

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 63-74.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022009
收稿日期:2022-01-06
修回日期:2022-03-03
出版日期:2023-01-20
发布日期:2022-11-07
通讯作者:
王自奎
作者简介:E-mail: wzk@lzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Wei-jie LI( ), Li WANG, Jing-yong MA, Zi-kui WANG(
), Li WANG, Jing-yong MA, Zi-kui WANG( )
)
Received:2022-01-06
Revised:2022-03-03
Online:2023-01-20
Published:2022-11-07
Contact:
Zi-kui WANG
摘要:
研究苹果园长期生草覆盖后深层土壤水分及果树根系的分布规律,以期阐明旱作条件下果园根水互作关系,为黄土旱塬区果园生草覆盖实践的优化提供依据。试验于甘肃庆阳草地农业生态系统国家野外科学观测研究站苹果园中进行,设置果园生草覆盖(生草为鸭茅草,2014年建植)和清耕处理,以一年生作物田为对照;连续两年夏季测定果树行上和行间距离树干100和200 cm共4个位置0~500 cm土层的土壤水分和果树细根长密度,分析生草覆盖对果园深层水分亏缺及细根长密度的影响。清耕果园0~300 cm土壤水分较对照农田下降了6.7%~8.3%(P<0.01),而300~500 cm土层土壤水分与对照农田差异不显著(P>0.05);生草覆盖果园0~500 cm整个剖面的土壤水分均低于清耕果园,平均下降了11.5%~12.3%。果园生草覆盖6~7年后0~500 cm土层土壤较对照农田水分亏缺量为163.9~172.1 mm,是清耕果园水分亏缺量的3.2~4.2倍。果树根系在0~100 cm土层的细根长密度最高,平均密度为0.187 cm·cm-3,生草覆盖促进了0~100 cm土层果树根系的分布,对深层根系影响不显著。清耕果园和生草覆盖果园0~500 cm土层土壤水分的含量随果树细根长密度的增加而降低,二者呈线性负相关关系,生草覆盖后二者相关性提高,干旱年份二者相关性更高。黄土旱塬区苹果园长期生草可促进果树根系生长,降低深层土壤水分,加剧土壤干燥化,对苹果树的利用年限和农田水分循环具有负面效应。旱作条件下应加强果园生草覆盖管理以保障水分的可持续性。
李惟婕, 王立, 马景永, 王自奎. 黄土旱塬区苹果园生草覆盖对深层土壤水分和根系分布特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 63-74.
Wei-jie LI, Li WANG, Jing-yong MA, Zi-kui WANG. Effects of a cover crop on deep soil water and root characteristics in a dryland apple orchard on the Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(1): 63-74.
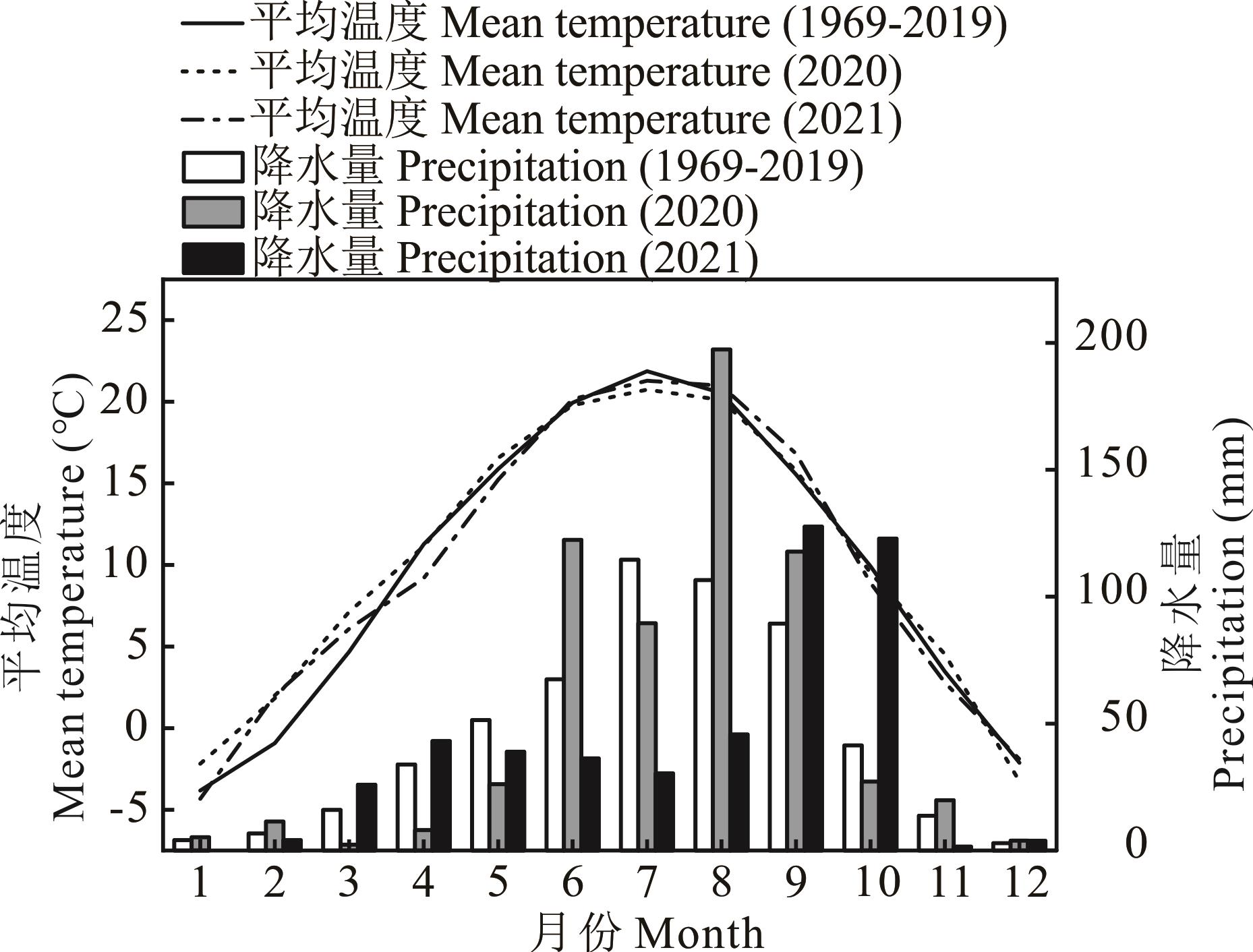
图1 庆阳试验站2020和2021年月降水气温变化趋势及其与多年平均值的比较
Fig.1 Dynamics of precipitation and air temperature at Qingyang experimental station in 2020 and 2021 and comparison with the long-term average
土层深度 Soil depth (cm) | 土壤容重 Soil bulk density (g·cm-3) | 田间持水量 Field water capacity (cm3·cm-3) |
|---|---|---|
| 0~10 | 1.43 | 28.0 |
| 10~20 | 1.38 | 27.8 |
| 20~30 | 1.36 | 28.4 |
| 30~40 | 1.35 | 29.0 |
| 40~60 | 1.43 | 30.0 |
| 60~80 | 1.39 | 31.6 |
| 80~100 | 1.43 | 28.8 |
| 100~150 | 1.40 | 29.8 |
| 150~200 | 1.38 | 28.7 |
| 200~250 | 1.39 | 29.4 |
| 250~300 | 1.40 | 29.3 |
| 300~350 | 1.39 | 28.5 |
| 350~400 | 1.39 | 27.8 |
| 400~450 | 1.37 | 28.6 |
| 450~500 | 1.36 | 28.2 |
表1 清耕苹果园0~500 cm不同土层土壤容重和田间持水量
Table 1 Soil bulk density and field water capacity in the 0-500 cm soil profiles in apple orchard
土层深度 Soil depth (cm) | 土壤容重 Soil bulk density (g·cm-3) | 田间持水量 Field water capacity (cm3·cm-3) |
|---|---|---|
| 0~10 | 1.43 | 28.0 |
| 10~20 | 1.38 | 27.8 |
| 20~30 | 1.36 | 28.4 |
| 30~40 | 1.35 | 29.0 |
| 40~60 | 1.43 | 30.0 |
| 60~80 | 1.39 | 31.6 |
| 80~100 | 1.43 | 28.8 |
| 100~150 | 1.40 | 29.8 |
| 150~200 | 1.38 | 28.7 |
| 200~250 | 1.39 | 29.4 |
| 250~300 | 1.40 | 29.3 |
| 300~350 | 1.39 | 28.5 |
| 350~400 | 1.39 | 27.8 |
| 400~450 | 1.37 | 28.6 |
| 450~500 | 1.36 | 28.2 |

图2 果园生草覆盖系统中果草配置及生草覆盖(a)和清耕果园(b)土壤取样位置
Fig.2 Diagram of apple tree-cover crop system and soil sampling points in cover crop (a) and clean tillage (b) treatments
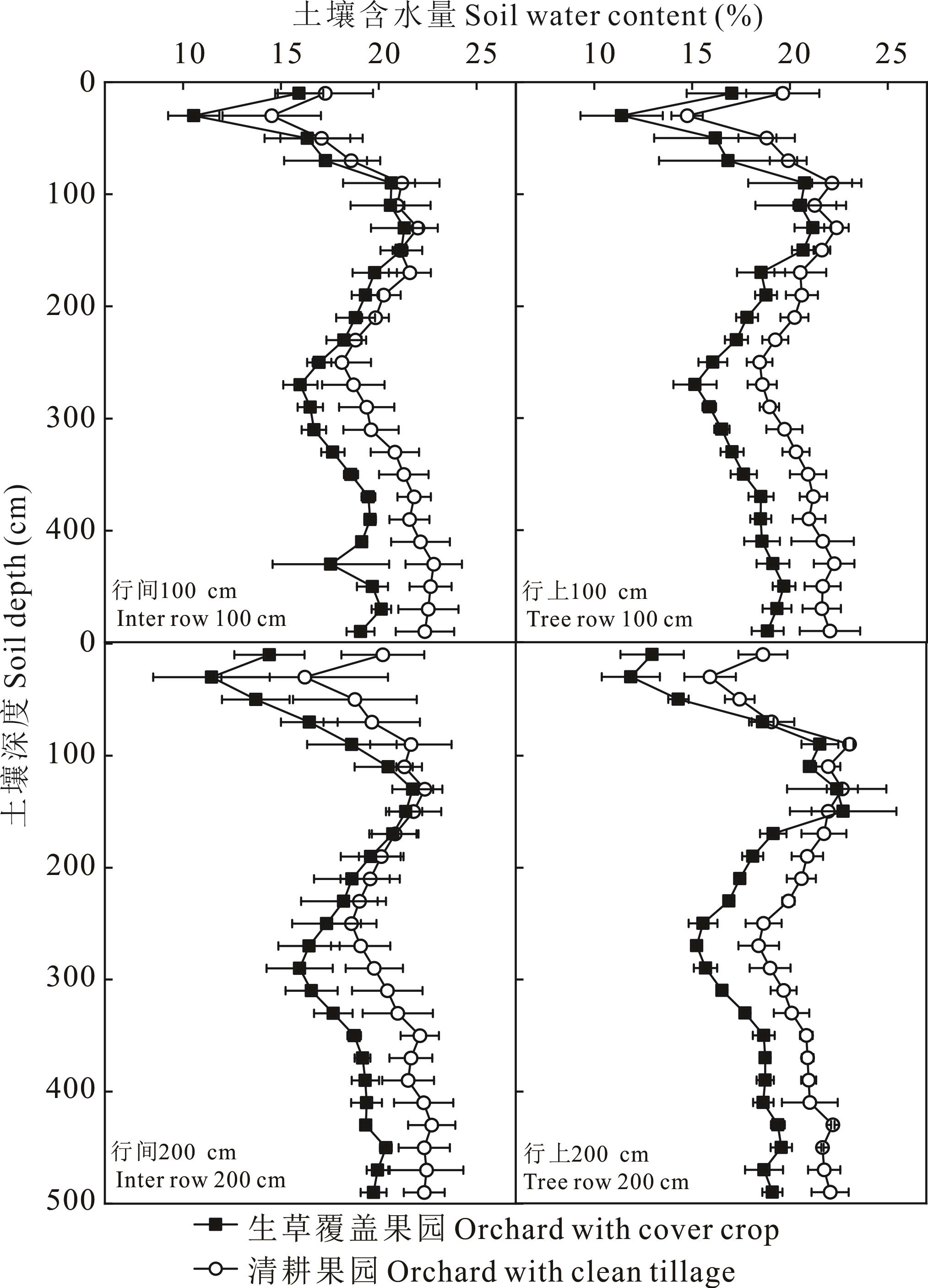
图4 2020年生草和清耕苹果园果树行上和行间距离树干不同位置0~500 cm剖面土壤含水量分布
Fig.4 Soil water content distribution of 0-500 cm profiles at different places on the tree row and inter row in apple orchards with and without cover crop in 2020

图5 2021年生草和清耕苹果园果树行上和行间距离树干不同位置0~500 cm剖面土壤含水量分布
Fig.5 Soil water content distribution of 0-500 cm profiles at different places on the tree row and inter row in apple orchards with and without cover crop in 2021
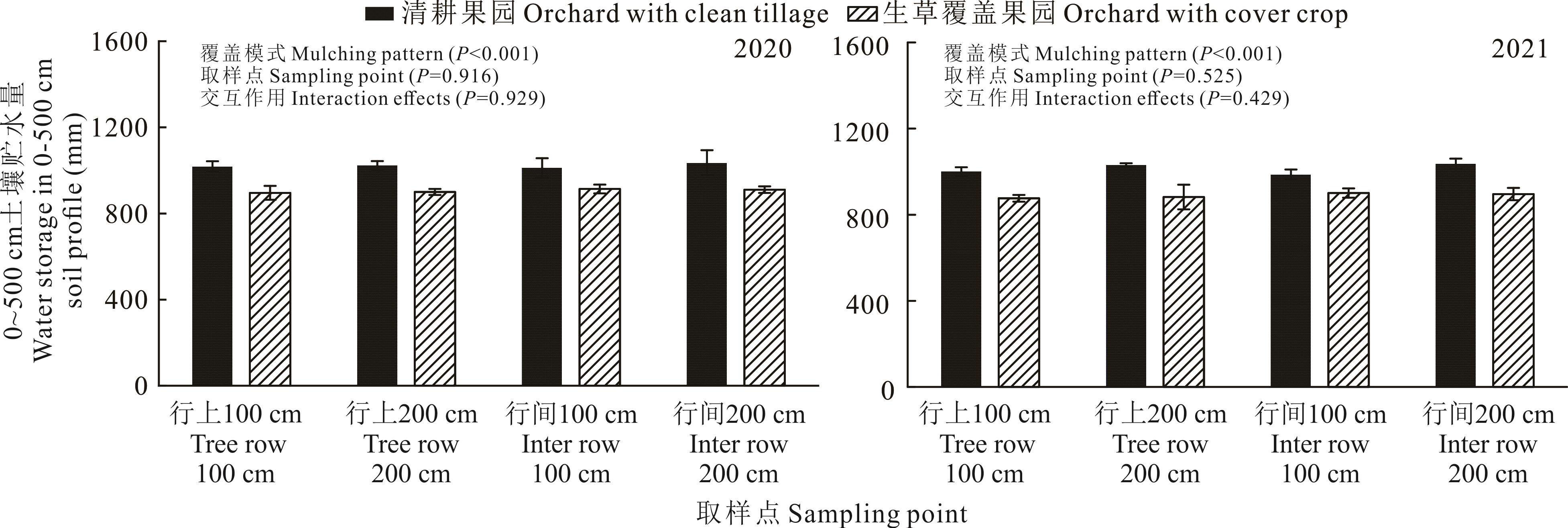
图6 2020和2021年清耕与生草覆盖果园不同取样点0~500 cm土层土壤总贮水量
Fig.6 Soil water storage in 0-500 cm soil profiles at different sampling points in apple orchards with and without cover crop in 2020 and 2021
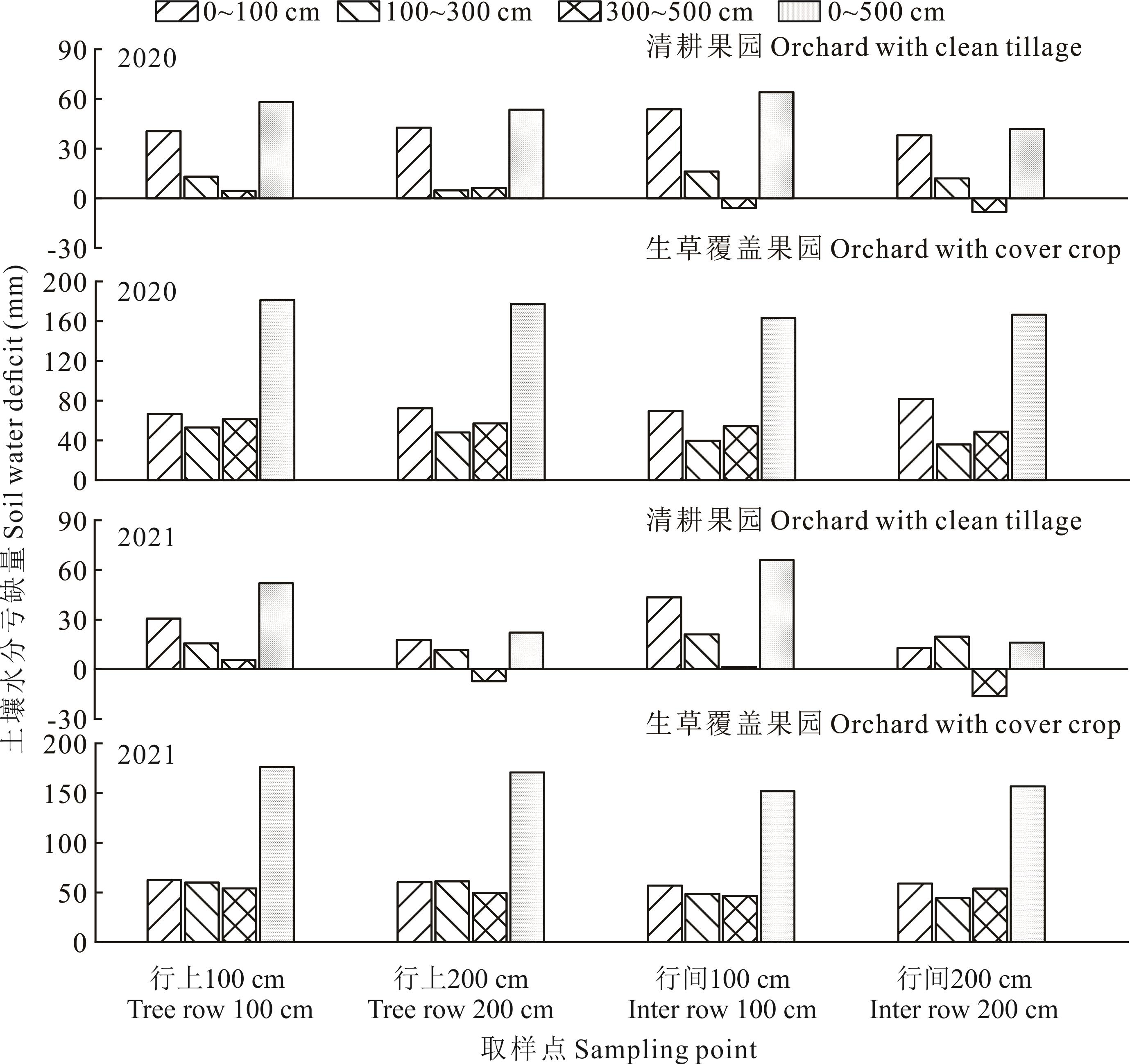
图7 2020和2021年与对照农田相比果园0~100 cm、100~300 cm和300~500 cm土层及0~500 cm整个剖面土壤水分亏缺量
Fig.7 Soil water deficit in 0-100 cm, 100-300 cm, 300-500 cm and 0-500 cm soil layers in apple orchards as compared with reference crop field in 2020 and 2021
土壤深度 Soil depth (cm) | 细根长密度 Fine root length density (cm·cm-3) | 年际 Year (Y) | 覆盖模式 Mulching pattern (MP) | 年际×覆盖模式 Y×MP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 | 0.121 | NS | NS | NS |
| 10~20 | 0.125 | NS | NS | NS |
| 20~30 | 0.197 | NS | NS | NS |
| 30~40 | 0.197 | ** | * | NS |
| 40~60 | 0.150 | ** | NS | NS |
| 60~80 | 0.121 | * | NS | NS |
| 80~100 | 0.059 | NS | NS | NS |
表2 苹果园0~100 cm浅层土壤细根长密度和统计分析
Table 2 Fine root length density and statistical analysis of 0-100 cm shallow soil in apple orchards
土壤深度 Soil depth (cm) | 细根长密度 Fine root length density (cm·cm-3) | 年际 Year (Y) | 覆盖模式 Mulching pattern (MP) | 年际×覆盖模式 Y×MP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 | 0.121 | NS | NS | NS |
| 10~20 | 0.125 | NS | NS | NS |
| 20~30 | 0.197 | NS | NS | NS |
| 30~40 | 0.197 | ** | * | NS |
| 40~60 | 0.150 | ** | NS | NS |
| 60~80 | 0.121 | * | NS | NS |
| 80~100 | 0.059 | NS | NS | NS |

图9 清耕与生草覆盖果园在30~40 cm土层土壤细根长密度不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments (P<0.05).
Fig.9 Fine root length density in 30-40 cm in apple orchards with and without cover crop
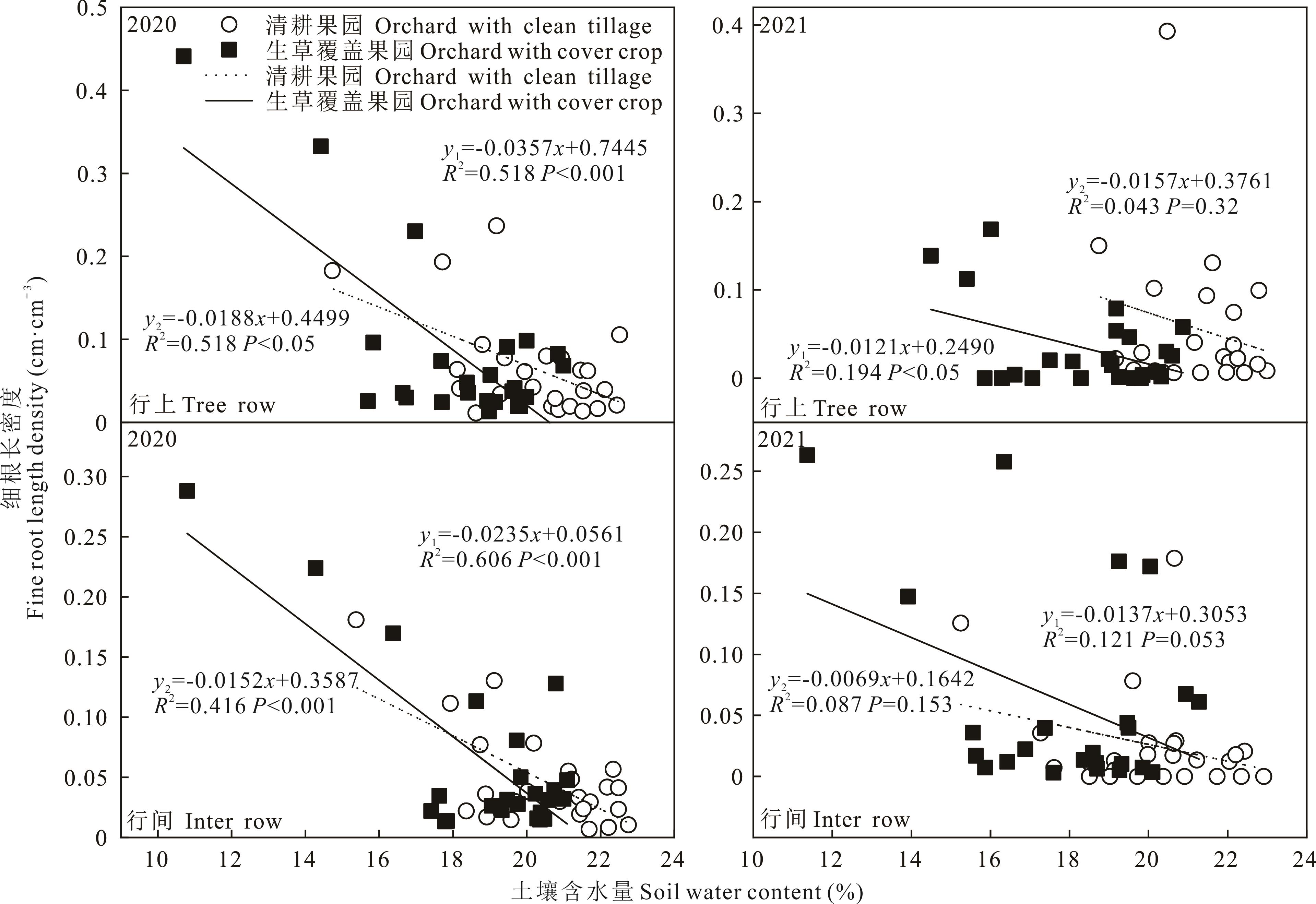
图10 清耕和生草果园土壤含水量与苹果树细根长密度的相关关系y1表示生草覆盖果园; y2表示清耕果园。y1 indicates orchard with cover crop; y2 indicates orchard with clean tillage.
Fig.10 Correlation between soil water content and fine root length density of apple trees in apple orchards with and without cover crop
| 1 | Zhang Y M. Problems and countermeasures in the development of apple industrialization of Qingyang. Xianyang: Northwest of A & F University, 2005. |
| 张永明. 庆阳市苹果产业化发展存在的问题与对策. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2005. | |
| 2 | Li H K, Zhang G J, Zhao Z Y. The theory and practice of grass interplanting in orchards. Pratacultural Science, 2005(8): 32-37. |
| 李会科, 张广军, 赵政阳. 果园生草的理论与实践——以黄土高原南部苹果园生草实践为例. 草业科学, 2005(8): 32-37. | |
| 3 | Greenham D W P. The environment of the fruit tree: Managing fruit soils. Scientific Horticulture, 1955, 12: 25-31. |
| 4 | Mason J L. Effect of cultivation and nitrogen on fruit quality, yield and color of Mcintosh apples grown in irrigated grass sod cover crop. Plant Science, 1969, 49(2): 149-154. |
| 5 | Jing Z B, Yang Y, Ruan X F. Effects of inter-planted grasses in persimmon orchard on soil microbes and enzyme activities. Northern Horticulture, 2019(9): 105-110. |
| 井赵斌, 杨勇, 阮小凤. 行间生草对甜柿果园土壤微生物和酶活性的影响. 北方园艺, 2019(9): 105-110. | |
| 6 | Li F L, Zheng Y R, Zheng T, et al. Research advances on soil and water conservation effect of pasture-planting in orchard. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013, 29(34): 34-39. |
| 李发林, 郑域茹, 郑涛, 等. 果园生草栽培水土保持效应研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(34): 34-39. | |
| 7 | Hui Z M, Li H, Zhang Z W, et al. Effect of green covering on vine growth in the vineyard//Proceedings of the Sixth Youth Symposium of Chinese Society of Horticulture. Xi’an: Shaanxi Science and Technology Press, 2004: 221-225. |
| 惠竹梅, 李华, 张振文, 等. 葡萄园行间生草对植株生长的影响//中国园艺学会第六届青年学术讨论会论文集. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社, 2004: 221-225. | |
| 8 | Zhang H M, Wang Z Y, Yang J, et al. Study on soil and water conservation effect under different inter-cropping for orchards on red soil slopeland. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2010, 17(3): 140-143. |
| 张华明, 王昭艳, 杨洁, 等. 红壤坡地不同果园套种模式水土保持效果研究. 水土保持研究, 2010, 17(3): 140-143. | |
| 9 | Li H K, Zhang G J, Zhao Z Y, et al. Effects of different herbage on soil quality characteristics of non-irrigated apple orchard in Weibei Loess Plateau. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2008, 41(7): 2070-2076. |
| 李会科, 张广军, 赵政阳, 等. 渭北黄土高原旱地果园生草对土壤物理性质的影响. 中国农业科学, 2008, 41(7): 2070-2076. | |
| 10 | Gao M S, Liao Y C, Li X, et al. Effects of different mulching patterns on soil water-holding capacity of non-irrigated apple orchard in the Weibei Plateau. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(10): 2080-2087. |
| 高茂盛, 廖允成, 李侠, 等. 不同覆盖方式对渭北旱作苹果园土壤贮水的影响. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(10): 2080-2087. | |
| 11 | Bai G S, Zheng S L, Zou C Y, et al. Influence of interplant herbage on soil moisture and apple tree growth in dry plateau of eastern Gansu. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(1): 173-183. |
| 白岗栓, 郑锁林, 邹超煜, 等. 陇东旱塬果园生草对土壤水分及苹果树生长的影响. 草地学报, 2018, 26(1): 173-183. | |
| 12 | Yang P. Effects of soil surface regulating measures on root morphology and physiology of Red Fuji Apple. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2013. |
| 杨萍. 表层土壤调控措施对红富士苹果根系形态及生理的影响. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2013. | |
| 13 | Dong Z Y. Kiwi fruit orchard sod effect analysis. Beijing Agriculture, 2012(33): 28. |
| 董志有. 猕猴桃果园生草效果分析. 北京农业, 2012(33): 28. | |
| 14 | Weng B Q, Ying C Y, Huang Y B, et al. Study on construction and application of comprehensive utilization mode and ecological rehabilitation of empoldered red soil mountains in northern Fujian. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2006, 20(1): 147-150. |
| 翁伯琦, 应朝阳, 黄毅斌, 等. 闽北山区红壤丘陵开发地生态恢复与综合利用模式构建及其应用研究. 水土保持学报, 2006, 20(1): 147-150. | |
| 15 | Huang Y N, Li C X, Lin G W, et al. Soil moisture characteristics and their responses to land use change on Luochuan loess tableland. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 37(6): 106-112. |
| 黄亚楠, 李晨曦, 林国伟, 等. 洛川塬土壤水分特征及其对土地利用变化的响应. 水土保持通报, 2017, 37(6): 106-112. | |
| 16 | Cao Q. Production, light utilization and evapotranspiration in apple tree and cocksfoot agroforestry systems on the loess plateau of China. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2020. |
| 曹铨. 黄土高原苹果树/鸭茅复合系统产量、光能利用及蒸散发特征研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2020. | |
| 17 | Li H K, Zheng Q L, Zhao Z Y, et al. Study on the root system distribution characteristics of several herbage species growing in apple orchard in Loess Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2008, 17(2): 92-96. |
| 李会科, 郑秋玲, 赵政阳, 等. 黄土高原果园种植牧草根系特征的研究. 草业学报, 2008, 17(2): 92-96. | |
| 18 | Xu M G, Wen S L, Gao J S. Effects of different forage planting model on soil and water conservation and environments in red hilly regions. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2001, 15(1): 77-80. |
| 徐明岗, 文石林, 高菊生. 红壤丘陵区不同种草模式的水土保持效果与生态环境效应. 水土保持学报, 2001, 15(1): 77-80. | |
| 19 | Kou J C, Yang W Q, Li S W, et al. Research advance on soil organic matter of orchard in China. Northern Horticulture, 2016(4): 185-191. |
| 寇建村, 杨文权, 李尚玮, 等. 我国果园土壤有机质研究进展. 北方园艺, 2016(4): 185-191. | |
| 20 | Chen K, Hu G Q, Rao H M, et al. Ecological effects of planting vetiver grass in citrus groves on sloping red soil fields. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1994, 14(3): 249-254. |
| 陈凯, 胡国谦, 饶辉茂, 等. 红壤坡地柑桔园栽植香根草的生态效应. 生态学报, 1994, 14(3): 249-254. | |
| 21 | Hao S Y, Liu H D, Niu J L, et al. Effects of herbage mulching to the apple yield and soil water and other soil physical properties in the Loess Plateau. Soil Fertilizer, 2003(1): 25-27. |
| 郝淑英, 刘蝴蝶, 牛俊玲, 等. 黄土高原区果园生草覆盖对土壤物理性状、水分及产量的影响. 土壤肥料, 2003(1): 25-27. | |
| 22 | Gan Z T. Distribution pattern of fine roots and soil moisture characteristics of apple orchard in Weibei rainfed tableland of the Loess Plateau. Xianyang: Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2008. |
| 甘卓亭. 渭北旱塬苹果园根系分布格局及其土壤水分生态特征研究. 咸阳: 中国科学院研究生院, 2008. | |
| 23 | Zhang X L, Li H K, Zhang G J, et al. Effects of interplanting different herbage on soil moisture in apple orchards of Weibei Plateau. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2005, 3(20): 56-59. |
| 张先来, 李会科, 张广军, 等. 种植不同牧草对渭北苹果园土壤水分影响的初步分析. 西北林学院学报, 2005, 3(20): 56-59. | |
| 24 | Li T C, Li H K, Guo H, et al. Soil moisture characteristics of different herbages on soil water in apple orchard in the area of Weibei Plateau in dry season. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 21(1): 29-33, 38. |
| 李同川, 李会科, 郭宏, 等. 渭北黄土高原果园生草地旱季土壤水分特征研究. 水土保持学报, 2014, 21(1): 29-33, 38. | |
| 25 | Li T C. Study on the characteristics of soil water change of interplanting different herbages for a long time in apple orchard in the area of Weibei Plateau. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University, 2014. |
| 李同川. 渭北黄土高原苹果园长期生草土壤水分变化特征. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2014. | |
| 26 | Yang X. Effects of climate change on yield, water use and soil nutrients of the crop production systems on the Loess Plateau. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019. |
| 杨轩. 气候变化对黄土高原作物生产系统产量、水分利用及土壤养分的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2019. | |
| 27 | Liu K Y, Si B C, Zhang Z Q. Responses of water uptake pattern of apple trees with different stand ages to precipitation on the Loess Plateau. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 32(4): 88-94, 108. |
| 刘柯渝, 司炳成, 张志强. 黄土高原不同林龄苹果树根系吸水策略对降水的响应. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(4): 88-94, 108. | |
| 28 | Wang Z K, Wu Y H, Cao Q, et al. Modeling the coupling processes of evapotranspiration and soil water balance in agroforestry systems. Agricultural Water Management, 2021, 250(1):106839. |
| 29 | Cao Q, Wang Z K, Yang X L, et al. The effects of cocksfoot cover crop on soil water balance, evapotranspiration partitioning, and system production in an apple orchard on the Loess Plateau of China. Soil and Tillage Research, 2021, 205: 104788. |
| 30 | Li Q S, Wu J J, Yan L J, et al. Effect of rye grass intercropped peach orchard on soil thermal regime and its simulation study. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 1996, 7: 39-44. |
| 李全胜, 吴建军, 严力蛟, 等. 桃园套种黑牧草对土壤热状况的影响及其模拟研究. 应用生态学报, 1996, 7: 39-44. | |
| 31 | Li X J, Zhang X Z, Wu J S, et al. Root biomass distribution in alpine ecosystems of the northern Tibetan Plateau. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2011, 64(7): 1911-1919. |
| 32 | Zhang H R, Gang F. Root biomass, carbon and nitrogen distribution pattern and correlation characteristics of alpine meadow in northern Tibet. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(9): 3625-3633. |
| 张豪睿, 刚付. 藏北高寒草甸根系生物量与碳氮分布格局及关联特征研究. 生态学报, 2021, 41(9): 3625-3633. | |
| 33 | Zhang J S, Meng P, Yin C J. Spatial distribution characteristics of apple tree roots in the apple-wheat intercropping. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2002, 38(4): 30-33. |
| 张劲松, 孟平, 尹昌君. 果农复合系统中果树根系空间分布特征. 林业科学, 2002, 38(4): 30-33. | |
| 34 | Zhang Y Q, Zhu Q K, Qi S, et al. Root system distribution characteristics of plants on the terrace banks and their impact on soil moisture. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2005, 25(3): 500-506. |
| 张宇清, 朱清科, 齐实, 等. 梯田埂坎立地植物根系分布特征及其对土壤水分的影响. 生态学报, 2005, 25(3): 500-506. | |
| 35 | Ismail M R, Noor K M. Growth, water relations and physiological processes of starfruit (Averrhoa carambola L.) plants under root growth restriction. Science Hortic-Amsterdam, 1996, 66(1/2): 51-58. |
| 36 | Oliveira M T, Merwin I A. Soil physical conditions in a New York orchard after eight years under different groundcover management systems. Plant Soil, 2001, 234(1): 233-237. |
| [1] | 古丽娜扎尔·艾力null, 陶海宁, 王自奎, 沈禹颖. 基于APSIM模型的黄土旱塬区苜蓿——小麦轮作系统深层土壤水分及水分利用效率研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 22-33. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||