

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 123-132.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024118
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
王文虎1,2( ), 梁国玲1,2(
), 梁国玲1,2( ), 刘文辉1,2, 王凤宇1,2, 李文1,2
), 刘文辉1,2, 王凤宇1,2, 李文1,2
收稿日期:2024-04-10
修回日期:2024-05-17
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2024-11-27
通讯作者:
梁国玲
作者简介:E-mail: qhliangguoling@163.com基金资助:
Wen-hu WANG1,2( ), Guo-ling LIANG1,2(
), Guo-ling LIANG1,2( ), Wen-hui LIU1,2, Feng-yu WANG1,2, Wen LI1,2
), Wen-hui LIU1,2, Feng-yu WANG1,2, Wen LI1,2
Received:2024-04-10
Revised:2024-05-17
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2024-11-27
Contact:
Guo-ling LIANG
摘要:
为了综合评价青藏高原区老芒麦资源的特点,本研究在海晏县开展了8份老芒麦资源的农艺性状与生产性能综合评价试验,分析了不同老芒麦资源的农艺性状和产量性状特征,揭示老芒麦饲草产量的影响因素,采用TOPSIS-多准则决策模型对供试老芒麦资源的各项指标进行综合评价,以期筛选出优质的老芒麦资源。结果表明:2龄时,16-364、17-195植株较高,为108.1和109.0 cm;16-093草层高度最高、单株饲草产量最高,分别为36.8 cm,170.3 g;15-025、17-195分蘖数较多,为123和124枝·株-1。3龄时,17-195植株最高、冠幅最大,分别为122.7 cm、140.8 cm;16-093草层高度最高、单株饲草产量最高,分别为51.8 cm,234.7 g;15-025分蘖数最多,为456枝·株-1。结构方程表明,株高和分蘖数是影响老芒麦饲草产量的关键因子,TOPSIS-多准则决策模型综合评价结果表明,16-093饲草生产性能更高、更稳定,是适宜海北州种植的最佳老芒麦资源,可作为下一步品种选育的亲本材料。
王文虎, 梁国玲, 刘文辉, 王凤宇, 李文. 青藏高原区8份老芒麦资源农艺性状与生产性能综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 123-132.
Wen-hu WANG, Guo-ling LIANG, Wen-hui LIU, Feng-yu WANG, Wen LI. Comprehensive evaluation of agronomic traits and yield of eight Elymus sibiricus varieties in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(2): 123-132.
种质编号 Germplasm number | 资源名 Variety name | 采集地点 Collection places | 地理位置 Geographic position | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 小生境 Microhabitat |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15-025 | 老芒麦 E. sibiricus | 青海省大通县斜沟乡斜沟村Xiegou Village, Xiegou Town, Datong County, Qinghai Province | 101°34.77′ E, 36°58.57′ N | 2760 | 河边Riverside |
| 15-285 | 老芒麦 E. sibiricus | 青海省大通县向化藏族乡黄茨坡Huangcipo, Xianghua Tibetan Town, Datong County, Qinghai Province | 101°52.57′ E, 37°5.18′ N | 3100 | 路边山坡Slope of roadside |
| 16-093 | 老芒麦 E. sibiricus | 青海省门源县皇城蒙古族乡扎沙村Zhasha Village, Huangcheng Mongol Town, Menyuan County, Qinghai Province | 101°9.23′ E, 37°38.23′ N | 3140 | 围栏封育草场Inside of fenced meadow |
| 16-317 | 老芒麦 E. sibiricus | 青海省互助县边滩乡大河欠村Daheqian Village, Biantan Town, Huzhu County, Qinghai Province | 102°6.31′ E, 37°0.4′ N | 3050 | 山坡围栏封育草场Fenced meadow of slope |
| 16-364 | 老芒麦 E. sibiricus | 青海省大通县青林乡白土牙合村Baituyahe Village, Qinglin Town, Datong County, Qinghai Province | 101°20.29′ E, 37°6.21′ N | 2870 | 河边Riverside |
| 17-152 | 老芒麦 E. sibiricus | 青海省贵德县新街回族乡鱼山村Yushan Village, Xinjie Hui Town, Guide County, Qinghai Province | 101°21.57′ E, 35°41.19′ N | 3030 | 路边灌丛Shrub of roadside |
| 17-195 | 老芒麦 E. sibiricus | 青海省贵德县豆后浪村Douhoulang Village, Guide County, Qinghai Province | 101°13.33′ E, 36°12.18′ N | 2975 | 路边围栏内Inside the fence of roadside |
| 19-027 | 老芒麦 E. sibiricus | 青海省同仁县双朋西村Shuangpengxi Village, Tongren County, Qinghai Province | 102°11.38′ E, 35°34.74′ N | 2570 | 路边Roadside |
表1 试验材料及来源
Table 1 The test materials and sources
种质编号 Germplasm number | 资源名 Variety name | 采集地点 Collection places | 地理位置 Geographic position | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 小生境 Microhabitat |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15-025 | 老芒麦 E. sibiricus | 青海省大通县斜沟乡斜沟村Xiegou Village, Xiegou Town, Datong County, Qinghai Province | 101°34.77′ E, 36°58.57′ N | 2760 | 河边Riverside |
| 15-285 | 老芒麦 E. sibiricus | 青海省大通县向化藏族乡黄茨坡Huangcipo, Xianghua Tibetan Town, Datong County, Qinghai Province | 101°52.57′ E, 37°5.18′ N | 3100 | 路边山坡Slope of roadside |
| 16-093 | 老芒麦 E. sibiricus | 青海省门源县皇城蒙古族乡扎沙村Zhasha Village, Huangcheng Mongol Town, Menyuan County, Qinghai Province | 101°9.23′ E, 37°38.23′ N | 3140 | 围栏封育草场Inside of fenced meadow |
| 16-317 | 老芒麦 E. sibiricus | 青海省互助县边滩乡大河欠村Daheqian Village, Biantan Town, Huzhu County, Qinghai Province | 102°6.31′ E, 37°0.4′ N | 3050 | 山坡围栏封育草场Fenced meadow of slope |
| 16-364 | 老芒麦 E. sibiricus | 青海省大通县青林乡白土牙合村Baituyahe Village, Qinglin Town, Datong County, Qinghai Province | 101°20.29′ E, 37°6.21′ N | 2870 | 河边Riverside |
| 17-152 | 老芒麦 E. sibiricus | 青海省贵德县新街回族乡鱼山村Yushan Village, Xinjie Hui Town, Guide County, Qinghai Province | 101°21.57′ E, 35°41.19′ N | 3030 | 路边灌丛Shrub of roadside |
| 17-195 | 老芒麦 E. sibiricus | 青海省贵德县豆后浪村Douhoulang Village, Guide County, Qinghai Province | 101°13.33′ E, 36°12.18′ N | 2975 | 路边围栏内Inside the fence of roadside |
| 19-027 | 老芒麦 E. sibiricus | 青海省同仁县双朋西村Shuangpengxi Village, Tongren County, Qinghai Province | 102°11.38′ E, 35°34.74′ N | 2570 | 路边Roadside |

图1 不同老芒麦资源农艺性状与饲草产量特征图中小写字母表示2龄时老芒麦资源间差异显著,大写字母表示3龄时老芒麦资源间差异显著(P<0.05)。Lowercase letters indicate the significant differences among the E. sibiricus varieties at the 2-year, capital letters indicate the significant differences among the E. sibiricus varieties at the 3-year (P<0.05).
Fig. 1 Agronomic traits and forage yield characteristics of different E. sibiricus varieties
项目 Item | 处理 Treatments | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方 Mean square | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
株高 Plant height | 年份 Years | 6096.441 | 2 | 3048.220 | 367.025 | 0.000 |
| 资源 Varieties | 7153.887 | 7 | 1021.984 | 123.053 | 0.000 | |
| 年份×资源Years×varieties | 7090.420 | 14 | 506.459 | 60.981 | 0.000 | |
叶长 Leaf length | 年份 Years | 239.878 | 2 | 119.939 | 1.669 | 0.193 |
| 资源 Varieties | 729.866 | 7 | 104.267 | 1.451 | 0.191 | |
| 年份×资源Years×varieties | 912.317 | 14 | 65.166 | 0.907 | 0.553 | |
叶宽 Leaf width | 年份 Years | 2.743 | 2 | 1.371 | 65.911 | 0.000 |
| 资源 Varieties | 3.785 | 7 | 0.541 | 25.991 | 0.000 | |
| 年份×资源Years×varieties | 0.542 | 14 | 0.039 | 1.860 | 0.037 | |
冠幅 Crown breadth | 年份 Years | 13704.681 | 2 | 6852.340 | 535.397 | 0.000 |
| 资源 Varieties | 34802.944 | 7 | 4971.849 | 388.468 | 0.000 | |
| 年份×资源Years×varieties | 6656.431 | 14 | 475.459 | 37.149 | 0.000 | |
草层高度 Grass height | 年份 Years | 3763.191 | 2 | 1881.595 | 856.487 | 0.000 |
| 资源 Varieties | 7603.707 | 7 | 1086.244 | 494.450 | 0.000 | |
| 年份×资源Years×varieties | 1254.059 | 14 | 89.576 | 40.774 | 0.000 | |
分蘖数 Number of tillers | 年份 Years | 902876.462 | 2 | 451438.231 | 40691.750 | 0.000 |
| 资源 Varieties | 413301.818 | 7 | 59043.117 | 5322.030 | 0.000 | |
| 年份×资源Years×varieties | 119406.677 | 14 | 8529.048 | 768.792 | 0.000 | |
单株草产量 Yield per plant | 年份 Years | 170269.347 | 2 | 85134.674 | 4335.925 | 0.000 |
| 资源 Varieties | 136282.549 | 7 | 19468.936 | 991.556 | 0.000 | |
| 年份×资源Years×varieties | 15022.431 | 14 | 1073.031 | 54.650 | 0.000 |
表2 年份和资源对老芒麦农艺性状与饲草产量影响的双因素方差分析
Table 2 Two-factor variance analysis of years and varieties on agronomic traits and forage yield of E. sibiricus
项目 Item | 处理 Treatments | 平方和 Sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方 Mean square | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
株高 Plant height | 年份 Years | 6096.441 | 2 | 3048.220 | 367.025 | 0.000 |
| 资源 Varieties | 7153.887 | 7 | 1021.984 | 123.053 | 0.000 | |
| 年份×资源Years×varieties | 7090.420 | 14 | 506.459 | 60.981 | 0.000 | |
叶长 Leaf length | 年份 Years | 239.878 | 2 | 119.939 | 1.669 | 0.193 |
| 资源 Varieties | 729.866 | 7 | 104.267 | 1.451 | 0.191 | |
| 年份×资源Years×varieties | 912.317 | 14 | 65.166 | 0.907 | 0.553 | |
叶宽 Leaf width | 年份 Years | 2.743 | 2 | 1.371 | 65.911 | 0.000 |
| 资源 Varieties | 3.785 | 7 | 0.541 | 25.991 | 0.000 | |
| 年份×资源Years×varieties | 0.542 | 14 | 0.039 | 1.860 | 0.037 | |
冠幅 Crown breadth | 年份 Years | 13704.681 | 2 | 6852.340 | 535.397 | 0.000 |
| 资源 Varieties | 34802.944 | 7 | 4971.849 | 388.468 | 0.000 | |
| 年份×资源Years×varieties | 6656.431 | 14 | 475.459 | 37.149 | 0.000 | |
草层高度 Grass height | 年份 Years | 3763.191 | 2 | 1881.595 | 856.487 | 0.000 |
| 资源 Varieties | 7603.707 | 7 | 1086.244 | 494.450 | 0.000 | |
| 年份×资源Years×varieties | 1254.059 | 14 | 89.576 | 40.774 | 0.000 | |
分蘖数 Number of tillers | 年份 Years | 902876.462 | 2 | 451438.231 | 40691.750 | 0.000 |
| 资源 Varieties | 413301.818 | 7 | 59043.117 | 5322.030 | 0.000 | |
| 年份×资源Years×varieties | 119406.677 | 14 | 8529.048 | 768.792 | 0.000 | |
单株草产量 Yield per plant | 年份 Years | 170269.347 | 2 | 85134.674 | 4335.925 | 0.000 |
| 资源 Varieties | 136282.549 | 7 | 19468.936 | 991.556 | 0.000 | |
| 年份×资源Years×varieties | 15022.431 | 14 | 1073.031 | 54.650 | 0.000 |
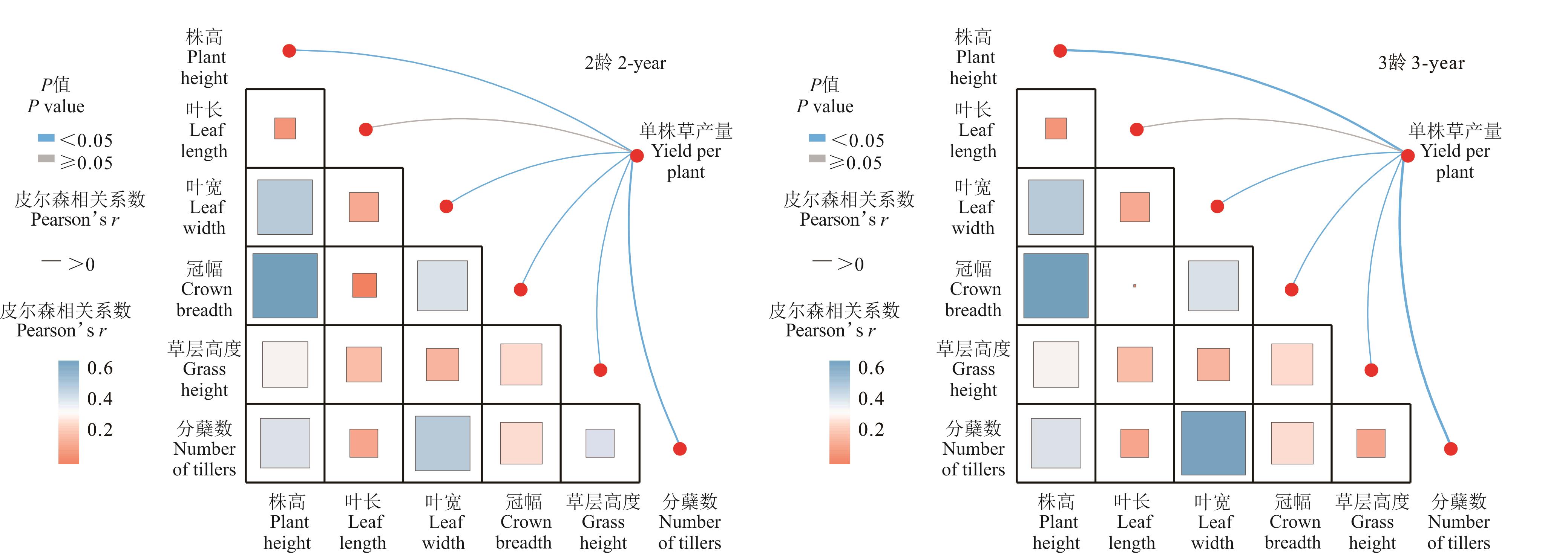
图2 不同老芒麦资源农艺性状与饲草产量Mantel test相关性分析
Fig. 2 Mantel test correlation analysis between agronomic traits and forage yield of different E. sibiricus varieties
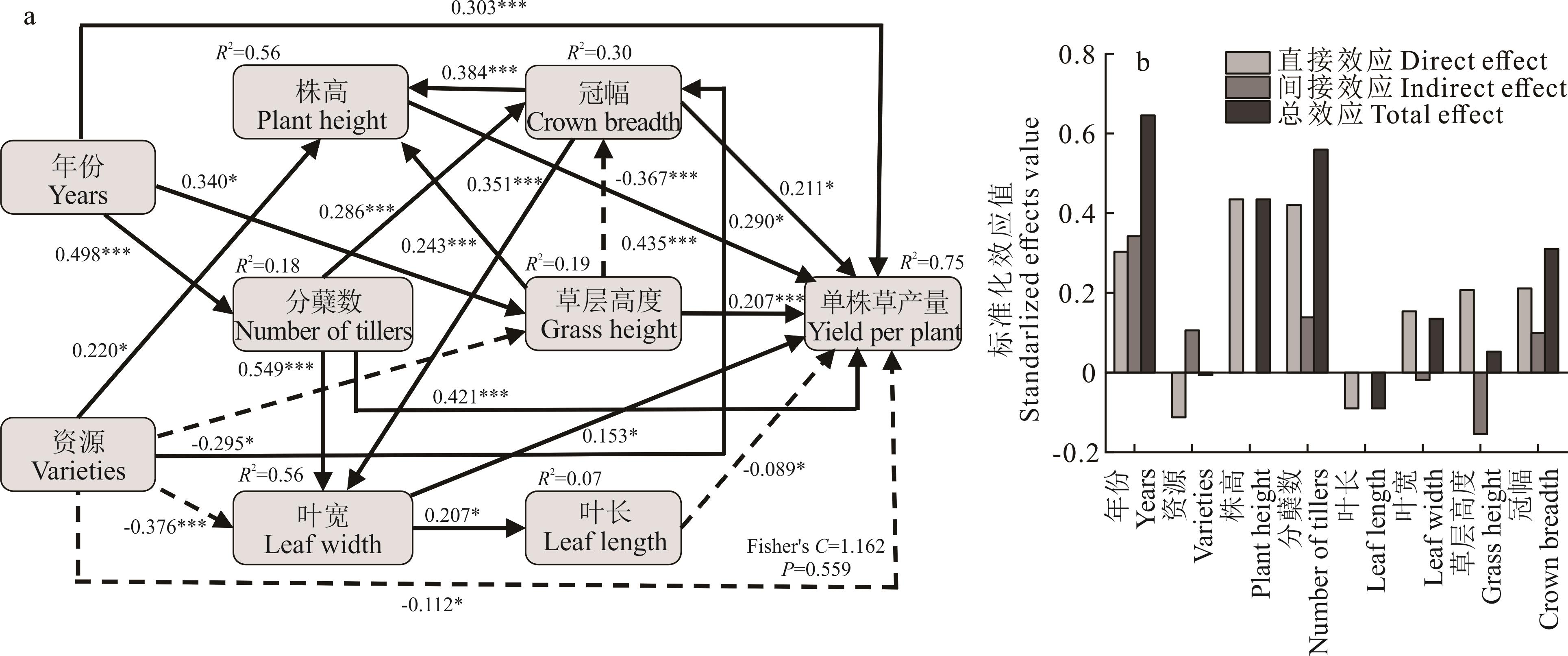
图5 结构方程模型分析年份和资源对单株饲草产量的影响路径(a)及各因子的标准化效应值(b)图中实线和虚线箭头分别表示显著正和负的路径关系。数值为标准化路径系数。*表示在0.05水平上差异显著,**表示在0.01水平上差异显著,***表示在0.001水平上差异显著。Solid and dashed arrows represent significantly positive or negative effects at the 0.05 level, respectively. The standard path coefficients were shown on arrows. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
Fig. 5 Structural equation model analyzed the influence paths of years and varieties on forage yield per plant (a) and the standardized effect values of each factor (b)
| 1 | Li M, Liu S, Sun Y, et al. Agriculture and animal husbandry increased carbon footprint on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during past three decades. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 278: 123963. |
| 2 | Li J H, Yang G J, Wang S P. Vegetation and soil characteristics of degraded alpine meadows on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China: A review. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(6): 2109-2118. |
| 李军豪, 杨国靖, 王少平. 青藏高原区退化高寒草甸植被和土壤特征. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(6): 2109-2118. | |
| 3 | Zhang Q, Yuan R, Singh V P, et al. Dynamic vulnerability of ecological systems to climate changes across the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 134: 108483. |
| 4 | Shang Z H, Dong Q M, Shi J J, et al. Research progress in recent 10 years of ecological restoration for ‘Black soil land’ degraded grassland on Tibet Plateau-concurrently discuss of ecological restoration in Sanjiangyuan region. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(1): 1-21. |
| 尚占环, 董全民, 施建军, 等. 青藏高原“黑土滩”退化草地及其生态恢复近10年研究进展-兼论三江源生态恢复问题. 草地学报, 2018, 26(1): 1-21. | |
| 5 | Zhang H M, Li X L, Li L P, et al. Effects of species combination on community diversity and productivity of alpine artificial grassland. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(5): 1436-1443. |
| 张慧敏, 李希来, 李兰平, 等. 草种配置对高寒人工草地群落多样性和生产力的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(5): 1436-1443. | |
| 6 | Li M F, Li X R, Li Y Z, et al. Identification of wild Elymus sibiricus germplasm resources and analysis of variation of dorsal hairs in basal leaf sheath. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(4): 1026-1035. |
| 李明峰, 李欣瑞, 李英主, 等. 野生老芒麦种质资源鉴定与基部叶鞘绒毛变异分析. 草地学报, 2023, 31(4): 1026-1035. | |
| 7 | Qi H F, Liu W H, Liu M J, et al. Interannual differences in ear traits and spike type division of E. sibiricus L. wheat ears on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 37(9): 1751-1763. |
| 起惠芳, 刘文辉, 刘敏洁, 等. 青藏高原老芒麦穗部性状年际差异分析和穗型划分. 核农学报, 2023, 37(9): 1751-1763. | |
| 8 | Liu W W, Liu X, Lei Y X, et al. A comprehensive evaluation of cold resistance and the physiological response of Elymus sibiricus genotypes. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(8): 152-163. |
| 柳文蔚, 刘鑫, 雷映霞, 等. 老芒麦种质资源抗寒性综合评价及冷胁迫下的生理反应. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 152-163. | |
| 9 | Li C Y, Wang Y, Li X R, et al. Morphological diversity and germplasm utilization potential of wild Elymus sibiricus. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 67-79. |
| 李春艳, 王艳, 李欣瑞, 等. 中国野生老芒麦形态多样性研究与种质利用潜力分析. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 67-79. | |
| 10 | Liu W H, Jia Z F, Wei X X, et al. Study on protection and utilization of forage germplasm resources in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Qinghai Science and Technology, 2017, 24(1): 32-35. |
| 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 魏小星, 等. 青藏高原牧草种质资源保护利用研究. 青海科技, 2017, 24(1): 32-35. | |
| 11 | Yan J J, Bai S Q, Zhang X Q, et al. Genetic diversity of native Elymus sibiricus populations in the southeast margin of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau as detected by SRAP and SSR markers. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2010, 19(4): 122-134. |
| 鄢家俊, 白史且, 张新全, 等. 青藏高原东南缘老芒麦自然居群遗传多样性的SRAP和SSR分析. 草业学报, 2010, 19(4): 122-134. | |
| 12 | Wu R, Liu W H, Zhang Y C, et al. Performance evaluation of different Elymus sibiricus L. germplasm resources in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2020, 21(4): 855-865. |
| 吴瑞, 刘文辉, 张永超, 等. 青藏高原地区不同老芒麦种质资源生产性能评价. 植物遗传资源学报, 2020, 21(4): 855-865. | |
| 13 | Wu R, Liu W H, Zhang Y C, et al. A study of the correlation between seed shattering and agronomic traits of Elymus sibiricus on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(4): 130-139. |
| 吴瑞, 刘文辉, 张永超, 等. 青藏高原老芒麦落粒性及农艺性状相关性研究. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 130-139. | |
| 14 | Ren C Y, Liu W H, Liang G L, et al. Differences of seed shattering and agronomic traits in six Elymus species on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(4): 1008-1015. |
| 任春燕, 刘文辉, 梁国玲, 等. 青藏高原六种披碱草属牧草落粒性差异及农艺性状分析. 草地学报, 2023, 31(4): 1008-1015. | |
| 15 | Wu Y H, Liu W H, Liu K Q, et al. Comprehensive evaluation and screening on the productive performance of 13 Bromus inermis Leyss. germplasm resources. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(11): 3472-3483. |
| 吴雨涵, 刘文辉, 刘凯强, 等. 13份无芒雀麦种质资源生产性能的综合评价及筛选. 草地学报, 2023, 31(11): 3472-3483. | |
| 16 | Wang X P, Bai Y X, Yao X H, et al. Effect of mowing stubble height on forage and grain yield and forage quality characteristics of hulless barley. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2023, 43(4): 513-523. |
| 王小萍, 白羿雄, 姚晓华, 等. 刈割留茬高度对青稞饲草与籽粒产量及饲用品质的影响. 麦类作物学报, 2023, 43(4): 513-523. | |
| 17 | Zhang H H, Liang W W, Zhang X Z, et al. Analysis on morphology and growth characteristics of wild Elymus sibiricus L. germplasm resources in Xinjiang. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(4): 701-708. |
| 张荟荟, 梁维维, 张学洲, 等. 新疆野生老芒麦种质资源形态及生长特性分析. 草地学报, 2021, 29(4): 701-708. | |
| 18 | Zhang W, Zhou Q P, Chen Y J, et al. Comparison of production performance and forage quality of 10 introduced oat varieties in Hulunbuir, China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(12): 129-142. |
| 张伟, 周青平, 陈有军, 等. 呼伦贝尔地区10个引进燕麦品种生产性能及饲草品质比较. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 129-142. | |
| 19 | Vera M L. Effects of altitude and seed size on germination and seedling survival of heathland plants in north Spain. Plant Ecology, 1997, 133: 101-106. |
| 20 | Hou Y, Liu M X, Sun H R. Responses of plant leaf traits to microhabitat change in subalpine meadow on the eastern edge of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(1): 71-79. |
| 侯媛, 刘旻霞, 孙辉荣. 青藏高原东缘亚高寒草甸植物叶性状对微生境变化的响应. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(1): 71-79. | |
| 21 | Fan Y K, Yun L, Li Z, et al. Correlation analysis of agronomic traits related to forage yield of Psathyrostachys juncea. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2020, 42(3): 119-125. |
| 范亚坤, 云岚, 李珍, 等. 新麦草饲草产量相关农艺性状的关联性分析.中国草地学报, 2020, 42(3): 119-125. | |
| 22 | Zhang D, Long H Y. Evaluation of production performance and nutritional value of eight alfalfa varieties in the hot-arid zone. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2024, 46(1): 70-77. |
| 张德, 龙会英. 8个紫花苜蓿品种在干热区生产性能和营养价值评价. 中国草地学报, 2024, 46(1): 70-77. | |
| 23 | Zhang Y C, Wei X X, Liang G L, et al. Phenotype changes during ageing over six years of Elymus sibiricus stands and the effects of nutrient addition. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(6): 101-111. |
| 张永超, 魏小星, 梁国玲, 等. 老芒麦衰老过程形态特征变化规律及对养分添加的响应. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 101-111. | |
| 24 | Zhou H, Yang B, Han J G. Studies on some structural characteristics of a community of grassland of Elymus sibiricus planted in different years. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2000, 8(4): 245-252. |
| 周禾, 杨波, 韩建国. 利用年限对老芒麦生物学特性及群落结构特征的影响. 草地学报, 2000, 8(4): 245-252. | |
| 25 | Yu J B, Chen S Y, Sangjie D J, et al. Morphological variation and genetic relationship analysis of short-awned Elymus sibiricus germplasm in northwest of Sichuan. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(9): 2787-2795. |
| 余静菠, 陈仕勇, 桑杰多吉, 等. 川西北高原短芒型老芒麦种质形态变异及遗传亲缘关系分析. 草地学报, 2023, 31(9): 2787-2795. | |
| 26 | Fu X N, Pan Z W, Meng X J, et al. The relationship of agronomic traits and fresh forage yield of Secale cereale L. ‘ganyin No1’. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2017, 25(2): 433-436. |
| 富新年, 潘正武, 孟祥君, 等. ‘甘引1号’黑麦农艺性状与鲜草产量的关系. 草地学报, 2017, 25(2): 433-436. | |
| 27 | Yuan Y, Chen D M, Liu W, et al. Correlation analysis and comprehensive evaluation of production and reproductive of forage oat in northwest Sichuan plateau. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2023, 41(6): 1116-1123. |
| 袁艺, 陈冬明, 刘伟, 等. 川西北高原饲用燕麦产量和生殖性状相关性分析及综合评价. 四川农业大学学报, 2023, 41(6): 1116-1123. | |
| 28 | Yin T T, Gu L L, Yan F, et al. Phenotypic diversity analysis of 59 Elymus sibiricus germplasm resources. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 34(11): 2307-2317. |
| 尹婷婷, 谷丽丽, 闫锋, 等. 59份老芒麦种质资源的表型多样性分析. 西南农业学报, 2021, 34(11): 2307-2317. | |
| 29 | Lei L, Zheng H L, Wang J G, et al. Genetic dissection of rice (Oryza sativa L.) tiller, plant height, and grain yield based on QTL mapping and meta analysis. Euphytica, 2018, 214: 1-17. |
| 30 | Wang Y, Lu J, Ren T, et al. Effects of nitrogen and tiller type on grain yield and physiological responses in rice. AoB Plants, 2017, 9(2): plx012. |
| 31 | Wang H Z, Mao L P, Wang Y H, et al. DNA fingerprinting construction based on the optimal sampling strategy and genetic diversity analysis of Elymus sibiricus germplasm. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(1): 1-7 |
| 王惠知, 毛丽萍, 王雨涵, 等. 基于最适取样策略的老芒麦种质指纹图谱构建及遗传多样性分析. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(1): 1-7. | |
| 32 | Liu X, Song S S, Yue M. Plant memory research in ecology. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(24): 9387-9395. |
| 刘晓, 宋姗姗, 岳明. 生态学中的植物记忆研究. 生态学报, 2019, 39(24): 9387-9395. |
| [1] | 张振豪, 贾子玉, 李鑫宇, 程云湘. 荒漠草原混牧牛羊的放牧行为特征[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 226-237. |
| [2] | 李中利, 蒋丛泽, 马仁诗, 高玮, 受娜, 沈禹颖, 杨宪龙. 陇东旱塬区5个饲用甜高粱品种生产适宜性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 50-62. |
| [3] | 桑瑞娟, 崔超杰, 何云, 张晓霞, 姚晋, 董春阳, 孙浩, 史莹华, 朱晓艳, 李德锋. 豫北地区18个秋播饲用燕麦品种抗倒伏特性及生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 74-85. |
| [4] | 熊军波, 张鹤山, 田宏, 陆姣云, 吴新江, 刘洋. 鄂东大别山区野生豆科牧草资源调查与评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 116-125. |
| [5] | 亓雯雯, 马红媛, 李亚晓, 杜艳, 孙梦丹, 武海涛. 优质牧草新品种选育方法研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 187-202. |
| [6] | 王敏, 李莉, 贾蓉, 包爱科. 10种紫花苜蓿在低温胁迫下的生理特性及耐寒性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 76-88. |
| [7] | 王萌, 鲁雪莉, 王菊英, 张梦超, 宋奕汝, 孟晨, 张莉, 徐宗昌. 小黑麦种质萌发期苗期耐盐资源评价与筛选[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 58-68. |
| [8] | 赵洁, 陈恒光, 裴晓蒙, 于昊, 徐银莹, 茆达干. 围产期日粮添加白藜芦醇对山羊生产性能、血液指标及炎症因子基因表达的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 210-220. |
| [9] | 李鸿飞, 周帮伟, 张淼, 施树楠, 李志坚. 不同燕麦品种在呼伦贝尔地区的引种适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 60-72. |
| [10] | 冯琴, 何小莉, 王斌, 王腾飞, 倪旺, 马霞, 明雪花, 邓建强, 兰剑. 宁夏引黄灌区燕麦与箭筈豌豆的混播效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 107-119. |
| [11] | 李妍, 马富龙, 韩路, 王海珍. 美国‘WL’系列不同秋眠级苜蓿品种在南疆的生产性能与适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 139-149. |
| [12] | 罗颖, 李聪, 王沛, 田莉华, 汪辉, 周青平, 雷映霞. 低氮胁迫下不同皮燕麦品种早期的响应研究及耐低氮性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 164-184. |
| [13] | 张永亮, 滕泽, 郝凤, 于铁峰, 张玉霞. 苜蓿混播方式及比例对混播草地生产力和稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 185-197. |
| [14] | 雷颖, 罗杰, 郭旭曼, 秘二停, 刘锦春. 小生境尺度下喀斯特弃耕地植物多样性、生物量及其影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 28-38. |
| [15] | 侯铭辉, 孙延亮, 杨开鑫, 齐军仓, 张前兵. 基于响应曲面法确定水培大麦饲草高产优质的氮磷钾养分投入量[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 172-185. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||