

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 13-28.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020410
罗超1( ), 郭小平1(
), 郭小平1( ), 冯昶栋1, 叶金鹏2, 薛东明1
), 冯昶栋1, 叶金鹏2, 薛东明1
收稿日期:2020-09-17
修回日期:2020-10-19
出版日期:2021-10-19
发布日期:2021-10-19
通讯作者:
郭小平
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: guoxp@bjfu.edu.cn基金资助:
Chao LUO1( ), Xiao-ping GUO1(
), Xiao-ping GUO1( ), Chang-dong FENG1, Jin-peng YE2, Dong-ming XUE1
), Chang-dong FENG1, Jin-peng YE2, Dong-ming XUE1
Received:2020-09-17
Revised:2020-10-19
Online:2021-10-19
Published:2021-10-19
Contact:
Xiao-ping GUO
摘要:
土壤种子库是植被自然更新和恢复的物质基础,对干旱荒漠区生态恢复具有重要意义。本研究以内蒙古乌海周边为研究区,选择典型生境和植被类型,通过样地植被调查、持久和短暂土壤种子库采样、萌发试验、土壤理化性质分析,对土壤种子库特征及其与地上植被和土壤因子的关系进行探讨。结果表明:1)乌海及周边土壤种子库平均密度为217~1547粒·m-2,物种以多年生草本为主,种子库密度随土壤深度的增加呈下降趋势。持久土壤种子库占种子库总密度的17.34%~64.22%,且轻度和中度干扰样地的持久种子库占比达40%以上。2)不同生境和植被类型下的土壤种子库差异较为显著,相近地理环境下的土壤种子库具有一定相似性,但中度干扰下的样地种子库密度和物种多样性要高于周边轻度干扰的样地。3)新星矿区周边土壤种子库与地上植被相似性较高,其他区域土壤种子库与地上植被在组成和结构上存在较大差异。4)土壤种子库物种在不同土壤环境中呈现不同的聚类,土壤因子只能部分(30%~40%)反映土壤种子库特征。影响0~5 cm和5~10 cm持久土壤种子库的最主要土壤因子分别为有机质、粉粒、黏粒含量和砾石含量,影响0~5 cm和5~10 cm短暂土壤种子库的最主要土壤因子分别为全磷、黏粒含量和容重、有机质。上述研究可为乌海周边表土种子库的植被恢复潜力及恢复技术提供理论依据和支撑。
罗超, 郭小平, 冯昶栋, 叶金鹏, 薛东明. 乌海周边土壤种子库特征及其与地上植被和土壤因子的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 13-28.
Chao LUO, Xiao-ping GUO, Chang-dong FENG, Jin-peng YE, Dong-ming XUE. The characteristics of the soil seed bank in Wuhai and surrounding areas and the relationship with vegetation and soil factors[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(11): 13-28.
样地代号 Name | 样地位置 Sample location | 地形 Topography | 土壤类型 Soil type | 土壤质地 Soil texture | 干扰程度 Disturbance | 植被盖度 Coverage (%) | 主要植物种 Major species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SHS | 四合木自然保护区 Sihemu Nature Reserve | 低山坡面 Slope of low mountain | 棕钙土 Brown soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 轻度 Mild | 22 | 四合木T. mongolica, 红砂Reaumuria songarica, 克氏针茅Stipa krylovii |
| SHP | 四合木自然保护区 Sihemu Nature Reserve | 山前平地 Piedmont plain | 棕钙土 Brown soil | 细砂土 Fine sand | 轻度 Mild | 48 | 四合木T. mongolica, 珍珠猪毛菜Salsola passerina, 克氏针茅S. krylovii |
| LTS | 骆驼山矿区周边 Luotuoshan Mining Area | 平地 Plain | 棕钙土 Brown soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 中度 Intermediate | 38 | 红砂R. songarica, 珍珠猪毛菜S. passerina, 克氏针茅S. krylovii |
| MX | 蒙西自然保护区 Mengxi Nature Reserve | 平地 Plain | 风沙土 Aeolian sandy soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 轻度 Mild | 37 | 红砂R. songarica, 霸王Sarcozygium xanthoxylon, 无芒隐子草Cleistogenes songorica |
| MXI | 蒙西工业区附近 Mengxi industrial zone | 平地 Plain | 风沙土 Aeolian sandy soil | 细砂土 Fine sand | 中度 Intermediate | 21 | 红砂R. songarica, 霸王S. xanthoxylon, 无芒隐子草C.songorica |
| QPJS | 棋盘井东南丘陵 Qipanjing Southeast hill | 丘陵坡面 Slope of hill | 灰漠土 Gray desert soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 轻度 Mild | 39 | 半日花H. songaricum, 砂蓝刺头Echinops gmelini, 戈壁针茅Stipa tianschanica |
| QPJP | 棋盘井东南丘陵 Qipanjing Southeast hill | 平地 Plain | 灰漠土 Gray desert soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 中度 Intermediate | 35 | 黑沙蒿Artemisia ordosica, 砂蓝刺头E. gmelini, 短花针茅Stipa breviflora |
| QPJI | 棋盘井工业区附近 Qipanjing industrial zone | 平地 Plain | 灰漠土 Gray desert soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 中度 Intermediate | 30 | 红砂R. songarica, 戈壁针茅S. tianschanica, 芨芨草Achnatherum splendens |
| XXS | 新星煤矿南侧区域 South of Xinxing Minging area | 平地 Plain | 灰漠土 Gray desert soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 中度 Intermediate | 33 | 猫头刺Oxytropis aciphylla, 沙生针茅Stipa glareosa, 无芒隐子草C. songorica |
| XXW | 新星煤矿西侧区域 West of Xinxing Minging area | 平地 Plain | 灰漠土 Gray desert soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 轻度 Mild | 35 | 猫头刺O. aciphylla, 红砂R. songarica, 沙生针茅S. glareosa, 无芒隐子草C. songorica |
| XXM | 新星煤矿采区附近 Xinxing Minging area | 平地 Plain | 灰漠土 Gray desert soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 重度 Severe | 23 | 沙生针茅S. glareosa, 无芒隐子草C. songorica, 雾冰藜Bassia dasyphylla |
| HLW | 贺兰山西坡北段 The northern part of the western slope of Helan Mountain | 台地 Meseta | 灰钙土 Sierozem soil | 粉砂土 Mealy sand | 轻度 Mild | 40 | 红砂R. songarica, 珍珠猪毛菜S. passerina, 无芒隐子草C. songorica |
表1 样地概况
Table 1 Sample plot overview
样地代号 Name | 样地位置 Sample location | 地形 Topography | 土壤类型 Soil type | 土壤质地 Soil texture | 干扰程度 Disturbance | 植被盖度 Coverage (%) | 主要植物种 Major species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SHS | 四合木自然保护区 Sihemu Nature Reserve | 低山坡面 Slope of low mountain | 棕钙土 Brown soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 轻度 Mild | 22 | 四合木T. mongolica, 红砂Reaumuria songarica, 克氏针茅Stipa krylovii |
| SHP | 四合木自然保护区 Sihemu Nature Reserve | 山前平地 Piedmont plain | 棕钙土 Brown soil | 细砂土 Fine sand | 轻度 Mild | 48 | 四合木T. mongolica, 珍珠猪毛菜Salsola passerina, 克氏针茅S. krylovii |
| LTS | 骆驼山矿区周边 Luotuoshan Mining Area | 平地 Plain | 棕钙土 Brown soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 中度 Intermediate | 38 | 红砂R. songarica, 珍珠猪毛菜S. passerina, 克氏针茅S. krylovii |
| MX | 蒙西自然保护区 Mengxi Nature Reserve | 平地 Plain | 风沙土 Aeolian sandy soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 轻度 Mild | 37 | 红砂R. songarica, 霸王Sarcozygium xanthoxylon, 无芒隐子草Cleistogenes songorica |
| MXI | 蒙西工业区附近 Mengxi industrial zone | 平地 Plain | 风沙土 Aeolian sandy soil | 细砂土 Fine sand | 中度 Intermediate | 21 | 红砂R. songarica, 霸王S. xanthoxylon, 无芒隐子草C.songorica |
| QPJS | 棋盘井东南丘陵 Qipanjing Southeast hill | 丘陵坡面 Slope of hill | 灰漠土 Gray desert soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 轻度 Mild | 39 | 半日花H. songaricum, 砂蓝刺头Echinops gmelini, 戈壁针茅Stipa tianschanica |
| QPJP | 棋盘井东南丘陵 Qipanjing Southeast hill | 平地 Plain | 灰漠土 Gray desert soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 中度 Intermediate | 35 | 黑沙蒿Artemisia ordosica, 砂蓝刺头E. gmelini, 短花针茅Stipa breviflora |
| QPJI | 棋盘井工业区附近 Qipanjing industrial zone | 平地 Plain | 灰漠土 Gray desert soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 中度 Intermediate | 30 | 红砂R. songarica, 戈壁针茅S. tianschanica, 芨芨草Achnatherum splendens |
| XXS | 新星煤矿南侧区域 South of Xinxing Minging area | 平地 Plain | 灰漠土 Gray desert soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 中度 Intermediate | 33 | 猫头刺Oxytropis aciphylla, 沙生针茅Stipa glareosa, 无芒隐子草C. songorica |
| XXW | 新星煤矿西侧区域 West of Xinxing Minging area | 平地 Plain | 灰漠土 Gray desert soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 轻度 Mild | 35 | 猫头刺O. aciphylla, 红砂R. songarica, 沙生针茅S. glareosa, 无芒隐子草C. songorica |
| XXM | 新星煤矿采区附近 Xinxing Minging area | 平地 Plain | 灰漠土 Gray desert soil | 粗砂土 Coarse sand | 重度 Severe | 23 | 沙生针茅S. glareosa, 无芒隐子草C. songorica, 雾冰藜Bassia dasyphylla |
| HLW | 贺兰山西坡北段 The northern part of the western slope of Helan Mountain | 台地 Meseta | 灰钙土 Sierozem soil | 粉砂土 Mealy sand | 轻度 Mild | 40 | 红砂R. songarica, 珍珠猪毛菜S. passerina, 无芒隐子草C. songorica |

图2 土壤种子库物种组成X1芨芨草A. splendens, X2小画眉草E. minor, X3砾苔草C. stenophylloides, X4红砂R. songarica, X5盐生草Halogeton glomeratus, X6克氏针茅S. krylovii, X7沙生针茅S. glareosa, X8戈壁针茅S. tianschanica, X9短花针茅S. breviflora, X10珍珠猪毛菜S. passerine, X11猪毛蒿A. scoparia, X12冷蒿A. frigida, X13沙蒿Artemisia desertorum, X14狗尾草Setaria viridis, X15三芒草Aristida adscensionis, X16霸王S. xanthoxylon, X17顶羽菊Rhaponticum repens, X18北高山大戟Euphorbia alpine, X19蝎虎驼蹄瓣Zygophyllum mucronatum, X20狭叶锦鸡儿Caragana stenophylla, X21柠条锦鸡儿Caragana korshinskii, X22兴安胡枝子Lespedeza potaninii, X23砂蓝刺头E. gmelini, X24狭叶米口袋Gueldenstaedtia stenophylla, X25冰草Agropyron cristatum, X26无芒隐子草C. songorica, X27冠芒草Enneapogon borealis, X28细叶韭Allium tenuissimum, X29蒺藜Tribulus terrestris, X30赖草Leymus secalinus, X31黄花葱Allium condensatum, X32蒙古韭Allium mongolicum, X33藜Chenopodium album, X34银灰旋花Convolvulus ammannii, X35猫头刺O. aciphylla, X36栉叶蒿Neopallasia petinata, X37中亚滨藜Atriplex centralasiatica, X38雾冰藜G. dasyphylla, X39四合木T. mongolica, X40骆驼蓬Peganum harmala, X41刺沙蓬Salsola ruthenica. F1百合科Liliaceae, F2柽柳科Tamaricaceae, F3大戟科Euphorbiaceae, F4豆科Leguminosae, F5禾本科Gramineae, F6蒺藜科Zygophyllaceae, F7菊科Asteraceae, F8藜科Chenopodiaceae, F9莎草科Cyperaceae, F10旋花科Convolvulaceae.
Fig.2 The species composition of soil seed bank
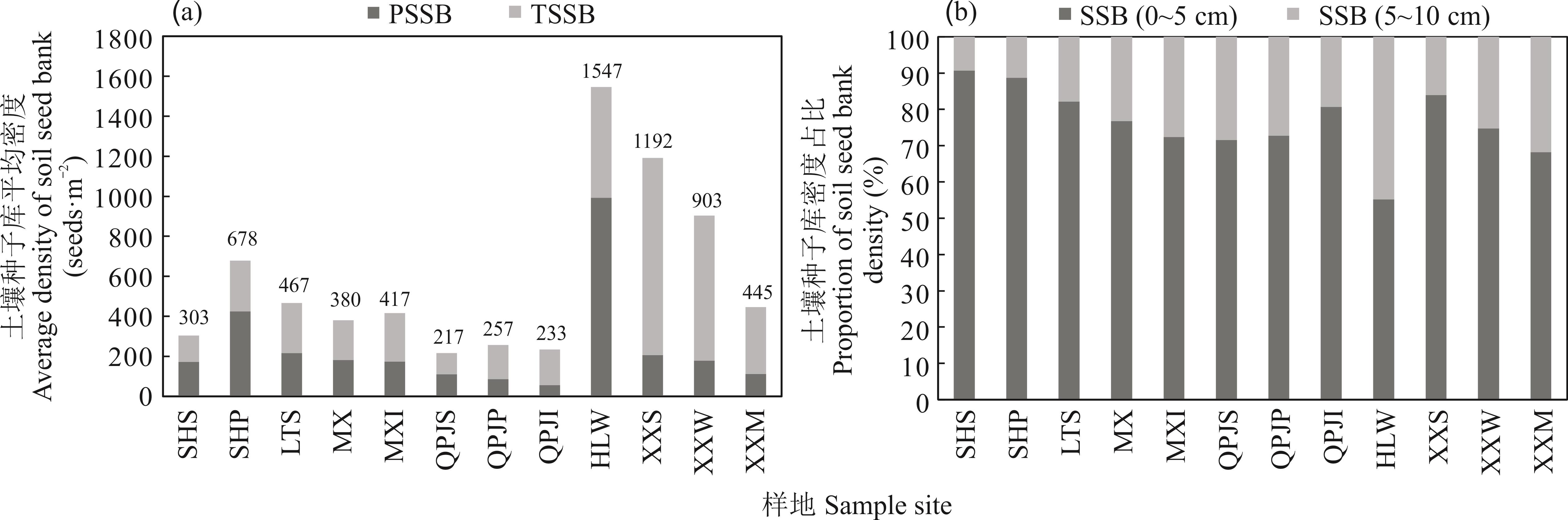
图4 各样地土壤种子库平均密度和垂直分布PSSB: 持久土壤种子库Persistent soil seed bank; TSSB: 短暂土壤种子库Transient soil seed bank; SSB: 土壤种子库Soil seed bank. 下同The same below.
Fig. 4 The average seed density and vertical distribution of soil seed bank in different sample
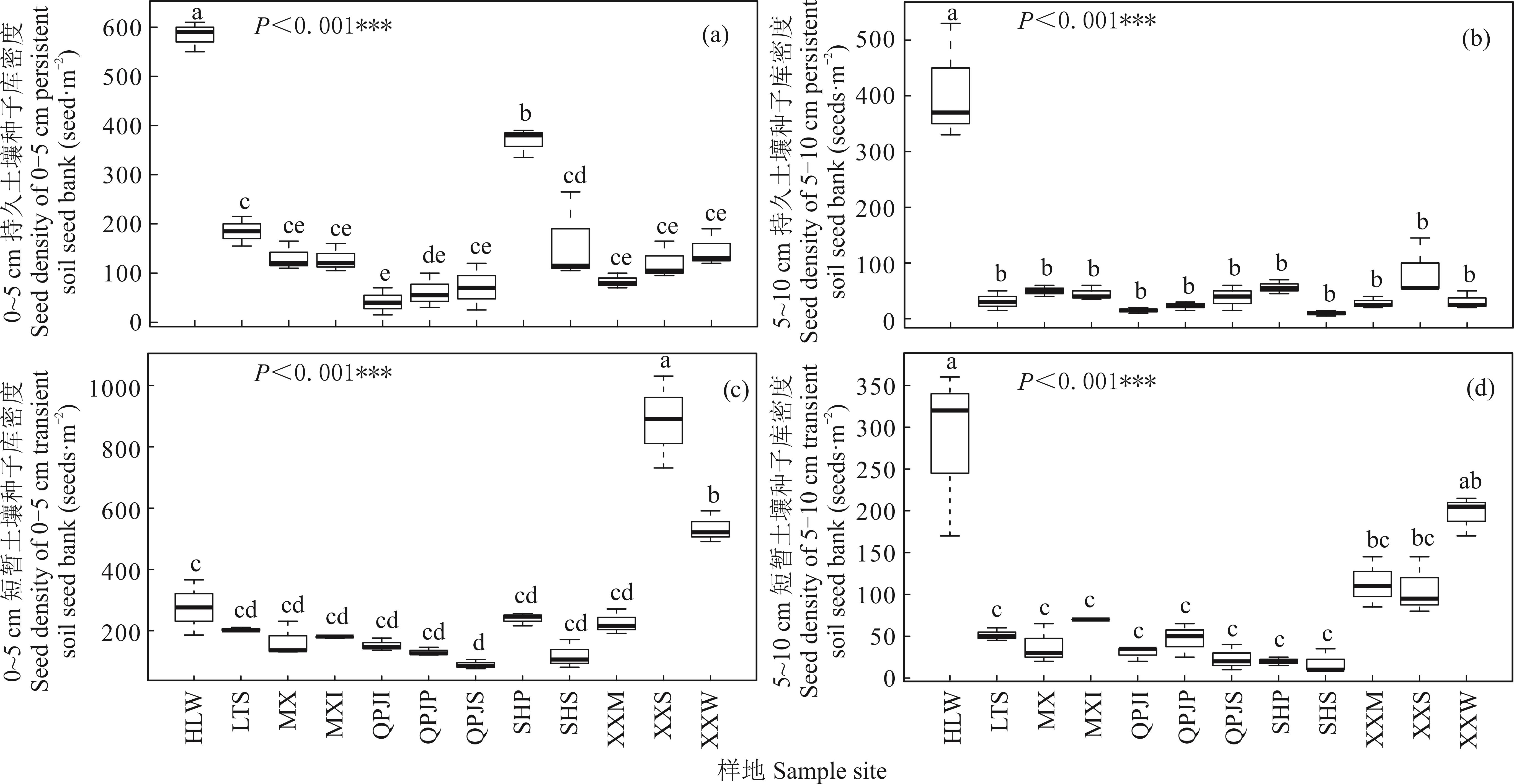
图5 不同深度持久和短暂土壤种子库密度不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different small letter indicates significance differences at the P<0.05 level, the same below.
Fig.5 The seed density of persistent and transient soil seed bank in different soil depth

图7 土壤种子库与地上植被物种相似性矩阵SHS_AGV为SHS样地的地上植被;SHS_TSSB为SHS样地的短暂土壤种子库;SHS_PSSB为SHS样地的持久土壤种子库;其他类推。SHS_AGV means aboveground vegetation in SHS sample site, SHS_TSSB means transient soil seed bank in SHS sample site, SHS_PSSB means persistent soil seed bank in SHS sample site. Other is in analogy.
Fig.7 The species similarity matrix of aboveground vegetation and soil seed bank

图8 土壤种子库与地上植被的NMDS排序SHS-ve为SHS样地的地上植被;SHS-t为SHS样地的短暂土壤种子库;SHS-p为SHS样地的持久土壤种子库;其他类推。SHS-ve means aboveground vegetation in SHS sample site, SHS-t means transient soil seed bank in SHS sample site, SHS-p means persistent soil seed bank in SHS sample site. Other are in analogy.
Fig.8 Nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) ordination of soil seed bank and aboveground vegetation
种子库类型 Types | 约束轴 Constraint axis | 所有约束轴特征值总和 Sum of all eigenvalue | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 物种方差累计占比 Cumulation percentage variance species date | 物种-土壤因子方差累计占比Cumulation percentage variance species-soil factor relation | 约束轴显著性检验Significance testing(P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSSB-5 cm | RDA1 | 0.386 | 0.137 | 0.240 | 0.422 | 0.009** |
| RDA2 | 0.065 | 0.354 | 0.619 | 0.009** | ||
| RDA3 | 0.049 | 0.441 | 0.768 | 0.009** | ||
| RDA4 | 0.028 | 0.489 | 0.852 | 0.027* | ||
| PSSB-10 cm | RDA1 | 0.361 | 0.099 | 0.168 | 0.341 | 0.009** |
| RDA2 | 0.061 | 0.271 | 0.539 | 0.009** | ||
| RDA3 | 0.049 | 0.354 | 0.704 | 0.009** | ||
| RDA4 | 0.036 | 0.416 | 0.822 | 0.036* | ||
| TSSB-5 cm | RDA1 | 0.444 | 0.105 | 0.164 | 0.314 | 0.008** |
| RDA2 | 0.097 | 0.315 | 0.599 | 0.008** | ||
| RDA3 | 0.047 | 0.388 | 0.734 | 0.008** | ||
| RDA4 | 0.039 | 0.448 | 0.844 | 0.008** | ||
| TSSB-10 cm | RDA1 | 0.297 | 0.097 | 0.169 | 0.378 | 0.006** |
| RDA2 | 0.074 | 0.299 | 0.670 | 0.006** | ||
| RDA3 | 0.045 | 0.377 | 0.809 | 0.024* | ||
| RDA4 | 0.034 | 0.436 | 0.901 | 0.330 |
表2 不同层土壤种子库与土壤因子的RDA分析
Table 2 Results of RDA between soil seed bank and soil factor in different soil depth
种子库类型 Types | 约束轴 Constraint axis | 所有约束轴特征值总和 Sum of all eigenvalue | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 物种方差累计占比 Cumulation percentage variance species date | 物种-土壤因子方差累计占比Cumulation percentage variance species-soil factor relation | 约束轴显著性检验Significance testing(P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSSB-5 cm | RDA1 | 0.386 | 0.137 | 0.240 | 0.422 | 0.009** |
| RDA2 | 0.065 | 0.354 | 0.619 | 0.009** | ||
| RDA3 | 0.049 | 0.441 | 0.768 | 0.009** | ||
| RDA4 | 0.028 | 0.489 | 0.852 | 0.027* | ||
| PSSB-10 cm | RDA1 | 0.361 | 0.099 | 0.168 | 0.341 | 0.009** |
| RDA2 | 0.061 | 0.271 | 0.539 | 0.009** | ||
| RDA3 | 0.049 | 0.354 | 0.704 | 0.009** | ||
| RDA4 | 0.036 | 0.416 | 0.822 | 0.036* | ||
| TSSB-5 cm | RDA1 | 0.444 | 0.105 | 0.164 | 0.314 | 0.008** |
| RDA2 | 0.097 | 0.315 | 0.599 | 0.008** | ||
| RDA3 | 0.047 | 0.388 | 0.734 | 0.008** | ||
| RDA4 | 0.039 | 0.448 | 0.844 | 0.008** | ||
| TSSB-10 cm | RDA1 | 0.297 | 0.097 | 0.169 | 0.378 | 0.006** |
| RDA2 | 0.074 | 0.299 | 0.670 | 0.006** | ||
| RDA3 | 0.045 | 0.377 | 0.809 | 0.024* | ||
| RDA4 | 0.034 | 0.436 | 0.901 | 0.330 |
| 项目Item | 土壤因子Soil factor | SOM | PC | CC | TK | TP | TN | GC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSSB-5 cm | 解释变异量Explain variance (%) | 11.67 | 6.26 | 4.70 | 3.91 | 3.63 | 2.48 | 2.42 | |
| 统计量Statistical magnitude | 16.37 | 8.78 | 6.60 | 5.48 | 5.10 | 3.48 | 3.40 | ||
| 显著性P | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.027 | 0.018 | ||
| 项目Item | 土壤因子Soil factor | CC | GC | SM | CP | SOM | PC | NCP | TK |
| PSSB-10 cm | 解释变异量Explain variance (%) | 5.14 | 4.94 | 4.87 | 4.74 | 4.70 | 4.27 | 2.54 | 2.76 |
| 统计量Statistical magnitude | 5.86 | 5.64 | 5.56 | 5.42 | 5.37 | 4.87 | 2.90 | 3.15 | |
| 显著性P | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.081 | 0.027 | |
| 项目Item | 土壤因子Soil factor | TP | CC | TK | SM | PC | PH | GC | SOM |
| TSSB-5 cm | 解释变异量Explain variance (%) | 8.37 | 8.14 | 5.94 | 4.55 | 3.49 | 3.30 | 3.24 | 2.99 |
| 统计量Statistical magnitude | 9.24 | 8.89 | 6.56 | 5.03 | 3.85 | 3.64 | 3.58 | 3.30 | |
| 显著性P | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.024 | 0.032 | |
| 项目Item | 土壤因子Soil factor | SBD | SOM | TK | GC | CC | CP | ||
| TSSB-10 cm | 解释变异量Explain variance (%) | 6.21 | 6.17 | 5.81 | 5.10 | 3.81 | 2.61 | ||
| 统计量Statistical magnitude | 6.51 | 6.46 | 6.08 | 5.34 | 3.99 | 2.74 | |||
| 显著性P | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.018 | 0.042 |
表3 土壤因子解释的重要性排序和显著性检验
Table 3 Importance and signification level of soil factors
| 项目Item | 土壤因子Soil factor | SOM | PC | CC | TK | TP | TN | GC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSSB-5 cm | 解释变异量Explain variance (%) | 11.67 | 6.26 | 4.70 | 3.91 | 3.63 | 2.48 | 2.42 | |
| 统计量Statistical magnitude | 16.37 | 8.78 | 6.60 | 5.48 | 5.10 | 3.48 | 3.40 | ||
| 显著性P | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.027 | 0.018 | ||
| 项目Item | 土壤因子Soil factor | CC | GC | SM | CP | SOM | PC | NCP | TK |
| PSSB-10 cm | 解释变异量Explain variance (%) | 5.14 | 4.94 | 4.87 | 4.74 | 4.70 | 4.27 | 2.54 | 2.76 |
| 统计量Statistical magnitude | 5.86 | 5.64 | 5.56 | 5.42 | 5.37 | 4.87 | 2.90 | 3.15 | |
| 显著性P | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.081 | 0.027 | |
| 项目Item | 土壤因子Soil factor | TP | CC | TK | SM | PC | PH | GC | SOM |
| TSSB-5 cm | 解释变异量Explain variance (%) | 8.37 | 8.14 | 5.94 | 4.55 | 3.49 | 3.30 | 3.24 | 2.99 |
| 统计量Statistical magnitude | 9.24 | 8.89 | 6.56 | 5.03 | 3.85 | 3.64 | 3.58 | 3.30 | |
| 显著性P | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.024 | 0.032 | |
| 项目Item | 土壤因子Soil factor | SBD | SOM | TK | GC | CC | CP | ||
| TSSB-10 cm | 解释变异量Explain variance (%) | 6.21 | 6.17 | 5.81 | 5.10 | 3.81 | 2.61 | ||
| 统计量Statistical magnitude | 6.51 | 6.46 | 6.08 | 5.34 | 3.99 | 2.74 | |||
| 显著性P | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.018 | 0.042 |
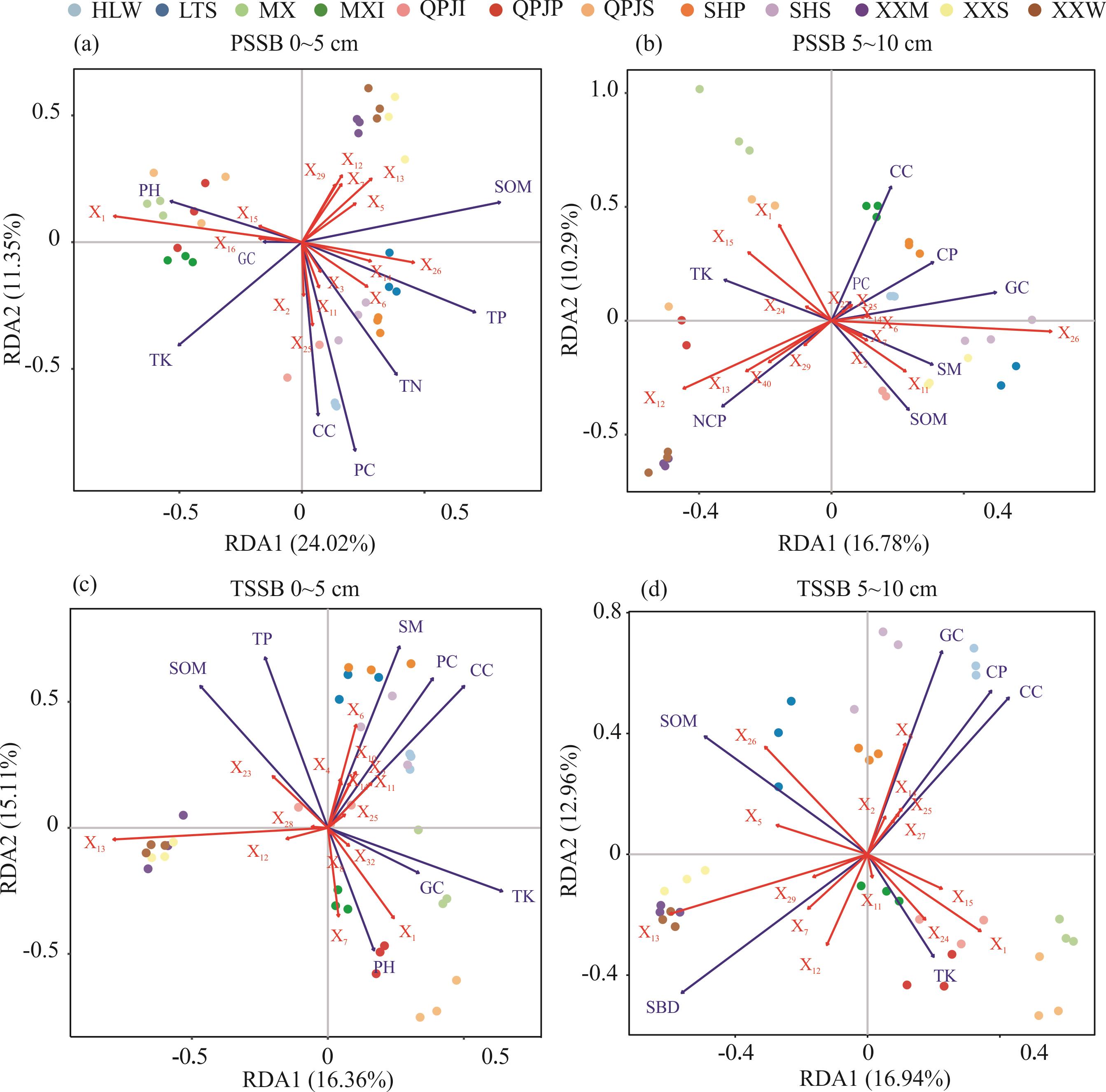
图9 土壤种子库与土壤因子的RDA排序排序图中红色箭头表示土壤因子,蓝色箭头表示植物种,各排序图仅展示土壤种子库密度前15的物种,编号对应的物种名称同前文图2。土壤因子简写同前文表3。The red arrows represent soil factors and the blue arrows represent plant species. Only the top 15 species in soil seed bank density were shown in each figure. The corresponding numbers of species names are the same as in Fig.2 above. The abbreviation of soil factors are the same as in Table 3 above.
Fig. 9 Biplot of the first two axes of the RDA for soil factor with soil seed bank
| 1 | Thompson K, Grime J P. Seasonal variation in the seed banks of herbaceous species in ten contrasting habitats. Journal of Ecology, 1979, 67(3): 893-921. |
| 2 | Ma M, Zhou X, Du G. Role of soil seed bank along a disturbance gradient in an alpine meadow on the Tibet Plateau. Flora, 2010, 205(2): 128-134. |
| 3 | Anderson T M, Schütz M, Risch A C. Seed germination cues and the importance of the soil seed bank across an environmental gradient in the Serengeti. Oikos, 2012, 121(2): 306-312. |
| 4 | Valkó O, Tóthmérész B, Kelemen A, et al. Environmental factors driving seed bank diversity in alkali grasslands. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2014, 182(1): 80-87. |
| 5 | Qian J, Liu Z, Hatier J H B, et al. The vertical distribution of soil seed bank and its restoration implication in an active sand dune of Northeastern Inner Mongolia, China. Land Degradation & Development, 2016, 27(2): 305-315. |
| 6 | Mndela M, Madakadze I C, Nherera-Chokuda F, et al. Dynamics of the soil seed bank over the short-term after bush clearing in a semi-arid shrubland in Springbokvlakte thornveld of South Africa. South African Journal of Botany, 2019, 125: 298-309. |
| 7 | Wang S M, Zhang X, Li Y, et al. Spatial distribution patterns of the soil seed bank of Stipagrostis pennata (Trin.) de Winter in the Gurbantonggut Desert of North-west China. Journal of Arid Environments, 2005, 63(1): 203-222. |
| 8 | Sanou L, Zida D, Savadogo P, et al. Comparison of aboveground vegetation and soil seed bank composition at sites of different grazing intensity around a savanna-woodland watering point in West Africa. Journal of Plant Research, 2018, 131(5): 773-788. |
| 9 | Zhang Q P, Wang J, Zhao C Z, et al. Relationships between the soil seed bank and above-ground vegetation of a Thermopsis lanceolata community in degraded alpine arid grasslands. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(14): 4619-4626. |
| 张起鹏, 王建, 赵成章, 等. 高寒干旱草原披针叶黄华植物群落土壤种子库与地上植被的关系. 生态学报, 2017, 37(14): 4619-4626. | |
| 10 | Chen Y Y, Wu Z R, Pan P, et al. The germination characteristics of soil seed bank and its relationship with soil properties in aerially-seeded Pinus massoiana plantations. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2016, 47(1): 92-97. |
| 陈颖颖, 吴自荣, 潘萍, 等. 飞播马尾松林土壤种子库的萌发特征及其与土壤理化性质的关系. 土壤通报, 2016, 47(1): 92-97. | |
| 11 | He F L, Guo C X, Ma J M, et al. Dynamic changes in soil seed banks and their relationships with aboveground vegetation during the decaying of Haloxylon ammodendron plantations at the edge of the Minqin oasis. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(13): 4657-4667. |
| 何芳兰, 郭春秀, 马俊梅, 等. 民勤绿洲边缘梭梭林衰败过程中土壤种子库动态及其与地上植被的关系. 生态学报, 2018, 38(13): 4657-4667. | |
| 12 | Zhao L Y, Li Y Z, Chen H B, et al. Relationship between soil seed banks characteristics and aboveground colonization community along natural restoration gradients in Horqin sandy land. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2018, 27(2): 199-208. |
| 赵丽娅, 李元哲, 陈红兵, 等. 科尔沁沙地恢复过程中地上定植群落与土壤种子库特征及其关系研究. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(2): 199-208. | |
| 13 | Li C, Wang Q H, Chen C, et al. The characteristic of soil seed bank and its relationship with vegetation and soil factor in the wetland region of Caijiahe, Beijing. Ecological Science, 2019, 38(3): 133-142. |
| 李翠, 王庆海, 陈超, 等. 蔡家河湿地土壤种子库特征及其与地上植被和土壤因子的关系. 生态科学, 2019, 38(3): 133-142. | |
| 14 | Xing X M, Ma X D, Zhang Y M. Effects of biological soil crusts on soil seed bank diversity and distribution characteristics in Gurbantunggut Desert. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(3): 612-620. |
| 邢旭明, 马晓东, 张元明. 古尔班通古特沙漠生物土壤结皮对土壤种子库多样性与分布特征的影响. 生态学杂志, 2016, 35(3): 612-620. | |
| 15 | He M Z. Environmental effects on distribution and composition of desert vegetations in Alxa Plateau: Ⅳ. Soil seed banks. Journal of Desert Research, 2010, 30(2): 287-295. |
| 何明珠. 阿拉善高原荒漠植被组成分布特征及其环境解释 Ⅳ.土壤种子库特征研究. 中国沙漠, 2010, 30(2): 287-295. | |
| 16 | Li G Q, Shao W S, Zhao P P, et al. Analysis of soil seed bank characteristics and soil physical properties of four plant communities in a desert steppe region. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(17): 1-11. |
| 李国旗, 邵文山, 赵盼盼, 等. 荒漠草原区4种植物群落土壤种子库特征与其土壤理化性质分析. 生态学报, 2019, 39(17): 1-11. | |
| 17 | Ma H. The heavy meatal distribution characteristics of nine kinds desert plants eastern Alxa-Western Ordos. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2017. |
| 马慧. 东阿拉善—西鄂尔多斯九种荒漠植物重金属分布特征. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2017. | |
| 18 | Wang X D, Li Z, Bao W M, et al. Response of climatic productivity to climate warming-drying trend in Wuhai. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2010, 24(12): 100-105. |
| 王旭东, 李忠, 包伟民, 等. 乌海气候生产力对气候暖干化的响应. 干旱区资源与环境, 2010, 24(12): 100-105. | |
| 19 | Walz U, Stein C. Indicators of hemeroby for the monitoring of landscapes in Germany. Journal for Nature Conservation, 2014, 22(3): 279-289. |
| 20 | Yang X L, Zhang M, Ma H P. Hemeroby appraisal on major scenic spot in Linzhi. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2009, 24(6): 158-161. |
| 杨小林, 张敏, 马和平. 西藏林芝地区主要景区生态干扰度评价. 西北林学院学报, 2009, 24(6): 158-161. | |
| 21 | Spence J R, Leck M A, Parker V T, et al. Ecology of soil seed banks. Salt Lake City: Academic Press, 1989. |
| 22 | Miao J, Zhang K B, Liu X D, et al. Diversity of plant community in relation to environment factors based on CCA in fencing region in Yanchi, Ningxia. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(5): 762-766. |
| 苗静, 张克斌, 刘小丹, 等. 宁夏盐池封育草地植被群落多样性及其与环境关系的典范对应分析. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(5): 762-766. | |
| 23 | Xie Y G, Li X. Methodology on rock fragments content evaluation: A review. Soils, 2012, 44(1): 17-22. |
| 解迎革, 李霞. 土壤中砾石含量的测定方法研究进展. 土壤, 2012, 44(1): 17-22. | |
| 24 | Feng T, Chen H S, Zhang W, et al. Comparative study on determining soil particle size distribution measured by laser diffraction and the sieve-pipette method in Karst Regions. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 2013, 34(1): 100-103. |
| 冯腾, 陈洪松, 张伟, 等. 激光粒度仪与沉降吸管法测定喀斯特地区土壤机械组成的对比研究. 农业现代化研究, 2013, 34(1): 100-103. | |
| 25 | Xing B T, Song S H, Liu L, et al. Comparative analysis on seed moisture between standard drying method and seed moisture measurement. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2015(3): 117-119. |
| 邢宝田, 宋顺华, 刘玲, 等. 水分速测仪与标准烘干法测定种子水分的比较分析. 黑龙江农业科学, 2015(3): 117-119. | |
| 26 | Bao S D. Soil agrochemical analysis. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 27 | Chen J L, Xie W X, Cui Y Q, et al. Research on the determination of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in soil using SmartChem140 automatic chemical analyzer. Journal of Analytical Science, 2016, 32(1): 84-88. |
| 陈剑磊, 谢文霞, 崔育倩, 等. SmartChem140全自动化学分析仪测定土壤全氮全磷的研究. 分析科学学报, 2016, 32(1): 84-88. | |
| 28 | Wang X Y, Ma Z W, Wang X J, et al. Relationship between soil surface environmental factors and community characteristics of alpine meadow in different desertification stages. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(19): 6850-6862. |
| 王新源, 马仲武, 王小军, 等. 不同沙化阶段高寒草甸植物群落与表土环境因子的关系. 生态学报, 2020, 40(19): 6850-6862. | |
| 29 | Zhang J T. Quantitative ecology. Beijing: Science Press, 2011. |
| 张金屯. 数量生态学. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011. | |
| 30 | He M X, Mo X Q, Li H Y, et al. Soil seed bank of typical saline wetlands in Tianjin Binhai District and CCA analysis. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2014, 33(7): 1762-1768. |
| 贺梦璇, 莫训强, 李洪远, 等. 天津滨海典型盐碱湿地土壤种子库特征及CCA分析. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(7): 1762-1768. | |
| 31 | Li G Q, Shao W S, Zhao P P, et al. Effects of enclosure on the soil seed bank of two plant communities on the desert steppe. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(6): 52-61. |
| 李国旗, 邵文山, 赵盼盼, 等. 封育对荒漠草原两种植物群落土壤种子库的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(6): 52-61. | |
| 32 | Yu S L, Chen H W, Lang N J. The classification systems of soil seed bank sand seed persistence in soil. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(5): 2099-2108. |
| 于顺利, 陈宏伟, 郎南军. 土壤种子库的分类系统和种子在土壤中的持久性. 生态学报, 2007, 27(5): 2099-2108. | |
| 33 | Li J M, Xu H L, Zhang Z J, et al. The characteristics of soil seed bank and standing vegetation in differently degraded areas in the lower reaches of Tarim River. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(8): 3626-3636. |
| 李吉玫, 徐海量, 张占江, 等. 塔里木河下游不同退化区地表植被和土壤种子库特征. 生态学报, 2008, 28(8): 3626-3636. | |
| 34 | Ma M, Walck J L, Ma Z, et al. Grazing disturbance increases transient but decreases persistent soil seed bank. Ecological Applications, 2018, 28(4): 1020-1031. |
| 35 | Thompson K. Small-scale heterogeneity in the seed bank of an acidic grassland. The Journal of Ecology, 1986, 74(3): 733-738. |
| 36 | Davis M A, Thompson K, Grime J P. Invasibility: The local mechanism driving community assembly and species diversity. Ecography, 2005, 28(5): 696-704. |
| 37 | Wang D L. Seed life-history strategies of plants and restoration by seed addition in the hilly-gully Loess Plateau region. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2014. |
| 王东丽. 黄土丘陵沟壑区植物种子生活史策略及种子补播恢复研究. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2014. | |
| 38 | Wagner M, Heinrich W, Jetschke G. Seed bank assembly in an unmanaged ruderal grassland recovering from long-term exposure to industrial emissions. Acta Oecologica, 2006, 30(3): 342-352. |
| 39 | Yang C H, Li Y, Shan L S, et al. Soil seed bank and natural regeneration potential of Reaumuria Soongorica shrubs at different slope positions in loess hilly and gully region. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2016, 36(2): 105-109. |
| 杨彩虹, 李毅, 单立山, 等. 黄土丘陵沟壑区红砂灌丛土壤种子库及其自然更新潜力评估. 水土保持通报, 2016, 36(2): 105-109. | |
| 40 | Zhang Q P, Zhao C Z, Wang Q, et al. Relationship between soil seed banks and vegetation functional group structure of Potentilla acaulis community in arid grassland. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2009, 29(6): 46-51. |
| 张起鹏, 赵成章, 王倩, 等. 干旱草原星毛委陵菜群落种子库与植被功能群结构的关系. 水土保持通报, 2009, 29(6): 46-51. | |
| 41 | Liu Y Q, Wang G D, Jiang M, et al. Characteristics of soil seed banks and their relationships with aboveground vegetation in ditches in the Sanjiang Plain. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38(1): 17-26. |
| 刘庆艳, 王国栋, 姜明, 等. 三江平原沟渠土壤种子库特征及其与地上植被的关系. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(1): 17-26. | |
| 42 | Shang Z H, Ren G H, Long R J. Review of soil seed bank studies: Size, pattern and impacting factors. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2009, 18(1): 144-154. |
| 尚占环, 任国华, 龙瑞军. 土壤种子库研究综述——规模、格局及影响因素. 草业学报, 2009, 18(1): 144-154. | |
| 43 | Lu L, Zhou Y R, Zhao Y N, et al. Responses of the soil seed bank to simulated rainfall levels and anthropogenically introduced shrub encroachment in the desert steppe. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(4): 41-50. |
| 于露, 周玉蓉, 赵亚楠, 等. 荒漠草原土壤种子库对灌丛引入和降水梯度的响应特征. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 41-50. | |
| 44 | White E, Tucker N, Meyers N, et al. Seed dispersal to revegetated isolated rainforest patches in North Queensland. Forest Ecology and Management, 2004,192(2/3): 409-426. |
| 45 | Li Y J, Bao W K, Wu F Z. Soil seed bank and natural regeneration potential of shrubland in dry valleys of Minjiang River. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(2): 399-407. |
| 李彦娇, 包维楷, 吴福忠. 岷江干旱河谷灌丛土壤种子库及其自然更新潜力评估. 生态学报, 2010, 30(2): 399-407. | |
| 46 | Yu X J, Shi S L, Long R J, et al. Research progress on effects of ecological factors on seed germination. Pratacultural Science, 2006, 23(10): 44-49. |
| 鱼小军, 师尚礼, 龙瑞军, 等. 生态条件对种子萌发影响研究进展. 草业科学, 2006, 23(10): 44-49. | |
| 47 | Chen Y, Zhu K, Liu L, et al. Effect of sand burial conditions and water conditions on soil seed bank under closing measures in mountainous region of North Hebei. Northern Horticulture, 2016(3): 163-169. |
| 陈颖, 朱凯, 刘琳, 等. 沙埋和土壤水分对冀北沙荒地封禁条件下土壤种子库的影响. 北方园艺, 2016(3): 163-169. | |
| 48 | Li H Y, Mo X Q, Hao C. A review of study on soil seed bank in the past thirty years. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2009, 18(2): 731-737. |
| 李洪远, 莫训强, 郝翠. 近30年来土壤种子库研究的回顾与展望. 生态环境学报, 2009, 18(2): 731-737. | |
| 49 | Csontos P. Seed banks: Ecological definitions and sampling considerations. Community Ecology, 2007, 8(1): 75-85. |
| 50 | Zhang L N. Soil seed bank and enzyme activity of different vegetation reconstructed types in open-pit mine dump. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2019. |
| 张丽娜. 露天矿排土场不同植被重建类型土壤种子库及酶活性研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2019. |
| [1] | 侯金伟, 陈焘, 南志标. 不同埋藏方式及杀菌剂处理对黄土高原3种植物种子存活的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 129-136. |
| [2] | 于露, 周玉蓉, 赵亚楠, 郭天斗, 孙忠超, 王红梅. 荒漠草原土壤种子库对灌丛引入和降水梯度的响应特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 41-50. |
| [3] | 田梦, 孙宗玖, 李莹, 李培英, 谢开云. 蒿类荒漠草地土壤种子库特征及其萌发植物多样性对降水增加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 17-28. |
| [4] | 李国旗, 邵文山, 赵盼盼, 靳长青. 封育对荒漠草原两种植物群落土壤种子库的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(6): 52-61. |
| [5] | 巴德木其其格, 孙宗玖, 李培英, 田梦, 吴咏梅. 增水对伊犁绢蒿荒漠草地土壤种子库种子萌发特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 136-146. |
| [6] | 张蕊, 马红彬, 贾希洋, 周瑶, 宿婷婷, 蔡育蓉, 周静静. 不同生态恢复措施下宁夏黄土丘陵区典型草原土壤种子库特征[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(1): 32-41. |
| [7] | 赵盼盼, 李国旗, 邵文山, 靳长青. 围封对荒漠草原区沙芦草群落土壤种子库及地上植被的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(1): 42-52. |
| [8] | 谢放, 张亚军, 常黎明, 刘帅, 陈晨. 甘肃省宽叶羌活品质对比及其与土壤因子的相关性[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(9): 75-82. |
| [9] | 杨树晶,李涛,干友民,王永,纪磊,宋中齐,刘焘. 阿坝牧区草地不同利用方式与程度对植被碳含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(3): 325-332. |
| [10] | 苏嫄,焦菊英,王巧利,杜华栋,王志杰,寇萌. 黄土丘陵沟壑区不同侵蚀环境下幼苗库及其与地上植被的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(5): 154-164. |
| [11] | 邓斌,任国华,刘志云,尚占环,裴世芳. 封育三年对三种高寒草地群落土壤种子库的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(5): 23-31. |
| [12] | 赵凌平,程积民,苏纪帅. 土壤种子库在黄土高原本氏针茅草地群落长期封禁演替过程中的作用[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(3): 38-44. |
| [13] | 孙向伟,王晓娟,陈牧,豆存艳,高飞翔,金樑. 生态环境因子对AM真菌孢子形成与分布的作用机制[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(1): 214-221. |
| [14] | 杨磊,王彦荣,余进德. 干旱荒漠区土壤种子库研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(2): 227-234. |
| [15] | 鱼小军,蒲小鹏,黄世杰,方强恩,徐宁,徐长林. 蚂蚁对东祁连山高寒草地生态系统的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(2): 140-145. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||