

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 114-123.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021008
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
李玉洁1( ), 沈启维1, 张澳1, 刘丹2, 叶代桦1(
), 沈启维1, 张澳1, 刘丹2, 叶代桦1( ), 李廷轩1
), 李廷轩1
收稿日期:2021-01-05
修回日期:2021-04-22
出版日期:2022-03-20
发布日期:2022-01-15
通讯作者:
叶代桦
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: daihua.ye@sicau.edu.cn基金资助:
Yu-jie LI1( ), Qi-wei SHEN1, Ao ZHANG1, Dan LIU2, Dai-hua YE1(
), Qi-wei SHEN1, Ao ZHANG1, Dan LIU2, Dai-hua YE1( ), Ting-xuan LI1
), Ting-xuan LI1
Received:2021-01-05
Revised:2021-04-22
Online:2022-03-20
Published:2022-01-15
Contact:
Dai-hua YE
摘要:
研究磷富集植物对畜禽粪便施用土壤中过量磷的积累及去除能力,可为利用植物提取土壤过剩磷以降低磷造成的非点源污染提供科学依据。采用两期土培盆栽试验,以矿山生态型水蓼为研究对象,探讨不同用量(0、25、50、75、100 g·kg-1)鸡粪、猪粪和牛粪处理下矿山生态型水蓼的磷积累能力,分析适宜用量畜禽粪便处理下矿山生态型水蓼在不同生长时期(6、8、10、12周)的磷积累特征及磷去除能力。结果表明:1)随着畜禽粪便用量的增加,矿山生态型水蓼地上部生物量和磷积累量均在75 g·kg-1鸡粪(PM75)、100 g·kg-1猪粪(SM100)和100 g·kg-1牛粪(DM100)时达到最大,地上部磷积累量分别为158.64、204.05和128.92 mg·株-1,是不施畜禽粪便处理的5.47~8.66倍。2)适宜用量畜禽粪便(PM75、SM100、DM100)处理下,矿山生态型水蓼生物量和磷积累量分别在12和8周时达到最大,地上部磷积累速率在6~8周时最高。8周后,各适宜用量畜禽粪便处理下矿山生态型水蓼磷去除能力无显著变化,磷提取率可达5.84%~19.36%、植株有效数为4~6株。8周为适宜用量畜禽粪便处理下矿山生态型水蓼的适宜收获时期。3)不同畜禽粪便处理下矿山生态型水蓼磷积累能力存在较大差异,在0~6周时,DM100处理下矿山生态型水蓼地上部磷积累速率明显高于其他处理;在6周后,PM75和SM100处理下矿山生态型水蓼地上部磷积累速率均迅速增加,地上部磷积累量在8周时分别是DM100处理的1.19和1.27倍。综上,在75 g·kg-1鸡粪、100 g·kg-1猪粪、100 g·kg-1牛粪的土壤中,矿山生态型水蓼生长良好,磷积累和磷去除能力强,可高效提取畜禽粪便施用土壤中的磷以降低过量磷对环境的威胁,且对猪粪、鸡粪处理土壤中磷的提取效果优于牛粪处理土壤。
李玉洁, 沈启维, 张澳, 刘丹, 叶代桦, 李廷轩. 畜禽粪便处理下矿山生态型水蓼磷积累及去除能力研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 114-123.
Yu-jie LI, Qi-wei SHEN, Ao ZHANG, Dan LIU, Dai-hua YE, Ting-xuan LI. P accumulation and P removal potential of a P-accumulating ecotype of Polygonum hydropiper for different manure types[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 114-123.
粪便种类 Manure type | pH | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鸡粪Poultry manure | 7.53 | 895.50 | 15.21 | 9.54 | 12.13 | 3.87 |
| 猪粪Swine manure | 6.69 | 496.80 | 14.04 | 23.92 | 3.50 | 6.88 |
| 牛粪Dairy manure | 7.48 | 473.40 | 12.95 | 8.35 | 12.22 | 3.33 |
表1 供试畜禽粪便基本理化性质
Table 1 Basic physico-chemical properties of the tested manures
粪便种类 Manure type | pH | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鸡粪Poultry manure | 7.53 | 895.50 | 15.21 | 9.54 | 12.13 | 3.87 |
| 猪粪Swine manure | 6.69 | 496.80 | 14.04 | 23.92 | 3.50 | 6.88 |
| 牛粪Dairy manure | 7.48 | 473.40 | 12.95 | 8.35 | 12.22 | 3.33 |
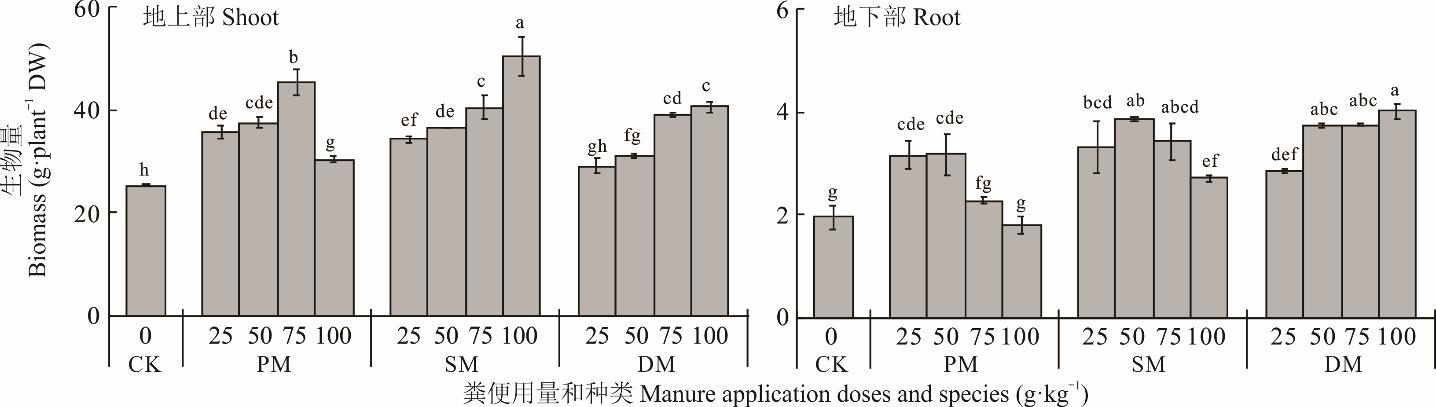
图1 不同用量畜禽粪便下矿山生态型水蓼地上部和地下部生物量不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著。下同。 Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05) among different treatments. The same below.
Fig.1 Shoot and root biomass in the mining ecotype of P. hydropiper under different manure doses
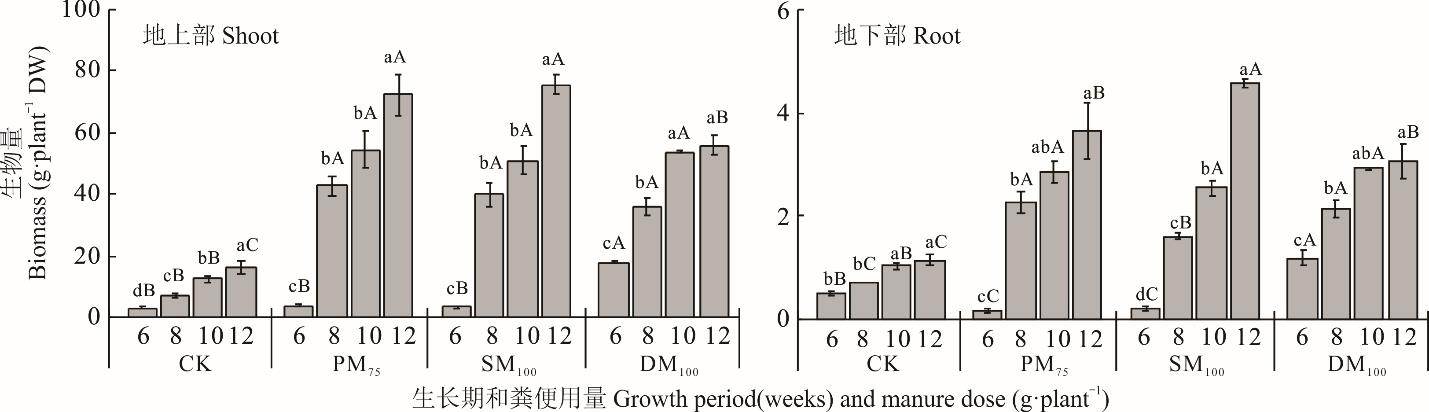
图3 适宜用量畜禽粪便下矿山生态型水蓼地上部和地下部生物量变化不同小写字母表示同一畜禽粪便处理下不同生长期间差异显著,不同大写字母表示同一生长期不同畜禽粪便处理间差异显著。下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05) among different growth periods in the same manure treatment. Different capital letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05) among different manure treatments in the same growth period. The same below.
Fig.3 Changes of shoot and root biomass in the mining ecotype of P. hydropiper under the optimum manure doses
处理 Treatment | 0~6周 0-6 weeks | 6~8周 6-8 weeks | 8~10周 8-10 weeks | 10~12周 10-12 weeks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.24 | 0.37 | 0.06 | 0.83 |
| PM75 | 0.72 | 13.26 | 0.09 | 2.98 |
| SM100 | 0.41 | 15.03 | 0.66 | 3.32 |
| DM100 | 2.72 | 4.84 | 1.68 | 0.86 |
表2 适宜用量畜禽粪便下矿山生态型水蓼地上部阶段性磷积累速率变化
Table 2 Changes of periodic P accumulation rate in shoot of the mining ecotype of P. hydropiper under the optimum manure dose (mg·plant-1·d-1)
处理 Treatment | 0~6周 0-6 weeks | 6~8周 6-8 weeks | 8~10周 8-10 weeks | 10~12周 10-12 weeks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.24 | 0.37 | 0.06 | 0.83 |
| PM75 | 0.72 | 13.26 | 0.09 | 2.98 |
| SM100 | 0.41 | 15.03 | 0.66 | 3.32 |
| DM100 | 2.72 | 4.84 | 1.68 | 0.86 |
处理 Treatment | 磷提取率P extraction ratio (%) | 植株有效数Plant effective number (株Plant) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
6周 6 weeks | 8周 8 weeks | 10周 10 weeks | 12周 12 weeks | 6周 6 weeks | 8周 8 weeks | 10周 10 weeks | 12周 12 weeks | |
| CK | 2.57cB | 4.06bC | 4.17bD | 7.55aC | 113aA | 71bA | 70bA | 38cA |
| PM75 | 2.26bB | 16.11aA | 16.20aA | 19.36aA | 34aC | 5bB | 5bB | 4bB |
| SM100 | 0.44bC | 5.84aC | 6.00aC | 7.05aC | 60aB | 4bB | 4bB | 4bB |
| DM100 | 7.80bA | 12.52aB | 14.19aB | 15.03aB | 9aD | 6bB | 5bB | 5bB |
表3 适宜用量畜禽粪便下矿山生态型水蓼磷提取率和植株有效数变化
Table 3 Changes of P extraction ratio and plant effective number of the mining ecotype of P. hydropiper under the optimum manure dose
处理 Treatment | 磷提取率P extraction ratio (%) | 植株有效数Plant effective number (株Plant) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
6周 6 weeks | 8周 8 weeks | 10周 10 weeks | 12周 12 weeks | 6周 6 weeks | 8周 8 weeks | 10周 10 weeks | 12周 12 weeks | |
| CK | 2.57cB | 4.06bC | 4.17bD | 7.55aC | 113aA | 71bA | 70bA | 38cA |
| PM75 | 2.26bB | 16.11aA | 16.20aA | 19.36aA | 34aC | 5bB | 5bB | 4bB |
| SM100 | 0.44bC | 5.84aC | 6.00aC | 7.05aC | 60aB | 4bB | 4bB | 4bB |
| DM100 | 7.80bA | 12.52aB | 14.19aB | 15.03aB | 9aD | 6bB | 5bB | 5bB |
| 1 | Sun T H, Song X Y. Problems on Chinese agricultural environment and countermeasures. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 2008, 29(6): 646-648. |
| 孙铁珩, 宋雪英. 中国农业环境问题与对策. 农业现代化研究, 2008, 29(6): 646-648. | |
| 2 | Wu H W, Sun X Q, Liang B W, et al. Analysis of livestock and poultry manure pollution in China and its treatment and resource utilization. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(6): 1168-1176. |
| 吴浩玮, 孙小淇, 梁博文, 等. 我国畜禽粪便污染现状及处理与资源化利用分析. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(6): 1168-1176. | |
| 3 | Zhang T L, Yan L, Wei D M. Characteristic distribution of livestock manure and warning analysis of environmental carrying capacity based on the consumption of cultivated land in China. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2020, 28(5): 745-755. |
| 张藤丽, 焉莉, 韦大明. 基于全国耕地消纳的畜禽粪便特征分布与环境承载力预警分析. 中国生态农业学报, 2020, 28(5): 745-755. | |
| 4 | Delgado A, Scalenghe R. Aspects of phosphorus transfer from soils in Europe. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 2008, 171(4): 552-575. |
| 5 | Chadwick D, Jia W, Tong Y A, et al. Improving manure nutrient management towards sustainable agricultural intensification in China. Agriculture Ecosystems Environment, 2015, 209: 34-46. |
| 6 | Sharpley A N, Mcdowell R W, Kleinman P J A. Amounts, forms, and solubility of phosphorus in soils receiving manure. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2004, 68(6): 2048-2057. |
| 7 | Li G H. Phosphorus fractions in animal manure and soil phosphorus management in China. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2015. |
| 李国华. 我国畜禽粪便磷组分与土壤磷养分资源管理策略. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2015. | |
| 8 | Liu D, Ye D H, Li T X, et al. Practicability of using Polygonum japonicum as a P accumulator for P phytoextraction from soil amended with swine manure. Applied Soil Ecology, 2017, 112: 11-17. |
| 9 | Ye D H, Liu D, Li T X, et al. Phosphorus accumulation characteristics in Polygonum hydropiper and rhizosphere properties affected by poultry manure application. Applied Soil Ecology, 2018, 131: 12-21. |
| 10 | Newton G L, Bernard J K, Hubbard R K, et al. Managing manure nutrients through multi-crop forage production. Journal of Dairy Science, 2003, 86(6): 2243-2252. |
| 11 | Kratochvil R J, Coale F J, Momen B, et al. Cropping systems for phytoremediation of phosphorus-enriched soils. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 2006, 8(2): 117-130. |
| 12 | Starnes D L, Padmanabhan P, Sahi S V. Effect of P sources on growth, P accumulation and activities of phytase and acid phosphatases in two cultivars of annual ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum L.). Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2008, 46(5/6): 580-589. |
| 13 | Ye D H, Li T X, Zhang X Z, et al. P uptake characteristics and P removal potentials of Pilea sinofasciata grown under soils amended with swine manure. Ecological Engineering, 2014, 73: 553-559. |
| 14 | Xiao Q, Yan L B, Zhu X Y, et al. Dynamic analysis of dry matter and NPK accumulation with time in summer maize. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2014, 20(3): 606-612. |
| 肖强, 闫连波, 朱欣宇, 等. 夏玉米植株干物质、氮磷钾养分积累速度和时间的动态分析. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(3): 606-612. | |
| 15 | Lu J Y, Duan B H, Yang M, et al. Research progress in nitrogen and phosphorus resorption from senesced leaves and the influence of ontogenetic and environmental factors. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(4): 178-188. |
| 陆姣云, 段兵红, 杨梅, 等. 植物叶片氮磷养分重吸收规律及其调控机制研究进展. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 178-188. | |
| 16 | Huang X. Effect of P incorporation on P accumulation characteristics, physiological and biochemical mechanism of Polygonum hydropiper. Ya’an: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2011. |
| 黄霞. 水蓼富磷特性及其生理生化机制研究. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2011. | |
| 17 | Ye D H, Li T X, Liu D, et al. P accumulation and physiological responses to different high P regimes in Polygonum hydropiper for understanding a P-phytoremediation strategy. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 17835. |
| 18 | Lu R K. Analytical methods of soil and agricultural chemistry. Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000. |
| 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000. | |
| 19 | Ye D H, Li T X, Zhang X Z, et al. Rhizosphere P composition, phosphatase and phytase activities of Polygonum hydropiper grown in excess P soils. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2017, 53(8): 823-836. |
| 20 | Yu H M, Li T X, Zheng Z C, et al. Enhanced P accumulation characteristics and P removal potentials of Pilea sinofasciata grown under P enriched soils supplied with nitrogen. Ecological Engineering, 2016, 91: 44-49. |
| 21 | García G, Faz A, Cunha M. Performance of Piptatherum miliaceum (Smilo grass) in edaphic Pb and Zn phytoremediation over a short growth period. International Biodeterioration Biodegradation, 2004, 54(2): 245-250. |
| 22 | Liu X P, Bi Q F, Qiu L L, et al. Increased risk of phosphorus and metal leaching from paddy soils after excessive manure application: Insights from a mesocosm study. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 666: 778-785. |
| 23 | Chen J, Huang Y S, Li T X. Phosphorous accumulation characteristics of two ecotypes of Pilea sinofasciata grown in soils amended with swine manure. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(11): 139-146. |
| 陈静, 黄有胜, 李廷轩. 猪粪有机肥施用下两种生态型粗齿冷水花磷积累特征变化. 草业学报, 2017, 26(11): 139-146. | |
| 24 | Sharma N C, Sahi S V. Characterization of phosphate accumulation in Lolium multiflorum for remediation of phosphorus-enriched soils. Environmental Science Technology, 2005, 39(14): 5475-5480. |
| 25 | Aziz T, Lambers H, Nicol D, et al. Mechanisms for tolerance of very high tissue phosphorus concentrations in Ptilotus polystachyus. Plant Cell Environment, 2015, 38(4): 790-799. |
| 26 | Yao L X, Li G L, Tu S H, et al. Salinity of animal manure and potential risk of secondary soil salinization through successive manure application. Science of the Total Environment, 2007, 383(1): 106-114. |
| 27 | Carballo M, Aguayo S, González M, et al. Prospects and potential of poultry manure. Journal of Environmental Protection, 2016, 7(1): 82-92. |
| 28 | Guo Y, Li T X, Zhang X Z. Application of nitrogen to increase phosphorus accumulation of Polygonum hydropiper with mining ecotype. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2018, 24(5): 1313-1320. |
| 郭瑀, 李廷轩, 张锡洲. 施氮提高矿山生态型水蓼富集土壤磷能力研究. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2018, 24(5): 1313-1320. | |
| 29 | Sharma N C, Sahi S V, Jain J C, et al. Enhanced accumulation of phosphate by Lolium multiflorum cultivars grown in phosphate enriched medium. Environmental Science and Technology, 2004, 38(8): 2443-2448. |
| 30 | Ryan M H, Ehrenberg S, Bennett R G, et al. Putting the P in Ptilotus: A phosphorus-accumulating herb native to Australia. Annals of Botany, 2009, 103(6): 901-911. |
| 31 | Sharma N C, Sahi S V. Enhanced organic phosphorus assimilation promoting biomass and shoot P hyperaccumulations in Lolium multiflorum grown under sterile conditions. Environmental Science and Technology, 2011, 45(24): 10531-10537. |
| 32 | Li G H, Li H G, Leffelaar P A, et al. Characterization of phosphorus in animal manure collected from three (dairy, swine, and broiler) farms in China. PLoS One, 2014, 9(7): e102698. |
| 33 | Yan Z J, Chen S, Wang M F, et al. Characteristics and availability of different forms of phosphorus in animal manures. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2015, 32(1): 31-39. |
| 严正娟, 陈硕, 王敏锋, 等. 不同动物粪肥的磷素形态特征及有效性分析. 农业资源与环境学报, 2015, 32(1): 31-39. | |
| 34 | Mullaney E J, Richardson A E, Turner B L. Inositol phosphates: Linking agriculture and the environment. Oxfordshire: CAB International, 2007. |
| 35 | Li T, Zhou L. Characteristics of several plants for removing nitrogen and phosphorus from wastewater in constructed wetland. Environmental Engineering, 2009, 27(4): 25-28. |
| 李涛, 周律. 湿地植物对污水中氮、磷去除效果的试验研究. 环境工程, 2009, 27(4): 25-28. | |
| 36 | Ye D H, Li T X, Zhang X Z, et al. Effect of high phosphate supply on P accumulation characteristics of mining ecotype of Polygonum hydropiper. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2014, 20(1): 186-194. |
| 叶代桦, 李廷轩, 张锡洲, 等. 高磷对矿山生态型水蓼磷富集特性的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(1): 186-194. | |
| 37 | Su Q, Liu C Q, Yang J, et al. Growth characteristics and nitrogen and phosphorus accumulation of Myriophyllum spicatum in Xiaoxidian. Journal of Hydroecology, 2012, 33(6): 50-55. |
| 苏倩, 刘存歧, 杨军, 等. 小西淀穗花狐尾藻的生长特性与氮磷吸收规律研究. 水生态学杂志, 2012, 33(6): 50-55. | |
| 38 | Zhang C Y, Wang Y Y, Wang Y. Removal effects of Bidens frondosa on pollutants in swine wastewater. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricutural Engineering, 2011, 27(4): 264-269. |
| 张彩莹, 王妍艳, 王岩. 大狼把草对猪场废水中污染物的净化效果. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(4): 264-269. | |
| 39 | Sharma N C, Starnes D L, Sahi S V. Phytoextraction of excess soil phosphorus. Environmental Pollution, 2007, 146(1): 120-127. |
| 40 | Veneklaas E J, Lambers H, Bragg J, et al. Opportunities for improving phosphorus-use efficiency in crop plants. New Phytologist, 2012, 195(2): 306-320. |
| 41 | Delorme T A, Angle J S, Coale F J, et al. Phytoremediation of phosphorus-enriched soils. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 2000, 2(2): 173-181. |
| 42 | Missaoui A M, Boerma H R, Bouton J H. Genetic variation and heritability of phosphorus uptake in Alamo switchgrass grown in high phosphorus soils. Field Crops Research, 2005, 93(2/3): 186-198. |
| 43 | Polomski R F, Taylor M D, Bielenberg D G, et al. Nitrogen and phosphorus remediation by three floating aquatic macrophytes in greenhouse-based laboratory-scale subsurface constructed wetlands. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 2009, 197(1/2/3/4): 223-232. |
| [1] | 郭文婷, 王国华, 缑倩倩, 刘婧. 河西走廊荒漠绿洲过渡带3种典型一年生藜科植物构件生长及生物量分配特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 25-38. |
| [2] | 卿悦, 李廷轩, 叶代桦. 无机氮处理对矿山生态型水蓼氮积累及根系形态的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 203-210. |
| [3] | 陈静, 黄有胜, 李廷轩. 猪粪有机肥施用下两种生态型粗齿冷水花磷积累特征变化[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(11): 139-146. |
| [4] | 张生伟, 黄旺洲, 姚拓, 杨巧丽, 王鹏飞, 李生贵, 闫尊强, 滚双宝. 高效微生物除臭剂在畜禽粪便堆制中的应用效果及其除臭机理研究[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(9): 142-151. |
| [5] | 韩勇, 邓蓉, 刁其玉. 不同生长期金荞麦营养成分含量及消化率测定研究[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(8): 107-117. |
| [6] | 杨巧丽, 姚拓, 王得武, 滚双宝. 木质纤维分解菌群筛选及其对秸秆分解与畜禽粪便除臭能力评价[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(1): 196-203. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||