

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1): 1-16.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024078
• 研究论文 •
侯晓磊1( ), 武春丽1, 邓雅元1, 麻文章1, 赵廷宁1(
), 武春丽1, 邓雅元1, 麻文章1, 赵廷宁1( ), 曾文杰1, 巩子涵1, 芦治源1, 吴国伟2
), 曾文杰1, 巩子涵1, 芦治源1, 吴国伟2
收稿日期:2024-03-16
修回日期:2024-05-08
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2024-11-04
通讯作者:
赵廷宁
作者简介:E-mail: zhtning@bjfu.edu.cn基金资助:
Xiao-lei HOU1( ), Chun-li WU1, Ya-yuan DENG1, Wen-zhang MA1, Ting-ning ZHAO1(
), Chun-li WU1, Ya-yuan DENG1, Wen-zhang MA1, Ting-ning ZHAO1( ), Wen-jie ZENG1, Zi-han GONG1, Zhi-yuan LU1, Guo-wei WU2
), Wen-jie ZENG1, Zi-han GONG1, Zhi-yuan LU1, Guo-wei WU2
Received:2024-03-16
Revised:2024-05-08
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2024-11-04
Contact:
Ting-ning ZHAO
摘要:
为建立稳定的煤矸石山人工植被生态系统,以宁东煤炭基地排矸场生态恢复初期人工植物群落为研究对象,基于样方法调查地上植被,并计算灌草植物种重要值,采用生态位宽度、生态位相似性、生态位重叠值、方差比率、卡方检验、Spearman相关性检验方法对矿区植物群落优势种进行种间联结与相关性分析。结果表明:研究区灌草植物44种,隶属于9科36属,以禾本科、豆科、菊科、苋科为主。灌木植物生态位宽度与重要值排序不完全一致,但总体趋势一致,以猫头刺和柠条锦鸡儿为优势种;草本植物生态位宽度与重要值排序一致,以雾冰藜和紫花苜蓿为优势种。灌木层与草本层植物总体联结性的方差比率值均大于1,其中灌木层植物种间呈显著正联结,草本层种间联结性不显著。综上,生态恢复区植物群落处于演替前期或中期阶段,种间竞争平缓,宁东煤炭基地植被配置应选择与优势植物种呈正联结的植物,形成稳定的植物群落结构,提高矿区生态恢复效率。
侯晓磊, 武春丽, 邓雅元, 麻文章, 赵廷宁, 曾文杰, 巩子涵, 芦治源, 吴国伟. 宁东煤炭基地排矸场人工植物群落优势种生态位和种间关系研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 1-16.
Xiao-lei HOU, Chun-li WU, Ya-yuan DENG, Wen-zhang MA, Ting-ning ZHAO, Wen-jie ZENG, Zi-han GONG, Zhi-yuan LU, Guo-wei WU. Niche and interspecific association of dominant plant species in artificial plant communities, the coal gangue dump of the Ningdong coal base, Middle East Ningxia[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(1): 1-16.

图1 研究区概况基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2019)3333号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map service website of the Ministry of Natural Resources with the drawing review No. GS(2019)3333, the boundary of the base map is not modified.
Fig.1 The overview of the study area
矿区 Mining area | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 经度 Longitude (E) | 平均海拔 Average altitude (m) | 恢复年限 Restoration period (a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 38°02′23″ | 106°41′24″ | 1276 | 4 |
| Ⅱ | 38°02′37″ | 106°37′34″ | 1292 | 4 |
| Ⅲ | 37°57′47″ | 106°43′03″ | 1329 | 2 |
| Ⅳ | 37°49′47″ | 106°43′16″ | 1376 | 3 |
| Ⅴ | 37°55′43″ | 106°31′28″ | 1339 | 2 |
| Ⅵ | 37°59′31″ | 106°35′10″ | 1331 | 4 |
表1 调查煤矸石山的基本情况
Table 1 Basic information of the investigated coal gangue hills
矿区 Mining area | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 经度 Longitude (E) | 平均海拔 Average altitude (m) | 恢复年限 Restoration period (a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 38°02′23″ | 106°41′24″ | 1276 | 4 |
| Ⅱ | 38°02′37″ | 106°37′34″ | 1292 | 4 |
| Ⅲ | 37°57′47″ | 106°43′03″ | 1329 | 2 |
| Ⅳ | 37°49′47″ | 106°43′16″ | 1376 | 3 |
| Ⅴ | 37°55′43″ | 106°31′28″ | 1339 | 2 |
| Ⅵ | 37°59′31″ | 106°35′10″ | 1331 | 4 |
序号 Number | 科 Family | 植物物种数Number of plant species | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
灌木 Bush | 草本Herb | |||||
| 一年生Annual | 一年生及二年生Annual and biennial | 多年生Perennial | 藤本Vine | |||
| 1 | 豆科Fabaceae | 4 | - | 1 | 5 | - |
| 2 | 禾本科Poaceae | - | 4 | - | 6 | - |
| 3 | 菊科Asteraceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | - |
| 4 | 苋科Amaranthaceae | 1 | 7 | - | - | - |
| 5 | 柽柳科Tamaricaceae | 2 | - | - | - | - |
| 6 | 夹竹桃科Apocynaceae | 1 | - | - | - | 1 |
| 7 | 白刺科Nitrariaceae | - | - | - | 1 | - |
| 8 | 葫芦科Cucurbitaceae | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| 9 | 紫葳科Bignoniaceae | - | - | - | 1 | - |
表2 植物群落组成
Table 2 Plant community composition
序号 Number | 科 Family | 植物物种数Number of plant species | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
灌木 Bush | 草本Herb | |||||
| 一年生Annual | 一年生及二年生Annual and biennial | 多年生Perennial | 藤本Vine | |||
| 1 | 豆科Fabaceae | 4 | - | 1 | 5 | - |
| 2 | 禾本科Poaceae | - | 4 | - | 6 | - |
| 3 | 菊科Asteraceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | - |
| 4 | 苋科Amaranthaceae | 1 | 7 | - | - | - |
| 5 | 柽柳科Tamaricaceae | 2 | - | - | - | - |
| 6 | 夹竹桃科Apocynaceae | 1 | - | - | - | 1 |
| 7 | 白刺科Nitrariaceae | - | - | - | 1 | - |
| 8 | 葫芦科Cucurbitaceae | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| 9 | 紫葳科Bignoniaceae | - | - | - | 1 | - |
编号 Number | 物种缩写 Species abbreviation | 物种 Species name | 重要值 Importance value (%) | 生态位宽度Niche breadth | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Levins | Shannon | ||||
| 1 | OA | 猫头刺O. aciphylla | 25.5 | 8.47 | 2.32 |
| 2 | RS | 红砂R. songarica | 0.9 | 1.30 | 0.39 |
| 3 | AO | 黑沙蒿A. ordosica | 6.6 | 2.70 | 1.15 |
| 4 | CK | 柠条锦鸡儿C. korshinskii | 22.9 | 5.79 | 1.83 |
| 5 | TG | 红花多枝柽柳T. gallica | 5.9 | 1.98 | 0.80 |
| 6 | HA | 梭梭Haloxylon ammodendron | 1.6 | 1.77 | 0.63 |
| 7 | AV | 罗布麻A. venetum | 0.3 | 1.31 | 0.40 |
| 8 | CF | 羊柴C. fruticosum | 6.8 | 1.43 | 0.48 |
表3 灌木层优势植物重要值与生态位宽度
Table 3 The important value and niche breadth of shrub dominant plants
编号 Number | 物种缩写 Species abbreviation | 物种 Species name | 重要值 Importance value (%) | 生态位宽度Niche breadth | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Levins | Shannon | ||||
| 1 | OA | 猫头刺O. aciphylla | 25.5 | 8.47 | 2.32 |
| 2 | RS | 红砂R. songarica | 0.9 | 1.30 | 0.39 |
| 3 | AO | 黑沙蒿A. ordosica | 6.6 | 2.70 | 1.15 |
| 4 | CK | 柠条锦鸡儿C. korshinskii | 22.9 | 5.79 | 1.83 |
| 5 | TG | 红花多枝柽柳T. gallica | 5.9 | 1.98 | 0.80 |
| 6 | HA | 梭梭Haloxylon ammodendron | 1.6 | 1.77 | 0.63 |
| 7 | AV | 罗布麻A. venetum | 0.3 | 1.31 | 0.40 |
| 8 | CF | 羊柴C. fruticosum | 6.8 | 1.43 | 0.48 |
编号 Number | 物种缩写 Species abbreviation | 物种 Species name | 重要值 Importance value (%) | 生态位宽度Niche breadth | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Levins | Shannon | ||||
| 1 | PM | 稷P. miliaceum | 4.0 | 1.99 | 0.75 |
| 2 | CAL | 藜C. album | 3.6 | 5.42 | 1.98 |
| 3 | GD | 雾冰藜G. dasyphylla | 18.7 | 10.84 | 2.48 |
| 4 | IS | 蓼子朴Inula salsoloides | 3.5 | 5.75 | 1.87 |
| 5 | SC | 猪毛菜S. collina | 1.3 | 2.76 | 1.05 |
| 6 | MS | 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 18.4 | 8.88 | 2.35 |
| 7 | CV | 虎尾草C. virgata | 4.5 | 4.26 | 1.64 |
| 8 | CE | 拂子茅C. epigeios | 7.6 | 3.65 | 1.42 |
| 9 | SV | 狗尾草S. viridis | 8.8 | 4.52 | 1.76 |
| 10 | CM | 蒙古虫实C. mongolicum | 0.7 | 3.70 | 1.35 |
| 11 | CAC | 尖头叶藜C. acuminatum | 1.4 | 1.82 | 0.69 |
| 12 | CC | 鹅绒藤C. chinense | 1.2 | 3.57 | 1.42 |
| 13 | LT | 乳苣Lactuca tatarica | 2.0 | 3.60 | 1.37 |
| 14 | PA | 芦苇P. australis | 4.9 | 5.45 | 1.83 |
| 15 | AA | 黄花蒿Artemisia annua | 3.6 | 3.76 | 1.55 |
| 16 | AF | 冷蒿Artemisia frigida | 0.3 | 1.99 | 0.69 |
| 17 | AC | 茵陈蒿Artemisia capillaris | 2.7 | 1.03 | 0.08 |
| 18 | HAR | 白茎盐生草H. arachnoideus | 1.2 | 3.69 | 1.46 |
| 19 | SS | 苦马豆Sphaerophysa salsula | 0.4 | 1.38 | 0.45 |
| 20 | AM | 草木樨状黄耆Astragalus melilotoides | 0.4 | 1.15 | 0.25 |
表4 草本层优势植物重要值与生态位宽度
Table 4 The important value and niche breadth of herb dominant plants
编号 Number | 物种缩写 Species abbreviation | 物种 Species name | 重要值 Importance value (%) | 生态位宽度Niche breadth | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Levins | Shannon | ||||
| 1 | PM | 稷P. miliaceum | 4.0 | 1.99 | 0.75 |
| 2 | CAL | 藜C. album | 3.6 | 5.42 | 1.98 |
| 3 | GD | 雾冰藜G. dasyphylla | 18.7 | 10.84 | 2.48 |
| 4 | IS | 蓼子朴Inula salsoloides | 3.5 | 5.75 | 1.87 |
| 5 | SC | 猪毛菜S. collina | 1.3 | 2.76 | 1.05 |
| 6 | MS | 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 18.4 | 8.88 | 2.35 |
| 7 | CV | 虎尾草C. virgata | 4.5 | 4.26 | 1.64 |
| 8 | CE | 拂子茅C. epigeios | 7.6 | 3.65 | 1.42 |
| 9 | SV | 狗尾草S. viridis | 8.8 | 4.52 | 1.76 |
| 10 | CM | 蒙古虫实C. mongolicum | 0.7 | 3.70 | 1.35 |
| 11 | CAC | 尖头叶藜C. acuminatum | 1.4 | 1.82 | 0.69 |
| 12 | CC | 鹅绒藤C. chinense | 1.2 | 3.57 | 1.42 |
| 13 | LT | 乳苣Lactuca tatarica | 2.0 | 3.60 | 1.37 |
| 14 | PA | 芦苇P. australis | 4.9 | 5.45 | 1.83 |
| 15 | AA | 黄花蒿Artemisia annua | 3.6 | 3.76 | 1.55 |
| 16 | AF | 冷蒿Artemisia frigida | 0.3 | 1.99 | 0.69 |
| 17 | AC | 茵陈蒿Artemisia capillaris | 2.7 | 1.03 | 0.08 |
| 18 | HAR | 白茎盐生草H. arachnoideus | 1.2 | 3.69 | 1.46 |
| 19 | SS | 苦马豆Sphaerophysa salsula | 0.4 | 1.38 | 0.45 |
| 20 | AM | 草木樨状黄耆Astragalus melilotoides | 0.4 | 1.15 | 0.25 |

图3 优势灌木层生态位相似比(a)及重叠值(b)OA: 猫头刺O. aciphylla; RS: 红砂R. songarica; AO: 黑沙蒿A. ordosica; CK: 柠条锦鸡儿C. korshinskii; TG: 红花多枝柽柳T. gallica; HA: 梭梭H. ammodendron; AV: 罗布麻A. venetum; CF: 羊柴C. fruticosum. 下同The same below.
Fig.3 The niche similarity ratio (a) and overlap value (b) of dominant shrub layer

图4 优势草本层生态位相似比(a)及重叠值(b)PM: 稷P. miliaceum; CAL: 藜C. album; GD: 雾冰藜G. dasyphylla; IS: 蓼子朴I. salsoloides; SC: 猪毛菜S. collina; MS: 紫花苜蓿M. sativa; CV: 虎尾草C. virgata; CE: 拂子茅C. epigeios; SV: 狗尾草S. viridis; CM: 蒙古虫实C. mongolicum; CAC: 尖头叶藜C. acuminatum; CC: 鹅绒藤C. chinense; LT: 乳苣L. tatarica; PA: 芦苇P. australis; AA: 黄花蒿A. annua; AF: 冷蒿A. frigida; AC: 茵陈蒿A. capillaris; HAR: 白茎盐生草H. arachnoideus; SS: 苦马豆S. salsula; AM: 草木樨状黄耆A. melilotoides. 下同The same below.
Fig.4 The niche similarity ratio (a) and overlap value (b) of dominant herb layer
生长型 Growth form | 样方数 Number of plots | 方差比 Variance ratio | 统计量 Statistic (W) | χ2临界值 Marginal value [χ | 结果 Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木Shrub | 18 | 2.03 | 36.46 | [9.390, 28.869] | 显著正联结Significant positive association |
| 草本Herbaceous | 25 | 1.20 | 29.96 | [14.611, 37.652] | 不显著正联结Non-significant positive association |
表5 生态恢复区植物群落总体联结
Table 5 Total species association of community in mining ecological restoration area
生长型 Growth form | 样方数 Number of plots | 方差比 Variance ratio | 统计量 Statistic (W) | χ2临界值 Marginal value [χ | 结果 Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木Shrub | 18 | 2.03 | 36.46 | [9.390, 28.869] | 显著正联结Significant positive association |
| 草本Herbaceous | 25 | 1.20 | 29.96 | [14.611, 37.652] | 不显著正联结Non-significant positive association |

图5 灌木层(a)及草本层(b)优势植物种间联结χ2值半矩阵图a图中In Figure a, 1: 猫头刺O. aciphylla; 2: 红砂R. songarica; 3: 黑沙蒿A. ordosica; 4: 柠条锦鸡儿C. korshinskii; 5: 红花多枝柽柳T. gallica; 6: 梭梭H. ammodendron; 7: 罗布麻A. venetum; 8: 羊柴C. fruticosum. b图中In Figure b, 1: 稷P. miliaceum; 2: 藜C. album; 3: 雾冰藜G. dasyphylla; 4: 蓼子朴I. salsoloides; 5: 猪毛菜S. collina; 6: 紫花苜蓿M. sativa; 7: 虎尾草C. virgata; 8: 拂子茅C. epigeios; 9: 狗尾草S. viridis; 10: 蒙古虫实C. mongolicum; 11: 尖头叶藜C. acuminatum; 12: 鹅绒藤C. chinense; 13: 乳苣L. tatarica; 14: 芦苇P. australis; 15: 黄花蒿A. annua; 16: 冷蒿A. frigida; 17: 茵陈蒿A. capillaris; 18: 白茎盐生草H. arachnoideus; 19: 苦马豆S. salsula; 20: 草木樨状黄耆A. melilotoides. 下同The same below.
Fig.5 Shrub layer (a) and herbaceous layer (b), half-matrix diagram of interspecific connectivity values for dominant plant species
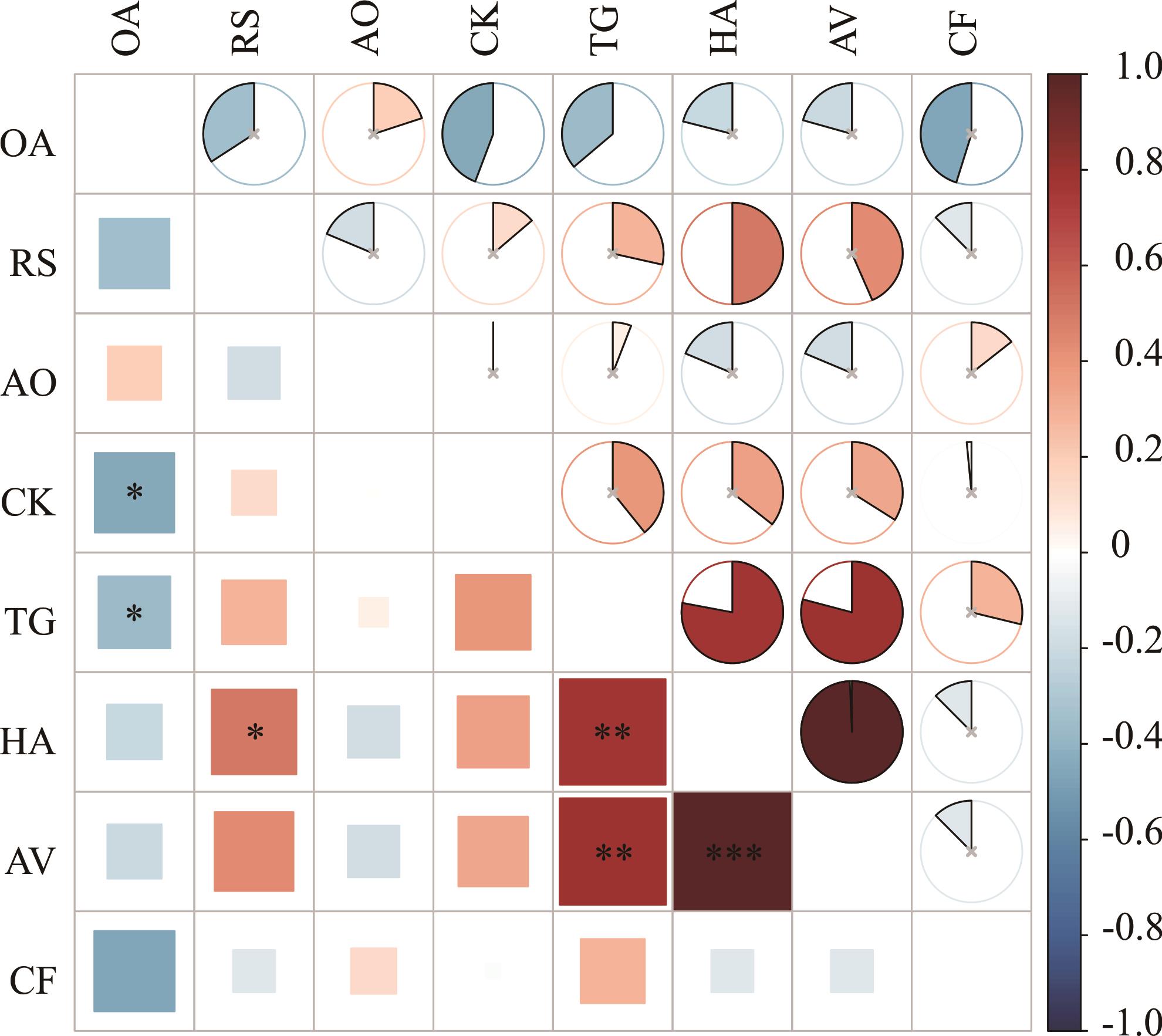
图6 优势灌木的Spearman秩相关检验分析*: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001. 下同The same below.
Fig.6 Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients of dominant shrub species
| 1 | Shan D, Xing E D, Rong H, et al. Ecological restoration of different vegetation collocations of coal mine dump in typical steppe. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(2): 336-342. |
| 珊丹, 邢恩德, 荣浩, 等. 草原矿区排土场不同植被配置类型生态恢复. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(2): 336-342. | |
| 2 | Li J T, Mu J, Shen K P, et al. Niche and interspecific association of dominant woody plants in Camellia luteoflora community. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(1): 283-294. |
| 李锦婷, 穆君, 申开平, 等. 小黄花茶群落优势木本植物生态位及种间联结性. 生态学报, 2024, 44(1): 283-294. | |
| 3 | Zhang L M, Lan B, Zhang D S, et al. Niche and interspecific association of dominant herbaceous plants in the water-level-fluctuating zone of Fuling-Fengjie section of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(8): 3228-3240. |
| 张乐满, 兰波, 张东升, 等. 三峡水库涪陵—奉节段消落带优势草本植物生态位与种间联结性研究. 生态学报, 2022, 42(8): 3228-3240. | |
| 4 | Huang Y Y, Han H, Tang C, et al. Plant community composition and interspecific relationships among dominant species on a post-seismic landslide in Hongchun Gully, China. Journal of Mountain Science, 2017, 14(10): 1985-1994. |
| 5 | He W L, Wang L L, Wang L, et al. Community stability was maintained by divergent mechanisms in arid desert ecosystem. Rangeland Ecology & Management, 2019, 72(5): 742-748. |
| 6 | Arnillas C A, Borer E T, Seabloom E W, et al. Opposing community assembly patterns for dominant and nondominant plant species in herbaceous ecosystems globally. Ecology and Evolution, 2021, 11(24): 17744-17761. |
| 7 | Navarro-Cano J A, Horner B, Goberna M, et al. Additive effects of nurse and facilitated plants on ecosystem functions. Journal of Ecology, 2019, 107(6): 2587-2597. |
| 8 | Khalil M I, Gibson D J, Baer S G. Functional response of subordinate species to intraspecific trait variability within dominant species. Journal of Ecology, 2019, 107(5): 2040-2053. |
| 9 | Li R P, Shi C Q, Yang J Y, et al. Ecological restoration effect evaluation of Zhangxuan iron tailings in Hebei Province of northern China under different vegetation patterns. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2022, 44(8): 66-76. |
| 李瑞鹏, 史常青, 杨建英, 等. 不同植被模式下张宣铁尾矿生态恢复效果评价. 北京林业大学学报, 2022, 44(8): 66-76. | |
| 10 | Shi L T, Shi C Q, Zhao T N, et al. Vegetation restoration effect in abandoned quarries: A case study of Dashiwo Town quarry in Fangshan District, Beijing. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2024, 43(5): 1416-1425. |
| 侍柳彤, 史常青, 赵廷宁, 等. 采石场废弃地植被恢复效果——以北京房山区大石窝镇采石场为例. 生态学杂志, 2024, 43(5): 1416-1425. | |
| 11 | Zhang Y, Zhao T N, Shi C Q, et al. Evaluation of vegetation and soil characteristics during slope vegetation recovery procedure. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2013, 29(3): 124-131. |
| 张艳, 赵廷宁, 史常青, 等. 坡面植被恢复过程中植被与土壤特征评价. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(3): 124-131. | |
| 12 | Zhang P, Shen Y, Zhang X J, et al. Study on leaf carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus eco-stoichiometric characteristics and community stability of dominant plants in Ningxia desert steppe. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(6): 18-26. |
| 张鹏, 沈艳, 张小菊, 等. 宁夏荒漠草原优势植物叶片C、N、P生态化学计量特征及群落稳定性研究. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(6): 18-26. | |
| 13 | Wu M H, Hou J, Zhang Y Q, et al. Ratio of dominant soil and water conservation plants in catchment of loess hilly region based on CATS model. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(8): 2455-2461. |
| 吴孟函, 侯健, 张彦勤, 等. 基于CATS模型的黄土丘陵小流域优势水土保持植物配比. 草地学报, 2023, 31(8): 2455-2461. | |
| 14 | Feng X H, Zhou L, Xiong W, et al. Tensile mechanical properties of the roots of the native shrubs and herbs in the dry-hot valley of Dadu river. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2023, 37(7): 159-169. |
| 冯旭环, 周璐, 熊伟, 等. 大渡河干热河谷区本土优势灌草植物根系的抗拉力学特性及其影响因素研究. 干旱区资源与环境, 2023, 37(7): 159-169. | |
| 15 | Liu Q, Yang J Y, Hou J, et al. Ratio of dominant dust retaining plants in waste dump of desert open-pit coal mine based on CATS model. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2022, 39(4): 775-782. |
| 刘琴, 杨建英, 侯健, 等. 基于CATS模型的干旱荒漠露天煤矿排土场优势滞尘植物配比. 浙江农林大学学报, 2022, 39(4): 775-782. | |
| 16 | Xu A Y, Cao B, Xie Y. Physiological-ecological responses of twelve herbaceous plant species under drought stress and evaluation of their drought resistance when planted in coal producting basis in arid windy and sandy areas. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(10): 22-34. |
| 许爱云, 曹兵, 谢云. 干旱风沙区煤炭基地12种草本植物对干旱胁迫的生理生态响应及抗旱性评价. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 22-34. | |
| 17 | Zhang D M, Zhao W Z, Luo W C. Niche and interspecific association of dominant plant species in saline-alkaline soils of desert steppe zone. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(5): 1307-1315. |
| 张东梅, 赵文智, 罗维成. 荒漠草原带盐碱地优势植物生态位与种间联结. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(5): 1307-1315. | |
| 18 | Yan X H, Niu J M, Li Y H, et al. Priority effects on plant community assembly and ecological restoration significance. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(10): 217-225. |
| 闫晓红, 牛建明, 李元恒, 等. 物种优先效应对植物群落构建的影响及其生态恢复意义. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 217-225. | |
| 19 | Liu L T, Wang X D, Wen Q, et al. Interspecific associations of plant populations in rare earth mining wasteland in southern China. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2017, 118: 82-88. |
| 20 | Xu L, Feng F, Liu Y, et al. Relationship between plant species diversity and soil chemical properties in coal gangue dump: early stage of ecological restoration in Lingwu Mining Area. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(4): 97-104. |
| 许丽, 丰菲, 刘莹, 等. 煤矸石山植物物种多样性与土壤化学因子的关系——以灵武矿区生态修复初期为例. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(4): 97-104. | |
| 21 | Yang S L, Liu C Y, Li M, et al. Determination of roadway cross-section shape in upward mining of Yangchangwan Coal Mine. Coal Engineering, 2022, 54(2): 5-11. |
| 杨胜利, 刘传义, 李明, 等. 羊场湾煤矿上行开采合理巷道断面形状确定. 煤炭工程, 2022, 54(2): 5-11. | |
| 22 | Li Y, Luo J F, Hou Z Y, et al. Plant diversity and environmental interpretation of Mang Shan Lang Pan Lake national important wetland. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(12): 1-11. |
| 李阳, 罗健夫, 侯志勇, 等. 莽山浪畔湖国家重要湿地植物多样性及环境解释. 生态学报, 2024, 44(12): 1-11. | |
| 23 | Wang J, Liu J J, Liu C, et al. Species niche and interspecific associations alter flora structure along a fertilization gradient in an alpine meadow of Tianshan Mountain, Xinjiang. Ecological Indicators, 2023, 147: 109953. |
| 24 | Liu Y P, Ye X Z, Ye L Q, et al. Niche and interspecific association of dominant tree species in Michelia odora community. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(10): 2670-2678. |
| 刘益鹏, 叶兴状, 叶利奇, 等. 观光木群落优势树种生态位和种间联结. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(10): 2670-2678. | |
| 25 | Ding M, Wang Y K, He Y R, et al. Changes of species diversity, interspecific associations and community stability for the deciduous broad-leaved forest in Yaoluoping National Nature Reserve, Anhui Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(7): 2818-2830. |
| 丁茂, 汪宇坤, 何煜然, 等. 安徽鹞落坪国家级自然保护区落叶阔叶林树种多样性、种间联结及群落稳定性变化. 生态学报, 2023, 43(7): 2818-2830. | |
| 26 | Xu M H, Liu M, Zhai D T, et al. A review of contents and methods used to analyze various aspects of plant interspecific associations. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(24): 8224-8233. |
| 徐满厚, 刘敏, 翟大彤, 等. 植物种间联结研究内容与方法评述. 生态学报, 2016, 36(24): 8224-8233. | |
| 27 | Guo W T, Wang G H, Gou Q Q, et al. Module growth and biomass allocation of three typical Chenopodiaceae annuals in a typical desert-oasis ecotone of the Hexi Corridor in Gansu Province, China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(2): 25-38. |
| 郭文婷, 王国华, 缑倩倩, 等. 河西走廊荒漠绿洲过渡带3种典型一年生藜科植物构件生长及生物量分配特征. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 25-38. | |
| 28 | Hu Y, Wang H C, Jia H P, et al. Ecological niche and interspecific association of plant communities in alpine desertification grasslands: A case study of Qinghai Lake Basin. Plants, 2022, 11(20): 2724. |
| 29 | Pastore A I, Barabás G, Bimler M D, et al. The evolution of niche overlap and competitive differences. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2021, 5(3): 330-337. |
| 30 | Zhang L J, Yue M, Zhang Y D, et al. Analysis on the niche of the main plant species of oasis-desert ecotone in Fukang of Xinjiang. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2002, 22(6): 969-972. |
| 张林静, 岳明, 张远东, 等. 新疆阜康绿洲荒漠过渡带主要植物种的生态位分析. 生态学报, 2002, 22(6): 969-972. | |
| 31 | Yao L B. Study on the optimization mode of the restored vegetation community structure in the middle and lower reaches of Tarim river. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2005. |
| 姚利兵. 塔里木河中下游植被重建中的群落结构配置优化模式研究. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2005. | |
| 32 | Zeng Y, Zhao C Y, Li C J, et al. Spatial distribution pattern and association of Populus euphratica community in different habitats along the Tarim River. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(11): 3273-3282. |
| 曾勇, 赵成义, 李传金, 等. 塔里木河沿岸不同生境下胡杨(Populus euphratica)群落的空间分布格局及关联性. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(11): 3273-3282. | |
| 33 | Wang J Y, Wang M L, Liu G M, et al. Analysis of the typical halophytic vegetation resistance and restoration process in abandoned salinized field. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 52(1): 129-136. |
| 王静娅, 王明亮, 刘广明, 等. 盐渍化弃耕地典型盐生植被抗逆性与恢复重建过程分析. 新疆农业科学, 2015, 52(1): 129-136. | |
| 34 | Helsen K, Hermy M, Honnay O. Trait but not species convergence during plant community assembly in restored semi-natural grasslands. Oikos, 2012, 121(12): 2121-2130. |
| 35 | Peng L, Mao Q, Cao L Y, et al. Insight into the adaptability of dominant plant Indigofera amblyantha Craib for ecological restoration of rock slopes in stone coal mine. Adsorption Science & Technology, 2021, DOI:10.1155/2021/3827991. |
| 36 | Woodbury D J, Yassir I, Arbainsyah, et al. Filling a void: Analysis of early tropical soil and vegetative recovery under leguminous, post-coal mine reforestation plantations in East Kalimantan, Indonesia. Land Degradation & Development, 2020, 31(4): 473-487. |
| 37 | Qi D H, Liu W S, Li S Y, et al. Relationship between aboveground vegetation and soil seed banks from different communities of initial restoration stage in Lanping Lead/Zinc Mining Area. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2013, 33(11): 2317-2325. |
| 齐丹卉, 刘文胜, 李世友, 等. 兰坪铅锌矿区植被恢复初期土壤种子库与地上植被关系的研究. 西北植物学报, 2013, 33(11): 2317-2325. | |
| 38 | Li T, Wu M H, Tang C D, et al. Advances in the key driving mechanism of vegetation succession and its guiding implication in metal mine remediation. Environmental Ecology, 2020, 2(12): 48-54. |
| 李婷, 吴明辉, 唐春东, 等. 植被演替的关键驱动机制研究及其在金属矿山修复中的指导意义. 环境生态学, 2020, 2(12): 48-54. | |
| 39 | Zhao X Y, Zhu C L, Hai Y, et al. Community characteristics of naturally established plants in mined site——Take the Awei Gobi Mining Area in Qinghe County, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region as an example. Journal of Xinjiang Normal University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2022, 41(4): 8-15. |
| 赵晓英, 朱成林, 海鹰, 等. 采矿废弃地自然定居植物的群落特征——以新疆维吾尔自治区青河县阿苇戈壁矿区为例. 新疆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 41(4): 8-15. | |
| 40 | Qi S, Liu Z S, Du D, et al. Spatial heterogeneity of plant community and its influencing factors in Longxiang Mountain. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2024, 43(1): 75-85. |
| 戚赏, 刘占时, 杜丹, 等. 龙翔山植物群落空间异质性及其影响因子. 生态学杂志, 2024, 43(1): 75-85. | |
| 41 | Gao R, Ai N, Liu G Q, et al. Characteristics of understory herb communities across time during restoration in coal mine reclamation areas and their coupling with soil properties. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(6): 61-68. |
| 高瑞, 艾宁, 刘广全, 等. 煤矿复垦区不同修复年限林下草本群落特征及其与土壤耦合关系. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 61-68. | |
| 42 | Costa D S, Gerschlauer F, Kiese R, et al. Plant niche breadths along environmental gradients and their relationship to plant functional traits. Diversity and Distributions, 2018, 24(12): 1869-1882. |
| 43 | Zhou G C, Yang Z, Xin J B, et al. Dynamic analysis of niche and diversity of populations in the early stage of dump reclamation. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2023, 50(4): 149-154. |
| 周国驰, 杨卓, 辛建宝, 等. 排土场复垦初期种群生态位与多样性动态分析. 矿业安全与环保, 2023, 50(4): 149-154. | |
| 44 | Zhang Y D, Pan X L, Gu F X, et al. Shrub and undershrub niches in vegetation of the Fukang Desert. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2001, 25(6): 741-745. |
| 张远东, 潘晓玲, 顾峰雪, 等. 阜康荒漠植被灌木与半灌木种群生态位的研究. 植物生态学报, 2001, 25(6): 741-745. | |
| 45 | Lyu J X, Liang K, Liu C M, et al. Spatial differentiation mechanism of land cover and related changes in water-carbon variables in Wuding River Basin. Arid Zone Research, 2023, 40(4): 563-572. |
| 吕锦心, 梁康, 刘昌明, 等. 无定河流域土地覆被空间分异机制及相关水碳变量变化. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(4): 563-572. | |
| 46 | Li M Z. Preliminary study on the benefits of non-irrigation vegetation restoration in the north mountain area of Lanzhou city. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2008, 28(1): 150-153, 157. |
| 李茂哉. 兰州市北山无灌溉区植被恢复效益初步研究. 水土保持通报, 2008, 28(1): 150-153, 157. | |
| 47 | Lei C Y, Wu M, Jiang L, et al. Sand-fixing experiment of Apocynum venetum without irrigation in grass-grid sand-barrier. Protection Forest Science and Technology, 2020(1): 5-7. |
| 雷春英, 吴明, 姜黎, 等. 草方格沙障内无灌溉种植罗布麻固沙试验研究. 防护林科技, 2020(1): 5-7. | |
| 48 | Qin S G, Wu B, Zhang Y Q. A review of belowground interspecific interactions and allelopathy in silvopasture systems. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2011, 20(2): 253-261. |
| 秦树高, 吴斌, 张宇清. 林草复合系统地下部分种间互作关系与化感作用研究进展. 草业学报, 2011, 20(2): 253-261. | |
| 49 | Wang F L, Xu X Y, Wang L D, et al. Research progress of allelopathy of arid desert plants in northwest. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2016, 32(5): 165-172. |
| 王方琳, 徐先英, 王理德, 等. 西北干旱荒漠区植物化感作用研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2016, 32(5): 165-172. |
| [1] | 周晓雷, 杨富强, 王明军, 黄海霞, 田青, 周旭姣, 赵安, 贺万鹏, 赵艳丽, 姜礼红. 青藏高原东北边缘云杉-巴山冷杉林火烧迹地草本植物群落主要种生态位特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 23-37. |
| [2] | 何光熊, 史正涛, 闫帮国, 杨淏舟, 孙毅, 王艳丹, 余建琳, 和润莲, 史亮涛, 方海东. 封育对干热河谷Savanna植物群落种间关联性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 1-14. |
| [3] | 张辉辉, 师尚礼, 武蓓, 李自立, 李小龙. 苜蓿与3种多年生禾草混播效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 159-170. |
| [4] | 张峰, 孙嘉伟, 孙宇, 郑佳华, 乔荠瑢, 赵萌莉. 不同载畜率对短花针茅荒漠草原优势物种间关系及其空间分布特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 1-11. |
| [5] | 聂莹莹, 陈金强, 辛晓平, 徐丽君, 杨桂霞, 王旭. 呼伦贝尔草甸草原区主要植物种群生态位特征与物种多样性对封育年限响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 15-25. |
| [6] | 聂莹莹, 徐丽君, 辛晓平, 陈宝瑞, 张保辉. 围栏封育对温性草甸草原植物群落构成及生态位特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 11-22. |
| [7] | 赵建华, 孙建好, 陈亮之. 三种豆科作物与玉米间作对玉米生产力和种间竞争的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 86-94. |
| [8] | 陈仕勇, 马啸, 张新全, 陈智华, 周青平. 基于SSR标记的小麦族St、H、Y基因组六倍体物种遗传变异及种间亲缘关系研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(9): 142-151. |
| [9] | 范顺祥, 郑建伟, 魏士凯, 黄选瑞, 张志东. 河北省森林草原区主要草本植物功能群适宜分布预测[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 24-32. |
| [10] | 张鲜花, 陈爱萍, 朱进忠, 李海琪. 天山北坡不同区域及海拔对天然草地鸭茅群落物种种间关系影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 12-23. |
| [11] | 杨萍, 李杰, 张中凯, 崔政军, 杨天庆, 牛俊义. 施氮对胡麻/大豆间作体系作物间作优势及种间关系的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 181-190. |
| [12] | 苗福泓, 薛冉, 郭正刚, 沈禹颖. 青藏高原东北边缘高寒草甸植物种群生态位特征对牦牛放牧的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(1): 88-97. |
| [13] | 井光花,程积民,苏纪帅,魏琳,史晓晓,金晶炜. 黄土区长期封育草地优势物种生态位宽度与生态位重叠对不同干扰的响应特征[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(9): 43-52. |
| [14] | 王翀,林慧龙,何兰,曹坳程. 紫茎泽兰潜在分布对气候变化响应的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(4): 20-30. |
| [15] | 刘贵河,王国杰,汪诗平,张英俊,宛新荣,郝树广. 内蒙古典型草原主要草食动物食性及其营养生态位研究——以羊草群落为例[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(1): 103-111. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||