

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 101-113.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021294
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
魏畅1( ), 焦秋娟1, 柳海涛1(
), 焦秋娟1, 柳海涛1( ), 张静静1, 申凤敏1, 姜瑛1(
), 张静静1, 申凤敏1, 姜瑛1( ), 张雪海2, 孙娈姿3, 杨芳4, 刘振5
), 张雪海2, 孙娈姿3, 杨芳4, 刘振5
收稿日期:2021-07-27
修回日期:2021-10-08
出版日期:2022-03-20
发布日期:2022-01-15
通讯作者:
柳海涛,姜瑛
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: liuhaitaoky@henau.edu.cn, jy27486@163.com基金资助:
Chang WEI1( ), Qiu-juan JIAO1, Hai-tao LIU1(
), Qiu-juan JIAO1, Hai-tao LIU1( ), Jing-jing ZHANG1, Feng-min SHEN1, Ying JIANG1(
), Jing-jing ZHANG1, Feng-min SHEN1, Ying JIANG1( ), Xue-hai ZHANG2, Luan-zi SUN3, Fang YANG4, Zhen LIU5
), Xue-hai ZHANG2, Luan-zi SUN3, Fang YANG4, Zhen LIU5
Received:2021-07-27
Revised:2021-10-08
Online:2022-03-20
Published:2022-01-15
Contact:
Hai-tao LIU,Ying JIANG
摘要:
为探究不同镉(Cd)浓度对玉米幼苗生长、Cd吸收动力学特征、根系构型及分级变化特征的影响,采用水培模拟方法,待玉米生长至两叶一心,施加不同浓度CdCl2·2.5H2O (0, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100, 200 μmol·L-1),胁迫5 d后采样并测定株高、主根长、地上地下部生物量、Cd含量和光合以及根系相关指标。结果表明,随着Cd胁迫程度的升高,玉米的株高、主根长、生物量、耐受指数、总根长、根表面积、根体积、分枝数和根尖数均显著下降,根平均直径和根冠比显著升高(P<0.05);Ⅰ~Ⅲ级(0~1.5 mm)根系分级下的根系参数(根长、根表面积和根体积)呈下降趋势,且与地下部Cd浓度呈显著负相关(P<0.05),处于0~0.5 mm径级区间的根长、根表面积和根体积所占的比例在Cd胁迫下有所降低。玉米幼苗地上地下部的Cd浓度及含量在Cd胁迫下显著提高,叶绿素含量降低,光合作用受到抑制。研究表明,Cd主要通过抑制细根的生长从而影响根系的形态发育,并抑制了光合作用的进行以及玉米地上和地下部的伸长和生物量的积累。
魏畅, 焦秋娟, 柳海涛, 张静静, 申凤敏, 姜瑛, 张雪海, 孙娈姿, 杨芳, 刘振. 镉暴露条件下玉米生长及根系构型分级特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 101-113.
Chang WEI, Qiu-juan JIAO, Hai-tao LIU, Jing-jing ZHANG, Feng-min SHEN, Ying JIANG, Xue-hai ZHANG, Luan-zi SUN, Fang YANG, Zhen LIU. Physiological effects of different Cd concentrations on maize root architecture and classification[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 101-113.
| 生长指标Growth index | Cd0 | Cd5 | Cd10 | Cd25 | Cd50 | Cd100 | Cd200 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height (cm) | 35.73±1.72a | 33.73±1.76b | 30.33±0.80c | 28.07±0.58d | 25.17±0.40e | 20.10±1.14f | 16.87±0.80g |
地上部鲜重Shoot fresh weight (g·plant-1) | 2.52±0.12a | 1.94±0.30b | 1.62±0.17c | 1.42±0.08cd | 1.30±0.05d | 0.80±0.13e | 0.48±0.10f |
地上部干重Shoot dry weight (g·plant -1) | 0.19±0.01a | 0.16±0.02b | 0.13±0.01c | 0.11±0.00cd | 0.11±0.00d | 0.08±0.02e | 0.06±0.01e |
| 主根长Main root length (cm) | 29.10±0.61a | 24.87±1.01ab | 21.33±1.76bc | 21.47±2.23bc | 22.30±4.23b | 17.63±2.86cd | 16.60±2.43d |
地下部鲜重Root fresh weight (g·plant -1) | 1.25±0.22a | 1.07±0.15ab | 0.97±0.11b | 0.88±0.07bc | 0.82±0.11bcd | 0.62±0.22cd | 0.60±0.07d |
地下部干重Root dry weight (g·plant -1) | 0.07±0.01a | 0.06±0.00ab | 0.05±0.01bc | 0.05±0.00bcd | 0.05±0.01cde | 0.04±0.01e | 0.04±0.01de |
| 根冠比Root/shoot | 0.37±0.04d | 0.39±0.03cd | 0.41±0.04bcd | 0.44±0.03bc | 0.43±0.05bcd | 0.48±0.04b | 0.68±0.03a |
茎耐受指数Shoot tolerance index (%) | - | 80.78±9.42a | 67.96±6.50b | 59.01±2.29b | 56.79±1.30b | 39.29±8.73c | 30.17±4.56c |
根耐受指数Root tolerance index (%) | - | 84.70±5.12a | 76.38±7.96ab | 70.19±2.58abc | 66.09±8.02bcd | 51.73±14.86d | 56.17±9.25cd |
表1 不同浓度Cd处理对玉米幼苗生长及耐受指数的影响
Table 1 Effect of different Cd treatment on the growth and tolerance index of maize seedlings (mean±SD)
| 生长指标Growth index | Cd0 | Cd5 | Cd10 | Cd25 | Cd50 | Cd100 | Cd200 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height (cm) | 35.73±1.72a | 33.73±1.76b | 30.33±0.80c | 28.07±0.58d | 25.17±0.40e | 20.10±1.14f | 16.87±0.80g |
地上部鲜重Shoot fresh weight (g·plant-1) | 2.52±0.12a | 1.94±0.30b | 1.62±0.17c | 1.42±0.08cd | 1.30±0.05d | 0.80±0.13e | 0.48±0.10f |
地上部干重Shoot dry weight (g·plant -1) | 0.19±0.01a | 0.16±0.02b | 0.13±0.01c | 0.11±0.00cd | 0.11±0.00d | 0.08±0.02e | 0.06±0.01e |
| 主根长Main root length (cm) | 29.10±0.61a | 24.87±1.01ab | 21.33±1.76bc | 21.47±2.23bc | 22.30±4.23b | 17.63±2.86cd | 16.60±2.43d |
地下部鲜重Root fresh weight (g·plant -1) | 1.25±0.22a | 1.07±0.15ab | 0.97±0.11b | 0.88±0.07bc | 0.82±0.11bcd | 0.62±0.22cd | 0.60±0.07d |
地下部干重Root dry weight (g·plant -1) | 0.07±0.01a | 0.06±0.00ab | 0.05±0.01bc | 0.05±0.00bcd | 0.05±0.01cde | 0.04±0.01e | 0.04±0.01de |
| 根冠比Root/shoot | 0.37±0.04d | 0.39±0.03cd | 0.41±0.04bcd | 0.44±0.03bc | 0.43±0.05bcd | 0.48±0.04b | 0.68±0.03a |
茎耐受指数Shoot tolerance index (%) | - | 80.78±9.42a | 67.96±6.50b | 59.01±2.29b | 56.79±1.30b | 39.29±8.73c | 30.17±4.56c |
根耐受指数Root tolerance index (%) | - | 84.70±5.12a | 76.38±7.96ab | 70.19±2.58abc | 66.09±8.02bcd | 51.73±14.86d | 56.17±9.25cd |
| 级别Class | Cd0 | Cd5 | Cd10 | Cd25 | Cd50 | Cd100 | Cd200 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RL (cm) | 791.90±85.86a | 481.32±84.38b | 399.81±88.06bc | 371.08±59.95bc | 308.53±51.62c | 146.42±50.80d | 176.85±42.44d |
| Ⅰ | 633.01±99.29a | 352.56±72.79b | 292.99±81.91b | 272.78±52.61b | 239.58±38.64b | 92.28±43.64c | 123.07±46.92c |
| Ⅱ | 136.22±9.90a | 113.27±13.51b | 88.40±5.58c | 86.84±6.27c | 51.87±10.50d | 44.24±5.65d | 40.78±8.14d |
| Ⅲ | 14.38±2.20a | 9.69±1.41bc | 12.01±0.07ab | 7.48±1.49cd | 9.48±2.13bc | 5.90±3.15d | 7.88±0.59cd |
| Ⅳ | 4.63±3.36a | 3.42±2.12a | 3.47±0.91a | 1.98±0.81a | 4.72±1.71a | 1.77±1.07a | 2.71±0.49a |
| Ⅴ | 1.01±1.23a | 0.50±0.28a | 0.85±0.28a | 0.75±0.59a | 0.85±0.35a | 0.21±0.28a | 0.70±0.23a |
| Ⅵ | 0.85±1.27a | 0.46±0.40a | 0.58±0.46a | 0.26±0.20a | 0.65±0.30a | 0.43±0.38a | 0.46±0.24a |
| Ⅶ | 0.65±0.80a | 0.63±0.28a | 0.27±0.23a | 0.07±0.07a | 0.54±0.66a | 0.26±0.46a | 0.37±0.07a |
| Ⅷ | 0.20±0.22a | 0.30±0.29a | 0.12±0.02a | 0.18±0.10a | 0.09±0.13a | 0.35±0.12a | 0.27±0.01a |
| Ⅸ | 0.39±0.29a | 0.09±0.15a | 0.22±0.19a | 0.08±0.14a | 0.19±0.16a | 0.29±0.21a | 0.13±0.22a |
| Ⅹ | 0.47±0.34a | 0.38±0.29a | 0.81±0.32a | 0.61±0.45a | 0.49±0.31a | 0.69±0.54a | 0.46±0.15a |
| SA (cm2) | 84.37±4.36a | 58.98±7.26b | 50.69±9.18bc | 44.19±5.84c | 40.72±8.42c | 24.91±8.48d | 27.37±4.08d |
| Ⅰ | 34.65±5.71a | 20.61±4.07b | 16.15±5.57bc | 15.86±3.95bc | 15.69±3.13bc | 7.30±3.59d | 8.77±4.49cd |
| Ⅱ | 29.31±2.06a | 24.88±3.34b | 20.11±1.79c | 17.86±0.81c | 12.02±2.69d | 9.57±1.35d | 8.90±1.10d |
| Ⅲ | 5.38±0.80a | 3.67±0.56bc | 4.50±0.05ab | 2.82±0.56cd | 3.54±0.81bcd | 2.27±1.20d | 3.00±0.26cd |
| Ⅳ | 2.48±1.84a | 1.84±1.18a | 1.86±0.52a | 1.07±0.42a | 2.54±0.89a | 0.94±0.58a | 1.44±0.26a |
| Ⅴ | 0.71±0.87a | 0.34±0.19a | 0.59±0.20a | 0.53±0.41a | 0.59±0.25a | 0.15±0.20a | 0.50±0.16a |
| Ⅵ | 0.73±1.09a | 0.39±0.34a | 0.48±0.38a | 0.23±0.17a | 0.56±0.28a | 0.37±0.33a | 0.39±0.20a |
| Ⅶ | 0.67±0.83a | 0.67±0.28a | 0.26±0.23a | 0.07±0.07a | 0.53±0.66a | 0.27±0.47a | 0.38±0.08a |
| Ⅷ | 0.23±0.25a | 0.34±0.34a | 0.15±0.02a | 0.25±0.08a | 0.11±0.15a | 0.43±0.13a | 0.32±0.01a |
| Ⅸ | 0.53±0.41a | 0.11±0.19a | 0.29±0.26a | 0.11±0.18a | 0.25±0.22a | 0.37±0.29a | 0.17±0.29a |
| Ⅹ | 0.83±0.56a | 0.71±0.53a | 1.42±0.66a | 1.15±0.88a | 0.79±0.44a | 1.16±0.99a | 0.84±0.23a |
| RV (cm3) | 0.72±0.08a | 0.58±0.04b | 0.51±0.07bc | 0.42±0.05cd | 0.43±0.11cd | 0.34±0.11d | 0.34±0.04d |
| Ⅰ | 0.19±0.04a | 0.12±0.02b | 0.09±0.03bc | 0.09±0.03bc | 0.10±0.02bc | 0.06±0.03c | 0.06±0.04c |
| Ⅱ | 0.52±0.04a | 0.45±0.07a | 0.37±0.04b | 0.30±0.01c | 0.23±0.05cd | 0.17±0.03d | 0.16±0.01d |
| Ⅲ | 0.16±0.02a | 0.11±0.02bc | 0.14±0.00ab | 0.09±0.02cd | 0.11±0.02bcd | 0.07±0.04d | 0.09±0.01cd |
| Ⅳ | 0.11±0.08a | 0.08±0.05a | 0.08±0.02a | 0.05±0.02a | 0.11±0.04a | 0.04±0.03a | 0.06±0.01a |
| Ⅴ | 0.04±0.05a | 0.02±0.01a | 0.03±0.01a | 0.03±0.02a | 0.03±0.01a | 0.01±0.01a | 0.03±0.01a |
| Ⅵ | 0.05±0.07a | 0.03±0.02a | 0.03±0.02a | 0.02±0.01a | 0.04±0.02a | 0.03±0.02a | 0.03±0.01a |
| Ⅶ | 0.06±0.07a | 0.06±0.02a | 0.02±0.02a | 0.01±0.01a | 0.04±0.05a | 0.02±0.04a | 0.03±0.01a |
| Ⅷ | 0.02±0.02a | 0.03±0.03a | 0.01±0.00a | 0.02±0.01a | 0.01±0.01a | 0.04±0.01a | 0.03±0.00a |
| Ⅸ | 0.06±0.05a | 0.01±0.02a | 0.03±0.03a | 0.01±0.02a | 0.03±0.02a | 0.04±0.03a | 0.02±0.03a |
| Ⅹ | 0.12±0.08a | 0.10±0.08a | 0.18±0.10a | 0.18±0.15a | 0.10±0.05a | 0.16±0.14a | 0.12±0.03a |
| RD (mm) | 0.34±0.03c | 0.39±0.02bc | 0.41±0.02b | 0.38±0.02bc | 0.42±0.03b | 0.54±0.01a | 0.50±0.06a |
| RF | 2761.00±223.55a | 1328.67±117.73b | 1259.00±385.32b | 999.67±208.20b | 1108.33±220.65b | 424.67±204.81c | 571.00±217.42c |
| RT | 1511.00±146.73a | 808.33±161.33b | 683.33±36.83b | 693.33±79.22b | 362.33±73.66c | 278.00±98.66c | 287.00±16.64c |
表2 不同浓度Cd处理对玉米根系结构和根系分级的影响
Table 2 Influence of Cd treatments with different concentrations on root structure and root classification of maize (mean±SD)
| 级别Class | Cd0 | Cd5 | Cd10 | Cd25 | Cd50 | Cd100 | Cd200 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RL (cm) | 791.90±85.86a | 481.32±84.38b | 399.81±88.06bc | 371.08±59.95bc | 308.53±51.62c | 146.42±50.80d | 176.85±42.44d |
| Ⅰ | 633.01±99.29a | 352.56±72.79b | 292.99±81.91b | 272.78±52.61b | 239.58±38.64b | 92.28±43.64c | 123.07±46.92c |
| Ⅱ | 136.22±9.90a | 113.27±13.51b | 88.40±5.58c | 86.84±6.27c | 51.87±10.50d | 44.24±5.65d | 40.78±8.14d |
| Ⅲ | 14.38±2.20a | 9.69±1.41bc | 12.01±0.07ab | 7.48±1.49cd | 9.48±2.13bc | 5.90±3.15d | 7.88±0.59cd |
| Ⅳ | 4.63±3.36a | 3.42±2.12a | 3.47±0.91a | 1.98±0.81a | 4.72±1.71a | 1.77±1.07a | 2.71±0.49a |
| Ⅴ | 1.01±1.23a | 0.50±0.28a | 0.85±0.28a | 0.75±0.59a | 0.85±0.35a | 0.21±0.28a | 0.70±0.23a |
| Ⅵ | 0.85±1.27a | 0.46±0.40a | 0.58±0.46a | 0.26±0.20a | 0.65±0.30a | 0.43±0.38a | 0.46±0.24a |
| Ⅶ | 0.65±0.80a | 0.63±0.28a | 0.27±0.23a | 0.07±0.07a | 0.54±0.66a | 0.26±0.46a | 0.37±0.07a |
| Ⅷ | 0.20±0.22a | 0.30±0.29a | 0.12±0.02a | 0.18±0.10a | 0.09±0.13a | 0.35±0.12a | 0.27±0.01a |
| Ⅸ | 0.39±0.29a | 0.09±0.15a | 0.22±0.19a | 0.08±0.14a | 0.19±0.16a | 0.29±0.21a | 0.13±0.22a |
| Ⅹ | 0.47±0.34a | 0.38±0.29a | 0.81±0.32a | 0.61±0.45a | 0.49±0.31a | 0.69±0.54a | 0.46±0.15a |
| SA (cm2) | 84.37±4.36a | 58.98±7.26b | 50.69±9.18bc | 44.19±5.84c | 40.72±8.42c | 24.91±8.48d | 27.37±4.08d |
| Ⅰ | 34.65±5.71a | 20.61±4.07b | 16.15±5.57bc | 15.86±3.95bc | 15.69±3.13bc | 7.30±3.59d | 8.77±4.49cd |
| Ⅱ | 29.31±2.06a | 24.88±3.34b | 20.11±1.79c | 17.86±0.81c | 12.02±2.69d | 9.57±1.35d | 8.90±1.10d |
| Ⅲ | 5.38±0.80a | 3.67±0.56bc | 4.50±0.05ab | 2.82±0.56cd | 3.54±0.81bcd | 2.27±1.20d | 3.00±0.26cd |
| Ⅳ | 2.48±1.84a | 1.84±1.18a | 1.86±0.52a | 1.07±0.42a | 2.54±0.89a | 0.94±0.58a | 1.44±0.26a |
| Ⅴ | 0.71±0.87a | 0.34±0.19a | 0.59±0.20a | 0.53±0.41a | 0.59±0.25a | 0.15±0.20a | 0.50±0.16a |
| Ⅵ | 0.73±1.09a | 0.39±0.34a | 0.48±0.38a | 0.23±0.17a | 0.56±0.28a | 0.37±0.33a | 0.39±0.20a |
| Ⅶ | 0.67±0.83a | 0.67±0.28a | 0.26±0.23a | 0.07±0.07a | 0.53±0.66a | 0.27±0.47a | 0.38±0.08a |
| Ⅷ | 0.23±0.25a | 0.34±0.34a | 0.15±0.02a | 0.25±0.08a | 0.11±0.15a | 0.43±0.13a | 0.32±0.01a |
| Ⅸ | 0.53±0.41a | 0.11±0.19a | 0.29±0.26a | 0.11±0.18a | 0.25±0.22a | 0.37±0.29a | 0.17±0.29a |
| Ⅹ | 0.83±0.56a | 0.71±0.53a | 1.42±0.66a | 1.15±0.88a | 0.79±0.44a | 1.16±0.99a | 0.84±0.23a |
| RV (cm3) | 0.72±0.08a | 0.58±0.04b | 0.51±0.07bc | 0.42±0.05cd | 0.43±0.11cd | 0.34±0.11d | 0.34±0.04d |
| Ⅰ | 0.19±0.04a | 0.12±0.02b | 0.09±0.03bc | 0.09±0.03bc | 0.10±0.02bc | 0.06±0.03c | 0.06±0.04c |
| Ⅱ | 0.52±0.04a | 0.45±0.07a | 0.37±0.04b | 0.30±0.01c | 0.23±0.05cd | 0.17±0.03d | 0.16±0.01d |
| Ⅲ | 0.16±0.02a | 0.11±0.02bc | 0.14±0.00ab | 0.09±0.02cd | 0.11±0.02bcd | 0.07±0.04d | 0.09±0.01cd |
| Ⅳ | 0.11±0.08a | 0.08±0.05a | 0.08±0.02a | 0.05±0.02a | 0.11±0.04a | 0.04±0.03a | 0.06±0.01a |
| Ⅴ | 0.04±0.05a | 0.02±0.01a | 0.03±0.01a | 0.03±0.02a | 0.03±0.01a | 0.01±0.01a | 0.03±0.01a |
| Ⅵ | 0.05±0.07a | 0.03±0.02a | 0.03±0.02a | 0.02±0.01a | 0.04±0.02a | 0.03±0.02a | 0.03±0.01a |
| Ⅶ | 0.06±0.07a | 0.06±0.02a | 0.02±0.02a | 0.01±0.01a | 0.04±0.05a | 0.02±0.04a | 0.03±0.01a |
| Ⅷ | 0.02±0.02a | 0.03±0.03a | 0.01±0.00a | 0.02±0.01a | 0.01±0.01a | 0.04±0.01a | 0.03±0.00a |
| Ⅸ | 0.06±0.05a | 0.01±0.02a | 0.03±0.03a | 0.01±0.02a | 0.03±0.02a | 0.04±0.03a | 0.02±0.03a |
| Ⅹ | 0.12±0.08a | 0.10±0.08a | 0.18±0.10a | 0.18±0.15a | 0.10±0.05a | 0.16±0.14a | 0.12±0.03a |
| RD (mm) | 0.34±0.03c | 0.39±0.02bc | 0.41±0.02b | 0.38±0.02bc | 0.42±0.03b | 0.54±0.01a | 0.50±0.06a |
| RF | 2761.00±223.55a | 1328.67±117.73b | 1259.00±385.32b | 999.67±208.20b | 1108.33±220.65b | 424.67±204.81c | 571.00±217.42c |
| RT | 1511.00±146.73a | 808.33±161.33b | 683.33±36.83b | 693.33±79.22b | 362.33±73.66c | 278.00±98.66c | 287.00±16.64c |
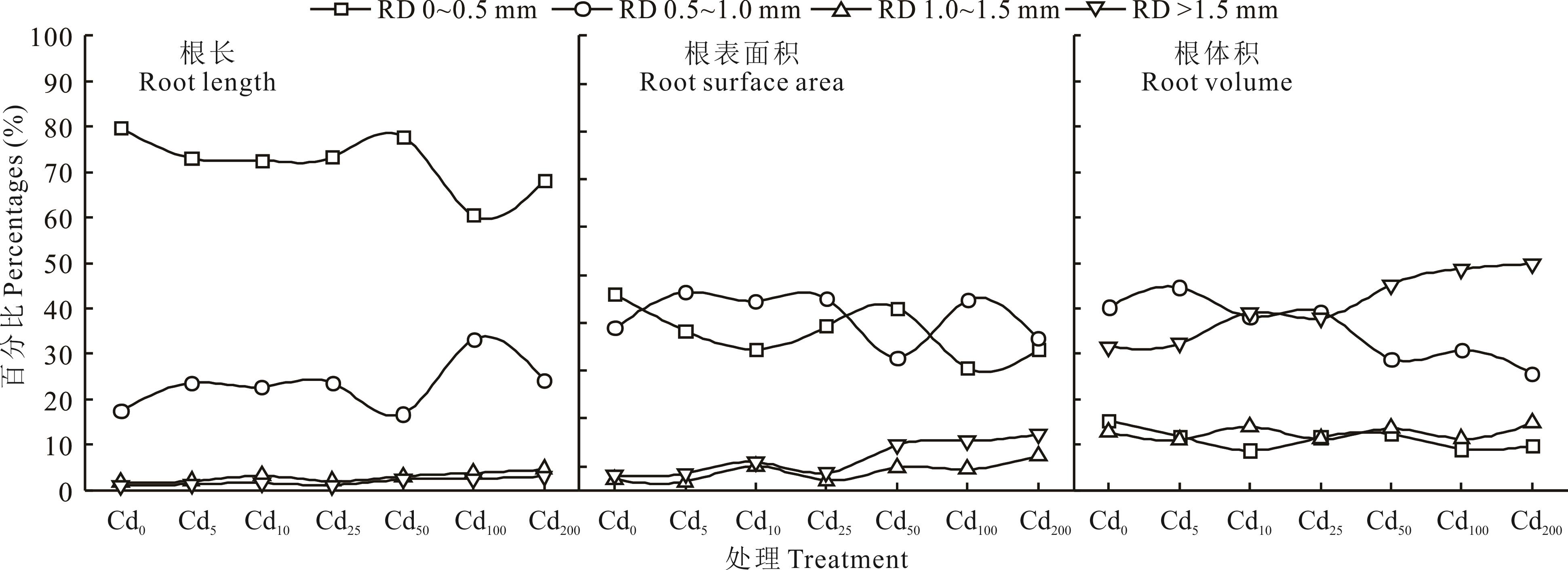
图2 不同浓度Cd处理下玉米幼苗根长、根表面积以及根体积在不同径级区间所占百分比
Fig.2 Maize seedling root length, root surface area and percentage of root volume in different root diameters under different Cd treatments
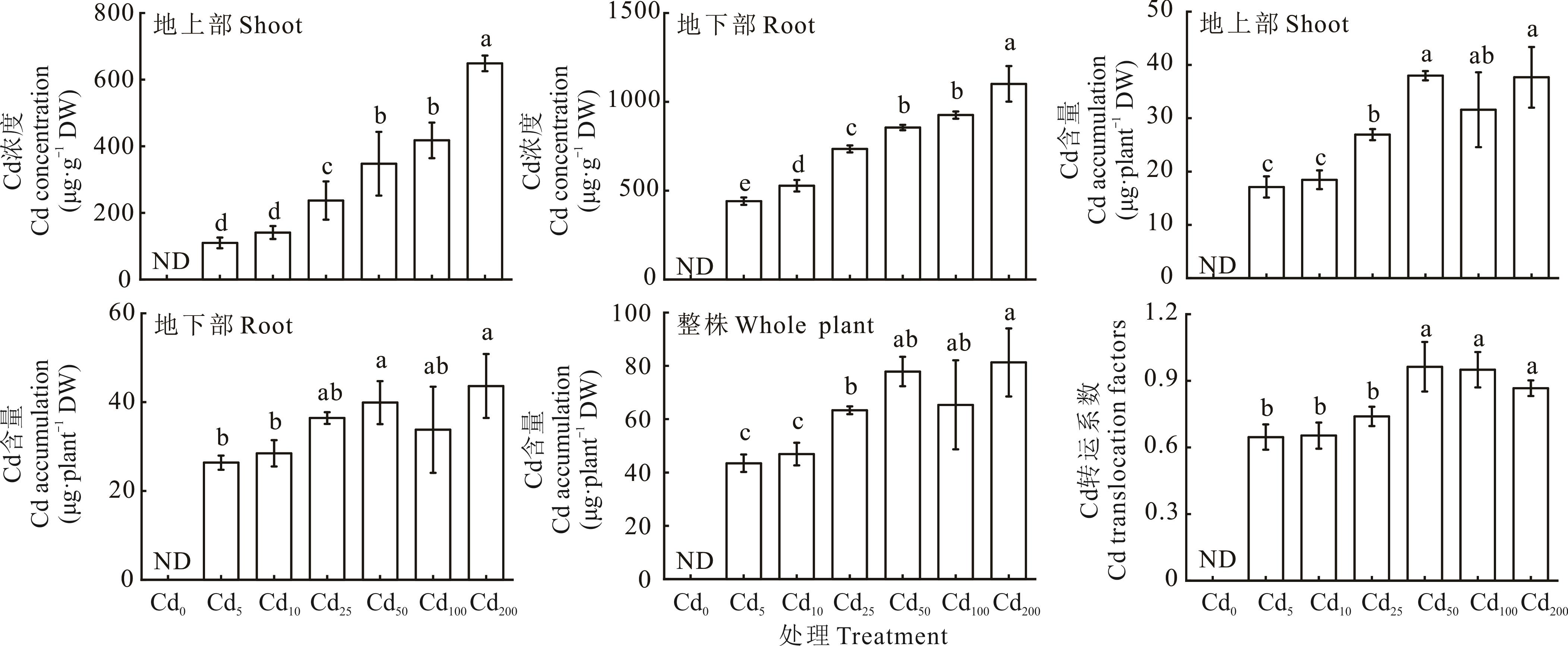
图3 不同浓度Cd处理对玉米幼苗组织内Cd浓度、Cd含量以及转运系数的影响不同小写字母代表不同Cd处理间差异达到显著水平(P<0.05),ND表示Cd未检出,下同。
Fig.3 Effects of different concentrations of Cd treatment on Cd concentration, Cd accumulation and Cd translocation factors of maize seedling tissueDifferent lowercase letters represent that the difference among different cadmium treatments has reached a significant level (P<0.05), ND means no Cd was detected, the same below.
部位 Part | Vmax (μg·g-1·h-1) | 米氏常数Km (μmol·L-1) | 吸收能力 α | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部 Shoot | 796.1 | 63.25 | 12.59 | 0.9469 |
| 地下部 Root | 1062.0 | 9.42 | 112.69 | 0.9417 |
表3 玉米幼苗对营养液中不同浓度Cd吸收的Michaelis-Menten方程常数
Table 3 Michaelis-Menten equation constants of Cd uptake by maize seedlings at different concentrations in growth medium
部位 Part | Vmax (μg·g-1·h-1) | 米氏常数Km (μmol·L-1) | 吸收能力 α | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部 Shoot | 796.1 | 63.25 | 12.59 | 0.9469 |
| 地下部 Root | 1062.0 | 9.42 | 112.69 | 0.9417 |

图4 不同浓度Cd处理对玉米幼苗光合参数和叶绿素含量的影响
Fig.4 Effects of different concentrations of Cd treatment on photosynthetic parameters and chlorophyll content of maize seedling

图5 不同浓度Cd处理玉米幼苗各指标变化的主成分分析Shoot FW: 地上部鲜重; Shoot DW: 地上部干重; Main RL: 主根长; Root FW: 地下部鲜重; Root DW: 地下部干重; R/S: 根冠比; Shoot Ti: 茎耐受指数; Root Ti: 根耐受指数; Cd conc.: Cd浓度; Cd accum.: Cd含量; Cd TF: Cd转运系数; 下同The same below.
Fig.5 Principal component analysis of the changes of each index of maize seedlings induced by Cd at different concentrations

图6 不同浓度Cd处理玉米幼苗各指标变化的相关性分析(A)和热图(B)
Fig.6 Correlation analysis (A) and thermography (B) of the changes of each index of maize seedlings induced by Cd at different concentrations
| 1 | Ministry of Environmental Protection, Ministry of Land and Resources. Report on the national general survey of soil contamination. Environmental Education, 2014(6): 8-10. |
| 环境保护部, 国土资源部. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报. 环境教育, 2014(6): 8-10. | |
| 2 | Fu Y C, Zhu X L, Yuan C, et al. Cadmium absorption and enrichment in wheat and its cadmium pollution prediction: Research progress. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(6): 37-41. |
| 符云聪, 朱晓龙, 袁毳, 等. 小麦对镉的吸收、富集及其镉污染预测研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(6): 37-41. | |
| 3 | Chen J J, Yu W, Zu Y Q, et al. Variety difference of Cd accumulation and translocation in Zea mays. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 23(10): 1671-1676. |
| 陈建军, 于蔚, 祖艳群, 等. 玉米(Zea mays)对镉积累与转运的品种差异研究. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(10): 1671-1676. | |
| 4 | Deng T, Lu W S, Wu J L, et al. Differences of soil cadmium accumulation and translocation in different maize varieties. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2019, 40(4): 33-39. |
| 邓婷, 卢维盛, 吴家龙, 等. 不同玉米品种对土壤镉富集和转运的差异研究. 华南农业大学学报, 2019, 40(4): 33-39. | |
| 5 | Sun J H, Chen T T, Qiu B, et al. Research on the distribution of heavy metal in corn plants. Crop Research, 2016, 30(4): 402-405. |
| 孙姣辉, 陈婷婷, 邱博, 等. 几种重金属(Cd、Cr、As)在玉米植株中的分布研究. 作物研究, 2016, 30(4): 402-405. | |
| 6 | Yuan L, Liu Y, Lan Y S, et al. Variations of cadmium absorption and accumulation among corn cultivars of metal pollution in soil from lead-zinc mining area. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 2018, 36(1): 22-27. |
| 袁林, 刘颖, 兰玉书, 等. 不同玉米品种对镉吸收累积特性研究. 四川农业大学学报, 2018, 36(1): 22-27. | |
| 7 | Potters G, Pasternak T P, Guisez Y, et al. Stress-induced morphogenic responses: Growing out of trouble? Trends in Plant Science, 2007, 12(3): 98-105. |
| 8 | Shi G, Xia S, Ye J, et al. PEG-simulated drought stress decreases cadmium accumulation in castor bean by altering root morphology. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2015, 111(3): 127-134. |
| 9 | Gunsé B, Llugany M, Ch P, et al. Growth, cell wall elasticity and plasticity in Zea mays L. coleoptiles exposed to cadmium. Suelo y Planta, 1992, 2: 179-188. |
| 10 | Qv D Y, Zhang L G, Gu W R, et al. Effects of chitosan on root growth and leaf photosynthesis of maize seedlings under cadmium stress. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(5): 1300-1309. |
| 曲丹阳, 张立国, 顾万荣, 等. 壳聚糖对镉胁迫下玉米幼苗根系生长及叶片光合的影响. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(5): 1300-1309. | |
| 11 | He J Y, Wang Y Y, Ren Y F, et al. Effect of cadmium on root morphology and physiological characteristics of rice seedlings. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2009, 18(5): 1863-1868. |
| 何俊瑜, 王阳阳, 任艳芳, 等. 镉胁迫对不同水稻品种幼苗根系形态和生理特性的影响. 生态环境学报, 2009, 18(5): 1863-1868. | |
| 12 | Arditti J, Dunn A. Environmental plant physiology: Experiments in cellular and plant physiology. New York: Holt. Rinehart and Winston Inc, 1969. |
| 13 | Wang Y P, Chang H, Li C, et al. Effects of exogenous Ca2+ on growth, photosynthetic charateristics and photosystem Ⅱ function of maize seedings under cadmium stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(5): 40-48. |
| 王玉萍, 常宏, 李成, 等. Ca2+对镉胁迫下玉米幼苗生长、光合特征和PSⅡ功能的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(5): 40-48. | |
| 14 | Li Y, Yu L J, Jin X X. Mechanism of heavy metal tolerance stress of plants. China Biotechnology, 2015, 35(9): 94-104. |
| 李洋, 于丽杰, 金晓霞. 植物重金属胁迫耐受机制. 中国生物工程杂志, 2015, 35(9): 94-104. | |
| 15 | Yang C G, Dou H, Liang Y C, et al. Influence of silicon on cadmium availability and cadmium uptake by maize in cadmium-contaminated soil. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2005, 38(1): 116-121. |
| 杨超光, 豆虎, 梁永超, 等. 硅对土壤外源镉活性和玉米吸收镉的影响. 中国农业科学, 2005, 38(1): 116-121. | |
| 16 | Wang H, Zhao S C, Xia W J, et al. Effect of cadmium stress on photosynthesis, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities in maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2008(1): 36-42. |
| 汪洪, 赵士诚, 夏文建, 等.不同浓度镉胁迫对玉米幼苗光合作用、脂质过氧化和抗氧化酶活性的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2008(1): 36-42. | |
| 17 | Wu Z C, Zhao X H, Sun X C, et al. Antioxidant enzyme systems and the ascorbate-glutathione cycle as contributing factors to cadmium accumulation and tolerance in two oilseed rape cultivars (Brassica napus L.) under moderate cadmium stress. Chemosphere, 2015, 138(11): 526-536. |
| 18 | Kim T H, Böhmer M, Hu H, et al. Guard cell signal transduction network: Advances in understanding abscisic acid, CO2, and Ca2+ signaling. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2010, 61: 561-591. |
| 19 | Liu D L, Sun Q X, Shao J, et al. Effects of Cd concentrations on growth, photosynthetic indices and bioconcentration of two Pennisetum during different growth stages. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(1): 84-93. |
| 刘大林, 孙启鑫, 邵将, 等. 镉胁迫对两种狼尾草不同生育时期生长性能、光合作用特征及镉吸收转运差异的影响. 草业科学, 2017, 34(1): 84-93. | |
| 20 | Tian Y, Zhang H H, Meng X Y, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Glomus mosseae) on growth and photosynthesis characteristics of Lolium perenne L. under Cd contaminated soil. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2013, 21(1): 135-141. |
| 田野, 张会慧, 孟祥英, 等. 镉(Cd)污染土壤接种丛枝菌根真菌(Glomus mosseae)对黑麦草生长和光合的影响. 草地学报, 2013, 21(1): 135-141. | |
| 21 | Qian L X, Hu C X, Zhao X H, et al. Effects of cadmium stress on nitrogen metabolism and photosynthesis of different Chinese cabbages. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2015, 34(3): 69-75. |
| 钱雷晓, 胡承孝, 赵小虎, 等. 镉胁迫对不同基因型小白菜氮代谢和光合作用的影响. 华中农业大学学报, 2015, 34(3): 69-75. | |
| 22 | Singh S, Singh V P, Prasad S M, et al. Interactive effect of silicon (Si) and salicylic acid (SA) in maize seedlings and their mechanisms of cadmium (Cd) toxicity alleviation. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2019, 38(4): 1587-1597. |
| 23 | Bhaduri A M, Fulekar M H. Antioxidant enzyme responses of plants to heavy metal stress. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio-Technology, 2012, 11(1): 55-69. |
| 24 | Vaculík M, Pavlovič A, Lux A. Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity by enhanced photosynthetic rate and modified bundle sheath’s cell chloroplasts ultrastructure in maize. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2015, 120(10): 66-73. |
| 25 | Wang F, Chang P P, Chen Y P, et al. Effect of exogenous nitric oxide on seedings growth and physiological characteristics of maize seedings under cadmium stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(2): 178-186. |
| 王芳, 常盼盼, 陈永平, 等. 外源NO对镉胁迫下玉米幼苗生长和生理特性的影响. 草业学报, 2013, 22(2): 178-186. | |
| 26 | Faller P, Kienzler K, Krieger-Liszkay A. Mechanism of Cd2+ toxicity: Cd2+ inhibits photoactivation of photosystem Ⅱ by competitive binding to the essential Ca2+ site. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Bioenergetics, 2005, 1706(1/2): 158-164. |
| 27 | Li J W, Yue F X, Wang Y F, et al. Effects of biochar amendment and arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculation on maize growth and physiological biochemistry under cadmium stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(5): 120-129. |
| 李继伟, 悦飞雪, 王艳芳,等. 施用生物炭和AM真菌对镉胁迫下玉米生长和生理生化指标的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5): 120-129. | |
| 28 | Zhang J B, Huang W N. Effect of cadmium stress on photosynthetic functions of strawberry. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2007, 18(7): 1673-1676. |
| 张金彪, 黄维南. 镉胁迫对草莓光合的影响. 应用生态学报, 2007, 18(7): 1673-1676. | |
| 29 | Liu J X, Ou X B, Wang J C. Physiological-ecological responses of naked oat to cadmium (Cd) stress and Cd accumulation. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2019, 39(5): 621-629. |
| 刘建新, 欧晓彬, 王金成. 裸燕麦对重金属镉(Cd)胁迫的生理生态响应及Cd累积特性. 麦类作物学报, 2019, 39(5): 621-629. | |
| 30 | Yu Z H, Li S B, Zhao X L, et al. Differences in root morphology, rhizosheath traits, and Cd uptake in maize cultivars. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(4): 747-755. |
| 于子昊, 李胜宝, 赵晓玲, 等. 玉米根系、根鞘性状与镉吸收的品种差异研究. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(4): 747-755. | |
| 31 | Li X M, Song G L. Cadmium uptake and root morphological changes in Medicago sativa under cadmium stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(2): 178-186. |
| 李希铭, 宋桂龙. 镉胁迫对紫花苜蓿镉吸收特征及根系形态影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2): 178-186. | |
| 32 | Qin T C, Wu Y S, Wang H X, et al. Effect of cadmium, lead and their interactions on the physiological and ecological characteristics of root system of Brassica chinensis. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1998, 18(3): 320-325. |
| 秦天才, 吴玉树, 王焕校, 等. 镉、铅及其相互作用对小白菜根系生理生态效应的研究. 生态学报, 1998, 18(3): 320-325. | |
| 33 | Xiao Y T, Wu H Q, Li Z Y, et al. Difference of cadmium accumulation by different genotypes of winter wheat and its relationship with root morphology. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 29(6): 276-280, 286. |
| 肖亚涛, 吴海卿, 李中阳, 等. 不同基因型冬小麦镉累积差异及其与根系形态的关系. 水土保持学报, 2015, 29(6): 276-280, 286. | |
| 34 | Yu R G, Xia S L, Liu C F, et al. Variations in root morphology among 18 herbaceous species and their relationship with cadmium accumulation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(5): 4731-4740. |
| 35 | Guo J M, Guo Y, Yang J, et al. Effects and interactions of cadmium and zinc on root morphology and metal translocation in two populations of Hylotelephium spectabile (Boreau) H. Ohba, a potential Cd-accumulating species. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(17): 21364-21375. |
| [1] | 吴欣明, 方志红, 池惠武, 贾会丽, 刘建宁, 石永红, 王学敏. 30个青贮玉米在雁门关地区品种评比试验[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 205-216. |
| [2] | 温媛媛, 张美琦, 刘桃桃, 沈宜钊, 高艳霞, 李秋凤, 曹玉凤, 李建国. 体外产气法评价生薯条加工副产品-稻草混贮与全株玉米青贮组合效应的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 154-163. |
| [3] | 张丹丹, 张元庆, 程景, 靳光, 李博, 王栋才, 徐芳, 孙锐锋. 不同粗饲料组合对晋南牛瘤胃体外发酵特性的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 93-100. |
| [4] | 黄丽琴, 李松桥, 袁振中, 唐晶, 闫景彩, 唐启源. 全株水稻与平菇菌糠共发酵料对浏阳黑山羊屠宰性能、肉品质和器官指数的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 133-140. |
| [5] | 祁鹤兴, 芦光新, 李宗仁, 徐成体, 德科加, 周孝娟, 王英成, 马桂花. 青海省青贮玉米链格孢叶枯病病原菌鉴定及其致病力分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 94-105. |
| [6] | 赵小强, 钟源, 周文期. 不同水分环境下玉米叶面积QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 103-120. |
| [7] | 李雄雄, 焦婷, 赵生国, 秦伟娜, 高雪梅, 王正文, 吴建平, 雷赵民. 牛至精油与有机钴协同对青贮玉米秸秆降解及绵羊瘤胃发酵特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 191-202. |
| [8] | 付东青, 贾春英, 连晓春, 张力, 张凡凡, 马春晖. 玉米秸秆与番茄皮渣裹包混贮发酵品质及瘤胃降解特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 147-158. |
| [9] | 刘桃桃, 王思伟, 李秋凤, 曹玉凤, 王昆, 王丽娟, 沈宜钊, 孙雪丽, 张美琦, 闫金玲, 李建国, 高艳霞, 王美美. 利用尼龙袋法比较3个全株玉米品种青贮前后肉牛瘤胃降解特性[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 159-169. |
| [10] | 李振松, 万里强, 李硕, 李向林. 苜蓿根系构型及生理特性对干旱复水的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 189-196. |
| [11] | 郭家萌, 何灵芝, 闫东良, 李卓, 王泳超, 邵瑞鑫, 杨青华. 控释氮肥和尿素配比对不同品种夏玉米氮素累积、转移及其利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 81-95. |
| [12] | 齐鹏, 王晓娇, 姚一铭, 陈晓龙, 武均, 蔡立群. 不同耕作方法和施氮量对旱作农田土壤CO2排放及碳平衡的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 96-106. |
| [13] | 雷恩, 邵迪, 朱天彪, 舒星, 杨永兵, 王岳东, 唐启源. 饲用玉米器官含水率、力学强度与籽粒机收质量的关系研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 125-135. |
| [14] | 吕汉强, 于爱忠, 王玉珑, 苏向向, 吕奕彤, 柴强. 干旱绿洲灌区玉米氮素吸收利用对绿肥还田利用方式的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 93-103. |
| [15] | 丁永福, 王纪良, 陈奋奇, 庄泽龙, 白明兴, 陆晏天, 金兵兵, 彭云玲. 玉米自交系SSR多样性与穗部性状的关联分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 143-153. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||