

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (9): 181-197.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022441
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
田甜1,2,3( ), 李军乔1,2,3(
), 李军乔1,2,3( ), 马斌4, 王鑫慈1,2,3, 曲俊儒1,2,3
), 马斌4, 王鑫慈1,2,3, 曲俊儒1,2,3
收稿日期:2022-11-09
修回日期:2023-01-12
出版日期:2023-09-20
发布日期:2023-07-12
通讯作者:
李军乔
作者简介:E-mail: ljqlily2002@126.com基金资助:
Tian TIAN1,2,3( ), Jun-qiao LI1,2,3(
), Jun-qiao LI1,2,3( ), Bin MA4, Xin-ci WANG1,2,3, Jun-ru QU1,2,3
), Bin MA4, Xin-ci WANG1,2,3, Jun-ru QU1,2,3
Received:2022-11-09
Revised:2023-01-12
Online:2023-09-20
Published:2023-07-12
Contact:
Jun-qiao LI
摘要:
利用SSR分子标记法,对青海、甘肃、四川和西藏自治区自然状态下的蕨麻进行了采样策略研究,旨在为后期蕨麻采样、育种等研究提供理论依据。试验样品采集设置为距离原点1、2、3、4、5、10、15、20、25、30、40、50、60、80、90、100、120、150、160、200、250、300、400、500、1000、1500、2000、2500、5000、10000、15000、20000、30000、40000、50000 m处分别采样,后使用20对SSR引物对蕨麻6个居群210份样品DNA进行PCR扩增,通过毛细管电泳检测扩增片段大小,使用POPGENE、NTSYS、GenAIEx 6.5等软件进行分析,结果表明:1)遗传变异主要来源于居群内(变异方差分量和占比分比为12.745和84%),居群间变异较低(变异方差分量和占比分比为2.477和16%);2)6个居群间遗传多样性较高,其中祁连县遗传多样性最高(平均杂合度H=0.2797,香农指数I=0.4287),河南县的遗传多样性最低(H=0.2273,I=0.3542),6个居群整体遗传水平较高,表示在这6个居群间遗传变异低,采样时需要扩大范围;3)同一居群内采集蕨麻样品个体时,最短采样距离为5 km,有小型山脉时,跨越山脉即可采样。居群间采样分两种情况:1)具有离地面高度为1000~1500 m山脉时,翻越大型山脉后可直接采集蕨麻样本。2)在平原地区,由于花粉的长距离传播,居群间有基因交流,建议采样距离不小于100 km。
田甜, 李军乔, 马斌, 王鑫慈, 曲俊儒. 基于SSR分子标记的自然状态下蕨麻采样策略研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 181-197.
Tian TIAN, Jun-qiao LI, Bin MA, Xin-ci WANG, Jun-ru QU. Study on sampling strategy of Potentilla anserina in the wild based on SSR molecular markers[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(9): 181-197.
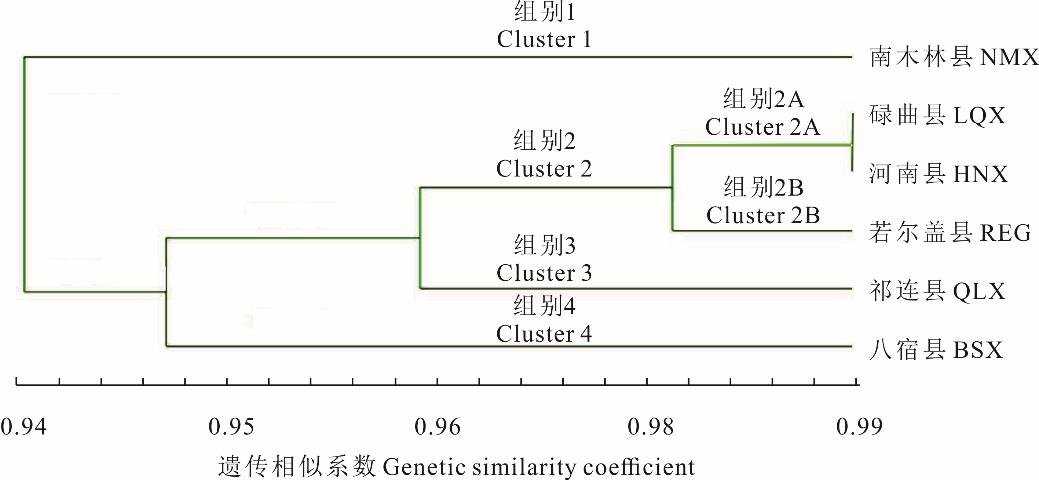
图1 6个蕨麻居群的UPGMA聚类树HNX: 河南县Henan County; QLX: 祁连县Qilian County; BSX: 八宿县Baxoi County; NMX: 南木林县Nanmulin County; LUX: 碌曲县Luqu County; REG: 若尔盖县Ruoergai County. 下同The same below.
Fig.1 UPMGA cluster trees for six P. anserina populations
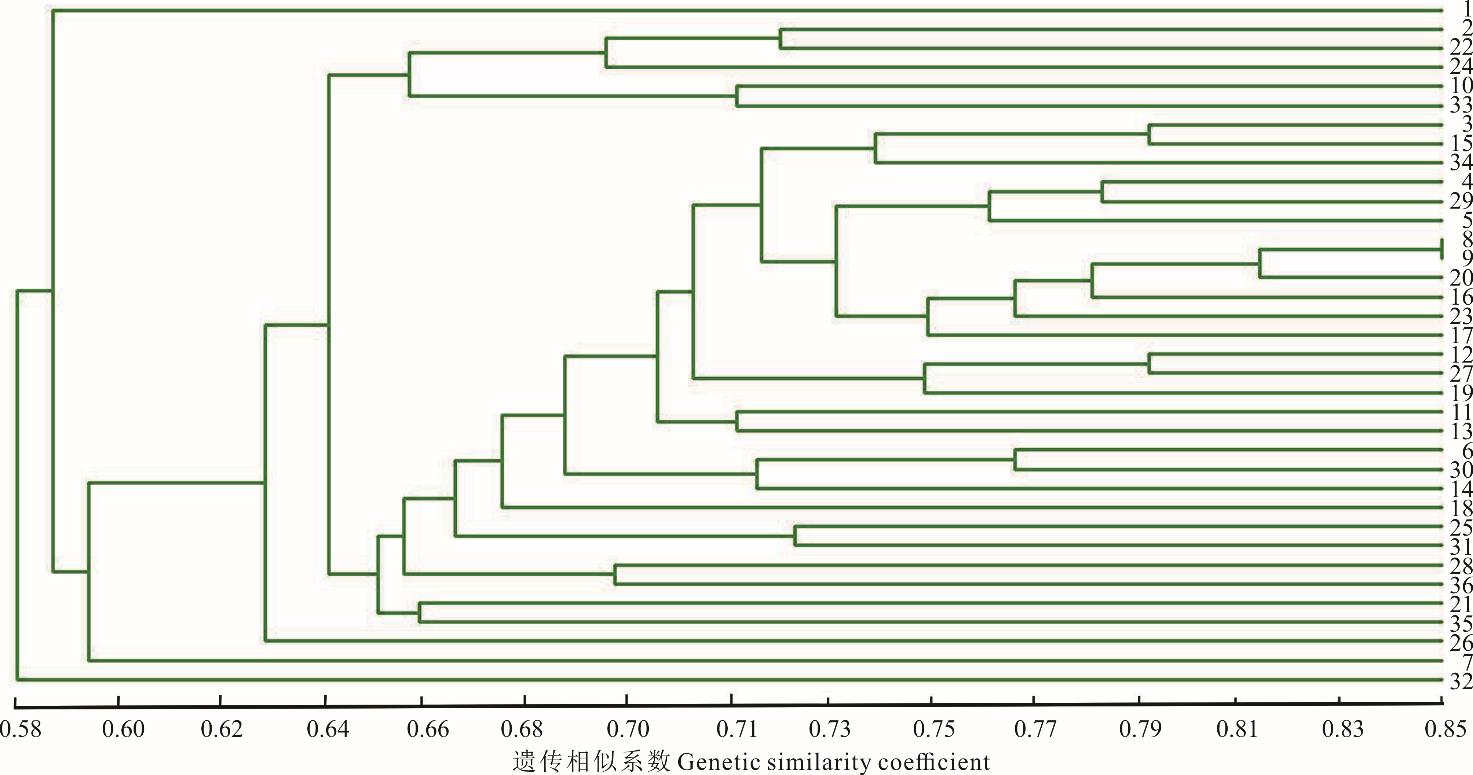
图3 甘肃省碌曲县蕨麻样品UPGMA聚类分析图中数字表示采样编号,下同。The number in the figure represents the sampling number, the same below.
Fig.3 The UPGMA cluster analysis of P. anserina samples in Luqu County, Gansu Province
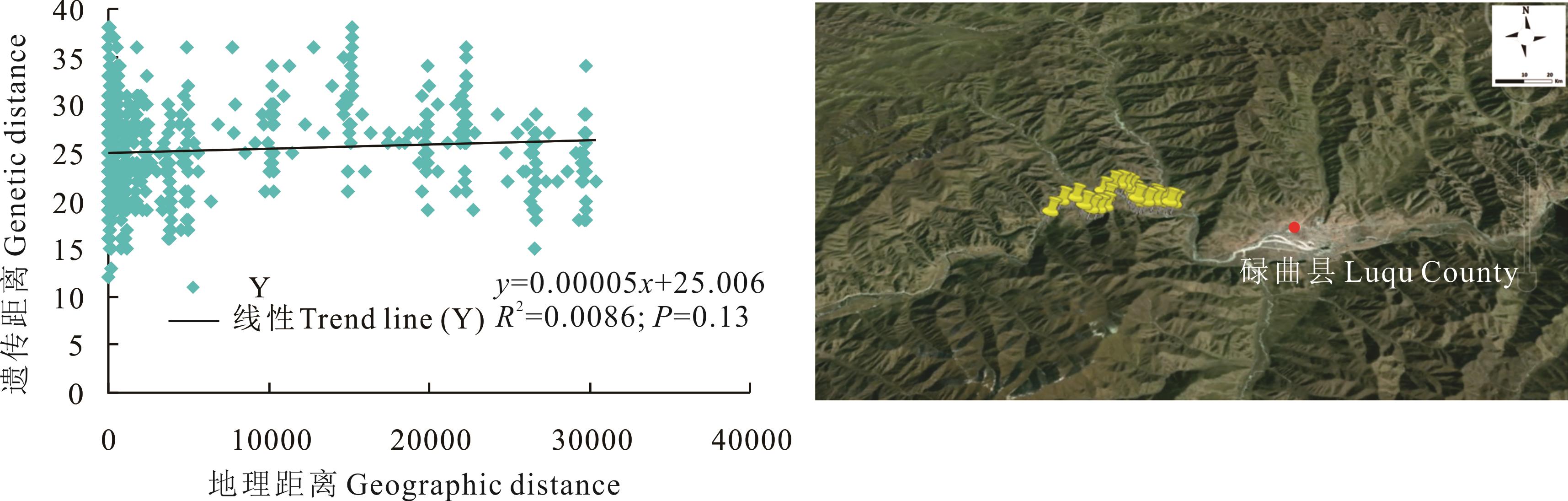
图4 甘肃省碌曲县蕨麻遗传距离与地理距离相关性分析及采样路线
Fig.4 Sample path and mantle test of relationship between genetic distance and geographic distance of P. anserina in Luqu County, Gansu Province
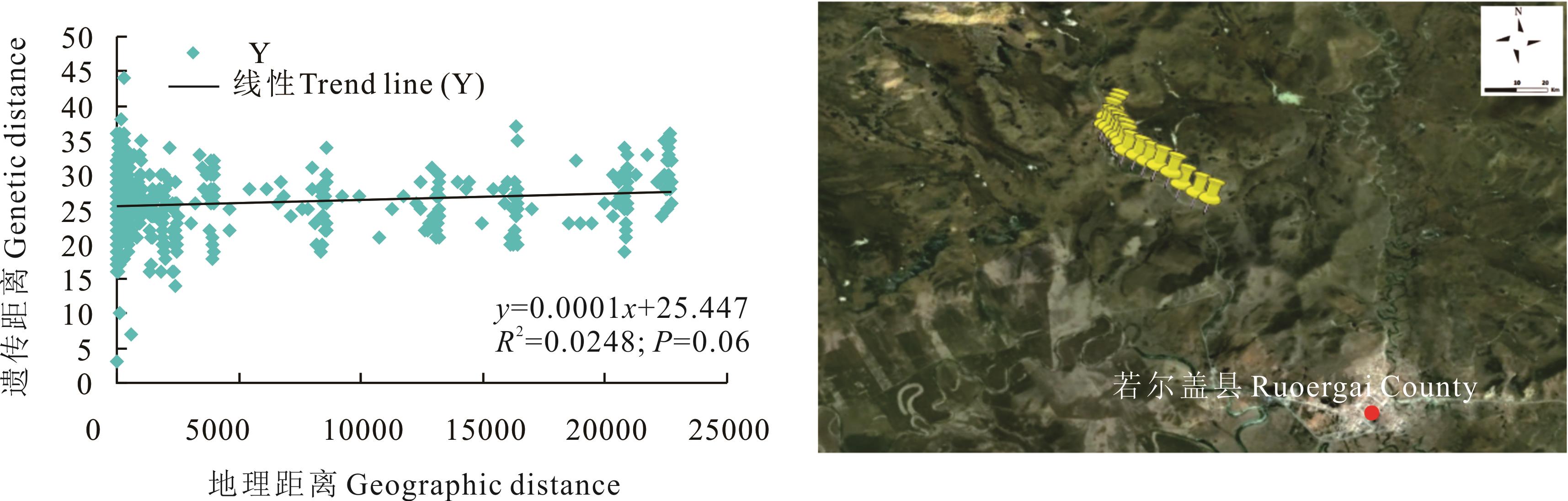
图6 四川省若尔盖县蕨麻遗传距离与地理距离相关性分析及采样路线
Fig.6 Sample path and mantle test of relationship between genetic distance and geographic distance of P. anserina in Ruoergai County, Sichuan Province
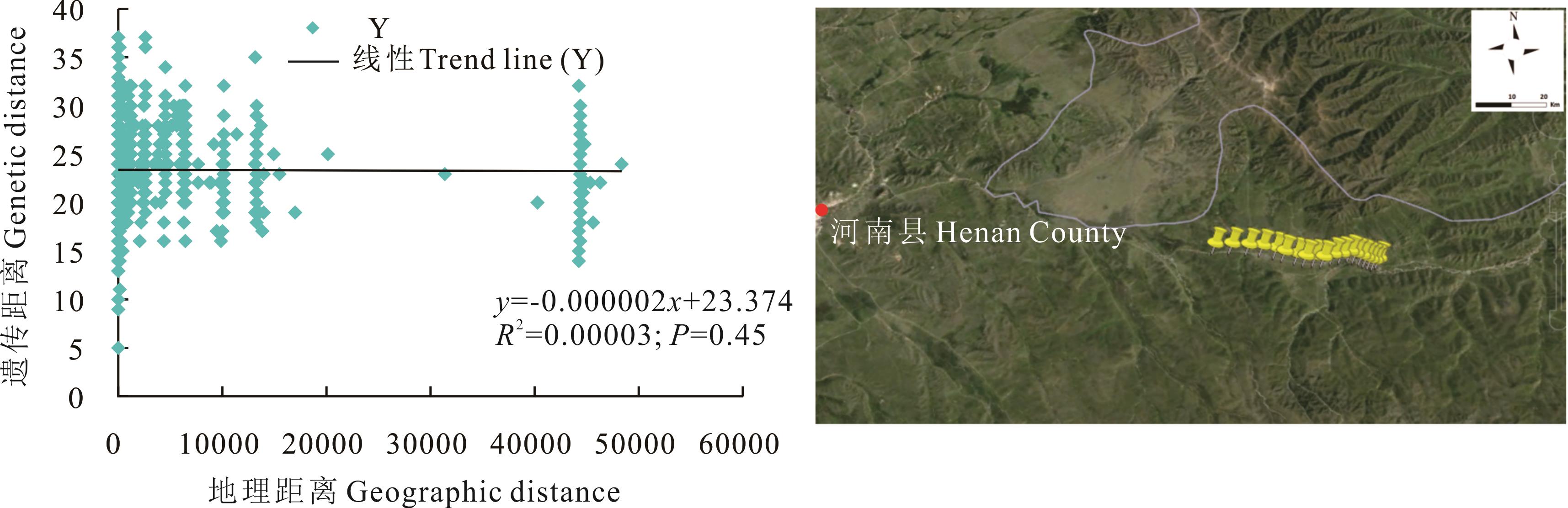
图8 青海省河南县蕨麻遗传距离与地理距离相关性分析及采样路线
Fig.8 Sample path and mantle test of relationship between genetic distance and geographic distance of P. anserina in Henan County, Qinghai Province
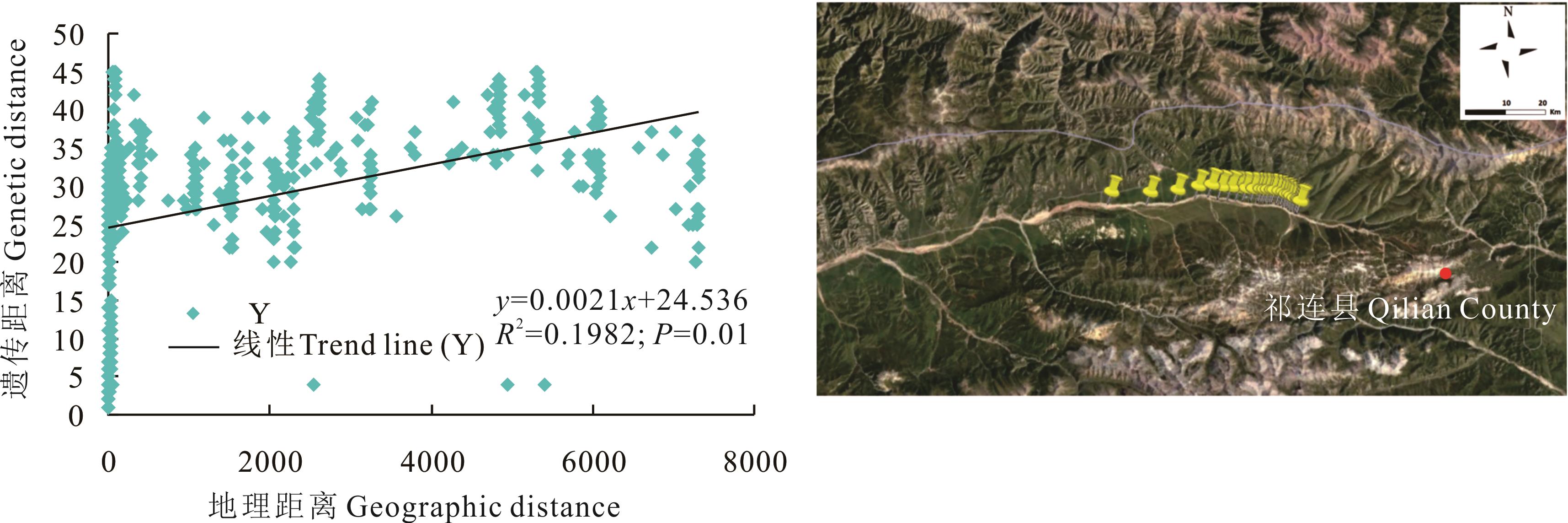
图10 青海省祁连县蕨麻遗传距离与地理距离相关性分析及采样路线
Fig.10 Sample path and mantle test of relationship between genetic distance and geographic distance of P. anserina in Qilian County, Qinghai Province
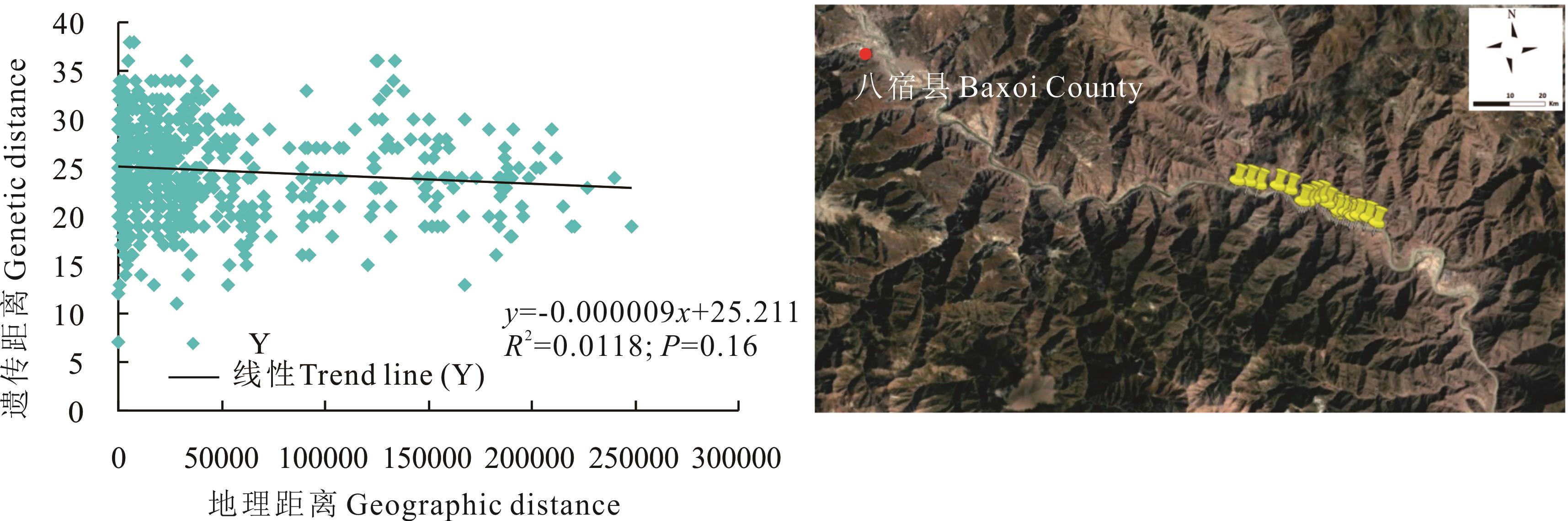
图12 西藏自治区八宿县蕨麻遗传距离与地理距离相关性分析及采样路线
Fig.12 Sample path and mantle test of relationship between genetic distance and geographic distance of P. anserina in Baxoi County, Tibet Autonomous Region
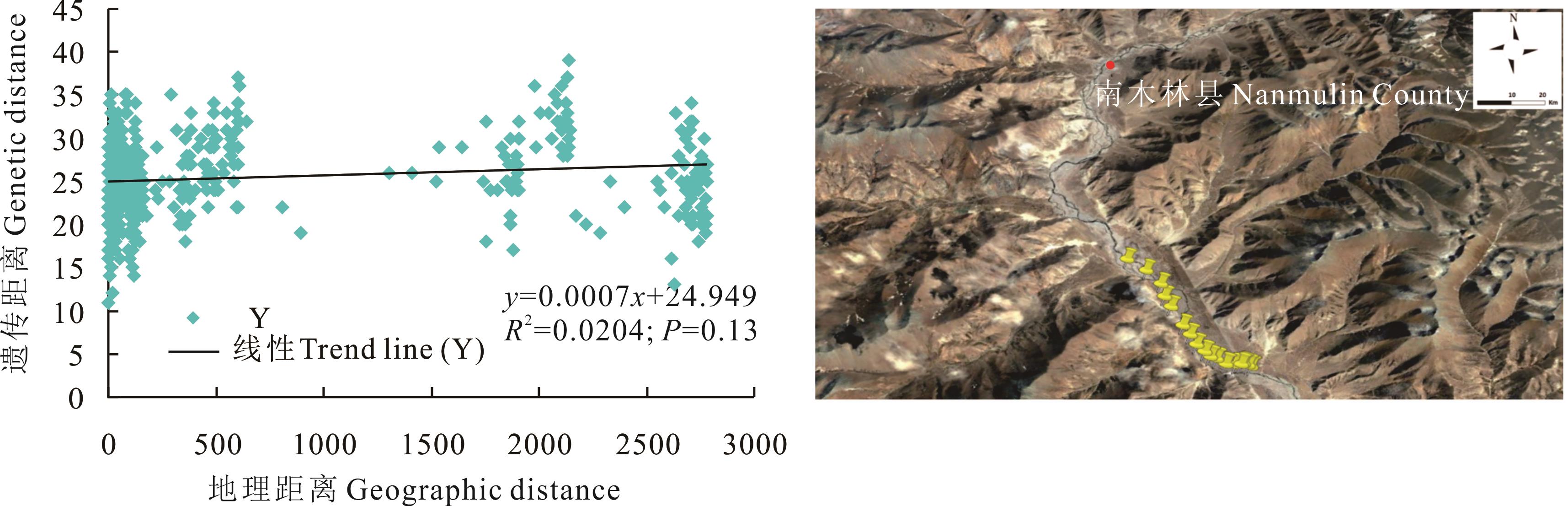
图14 西藏自治区南木林县蕨麻遗传距离与地理距离相关性分析及采样路线
Fig.14 Sample path and mantle test of relationship between genetic distance and geographic distance of P. anserina in Nanmulin County, Tibet Autonomous Region
采样地点 Sampling site | 居群编号 Name of population | 采样数量 Samples size | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 经度 Longitude (E) | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 伴生植物 Accompanying plants |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 青海省河南县Henan County, Qinghai Province | HNX | 37 | 3550~3792 | 34°47′21″- 35°05′03″ | 101°28′23″- 101°39′17″ | 金露梅Potentilla fruticosa,珍珠梅Sorbaria sorbifolia,龙芽草Agrimonia pilosa, 东方草莓Fragaria orientalis,纤细草莓Fragaria gracilis,绣线菊Spiraea salicifolia,高山绣线菊Spiraea alpina,鲜卑花Sibiraea laevigata,二裂叶委陵菜Potentilla bifurca,多茎委陵菜Potentilla multicaulis,莓叶委陵菜Potentilla fragarioides,委陵菜Potentilla chinensis |
| 青海省祁连县Qilian County, Qinghai Province | QLX | 36 | 2991~3483 | 37°22′33″- 37°38′35″ | 101°22′41″- 101°25′32″ | |
| 西藏自治区八宿县Baxoi County, Tibet Autonomous Region | BSX | 34 | 3913~4457 | 30°16′43″- 30°48′27″ | 97°02′01″- 99°15′60″ | |
| 西藏自治区南木林县Nanmulin County, Tibet Autonomous Region | NMX | 33 | 3835~3926 | 29°22′41″- 29°33′59″ | 89°04′32″- 89°06′02″ | |
| 甘肃省碌曲县Luqu County, Gansu Province | LUX | 36 | 2988~3335 | 34°34′24″- 34°48′55″ | 102°27′46″- 102°43′59″ | |
| 四川省若尔盖县Ruoergai County, Sichuan Province | REG | 34 | 3446~3480 | 33°42′34″- 33°59′52″ | 102°46′14″- 102°57′53″ |
表1 采样点基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of sampling points
采样地点 Sampling site | 居群编号 Name of population | 采样数量 Samples size | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 经度 Longitude (E) | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 伴生植物 Accompanying plants |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 青海省河南县Henan County, Qinghai Province | HNX | 37 | 3550~3792 | 34°47′21″- 35°05′03″ | 101°28′23″- 101°39′17″ | 金露梅Potentilla fruticosa,珍珠梅Sorbaria sorbifolia,龙芽草Agrimonia pilosa, 东方草莓Fragaria orientalis,纤细草莓Fragaria gracilis,绣线菊Spiraea salicifolia,高山绣线菊Spiraea alpina,鲜卑花Sibiraea laevigata,二裂叶委陵菜Potentilla bifurca,多茎委陵菜Potentilla multicaulis,莓叶委陵菜Potentilla fragarioides,委陵菜Potentilla chinensis |
| 青海省祁连县Qilian County, Qinghai Province | QLX | 36 | 2991~3483 | 37°22′33″- 37°38′35″ | 101°22′41″- 101°25′32″ | |
| 西藏自治区八宿县Baxoi County, Tibet Autonomous Region | BSX | 34 | 3913~4457 | 30°16′43″- 30°48′27″ | 97°02′01″- 99°15′60″ | |
| 西藏自治区南木林县Nanmulin County, Tibet Autonomous Region | NMX | 33 | 3835~3926 | 29°22′41″- 29°33′59″ | 89°04′32″- 89°06′02″ | |
| 甘肃省碌曲县Luqu County, Gansu Province | LUX | 36 | 2988~3335 | 34°34′24″- 34°48′55″ | 102°27′46″- 102°43′59″ | |
| 四川省若尔盖县Ruoergai County, Sichuan Province | REG | 34 | 3446~3480 | 33°42′34″- 33°59′52″ | 102°46′14″- 102°57′53″ |
引物 Primer | 正向引物 Forward primer (5′→3′) | 反向引物 Reverse primer (3′→5′) | 重复基元 Repeat elements | 目的片段 Target segments size (bp) | 退火温度 Annealing temperature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P3 | TTTCTGCACGTTGGCTTCTT | CAAACTTCAATTTGGTTTCC | (CT)12 | 148 | 54 |
| P5 | GAGATAGATCGACGAGAAGGG | AACAAGACAATGCAGAAAAGG | (AG)21 | 190 | 58 |
| P6 | AAGTAAGAACCGAGGCAAAAT | GATAAAAGAGCCCATCATCAC | (GA)13 | 151 | 55 |
| P8 | CCGTGAAGCAGACCATAATAGC | TCTACACCCTTTCGCCCATAT | (CT)13 | 254 | 58 |
| P12 | AACAATAGAGCCGTTGGAGA | CCTTGGATGCTAGACTGGAC | (TC)14 | 125 | 55 |
| P14 | AGGAGGGACCTGGTTTGGTT | CAGTGCAGCTCAGCCTCACG | (GA)9 | 227 | 60 |
| P15 | GAAGACTGAAGACCCAACAT | GAATTCTCACCGGCCATTAT | (CT)12 | 104 | 56 |
| P18 | GCCCTGCATTCATTCACAAGA | ACCACCCAACCCTGAATCCTA | (TG)8(AG)14 | 188 | 58 |
| P19 | CAGAAGTCCAACAGTCGGTGAG | TTTGCAGCTAGAGGGATGTCA | (TC)14 | 165 | 57 |
| P21 | AACCCAACAGAATCAAAACAC | TAAGTTTTCAGGATAGTGATG | (TC)13 | 164 | 57 |
| P24 | ACTAATACTGGTAAGCGAGAAA | GCTGAAAGTTATTGAAGAGCC | (GT)8 | 295 | 53 |
| P25 | GTGAATTTAGAAGCCATTTA | TAGTATTGGAACGCAACTAC | (AT)10(GT)7 | 157 | 56 |
| P26 | GCGATCTAACAAGAGCTGAAC | GAGGAAAGGAATTTTGAAGTG | (AC)7 | 197 | 55 |
| P27 | GAATTCAGCGCAACAATTCAT | TTCATGTTTATGGACAAGGCA | (AC)9 | 130 | 56 |
| P28 | AGTTGCCGGGATCAGAAGAAG | AAAGTGACCTCCCATCAAGAA | (TG)4(TG)8 | 181 | 58 |
| P30 | ATTCTAGCAAACAACACCAT | TCAACCAAAATAACGACAGT | (CA)8(TA)5 | 129 | 54 |
| P31 | TTAATGGCAGTGCAAGCATGC | CATCAATCCAGGCATTCCCAA | (AC)8 | 105 | 56 |
| P32 | TGGTGATGGGAGACAAAGTAT | TGAGATCTACTGCAAATTCCT | (AC)7 | 103 | 53 |
| P34 | GTTGTGAACGCAAATAAACC | ATTCCTCCTCTTCCGTAATC | (AG)11 | 243 | 58 |
| P40 | ACAGAGGTTCAAACGCAAAGA | GGCAGGTACTGATACCACAAA | (CA)6 | 83 | 55 |
表2 SSR引物序列信息
Table 2 The information of SSR primer sequence
引物 Primer | 正向引物 Forward primer (5′→3′) | 反向引物 Reverse primer (3′→5′) | 重复基元 Repeat elements | 目的片段 Target segments size (bp) | 退火温度 Annealing temperature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P3 | TTTCTGCACGTTGGCTTCTT | CAAACTTCAATTTGGTTTCC | (CT)12 | 148 | 54 |
| P5 | GAGATAGATCGACGAGAAGGG | AACAAGACAATGCAGAAAAGG | (AG)21 | 190 | 58 |
| P6 | AAGTAAGAACCGAGGCAAAAT | GATAAAAGAGCCCATCATCAC | (GA)13 | 151 | 55 |
| P8 | CCGTGAAGCAGACCATAATAGC | TCTACACCCTTTCGCCCATAT | (CT)13 | 254 | 58 |
| P12 | AACAATAGAGCCGTTGGAGA | CCTTGGATGCTAGACTGGAC | (TC)14 | 125 | 55 |
| P14 | AGGAGGGACCTGGTTTGGTT | CAGTGCAGCTCAGCCTCACG | (GA)9 | 227 | 60 |
| P15 | GAAGACTGAAGACCCAACAT | GAATTCTCACCGGCCATTAT | (CT)12 | 104 | 56 |
| P18 | GCCCTGCATTCATTCACAAGA | ACCACCCAACCCTGAATCCTA | (TG)8(AG)14 | 188 | 58 |
| P19 | CAGAAGTCCAACAGTCGGTGAG | TTTGCAGCTAGAGGGATGTCA | (TC)14 | 165 | 57 |
| P21 | AACCCAACAGAATCAAAACAC | TAAGTTTTCAGGATAGTGATG | (TC)13 | 164 | 57 |
| P24 | ACTAATACTGGTAAGCGAGAAA | GCTGAAAGTTATTGAAGAGCC | (GT)8 | 295 | 53 |
| P25 | GTGAATTTAGAAGCCATTTA | TAGTATTGGAACGCAACTAC | (AT)10(GT)7 | 157 | 56 |
| P26 | GCGATCTAACAAGAGCTGAAC | GAGGAAAGGAATTTTGAAGTG | (AC)7 | 197 | 55 |
| P27 | GAATTCAGCGCAACAATTCAT | TTCATGTTTATGGACAAGGCA | (AC)9 | 130 | 56 |
| P28 | AGTTGCCGGGATCAGAAGAAG | AAAGTGACCTCCCATCAAGAA | (TG)4(TG)8 | 181 | 58 |
| P30 | ATTCTAGCAAACAACACCAT | TCAACCAAAATAACGACAGT | (CA)8(TA)5 | 129 | 54 |
| P31 | TTAATGGCAGTGCAAGCATGC | CATCAATCCAGGCATTCCCAA | (AC)8 | 105 | 56 |
| P32 | TGGTGATGGGAGACAAAGTAT | TGAGATCTACTGCAAATTCCT | (AC)7 | 103 | 53 |
| P34 | GTTGTGAACGCAAATAAACC | ATTCCTCCTCTTCCGTAATC | (AG)11 | 243 | 58 |
| P40 | ACAGAGGTTCAAACGCAAAGA | GGCAGGTACTGATACCACAAA | (CA)6 | 83 | 55 |
引物 Primer | 等位基因数目 Number of alleles | 多态性指数 Polymorphism information content (PIC) | 扩增产物大小 Amplified product size (bp) | 引物 Primer | 等位基因数目 Number of alleles | 多态性指数 Polymorphism information content (PIC) | 扩增产物大小 Amplified product size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P3 | 7 | 0.82 | 128~158 | P24 | 4 | 0.66 | 286~306 |
| P5 | 4 | 0.63 | 166~184 | P25 | 6 | 0.75 | 144~172 |
| P6 | 6 | 0.55 | 148~198 | P26 | 3 | 0.44 | 180~200 |
| P8 | 3 | 0.58 | 248~256 | P27 | 4 | 0.58 | 118~126 |
| P12 | 5 | 0.67 | 118~138 | P28 | 6 | 0.73 | 162~188 |
| P14 | 4 | 0.43 | 200~234 | P30 | 4 | 0.62 | 122~134 |
| P15 | 6 | 0.62 | 86~118 | P31 | 3 | 0.58 | 92~104 |
| P18 | 6 | 0.72 | 182~244 | P32 | 4 | 0.69 | 96~104 |
| P19 | 7 | 0.80 | 152~188 | P34 | 2 | 0.25 | 212~220 |
| P21 | 5 | 0.52 | 158~180 | P40 | 4 | 0.65 | 78~92 |
表3 20对核心引物多态性指数
Table 3 The polymorphic information content of 20 SSR primers
引物 Primer | 等位基因数目 Number of alleles | 多态性指数 Polymorphism information content (PIC) | 扩增产物大小 Amplified product size (bp) | 引物 Primer | 等位基因数目 Number of alleles | 多态性指数 Polymorphism information content (PIC) | 扩增产物大小 Amplified product size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P3 | 7 | 0.82 | 128~158 | P24 | 4 | 0.66 | 286~306 |
| P5 | 4 | 0.63 | 166~184 | P25 | 6 | 0.75 | 144~172 |
| P6 | 6 | 0.55 | 148~198 | P26 | 3 | 0.44 | 180~200 |
| P8 | 3 | 0.58 | 248~256 | P27 | 4 | 0.58 | 118~126 |
| P12 | 5 | 0.67 | 118~138 | P28 | 6 | 0.73 | 162~188 |
| P14 | 4 | 0.43 | 200~234 | P30 | 4 | 0.62 | 122~134 |
| P15 | 6 | 0.62 | 86~118 | P31 | 3 | 0.58 | 92~104 |
| P18 | 6 | 0.72 | 182~244 | P32 | 4 | 0.69 | 96~104 |
| P19 | 7 | 0.80 | 152~188 | P34 | 2 | 0.25 | 212~220 |
| P21 | 5 | 0.52 | 158~180 | P40 | 4 | 0.65 | 78~92 |
居群 Populations | 位点数 Loci | 多态位点数 Number of polymorphic loci | 观测等位基因 Observed number of alleles (Na) | 有效等位基因 Effective number of allele (Ne) | 平均杂合度 Average heterozygosity (H) | 香农指数 Shannon index (I) | 多态位点百分率 Percentage of polymorphic (PPB, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 南木林县NMX | 93 | 78 | 1.8387 | 1.4076 | 0.2426 | 0.3713 | 83.87 |
| 碌曲县LQX | 93 | 85 | 1.9140 | 1.4225 | 0.2519 | 0.3877 | 91.40 |
| 河南县HNX | 93 | 79 | 1.8495 | 1.3725 | 0.2273 | 0.3542 | 84.95 |
| 祁连县QLX | 93 | 89 | 1.9570 | 1.4644 | 0.2797 | 0.4287 | 95.70 |
| 八宿县BSX | 93 | 75 | 1.8065 | 1.4094 | 0.2445 | 0.3725 | 80.65 |
| 若尔盖县REG | 93 | 79 | 1.8495 | 1.4006 | 0.2407 | 0.3709 | 84.95 |
| 平均Average | 93 | 81 | 1.8387 | 1.4128 | 0.2478 | 0.3809 | 86.92 |
表4 6个蕨麻居群的遗传多样性
Table 4 Genetic diversity of the six P. anserina populations
居群 Populations | 位点数 Loci | 多态位点数 Number of polymorphic loci | 观测等位基因 Observed number of alleles (Na) | 有效等位基因 Effective number of allele (Ne) | 平均杂合度 Average heterozygosity (H) | 香农指数 Shannon index (I) | 多态位点百分率 Percentage of polymorphic (PPB, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 南木林县NMX | 93 | 78 | 1.8387 | 1.4076 | 0.2426 | 0.3713 | 83.87 |
| 碌曲县LQX | 93 | 85 | 1.9140 | 1.4225 | 0.2519 | 0.3877 | 91.40 |
| 河南县HNX | 93 | 79 | 1.8495 | 1.3725 | 0.2273 | 0.3542 | 84.95 |
| 祁连县QLX | 93 | 89 | 1.9570 | 1.4644 | 0.2797 | 0.4287 | 95.70 |
| 八宿县BSX | 93 | 75 | 1.8065 | 1.4094 | 0.2445 | 0.3725 | 80.65 |
| 若尔盖县REG | 93 | 79 | 1.8495 | 1.4006 | 0.2407 | 0.3709 | 84.95 |
| 平均Average | 93 | 81 | 1.8387 | 1.4128 | 0.2478 | 0.3809 | 86.92 |
变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 Degree of freedom (df) | 均方和 Sum of squares (SS) | 均方偏差 Mean square error (MS) | 变异方差分量 Variance components | 方差分量占比 Percentage of variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 居群间Among pops | 5 | 497.137 | 99.427 | 2.477 | 16 |
| 居群内Within pops | 204 | 2600.025 | 12.745 | 12.745 | 84 |
| 总计Total | 209 | 3097.162 | - | 15.223 | 100 |
表5 蕨麻6个群体分子方差分析
Table 5 AMOVA analysis of six P. anserina populations
变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 Degree of freedom (df) | 均方和 Sum of squares (SS) | 均方偏差 Mean square error (MS) | 变异方差分量 Variance components | 方差分量占比 Percentage of variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 居群间Among pops | 5 | 497.137 | 99.427 | 2.477 | 16 |
| 居群内Within pops | 204 | 2600.025 | 12.745 | 12.745 | 84 |
| 总计Total | 209 | 3097.162 | - | 15.223 | 100 |
群体1 Population 1 | 群体2 Population 2 | 遗传分化指数 Gene differentiation coefficient (Fst) | 基因流 Gene flow (Nm) | 种质数Accessions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群体1 Population 1 | 群体2 Population 2 | ||||
| 八宿县BSX | 河南县HNX | 0.069 | 0.933 | 34 | 37 |
| 八宿县BSX | 碌曲县LQX | 0.066 | 0.936 | 34 | 36 |
| 河南县HNX | 碌曲县LQX | 0.014 | 0.986 | 37 | 36 |
| 八宿县BSX | 南木林县NMX | 0.084 | 0.919 | 34 | 33 |
| 河南县HNX | 南木林县NMX | 0.070 | 0.932 | 37 | 33 |
| 碌曲县LQX | 南木林县NMX | 0.068 | 0.934 | 36 | 33 |
| 八宿县BSX | 祁连县QLX | 0.073 | 0.930 | 34 | 36 |
| 河南县HNX | 祁连县QLX | 0.046 | 0.955 | 37 | 36 |
| 碌曲县LQX | 祁连县QLX | 0.040 | 0.961 | 36 | 36 |
| 南木林县NMX | 祁连县QLX | 0.074 | 0.929 | 33 | 36 |
| 八宿县BSX | 若尔盖县REG | 0.040 | 0.961 | 34 | 34 |
| 河南县HNX | 若尔盖县REG | 0.027 | 0.973 | 37 | 34 |
| 碌曲县LQX | 若尔盖县REG | 0.026 | 0.975 | 36 | 34 |
| 南木林县NMX | 若尔盖县REG | 0.064 | 0.938 | 33 | 34 |
| 碌曲县LQX | 若尔盖县REG | 0.047 | 0.954 | 36 | 34 |
表6 蕨麻群体间的遗传分化系数和基因流
Table 6 The Fst and Nm among P. anserina populations
群体1 Population 1 | 群体2 Population 2 | 遗传分化指数 Gene differentiation coefficient (Fst) | 基因流 Gene flow (Nm) | 种质数Accessions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群体1 Population 1 | 群体2 Population 2 | ||||
| 八宿县BSX | 河南县HNX | 0.069 | 0.933 | 34 | 37 |
| 八宿县BSX | 碌曲县LQX | 0.066 | 0.936 | 34 | 36 |
| 河南县HNX | 碌曲县LQX | 0.014 | 0.986 | 37 | 36 |
| 八宿县BSX | 南木林县NMX | 0.084 | 0.919 | 34 | 33 |
| 河南县HNX | 南木林县NMX | 0.070 | 0.932 | 37 | 33 |
| 碌曲县LQX | 南木林县NMX | 0.068 | 0.934 | 36 | 33 |
| 八宿县BSX | 祁连县QLX | 0.073 | 0.930 | 34 | 36 |
| 河南县HNX | 祁连县QLX | 0.046 | 0.955 | 37 | 36 |
| 碌曲县LQX | 祁连县QLX | 0.040 | 0.961 | 36 | 36 |
| 南木林县NMX | 祁连县QLX | 0.074 | 0.929 | 33 | 36 |
| 八宿县BSX | 若尔盖县REG | 0.040 | 0.961 | 34 | 34 |
| 河南县HNX | 若尔盖县REG | 0.027 | 0.973 | 37 | 34 |
| 碌曲县LQX | 若尔盖县REG | 0.026 | 0.975 | 36 | 34 |
| 南木林县NMX | 若尔盖县REG | 0.064 | 0.938 | 33 | 34 |
| 碌曲县LQX | 若尔盖县REG | 0.047 | 0.954 | 36 | 34 |
居群 Populations | 南木林县 NMX | 碌曲县 LQX | 河南县 HNX | 祁连县 QLX | 八宿县 BSX | 若尔盖县 REG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 南木林县NMX | - | 0.9344 | 0.9321 | 0.9290 | 0.9194 | 0.9379 |
| 碌曲县LQX | 0.0678 | - | 0.9860 | 0.9608 | 0.9358 | 0.9747 |
| 河南县HNX | 0.0703 | 0.0141 | - | 0.9549 | 0.9335 | 0.9729 |
| 祁连县QLX | 0.0736 | 0.0400 | 0.0462 | - | 0.9296 | 0.9542 |
| 八宿县BSX | 0.0840 | 0.0663 | 0.0689 | 0.0730 | - | 0.9613 |
| 若尔盖县REG | 0.0641 | 0.0256 | 0.0274 | 0.0468 | 0.0395 | - |
表7 蕨麻各居群之间的遗传相似度与遗传距离
Table 7 Genetic identity and genetic distance of six P. anserina populations
居群 Populations | 南木林县 NMX | 碌曲县 LQX | 河南县 HNX | 祁连县 QLX | 八宿县 BSX | 若尔盖县 REG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 南木林县NMX | - | 0.9344 | 0.9321 | 0.9290 | 0.9194 | 0.9379 |
| 碌曲县LQX | 0.0678 | - | 0.9860 | 0.9608 | 0.9358 | 0.9747 |
| 河南县HNX | 0.0703 | 0.0141 | - | 0.9549 | 0.9335 | 0.9729 |
| 祁连县QLX | 0.0736 | 0.0400 | 0.0462 | - | 0.9296 | 0.9542 |
| 八宿县BSX | 0.0840 | 0.0663 | 0.0689 | 0.0730 | - | 0.9613 |
| 若尔盖县REG | 0.0641 | 0.0256 | 0.0274 | 0.0468 | 0.0395 | - |
| 1 | Delectis Florae Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae Agendae Acadfmiae Sinicae Edita. Flora reipublicae popularis sinicae (Tomus 37). Beijing: Science Press, 1996: 275. |
| 中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会. 中国植物志(第三十七卷). 北京: 科学出版社, 1996: 275. | |
| 2 | Li J Q. Potentilla anserine from Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Beijing: Science Press, 2011: 100-104. |
| 李军乔. 青藏高原蕨麻. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011: 100-104. | |
| 3 | Wang J Q, Zhou B. Research progress of Tibetan medicine Potentilla anserine. Medical Journal of National Defending Forces, 2010, 20(2): 217-219. |
| 王建军, 周斌. 藏药蕨麻的研究进展. 西南国防医药, 2010, 20(2): 217-219. | |
| 4 | Chen H Q, Zhang R X, Huang L Q, et al. Literature review of Tibetan medicine Potentilla anserine. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2000(5): 55-56. |
| 陈惠清, 张瑞贤, 黄璐琦, 等. 藏药蕨麻的文献考察. 中国中药杂志, 2000(5): 55-56. | |
| 5 | Liu X, Zhang J M, Zhang Z, et al. Preparation and optimization of callus protoplast of Potentilla anserina. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2017, 37(8): 1664-1671. |
| 刘欣, 张金铭, 张昭, 等. 蕨麻愈伤组织原生质体制备条件的优化. 西北植物学报, 2017, 37(8): 1664-1671. | |
| 6 | Liu H H, Jiang H X, Fu G, et al. Genetic diversity of Potentilla anserinain Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau of China based on peroxidase isozyme. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2016, 25(3): 413-422. |
| 刘贺贺, 蒋红霞, 富贵, 等. 青藏高原蕨麻种质资源遗传多样性POD同工酶分析. 西北农业学报, 2016, 25(3): 413-422. | |
| 7 | Xie X Y, Wang Q. A study on anti-aging action of Potentilla anserina lextract. Chongqing Medicine, 2007(8): 734-736. |
| 谢学渊, 王强. 蕨麻提取物抗衰老作用研究. 重庆医学, 2007(8): 734-736. | |
| 8 | Liu S J, Li S Y, Song J H, et al. Anticancer effects of polysaccharide from Potentilla anserine L. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy, 2011, 28(3): 185-188. |
| 刘素君, 李世元, 宋九华, 等. 鹅绒委陵菜多糖抗肿瘤作用研究. 中国现代应用药学, 2011, 28(3): 185-188. | |
| 9 | Liu H H. SSR primer development and henetic diversity analysis of Potentilla anserine germplasm resources. Xining: Qinghai Minzu University, 2017. |
| 刘贺贺. 蕨麻SSR引物开发及种质资源遗传多样性分析. 西宁: 青海民族大学, 2017. | |
| 10 | Eriksson O. Patterns of ramet survivorship in clonal fragments of the stoloniferous plant Potentilla anserina. Ecology, 1988, 69(3): 736-740. |
| 11 | Li J Q, Cai G M, Li L Z. Chinese Juema. Beijing: Science Press, 2020. |
| 李军乔, 蔡光明, 李灵芝. 中国蕨麻. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020. | |
| 12 | Fu G, Li J Q, Bao J Y, et al. Development of microsatellite primers in Potentilla anserina by magnetic beads enrichment. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(2): 124-134. |
| 富贵, 李军乔, 包锦渊, 等. 磁珠富集法开发蕨麻SSR标记引物. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 124-134. | |
| 13 | Li J Q. The exploiture and utilization of wild resources foliage Potentilla anserine L. in Qinghai Province. Journal of Biology, 2003(5): 34-36. |
| 李军乔. 青海省野生资源植物——鹅绒委陵菜(Potentilla anserine L.)的应用研究. 生物学杂志, 2003(5): 34-36. | |
| 14 | Ma B, Li J Q, Liu H H, et al. Construction and analysis of genetic similarity of SSR fingerprints in Juema. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2019, 17(13): 4367-4377. |
| 马斌, 李军乔, 刘贺贺, 等. 蕨麻品种SSR指纹图谱的构建及遗传相似性分析. 分子植物育种, 2019, 17(13): 4367-4377. | |
| 15 | Wei S S, Yang M S, Liang H Y. Genetic diversity of SSR analysis of Prunus persica cultivars. Tillage and Cultivation, 2022, 42(1): 1-5, 9. |
| 魏姗姗, 杨敏生, 梁海永. 桃品种遗传多样性SSR分析. 耕作与栽培, 2022, 42(1): 1-5, 9. | |
| 16 | Li J Q, Jiang H X, Wen X, et al. Karyotype analysis of sextuploid Juema. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 53(11): 2569-2572. |
| 李军乔, 蒋红霞, 温馨, 等. 六倍体蕨麻的核型分析. 湖北农业科学, 2014, 53(11): 2569-2572. | |
| 17 | Eriksson O. Mobility and space capture in the stoloniferous plant Potentilla anserina. Oikos, 1986, 46(1): 82-87. |
| 18 | Eriksson O. Ramet behaviour and population growth in the clonal herb Potentilla anserina. Journal of Ecology, 1988, 76(2): 522-536. |
| 19 | Zhou H K, Zhou X M, Zhou L, et al. The clonal growing characteristic in the stoloniferous herb, Potentilla anserine. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2002, 22(1): 9-17. |
| 周华坤, 周兴民, 周立, 等. 鹅绒委陵菜(Potentilla anserine)生长特征. 西北植物学报, 2002, 22(1): 9-17. | |
| 20 | Saikkonen K, Koivunen S, Vuorisalo T, et al. Interactive effects of pollination and heavy metals on resource allocation in Potentilla anserine L. Ecology, 1998, 79(5): 1620-1629. |
| 21 | Rautiainen P, Koivula K M. The effect of within-genet and between-genet competition on sexual reproduction and vegetative spread in Potentilla anserine ssp egedii. Journal of Ecology, 2004, 92(3): 505-511. |
| 22 | Kovaleva A M, Abdulkafarova E R. Phenolic compounds from Potentilla anserina. Chemistry of Natural Compounds, 2011, 47(3): 446-447. |
| 23 | Zhang X Q, Zhao Y L, Shan L M, et al. Study on protective mechanism of JMS on chemical liver injury. Pharmaceutical Journal of Chinese Peoples Liberation Army, 2004(4): 259-261. |
| 张新全, 赵艳玲, 山丽梅, 等. 蕨麻素对化学性肝损伤保护作用机制的研究. 解放军药学学报, 2004(4): 259-261. | |
| 24 | Li J Y, Li L Z, Zhang Y L, et al. Protective effect of Potentilla anserina L. on hypoxia injury in neonate rats cardiomyocytes. Chinese Journal of New Drugs, 2007(12): 944-946. |
| 李建宇, 李灵芝, 张永亮, 等. 蕨麻醇提物对心肌细胞缺氧损伤的保护作用. 中国新药杂志, 2007(12): 944-946. | |
| 25 | Chen K S, Li F, Xu C J, et al. An efficient macro-method of genomic DNA isolation from Actinidia chinensis leaves. Hereditas (Beijing), 2004(4): 529-531. |
| 陈昆松, 李方, 徐昌杰, 等. 改良CTAB法用于多年生植物组织基因组DNA的大量提取. 遗传, 2004(4): 529-531. | |
| 26 | Zhang M, Tan T M, Xu C C, et al. Application of SSR molecular markers technique in purity identification of Solanum melongena hybrid seed. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 52(8): 1959-1962. |
| 张敏, 谈太明, 徐长城, 等. SSR分子标记技术在茄子杂交种子纯度鉴定中的应用. 湖北农业科学, 2013, 52(8): 1959-1962. | |
| 27 | Zhu Y L, Xie Y L, Huang L Z, et al. Establishment of SSR fingerprint fap and preliminary analysis of genetic diversity among aromatic rice from Taihu and other areasin China. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2012, 13(4): 666-671. |
| 朱勇良, 谢裕林, 黄凌哲, 等. 太湖稻区及国内部分香稻SSR指纹图谱构建及遗传多样性初析. 植物遗传资源学报, 2012, 13(4): 666-671. | |
| 28 | Ma Q Q. Clonal structure of Fargesia qinlingensis populations inferred from SSR fingerprints in Foping national nature reserve. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University, 2015. |
| 马青青. 佛坪国家级自然保护区秦岭箭竹居群克隆结构的SSR分析. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2015. | |
| 29 | Sun M. Genetic diversity in three colonizing orchids with contrasting mating systems. American Journal of Botany, 1997, 84(2): 224-232. |
| 30 | Song Y, Zhang X R, Li Z, et al. Genetic diversity and genetic structure analysis of Bupleurum chinense DC. based on SSR molecular marker. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica, 2022, 57(4): 1193-1202. |
| 宋芸, 张鑫瑞, 李政, 等. 基于SSR分子标记的柴胡遗传多样性与遗传结构分析. 药学学报, 2022, 57(4): 1193-1202. | |
| 31 | Botstein D, White R L, Skolnick M, et al. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. American Journal of Human Genet, 1980, 32(3): 314-331. |
| 32 | Zuo S M, Zhou N N, Chen Z X, et al. Identification of japonica rice varieties released in Jiangsu province by SSR markers. Journal of Yangzhou University (Agricultural and Life Science Edition), 2014, 35(4): 45-51. |
| 左示敏, 周娜娜, 陈宗祥, 等. SSR标记在江苏粳稻品种鉴定中的应用研究. 扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2014, 35(4): 46-51. | |
| 33 | Shen X T. The analysis of fine-scale genetic diversity in Phyllostachys edulis and a preliminary study on it’s sampling strategy. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 2012. |
| 沈晓婷. 毛竹小尺度遗传多样性及取样策略的初步研究. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2012. | |
| 34 | Chen Y F. Study on sampling strategy of Chimonobambusa utilis based on genetic diversity. Guizhou: Guiyang University, 2018. |
| 陈云飞. 基于遗传多样性的金佛山方竹采样策略初探. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2018. | |
| 35 | Diao X. EST-SSR primer development and genetic diversity research of Fragaria nilgerrensis Schldl. Kunming:Yunnan University, 2019. |
| 刁霞. 黄毛草莓(Fragaria nilgerrensis Schldl) EST-SSR引物开发及遗传多样性研究. 昆明: 云南大学, 2019. | |
| 36 | Liu C X, Li J M, Li H L, et al. Genetic diversity and genetic structure of stoloniferous clonal plant in Duchesnea indica Focke. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(2): 215-220. |
| 刘春香, 李钧敏, 李红丽, 等. 匍匐茎克隆植物蛇莓的遗传多样性和遗传结构. 江苏农业科学, 2016, 44(2): 215-220. | |
| 37 | Du X J, Li X F, Wu M, et al. Effects of life history traits and sampling strategies on microsatellite based genetic diversity estimates in plants. Journal of Natural Science of Hunan Normal University, 2015, 38(4): 21-28. |
| 杜夏瑾, 黎啸峰, 吴敏, 等. 生活史性状和取样策略对植物微卫星遗传多样性参数估算的影响. 湖南师范大学自然科学学报, 2015, 38(4): 21-28. | |
| 38 | Jin Y, Lu B R. Sampling strategy for genetic diversity. Biodiversity Science, 2003(2): 155-161. |
| 金燕, 卢宝荣. 遗传多样性的取样策略. 生物多样性, 2003(2): 155-161. | |
| 39 | Xiang X Y, Zhang X P, Duan R Y, et al. Pollen dispersal patterns of the endangered plant Pinus dabeshanensis in a seed production stand. Guihaia, 2014, 34(3): 333-337, 392. |
| 项小燕, 张小平, 段仁燕, 等. 濒危植物大别山五针松母树林花粉传播规律. 广西植物, 2014, 34(3): 333-337, 392. |
| [1] | 李晨芹, 李军乔, 王鑫慈, 牛永昆, 曲俊儒. 蕨麻根腐病病原菌的分离鉴定及其生物学特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 113-123. |
| [2] | 富贵, 李军乔, 包锦渊, 白世俊, 韦梅琴. 磁珠富集法开发蕨麻SSR标记引物[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 123-134. |
| [3] | 武炳超, 张欢, 童磊, 杜昭昌, 胡家菱, 陈燚, 张新全, 刘伟, 黄琳凯. 象草不同辐射剂量诱变系表型及遗传变异研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(11): 77-86. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||