

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 133-148.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024161
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
宁建凤( ), 陈勇, 姚建武, 梁紫薇, 曾瑞锟, 王荣辉, 李彤
), 陈勇, 姚建武, 梁紫薇, 曾瑞锟, 王荣辉, 李彤
收稿日期:2024-04-30
修回日期:2024-06-14
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2024-11-27
通讯作者:
宁建凤
作者简介:宁建凤(1978-),女,河北邯郸人,博士,研究员。E-mail: Jianfengning@gdaas.cn
基金资助:
Jian-feng NING( ), Yong CHEN, Jian-wu YAO, Zi-wei LIANG, Rui-kun ZENG, Rong-hui WANG, Tong LI
), Yong CHEN, Jian-wu YAO, Zi-wei LIANG, Rui-kun ZENG, Rong-hui WANG, Tong LI
Received:2024-04-30
Revised:2024-06-14
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2024-11-27
Contact:
Jian-feng NING
摘要:
磷既是作物营养必需元素也是重要面源污染因子,研究集约化菜地土壤磷库特征,为有针对性地制定菜地磷养分管理措施,降低菜地磷素面源污染风险提供依据。以珠三角地区(广州、江门、肇庆、惠州等地)赤红壤常年菜地系统为研究对象,共采集89份城郊菜地土壤样品,采用修正的Hedley磷库分级法分析土壤磷组分,探明土壤性质与磷库相关性。赤红壤菜地土壤磷库以无机磷(Pi)为主要赋存形态,无机磷在磷库占比达88%,有机磷(Po)、残余磷在磷库占比均较低,分别为8.1%、3.9%。菜地土壤无机磷含量为1176.78 mg·kg-1,远高于有机磷(109.03 mg·kg-1)和残余磷含量(52.19 mg·kg-1)。无机磷库中,H2O-Pi、NaHCO3-Pi、NaOH-Pi、稀HCl-Pi、浓HCl-Pi含量分别为46.35 mg·kg-1、264.64 mg·kg-1、427.45 mg·kg-1、274.82 mg·kg-1、163.52 mg·kg-1,在总磷中相应占比分别为3.32%、20.74%、31.29%、16.32%、14.13%。有机磷库中,NaHCO3-Po、NaOH-Po、浓HCl-Po含量分别为27.24 mg·kg-1、62.35 mg·kg-1、19.44 mg·kg-1,占总磷比例依次为2.33%、5.70%、1.56%。NaOH提取磷(NaOH-P)在菜地无机磷库、有机磷库中均占主导地位。从土壤磷活性角度分析,活性磷、中等活性磷、稳定性磷含量分别为338.23 mg·kg-1、764.62 mg·kg-1、235.15 mg·kg-1,在总磷中相应占比分别为25.3%、57.1%、17.6%。几乎全部89个样点土壤活性磷与中等活性磷之和在总磷库占比均超过50%。土壤有机质、全氮、碱解氮、速效钾、阳离子交换量(CEC)均与活性磷、中等活性磷含量呈显著正相关,且存在浓度效应。赤红壤菜地土壤总体上磷含量丰富、有效性高。施肥、耕作管理等人为活动及赤红壤特性共同影响土壤磷库形成。考虑到赤红壤区的强降水气候特征,常年菜地磷素面源污染风险大,应注意通过合理施肥降低磷的污染风险。
宁建凤, 陈勇, 姚建武, 梁紫薇, 曾瑞锟, 王荣辉, 李彤. 珠三角赤红壤常年连作菜地土壤磷库特征[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 133-148.
Jian-feng NING, Yong CHEN, Jian-wu YAO, Zi-wei LIANG, Rui-kun ZENG, Rong-hui WANG, Tong LI. Characteristics of the soil phosphorus pool in continuously cultivated vegetable fields in the latosolic red soil zone of the Pearl River Delta[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(2): 133-148.

图1 菜地土壤样点分布基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2017)3320号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on GS(2017)3320 standard map of the standard map service website of the Ministry of Natural Resources, the boundary of the base map is not modified.
Fig.1 Location of the study area and sampling sites
指标 Parameters | pH | 砂粒 (0.05~2.00 mm,%) | 粉粒 (0.002~0.050 mm,%) | 黏粒 (<0.002 mm,%) | 阳离子交换量 CEC (cmol·kg-1) | 有机质 OM (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值Average | 5.83 | 43.70 | 40.30 | 16.00 | 8.67 | 23.83 |
| 范围Range | 4.37~7.23 | 10.20~86.80 | 7.80~62.40 | 2.60~47.40 | 3.46~20.09 | 7.79~56.59 |
| 变异系数CV (%) | 11.20 | 38.40 | 30.89 | 49.66 | 40.20 | 42.00 |
指标 Parameters | 全氮 TN (g·kg-1) | 全磷 TP (g·kg-1) | 全钾 TK (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 AN (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 AP (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 AK (mg·kg-1) |
| 均值Average | 1.19 | 1.47 | 12.53 | 135.24 | 120.24 | 222.48 |
| 范围Range | 0.06~2.91 | 0.44~3.92 | 0.80~38.29 | 60.12~298.80 | 13.80~306.87 | 33.00~758.79 |
| 变异系数CV (%) | 57.10 | 50.10 | 51.50 | 35.30 | 21.80 | 51.80 |
表1 研究区常年菜地土壤基础理化性质
Table 1 Basic physicochemical properties of soil in perennial vegetable fields of the research area
指标 Parameters | pH | 砂粒 (0.05~2.00 mm,%) | 粉粒 (0.002~0.050 mm,%) | 黏粒 (<0.002 mm,%) | 阳离子交换量 CEC (cmol·kg-1) | 有机质 OM (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值Average | 5.83 | 43.70 | 40.30 | 16.00 | 8.67 | 23.83 |
| 范围Range | 4.37~7.23 | 10.20~86.80 | 7.80~62.40 | 2.60~47.40 | 3.46~20.09 | 7.79~56.59 |
| 变异系数CV (%) | 11.20 | 38.40 | 30.89 | 49.66 | 40.20 | 42.00 |
指标 Parameters | 全氮 TN (g·kg-1) | 全磷 TP (g·kg-1) | 全钾 TK (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 AN (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 AP (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 AK (mg·kg-1) |
| 均值Average | 1.19 | 1.47 | 12.53 | 135.24 | 120.24 | 222.48 |
| 范围Range | 0.06~2.91 | 0.44~3.92 | 0.80~38.29 | 60.12~298.80 | 13.80~306.87 | 33.00~758.79 |
| 变异系数CV (%) | 57.10 | 50.10 | 51.50 | 35.30 | 21.80 | 51.80 |
指标 Parameters | 无机磷 Inorganic phosphorus (Pi) | 有机磷 Organic phosphorus (Po) | 残余磷 Residual phosphorus |
|---|---|---|---|
| 均值Average (mg·kg-1) | 1176.78 | 109.03 | 52.19 |
| 范围Range (mg·kg-1) | 314.63~3785.96 | 31.46~367.41 | 9.97~122.56 |
| 变异系数Coefficient of variations (CV,%) | 57.79 | 41.81 | 43.04 |
| 占全磷比例均值Average percentage in total (%) | 88.0 | 8.1 | 3.9 |
表2 常年菜地土壤磷库组成
Table 2 Composition of phosphorus pool in soil of perennial vegetable fields
指标 Parameters | 无机磷 Inorganic phosphorus (Pi) | 有机磷 Organic phosphorus (Po) | 残余磷 Residual phosphorus |
|---|---|---|---|
| 均值Average (mg·kg-1) | 1176.78 | 109.03 | 52.19 |
| 范围Range (mg·kg-1) | 314.63~3785.96 | 31.46~367.41 | 9.97~122.56 |
| 变异系数Coefficient of variations (CV,%) | 57.79 | 41.81 | 43.04 |
| 占全磷比例均值Average percentage in total (%) | 88.0 | 8.1 | 3.9 |

图2 常年菜地无机磷组分含量及其所占百分比A: 无机磷组分含量 Concentration of inorganic phosphorus; B: 无机磷组分占无机磷库百分比 Percentage of inorganic phosphorus fraction in the total inorganic phosphorus pool; C: 无机磷组分占无机磷库百分比均值Average percentage of inorganic phosphorus in the total inorganic phosphorus pool.
Fig.2 Concentration of inorganic phosphorus fractions and their percentage in the total inorganic P pool in soil of perennial vegetable fields
| 指标Parameters | H2O-Pi | NaHCO3-Pi | NaOH-Pi | Dli HCl-Pi | Con HCl-Pi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值Average | 3.32 | 20.74 | 31.29 | 16.32 | 14.13 |
| 范围Range | 0.45~9.76 | 4.38~35.12 | 13.82~47.04 | 0.80~52.28 | 2.74~48.29 |
| 变异系数Coefficient of variations (CV) | 51.73 | 28.41 | 24.04 | 71.99 | 62.83 |
表3 常年菜地土壤无机磷组分占全磷比例
Table 3 Percentage of inorganic phosphorus fractions in the total phosphorus pool in soil of perennial vegetable fields (%)
| 指标Parameters | H2O-Pi | NaHCO3-Pi | NaOH-Pi | Dli HCl-Pi | Con HCl-Pi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值Average | 3.32 | 20.74 | 31.29 | 16.32 | 14.13 |
| 范围Range | 0.45~9.76 | 4.38~35.12 | 13.82~47.04 | 0.80~52.28 | 2.74~48.29 |
| 变异系数Coefficient of variations (CV) | 51.73 | 28.41 | 24.04 | 71.99 | 62.83 |

图3 常年菜地有机磷组分含量及其所占百分比A: 有机磷组分含量 Concentration of organic phosphorus; B: 有机磷组分占有机磷库百分比 Percentage of organic phosphorus fraction in the total organic phosphorus pool; C: 有机磷组分占有机磷库百分比均值Average percentage of organic phosphorus in the total organic phosphorus pool.
Fig.3 Concentration of organic phosphorus fractions and their percentage in the total organic phosphorus pool in soil of perennial vegetable fields
| 指标Parameters | NaHCO3-Po | NaOH-Po | Con HCl-Po |
|---|---|---|---|
| 均值Average | 2.33 | 5.70 | 1.56 |
| 范围Range | 0.22~9.20 | 0.54~27.38 | 0.19~9.45 |
| 变异系数Coefficient of variations (CV) | 59.31 | 70.19 | 76.12 |
表4 常年菜地土壤有机磷组分占全磷比例
Table 4 Percentage of organic phosphorus fractions in the total phosphorus pool in soil of perennial vegetable fields (%)
| 指标Parameters | NaHCO3-Po | NaOH-Po | Con HCl-Po |
|---|---|---|---|
| 均值Average | 2.33 | 5.70 | 1.56 |
| 范围Range | 0.22~9.20 | 0.54~27.38 | 0.19~9.45 |
| 变异系数Coefficient of variations (CV) | 59.31 | 70.19 | 76.12 |
指标 Parameters | 活性磷 Labile phosphorus | 中等活性磷 Moderately labile phosphorus | 稳定性磷 Recalcitrant phosphorus |
|---|---|---|---|
| 均值Average (mg·kg-1) | 338.23 | 764.62 | 235.15 |
| 范围Range (mg·kg-1) | 39.49~766.11 | 158.72~3102.86 | 57.40~536.09 |
| 变异系数Coefficient of variations (CV, %) | 45.18 | 68.81 | 48.88 |
| 占全磷比例Percentage (%) | 25.3 | 57.1 | 17.6 |
表5 常年菜地不同活性磷组分
Table 5 Fractions of phosphorus with different availability in soil of perennial vegetable fields
指标 Parameters | 活性磷 Labile phosphorus | 中等活性磷 Moderately labile phosphorus | 稳定性磷 Recalcitrant phosphorus |
|---|---|---|---|
| 均值Average (mg·kg-1) | 338.23 | 764.62 | 235.15 |
| 范围Range (mg·kg-1) | 39.49~766.11 | 158.72~3102.86 | 57.40~536.09 |
| 变异系数Coefficient of variations (CV, %) | 45.18 | 68.81 | 48.88 |
| 占全磷比例Percentage (%) | 25.3 | 57.1 | 17.6 |

图4 常年菜地活性磷组分占活性磷库百分比及其均值A: 活性磷组分占活性磷库百分比Percentage of labile phosphorus fraction in the total labile phosphorus pool; B: 活性磷组分占活性磷库百分比均值 Average percentage of labile phosphorus in the total labile phosphorus pool.
Fig.4 Percentage of labile phosphorus fraction in soil total labile phosphorus pool and their average in soil of the perennial vegetable fields
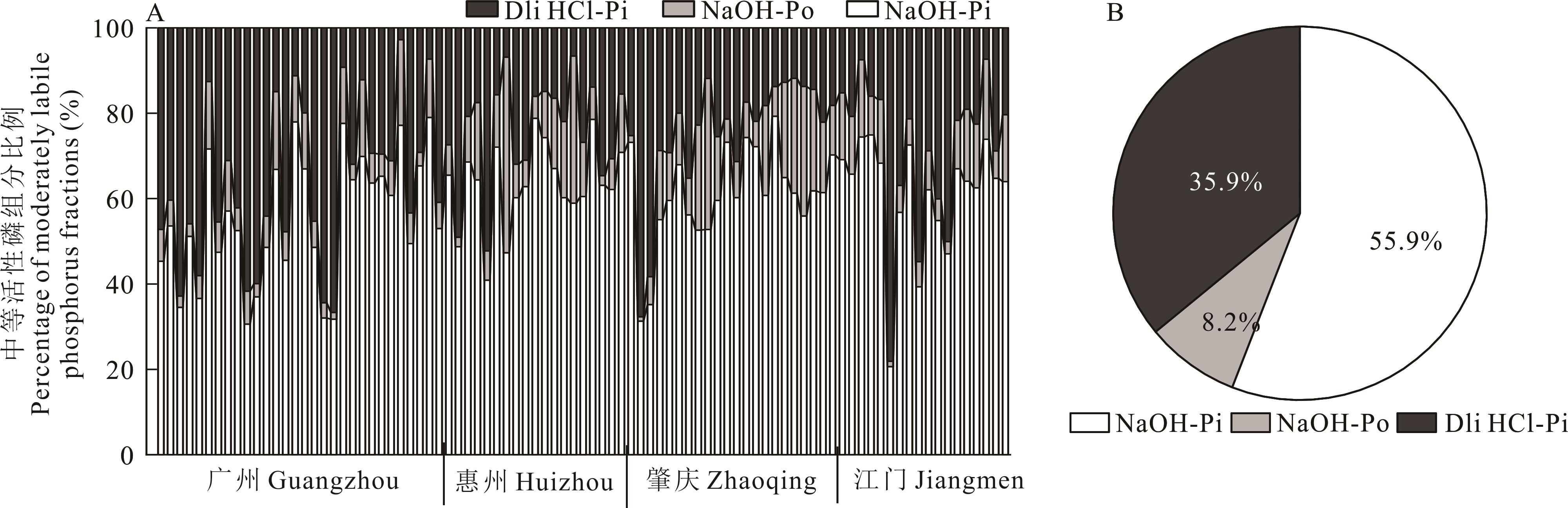
图5 常年菜地中等活性磷组分占中等活性磷库百分比及其均值A:中等活性磷组分占中等活性磷库百分比Percentage of moderately labile phosphorus fractions in the total moderately labile phosphorus pool; B: 中等活性磷组分占中等活性磷库百分比均值 Average percentage of moderately labile phosphorus in the total moderately labile phosphorus pool.
Fig.5 Percentage of moderately labile phosphorus fractions in the total moderately labile phosphorus pool and their average in in soil of the perennial vegetable fields
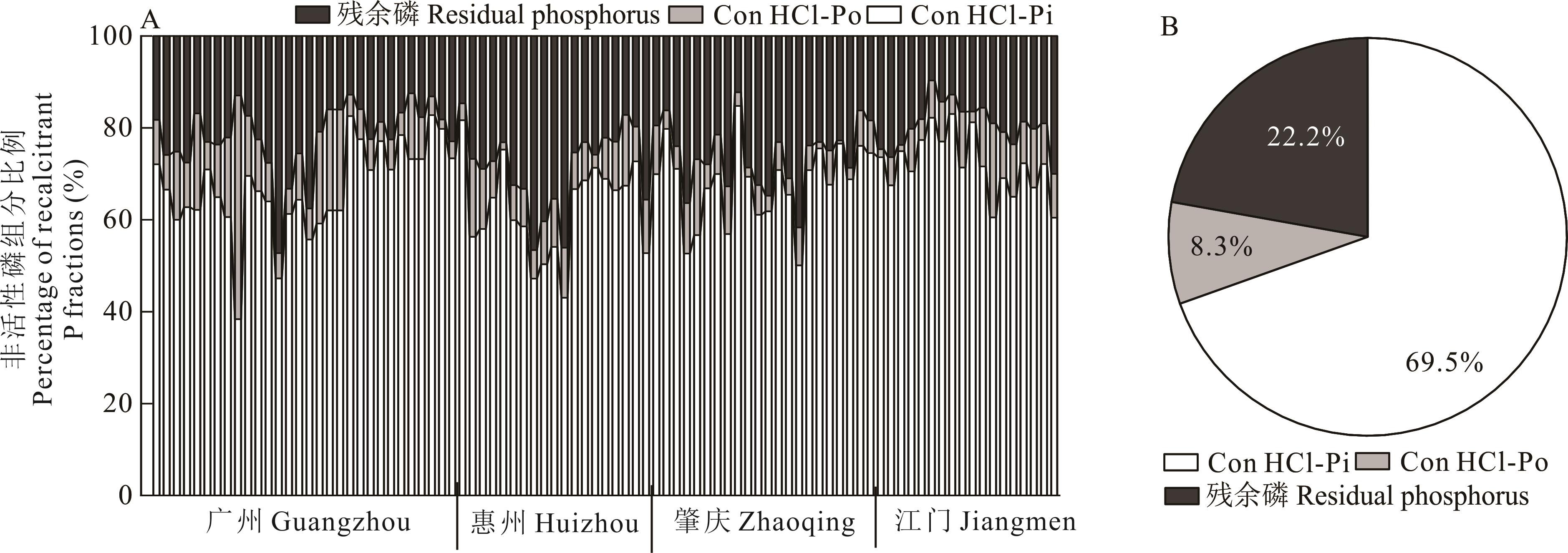
图6 常年菜地稳定性磷组分占稳定性磷库百分比及其均值A, 稳定性磷组分占稳定性磷库百分比Percentage of recalcitrant phosphorus fractions in the total recalcitrant phosphorus pool; B, 稳定性磷组分占稳定性磷库百分比均值 Average percentage of recalcitrant phosphorus in the total recalcitrant phosphorus pool.
Fig.6 Percentage of recalcitrant phosphorus fractions in the total recalcitrant P pool and their average in soil of the perennial vegetable fields

图7 常年菜地土壤性质与磷库相关性* P≤0.05, ** P≤0.01, *** P≤0.001. OM:有机质Organic matter;CEC:阳离子交换量Cation exchange capacity; TN:全氮Total nitrogen; TP:全磷Total phosphorus; TK:全钾Total potassium; AN:碱解氮Available nitrogen; AP:有效磷Available phosphorus; AK:速效钾Available potassium; LP:活性磷Labile phosphorus; MLP:中等活性磷Moderately labile phosphorus; RTP:稳定性磷Recalcitrant phosphorus.
Fig.7 Correlations between soil properties and phosphorus pool
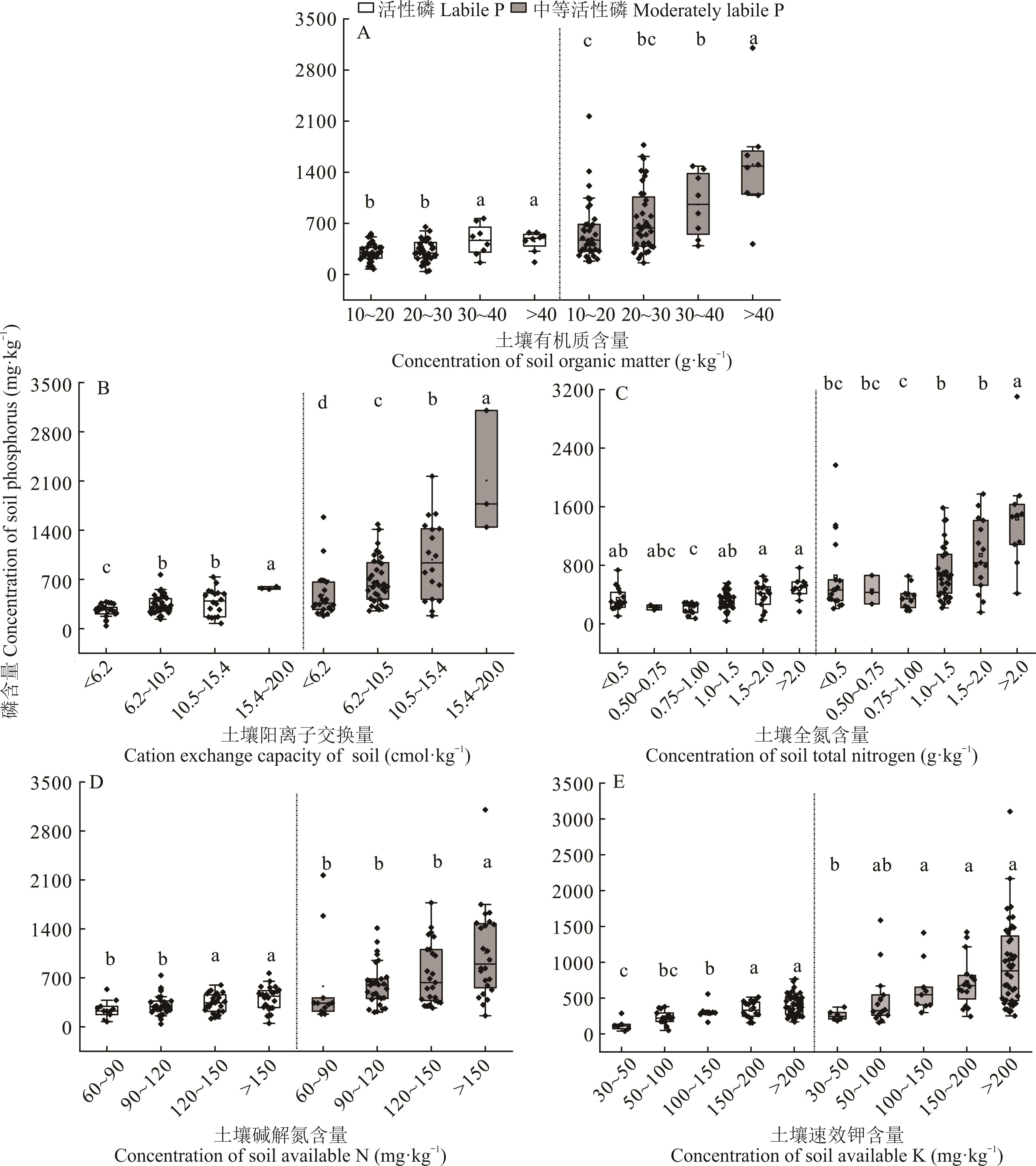
图8 土壤有机质、阳离子交换量、全氮、碱解氮、速效钾分级条件下土壤活性磷、中等活性磷含量分布不同小写字母代表指标梯度含量间差异显著。Different lowercase letters mean the significant difference among the gradient concentrations of soil parameters.
Fig.8 Distribution of labile P, moderately labile P concentration under different grades of soil organic matter, cation exchange capacity, total nitrogen, available nitrogen and available potassium in soil
| 1 | Cordell D, Drangert J O, Whit S. The story of phosphorus: Global food security and food for thought. Global Environmental Change, 2009, 19: 292-305. |
| 2 | Zhang W, Chen X J, Ma L, et al. Re-prediction of phosphate fertilizer demand in China based on agriculture green development. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2023, 60(5): 1389-1397. |
| 张伟, 陈轩敬, 马林, 等. 再论中国磷肥需求预测-基于农业绿色发展视角. 土壤学报, 2023, 60(5): 1389-1397. | |
| 3 | Zou T, Zhang X, Davidson E A. Global trends of cropland phosphorus use and sustainability challenges. Nature, 2022, 611: 81-87. |
| 4 | Zeng Z B, Zeng S J, Tang J D, et al. Space-temporal variation of farmland soil AP in Guangdong province and their causing factors. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 23(3): 444-451. |
| 曾招兵, 曾思坚, 汤建东, 等. 广东省耕地土壤有效磷时空变化特征及影响因素分析. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(3): 444-451. | |
| 5 | Tian J, Boitt G, Black A, et al. Accumulation and distribution of phosphorus in the soil profile under fertilized grazed pasture. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2017, 239: 228-235. |
| 6 | Su N, Xie G, Mao Z, et al. The effectiveness of eight-years phosphorus reducing inputs on double cropping paddy: Insights into productivity and soil-plant phosphorus tradeoff. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 866: 161429. |
| 7 | Guangdong Rural Statistical Yearbook Editorial Board. 2022 Guangdong rural statistical yearbook. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2022. |
| 《广东农村统计年鉴》编辑委员会. 2022广东农村统计年鉴. 北京:中国统计出版社, 2022. | |
| 8 | Olsen S R, Cole C V, Watanabe F S, et al. Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. Circular (United States. Department of Agriculture), 1954: 939. |
| 9 | Wyngaard N, Cabrera M L, Jarosch K A, et al. Phosphorus in the coarse soil fraction is related to soil organic phosphorus mineralization measured by isotopic dilution. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2016, 96: 107-118. |
| 10 | Hedley M J, Stewart J W B, Chauhan B S. Changes inorganic and organic soil phosphorus fractions induced by cultivation practices and by laboratory incubations. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1982, 46: 970-976. |
| 11 | Cross A F, Schlesinger W H. A literature review and evaluation of the Hedley fractionation: Applications to the biogeochemical cycle of soil phosphorus in natural ecosystems. Geoderma, 1995, 64: 197-214. |
| 12 | Negassa W, Leinweber P. How does the Hedley sequential phosphorus fractionation reflect impacts of land use and management on soil phosphorus: A review. Journal of Plant Nutrition & Soil Science, 2010, 172: 305-325. |
| 13 | Biassoni M M, Vivas H, Gutiérrez-Boem F H, et al. Changes in soil phosphorus (P) fractions and P bioavailability after 10 years of continuous P fertilization. Soil and Tillage Research, 2023, 232: 105777. |
| 14 | Maranguit D, Guillaume T, Kuzyakov Y. Land-use change affects phosphorus fractions in highly weathered tropical soils. Catena, 2017, 149: 385-393. |
| 15 | Damian J M, Firmano R F, Cherubin M R, et al. Changes in soil phosphorus pool induced by pastureland intensification and diversification in Brazil. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 703: 135463. |
| 16 | Meason Dean F, Idol Travis W, Friday J B, et al. Effects of fertilisation on phosphorus pools in the volcanic soil of a managed tropical forest. Forest Ecology and Management, 2009, 258: 2199-2206. |
| 17 | Fan T, Luo M, Tan J, et al. Incorporating biotic phosphorus-acquisition strategies into soil phosphorus transformation under long-term salinization in a tidal wetland. Catena, 2023, 231: 107274. |
| 18 | Li J, Wu B, Zhang D, et al. Elevational variation in soil phosphorus pools and controlling factors in alpine areas of Southwest China. Geoderma, 2023, 431: 116361. |
| 19 | Anthonio C K, Jing H, Jin C, et al. Impact of long-term fertilization on phosphorus fractions and manganese oxide with their interactions in paddy soil aggregates. Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, 333: 117440. |
| 20 | Zheng L, Zhao Q, Lin G, et al. Nitrogen addition impacts on soil phosphorus transformations depending upon its influences on soil organic carbon and microbial biomass in temperate larch forests across northern China. Catena, 2023, 230: 107252. |
| 21 | Guangdong Provincial Soil Survey Office. Guangdong soil. Beijing: Science Press, 1993. |
| 广东省土壤普查办公室. 广东土壤. 北京: 科学出版社, 1993. | |
| 22 | Kochian L V. Rooting for more phosphorus. Nature, 2012, 488: 466-467. |
| 23 | Ning J, Yao J, Wang R, et al. Phosphorus status and adsorption characteristics of perennial vegetable-cultivated soils in South China. PLoS One, 2022, 17: e0264189. |
| 24 | Ning J F, Li T, Zeng R K, et al. Soil fertility in perennial vegetable fields in the latosolic red soil zone of the Pearl River Delta. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(5): 25-40. |
| 宁建凤, 李彤, 曾瑞锟, 等. 珠三角赤红壤常年菜地土壤肥力质量评价. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 25-40. | |
| 25 | National Soil Census Office. China soil census technology. Beijing: Agricultural Publishing House, 1992. |
| 全国土壤普查办公室. 中国土壤普查技术. 北京: 农业出版社, 1992. | |
| 26 | Tiessen H, Moir J O. Characterization of available P by sequential extraction//Carter M R. (Ed.), Soil sampling and methods of analysis. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, Canadian Society of Soil Science, 1993: 75-86. |
| 27 | Murphy J, Riley J P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimuca Acta, 1962, 27: 31-36. |
| 28 | Lu R K. Methods of soil agrochemical analysis. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000. |
| 鲁如坤. 土壤农化分析方法. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000. | |
| 29 | Bowman R A, Cole C V. An exploratory method for fractionation of organic phosphorus from grassland soils. Soil Science, 1978, 125: 95-101. |
| 30 | Ahmed W, Qaswar M, Huang J, et al. Tillage practices improve rice yield and soil phosphorus fractions in two typical paddy soils. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2020, 20: 850-861. |
| 31 | Harrison A F. Soil organic phosphorus-A review of world literature. Oxon C.A.B. International United Kingdom, Wallingford, 1987. |
| 32 | Chen H, Chen M, Li D, et al. Responses of soil phosphorus availability to nitrogen addition in a legume and a non-legume plantation. Geoderma, 2018, 322: 12-18. |
| 33 | Li Y H. Accumulation and paleo environmental implications of phosphorus in mid-high latitude peatlands, Northeast China. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022. |
| 李蕴慧. 中高纬湿地磷的累积及环境指示意义. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2022. | |
| 34 | Gao X L, Li X G, Zhao L, et al. Regulation of soil phosphorus cycling in grasslands by shrubs. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2019, 133: 1-11. |
| 35 | Lin C, Wang F, He C M, et al. Effects of long term fertilization on phosphorus pools and forms in yellow paddy fields of southern China. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2014, 20(3): 541-549. |
| 林诚, 王飞, 何春梅, 等. 长期不同施肥对南方黄泥田磷库及其形态的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(3): 541-549. | |
| 36 | Chen F, Wang X S, Gan G Y, et al. Effects of long-term application of phosphorus fertilizer on soil phosphorus fractions and microbial diversity in rice-rapeseed rotation. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021, 40(1): 168-178. |
| 陈凤, 王晓双, 甘国渝, 等. 长期施用磷肥对稻-油轮作土壤磷组分及微生物多样性的影响. 华中农业大学学报, 2021, 40(1): 168-178. | |
| 37 | Sun R P. Changes in phosphorus fractions in the plough layer of loess soil under long-term contrasting soil management regimes. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2015. |
| 孙锐璞. 不同管理壤土耕层土壤磷组分的变化. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2015. | |
| 38 | Department of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of Guangdong Provincial. Brief report on cultivated land quality monitoring in Guangdong Province in 2019. http://dara.gd.gov.cn/zwgk2278/bmdt/content/post_3077919.html. |
| 广东省农业农村厅. 广东省2019年度耕地质量监测简报. http://dara.gd.gov.cn/zwgk2278/bmdt/content/post_3077919.html. | |
| 39 | Zhang Y J, Gao W, Luan H A, et al. Effects of a decade of organic fertilizer substitution on vegetable yield and soil phosphorus pools, phosphatase activities, and the microbial community in a greenhouse vegetable production system. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2022, 21: 2119-2133. |
| 40 | Wang Y, Zhang H, Tang J, et al. Accelerated phosphorus accumulation and acidification of soils under plastic greenhouse condition in four representative organic vegetable cultivation sites. Scientia Horticulturae, 2015, 195: 67-73. |
| 41 | Zhang G S, Ni Z W. Soil phosphorus fractions in aggregate size classes in southwestern China. Soil Use and Management, 2018, 34: 266-275. |
| 42 | McDowell R W, Condron L M. Phosphorus and the Winchmore trials: Review and lessons learnt. New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research, 2012, 55: 119-132. |
| 43 | Yan Z, Chen S, Li J, et al. Manure and nitrogen application enhances soil phosphorus mobility in calcareous soil in greenhouses. Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 181: 26-35. |
| 44 | Chen S, Yan Z, Zhang S, et al. Nitrogen application favors soil organic phosphorus accumulation in calcareous vegetable fields. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2019, 55: 481-496. |
| 45 | Liu J L, Zhang F S. Dynamics of soil P pool in a long-term fertilizing experiment of wheat-maize rotation I. Crop yield effect of fertilizer P and dynamics of soil total P and inorganic P. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2000, 11(3): 360-364. |
| 刘建玲, 张福锁. 小麦-玉米轮作长期肥料定位试验中土壤磷库的变化I. 磷肥产量效应及土壤总磷库、无机磷库的变化. 应用生态学报, 2000, 11(3): 360-364. | |
| 46 | Wang Z R, Li F R, Liu L L, et al. Changes in soil phosphorus fractions under different land uses in desert grasslands in Northwestern China. European Journal of Soil Science, 2022, 73: e13255. |
| 47 | Weand M P, Arthur M A, Lovett G M, et al. The phosphorus status of northern hardwoods differs by species but is unaffected by nitrogen fertilization. Biogeochemistry, 2010, 97(2): 159-181. |
| 48 | Gong M Y, Li Q Y, Chen A L, et al. Long-term abandonment of reddish paddy fields decreases soil phosphorus pool. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(8): 1398-1408. |
| 龚梦瑶, 李巧云, 陈安磊, 等. 长期弃耕降低红壤稻田土壤磷库. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(8): 1398-1408. | |
| 49 | Zhu J Y, Han X R, Yang J F, et al. Effect of 30 years’ crop rotated fertilization on the temporal variation of phosphorus pool in brown earth. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2011, 42(4): 891-895. |
| 朱佳颖, 韩晓日, 杨劲峰, 等. 30年轮作施肥对棕壤磷库时间变异特征的影响. 土壤通报, 2011, 42(4) : 891-895. | |
| 50 | Li H B, Li D P, Wu Z J, et al. Albic soil phosphorus fractions after different years of cultivation. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2014, 45(1): 135-140. |
| 李会彬, 李东坡, 武志杰, 等. 不同开垦年限白浆土土壤磷库特征. 土壤通报, 2014, 45(1): 135-140. | |
| 51 | Tian L, Guo Q, Yu G, et al. Phosphorus fractions and oxygen isotope composition of inorganic phosphate in typical agricultural soils. Chemosphere, 2020, 239: 124622. |
| 52 | Teng Z Q, Li X D, Han H G, et al. Effects of land use patterns on soil phosphorus fractions in the Longzhong part of the Loess Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(2): 30-37. |
| 滕泽琴, 李旭东, 韩会阁, 等. 土地利用方式对陇中黄土高原土壤磷组分的影响. 草业学报, 2013, 22(2) : 30-37. | |
| 53 | Richter D D, Allen H L, Li J W, et al. Bioavailability of slowly cycling soil phosphorus: Major restructuring of soil P fractions over four decades in an aggrading forest. Oecologia, 2006, 150(2): 259-271. |
| 54 | Liao D, Zhang C C, Lambers H, et al. Changes in soil phosphorus fractions in response to long-term phosphate fertilization under sole cropping and intercropping of maize and faba bean on a calcareous soil. Plant and Soil, 2021, 463(1/2): 589-600. |
| 55 | Li G H, Xu R S, Meng H Y, et al. Current situation and countermeasures of fertilizer use in vegetable fields in Nanhai District, Foshan City. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2005(6): 52-53. |
| 李广豪, 徐润生, 蒙辉远, 等. 佛山市南海区菜地化肥使用现状及对策. 广东农业科学, 2005(6): 52-53. | |
| 56 | Guan L L, Fu G N, Xu P J, et al. Investigation and analysis of fertilization status of vegetable soil in Guangdong Province. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2014, 45(3): 420-424. |
| 官利兰, 伏广农, 徐鹏举, 等. 广东省菜园土壤施肥状况调查与分析. 南方农业学报, 2014, 45(3): 420-424. | |
| 57 | Zhan X Y. Relationship between available phosphorus and phosphorus balance and its mechanism under different long-term fertilizations in black soil. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2016. |
| 展晓莹. 长期不同施肥模式黑土有效磷与磷盈亏响应关系差异的机理. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2016. | |
| 58 | Zhang X Z, Yang X B, Li T X, et al. Characteristics of phosphorus uptake and phosphorus fractions in the rhizosphere among different phosphorus efficiency wheat cultivars. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2012, 45(15): 3083-3092. |
| 张锡洲, 阳显斌, 李廷轩, 等. 不同磷效率小麦对磷的吸收及根际土壤磷组分特征差异. 中国农业科学, 2012, 45(15): 3083-3092. | |
| 59 | Li B Z, Gunina A, Zhran M, et al. Fate of low-molecular-weight organic phosphorus compounds in the P-rich and P-poor paddy soils. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2021, 20(9): 2526-2534. |
| 60 | Lu R K, Shi Z Y, Qian C L. Study on soil accumulated phosphorus-morphological characteristics and effectiveness of accumulated phosphorus in several typical soils. Soils, 1997(2): 57-60, 75. |
| 鲁如坤, 时正元, 钱承梁. 土壤积累态磷研究-几种典型土壤中积累态磷的形态特征及其有效性. 土壤, 1997(2): 57-60, 75. | |
| 61 | Darch T, Blackwell M S A, Hawkins J M B, et al. A meta-analysis of organic and inorganic phosphorus in organic fertilizers, soils, and water: implications for water quality. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2014, 44: 2172-2202. |
| 62 | Carreira J A, García-Ruiz R, Liétor J, et al. Changes in soil phosphatase activity and P transformation rates induced by application of N- and S-containing acid mist to a forest canopy. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2000, 32(13): 1857-1865. |
| 63 | Qin L, Jian M, Freeman C, et al. Agricultural land use regulates the fate of soil phosphorus fractions following the reclamation of wetlands. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 863: 160891. |
| 64 | Sui L, Tang C, Cheng K, et al. Biochar addition regulates soil phosphorus fractions and improves release of available phosphorus under freezing-thawing cycles. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 848: 157748. |
| 65 | Zheng C, Guo Z X, Yuan Y Z, et al. Spatial and temporal changes of farmland soil acidification and their influencing factors in different regions of Guangdong Province, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(2): 593-601. |
| 郑超, 郭治兴, 袁宇志, 等. 广东省不同区域农田土壤酸化时空变化及其影响因素. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(2) : 593-601. | |
| 66 | Schleuss P M, Widdig M, Heintz-Buschar A, et al. Stoichiometric controls of soil carbon and nitrogen cycling after long-term nitrogen and phosphorus addition in a mesic grassland in South Africa. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2019, 135: 294-303. |
| 67 | Wang Z, Zhao M, Yan Z, et al. Global patterns and predictors of soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in terrestrial ecosystems. Catena, 2022, 211: 106037. |
| 68 | Marklein A R, Houlton B Z. Nitrogen inputs accelerate phosphorus cycling rates across a wide variety of terrestrial ecosystems. New Phytologist, 2012, 193: 696-704. |
| 69 | Lu P, Li W H, Niu J C, et al. Phosphorus availability and transformation of inorganic phosphorus forms under different organic carbon levels in a tier soil. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(1): 111-122. |
| 路鹏, 李文海, 牛金璨, 等. 不同有机碳水平下塿土磷的有效性及无机磷形态转化. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(1): 111-122. | |
| 70 | Liu Y, Bing H J, Wu Y H, et al. Nitrogen addition promotes soil phosphorus availability in the subalpine forest of eastern Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Soil and Sediments, 2022, 22: 1-11. |
| 71 | Wang H, Tang S, Han S, et al. Effects of long-term substitution of chemical fertilizer with Chinese milk vetch on soil phosphorus availability and leaching risk in the double rice systems of Eastern China. Field Crops Research, 2023, 302: 109047. |
| 72 | Cui H J, Wang M K, Fu M L, et al. Enhancing phosphorus availability in phosphorus-fertilized zones by reducing phosphate adsorbed on ferrihydrite using rice straw-derived biochar. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2011, 11: 1135. |
| 73 | Zhao D, Qiu S K, Li M M, et al. Modified biochar improves the storage capacity and adsorption affinity of organic phosphorus in soil. Environmental Research, 2022, 205: 112455. |
| 74 | Xue P, Hou R, Fu Q, et al. Potentially migrating and residual components of biochar: Effects on phosphorus adsorption performance and storage capacity of black soil. Chemosphere, 2023, 336: 139250. |
| 75 | Han T, Li D, Liu K, et al. Soil potassium regulation by initial K level and acidification degree when subjected to liming: A meta-analysis and long-term field experiment. Catena, 2023, 232: 107408. |
| [1] | 谭湘蛟, 董逵才, 张华, 唐川川, 杨燕. 积雪增加对青藏高原高寒草甸土壤磷有效性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 205-214. |
| [2] | 郭彦军,倪郁,韩建国. 农牧交错带人工种草对土壤磷素有效性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(2): 169-174. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||