

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 137-149.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020333
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2020-07-14
修回日期:2020-10-10
出版日期:2021-08-30
发布日期:2021-08-30
通讯作者:
牛学礼
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: niuxl05@qq.com基金资助:
Wu ZHANG( ), Jin-yu YANG, Xiang LU, Jin-mei LIN, Xue-li NIU(
), Jin-yu YANG, Xiang LU, Jin-mei LIN, Xue-li NIU( )
)
Received:2020-07-14
Revised:2020-10-10
Online:2021-08-30
Published:2021-08-30
Contact:
Xue-li NIU
摘要:
木霉菌是自然界中普遍存在的拮抗微生物,多种木霉菌对植物病原菌具有重要的生防价值。为挖掘出防治草坪草病害的生防菌剂,采用对峙培养法测定了4株木霉菌株对14种草坪草病原菌的拮抗作用,通过显微镜观察、玻璃纸法及粗提液抑菌试验研究了其抑菌机理。研究结果表明,供试木霉菌对所有供试病原菌均有拮抗作用,其中菌株SQ-1Q-18抑菌效果最佳,对玉蜀黍丝核菌和地衣状伏革菌的拮抗等级为I级,抑制率高达100%,对灰葡萄孢菌、地毯草炭疽菌和立枯丝核菌的拮抗等级为Ⅱ级,抑制率大于80%,且对供试病原菌的平均抑制率高达72.8%。进一步研究菌株SQ-1Q-18的抑菌机理发现,该菌株在培养基上产生抑菌圈侵占病原菌的生长空间,覆盖和深入病原菌内部并与其相互缠绕使得病原菌菌丝变细、缢缩甚至断裂,或直接穿入病原菌菌丝内部吸取营养致使菌丝细胞溶解,也可产生拮抗物质,其中玻璃纸法中对草坪草币斑病菌、球黑孢霉及地衣状伏革菌的相对抑制率分别高达91.77%、89.80%和79.59%;粗提取液对草坪草币斑病菌和佩立金平脐蠕孢的抑制率分别为43.60%和42.91%。经鉴定,SQ-1Q-18为哈茨木霉。研究结果为高效防治草坪草真菌病害的生防菌剂的研制、开发提供了科学资料。
章武, 杨锦玉, 卢翔, 林金梅, 牛学礼. 木霉菌对草坪草病原菌的抑菌效果及其机理初步研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 137-149.
Wu ZHANG, Jin-yu YANG, Xiang LU, Jin-mei LIN, Xue-li NIU. A preliminary study of the antifungal activity and antagonism mechanisms of Trichoderma spp. against turfgrass pathogens[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(9): 137-149.
| 序号No. | 菌株Isolates | 菌株代号Isolate code |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 木贼镰刀菌Fusarium equiseti | FE |
| 2 | 新月弯孢霉Curvularia lunata | CL |
| 3 | 球黑孢霉Nigrospora sphaerica | NS |
| 4 | 草坪草墨斑病菌Curvularia malina | CM |
| 5 | 佩立金平脐蠕孢Bipolaris peregianensis | BP |
| 6 | 草茎点霉Phoma herbarum | PH |
| 7 | 立枯丝核菌Rhizoctonia solani | RS |
| 8 | 地衣状伏革菌Laetisaria fuciformis | LF |
| 9 | 地毯草炭疽菌Colletotrichum hainanese | CH |
| 10 | 灰葡萄孢菌Botrytis cinerea | BC |
| 11 | 草坪草币斑病病原菌Sclerotinia homoeocarpa | SH |
| 12 | 禾顶囊壳禾谷变种Gaeumannomyces graminis var. graminis | GG |
| 13 | 雀稗微座孢Microdochium paspali | MP |
| 14 | 玉蜀黍丝核菌Rhizoctonia zeae | RZ |
表1 供试草坪草病原菌信息
Table 1 Information of turfgrass pathogens tested in current study
| 序号No. | 菌株Isolates | 菌株代号Isolate code |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 木贼镰刀菌Fusarium equiseti | FE |
| 2 | 新月弯孢霉Curvularia lunata | CL |
| 3 | 球黑孢霉Nigrospora sphaerica | NS |
| 4 | 草坪草墨斑病菌Curvularia malina | CM |
| 5 | 佩立金平脐蠕孢Bipolaris peregianensis | BP |
| 6 | 草茎点霉Phoma herbarum | PH |
| 7 | 立枯丝核菌Rhizoctonia solani | RS |
| 8 | 地衣状伏革菌Laetisaria fuciformis | LF |
| 9 | 地毯草炭疽菌Colletotrichum hainanese | CH |
| 10 | 灰葡萄孢菌Botrytis cinerea | BC |
| 11 | 草坪草币斑病病原菌Sclerotinia homoeocarpa | SH |
| 12 | 禾顶囊壳禾谷变种Gaeumannomyces graminis var. graminis | GG |
| 13 | 雀稗微座孢Microdochium paspali | MP |
| 14 | 玉蜀黍丝核菌Rhizoctonia zeae | RZ |
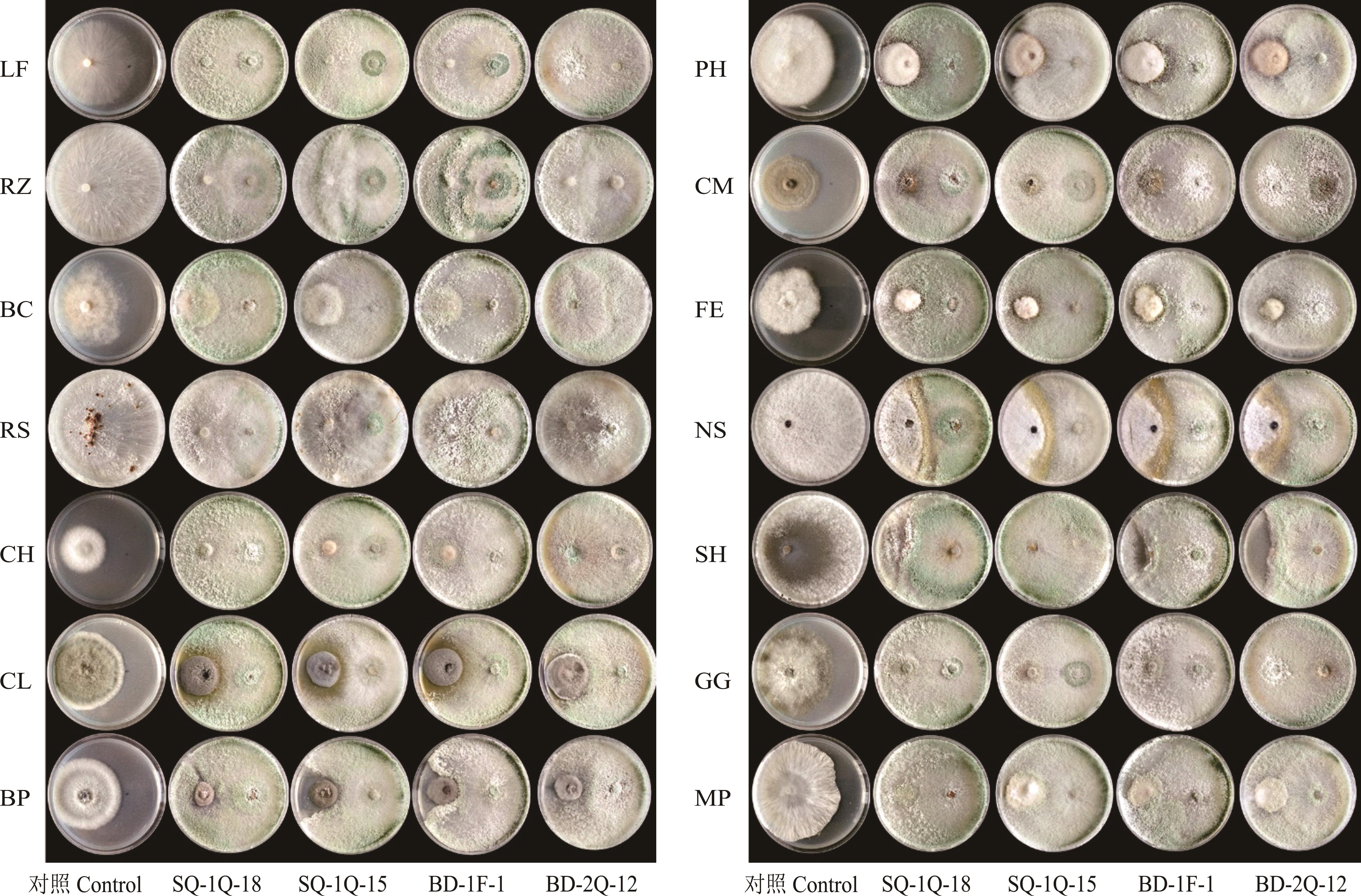
图1 对峙培养第5天时4种木霉菌与14种草坪草病原菌平板生长状况
Fig.1 The growth status of 4 Trichoderma spp. isolates and 14 turfgrasses pathogens on the 5th day of agar confrontation culture

图2 对峙培养第5天时4种木霉菌对14种草坪草病原菌的抑制率热图中方格内数字表示标准差,同列不同小写字母表示相同木霉菌株下不同病原菌株间差异显著(P<0.05);颜色越接近红色表示抑制率越高,最高100%;越接近蓝色表示抑制率越低,最低40%。Number in each cell of the heatmap indicates standard error, different lowercase letters in the same column indicate significant differences (P<0.05) among different pathogenic strains under the same Trichoderma isolate treatment. The closer the color is to red, the higher the inhibition rate is, the highest is 100%. The closer to blue, the lower the inhibition rate, as low as 40%.
Fig.2 The inhibition rate of 4 Trichoderma spp. isolates and 14 turfgrass pathogens on the 5th day of confrontation culture
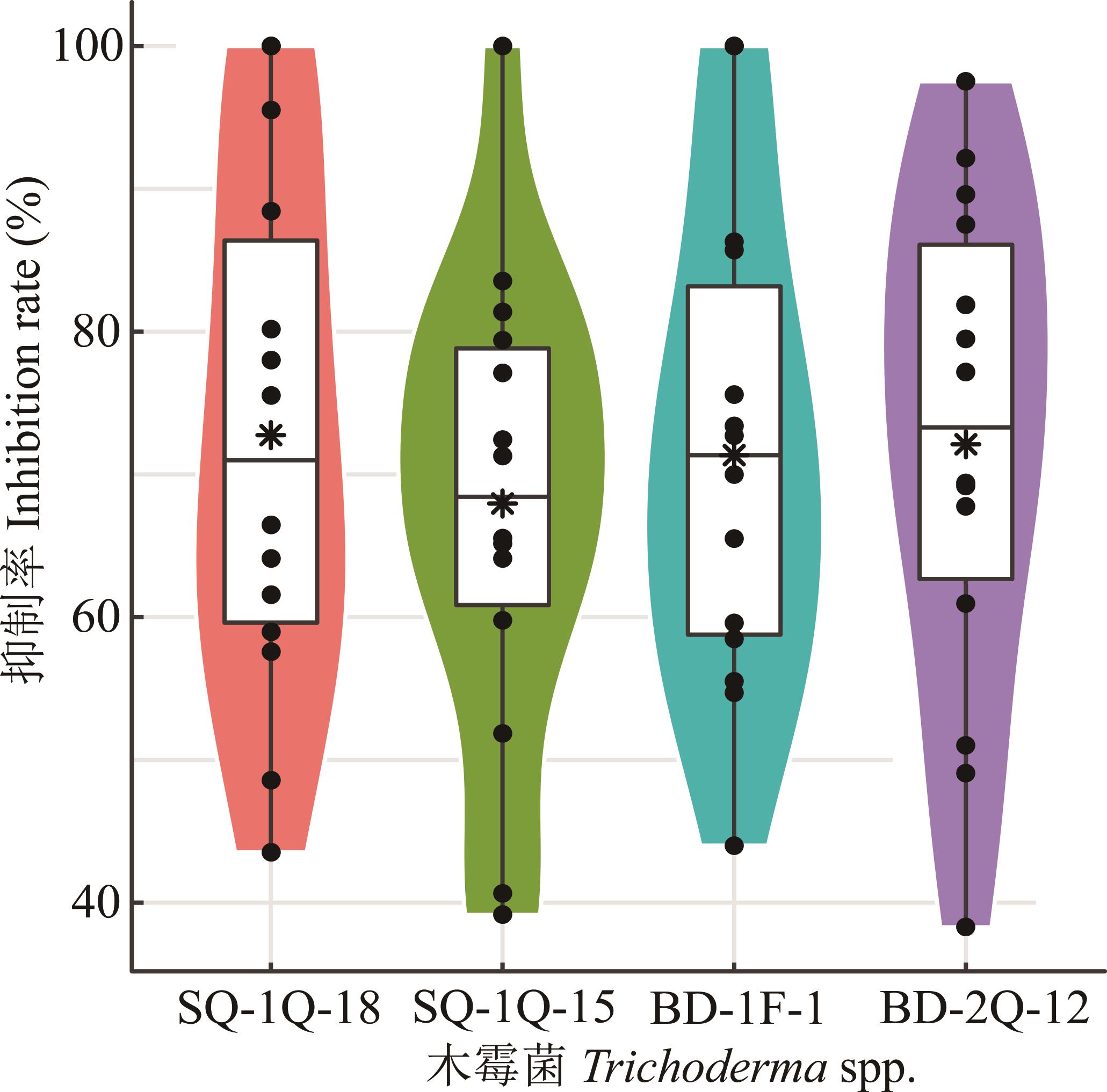
图3 4种木霉菌对14种草坪草病原菌的总体抑制率*表示相同木霉菌株对供试病原菌抑制率的平均值,实心圆点表示供试病原真菌的抑制率。* indicates mean value of inhibition rate of tested pathogenic strains under the same Trichoderma strain, solid dot indicates the inhibition rate of each pathogenic strain.
Fig.3 The overall inhibition rate of 4 Trichoderma spp. isolates to 14 turfgrass pathogens
病原菌 Pathogens | 对峙培养结果 Confrontation incubation results | 拮抗等级 Antagonist level |
|---|---|---|
地衣状伏革菌 L. fuciformis | 当两菌菌落接触后地衣状伏革菌停止生长,3 d后木霉菌菌丝迅速覆盖地衣状伏革菌菌落表面,5 d后地衣状伏革菌整个菌落被长枝木霉菌菌丝完全覆盖,并产生大量孢子。When the two colonies contact, the growth of L. fuciformis stop, Trichoderma spp. mycelium quickly cover the surface of L. fuciformis colony after 3 days, and Trichoderma spp. mycelium completely covered the entire colony after 5 days, and produced a large number of conidia. | Ⅰ |
玉蜀黍丝核菌 R. zeae | 对峙培养2 d后两菌落开始接触,木霉菌菌丝开始覆盖玉蜀黍丝核菌菌落表面,5 d后玉蜀黍丝核菌整个菌落被木霉菌菌丝完全侵占,并产生大量孢子抑制其生长。After 2 days of culture, the two colonies began to contact, and Trichoderma spp. mycelium began to cover the surface of R. zeae colony. After 5 days, the entire colony of R. zeae was completely invaded by Trichoderma spp. mycelium, and a large number of conidia were produced to R. zeae its growth. | Ⅰ |
草坪草墨斑病菌 C. malina | 两菌菌落交接后,草坪草墨斑病菌停止生长,无明显的抑菌圈,但5 d后SQ-1Q-18木霉菌菌丝围绕草坪草墨斑病菌菌落周围生长,并逐渐向草坪草墨斑病菌菌落中心扩展及蔓延。After the two colonies contract, the growth of C. malina stopped and there was no obvious bacteriostatic circle. However, after 5 days, the mycelium of Trichohypha spp. isolate SQ-1Q-18 grew around the C. malina, and gradually expanded and spread to the center of the colony of C. malina. | Ⅱ |
| 佩立金平脐蠕孢B. peregianensis | 两菌落接触后,SQ-1Q-18木霉菌大面积侵占佩立金平脐蠕孢的生长空间,使佩立金平脐蠕孢的生长受到抑制,5 d后木霉菌菌丝将其包围,并在其边缘产生大量的分生孢子。After the two colonies contacted, the Trichohypha spp. isolate SQ-1Q-18 occupied a large area of the growth space of B. peregianensis, which inhibited the growth of B. peregianensis. After 5 days, Trichoderma spp. surrounded the colony of B. peregianensis and produced a large number of conidia at its edge. | Ⅱ |
立枯丝核菌 R. solani | 立枯丝核菌生长速度快,但菌丝少,2 d后两菌落开始接触,5 d后木霉菌落几乎蔓延整个平板,使立枯丝核菌的生长空间受到极大的限制,无明显的交界及抑菌带。The rate of growth of R. solani was fast, but the mycelium were sparse. After 2 days, the two colonies began to contact, and after 5 days, Trichoderma spp. colonies almost occupied over the entire plate, which greatly restricted the growth space of R. solani. | Ⅱ |
| 地毯草炭疽菌C. hainanese | 地毯草炭疽菌生长较慢,木霉菌生长较快,当两菌落菌丝接触时,木霉菌菌落已占据大部分生长空间,导致地毯草炭疽菌停止生长,被木霉菌菌落迅速包围并覆盖。C. hainanese mycelium grew slowly, while Trichoderma spp. grows faster. When the two colonies contact, Trichoderma spp. colonies have occupied most of the growth space, resulting in the stopped growth of C. hainanese mycelium and the colonies are quickly surrounded and covered by Trichoderma spp. | Ⅱ |
灰葡萄孢菌 B. cinerea | 当两菌菌落接触后,灰葡萄孢菌停止生长,3 d后木霉菌菌丝迅速覆盖灰葡萄孢菌菌落表面,5 d后木霉菌菌丝已将灰葡萄孢菌菌落覆盖了一半,并产生大量孢子。When the two colonies contacted, the growth of B. cinerea stopped, and Trichoderma spp. mycelium covered the surface of B. cinerea rapidly after 3 days, then Trichoderma spp. mycelium covered half of B. cinerea after 5 days, and produced a large number of conidia. | Ⅱ |
| 禾顶囊壳禾谷变种G. graminis var. graminis | 禾顶囊壳禾谷变种病原菌生长较慢,当两菌落菌丝接触时,木霉菌菌落已占据大部分生长空间,导致禾顶囊壳禾谷变种停止生长,被木霉菌菌落迅速覆盖。The growth rate of G. graminis var. graminis was relatively slow. When the two colonies contacted, Trichoderma spp. had occupied most of the growth space, leading to the stop of growth of G. graminis var. graminis and the rapid coverage Trichoderma spp. | Ⅱ |
雀稗微座孢 M. paspali | 两菌落开始接触后,木霉菌逐渐侵占雀稗微座孢的营养及生长空间,使雀稗微座孢无法继续生长,很快被木霉菌落覆盖。After the two colonies began to contact, Trichoderma spp. gradually invaded the nutrition and growth space of M. paspali, making it impossible to continue to grow and was soon covered by Trichoderma spp. colony. | Ⅱ |
木贼镰刀菌 F. equiseti | 两菌落接触后,木贼镰刀菌菌落停止生长,5 d后整个菌落被木霉菌包围,但没有被覆盖,并在两菌交接处产生大量分生孢子。After the two colonies began to contact, the growth of F. equiseti stopped. After 5 days growth, the entire colony was surrounded but not covered by Trichoderma spp., and a large number of conidia were produced at the junction of the two colonies. | Ⅲ |
| 草坪草币斑病病原菌S. homoeocarpa | 当两菌落接触后,木霉菌菌丝开始向草坪草币斑病病原菌中心扩展和蔓延,使其生长受到抑制,无明显的抑菌带。5 d后,草坪草币斑病病原菌已被大面积覆盖。When the two colonies contacted, Trichoderma spp. mycelium began to expand and spread to the center of the colony S. homoeocarpa, which inhibited its growth without obvious bacteriostatic zone. After 5 days growth, the colony S. homoeocarpa had been extensively covered. | Ⅲ |
新月弯孢霉 C. lunata | 两菌落接触后,在接触边缘产生了棕色抑菌带,新月弯孢霉停止生长,抑菌带处木霉孢子较少,也无覆盖病原菌的趋势。After the two colonies contacted, there was a brown bacteriostatic zone at the contact edge, and the growth of C. lunata stopped, and there were few of Trichoderma spp. conidia in the bacteriostatic zone, and there was no tendency to cover the colony of C. lunata. | Ⅳ |
球黑孢霉 N. sphaerica | 两菌菌落交接后球黑孢霉停止生长,产生明显棕黄色的抑菌圈,且交接处球黑孢霉部分菌丝消解,使球黑孢霉菌丝不能向外扩展和生长,但木霉菌菌丝并没有将其覆盖。After the two colonies contacted, the growth of N. sphaerica stopped, resulting in an obvious brownish yellow inhibition zone. Moreover, part of mycelium of N. sphaerica were destroyed at the junction, making the mycelium of N. sphaerica unable to grow outward, but the mycelium of Trichoderma spp. did not cover colony of N. sphaerica. | Ⅳ |
草茎点霉 P. herbarum | 当两菌落接触后,SQ-1Q-18木霉大量侵占草茎点霉的生长空间,使草茎点霉的生长受到抑制,5 d后木霉菌菌丝将其包围,并在其边缘产生大量的分生孢子。When the two colonies contacted, Trichoderma spp. isolate SQ-1Q-18 invaded the growth space of P. herbarum, which inhibited its growth. After 5 days, Trichoderma spp. mycelium surrounded the colony of P. herbarum and produced a large number of conidia at its edge. | Ⅳ |
表2 木霉菌SQ-1Q-18对14种病原菌生长的拮抗效果及等级
Table 2 Inhibition effect of Trichoderma spp. isolatesSQ-1Q-18on the growth of fourteen pathogens
病原菌 Pathogens | 对峙培养结果 Confrontation incubation results | 拮抗等级 Antagonist level |
|---|---|---|
地衣状伏革菌 L. fuciformis | 当两菌菌落接触后地衣状伏革菌停止生长,3 d后木霉菌菌丝迅速覆盖地衣状伏革菌菌落表面,5 d后地衣状伏革菌整个菌落被长枝木霉菌菌丝完全覆盖,并产生大量孢子。When the two colonies contact, the growth of L. fuciformis stop, Trichoderma spp. mycelium quickly cover the surface of L. fuciformis colony after 3 days, and Trichoderma spp. mycelium completely covered the entire colony after 5 days, and produced a large number of conidia. | Ⅰ |
玉蜀黍丝核菌 R. zeae | 对峙培养2 d后两菌落开始接触,木霉菌菌丝开始覆盖玉蜀黍丝核菌菌落表面,5 d后玉蜀黍丝核菌整个菌落被木霉菌菌丝完全侵占,并产生大量孢子抑制其生长。After 2 days of culture, the two colonies began to contact, and Trichoderma spp. mycelium began to cover the surface of R. zeae colony. After 5 days, the entire colony of R. zeae was completely invaded by Trichoderma spp. mycelium, and a large number of conidia were produced to R. zeae its growth. | Ⅰ |
草坪草墨斑病菌 C. malina | 两菌菌落交接后,草坪草墨斑病菌停止生长,无明显的抑菌圈,但5 d后SQ-1Q-18木霉菌菌丝围绕草坪草墨斑病菌菌落周围生长,并逐渐向草坪草墨斑病菌菌落中心扩展及蔓延。After the two colonies contract, the growth of C. malina stopped and there was no obvious bacteriostatic circle. However, after 5 days, the mycelium of Trichohypha spp. isolate SQ-1Q-18 grew around the C. malina, and gradually expanded and spread to the center of the colony of C. malina. | Ⅱ |
| 佩立金平脐蠕孢B. peregianensis | 两菌落接触后,SQ-1Q-18木霉菌大面积侵占佩立金平脐蠕孢的生长空间,使佩立金平脐蠕孢的生长受到抑制,5 d后木霉菌菌丝将其包围,并在其边缘产生大量的分生孢子。After the two colonies contacted, the Trichohypha spp. isolate SQ-1Q-18 occupied a large area of the growth space of B. peregianensis, which inhibited the growth of B. peregianensis. After 5 days, Trichoderma spp. surrounded the colony of B. peregianensis and produced a large number of conidia at its edge. | Ⅱ |
立枯丝核菌 R. solani | 立枯丝核菌生长速度快,但菌丝少,2 d后两菌落开始接触,5 d后木霉菌落几乎蔓延整个平板,使立枯丝核菌的生长空间受到极大的限制,无明显的交界及抑菌带。The rate of growth of R. solani was fast, but the mycelium were sparse. After 2 days, the two colonies began to contact, and after 5 days, Trichoderma spp. colonies almost occupied over the entire plate, which greatly restricted the growth space of R. solani. | Ⅱ |
| 地毯草炭疽菌C. hainanese | 地毯草炭疽菌生长较慢,木霉菌生长较快,当两菌落菌丝接触时,木霉菌菌落已占据大部分生长空间,导致地毯草炭疽菌停止生长,被木霉菌菌落迅速包围并覆盖。C. hainanese mycelium grew slowly, while Trichoderma spp. grows faster. When the two colonies contact, Trichoderma spp. colonies have occupied most of the growth space, resulting in the stopped growth of C. hainanese mycelium and the colonies are quickly surrounded and covered by Trichoderma spp. | Ⅱ |
灰葡萄孢菌 B. cinerea | 当两菌菌落接触后,灰葡萄孢菌停止生长,3 d后木霉菌菌丝迅速覆盖灰葡萄孢菌菌落表面,5 d后木霉菌菌丝已将灰葡萄孢菌菌落覆盖了一半,并产生大量孢子。When the two colonies contacted, the growth of B. cinerea stopped, and Trichoderma spp. mycelium covered the surface of B. cinerea rapidly after 3 days, then Trichoderma spp. mycelium covered half of B. cinerea after 5 days, and produced a large number of conidia. | Ⅱ |
| 禾顶囊壳禾谷变种G. graminis var. graminis | 禾顶囊壳禾谷变种病原菌生长较慢,当两菌落菌丝接触时,木霉菌菌落已占据大部分生长空间,导致禾顶囊壳禾谷变种停止生长,被木霉菌菌落迅速覆盖。The growth rate of G. graminis var. graminis was relatively slow. When the two colonies contacted, Trichoderma spp. had occupied most of the growth space, leading to the stop of growth of G. graminis var. graminis and the rapid coverage Trichoderma spp. | Ⅱ |
雀稗微座孢 M. paspali | 两菌落开始接触后,木霉菌逐渐侵占雀稗微座孢的营养及生长空间,使雀稗微座孢无法继续生长,很快被木霉菌落覆盖。After the two colonies began to contact, Trichoderma spp. gradually invaded the nutrition and growth space of M. paspali, making it impossible to continue to grow and was soon covered by Trichoderma spp. colony. | Ⅱ |
木贼镰刀菌 F. equiseti | 两菌落接触后,木贼镰刀菌菌落停止生长,5 d后整个菌落被木霉菌包围,但没有被覆盖,并在两菌交接处产生大量分生孢子。After the two colonies began to contact, the growth of F. equiseti stopped. After 5 days growth, the entire colony was surrounded but not covered by Trichoderma spp., and a large number of conidia were produced at the junction of the two colonies. | Ⅲ |
| 草坪草币斑病病原菌S. homoeocarpa | 当两菌落接触后,木霉菌菌丝开始向草坪草币斑病病原菌中心扩展和蔓延,使其生长受到抑制,无明显的抑菌带。5 d后,草坪草币斑病病原菌已被大面积覆盖。When the two colonies contacted, Trichoderma spp. mycelium began to expand and spread to the center of the colony S. homoeocarpa, which inhibited its growth without obvious bacteriostatic zone. After 5 days growth, the colony S. homoeocarpa had been extensively covered. | Ⅲ |
新月弯孢霉 C. lunata | 两菌落接触后,在接触边缘产生了棕色抑菌带,新月弯孢霉停止生长,抑菌带处木霉孢子较少,也无覆盖病原菌的趋势。After the two colonies contacted, there was a brown bacteriostatic zone at the contact edge, and the growth of C. lunata stopped, and there were few of Trichoderma spp. conidia in the bacteriostatic zone, and there was no tendency to cover the colony of C. lunata. | Ⅳ |
球黑孢霉 N. sphaerica | 两菌菌落交接后球黑孢霉停止生长,产生明显棕黄色的抑菌圈,且交接处球黑孢霉部分菌丝消解,使球黑孢霉菌丝不能向外扩展和生长,但木霉菌菌丝并没有将其覆盖。After the two colonies contacted, the growth of N. sphaerica stopped, resulting in an obvious brownish yellow inhibition zone. Moreover, part of mycelium of N. sphaerica were destroyed at the junction, making the mycelium of N. sphaerica unable to grow outward, but the mycelium of Trichoderma spp. did not cover colony of N. sphaerica. | Ⅳ |
草茎点霉 P. herbarum | 当两菌落接触后,SQ-1Q-18木霉大量侵占草茎点霉的生长空间,使草茎点霉的生长受到抑制,5 d后木霉菌菌丝将其包围,并在其边缘产生大量的分生孢子。When the two colonies contacted, Trichoderma spp. isolate SQ-1Q-18 invaded the growth space of P. herbarum, which inhibited its growth. After 5 days, Trichoderma spp. mycelium surrounded the colony of P. herbarum and produced a large number of conidia at its edge. | Ⅳ |
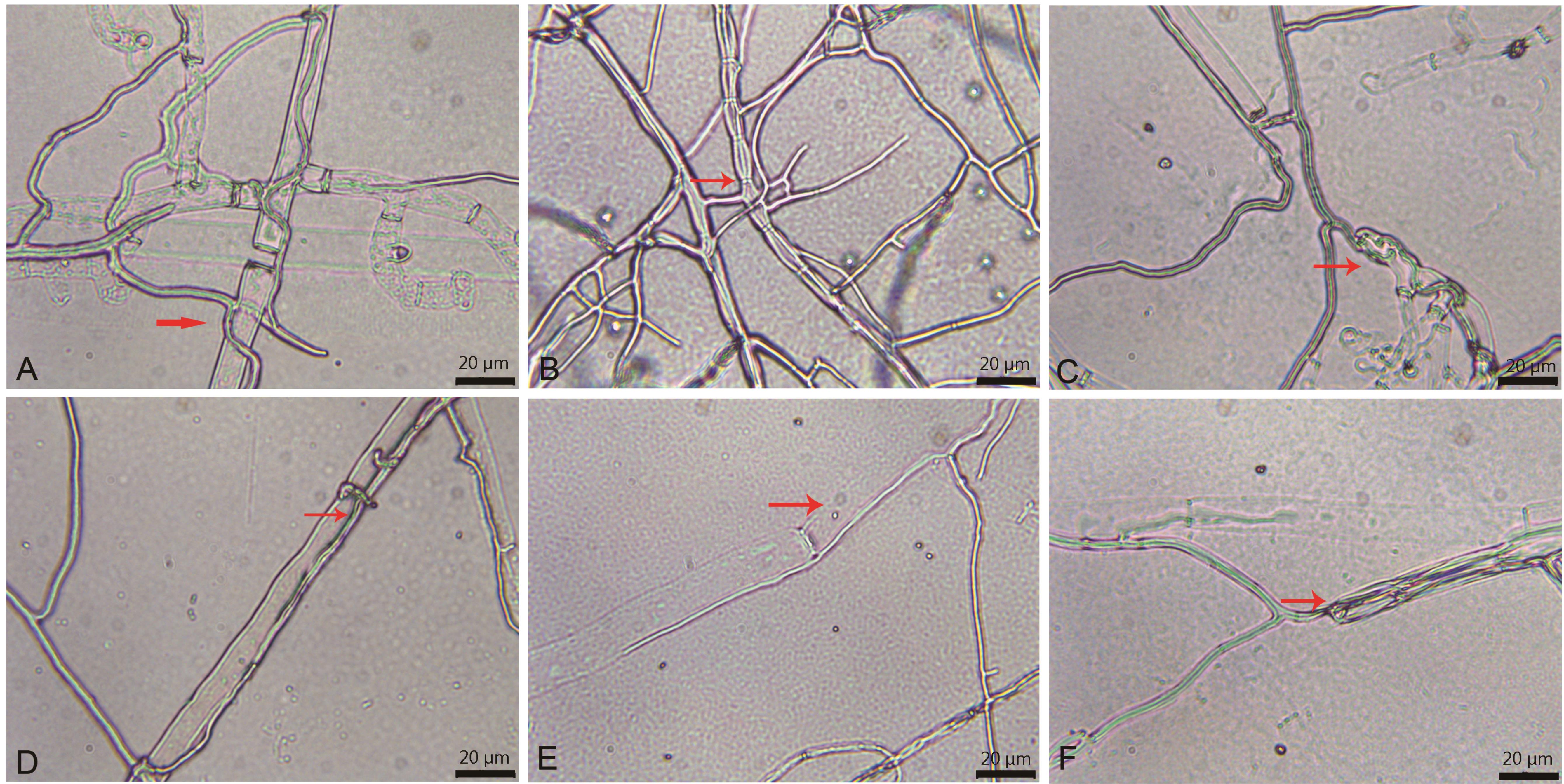
图4 木霉菌株SQ-1Q-18对立枯丝核菌菌丝的作用方式A: 缠绕Intertwine; B: 缢缩Constriction; C: 断裂Breakage; D: 穿入Penetration; E: 寄生Parasitism; F: 降解Degradation.
Fig.4 Effect of Trichoderma isolate SQ-1Q-18 on the hyphae growth of R. solani
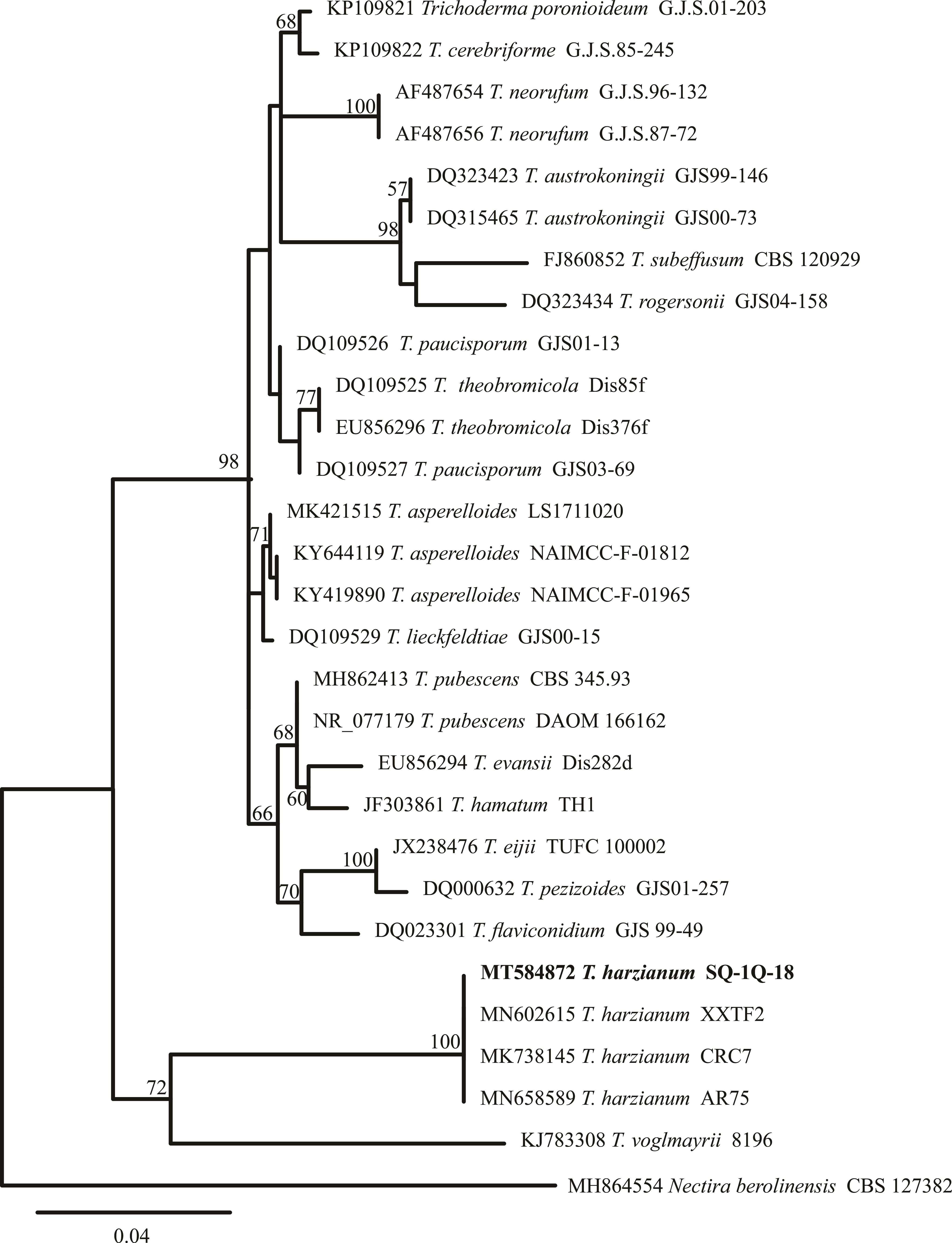
图7 基于木霉属真菌ITS序列建立的最大似然法系统发育树自展支持率大于50%的数值置于分支处。菌株SQ-1Q-18加粗显示。Maximum likelihood bootstrap support values (>50%) are shown at the nodes. Stain SQ-1Q-18 was marked with bold.
Fig.7 Phylogenetic tree of Trichoderma spp.resulting from a maximum likelihood analysis of the ITS sequence alignment
| 1 | Garrett K A, Nita M, De Wolf E D, et al. Plant pathogens as indicators of climate change. Climate Change, 2009: 425-437. |
| 2 | Kashyap P L, Rai P, Srivastava A K, et al. Trichoderma for climate resilient agriculture. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2017, 33(8): 155. |
| 3 | Zhang S W, Liu J, Xu B L, et al. Parasitic and lethal effects of Trichoderma longibrachiatum on Heterodera avenae: Microscopic observation and bioassay. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(10): 2955-2960. |
| 张树武, 刘佳, 徐秉良, 等. 长枝木霉对禾谷胞囊线虫寄生和致死作用的显微观察及测定. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(10): 2955-2960. | |
| 4 | Giurgiu R M, Dumitraᶊ A, Morar G, et al. A study on the biological control of Fusarium oxysporum using Trichoderma spp., on soil and rockwool substrates in controlled environment. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca, 2018, 46(1): 260-269. |
| 5 | Jaklitsch W M, Voglmayr H. Biodiversity of Trichoderma (Hypocreaceae) in Southern Europe and Macaronesia. Studies in Mycology, 2015, 80: 1-87. |
| 6 | Howell C R. Mechanisms employed by Trichoderma species in the biological control of plant diseases: The history and evolution of current concepts. Plant Disease, 2003, 87(1): 4-10. |
| 7 | Peng K W, Li C. Review on biocontrol research with Trichoderma. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(2): 780-782. |
| 彭可为, 李婵. 木霉菌的生物防治研究进展. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(2): 780-782. | |
| 8 | Saravanakumar K, Yu C, Dou K, et al. Synergistic effect of Trichoderma-derived antifungal metabolites and cell wall degrading enzymes on enhanced biocontrol of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cucumerinum. Biological Control, 2016, 94: 37-46. |
| 9 | Barak R. Lectins: A possible basis for specific recognition in the interaction of Trichoderma and Sclerotium rolfsii. Phytopathology, 1985, 75(4): 458-462. |
| 10 | Chen J, Zhu J W, Zhang T, et al. Progress on mechanism and applications of Trichoderma as a biocontrol microbe. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2011, 27(2): 145-151. |
| 陈捷, 朱洁伟, 张婷, 等. 木霉菌生物防治作用机理与应用研究进展. 中国生物防治学报, 2011, 27(2): 145-151. | |
| 11 | Hanson L E, Howell C R. Elicitors of plant defense responses from biocontrol strains of Trichoderma virens. Phytopathology, 2004, 94(2): 171-176. |
| 12 | Yedidia I, Benhamou N, Chet I. Induction of defense responses in cucumber plants (Cucumis sativus L.) by the biocontrol agent Trichoderma harzinum. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(3): 1061-1070. |
| 13 | Bisen K, Keswani C, Patel J S, et al. Trichoderma spp.: Efficient inducers of systemic resistance in plants. Springer Singapore, 2016: 185-195. |
| 14 | Weindling R. Studies on lethal principle effective in the parasitic action of Trichoderma hamaium on Rhizoclonia solani and other soil fungi. Phytopathology, 1934, 24: 1153-1179. |
| 15 | Zhang F L, Ge H L, Zhang F, et al. Biocontrol potential of Trichoderma harzianum isolate T-aloe against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in soybean. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2016, 100: 64-74. |
| 16 | Macías-Rodríguez L, Guzmán-Gómez A, García-Juárez P, et al. Trichoderma atroviride promotes tomato development and alters the root exudation of carbohydrates, which stimulates fungal growth and the biocontrol of the phytopathogen Phytophthora cinnamomi in a tripartite interaction system. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2018, 94(9): 137. |
| 17 | Harman G E. Myths and dogmas of biocontrol changes in perceptions derived from research on Trichoderma harziamum T-22. Plant Discase, 2000, 84(4): 377-393. |
| 18 | Zimand G. Effect of Trichoderma harzianum on Botrytis cinerea pathogenicity. Phytothology, 1996, 86(11): 1255-1260. |
| 19 | Li X M,Li Q, Wei L L, et al. Research on water dispersible granules of Trichoderma harzianum T4 Chlamydospores. Agrochemicals, 2013, 52(1): 24-27, 40. |
| 李秀明, 李卿, 韦灵林, 等. 哈茨木霉T4厚垣孢子水分散粒剂的研制. 农药, 2013, 52(1): 24-27, 40. | |
| 20 | Jing F, Xu B L, Liang Q L, et al. Research and development of water dispersible granules of Trichoderma longibrachiatum T6. Chinese Journal of Pestcide Science, 2016, 18(2): 241-248. |
| 景芳, 徐秉良, 梁巧兰, 等. 长枝木霉Trichoderma longibrachiatum T6水分散粒剂的研制. 农药学学报, 2016, 18(2): 241-248. | |
| 21 | Yang C P, Zhang J K, Chen H B, et al. Preparation of Trichoderm viride L24 conidia wettable powder. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2010, 19(9): 43-47. |
| 杨春平, 张晋康, 陈华保, 等. 绿色木霉L24菌株分生孢子可湿性粉剂的研制. 西北农业学报, 2010, 19(9): 43-47. | |
| 22 | Zeng Y J. Application effects of Telixe against tomato gray mold. Liaoning Agricultural Sciences, 2009(6): 53-54. |
| 曾艳君. 特立克防治番茄灰霉病应用效果. 辽宁农业科学, 2009(6): 53-54. | |
| 23 | Shang H S, Wang F K. Turf diseases and insect pests and their control. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1997. |
| 商鸿生, 王凤葵. 草坪病虫害及其防治. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1997. | |
| 24 | Nan Z B, Li C J. Compendium of fungal diseases of forage grass of China. Pratacultural Science (Supplement), 1994: 3-30. |
| 南志标, 李春杰. 中国牧草真菌病害名录. 草业科学(增刊), 1994: 3-30. | |
| 25 | Smiley R W, Dernoeden P H, Clarke B B. Compendium of turfgrass diseases. Saint Paul: The American Phytopathological Society Press, 2005. |
| 26 | Xu B L. Turfgrass protection. Beijing: China Forestry Pubishing House, 2013. |
| 徐秉良. 草坪保护学. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2013. | |
| 27 | Xie L M, Chang C L, Yao Z H, et al. Growth promotion and resistance induction effect of Trichoderma harzianum on Festuca rubra and Poa pratensis. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(9): 2079-2086. |
| 谢琳淼, 常春丽, 姚志红, 等. 哈茨木霉对紫羊茅和草地早熟禾的促生及抗性诱导作用. 草业科学, 2018, 35(9): 2079-2086. | |
| 28 | Yao Y P, Lv G Z, Zhang S J, et al. Antagonistic effect of Trichoderma against Rhizoctonia Solani and Fusarium Oxysporum occurring on turfgrass. Grassland and Turf, 2006(6): 52-55, 59. |
| 姚彦波, 吕国忠, 张淑金, 等. 草坪褐斑病病菌和镰刀枯萎病菌拮抗木霉菌的筛选及效果研究. 草原与草坪, 2006(6): 52-55, 59. | |
| 29 | Chao L J, Shan X M, Che S C, et al. Study on causal agent, epidemic law and integrated control techniques of turfgrass brown patch disease. Grassland of China, 2000(4): 42-47. |
| 晁龙军, 单学敏, 车少臣, 等. 草坪草褐斑病病原菌鉴定、流行规律及其综合控制技术的研究. 中国草地, 2000(4): 42-47. | |
| 30 | Gu L J, Xu B L, Liang Q L, et al. Antagonism and mechanism of action of Trichoderma aureoviride against Pythium a phanidermatum causing turfgrass root rot. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2011, 20(2): 46-51. |
| 古丽君, 徐秉良, 梁巧兰, 等. 生防木霉菌T2菌株对禾草腐霉病抑菌作用及机制研究. 草业学报, 2011, 20(2): 46-51. | |
| 31 | Lo C T, Nelson E B, Harman G E. Improved biocontrol efficacy of Trichoderma harzianum 1295-22 for foliar phases of turf diseases by use of spray applications. Plant Disease, 1997, 81(10): 1132-1138. |
| 32 | Gao K X, Liu X G, Guo R F, et al. Mycoparasitism of Trichoderma spp. on five plant pathogenic fungi. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University (Natural Science), 2002, 33(1): 37-42. |
| 高克祥, 刘晓光, 郭润芳, 等. 木霉菌对五种植物病原真菌的重寄生作用. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 33(1): 37-42. | |
| 33 | ZhangJ, Zhang S W, Xu B L, et al. Determining antifungal spectrum and mechanism of Trichoderma longibrachiatum in vitro. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2014, 22(6): 661-667. |
| 张瑾, 张树武, 徐秉良, 等. 长枝木霉菌抑菌谱测定及其抑菌作用机理研究. 中国生态农业学报, 2014, 22(6): 661-667. | |
| 34 | Van Burik J H, Schreckhise R W, White T C, et al. Comparison of six extraction techniques for isolation of DNA from filamentous fungi. Medical Mycology, 1998, 36(5): 299-303. |
| 35 | White T J, Bruns T, Lee S, et al. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR Protocols : A Guide to Methods & Applications, 1990, 18(1): 315-322. |
| 36 | Da Silva J A T, De Medeiros E V, Da Silva J M, et al. Trichoderma aureoviride URM 5158 and Trichoderma hamatum URM 6656 are biocontrol agents that act against cassava root rot through different mechanisms. Journal of Phytopathology, 2016, 164(11/12): 1003-1011. |
| 37 | Nawrocka J, Małolepsza U, Szymczak K, et al. Involvement of metabolic components, volatile compounds, PR proteins, and mechanical strengthening in multilayer protection of cucumber plants against Rhizoctonia solani activated by Trichoderma atroviride TRS25. Protoplasma, 2018, 255(1): 359-373. |
| 38 | Singh A, Shukla N, Kabadwal B C, et al. Review on plant-Trichoderma-pathogen interaction. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 2018, 7(2): 2382-2397. |
| 39 | Zhang M, Wu B, Xu D K, et al. Antagonistic mechanism of Trichoderma asperellum JM-1 against Bipolaris sorokiniana. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 51(3): 92-96. |
| 张眉, 吴斌, 徐德坤, 等. 棘孢木霉JM-1菌株对麦根腐离蠕孢的拮抗机制. 山东农业科学, 2019, 51(3): 92-96. | |
| 40 | El-Katatny M H, Emam A S. Control of postharvest tomato rot by spore suspension and antifungal metabolites of Trichoderma harzianum. Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology & Food Sciences, 2012, 1(6): 1505-1528. |
| 41 | Almassi F, Ghisalberti E L, Narbey M J, et al. New antibiotics from strains of Trichoderma harzianum. Journal of Natural Products, 1991, 54(2): 396-402. |
| 42 | Vinale F, Marra R, Scala F, et al. Major secondary metabolites produced by two commercial Trichoderma strains active against different phytopathogens. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 2006, 43(2): 143-148. |
| 43 | Zeilinger S, Gruber S, Bansal R, et al. Secondary metabolism in Trichoderma-Chemistry meets genomics. Fungal Biology Reviews, 2016, 30(2): 74-90. |
| 44 | Xie K Z, Hu X Y, Zhang T T, et al. Effects of different soil amendment measures on soil water relations, microbial community structure and yield in potato continuous cropping in dry land. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(7): 103-111. |
| 谢奎忠, 胡新元, 张彤彤, 等. 不同杀菌剂对旱地连作马铃薯土壤水分效应、微生物和产量的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 103-111. | |
| 45 | Ji C D, Li J F. Isolation and screening of antagonistic Trichoderma strains against fairy ring on golf turf. Grassland and Turf, 2017, 37(3): 81-85. |
| 姬承东, 李剑峰. 高尔夫草坪蘑菇圈真菌拮抗木霉菌株的筛选及其抑菌作用. 草原与草坪, 2017, 37(3): 81-85. | |
| 46 | Yao Y P, Yao X M, Wang H Y, et al. A strain of Trichoderma hamatum and its application in the control of Fusarium diseases of turfgrass: China. CN103952320A. 2014-07-30. |
| 姚彦坡, 姚贤民, 王洪瑛, 等. 一株哈茨木霉及其在防控草坪镰刀枯萎病中的应用: 中国. CN103952320A. 2014-07-30. | |
| 47 | Yao Y P, Wang Y, Wang H Y, et al. A strain of Trichoderma hamatum and its application in the control of Brown patch of turfgrass: China. CN103952321A. 2014-07-30. |
| 姚彦坡, 王禹, 王洪瑛, 等. 一株哈茨木霉及其在防控草坪褐斑病中的应用: 中国. CN103952321A. 2014-07-30. |
| [1] | 古丽君,徐秉良,梁巧兰,李荣峰. 生防木霉菌T2菌株对禾草腐霉病抑菌作用及机制研究[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(2): 46-51. |
| [2] | 张茹,李金花,柴兆祥,王蒂. 甘肃河西马铃薯根际生防木霉菌对接骨木镰刀菌的拮抗筛选及鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2009, 18(2): 138-145. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||