 植物逆境胁迫相关蛋白激酶的研究进展. 西北植物学报, 2012, 32(5): 1052-1061. | |
| 18 | Li R Q, Yu C, Li G R, et al. SOAP2: An improved ultrafast tool for short read alignment. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(15): 1966-1967. |
| 19 | Zhang G J, Guo G W, Hu X D, et al. Deep RNA sequencing at single base-pair resolution reveals high complexity of the rice transcriptome. Genome Research, 2010, 20(5): 646-654. |
| 20 | Audic S, Claverie J M. The significance of digital gene expression profiles. Genome Research, 1997, 7(10): 986-995. |
| 21 | Wang Q, Yu Q S, Liu J Q. Are nuclear loci ideal for barcoding plants? A case study of genetic delimitation of two sister species using multiple loci and multiple intraspecific individuals. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 2011, 49(3): 182-188. |
| 22 | de Lorenzo L, Merchan F, Laporte P, et al. A novel plant leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase regulates the response of Medicago truncatula roots to salt stress. The Plant Cell, 2009, 21(2): 668-680. |
| 23 | Wu T, Tian Z D, Liu J, et al. A novel leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase gene in potato, StLRPK1, is involved in response to diverse stresses. Molecular Biology Reports, 2009, 36(8): 2365-2374. |
| 24 | Wang J, Zhang P Y, Liu S G, et al. A leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase from the antarctic moss Pohlia nutans confers salinity and ABA stress tolerance. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 2016, 34(6): 1136-1145. |
| 25 | Xu H N, Li K Z, Yang F J, et al. Overexpression of CsNMAPK in tobacco enhanced seed germination under salt and osmotic stresses. Molecular Biology Reports, 2010, 37(7): 3157-3163. |
| 26 | Kong X P, Pan J W, Zhang M Y, et al. ZmMKK4, a novel group C mitogen-activated protein kinase in maize (Zea mays), confers salt and cold tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell and Environment, 2011, 34(8): 1291-1303. |
| 27 | Yang C J, Wang R N, Gou L Z, et al. Overexpression of Populus trichocarpa mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 enhances salt tolerance in tobacco. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2017, 18(10): 2090. |
| 28 | Mi C L, Wen X J, Zhang X Y, et al. Cloning and characterization of a putative CTR1 gene from wheat. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2009, 42(11): 3785-3794. |
| 秘彩莉, 温小杰, 张学勇, 等. 小麦类CTR1基因的克隆和特性分析. 中国农业科学, 2009, 42(11): 3785-3794. | |
| 29 | Achard P, Cheng H, De Grauwe L, et al. Integration of plant responses to environmentally activated phytohormonal signals. Science, 2006, 311: 91-94. |
| 30 | Wang Y N, Liu C, Li K X, et al. Arabidopsis EIN2 modulates stress response through abscisic acid response pathway. Plant Molecular Biology, 2007, 64(6): 633-644. |
| 31 | Jiang C F, Belfield E J, Cao Y, et al. An Arabidopsis soil-salinity-tolerance mutation confers ethylene-mediated enhancement of sodium/potassium homeostasis. The Plant Cell, 2013, 25: 3535-3552. |
| [1] | 陆安桥, 张峰举, 许兴, 王学琴, 姚姗. 盐胁迫对湖南稷子苗期生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 84-93. |
| [2] | 周晶, 陈思齐, 史文娇, 阳伏林, 林辉, 林占熺. 巨菌草幼叶及根转录组功能基因测序及分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 143-155. |
| [3] | 王苗苗, 周向睿, 梁国玲, 赵桂琴, 焦润安, 柴继宽, 高雪梅, 李娟宁. 5份燕麦材料苗期耐盐性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 143-154. |
| [4] | 黄勇, 郭猛, 张红瑞, 周艳, 李贺敏, 高致明, 王盼盼. 盐胁迫对石竹种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 105-111. |
| [5] | 王桔红, 史生晶, 陈文, 甘桂媚, 陈赛娜, 李张伟. 枯草芽孢杆菌和3种放线菌对盐胁迫下鬼针草和鳢肠种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 112-120. |
| [6] | 何建军, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 边秀秀, 司二静, 杨轲, 王化俊, 马小乐, 李葆春, 尚勋武, 孟亚雄. 干旱和盐胁迫对盐生植物盐生草种子萌发特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 129-140. |
| [7] | 李珍, 云岚, 石子英, 王俊, 张晨, 郭宏宇, 盛誉. 盐胁迫对新麦草种子萌发及幼苗期生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 119-129. |
| [8] | 伍国强, 李辉, 雷彩荣, 蔺丽媛, 金娟, 李善家. 添加KCl对高盐胁迫下红豆草生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(6): 45-55. |
| [9] | 钱晨, 刘智微, 钟小仙, 吴娟子, 张建丽, 潘玉梅. 海滨雀稗自交结实突变体及野生型幼穗组织的转录组分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(5): 132-142. |
| [10] | 孙亚男, 林茹, 潘晓阳, 陈月, 陶磊, 郭长虹. 紫花苜蓿MsZAT10基因的克隆及其在烟草中的功能验证[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 94-102. |
| [11] | 王小山, 季晓敏, 刘隆阳, 纪冰沁, 田银芳. EBR对NaCl胁迫下苜蓿属植物离子吸收和分配的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(9): 110-119. |
| [12] | 王雨, 周睿颖, 马立敏, 白钰, 关佳莉, 唐晓清. 5个产地菘蓝种子萌发及幼苗生长对盐胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(7): 145-154. |
| [13] | 米永伟, 王国祥, 龚成文, 蔡子平, 武伟国. 盐胁迫对菘蓝幼苗生长和抗性生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(6): 43-51. |
| [14] | 钟华,董洁,董宽虎. 盐胁迫对扁蓿豆幼苗脯氨酸积累及其代谢关键酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 189-194. |
| [15] | 孙守江, 师尚礼, 吴召林, 何丽娟, 金鑫, 祁娟. 激动素对盐胁迫下老芒麦幼苗端粒酶活性及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(11): 87-94. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||