

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (1): 102-116.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023100
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
韩硕1,2( ), 韩晓文1,2, 胡义锋4, 陈中义1,3, 朱永兴1,3, 尹军良1,2(
), 韩晓文1,2, 胡义锋4, 陈中义1,3, 朱永兴1,3, 尹军良1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2023-04-03
修回日期:2023-06-14
出版日期:2024-01-20
发布日期:2023-11-23
通讯作者:
尹军良
作者简介:E-mail: w.yinzi@163.com基金资助:
Shuo HAN1,2( ), Xiao-wen HAN1,2, Yi-feng HU4, Zhong-yi CHEN1,3, Yong-xing ZHU1,3, Jun-liang YIN1,2(
), Xiao-wen HAN1,2, Yi-feng HU4, Zhong-yi CHEN1,3, Yong-xing ZHU1,3, Jun-liang YIN1,2( )
)
Received:2023-04-03
Revised:2023-06-14
Online:2024-01-20
Published:2023-11-23
Contact:
Jun-liang YIN
摘要:
超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)是一类保守的抗氧化酶,在植物生长发育和胁迫应答响应过程中发挥重要作用。目前,尚缺乏对空心莲子草SOD家族成员的系统认识。本研究通过生物信息学对空心莲子草SOD基因家族进行了系统的鉴定及分析,并对其理化性质、保守基序、基因结构、系统发育进化关系、miRNA靶向关系和表达模式等进行了分析。结果表明,在空心莲子草中共鉴定到43个ApSOD,其中22个属于Cu/ZnSOD亚家族,21个属于Fe/MnSOD亚家族;蛋白质特征分析表明,36个ApSOD蛋白为亲水蛋白,37个ApSOD蛋白为稳定蛋白;亚细胞定位预测发现,大部分Cu/ZnSOD定位在叶绿体或细胞质,大多数Fe/MnSOD定位在线粒体。保守结构域分析发现,同亚家族中的成员具有相似的保守基序与基因结构。miRNA靶向关系预测发现,17个空心莲子草miRNA通过切割或翻译抑制作用靶向14个ApSODs。表达模式分析发现,ApSODs在不同环境条件和组织中表达水平相对稳定。利用RT-qPCR分析了6个ApSODs在除草剂处理下的表达模式,结果表明,在噁草酮和氯氟吡氧乙酸胁迫下,6个ApSODs在药后7 d内显著上调表达;在乙羧氟草醚胁迫下,4个ApSODs随着处理时间的延长表达量呈先上升后下降再回升的趋势;在草甘膦胁迫下,6个ApSODs在7 d时显著上调表达;在异丙隆胁迫下,4个ApSODs在1 d时均显著下调表达。说明在除草剂胁迫下ApSODs表现出不同的表达模式。本研究对空心莲子草ApSOD家族成员进行系统鉴定和特征分析,并初步揭示了6个基因在除草剂胁迫下的表达特征,为进一步研究ApSODs在响应除草剂胁迫中的生物学功能奠定了基础。
韩硕, 韩晓文, 胡义锋, 陈中义, 朱永兴, 尹军良. 空心莲子草SOD基因家族鉴定和表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 102-116.
Shuo HAN, Xiao-wen HAN, Yi-feng HU, Zhong-yi CHEN, Yong-xing ZHU, Jun-liang YIN. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the SOD gene family in Alternanthera philoxeroides[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(1): 102-116.
试验措施 Test measure | |||
|---|---|---|---|
草甘膦 | 0.080 | 江苏快达农化股份有限公司Jiangsu Kuaida Agrochemical Co., Ltd., http://www.kuaida.cn | 41% |
异丙隆 | 0.050 | 美丰农业科技(上海)有限公司Meifeng Agricultural Technology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., https://www.maigoo.com/ | 50% |
噁草酮 | 0.040 | 大连越达农药化工有限公司Dalian Yueda Pesticide Chemical Co., Ltd., http://www.lnydnh.com/ | 13% |
乙羧氟草醚 | 0.008 | 潍坊鸿汇化工有限公司Weifang Honghui Chemical Co., Ltd., https://www.11315.com/ac/bs/10467196 | 10%,乳油Emulsifiable concentrate |
氯氟吡氧乙酸 Fluroxypyr | 0.010 | 山东绿霸化工股份有限公司Shandong Lvba Chemical Co., Ltd., http://www.lubachem.com/ | 20%,乳油Emulsifiable concentrate |
表1 试验药剂和浓度
Table 1 Test the agent and the concentration
试验措施 Test measure | |||
|---|---|---|---|
草甘膦 | 0.080 | 江苏快达农化股份有限公司Jiangsu Kuaida Agrochemical Co., Ltd., http://www.kuaida.cn | 41% |
异丙隆 | 0.050 | 美丰农业科技(上海)有限公司Meifeng Agricultural Technology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., https://www.maigoo.com/ | 50% |
噁草酮 | 0.040 | 大连越达农药化工有限公司Dalian Yueda Pesticide Chemical Co., Ltd., http://www.lnydnh.com/ | 13% |
乙羧氟草醚 | 0.008 | 潍坊鸿汇化工有限公司Weifang Honghui Chemical Co., Ltd., https://www.11315.com/ac/bs/10467196 | 10%,乳油Emulsifiable concentrate |
氯氟吡氧乙酸 Fluroxypyr | 0.010 | 山东绿霸化工股份有限公司Shandong Lvba Chemical Co., Ltd., http://www.lubachem.com/ | 20%,乳油Emulsifiable concentrate |
基因 Gene | 上游引物序列 Forward primer sequence (5′-3′) | 下游引物序列 Reverse primer sequence (5′-3′) | 序列长度 Sequence length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ApSOD8 | GAAGAATAACAGGGCTTACACCTG | GCATGGCGTTCACTATCAAAA | 145 |
| ApSOD9 | AGATGAAGTCCGACACGCG | TCCACCAGCATTCCCAGTAG | 202 |
| ApSOD11 | ATCATTGACAGCCAGATTCCTC | ACCAATAATACCACAAGCCACTC | 156 |
| ApSOD21 | GATACCTCCAACACTTCTACTCATGA | TCAAGTCCACCTCAACATTCTTC | 151 |
| ApSOD35 | CGCTGTCAACCCTCTTGTATG | ATGCGACTTCTTTCTCACTTTCA | 200 |
| ApSOD43 | CTCTGGGTTGGGCTATTGATT | TCCTGATTTGCGGTAGTTTCA | 157 |
| Tubby | CGGTCTAGCCGAAGATTCCA | CGCTTGGTGAAGGCAGACATT | 232 |
表2 ApSODs基因的RT-qPCR引物
Table 2 RT-qPCR primers for ApSODs genes
基因 Gene | 上游引物序列 Forward primer sequence (5′-3′) | 下游引物序列 Reverse primer sequence (5′-3′) | 序列长度 Sequence length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ApSOD8 | GAAGAATAACAGGGCTTACACCTG | GCATGGCGTTCACTATCAAAA | 145 |
| ApSOD9 | AGATGAAGTCCGACACGCG | TCCACCAGCATTCCCAGTAG | 202 |
| ApSOD11 | ATCATTGACAGCCAGATTCCTC | ACCAATAATACCACAAGCCACTC | 156 |
| ApSOD21 | GATACCTCCAACACTTCTACTCATGA | TCAAGTCCACCTCAACATTCTTC | 151 |
| ApSOD35 | CGCTGTCAACCCTCTTGTATG | ATGCGACTTCTTTCTCACTTTCA | 200 |
| ApSOD43 | CTCTGGGTTGGGCTATTGATT | TCCTGATTTGCGGTAGTTTCA | 157 |
| Tubby | CGGTCTAGCCGAAGATTCCA | CGCTTGGTGAAGGCAGACATT | 232 |

图2 ApSODs基因家族的基因结构、保守基序和结构域分析A: ApSODs系统发育树Phylogenetic tree of ApSODs; B: ApSODs基因结构Gene structure of ApSODs; C: ApSODs蛋白Motif分布Motif distribution of ApSODs; D: ApSODs中10个基序的保守氨基酸序列和功能结构域Conserved amino acid sequences and functional domain of 10 Motifs in ApSODs. B中黄色代表编码序列,绿色代表非编码区。D中字母大小高低表示序列保守程度,字母越大越高代表保守性越高。The yellow box and green box in B represented the coding sequence and untranslated regions, respectively. The letter size in D indicates the conservatism of the sequence, the larger the letter, the higher the letter is, the higher the conservatism is. Motif 1-10: 基序1~10.
Fig.2 Gene structure, conserved Motif and domain analysis of ApSODs gene family
蛋白命名 Protein name | 蛋白ID Protein ID | Len (aa) | MW (kDa) | pI | Ins | GRAVY | Sub Loc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ApSOD1 | TR111530|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 205 | 21.09 | 6.85 | 36.23 | -0.259 | 叶绿体/细胞质Chloroplast/cytoplasm |
| ApSOD2 | TR109813|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 15.73 | 叶绿体/细胞质Chloroplast/cytoplasm | ||||
| ApSOD3 | TR241345|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 16.37 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD4 | TR236337|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 12.99 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | ||||
| ApSOD5 | TR248740|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 9.69 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD6 | TR126747|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 10.19 | 细胞质/线粒体Cytoplasm/mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD7 | TR213092|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 15.42 | 叶绿体/细胞质/线粒体/细胞核Chloroplast/cytoplasm/mitochondrion/nucleus | ||||
| ApSOD8 | TR54897|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 16.08 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD9 | TR34452|c3_g1_i3.p1 | 22.70 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD10 | TR14803|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 7.98 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD11 | TR110003|c0_g2_i1.p1 | 15.18 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD12 | TR37745|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 16.18 | 叶绿体/细胞质Chloroplast/cytoplasm | ||||
| ApSOD13 | TR262285|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 22.40 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD14 | TR60741|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 22.59 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD15 | TR41468|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 20.46 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD16 | TR279215|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 10.78 | 叶绿体/细胞质Chloroplast/cytoplasm | ||||
| ApSOD17 | TR105699|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 50.96 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD18 | TR109227|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 8.19 | 叶绿体/细胞质Chloroplast/cytoplasm | ||||
| ApSOD19 | TR286036|c1_g1_i1.p1 | 34.96 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD20 | TR184370|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 21.48 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD21 | TR109991|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 33.09 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD22 | TR224061|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 9.10 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD23 | TR20651|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 13.09 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD24 | TR113639|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 10.64 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD25 | TR110087|c5_g5_i2.p1 | 14.27 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD26 | TR110087|c5_g3_i1.p1 | 19.32 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD27 | TR128622|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 8.52 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD28 | TR47142|c1_g1_i1.p1 | 13.80 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD29 | TR286587|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 25.44 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD30 | TR247726|c0_g2_i1.p1 | 20.75 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD31 | TR247726|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 28.63 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD32 | TR37189|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 24.81 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD33 | TR182990|c0_g1_i1.p3 | 10.75 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD34 | TR137752|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 8.47 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD35 | TR97445|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 31.26 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD36 | TR66090|c9_g1_i1.p1 | 30.14 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD37 | TR266216|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 18.24 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD38 | TR172914|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 23.33 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD39 | TR41361|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 9.40 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD40 | TR272187|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 6.98 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD41 | TR109124|c3_g1_i1.p1 | 8.97 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD42 | TR110087|c5_g4_i1.p1 | 8.39 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD43 | TR110087|c5_g1_i1.p1 | 16.55 | 线粒体Mitochondrion |
表3 ApSODs蛋白质特征分析
Table 3 Protein characterization of ApSODs
蛋白命名 Protein name | 蛋白ID Protein ID | Len (aa) | MW (kDa) | pI | Ins | GRAVY | Sub Loc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ApSOD1 | TR111530|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 205 | 21.09 | 6.85 | 36.23 | -0.259 | 叶绿体/细胞质Chloroplast/cytoplasm |
| ApSOD2 | TR109813|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 15.73 | 叶绿体/细胞质Chloroplast/cytoplasm | ||||
| ApSOD3 | TR241345|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 16.37 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD4 | TR236337|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 12.99 | 细胞质Cytoplasm | ||||
| ApSOD5 | TR248740|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 9.69 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD6 | TR126747|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 10.19 | 细胞质/线粒体Cytoplasm/mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD7 | TR213092|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 15.42 | 叶绿体/细胞质/线粒体/细胞核Chloroplast/cytoplasm/mitochondrion/nucleus | ||||
| ApSOD8 | TR54897|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 16.08 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD9 | TR34452|c3_g1_i3.p1 | 22.70 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD10 | TR14803|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 7.98 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD11 | TR110003|c0_g2_i1.p1 | 15.18 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD12 | TR37745|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 16.18 | 叶绿体/细胞质Chloroplast/cytoplasm | ||||
| ApSOD13 | TR262285|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 22.40 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD14 | TR60741|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 22.59 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD15 | TR41468|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 20.46 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD16 | TR279215|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 10.78 | 叶绿体/细胞质Chloroplast/cytoplasm | ||||
| ApSOD17 | TR105699|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 50.96 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD18 | TR109227|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 8.19 | 叶绿体/细胞质Chloroplast/cytoplasm | ||||
| ApSOD19 | TR286036|c1_g1_i1.p1 | 34.96 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD20 | TR184370|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 21.48 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD21 | TR109991|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 33.09 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD22 | TR224061|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 9.10 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD23 | TR20651|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 13.09 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD24 | TR113639|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 10.64 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD25 | TR110087|c5_g5_i2.p1 | 14.27 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD26 | TR110087|c5_g3_i1.p1 | 19.32 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD27 | TR128622|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 8.52 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD28 | TR47142|c1_g1_i1.p1 | 13.80 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD29 | TR286587|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 25.44 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD30 | TR247726|c0_g2_i1.p1 | 20.75 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD31 | TR247726|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 28.63 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD32 | TR37189|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 24.81 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD33 | TR182990|c0_g1_i1.p3 | 10.75 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD34 | TR137752|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 8.47 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD35 | TR97445|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 31.26 | 叶绿体Chloroplast | ||||
| ApSOD36 | TR66090|c9_g1_i1.p1 | 30.14 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD37 | TR266216|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 18.24 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD38 | TR172914|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 23.33 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD39 | TR41361|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 9.40 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD40 | TR272187|c0_g1_i1.p1 | 6.98 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD41 | TR109124|c3_g1_i1.p1 | 8.97 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD42 | TR110087|c5_g4_i1.p1 | 8.39 | 线粒体Mitochondrion | ||||
| ApSOD43 | TR110087|c5_g1_i1.p1 | 16.55 | 线粒体Mitochondrion |

图4 不同水分环境、低钾胁迫和不同种群的ApSODs表达热图MT: 混合组织样本Mixed tissue samples; ST: 茎节组织样本Stem node tissue samples; 1~3 LT: 上部第1~3对叶片组织样本The upper 1-3 pairs of leaf tissue samples; JN: 山东济南收集的“北方”种群The “northern” population collected in Jinan, Shandong Province; SH: 上海收集的“中央”种群The “central” population collected in Shanghai; L: 陆地Land; P: 池塘Pond; LPS: 低钾胁迫Low potassium stress. 不同的颜色代表不同大小的log2(TPM+1)值,红色代表的log2(TPM+1)值最大,蓝色最小。Different colors in the legend represent different log2(TPM+1) values, red represents the largest log2(TPM+1) value, and blue represents the smallest value. CK:对照,指未做任何胁迫处理的样本;0~288 h:池塘种植(采集池塘植株在水中培育且种植盆水面高度为50 cm)和陆地种植(每日浇灌1 L清水)处理后0~288 h的茎节组织样本。CK: Control, referring to samples that have not undergone any stress treatment; 0-288 h: Stem node tissue samples from 0-288 hours after pond (collecting pond plants were cultivated in water and the water surface height of the planting basin was 50 cm) and land (watering 1 L of clean water daily) planting treatments.
Fig.4 Heat maps of ApSODs expression in different water environments, low potassium stress and different populations
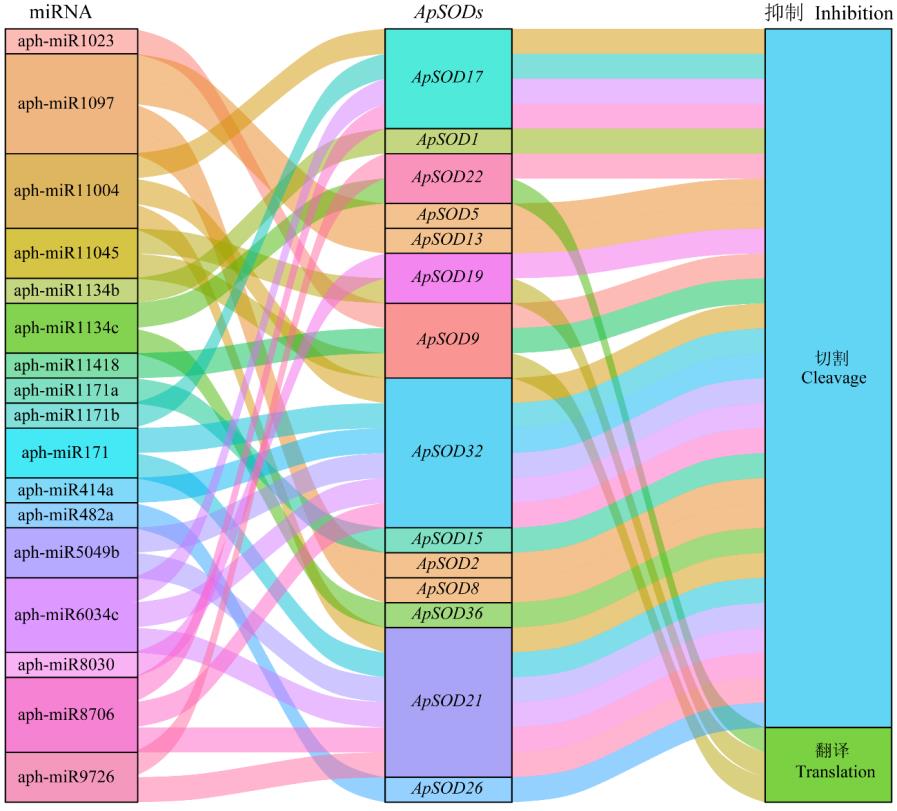
图5 miRNA与ApSODs靶向关系桑基图三纵列代表miRNA、mRNA和抑制效应。The three columns represent miRNA, mRNA, and inhibition effect.
Fig.5 Sankey diagram of miRNA targeting relationship with ApSODs
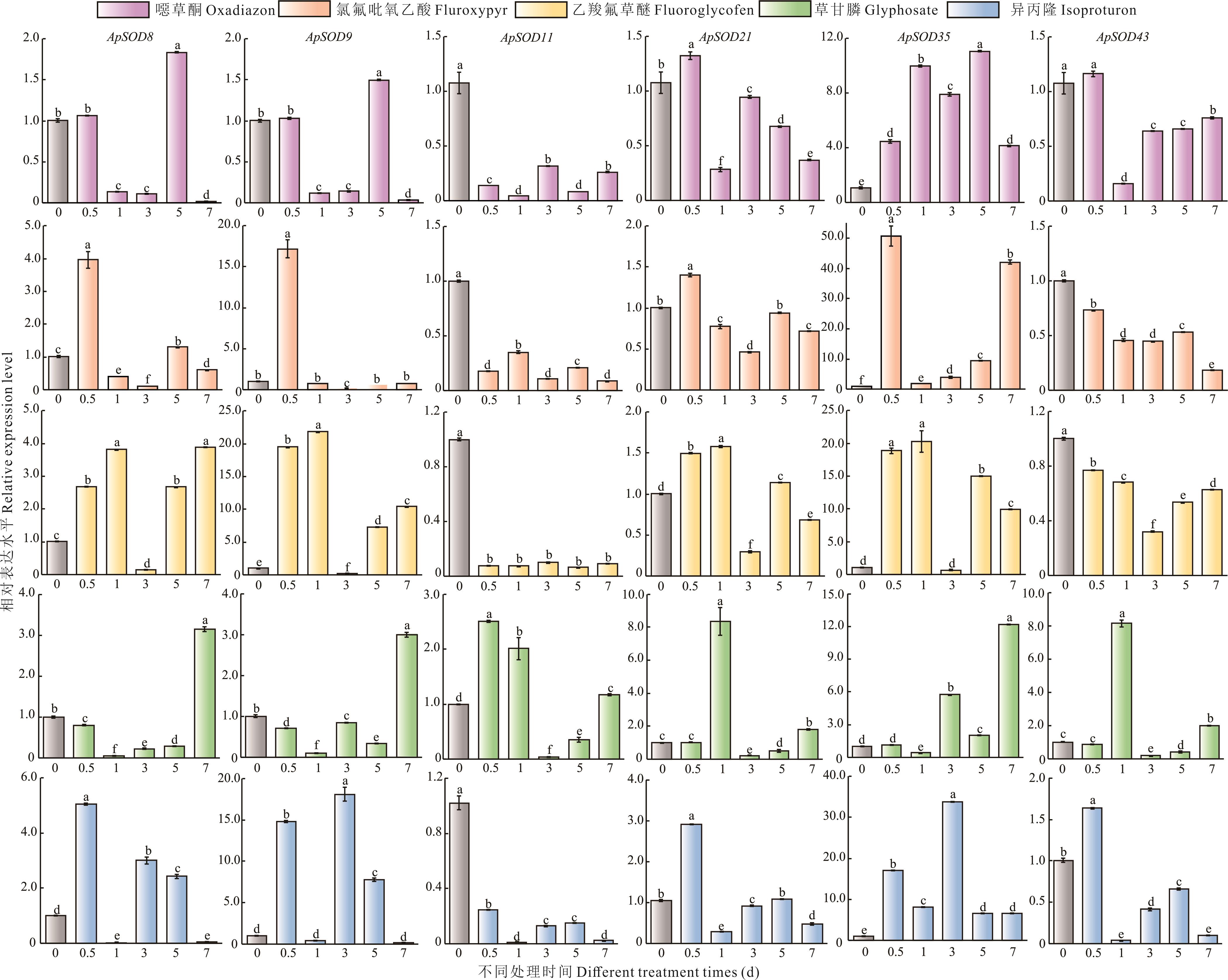
图7 不同除草剂处理下ApSODs的相对表达水平5种除草剂为13%噁草酮、20%氯氟吡氧乙酸、10%乙羧氟草醚、41%草甘膦和50%异丙隆。不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。Five herbicides include 13% oxadiazon, 20% fluroxypyr, 10% fluoroglycofen, 41% glyphosate, and 50% isoproturon. The different lowercase letters indicate significant differences.
Fig.7 Relative expression levels of ApSODs under different herbicides treatments
| 1 | Sun S A, Deng Z Y, Xiong J Y, et al. Research progress on biological and ecological control of Alternanthera philoxeroides. South China Agriculture, 2022, 16(9): 164-167. |
| 孙思昂, 邓梓妍, 熊佳瑶, 等. 空心莲子草生物及生态防治研究进展. 南方农业, 2022, 16(9): 164-167. | |
| 2 | Su T, Wu S J, Hu S Z, et al. Advance in invasion and clonal characteristics of the alien species Alternanthera philoxeroides. South China Forestry Science, 2021, 49(1): 44-47, 54. |
| 苏田, 吴姝瑾, 胡姝珍, 等. 外来种空心莲子草的入侵及其克隆特性综述. 南方林业科学, 2021, 49(1): 44-47, 54. | |
| 3 | Gupta S, Dong Y N, Dijkwel P P, et al. Genome-wide analysis of ROS antioxidant genes in resurrection species suggest an involvement of distinct ROS detoxification systems during desiccation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(12): 3101. |
| 4 | Mhamdi A, Van B F. Reactive oxygen species in plant development. Development, 2018, 145(15): dev164376. |
| 5 | Abreu I A, Cabelli D E. Superoxide dismutases-A review of the metal-associated mechanistic variations. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Proteins and Proteomics, 2010, 1804(2): 263-274. |
| 6 | Dong L, He Y Z, Wang Y L, et al. Research progress on application of superoxide dismutase (SOD). Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2013, 15(5): 53-58. |
| 董亮, 何永志, 王远亮, 等. 超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)的应用研究进展. 中国农业科技导报, 2013, 15(5): 53-58. | |
| 7 | Ren Y Y, Jiang H, Ma L, et al. Identification of potato (Solanum tuberosum) SOD gene family and its response in damaged tubers. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2021, 29(7): 1248-1259. |
| 任映玥, 姜红, 马丽, 等. 马铃薯SOD基因家族鉴定及其在损伤块茎中的响应. 农业生物技术学报, 2021, 29(7): 1248-1259. | |
| 8 | Hao H D. Studies on the phytotoxicity symptoms of commonly used herbicides to radish and cabbage and the mitigation effects of some antidotes. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2015. |
| 郝红丹. 常用除草剂对萝卜、白菜的药害和几种缓解剂对其药害的缓解效果研究. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2015. | |
| 9 | Matters G L, Scandalios J G. Effect of the free radical-generating herbicide paraquat on the expression of the superoxide dismutase (SOD) genes in maize. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 1986, 882(1): 29-38. |
| 10 | Dong Y. Study on the physiological response of broomcorn millet to different herbicides. Crops, 2022, 38(5): 255-260. |
| 董扬. 糜子对不同除草剂的生理响应机制研究. 作物杂志, 2022, 38(5): 255-260. | |
| 11 | Gao J M, Xiao Q, Ding L P, et al. Differential responses of lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in Alternanthera philoxeroides and Oryza sativa subjected to drought stress. Plant Growth Regulation, 2008, 56(1): 89-95. |
| 12 | Xu X Y, Shi G X, Wang J, et al. Copper-induced oxidative stress in Alternanthera philoxeroides callus. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC), 2011, 106(2): 243-251. |
| 13 | Zang Y, Chen J, Li R X, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family in Zostera marina and expression profile analysis under temperature stress. PeerJ, 2020, 8(4): e9063. |
| 14 | Song J B, Zeng L M, Chen R R, et al. In silico identification and expression analysis of superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family in Medicago truncatula. 3 Biotech, 2018, 8(8): 348. |
| 15 | Wang W, Zhang X P, Deng F N, et al. Genome-wide characterization and expression analyses of superoxide dismutase (SOD) genes in Gossypium hirsutum. BMC Genomics, 2017, 18(1): 376. |
| 16 | Feng X, Lai Z X, Lin Y L, et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the superoxide dismutase gene family in Musa acuminata cv. Tianbaojiao (AAA group). BMC Genomics, 2015, 16(1): 823. |
| 17 | Jiang W Q, Yang L, He Y Q, et al. Genome-wide identification and transcriptional expression analysis of superoxide dismutase (SOD) family in wheat (Triticum aestivum). PeerJ, 2018, 7: e8062. |
| 18 | Zhu Y X, Jiang X C, Han X W, et al. Characterization the coding and non-coding RNA components in the transcriptome of invasion weed Alternanthera philoxeroides. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca, 2021, 49(1): 12242. |
| 19 | Yin J L, Wang L X, Zhao J, et al. Genome-wide characterization of the C2H2 zinc-finger genes in Cucumis sativus and functional analyses of four CsZFPs in response to stresses. BMC Plant Biology, 2020, 20(1): 359. |
| 20 | Chen Q, Xu X Y, Wang J C, et al. Identification of a WRKY gene family based on full-length transcriptome sequences and analysis of response patterns under salt stress in Halogeton glomeratus. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(12): 146-157. |
| 陈倩, 徐晓芸, 汪军成, 等. 基于全长转录组的盐生草WRKY基因家族的鉴定及其盐胁迫响应模式分析. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 146-157. | |
| 21 | Thompson J D, Higgins D G, Gibson T J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Research, 1994, 22(22): 4673-4680. |
| 22 | Zou Z, Huang Q X, An F. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of Lhc supergene family in castor bean (Ricinus communis L.). Agricultural Biotechnology, 2013, 2(6): 44-48, 51. |
| 23 | Li Y T, Liu X, Xiao Y X, et al. Genome-wide characterization and function analysis uncovered roles of wheat LIMs in responding to adverse stresses and TaLIM8-4D function as a susceptible gene. The Plant Genome, 2022, 15(3): e20246. |
| 24 | Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, et al. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server//Walker, John M. The proteomics protocols handbook. Totowa: Humana Press, 2005: 571-607. |
| 25 | Li W, Zhao L R, Zhang J P, et al. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the DMP gene family in flax(Linum usitatissimum). Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 91-106. |
| 李雯, 赵丽蓉, 张建平, 等. 亚麻DMP基因家族的全基因组鉴定与分析. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 91-106. | |
| 26 | Yang L, Jiang X C, Yang J, et al. Identification, characterization, and expression analysis of metal tolerance protein (MTP) genes in Alternanthera philoxeroides. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(8): 1516-1527. |
| 杨蕾, 蒋昕晨, 杨杰, 等. 空心莲子草MTP基因家族的鉴定、特征及表达分析. 草业科学, 2020, 37(8): 1516-1527. | |
| 27 | Li Y P, Wei N, Zhai Q Y, et al. Genome-wide identification of members of the TCP gene family in Melilotus albus and their expression patterns under drought stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(4): 101-111. |
| 李艳鹏, 魏娜, 翟庆妍, 等. 全基因组水平白花草木樨TCP基因家族的鉴定及在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 101-111. | |
| 28 | Zhu Y X, Yin J L, Liang Y F, et al. Transcriptomic dynamics provide an insight into the mechanism for silicon-mediated alleviation of salt stress in cucumber plants. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 174: 245-254. |
| 29 | Tian J, Li Y T, Hu Y F, et al. Mining the roles of cucumber DUF966 genes in fruit development and stress response. Plants, 2022, 11(19): 2497. |
| 30 | Yin J L, Liu M Y, Ma D F, et al. Identification of circular RNAs and their targets during tomato fruit ripening. Postharvest Biology & Technology, 2018, 136: 90-98. |
| 31 | Liu J L, Ouyang L J, Zeng J L, et al. Genome-wide analysis of rice SOD gene family and expression research under stress. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2018, 16(9): 8. |
| 刘家林, 欧阳林娟, 曾嘉丽, 等. 水稻SOD基因家族的全基因组分析及逆境胁迫下表达研究. 分子植物育种, 2018, 16(9): 8. | |
| 32 | Zhang X, Zhang L T, Chen Y Y, et al. Genome-wide identification of the SOD gene family and expression analysis under drought and salt stress in barley. Plant Growth Regulation, 2021, 94(1): 49-60. |
| 33 | Ye W H, Li J, Cao H L, et al. Genetic uniformity of Alternanthera philoxeroides in South China. Weed Research, 2003, 43(4): 297-302. |
| 34 | Gao Z J, Li M, Gao X X, et al. Biological activity of 24 herbicides against Alternanthera philoxeroides (Mart.) Griseb. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(21): 256-261. |
| 高宗军, 李美, 高兴祥, 等. 24种除草剂对空心莲子草的生物活性. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(21): 256-261. | |
| 35 | Ma M Y, Fu J W, Zhu D H, et al. Control effects of three herbicides on the alligator weed Alternanthera philoxeroides. Plant Protection, 2009, 35(4): 154-157. |
| 马明勇, 傅建炜, 朱道弘, 等. 不同除草剂对空心莲子草的控制作用评价. 植物保护, 2009, 35(4): 154-157. | |
| 36 | Wu T X, He J R, Wang H C, et al. Susceptibility of Alternanthera philoxeroides (Mart.) Griseb to different herbicides. Journal of Weed Science, 2019, 37(4): 45-49. |
| 吴田乡, 贺建荣, 王红春, 等. 外来入侵植物空心莲子草对不同除草剂的敏感性. 杂草学报, 2019, 37(4): 45-49. | |
| 37 | Su W, Raza A, Gao A, et al. Genome-wide analysis and expression profile of superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) under different hormones and abiotic stress conditions. Antioxidants, 2021, 10(8): 1182. |
| 38 | Filiz E, Tombuloglu H. Genome-wide distribution of superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene families in Sorghum bicolor. Turkish Journal of Biology, 2015, 39(1): 49-59. |
| 39 | Han L M, Hua W P, Cao X Y, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene family in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Gene, 2020, 742: 144603. |
| 40 | Cai K. Bioinformatics and function analysis of SOD gene family in Phyllostachys edulis. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Agricultural and Forestry University, 2018. |
| 蔡凯. 毛竹SOD基因家族生物信息学与功能分析. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2018. | |
| 41 | Feng K, Yu J H, Cheng Y, et al. The SOD gene family in tomato: Identification, phylogenetic relationships, and expression patterns. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 1279. |
| 42 | Wang W, Xia M X, Chen J, et al. Genome-wide analysis of superoxide dismutase gene family in Gossypium raimondii and G. arboreum. Plant Gene, 2016, 6: 18-29. |
| 43 | Kliebenstein D J, Monde R A, Last R L. Superoxide dismutase in Arabidopsis: An eclectic enzyme family with disparate regulation and protein localization. Plant Physiology, 1998, 118(2): 637-650. |
| 44 | Huang W L. Study on the control of 20% fluroxypyr emulsified oil against hollow lotus seed grass in rice ridge. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2005(8): 27-28. |
| 黄蔚兰. 20%氯氟吡氧乙酸乳油防除水稻田埂空心莲子草试验研究. 现代农业科技, 2005(8): 27-28. | |
| 45 | Lou Y L, Deng Y Y, Shen J L, et al. Effects of mestsulfuron-methyl and glyphosate on acetolactate synthase activities and shikimate levels of Alternanthera philoxeroides. Journal of Plant Protection, 2005(2): 185-188. |
| 娄远来, 邓渊钰, 沈晋良, 等. 甲磺隆和草甘膦对空心莲子草乙酰乳酸合酶活性和莽草酸含量的影响. 植物保护学报, 2005(2): 185-188. | |
| 46 | Yu Y K. Study on safety of seven herbicides to water direct-seeding rice. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2017. |
| 郁延坤. 7种除草剂对水直播水稻安全性影响的研究. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2017. | |
| 47 | Guo M J, Shen J, Song X E, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of fluroxypyr herbicide on physiological parameters of spring hybrid millet. PeerJ, 2019, 7(1): e7794. |
| 48 | Tan W, Li Q L, Zhai H. Photosynthesis and growth responses of grapevine to acetochlor and fluoroglycofen. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 2012, 103(3): 210-218. |
| 49 | Shen L Y. Effect of glyphosate on physiology and growth of Vallisneria natans. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2021. |
| 沈路遥. 草甘膦对苦草生理生长的影响. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2021. | |
| 50 | Yin X L. Toxic reactivity of wheat (Triticum aestivum) plants to herbicide isoproturon. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2008. |
| 尹小乐. 除草剂异丙隆对小麦生物毒性的影响. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2008. |
| [1] | 吴昊, 张辰, 代文魁. 气候变暖和物种多样性交互效应对空心莲子草入侵的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 38-48. |
| [2] | 董文科, 陈春艳, 马晖玲. 转OvBAN/bar双价基因的紫花苜蓿对虫蚀及除草剂的耐受性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 159-167. |
| [3] | 鲍根生, 王玉琴, 宋梅玲, 王宏生, 尹亚丽, 刘生财, 杨有武, 杨铭. 狼毒斑块对狼毒型退化草地植被和土壤理化性质影响的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 51-61. |
| [4] | 索雅飞,杜超,李宁宁,王燕,王迎春. 珍稀泌盐植物长叶红砂RtSOD基因的克隆及功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 98-110. |
| [5] | 李健, 李岩, 高兴祥, 房锋, 李美. 马唐生防菌厚垣孢镰刀菌ZC201301的生物学特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 234-239. |
| [6] | 宋旭东, 赵桂琴, 柴继宽. 不同类型除草剂的田间防效及其对裸燕麦带壳率和产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(1): 171-178. |
| [7] | 刘欢, 慕平, 赵桂琴, 周向睿. 除草剂对燕麦产量及抗氧化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(2): 41-48. |
| [8] | 贾小霞, 齐恩芳, 马胜, 胡新元, 王一航, 文国宏, 龚成文, 李建武. 转DREB1A/Bar双价基因马铃薯的耐旱性及除草剂抗性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(11): 58-64. |
| [9] | 马国兰,柏连阳,刘都才,刘雪源,唐涛,彭亚军. 抗二氯喹啉酸稗草对6种除草剂的多抗性分析及田间控制效果评价[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(6): 259-265. |
| [10] | 高兴祥,李美,房锋,张悦丽,齐军山. 防除多花黑麦草等4种禾本科杂草的药剂活性测定[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(6): 349-354. |
| [11] | 张志忠,石秋香,孙志浩,蓝茂锋. 入侵植物空心莲子草对生菜和萝卜的化感效应[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(1): 288-293. |
| [12] | 王桂芹,高瑞如,王玉良,柴瑞娟. 异质生境空心莲子草的结构基础与生态适应性[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(4): 143-152. |
| [13] | 游明鸿,刘金平,白史且,张新全,卞志高. 肥料和除草剂混施对老芒麦生产性能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(5): 283-286. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||