

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (1): 1-18.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023185
• 研究论文 •
余万洋1( ), 陈怡帆1, 方发永1, 张金鑫2(
), 陈怡帆1, 方发永1, 张金鑫2( ), 李舟3, 赵龙山1(
), 李舟3, 赵龙山1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-31
修回日期:2023-06-28
出版日期:2024-01-20
发布日期:2023-11-23
通讯作者:
张金鑫,赵龙山
作者简介:longshanzh@163.com基金资助:
Wan-yang YU1( ), Yi-fan CHEN1, Fa-yong FANG1, Jin-xin ZHANG2(
), Yi-fan CHEN1, Fa-yong FANG1, Jin-xin ZHANG2( ), Zhou LI3, Long-shan ZHAO1(
), Zhou LI3, Long-shan ZHAO1( )
)
Received:2023-05-31
Revised:2023-06-28
Online:2024-01-20
Published:2023-11-23
Contact:
Jin-xin ZHANG,Long-shan ZHAO
摘要:
草地在喀斯特地区石漠化治理和畜牧业发展中发挥重要作用,探明草地空间分布格局演变特征及其驱动力,对维护区域草地生态功能,实现可持续发展具有重要意义。本研究基于土地利用数据集,分析贵州省1980-2020年草地空间转移特征,将景观格局与空间自相关相结合,深入识别草地空间分布格局演化规律及有效管理区域,并利用地理探测器量化草地空间分布格局演变的驱动力。结果表明:1)40年来,贵州省草地面积变化可划分为增长期(1980-2000年)、衰退期(2000-2015年)、恢复期(2015-2020年)3个阶段,草地面积总体上减少了176.88 km2。发生变化区域集中在西部与南部地区,以草地和林地、耕地之间的转移为主,草地总体空间分布格局表现出“西部与南部高,东部与北部低”的特征;2)草地整体景观破碎程度增加,聚合度降低,形状趋于复杂,区县尺度的草地斑块更破碎和分散,但形状更规则;3)草地全局空间自相关程度减弱,局部自相关存在高-高聚集和低-高聚集的空间聚类现象,且集中分布在西部与南部地区;4)草地空间分布格局主要受自然因素的影响,海拔是主导因子,解释力最高,为42.9%。双因子的交互作用可增强对草地空间分布格局的解释力,海拔与牧业产值、年平均气温、人口密度、GDP均存在较强的交互作用,在海拔主导的草地总体分布格局下,区域间社会经济因素的不同和变化显著影响草地空间分布格局的演变,同时地区政策起重要导向作用。
余万洋, 陈怡帆, 方发永, 张金鑫, 李舟, 赵龙山. 1980-2020年贵州省草地空间分布格局演变及驱动力分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 1-18.
Wan-yang YU, Yi-fan CHEN, Fa-yong FANG, Jin-xin ZHANG, Zhou LI, Long-shan ZHAO. An analysis of grassland spatial distribution and driving forces of patterns of change in grassland distribution in Guizhou Province from 1980 to 2020[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(1): 1-18.
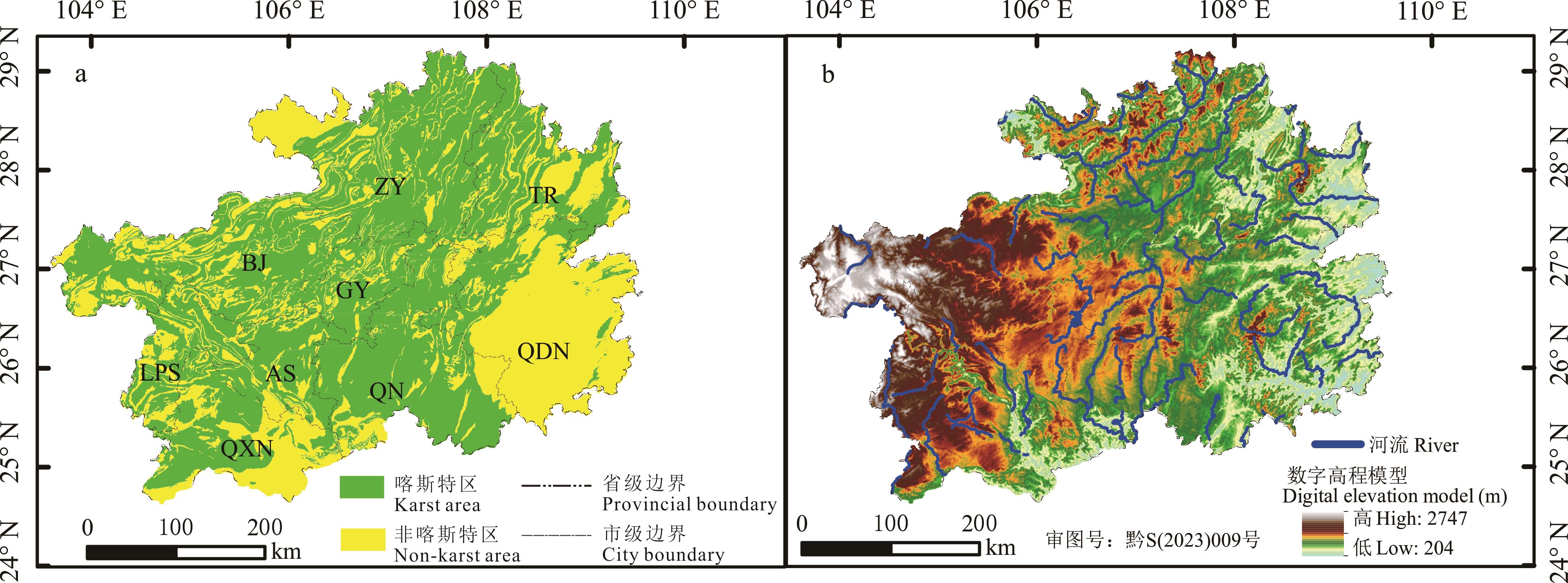
图1 研究区概况a是研究区喀斯特分布,其中ZY、TR、BJ、GY、LPS、AS、QN、QDN、QXN分别代表遵义市、铜仁市、毕节市、贵阳市、六盘水市、安顺市、黔南布依族苗族自治州、黔东南苗族侗族自治州、黔西南布依族苗族自治州。下同。b是研究区数字高程模型(DEM)。该图基于自然资源部标准地图服务系统(http://bzdt.ch.mnr.gov.cn/index.html)中黔S(2023)009号标准地图制作,底图无修改。a shows the distribution of karst in the study area, where ZY, TR, BJ, GY, LPS, AS, QN, QDN, and QXN represent Zunyi City, Tongren City, Bijie City, Guiyang City, Liupanshui City, Anshun City, Qiannan Buyi and Miao Autonomous Prefecture, Qiandongnan Miao and Dong Autonomous Prefecture, Qianxinan Buyi and Miao Autonomous Prefecture, respectively. The same below. b shows the distribution of digital elevation model in the study area. The map was based on the standard map service website of the ministry of natural resources (http://bzdt.ch.mnr.gov.cn/index.html) with the drawing review No. 黔S(2023)009, and the base map was not modified.
Fig.1 Location of the study area
数据类型 Data type | 年份 Year | 空间分辨率 Space resolution (m) | 数据来源 Data sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| 土地利用类型Land use types | 1980、1990、1995、2000、2005、2010、2015、2020 | 30 | 中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所Data Center for Resources and Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (RESDC, http://www.resdc.cn) |
| 年降水量Annual precipitation | 1995、2000、2005、2010、2015、2020 | 1000 | |
| 年平均气温Mean annual temperature | 1995、2000、2005、2010、2015、2020 | 1000 | |
| 国内生产总值GDP | 1995、2000、2005、2010、2015、2020 | 1000 | |
| 人口密度Density of population | 1995、2000、2005、2010、2015、2020 | 1000 | |
| 数字高程模型Digital elevation model | - | 30 | 地理空间数据云Geospatial data cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn/) |
| 牧业产值Livestock industry output | 1995、2000、2005、2010、2015、2020 | 各区县Districts and counties | 贵州省经济社会发展统计数据库Guizhou economic and social development statistical database (https://data.cnki.net/) |
表1 数据来源和说明
Table 1 Data source and description
数据类型 Data type | 年份 Year | 空间分辨率 Space resolution (m) | 数据来源 Data sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| 土地利用类型Land use types | 1980、1990、1995、2000、2005、2010、2015、2020 | 30 | 中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所Data Center for Resources and Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (RESDC, http://www.resdc.cn) |
| 年降水量Annual precipitation | 1995、2000、2005、2010、2015、2020 | 1000 | |
| 年平均气温Mean annual temperature | 1995、2000、2005、2010、2015、2020 | 1000 | |
| 国内生产总值GDP | 1995、2000、2005、2010、2015、2020 | 1000 | |
| 人口密度Density of population | 1995、2000、2005、2010、2015、2020 | 1000 | |
| 数字高程模型Digital elevation model | - | 30 | 地理空间数据云Geospatial data cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn/) |
| 牧业产值Livestock industry output | 1995、2000、2005、2010、2015、2020 | 各区县Districts and counties | 贵州省经济社会发展统计数据库Guizhou economic and social development statistical database (https://data.cnki.net/) |
景观格局指数 Landscape pattern index | 生态学意义 Ecological meaning | 取值范围 Range |
|---|---|---|
| 斑块密度Patch density (PD,No.·km-2) | 斑块在单位面积上的分布数量,反映景观的斑块分化程度或破碎化程度,值越大景观越破碎。The number of patches per unit area, which reflects the degree of patch differentiation or fragmentation in the landscape, and the larger the value, the more fragmented the landscape. | PD≥0 |
| 聚集度指数Aggregation index (AI,%) | 反映景观中斑块的聚集程度,值越大聚集程度越高。Reflects the degree of patch aggregation in the landscape, the larger the value, the higher the degree of aggregation. | 0<AI≤100 |
| 景观形状指数Landscape shape index (LSI) | 描述斑块边界形状的复杂程度,值越大斑块形状越不规则。Describe the complexity of the shape of patch boundaries, with larger values indicating more irregular patch shapes. | LSI≥1 |
表2 景观格局指数及其生态学意义
Table 2 Landscape pattern indexes and their ecological significance
景观格局指数 Landscape pattern index | 生态学意义 Ecological meaning | 取值范围 Range |
|---|---|---|
| 斑块密度Patch density (PD,No.·km-2) | 斑块在单位面积上的分布数量,反映景观的斑块分化程度或破碎化程度,值越大景观越破碎。The number of patches per unit area, which reflects the degree of patch differentiation or fragmentation in the landscape, and the larger the value, the more fragmented the landscape. | PD≥0 |
| 聚集度指数Aggregation index (AI,%) | 反映景观中斑块的聚集程度,值越大聚集程度越高。Reflects the degree of patch aggregation in the landscape, the larger the value, the higher the degree of aggregation. | 0<AI≤100 |
| 景观形状指数Landscape shape index (LSI) | 描述斑块边界形状的复杂程度,值越大斑块形状越不规则。Describe the complexity of the shape of patch boundaries, with larger values indicating more irregular patch shapes. | LSI≥1 |
| 驱动因素Driving factor | 因子Factor | 变量Variable | 离散化方法Discretization method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 地形Terrain factors | 坡度Slope (°) | X1 | 专家经验法Expert experience method |
| 海拔Elevation (m) | X2 | 自然间断法Natural breaks | |
| 气候Climate factors | 年平均气温Mean annual temperature (℃) | X3 | 自然间断法Natural breaks |
| 年降水量Annual precipitation (mm) | X4 | 自然间断法Natural breaks | |
| 社会经济Social and economic factors | 人口密度Density of population (person·km-2) | X5 | 分位数法Quantile method |
| 国内生产总值GDP (×104 yuan·km-2) | X6 | 分位数法Quantile method | |
| 牧业产值Livestock industry output (×104 yuan) | X7 | 自然间断法Natural breaks |
表3 草地空间格局驱动因素指标
Table 3 The driving factors of grassland spatial pattern
| 驱动因素Driving factor | 因子Factor | 变量Variable | 离散化方法Discretization method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 地形Terrain factors | 坡度Slope (°) | X1 | 专家经验法Expert experience method |
| 海拔Elevation (m) | X2 | 自然间断法Natural breaks | |
| 气候Climate factors | 年平均气温Mean annual temperature (℃) | X3 | 自然间断法Natural breaks |
| 年降水量Annual precipitation (mm) | X4 | 自然间断法Natural breaks | |
| 社会经济Social and economic factors | 人口密度Density of population (person·km-2) | X5 | 分位数法Quantile method |
| 国内生产总值GDP (×104 yuan·km-2) | X6 | 分位数法Quantile method | |
| 牧业产值Livestock industry output (×104 yuan) | X7 | 自然间断法Natural breaks |
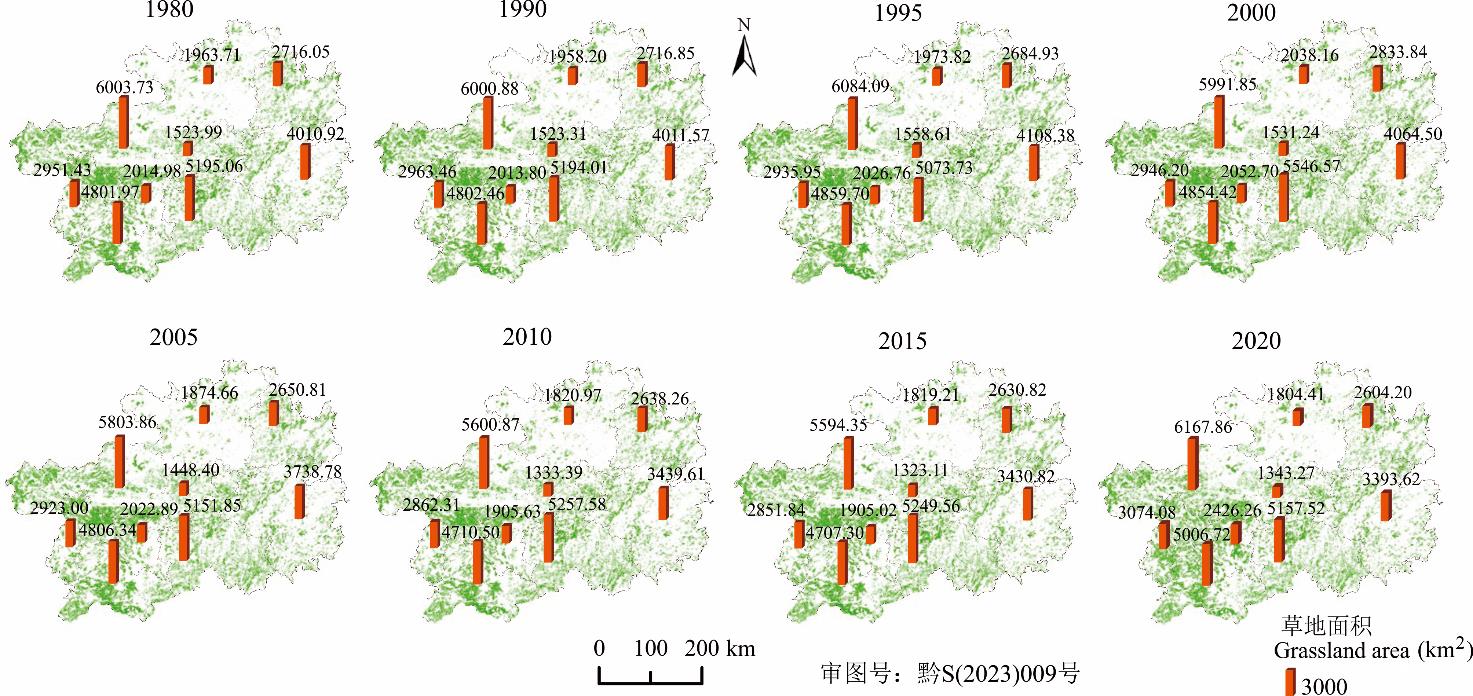
图3 贵州省1980-2020年草地空间分布该图基于自然资源部标准地图服务系统(http://bzdt.ch.mnr.gov.cn/index.html)中黔S(2023)009号标准地图制作,底图无修改。The map was based on the standard map service website of the ministry of natural resources (http://bzdt.ch.mnr.gov.cn/index.html) with the drawing review No. 黔S(2023)009, and the base map was not modified.
Fig.3 Spatial distribution of grassland in Guizhou Province from 1980 to 2020
草地转入 The grassland transfer in | 时段Period | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995-2000 | 2000-2005 | 2015-2020 | 1980-2020 | |
| 耕地Cultivated land | 268.27 | 245.34 | 1101.27 | 1235.40 |
| 林地Forest land | 1500.23 | 200.75 | 3656.43 | 4600.20 |
| 水域Water body | 1.40 | 1.18 | 14.24 | 9.44 |
| 建设用地Construction land | 8.70 | 2.21 | 21.45 | 7.40 |
| 未利用地Unused land | 1.80 | 0.15 | 1.74 | 2.59 |
草地转出 The grassland transfer out | 时段Period | |||
| 1995-2000 | 2000-2005 | 2015-2020 | 1980-2020 | |
| 耕地Cultivated land | 582.01 | 693.00 | 979.77 | 1523.79 |
| 林地Forest land | 622.91 | 1178.72 | 1999.91 | 3972.32 |
| 水域Water body | 12.03 | 4.29 | 88.88 | 159.04 |
| 建设用地Construction land | 9.79 | 12.51 | 233.00 | 374.11 |
| 未利用地Unused land | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.66 | 1.24 |
表4 贵州省不同时段草地转移面积
Table 4 Grassland transfer area at different time periods in Guizhou Province (km2)
草地转入 The grassland transfer in | 时段Period | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995-2000 | 2000-2005 | 2015-2020 | 1980-2020 | |
| 耕地Cultivated land | 268.27 | 245.34 | 1101.27 | 1235.40 |
| 林地Forest land | 1500.23 | 200.75 | 3656.43 | 4600.20 |
| 水域Water body | 1.40 | 1.18 | 14.24 | 9.44 |
| 建设用地Construction land | 8.70 | 2.21 | 21.45 | 7.40 |
| 未利用地Unused land | 1.80 | 0.15 | 1.74 | 2.59 |
草地转出 The grassland transfer out | 时段Period | |||
| 1995-2000 | 2000-2005 | 2015-2020 | 1980-2020 | |
| 耕地Cultivated land | 582.01 | 693.00 | 979.77 | 1523.79 |
| 林地Forest land | 622.91 | 1178.72 | 1999.91 | 3972.32 |
| 水域Water body | 12.03 | 4.29 | 88.88 | 159.04 |
| 建设用地Construction land | 9.79 | 12.51 | 233.00 | 374.11 |
| 未利用地Unused land | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.66 | 1.24 |
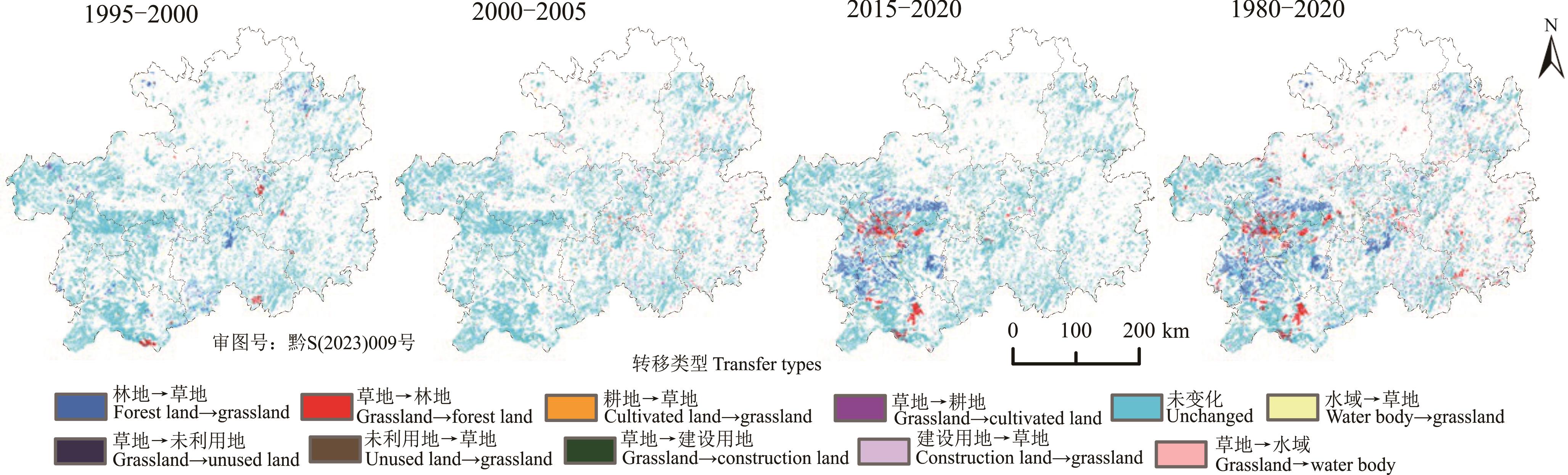
图4 不同时段草地空间转移情况该图基于自然资源部标准地图服务系统(http://bzdt.ch.mnr.gov.cn/index.html)中黔S(2023)009号标准地图制作,底图无修改。The map was based on the standard map service website of the ministry of natural resources (http://bzdt.ch.mnr.gov.cn/index.html) with the drawing review No. 黔S(2023)009, and the base map was not modified.
Fig.4 Spatial transfer of grassland at different time periods
类型 Type | 指数意义 Index meaning | 分级标准 Classification standard | 范围 Range (km2) | 区县数量Number of counties (No.) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995-2000 | 2000-2005 | 2015-2020 | 1980-2020 | ||||
草地增加 Grassland increase | 急剧增加Drastic increase | >Ai+2Si | >156.25 | 2 | 0 | 6 | 2 |
| 中度增加Moderate increase | ≥Ai+Si, ≤Ai+2Si | ≥102.48, ≤156.25 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | |
| 轻度增加Slight increase | ≥Ai, <Ai+Si | ≥48.70, <102.48 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 12 | |
| 微度增加Very slight increase | >0, <Ai | >0, <48.70 | 33 | 3 | 9 | 51 | |
草地减少 Grassland decrease | 微度减少Very slight decrease | ≥Ad, <0 | ≥-24.66, <0 | 46 | 62 | 60 | 6 |
| 轻度减少Slight decrease | ≥Ad-Sd, <Ad | ≥-70.72, <-24.66 | 3 | 23 | 5 | 2 | |
| 中度减少Moderate decrease | ≥Ad-2Sd, <Ad-Sd | ≥-116.79, <-70.72 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 | |
| 急剧减少Drastic decrease | <Ad-2Sd | <-116.79 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 8 | |
表5 贵州省不同时期区县尺度草地变化分级统计
Table 5 Classification statistics of grassland change at county level at different periods in Guizhou Province
类型 Type | 指数意义 Index meaning | 分级标准 Classification standard | 范围 Range (km2) | 区县数量Number of counties (No.) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995-2000 | 2000-2005 | 2015-2020 | 1980-2020 | ||||
草地增加 Grassland increase | 急剧增加Drastic increase | >Ai+2Si | >156.25 | 2 | 0 | 6 | 2 |
| 中度增加Moderate increase | ≥Ai+Si, ≤Ai+2Si | ≥102.48, ≤156.25 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | |
| 轻度增加Slight increase | ≥Ai, <Ai+Si | ≥48.70, <102.48 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 12 | |
| 微度增加Very slight increase | >0, <Ai | >0, <48.70 | 33 | 3 | 9 | 51 | |
草地减少 Grassland decrease | 微度减少Very slight decrease | ≥Ad, <0 | ≥-24.66, <0 | 46 | 62 | 60 | 6 |
| 轻度减少Slight decrease | ≥Ad-Sd, <Ad | ≥-70.72, <-24.66 | 3 | 23 | 5 | 2 | |
| 中度减少Moderate decrease | ≥Ad-2Sd, <Ad-Sd | ≥-116.79, <-70.72 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 | |
| 急剧减少Drastic decrease | <Ad-2Sd | <-116.79 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 8 | |

图5 贵州省1980-2020年景观格局指数及其尺度效应a表示全省草地景观格局指数;b表示市州和区县尺度的草地景观格局指数平均值。a shows the grassland landscape pattern index in the province; b shows the average value of grassland landscape pattern index at the city and county scales.
Fig.5 Landscape pattern indexes and their scale effects of Guizhou Province from 1980 to 2020
转移特征 Transfer character | 变化类型 Transfer types | 景观格局指数Landscape pattern index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 斑块密度PD | 景观形状指数LSI | 聚集度指数AI | ||
草地转出 The grassland transfer out | 草地→林地Grassland→forest land | 1.18 | 156.43 | 65.14 |
| 草地→耕地Grassland→cultivated land | 2.10 | 276.85 | 12.94 | |
| 草地→水域Grassland→water bodies | 0.05 | 55.11 | 41.82 | |
| 草地→建设用地Grassland→construction land | 0.08 | 60.39 | 60.91 | |
| 草地→未利用地Grassland→unused land | 0.00 | 7.24 | 7.83 | |
草地转入 The grassland transfer in | 林地→草地Forest land→grassland | 1.17 | 167.62 | 72.39 |
| 耕地→草地Cultivated land→grassland | 2.31 | 288.60 | 11.72 | |
| 水域→草地Water bodies→grassland | 0.03 | 31.14 | 20.29 | |
| 建设用地→草地Construction land→grassland | 0.04 | 34.31 | 24.51 | |
| 未利用地→草地Unused land→grassland | 0.00 | 6.67 | 51.74 | |
表6 贵州省2015-2020年草地变化类型的景观格局指数
Table 6 Landscape pattern indexs of grassland change types in Guizhou Province from 2015 to 2020
转移特征 Transfer character | 变化类型 Transfer types | 景观格局指数Landscape pattern index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 斑块密度PD | 景观形状指数LSI | 聚集度指数AI | ||
草地转出 The grassland transfer out | 草地→林地Grassland→forest land | 1.18 | 156.43 | 65.14 |
| 草地→耕地Grassland→cultivated land | 2.10 | 276.85 | 12.94 | |
| 草地→水域Grassland→water bodies | 0.05 | 55.11 | 41.82 | |
| 草地→建设用地Grassland→construction land | 0.08 | 60.39 | 60.91 | |
| 草地→未利用地Grassland→unused land | 0.00 | 7.24 | 7.83 | |
草地转入 The grassland transfer in | 林地→草地Forest land→grassland | 1.17 | 167.62 | 72.39 |
| 耕地→草地Cultivated land→grassland | 2.31 | 288.60 | 11.72 | |
| 水域→草地Water bodies→grassland | 0.03 | 31.14 | 20.29 | |
| 建设用地→草地Construction land→grassland | 0.04 | 34.31 | 24.51 | |
| 未利用地→草地Unused land→grassland | 0.00 | 6.67 | 51.74 | |

图6 贵州省1980-2020年草地局部空间自相关LISA结果和全局Moran’s I指数该图基于自然资源部标准地图服务系统(http://bzdt.ch.mnr.gov.cn/index.html)中黔S(2023)009号标准地图制作,底图无修改。The map was based on the standard map service website of the ministry of natural resources (http://bzdt.ch.mnr.gov.cn/index.html) with the drawing review No. 黔S(2023)009, and the base map was not modified.
Fig.6 Local spatial autocorrelation LISA results and Global Moran’s I indexs of grassland in Guizhou Province from 1980 to 2020
行政区 Administrative region | 年份Year | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 2000 | 2015 | 2020 | |||||
| HH | LH | HH | LH | HH | LH | HH | LH | |
| 贵阳市Guiyang City | 0.20 | 0.61 | 0.14 | 0.54 | 0.09 | 0.45 | 0.11 | 0.46 |
| 六盘水市Liupanshui City | 0.94 | 1.16 | 0.65 | 0.85 | 0.63 | 0.82 | 0.52 | 1.04 |
| 遵义市Zunyi City | 0.20 | 0.63 | 0.19 | 0.58 | 0.15 | 0.51 | 0.14 | 0.51 |
| 安顺市Anshun City | 0.61 | 0.84 | 0.36 | 0.65 | 0.32 | 0.60 | 0.46 | 0.75 |
| 铜仁市Tongren City | 0.31 | 0.95 | 0.27 | 0.91 | 0.23 | 0.83 | 0.22 | 0.82 |
| 黔南布依族苗族自治州Qiannan Buyi and Miao Autonomous Prefecture | 0.77 | 2.03 | 0.61 | 1.89 | 0.59 | 1.73 | 0.56 | 1.72 |
| 黔东南苗族侗族自治州Qiandongnan Miao and Dong Autonomous Prefecture | 0.46 | 1.36 | 0.39 | 1.27 | 0.33 | 1.02 | 0.32 | 1.04 |
| 黔西南布依族苗族自治州Qianxinan Buyi and Miao Autonomous Prefecture | 1.49 | 1.62 | 1.09 | 1.36 | 1.00 | 1.34 | 0.98 | 1.51 |
| 毕节市Bijie City | 1.38 | 2.12 | 1.09 | 1.84 | 0.97 | 1.71 | 1.00 | 1.93 |
| 总计Total | 6.36 | 11.32 | 4.79 | 9.90 | 4.31 | 9.01 | 4.32 | 9.78 |
表7 贵州省1995-2020年各市州局部自相关类型比例
Table 7 Proportion of local autocorrelation types in each city of Guizhou Province from 1995 to 2020 (%)
行政区 Administrative region | 年份Year | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 2000 | 2015 | 2020 | |||||
| HH | LH | HH | LH | HH | LH | HH | LH | |
| 贵阳市Guiyang City | 0.20 | 0.61 | 0.14 | 0.54 | 0.09 | 0.45 | 0.11 | 0.46 |
| 六盘水市Liupanshui City | 0.94 | 1.16 | 0.65 | 0.85 | 0.63 | 0.82 | 0.52 | 1.04 |
| 遵义市Zunyi City | 0.20 | 0.63 | 0.19 | 0.58 | 0.15 | 0.51 | 0.14 | 0.51 |
| 安顺市Anshun City | 0.61 | 0.84 | 0.36 | 0.65 | 0.32 | 0.60 | 0.46 | 0.75 |
| 铜仁市Tongren City | 0.31 | 0.95 | 0.27 | 0.91 | 0.23 | 0.83 | 0.22 | 0.82 |
| 黔南布依族苗族自治州Qiannan Buyi and Miao Autonomous Prefecture | 0.77 | 2.03 | 0.61 | 1.89 | 0.59 | 1.73 | 0.56 | 1.72 |
| 黔东南苗族侗族自治州Qiandongnan Miao and Dong Autonomous Prefecture | 0.46 | 1.36 | 0.39 | 1.27 | 0.33 | 1.02 | 0.32 | 1.04 |
| 黔西南布依族苗族自治州Qianxinan Buyi and Miao Autonomous Prefecture | 1.49 | 1.62 | 1.09 | 1.36 | 1.00 | 1.34 | 0.98 | 1.51 |
| 毕节市Bijie City | 1.38 | 2.12 | 1.09 | 1.84 | 0.97 | 1.71 | 1.00 | 1.93 |
| 总计Total | 6.36 | 11.32 | 4.79 | 9.90 | 4.31 | 9.01 | 4.32 | 9.78 |
驱动因子 Driving factor | q值q value | 平均q值 Mean q value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | ||
| X1 | 0.054* | 0.057* | 0.054* | 0.055* | 0.056* | 0.064* | 0.057 |
| X2 | 0.425* | 0.403* | 0.411* | 0.406* | 0.406* | 0.429* | 0.413 |
| X3 | 0.462* | 0.406* | 0.301* | 0.194* | 0.285* | 0.255* | 0.317 |
| X4 | 0.179* | 0.348* | 0.115* | 0.126* | 0.215* | 0.251* | 0.206 |
| X5 | 0.047* | 0.057* | 0.078* | 0.070* | 0.043* | 0.154* | 0.075 |
| X6 | 0.120* | 0.114* | 0.034* | 0.064* | 0.053* | 0.070* | 0.076 |
| X7 | 0.114* | 0.130* | 0.146* | 0.234* | 0.254* | 0.411* | 0.215 |
表8 各驱动因子对草地空间分布格局的解释力
Table 8 The explanatory power of each driving factors on grassland spatial distribution pattern
驱动因子 Driving factor | q值q value | 平均q值 Mean q value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | ||
| X1 | 0.054* | 0.057* | 0.054* | 0.055* | 0.056* | 0.064* | 0.057 |
| X2 | 0.425* | 0.403* | 0.411* | 0.406* | 0.406* | 0.429* | 0.413 |
| X3 | 0.462* | 0.406* | 0.301* | 0.194* | 0.285* | 0.255* | 0.317 |
| X4 | 0.179* | 0.348* | 0.115* | 0.126* | 0.215* | 0.251* | 0.206 |
| X5 | 0.047* | 0.057* | 0.078* | 0.070* | 0.043* | 0.154* | 0.075 |
| X6 | 0.120* | 0.114* | 0.034* | 0.064* | 0.053* | 0.070* | 0.076 |
| X7 | 0.114* | 0.130* | 0.146* | 0.234* | 0.254* | 0.411* | 0.215 |
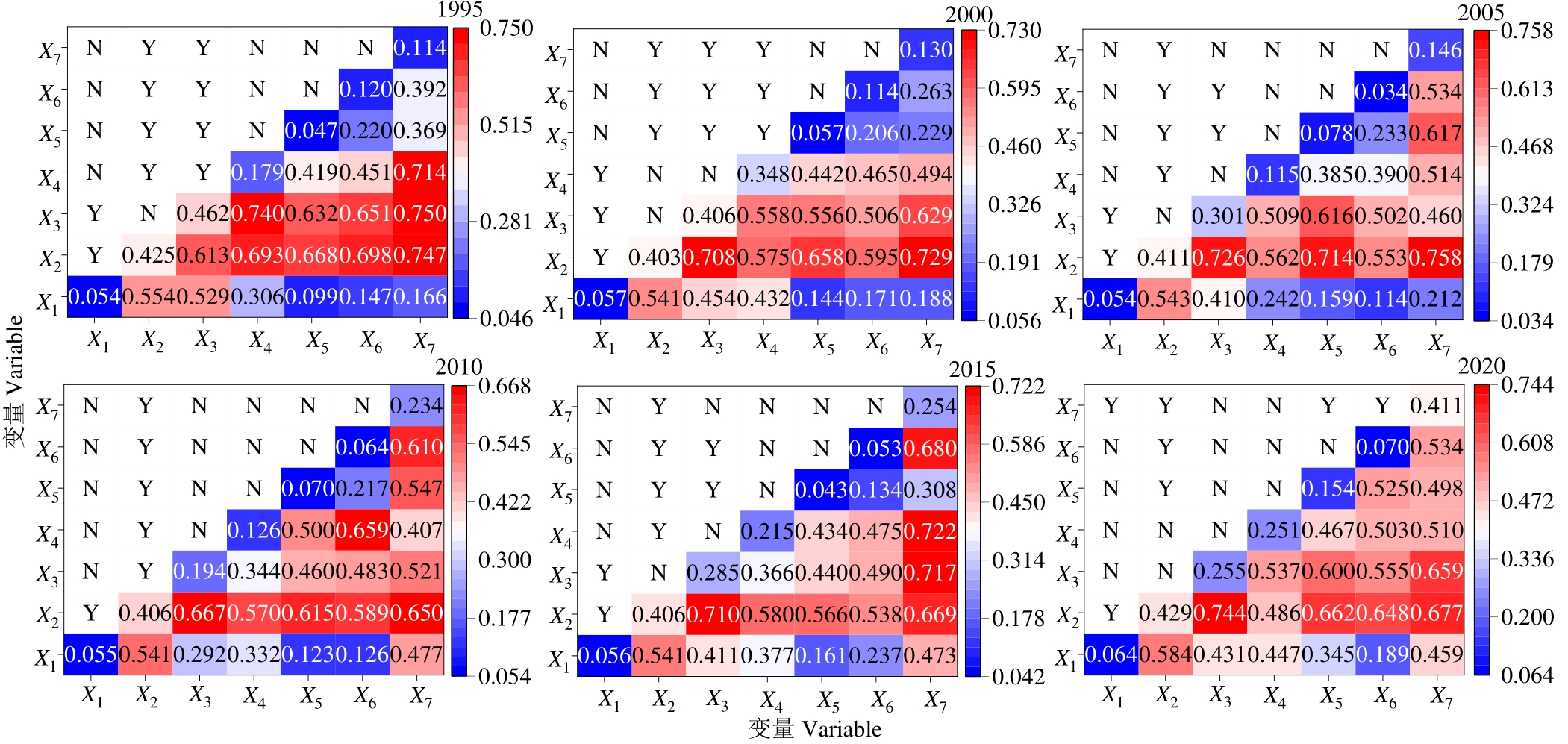
图7 草地空间分布格局影响因子交互和生态探测结果X1: 坡度Slope; X2: 海拔Elevation; X3: 年平均气温Mean annual temperature; X4: 年降水量Annual precipitation; X5: 人口密度Density of population; X6: 国内生产总值GDP; X7: 牧业产值Livestock industry output.
Fig.7 Detection results of interaction and ecological between factors affecting grassland spatial distribution pattern
驱动因子 Driving factor | 年份Year | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | |
| 坡度Slope (°) | 25~35 | 25~35 | 25~35 | 25~35 | 25~35 | 25~35 |
| 海拔Elevation (m) | 1980~2748 | 1980~2748 | 1980~2748 | 1980~2748 | 1980~2748 | 1980~2748 |
| 年平均气温Mean annual temperature (℃) | 6.7~11.9 | 6.2~11.4 | 7.1~12.7 | 7.6~13.4 | 6.9~13.0 | 5.8~12.1 |
| 年降水量Annual precipitation (mm) | 983~1160 | 894~1157 | 1294~1467 | 838~997 | 820~969 | 607~999 |
| 人口密度Density of population (person·km-2) | 10~102 | 41~88 | 41~108 | 116~195 | 139~239 | 171~205 |
| 国内生产总值GDP (×104 yuan·km-2) | 59~124 | 7~356 | 60~110 | 72~118 | 509~820 | 542~721 |
| 牧业产值Livestock industry output (×104 yuan) | 2161~4239 | 2910~4236 | 4722~7122 | 4987~8619 | 38579~54373 | 59685~80528 |
表9 1995-2020年草地在各驱动因子中集中分布的范围
Table 9 The range of driving factors for grassland aggregation from 1995 to 2020
驱动因子 Driving factor | 年份Year | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | |
| 坡度Slope (°) | 25~35 | 25~35 | 25~35 | 25~35 | 25~35 | 25~35 |
| 海拔Elevation (m) | 1980~2748 | 1980~2748 | 1980~2748 | 1980~2748 | 1980~2748 | 1980~2748 |
| 年平均气温Mean annual temperature (℃) | 6.7~11.9 | 6.2~11.4 | 7.1~12.7 | 7.6~13.4 | 6.9~13.0 | 5.8~12.1 |
| 年降水量Annual precipitation (mm) | 983~1160 | 894~1157 | 1294~1467 | 838~997 | 820~969 | 607~999 |
| 人口密度Density of population (person·km-2) | 10~102 | 41~88 | 41~108 | 116~195 | 139~239 | 171~205 |
| 国内生产总值GDP (×104 yuan·km-2) | 59~124 | 7~356 | 60~110 | 72~118 | 509~820 | 542~721 |
| 牧业产值Livestock industry output (×104 yuan) | 2161~4239 | 2910~4236 | 4722~7122 | 4987~8619 | 38579~54373 | 59685~80528 |
年份 Year | 人口密度 Density of population (Person·km-2) | 国内生产总值GDP (×108 yuan) | 牧业产值 Livestock industry output (×108 yuan) | 城镇化率 Urbanization rate (%) | 牛羊出栏量 The amount of cattle and sheep slaughter (×104 heads) | 农作物播种面积 Crop sown area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 199 | 636 | 102 | 23.83 | 160.40 | 42053 |
| 2000 | 200 | 1029 | 110 | 23.87 | 216.82 | 70440 |
| 2005 | 1178 | 1939 | 194 | 26.87 | 383.34 | 48041 |
| 2010 | 1948 | 4519 | 304 | 33.81 | 295.26 | 48893 |
| 2015 | 2463 | 10541 | 665 | 42.01 | 379.40 | 55422 |
| 2020 | 2231 | 17860 | 1019 | 53.15 | 473.51 | 54754 |
表10 贵州省1995-2020年各社会经济因子统计值
Table 10 Statistical values of each social and economic factors in Guizhou Province from 1995 to 2020
年份 Year | 人口密度 Density of population (Person·km-2) | 国内生产总值GDP (×108 yuan) | 牧业产值 Livestock industry output (×108 yuan) | 城镇化率 Urbanization rate (%) | 牛羊出栏量 The amount of cattle and sheep slaughter (×104 heads) | 农作物播种面积 Crop sown area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 199 | 636 | 102 | 23.83 | 160.40 | 42053 |
| 2000 | 200 | 1029 | 110 | 23.87 | 216.82 | 70440 |
| 2005 | 1178 | 1939 | 194 | 26.87 | 383.34 | 48041 |
| 2010 | 1948 | 4519 | 304 | 33.81 | 295.26 | 48893 |
| 2015 | 2463 | 10541 | 665 | 42.01 | 379.40 | 55422 |
| 2020 | 2231 | 17860 | 1019 | 53.15 | 473.51 | 54754 |
| 安沙舟 | 安 渊 | 毕玉蓉 | 邴孝利 | 曹成有 | 陈兵林 | 陈旭君 | 陈长青 | 程建峰 | 程金花 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 戴伟民 | 丁成龙 | 丁国华 | 董全民 | 董召荣 | 杜自强 | 段廷玉 | 方香玲 | 冯彦皓 | 高学文 |
| 耿玉清 | 龚吉蕊 | 郭 丁 | 郭继勋 | 郭 龙 | 郭正刚 | 韩立强 | 韩烈保 | 韩玉竹 | 韩云华 |
| 杭苏琴 | 何树斌 | 贺 晓 | 胡 涛 | 黄晓东 | 贾倩民 | 贾善刚 | 雷 蕾 | 李 飞 | 李惠侠 |
| 李建龙 | 李 美 | 李胜利 | 李万宏 | 李伟斌 | 李旭东 | 李彦忠 | 李造哲 | 李镇清 | 李志强 |
| 林慧龙 | 蔺吉祥 | 凌 宁 | 刘慧霞 | 刘 杰 | 刘金荣 | 刘 权 | 刘世亮 | 刘文献 | 刘永杰 |
| 刘志民 | 吕晓涛 | 马景永 | 马 清 | 马 啸 | 马永清 | 毛培胜 | 毛胜勇 | 穆春生 | 彭远英 |
| 尚占环 | 邵 涛 | 沈益新 | 沈禹颖 | 时 磊 | 苏艳军 | 苏永中 | 苏 勇 | 孙洪仁 | 孙丽娟 |
| 唐 增 | 田 沛 | 汪诗平 | 王德利 | 王虎成 | 王剑峰 | 王竞红 | 王丽佳 | 王三根 | 王晓娟 |
| 王新宇 | 谢文刚 | 徐世健 | 闫 涛 | 杨成德 | 杨惠敏 | 杨宪龙 | 姚 拓 | 于应文 | 于 卓 |
| 袁明龙 | 曾彦军 | 查同刚 | 张吉宇 | 张建国 | 张金屯 | 张世挺 | 张万军 | 张卫建 | 张兴旭 |
| 赵 宁 | 赵 祺 | 赵 威 | 朱 宏 | 朱剑霄 | 庄 苏 |
(以姓氏拼音为序)
| 安沙舟 | 安 渊 | 毕玉蓉 | 邴孝利 | 曹成有 | 陈兵林 | 陈旭君 | 陈长青 | 程建峰 | 程金花 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 戴伟民 | 丁成龙 | 丁国华 | 董全民 | 董召荣 | 杜自强 | 段廷玉 | 方香玲 | 冯彦皓 | 高学文 |
| 耿玉清 | 龚吉蕊 | 郭 丁 | 郭继勋 | 郭 龙 | 郭正刚 | 韩立强 | 韩烈保 | 韩玉竹 | 韩云华 |
| 杭苏琴 | 何树斌 | 贺 晓 | 胡 涛 | 黄晓东 | 贾倩民 | 贾善刚 | 雷 蕾 | 李 飞 | 李惠侠 |
| 李建龙 | 李 美 | 李胜利 | 李万宏 | 李伟斌 | 李旭东 | 李彦忠 | 李造哲 | 李镇清 | 李志强 |
| 林慧龙 | 蔺吉祥 | 凌 宁 | 刘慧霞 | 刘 杰 | 刘金荣 | 刘 权 | 刘世亮 | 刘文献 | 刘永杰 |
| 刘志民 | 吕晓涛 | 马景永 | 马 清 | 马 啸 | 马永清 | 毛培胜 | 毛胜勇 | 穆春生 | 彭远英 |
| 尚占环 | 邵 涛 | 沈益新 | 沈禹颖 | 时 磊 | 苏艳军 | 苏永中 | 苏 勇 | 孙洪仁 | 孙丽娟 |
| 唐 增 | 田 沛 | 汪诗平 | 王德利 | 王虎成 | 王剑峰 | 王竞红 | 王丽佳 | 王三根 | 王晓娟 |
| 王新宇 | 谢文刚 | 徐世健 | 闫 涛 | 杨成德 | 杨惠敏 | 杨宪龙 | 姚 拓 | 于应文 | 于 卓 |
| 袁明龙 | 曾彦军 | 查同刚 | 张吉宇 | 张建国 | 张金屯 | 张世挺 | 张万军 | 张卫建 | 张兴旭 |
| 赵 宁 | 赵 祺 | 赵 威 | 朱 宏 | 朱剑霄 | 庄 苏 |
| 1 | Song Y Q, Xu M, Xu T T, et al. Changes in plant community assembly from patchy degradation of grasslands and grazing by different-sized herbivores. Ecological Applications, 2023, 33(2): e2803. |
| 2 | Zhang X N, Li X D, Nian L L, et al. A bibliometric evaluation of the status of the water conservation function of grassland ecosystems. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(6): 35-49. |
| 张晓宁, 李晓丹, 年丽丽, 等. 基于文献计量的草地生态系统水源涵养功能研究现状. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 35-49. | |
| 3 | Scurlock J M, Hall D M. The global carbon sink: A grassland perspective. Global Change Biology, 1998, 4: 229-233. |
| 4 | Gao L, Ding Y. Progress in research and practice of restoration of degraded grassland around the world. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(10): 189-205. |
| 高丽, 丁勇. 世界退化草地恢复研究和实践进展. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 189-205. | |
| 5 | Reinermann S, Asam S, Kuenzer C. Remote sensing of grassland production and management-A review. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(12): 1949. |
| 6 | Zhou Y, Li X H, Liu Y S. Land use change and driving factors in rural China during the period 1995-2015. Land Use Policy, 2020, 99, 105048. |
| 7 | Fu F, Deng S M, Wu D, et al. Research on the spatiotemporal evolution of land use landscape pattern in a county area based on CA-Markov model. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2022, 80: 103760. |
| 8 | Zhang J D, Mei Z X, Lv J H, et al. Simulating multiple land use scenarios based on the FLUS model considering spatial autocorrelation. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2020, 22(3): 531-542. |
| 张经度, 梅志雄, 吕佳慧, 等. 纳入空间自相关的FLUS模型在土地利用变化多情景模拟中的应用. 地球信息科学学报, 2020, 22(3): 531-542. | |
| 9 | Wan H W, Li H X, Gao J X, et al. Spatial pattern analysis of carbon sequestration potential of vegetation ecosystem in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(21): 8568-8580. |
| 万华伟, 李灏欣, 高吉喜, 等. 我国植被生态系统固碳能力提升潜力空间格局研究. 生态学报, 2022, 42(21): 8568-8580. | |
| 10 | Cui W L, Chen M Y, Zhong H Y. Spatial differentiation and differentiated management of ecological security in the Bay Area based on ESDA and GA: A case study of the Zhejiang Greater Bay Area. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(5): 2074-2087. |
| 崔旺来, 陈梦圆, 钟海玥. 基于探索性空间数据分析和地统计分析的湾区生态安全空间分异及差异化管理——以浙江大湾区为例. 生态学报, 2023, 43(5): 2074-2087. | |
| 11 | Song C Q, You S C, Liu G H, et al. Spatio-temporal pattern and change of Nagqu grassland and the influence of human factors. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(3): 1-10. |
| 宋春桥, 游松财, 刘高焕, 等. 那曲地区草地植被时空格局与变化及其人文因素影响研究. 草业学报, 2012, 21(3): 1-10. | |
| 12 | Wang Z Q, Zhang Y Z, Yang Y, et al. Quantitative assess the driving forces on the grassland degradation in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, in China. Ecological Informatics, 2016, 33: 32-44. |
| 13 | Wang J F, Xu C D. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2017, 72(1): 116-134. |
| 王劲峰, 徐成东. 地理探测器: 原理与展望. 地理学报, 2017, 72(1): 116-134. | |
| 14 | Liao C J, Yue Y M, Wang K, et al. Ecological restoration enhances ecosystem health in the karst regions of southwest China. Ecological Indicators, 2018, 90: 416-425. |
| 15 | Chi Y K, Xiong K N, Zhang Y, et al. The beneficial results, problems and suggestions of grass-planting and livestock-raising to bring rocky desertification under control in the Karst areas of southwest China. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2015, 479(11): 143-147. |
| 池永宽, 熊康宁, 张俞, 等. 西南喀斯特地区种草养畜治理石漠化的效益、问题与建议. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2015, 479(11): 143-147. | |
| 16 | Yang Z H. Improve the grassland construction and achieve the herbivorous animal husbandry developing and rock desertification control. Pratacultural Science, 2008, 182(9): 59-63. |
| 杨振海. 加快岩溶地区草地建设步伐 实现草食畜牧业发展和石漠化治理双赢. 草业科学, 2008, 182(9): 59-63. | |
| 17 | Fang J Z, Xiong K N, Chi Y K, et al. Research advancement in grassland ecosystem vulnerability and ecological resilience and its inspiration for improving grassland ecosystem services in the karst desertification control. Plants, 2022, 11(10): 1290. |
| 18 | Zhang Z H. Exploring the way of controlling rocky desertification and developing ecological animal husbandry in Guizhou Province. Pratacultural Science, 2006, 23(8): 63-67. |
| 张自和. 贵州治理石漠化发展生态畜牧业探索之路. 草业科学, 2006, 23(8): 63-67. | |
| 19 | Huangfu J Y, Lu X S, Zhao X G, et al. The present situation of natural grassland resource in Guizhou Province and its development and utilization strategy. Pratacultural Science, 2009, 26(9): 70-76. |
| 皇甫江云, 卢欣石, 赵熙贵, 等. 贵州草地资源现状及开发利用对策. 草业科学, 2009, 26(9): 70-76. | |
| 20 | Gao J F, Su X L, Xiong K N, et al. Grasslands eco-environment and stockbreeding development in the karst areas of Guizhou province. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2011, 20(4): 279-286. |
| 高渐飞, 苏孝良, 熊康宁, 等. 贵州岩溶地区的草地生态环境与草地畜牧业发展. 草业学报, 2011, 20(4): 279-286. | |
| 21 | Lin T, Wu D F, Yang M Z, et al. Evolution and simulation of terrestrial ecosystem carbon storage and sustainability assessment in karst areas: A case study of Guizhou Province. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2022, 19(23): 16219. |
| 22 | Chen Q W, Xiong K N, Dan W H, et al. Coupling characteristics of ecology and poverty in typical karst areas: case study of 9000 provincial level poor villages in Guizhou Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(8): 2968-2982. |
| 陈起伟, 熊康宁, 但文红, 等. 典型喀斯特区生态与贫困耦合特征分析——以贵州省9000个省级贫困村为例. 生态学报, 2021, 41(8): 2968-2982. | |
| 23 | Gao J B, Wu S H, Cai Y L. Investigating the spatial heterogeneity of vegetation cover at multi-scales: A case study in karst Guizhou Plateau of China. Geographical Research, 2013, 32(12): 2179-2188. |
| 高江波, 吴绍洪, 蔡运龙. 区域植被覆盖的多尺度空间变异性——以贵州喀斯特高原为例. 地理研究, 2013, 32(12): 2179-2188. | |
| 24 | Liu J Y, Ning J, Kuang W H, et al. Spatia-temporal patterns and characteristics of land-use change in China during 2010-2015. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2018, 73(5): 789-802. |
| 刘纪远, 宁佳, 匡文慧, 等. 2010-2015年中国土地利用变化的时空格局与新特征. 地理学报, 2018, 73(5): 789-802. | |
| 25 | Zhu H Y, Li X B. Discussion on the method of regional land use change index model. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2003(5): 643-650. |
| 朱会义, 李秀彬. 关于区域土地利用变化指数模型方法的讨论. 地理学报, 2003(5): 643-650. | |
| 26 | Oom D, Pereira J M C. Exploratory spatial data analysis of global MODIS active fire data. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2013, 21: 326-340. |
| 27 | Dadashpoor H, Azizi P, Moghadasi M. Land use change, urbanization, and change in landscape pattern in a metropolitan area. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 655: 707-719. |
| 28 | Wu W Y, Zhang J, Sun Z Y, et al. Attribution analysis of land degradation in Hainan Island based on geographical detector. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 141: 109119. |
| 29 | Mei Z M. On the developmental ways for returning farmland to woodland or grassland and water-saving agro-forestry in the ecological fragile Karst area of Guizhou. Carsologica Sinica, 2003(4): 44-49. |
| 梅再美. 贵州喀斯特脆弱生态区退耕还林还草与节水型混农林业发展的途径探讨. 中国岩溶, 2003(4): 44-49. | |
| 30 | Chen L H, He Z H, Pan S, et al. Spatial and temporal evolution characteristics of karst agricultural drought based on different time scales and driving detection. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2023, 37(2): 136-148. |
| 陈莉会, 贺中华, 潘杉, 等. 基于不同时间尺度的喀斯特农业干旱时空演变特征及驱动探测——以贵州省为例. 水土保持学报, 2023, 37(2): 136-148. | |
| 31 | Deng L Z, Su W C, Yang Z H. Analysis of agricultural structure evolution and driving forces in karst area based on CCA and PCA Model. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 30(4): 869-875. |
| 邓灵稚, 苏维词, 杨振华. 基于CCA与PCA模型的岩溶地区农业结构演变及其驱动力分析. 西南农业学报, 2017, 30(4): 869-875. | |
| 32 | Song S Z, Xiong K N, Chi Y K, et al. Study on improvement of degraded grassland in rocky desertification control in the karst areas of Southern China. Journal of Domestic Animal Ecology, 2019, 40(3): 82-87, 96. |
| 宋淑珍, 熊康宁, 池永宽, 等. 中国南方喀斯特石漠化治理中的退化草地改良研究综述. 家畜生态学报, 2019, 40(3): 82-87, 96. | |
| 33 | Sun Q Z, Liu R L, Chen J Y, et al. Effect of planting grass on soil erosion in karst demonstration areas of rocky desertification integrated rehabilitation in Guizhou Province. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 27(4): 67-72, 77. |
| 孙泉忠, 刘瑞禄, 陈菊艳, 等. 贵州省石漠化综合治理人工种草对土壤侵蚀的影响. 水土保持学报, 2013, 27(4): 67-72, 77. | |
| 34 | Statistics Bureau of Guizhou Province. Guizhou Statistic Yearbook. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2019. |
| 贵州省统计局. 贵州统计年鉴. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2019. | |
| 35 | National Forestry and Grassland Administration. China Forestry and Grassland Statistic Yearbook. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2021. |
| 国家林业和草原局. 中国林业和草原年鉴. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2021. | |
| 36 | Wang Y H, Tang W J, Li S, et al. Change in grassland productivity in Qinghai Province and its driving factors. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(2): 1-13. |
| 王亚晖, 唐文家, 李森, 等. 青海省草地生产力变化及其驱动因素. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 1-13. | |
| 37 | Zhang Y R, He Y, Li Y L, et al. Spatiotemporal variation and driving forces of NDVI from 1982 to 2015 in the Qinba Mountains, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2022, 29(34): 52277-52288. |
| 38 | Zhu L J, Meng J J, Zhu L K. Applying Geodetector to disentangle the contributions of natural and anthropogenic factors to NDVI variations in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin. Ecological Indicators, 2020, 117: 106545. |
| 39 | Shu S J, Wang Y, Chu H Y. Spatial distribution of temperature in China: Geographic and orographic influences. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 2009, 45(3): 334-342. |
| 舒守娟, 王元, 储惠芸. 地理和地形影响下我国区域的气温空间分布. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 2009, 45(3): 334-342. | |
| 40 | Zhu M, Zhou Z F, Jiang Y, et al. Spatial and temporal heterogeneity of precipitation based on the landforms of Guizhou Plateau. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 27(3): 181-189. |
| 朱孟, 周忠发, 蒋翼, 等. 基于贵州高原地貌分区的降水时空异质性特征. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(3): 181-189. | |
| 41 | Su D X. Characteristics of natural grassland in Guizhou Province and it’s evaluation. Journal of Natural Resources, 1987(2): 153-160. |
| 苏大学. 贵州天然草地资源的自然特征和评价. 自然资源学报, 1987(2): 153-160. | |
| 42 | Huangfu J Y, Mao F X, Lu X S. Analysis of grassland resources in southwest China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(1): 75-82. |
| 皇甫江云, 毛凤显, 卢欣石. 中国西南地区的草地资源分析. 草业学报, 2012, 21(1): 75-82. | |
| 43 | Xu L X, Xiong K N, Zhang J H, et al. Advantages and potentials for the development of animal husbandry in Guizhou Karst area. Journal of Domestic Animal Ecology, 2015, 36(12): 60-66. |
| 许留兴, 熊康宁, 张锦华, 等. 贵州喀斯特地区草地畜牧业发展优势与潜力分析. 家畜生态学报, 2015, 36(12): 60-66. | |
| 44 | Bardgett R D, Bullock J M, Lavorel S, et al. Combatting global grassland degradation. Nature Reviews Earth and Environment, 2021, 2(10): 720-735. |
| 45 | Jiang A P, Jin T T, Zhang L P, et al. Influence of road construction on vegetation net primary productivity in southwest China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(9): 3624-3632. |
| 蒋爱萍, 靳甜甜, 张丽萍, 等. 西南地区道路建设对植被净初级生产力的影响. 生态学报, 2022, 42(9): 3624-3632. | |
| 46 | Liu J Y, Kuang W H, Zhang Z X, et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns and causes of land use changes in China since the late 1980s. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2014, 69(1): 3-14. |
| 刘纪远, 匡文慧, 张增祥, 等. 20世纪80年代末以来中国土地利用变化的基本特征与空间格局. 地理学报, 2014, 69(1): 3-14. | |
| 47 | Zhang B F, Miao C H. Spatiotemporal changes and driving forces of land use in the Yellow River Basin. Resources Science, 2020, 42(3): 460-473. |
| 张佰发, 苗长虹. 黄河流域土地利用时空格局演变及驱动力. 资源科学, 2020, 42(3): 460-473. | |
| 48 | Fang J Y, Geng X Q, Zhao X, et al. How many areas of grasslands are there in China? Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(17): 1731-1739. |
| 方精云, 耿晓庆, 赵霞, 等. 我国草地面积有多大? 科学通报, 2018, 63(17): 1731-1739. | |
| 49 | Li Z, Han W C, Hu Q Y, et al. Land use/cover classification based on combining spectral mixture analysis model and object-oriented method. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2021, 37(17): 225-233. |
| 李卓, 韩文超, 胡起源, 等. 融合光谱混合分解与面向对象的土地利用/覆被分类. 农业工程学报, 2021, 37(17): 225-233. | |
| 50 | Guo M R, Liu T, Han P, et al. Discriminating data of spacial distribution of artificial grassland based on multi-source satellite remote sensing date fusion. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2019, 41(5): 53-62. |
| 郭茉苒, 刘涛, 韩鹏, 等. 基于多源卫星遥感数据融合的人工草地空间分布信息提取. 中国草地学报, 2019, 41(5): 53-62. | |
| 51 | Chen H, Wang Y, Zhang X, et al. Extraction and application of land use/land cover information in the middle and lower reaches of Ziwu River on the south slope of Qinling Mountains. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(22): 9239-9249. |
| 陈航, 王颖, 张昕, 等. 秦岭南坡子午河中下游流域土地利用/土地覆被信息提取及其应用. 生态学报, 2022, 42(22): 9239-9249. |
| [1] | 杨志贵, 张建国, 李锦荣, 于红妍, 常丽, 宜树华, 吕燕燕, 张玉琢, 孟宝平. 内蒙古温性草原草地类型近20年时空动态变化研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 1-16. |
| [2] | 张东, 侯晨, 马文明, 王长庭, 邓增卓玛, 张婷. 高寒草地不同灌丛化梯度下土壤酶活性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 79-92. |
| [3] | 张慧龙, 杨秀春, 杨东, 陈昂, 张敏. 2000-2020年内蒙古草地植被覆盖度时空变化及趋势预测[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 1-13. |
| [4] | 康燕霞, 姜渊博, 齐广平, 银敏华, 马彦麟, 汪精海, 贾琼, 唐仲霞, 汪爱霞. 红豆草与无芒雀麦混播草地生产力提升的水分调控模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 115-128. |
| [5] | 李雪敏, 李同宁, 吴芝雨, 武振国. 多情景模拟下内蒙古草地生态系统服务价值时空演变[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 14-27. |
| [6] | 邢虎成, 王贤芳, 周清, 闫景彩, 揭雨成. 湖南52县草地资源的类型、等级及利用现状分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 91-103. |
| [7] | 黄治鹏, 黄毅, 杨全俊, 夏超, 张岩. 蒙古国草地农业及对我国的启示[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 1-15. |
| [8] | 崔婷, 王勇, 马晖玲. 外源IAA作用下草地早熟禾中调控Cd长距离运输的关键基因表达及其代谢通路分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 146-156. |
| [9] | 高婕, 赵新全, 刘文亭, 杨晓霞, 张春平, 俞旸, 曹铨, 刘玉祯, 张雪, 董全民. 基于供给—消耗关系的青海省高寒草地承载力时空变化分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 1-12. |
| [10] | 马婧, 郭方君, 邹枝慧, 孙琳, 陈芳. 腾格里沙漠南缘不同恢复阶段沙质草地植被的季节变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 203-210. |
| [11] | 郭芮, 伏帅, 侯蒙京, 刘洁, 苗春丽, 孟新月, 冯琦胜, 贺金生, 钱大文, 梁天刚. 基于Sentinel-2数据的青海门源县天然草地生物量遥感反演研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 15-29. |
| [12] | 马源, 王晓丽, 王彦龙, 马玉寿, 崔海鹏. 生态恢复领域草种丸粒化研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 197-207. |
| [13] | 江奥, 敬路淮, 泽让东科, 田黎明. 放牧影响草地凋落物分解研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 208-220. |
| [14] | 哈雪, 张金青, 白方旭, 马祥荣, 王安琦, 马晖玲. 甘肃野生草地早熟禾种质种子产量相关性状分析及其对矿质元素利用效应评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 54-67. |
| [15] | 雷石龙, 廖李容, 王杰, 张路, 叶振城, 刘国彬, 张超. 高寒草地植物多样性与Godron群落稳定性关系及其环境驱动因素[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 1-12. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||