

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 118-127.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022025
邹博坤( ), 王欣铭, 褚章杉, 黄馨慧, 陈雨峰, 钱永强(
), 王欣铭, 褚章杉, 黄馨慧, 陈雨峰, 钱永强( )
)
收稿日期:2022-01-12
修回日期:2022-03-17
出版日期:2022-11-20
发布日期:2022-10-01
通讯作者:
钱永强
作者简介:E-mail: qianyq@caf.ac.cn基金资助:
Bo-kun ZOU( ), Xin-ming WANG, Zhang-shan CHU, Xin-hui HUANG, Yu-feng CHEN, Yong-qiang QIAN(
), Xin-ming WANG, Zhang-shan CHU, Xin-hui HUANG, Yu-feng CHEN, Yong-qiang QIAN( )
)
Received:2022-01-12
Revised:2022-03-17
Online:2022-11-20
Published:2022-10-01
Contact:
Yong-qiang QIAN
摘要:
为探究野牛草对氮素的吸收偏好,提高野牛草全生育期精细化管理水平,以野牛草‘Sundancer’和‘Texoka’为试验材料,以不施氮(N0)为对照,设置尿素(N1)、硝态氮(N2)、铵态氮(N3)和硝铵1∶1混合(N4)4种氮素形态,施氮量500 mg·kg-1,分析了不同氮素形态对野牛草生长及氮素吸收利用的影响。结果表明:混合态氮显著提高(P<0.05)野牛草总氮含量及地下部硝酸还原酶(NR)、谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)和地上部谷氨酸合酶(GOGAT)活性。硝态氮显著提高(P<0.05)野牛草地上部硝态氮含量,尿素显著提高(P<0.05)野牛草地下部硝态氮和铵态氮含量,铵态氮显著提高(P<0.05)野牛草地上部铵态氮含量和NR活性。野牛草地上部GS活性在铵态氮处理下显著降低(P<0.05),地下部GOGAT活性在硝态氮处理下显著降低(P<0.05)。混合态氮能更好地提高野牛草生理活性并促进其生长,单一氮源会抑制部分氮同化酶活性,建议在野牛草实际生产中应以1∶1混合态氮或以尿素为氮源。
邹博坤, 王欣铭, 褚章杉, 黄馨慧, 陈雨峰, 钱永强. 氮素形态对野牛草生长及氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 118-127.
Bo-kun ZOU, Xin-ming WANG, Zhang-shan CHU, Xin-hui HUANG, Yu-feng CHEN, Yong-qiang QIAN. Effects of nitrogen forms on growth and nitrogen assimilation and utilization of Buchloe dactyloides[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(11): 118-127.
处理 Treatments | 株高Height | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 d | 14 d | 21 d | 28 d | 35 d | 42 d | 49 d | 56 d | |
| S-N0 | 72.4±2.76cd | 85.4±3.16f | 90.1±1.76f | 100.8±1.21h | 103.2±1.95i | 105.6±1.46h | 108.3±1.77g | 110.9±1.29h |
| S-N1 | 83.5±1.29ab | 96.9±1.57de | 144.9±1.80b | 155.4±1.31e | 168.9±1.86f | 179.7±2.27e | 190.1±1.76d | 191.7±1.36f |
| S-N2 | 83.7±1.55ab | 100.7±3.90cde | 153.8±1.34a | 169.3±2.83b | 182.8±1.23b | 198.2±1.47b | 205.0±1.58b | 209.5±0.98cd |
| S-N3 | 91.9±2.14a | 106.1±1.63abc | 125.6±3.91d | 147.4±0.78f | 160.6±2.14g | 170.9±2.00f | 178.5±0.90e | 189.9±1.60f |
| S-N4 | 89.7±2.27a | 108.5±2.62ab | 144.3±2.91b | 163.6±2.38c | 176.3±1.19cd | 185.5±1.85c | 189.4±3.72d | 197.8±1.45e |
| T-N0 | 55.0±1.55d | 83.1±3.89f | 111.1±1.36e | 116.0±1.86g | 119.4±1.70h | 123.0±2.03g | 126.1±3.52f | 125.7±1.91g |
| T-N1 | 75.5±1.63bcd | 96.5±3.76e | 142.8±1.90bc | 160.1±2.00d | 173.1±3.82de | 181.3±0.87de | 196.4±2.69c | 208.2±1.37d |
| T-N2 | 76.4±1.50bc | 97.6±2.03de | 140.0±1.71c | 160.3±1.61d | 169.3±2.28ef | 184.6±3.27cd | 196.4±1.38c | 211.6±0.86c |
| T-N3 | 78.7±0.62bc | 102.8±1.13bcd | 153.4±3.30a | 167.8±1.82b | 180.1±1.99bc | 196.3±2.14b | 209.4±0.75a | 215.9±3.30b |
| T-N4 | 83.0±1.17abc | 110.2±1.49a | 156.6±3.69a | 173.2±1.92a | 189.2±2.21a | 205.5±0.71a | 211.5±0.80a | 218.8±1.01a |
表1 氮素形态对野牛草株高的影响
Table 1 Effects of different nitrogen forms on height of B. dactyloides (mm)
处理 Treatments | 株高Height | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 d | 14 d | 21 d | 28 d | 35 d | 42 d | 49 d | 56 d | |
| S-N0 | 72.4±2.76cd | 85.4±3.16f | 90.1±1.76f | 100.8±1.21h | 103.2±1.95i | 105.6±1.46h | 108.3±1.77g | 110.9±1.29h |
| S-N1 | 83.5±1.29ab | 96.9±1.57de | 144.9±1.80b | 155.4±1.31e | 168.9±1.86f | 179.7±2.27e | 190.1±1.76d | 191.7±1.36f |
| S-N2 | 83.7±1.55ab | 100.7±3.90cde | 153.8±1.34a | 169.3±2.83b | 182.8±1.23b | 198.2±1.47b | 205.0±1.58b | 209.5±0.98cd |
| S-N3 | 91.9±2.14a | 106.1±1.63abc | 125.6±3.91d | 147.4±0.78f | 160.6±2.14g | 170.9±2.00f | 178.5±0.90e | 189.9±1.60f |
| S-N4 | 89.7±2.27a | 108.5±2.62ab | 144.3±2.91b | 163.6±2.38c | 176.3±1.19cd | 185.5±1.85c | 189.4±3.72d | 197.8±1.45e |
| T-N0 | 55.0±1.55d | 83.1±3.89f | 111.1±1.36e | 116.0±1.86g | 119.4±1.70h | 123.0±2.03g | 126.1±3.52f | 125.7±1.91g |
| T-N1 | 75.5±1.63bcd | 96.5±3.76e | 142.8±1.90bc | 160.1±2.00d | 173.1±3.82de | 181.3±0.87de | 196.4±2.69c | 208.2±1.37d |
| T-N2 | 76.4±1.50bc | 97.6±2.03de | 140.0±1.71c | 160.3±1.61d | 169.3±2.28ef | 184.6±3.27cd | 196.4±1.38c | 211.6±0.86c |
| T-N3 | 78.7±0.62bc | 102.8±1.13bcd | 153.4±3.30a | 167.8±1.82b | 180.1±1.99bc | 196.3±2.14b | 209.4±0.75a | 215.9±3.30b |
| T-N4 | 83.0±1.17abc | 110.2±1.49a | 156.6±3.69a | 173.2±1.92a | 189.2±2.21a | 205.5±0.71a | 211.5±0.80a | 218.8±1.01a |
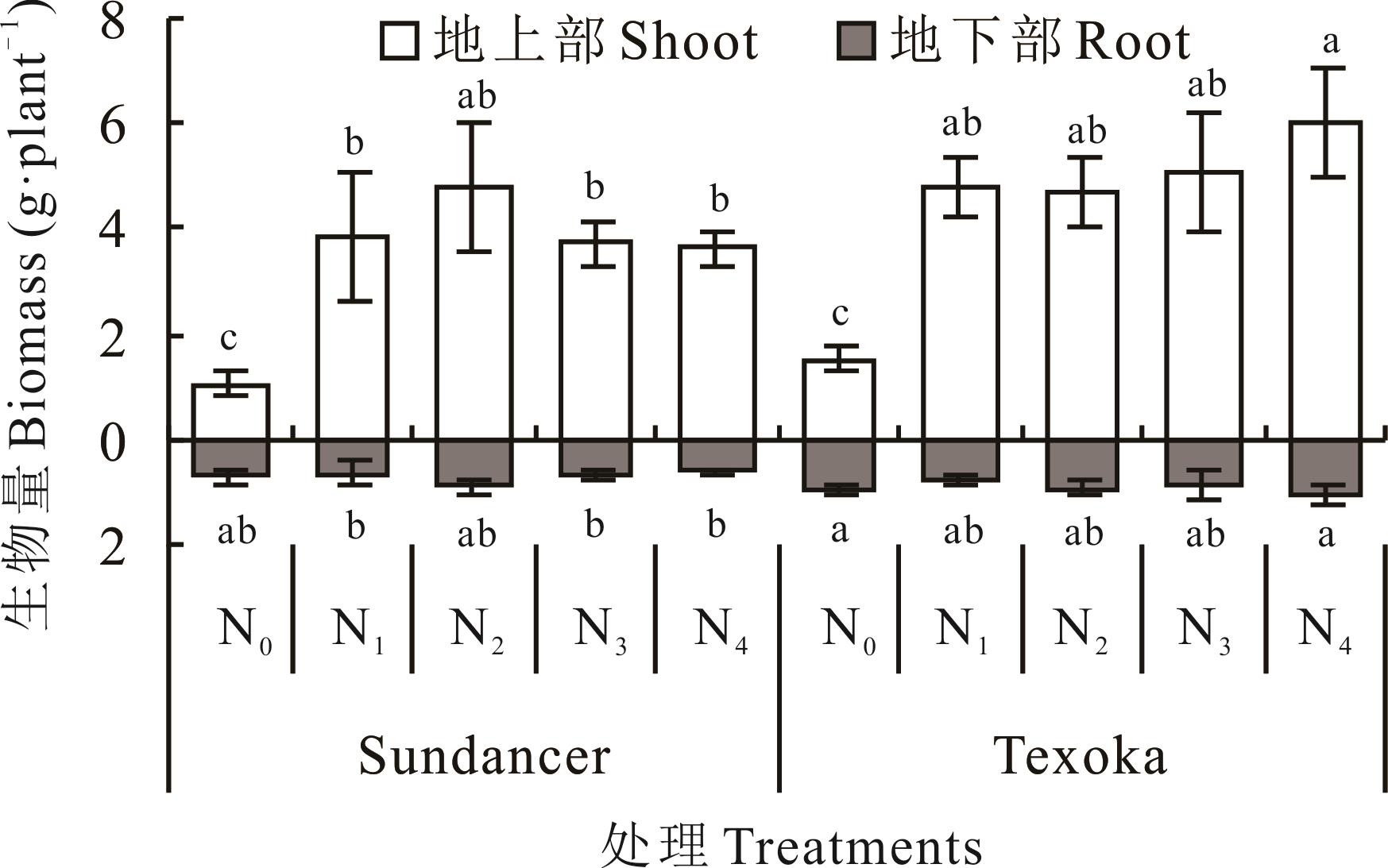
图1 氮素形态对野牛草生物量的影响不同小写字母表示两个品种同一部位不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences, at the same tissue, among different treatments for the two cultivars at the 0.05 level, the same below.
Fig.1 Effects of different nitrogen forms on biomass of B. dactyloides
处理 Treatments | 地上部Shoot | 地下部Root | 隶属度值Subordinate values | 排名Rank | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH | BI | NI | AM | NC | NR | GS | GOGAT | BI | NI | AM | NC | NR | GS | GOGAT | |||
| S-N0 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.078 | 0.077 | 0.106 | 0.352 | 0.285 | 0.227 | 0.012 | 0.000 | 0.018 | 0.000 | 0.462 | 0.000 | 0.102 | 10 |
| S-N1 | 0.747 | 0.562 | 0.672 | 0.470 | 0.810 | 0.561 | 0.476 | 0.531 | 0.018 | 1.000 | 0.862 | 0.546 | 0.916 | 0.241 | 0.782 | 0.642 | 5 |
| S-N2 | 0.901 | 0.753 | 1.000 | 0.478 | 0.857 | 0.717 | 0.559 | 0.577 | 0.675 | 0.682 | 0.318 | 0.785 | 0.889 | 0.072 | 0.544 | 0.647 | 4 |
| S-N3 | 0.736 | 0.541 | 0.422 | 1.000 | 0.730 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.462 | 0.022 | 0.376 | 0.356 | 0.778 | 0.712 | 0.064 | 0.677 | 0.519 | 8 |
| S-N4 | 0.794 | 0.523 | 0.129 | 0.712 | 1.000 | 0.672 | 1.000 | 0.831 | 0.000 | 0.912 | 0.498 | 1.000 | 0.984 | 0.353 | 1.000 | 0.699 | 2 |
| T-N0 | 0.155 | 0.102 | 0.112 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.086 | 0.000 | 0.900 | 0.000 | 0.133 | 0.000 | 0.239 | 1.000 | 0.028 | 0.163 | 9 |
| T-N1 | 0.898 | 0.752 | 0.681 | 0.402 | 0.764 | 0.695 | 0.202 | 0.646 | 0.368 | 0.847 | 1.000 | 0.554 | 1.000 | 0.297 | 0.677 | 0.656 | 3 |
| T-N2 | 0.927 | 0.732 | 1.000 | 0.680 | 0.887 | 0.627 | 0.308 | 0.723 | 0.699 | 0.635 | 0.482 | 0.743 | 0.590 | 0.072 | 0.501 | 0.622 | 6 |
| T-N3 | 0.969 | 0.809 | 0.397 | 0.839 | 0.812 | 0.817 | 0.006 | 0.585 | 0.672 | 0.365 | 0.402 | 0.680 | 0.446 | 0.000 | 0.688 | 0.523 | 7 |
| T-N4 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.138 | 0.869 | 0.933 | 0.696 | 0.311 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.747 | 0.727 | 0.935 | 0.827 | 0.896 | 0.737 | 0.736 | 1 |
| 权重Weight | 0.034 | 0.066 | 0.032 | 0.100 | 0.099 | 0.065 | 0.066 | 0.049 | 0.052 | 0.075 | 0.072 | 0.077 | 0.075 | 0.050 | 0.088 | ||
表2 氮素形态对野牛草影响的隶属函数综合分析
Table 2 Comprehensive analysis of membership functions of the effect of nitrogen forms on B. dactyloides
处理 Treatments | 地上部Shoot | 地下部Root | 隶属度值Subordinate values | 排名Rank | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH | BI | NI | AM | NC | NR | GS | GOGAT | BI | NI | AM | NC | NR | GS | GOGAT | |||
| S-N0 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.078 | 0.077 | 0.106 | 0.352 | 0.285 | 0.227 | 0.012 | 0.000 | 0.018 | 0.000 | 0.462 | 0.000 | 0.102 | 10 |
| S-N1 | 0.747 | 0.562 | 0.672 | 0.470 | 0.810 | 0.561 | 0.476 | 0.531 | 0.018 | 1.000 | 0.862 | 0.546 | 0.916 | 0.241 | 0.782 | 0.642 | 5 |
| S-N2 | 0.901 | 0.753 | 1.000 | 0.478 | 0.857 | 0.717 | 0.559 | 0.577 | 0.675 | 0.682 | 0.318 | 0.785 | 0.889 | 0.072 | 0.544 | 0.647 | 4 |
| S-N3 | 0.736 | 0.541 | 0.422 | 1.000 | 0.730 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.462 | 0.022 | 0.376 | 0.356 | 0.778 | 0.712 | 0.064 | 0.677 | 0.519 | 8 |
| S-N4 | 0.794 | 0.523 | 0.129 | 0.712 | 1.000 | 0.672 | 1.000 | 0.831 | 0.000 | 0.912 | 0.498 | 1.000 | 0.984 | 0.353 | 1.000 | 0.699 | 2 |
| T-N0 | 0.155 | 0.102 | 0.112 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.086 | 0.000 | 0.900 | 0.000 | 0.133 | 0.000 | 0.239 | 1.000 | 0.028 | 0.163 | 9 |
| T-N1 | 0.898 | 0.752 | 0.681 | 0.402 | 0.764 | 0.695 | 0.202 | 0.646 | 0.368 | 0.847 | 1.000 | 0.554 | 1.000 | 0.297 | 0.677 | 0.656 | 3 |
| T-N2 | 0.927 | 0.732 | 1.000 | 0.680 | 0.887 | 0.627 | 0.308 | 0.723 | 0.699 | 0.635 | 0.482 | 0.743 | 0.590 | 0.072 | 0.501 | 0.622 | 6 |
| T-N3 | 0.969 | 0.809 | 0.397 | 0.839 | 0.812 | 0.817 | 0.006 | 0.585 | 0.672 | 0.365 | 0.402 | 0.680 | 0.446 | 0.000 | 0.688 | 0.523 | 7 |
| T-N4 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.138 | 0.869 | 0.933 | 0.696 | 0.311 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.747 | 0.727 | 0.935 | 0.827 | 0.896 | 0.737 | 0.736 | 1 |
| 权重Weight | 0.034 | 0.066 | 0.032 | 0.100 | 0.099 | 0.065 | 0.066 | 0.049 | 0.052 | 0.075 | 0.072 | 0.077 | 0.075 | 0.050 | 0.088 | ||
| 1 | Kraap A. Plant nitrogen assimilation and its regulation: a complex puzzle with missing pieces. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2015, 25: 115-122. |
| 2 | Reddy K, Mallesham B, Aakanksha W, et al. An overview of important enzymes involved in nitrogen assimilation of plants// Kapuganti J G. Nitrogen metabolism in plants methods and protocols. New York: Springer Science, Business Media, 2020: 1-13. |
| 3 | O’brien J A, Vega A, Bouguion E, et al. Nitrate transport, sensing, and responses in plants. Molecular Plant, 2016, 9(6): 837-856. |
| 4 | Liu W T, Wang Y Q, Sun S N, et al. Effects of nitrogen forms on nitrogen accumulation and utilization of alfalfa in different stubbles. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(4): 716-725. |
| 刘文涛, 王玉强, 孙盛楠, 等. 氮素形态对不同茬次紫花苜蓿氮素积累及利用的影响. 草业科学, 2021, 38(4): 716-725. | |
| 5 | Mckane R B, Johnson L C, Shaver G R, et al. Resource-based niches provide a basis for plant species diversity and dominance in arctic tundra. Nature, 2002, 413: 68-71. |
| 6 | Weight A, Bol R, Bardegtt R D. Preferential uptake of soil nitrogen forms by grassland plant species. Oecologia, 2005, 142(4): 627-635. |
| 7 | Quinn J A, Engel J L. Life-history strategies and sex ratios for a cultivar and a wild population of Buchloe dactyloides. American Journal of Botany, 1986, 73(6): 874-881. |
| 8 | Alderman E J, Hoyle J A, Keeley S J, et al. Buffalograss divot recovery as affected by nitrogen source and rate. Crop, Forage & Turfgrass Management, 2017, 3(1): 1-6. |
| 9 | Frank K W, Miltner E D, Fry J D, et al. Nitrogen rate and mowing height effects on turf-type buffalograss. Crop Science, 2004, 44(5): 1615-1621. |
| 10 | Li H B, Zhao Y J, Wang L H, et al. Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization ratios on turf quality of buffalograss. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 1: 93-95. |
| 李会彬, 赵玉靖, 王丽宏, 等. 氮磷配施对野牛草草坪质量的影响. 安徽农业科学, 2012, 1: 93-95. | |
| 11 | Quan X Y. Studies on mechanisms of low nitrogen tolerance in Tibetan wild barley. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2016. |
| 全晓艳. 西藏野生大麦低氮耐性机理研究. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2016. | |
| 12 | Bao S D. Soil agro-chemistrical analysis (The Third Edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2018. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2018. | |
| 13 | Gao J F. Experimental guidance of plant physiology. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006: 68-138. |
| 高俊凤. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006: 68-138. | |
| 14 | Shi H T. Experimental guidance of plant stress physiology. Beijing: Science Press, 2016. |
| 施海涛. 植物逆境生理学实验指导. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016. | |
| 15 | Wang X L, Song B Q. Nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency: research progress. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(5): 93-97. |
| 王响玲, 宋柏权. 氮肥利用率的研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(5): 93-97. | |
| 16 | Wu Z L, Qi J, Liu W H, et al. Effects of nitrogen forms and proportions of nitrogen forms on the growth and physiological characteristics of Elymus sibiricus. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(5): 942-951. |
| 吴召林, 祁娟, 刘文辉, 等. 氮素形态及其配比对老芒麦生长及生理特性的影响. 草业科学, 2020, 37(5): 942-951. | |
| 17 | El-metwally I, Ssudy H, El-ashry S. Response of maize and associated weeds to irrigation intervals, weed management and nitrogen forms. Journal of Plant Production, 2009, 34(5): 5003-5017. |
| 18 | Ravazzolo L, Trevisan S, Forestan C, et al. Nitrate and ammonium affect the overall maize response to nitrogen availability by triggering specific and common transcriptional signatures in roots. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(2): 686. |
| 19 | Guo J X, Jia Y, Chen H H, et al. Growth, photosynthesis, and nutrient uptake in wheat are affected by differences in nitrogen levels and forms and potassium supply. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 1248. |
| 20 | Asif M, Zora S, Ceylan Y, et al. Nitrogen supply in combination of nitrate and ammonium enhances harnessing of elevated atmospheric CO2 through improved nitrogen and carbon metabolism in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Crop & Pasture Science, 2020, 71(2): 101-112. |
| 21 | Liu D J. Effects of different nitrogen nutrition forms on physiology characteristics at seedling stage of wheat. Crops, 2011, 1: 20-24. |
| 刘东军. 不同形态氮素对春小麦苗期生理特性及氮代谢酶的影响. 作物杂志, 2011, 1: 20-24. | |
| 22 | He W J, Tian P, Xiao L L, et al. Effects of different nitrogen forms and proportion on growth and quality of flue-cured tobacco under the integration with water and fertilizer. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(3): 45-49. |
| 贺文俊, 田培, 肖磊磊, 等. 水肥一体化模式下氮素形态及配比对烤烟生长及品质的影响. 贵州农业科学, 2019, 47(3): 45-49. | |
| 23 | Zhang J B, Cheng Y, Cai Z C. The mechanisms of soil regulating nitrogen dynamics. Advances in Earth Science, 2019, 34(1): 11-19. |
| 张金波, 程谊, 蔡祖聪. 土壤调配氮素迁移转化的机理. 地球科学进展, 2019, 34(1): 11-19. | |
| 24 | Li C C, Gao Y H, Guo L Z, et al. Effects of different forms and ratios of nitrogen on nutrient accumulation and transfer of whole plastic-film mulching on double ridges and planting in catchment furrows of maize. Journal of Maize Science, 2018, 26(1): 134-141. |
| 李春春, 高玉红, 郭丽琢, 等. 氮素形态配比对玉米氮素积累及转运的影响. 玉米科学, 2018, 26(1): 134-141. | |
| 25 | Ali A. Nitrate assimilation pathway in higher plants: critical role in nitrogen signalling and utilization. Plant Science Today, 2020, 7(2): 182-192. |
| 26 | Kong F J. Effects of plant growth and nitrogen assimilation enzyme activity of different nitrogen on Pinus koraiensis seedings. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2010. |
| 孔凡婧. 氮素形态对红松幼苗生长及氮同化酶活性的影响. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2010. | |
| 27 | Sun M H, Wu L, Xie S X. Effect of nitrate and ammonium nutrition on glutamine synthetase activities and relative genes for citrange. Plant Physiology Journal, 2018, 54(11): 1703-1710. |
| 孙敏红, 吴炼, 谢深喜. 铵硝营养对枳橙幼苗谷氨酰胺合成酶活性及相关基因表达的影响. 植物生理学报, 2018, 54(11): 1703-1710. | |
| 28 | Wang R, Chen L S, Wang X N, et al. Effects of different proportion of nitrogen forms on the growth and physiological characteristics of Camellia oleifera seedlings. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2019, 43(4): 26-32. |
| 王瑞, 陈隆升, 王湘南, 等. 氮素形态对油茶苗木生长及生理指标的影响. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 43(4): 26-32. |
| [1] | 刘彩婷, 毛丽萍, 阿依谢木, 于应文, 沈禹颖. 紫花苜蓿与垂穗披碱草混播比例对其抗寒生长生理特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 133-143. |
| [2] | 汪梦寒, 董利利, 李富翠, 韩烈保, 王祥. 不同有机/无机氮添加对草原土壤氮素分配和转化特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 36-46. |
| [3] | 李岩, 苏德荣, 李宏韬. 西北旱区喷灌条件下紫花苜蓿生长特征与品质指标的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 54-65. |
| [4] | 王茜, 纪树仁, 沈益新. 土壤水分和施氮水平对紫花苜蓿苗期生长的互作效应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(12): 48-55. |
| [5] | 刘兆娜, 郭绍霞, 李伟. AM真菌对百合生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(11): 85-93. |
| [6] | 邹长明, 王允青, 曹卫东, 张晓红, 刘英, 杨杰, 唐杉. 高光合效率小豆筛选与营养价值评价[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(7): 52-59. |
| [7] | 高欢欢, 曾凡江, 鲁艳, 刘镇, 安桂香, 刘波. 不同干扰方式对疏叶骆驼刺生长及生理特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(2): 202-207. |
| [8] | 罗栋,钱永强,刘俊祥,韩蕾,李伟,孙振元. 克隆植物野牛草对异质营养的表型可塑性响应[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(3): 104-109. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||