

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 113-123.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021323
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
李晨芹1,2,3( ), 李军乔1,2,3(
), 李军乔1,2,3( ), 王鑫慈1,2,3, 牛永昆1,2,3, 曲俊儒1,2,3
), 王鑫慈1,2,3, 牛永昆1,2,3, 曲俊儒1,2,3
收稿日期:2021-08-30
修回日期:2021-10-18
出版日期:2022-04-20
发布日期:2022-01-25
通讯作者:
李军乔
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: ljqlily2002@126.com基金资助:
Chen-qin LI1,2,3( ), Jun-qiao LI1,2,3(
), Jun-qiao LI1,2,3( ), Xin-ci WANG1,2,3, Yong-kun NIU1,2,3, Jun-ru QU1,2,3
), Xin-ci WANG1,2,3, Yong-kun NIU1,2,3, Jun-ru QU1,2,3
Received:2021-08-30
Revised:2021-10-18
Online:2022-04-20
Published:2022-01-25
Contact:
Jun-qiao LI
摘要:
对从青海省湟源县蕨麻人工种植基地的蕨麻块根部位分离得到的菌株D2进行了致病性检测、形态学观察、rDNA-ITS序列分析鉴定,同时开展相关生物学特性研究,结果表明,分离所得菌株D2为镰刀菌Fusarium perseae,是蕨麻根腐病的病原真菌。生物学特性研究表明,菌株D2菌丝生长、产孢和孢子萌发的最适温度分别为25、30和25 ℃,菌丝致死温度为64 ℃ (10 min),全光照条件不利于菌丝生长。pH值5.0~12.0菌丝均能较好生长,弱碱条件更利于其生长和产孢。该菌能利用多种碳、氮源,最适碳源为果糖,最适氮源为牛肉浸膏,部分碳、氮源可以促进菌株D2产生绿色色素。D2菌株对氮的有效利用表现为有机氮>硝态氮>铵态氮,而铵态氮更利于其产孢。因此,在蕨麻人工种植田间应当多注意田园卫生和水肥管理,防止蕨麻根腐病的发生与蔓延。该研究结果可为蕨麻根腐病的诊断及防控提供较为可靠的基础理论依据。
李晨芹, 李军乔, 王鑫慈, 牛永昆, 曲俊儒. 蕨麻根腐病病原菌的分离鉴定及其生物学特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 113-123.
Chen-qin LI, Jun-qiao LI, Xin-ci WANG, Yong-kun NIU, Jun-ru QU. Isolation, identification, and biological characteristics of Fusarium perseae isolated from Potentilla anserina roots[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(4): 113-123.

图1 蕨麻根腐病症状a: 健康植株根部The roots of healthy P. anserina; b: 健康植株根部及其根际土壤The roots of healthy P. anserina and its interstate soil; c: 健康植株块根The earthnut of healthy P. anserina; d: 健康植株横切面The cross-section of healthy P. anserina; e: 发病植株根部The roots of diseased P. anserina; f: 密布白色菌丝的发病植株根部The roots of diseased P. anserina with white mycelium densely; g: 黑褐色的蕨麻块根 The dark brown earthnut of P. anserina; h: 发病块根的横切面The cross-section of diseased P. anserina.
Fig.1 P. anserina root rot symptoms
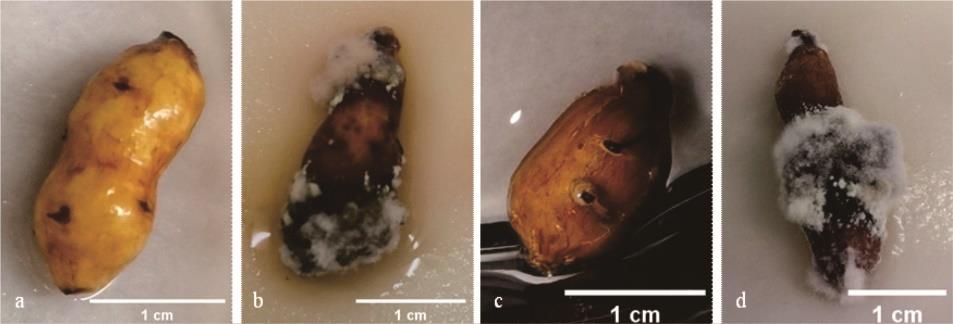
图2 菌株D2致病性测定结果(离体回接)a: 无伤口离体回接CK Control group (no wound in vitro inoculation); b: 无伤口离体回接处理Treatment group (no wound in vitro inoculation); c: 有伤口离体回接CK Control group (wound in vitro inoculation); d: 有伤口离体回接处理Treatment group (wound in vitro inoculation).
Fig.2 Pathogenicity determination results of strains D2 (in vitro inoculation)

图3 菌株D2致病性测定结果(活体回接)a: 植株感病叶部位症状Symptoms of the diseased leaves; b: 植株感病茎基部症状Symptoms of the base of the diseased stem; c: 植株感病块根部位症状Symptoms of the diseased earthnut; d: 感病块根的横切面The cross-section of the diseased earthnut; e: 健康植株块根The earthnut of healthy P. anserina; f: 健康块根的横切面The cross-section of the healthy earthnut; g: 感病植株Diseased P. anserina; h: 健康植株CK Healthy P. anserina (CK).
Fig.3 Pathogenicity determination results of strains D2 (in vivo inoculation)
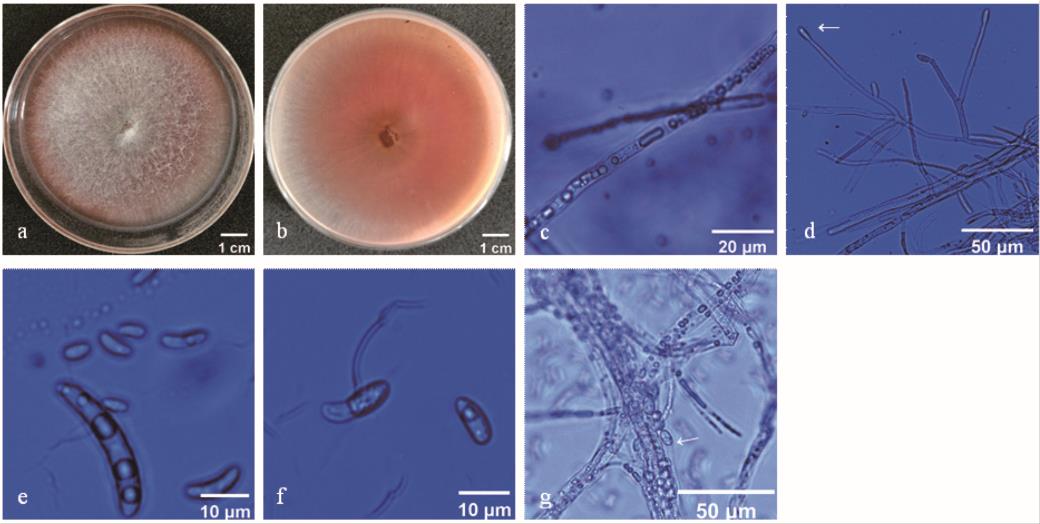
图4 菌株D2在PDA培养基上的菌落形态及显微形态a: 菌落形态 (正面) Colonial morphology (front); b: 菌落形态(背面) Colonial morphology (back); c: 有隔菌丝Septahypha; d: 产孢结构Conidiogenous structure; e: 大型分生孢子Macroconidium; f: 小型分生孢子Microconidium; g: 厚垣孢子Chlamydospore.
Fig.4 Colony and microscopic morphologies of D2 on PDA medium
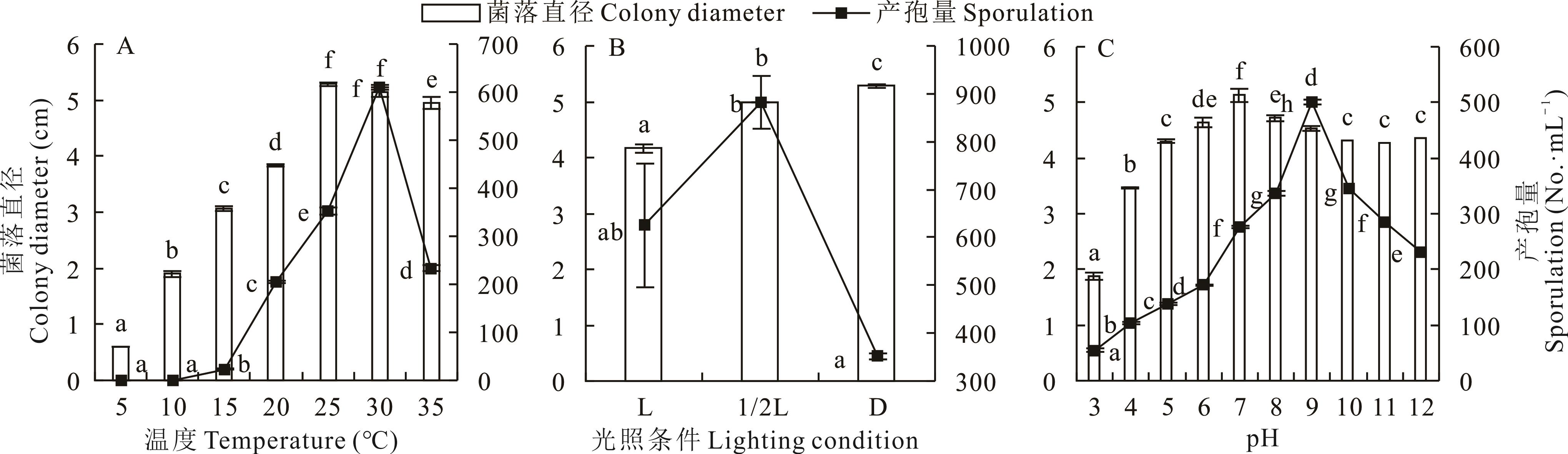
图6 不同生物学特性对菌株D2菌丝生长和产孢的影响不同小写字母表示数据在0.05水平上差异显著。下同。Different lowercase letters represented significant differences at 0.05 levels. The same below.
Fig.6 Effects of different biological characteristics on mycelium growth and sporulation of strain D2
处理 Treatment | 菌落直径 Colony diameter (cm) | 产孢量 Sporulation (×105·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 缺碳对照 No carbon source (C1) | 4.67±0.07Aa | 16.67±1.67Aa |
| 葡萄糖 Glucose (C2) | 5.43±0.02Cd | 93.33±4.41Bb |
| 蔗糖Sucrose (C3) | 5.18±0.07BCc | 223.33±7.26Ee |
| 乳糖Lactose (C4) | 4.65±0.08Aa | 178.33±8.82Dd |
| 可溶性淀粉Soluble starch (C5) | 5.37±0.07Ccd | 236.67±7.26Ee |
| 果糖Fructose (C6) | 4.98±0.07Bb | 263.33±7.26Ff |
| 甘露醇Mannitol (C7) | 5.28±0.02Ccd | 141.67±1.67Cc |
表1 不同碳源对病原菌菌丝生长及产孢的影响
Table 1 Effects of different carbon source on mycelium growth and sporulation
处理 Treatment | 菌落直径 Colony diameter (cm) | 产孢量 Sporulation (×105·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 缺碳对照 No carbon source (C1) | 4.67±0.07Aa | 16.67±1.67Aa |
| 葡萄糖 Glucose (C2) | 5.43±0.02Cd | 93.33±4.41Bb |
| 蔗糖Sucrose (C3) | 5.18±0.07BCc | 223.33±7.26Ee |
| 乳糖Lactose (C4) | 4.65±0.08Aa | 178.33±8.82Dd |
| 可溶性淀粉Soluble starch (C5) | 5.37±0.07Ccd | 236.67±7.26Ee |
| 果糖Fructose (C6) | 4.98±0.07Bb | 263.33±7.26Ff |
| 甘露醇Mannitol (C7) | 5.28±0.02Ccd | 141.67±1.67Cc |
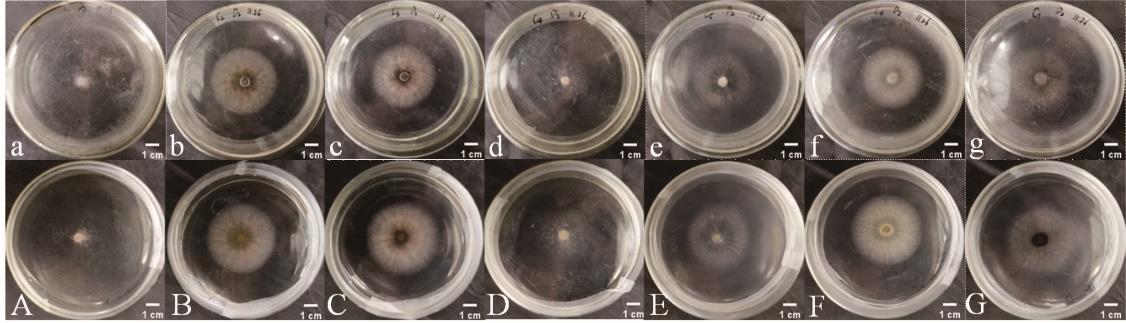
图7 菌株D2在不同碳源培养基上的菌落形态a~g分别为C1~C7不同培养基培养D2菌株第5天的菌落正面图;A~G分别为C1~C7不同培养基培养D2菌株第5天的菌落背面图。Pictures (a-g) show the colonial morphology (front) with different carbon sources (C1-C7) on the fifth day; Pictures (A-G) show the colonial morphology (back) with different carbon sources (C1-C7) on the fifth day.
Fig.7 Colony morphologies of D2 on different carbon source medium
处理 Treatment | 菌落直径 Colony diameter (cm) | 产孢量 Sporulation (×105·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 缺氮对照 No nitrogen source (N1) | 4.22±0.04Dd | 153.33±4.41Bb |
| 甘氨酸Glycine (N2) | 4.47±0.04Ee | 241.67±6.67Dd |
| 磷酸二氢铵Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (N3) | 2.45±0.03Aa | 280.00±7.64Ee |
| 硝酸铵Ammonium nitrate (N4) | 3.17±0.03Bb | 186.67±3.33Cc |
| 硫酸铵Ammonium sulphate (N5) | 3.27±0.03Bb | 320.00±8.66Ff |
| 蛋白胨Peptone (N6) | 3.53±0.02Cc | 90.00±0.00Aa |
| 牛肉浸膏Beef extract (N7) | 4.27±0.02Dd | 285.00±7.64Ee |
| 硝酸钠Sodium nitrate (N8) | 5.18±0.07Ff | 223.33±7.26Dd |
表2 不同氮源对病原菌菌丝生长及产孢的影响
Table 2 Effects of different nitrogen source on mycelium growth and sporulation
处理 Treatment | 菌落直径 Colony diameter (cm) | 产孢量 Sporulation (×105·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 缺氮对照 No nitrogen source (N1) | 4.22±0.04Dd | 153.33±4.41Bb |
| 甘氨酸Glycine (N2) | 4.47±0.04Ee | 241.67±6.67Dd |
| 磷酸二氢铵Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (N3) | 2.45±0.03Aa | 280.00±7.64Ee |
| 硝酸铵Ammonium nitrate (N4) | 3.17±0.03Bb | 186.67±3.33Cc |
| 硫酸铵Ammonium sulphate (N5) | 3.27±0.03Bb | 320.00±8.66Ff |
| 蛋白胨Peptone (N6) | 3.53±0.02Cc | 90.00±0.00Aa |
| 牛肉浸膏Beef extract (N7) | 4.27±0.02Dd | 285.00±7.64Ee |
| 硝酸钠Sodium nitrate (N8) | 5.18±0.07Ff | 223.33±7.26Dd |
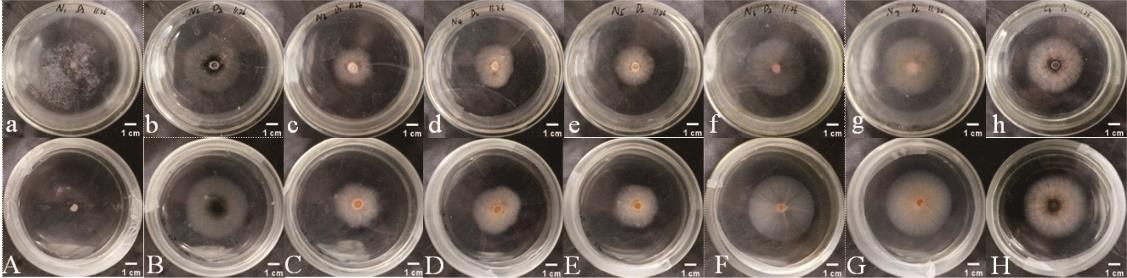
图8 菌株D2在不同氮源培养基上的菌落形态a~h分别为N1~N8不同培养基培养D2菌株第5天的菌落正面图;A~H分别为N1~N8不同培养基培养D2菌株第5天的菌落背面图。Pictures (a-h) show the colonial morphology (front) with different nitrogen sources (N1-N8) on the fifth day; Pictures (A-H) show the colonial morphology (back) with different nitrogen sources (N1-N8) on the fifth day.
Fig.8 Colony morphologies of D2 on different nitrogen source medium
培养基 Medium | 菌落直径 Colony diameter (cm) | 产孢量 Sporulation (×105·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 蕨麻煎汁培养基 P. anserina juice medium (JM) | 4.35±0.08Aa | 251.67±3.33BCc |
| 硝酸钠为氮源的蕨麻煎汁培养基 P. anserina juice medium with sodium nitrate (JMN) | 4.33±0.04Aa | 261.67±10.14Cc |
| 葡萄糖为碳源的蕨麻煎汁培养基 P. anserina juice medium with glucose (JMC) | 5.18±0.09Bb | 353.33±1.67Dd |
| Luria-Bertani培养基Lysogeny broth medium (LB) | 4.50±0.00Aa | 155.00±10.41Aa |
| 马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂培养基 Potato dextrose agar medium (PDA) | 5.28±0.03Bb | 351.67±7.26Dd |
| 查贝克氏培养基 Czapek’s medium (CZ) | 5.18±0.07Bb | 223.33±7.26Bb |
表3 培养基对病原菌菌丝生长及产孢的影响
Table 3 Effects of medium on mycelium growth and sporulation
培养基 Medium | 菌落直径 Colony diameter (cm) | 产孢量 Sporulation (×105·mL-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 蕨麻煎汁培养基 P. anserina juice medium (JM) | 4.35±0.08Aa | 251.67±3.33BCc |
| 硝酸钠为氮源的蕨麻煎汁培养基 P. anserina juice medium with sodium nitrate (JMN) | 4.33±0.04Aa | 261.67±10.14Cc |
| 葡萄糖为碳源的蕨麻煎汁培养基 P. anserina juice medium with glucose (JMC) | 5.18±0.09Bb | 353.33±1.67Dd |
| Luria-Bertani培养基Lysogeny broth medium (LB) | 4.50±0.00Aa | 155.00±10.41Aa |
| 马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂培养基 Potato dextrose agar medium (PDA) | 5.28±0.03Bb | 351.67±7.26Dd |
| 查贝克氏培养基 Czapek’s medium (CZ) | 5.18±0.07Bb | 223.33±7.26Bb |
| 1 | Qiao Q, Wang Q, Han X, et al. Transcriptome sequencing of Crucihimalaya himalaica (Brassicaceae) reveals how Arabidopsis close relative adapt to the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 21729. |
| 2 | Sun H L, Zheng D, Yao T D, et al. Protection and construction of the national ecological security shelter zone on Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2012, 67(1): 3-12. |
| 孙鸿烈, 郑度, 姚檀栋, 等. 青藏高原国家生态安全屏障保护与建设. 地理学报, 2012, 67(1): 3-12. | |
| 3 | Li J Q, Cai G M, Li L Z, et al. Chinese Juema. Beijing: Science Press, 2019: 1-4. |
| 李军乔, 蔡光明, 李灵芝, 等. 中国蕨麻. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019: 1-4. | |
| 4 | Ma B, Li J Q, Liu H H, et al. Construction and analysis of genetic similarity of SSR fingerprints in Juema. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2019, 17(13): 4367-4377. |
| 马斌, 李军乔, 刘贺贺, 等. 蕨麻品种SSR指纹图谱的构建及遗传相似性分析. 分子植物育种, 2019, 17(13): 4367-4377. | |
| 5 | Fu G, Li J Q, Bao J Y, et al. Development of microsatellite primers in Potentilla anserina by magnetic beads enrichment. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(2): 124-134. |
| 富贵, 李军乔, 包锦渊, 等. 磁珠富集法开发蕨麻SSR标记引物. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 124-134. | |
| 6 | Wang Y Q, Li J Q, Bai S J, et al. Status and changes of soil nutrients in rhizosphere of Potentilla anserina different planting age. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2020, 38(4): 56-63. |
| 王雅琼, 李军乔, 白世俊, 等. 不同种植年限蕨麻根际土壤养分变化规律. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 38(4): 56-63. | |
| 7 | Zhao B T, Tao F Q, Wang J L, et al. The sulfated modification and antioxidative activity of polysaccharides from Potentilla anserine L.. New Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 44: 4726-4735. |
| 8 | Mari A, Lyon D, Fragner L, et al. Phytochemical composition of Potentilla anserina L. analyzed by an integrative GC-MS and LC-MS metabolomics platform.Metabolomics, 2013, 9(3): 599-607. |
| 9 | Feng X L, Shen H Y, Li W Z, et al. Spatiotemporal changes for extreme precipitation in wet season over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and the surroundings during 1961-2017. Plateau Meteorology, 2020, 39(4): 694-705. |
| 冯晓莉, 申红艳, 李万志, 等. 1961-2017年青藏高原暖湿季节极端降水时空变化特征. 高原气象, 2020, 39(4): 694-705. | |
| 10 | Li L, Li H M, Shen H Y, et al. The truth and inter-annual oscillation causes for climate change in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2018, 40(6): 1079-1089. |
| 李林, 李红梅, 申红艳, 等. 青藏高原气候变化的若干事实及其年际振荡的成因探讨. 冰川冻土, 2018, 40(6): 1079-1089. | |
| 11 | Liao C H, Chen J W, Lv W W, et al. Research progress on root rot of roots and rhizomes of medicinal plants. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2017, 40(2): 492-497. |
| 廖长宏, 陈军文, 吕婉婉, 等. 根和根茎类药用植物根腐病研究进展. 中药材, 2017, 40(2): 492-497. | |
| 12 | Fang X L, Zhang C X, Nan Z B. Research advances in Fusarium root rot of alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(12): 169-183. |
| 方香玲, 张彩霞, 南志标. 紫花苜蓿镰刀菌根腐病研究进展. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 169-183. | |
| 13 | Cao L X, Zhao C H, Kong Q Q, et al. Research progress of control and pathogen in alfalfa root rot. Inner Mongolia Agricultural Science and Technology, 2006(3): 36-37, 51. |
| 曹丽霞, 赵存虎, 孔庆全, 等. 紫花苜蓿根腐病病原及防治研究进展. 内蒙古农业科技, 2006(3): 36-37, 51. | |
| 14 | Barbara S, Virgilio B, Francesca S, et al. Fusarium culmorum: Causal agent of foot and root rot and head blight on wheat. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2013, 14(4): 323-341. |
| 15 | Fang Z D. The method on studies of plant pathology. Beijing: Chinese Agriculture Press, 1998: 122-145. |
| 方中达. 植病研究方法. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1998: 122-145. | |
| 16 | Qiu X Y, Tang Z P, Zhang M, et al. Research on the isolation method of single spore of most plant pathogenic fungi. Journal of Anhui Agriculture Science, 2011, 39(9): 5263-5264. |
| 邱小燕, 汤智鹏, 张敏, 等. 一种适用于多数植物病原真菌的单孢分离方法. 安徽农业科学, 2011, 39(9): 5263-5264. | |
| 17 | Booth C. The genus Fusarium. Beijing: Agriculture Press, 1988. |
| 布斯 C. 镰刀菌属. 北京: 农业出版社, 1988. | |
| 18 | Zhang Z Y, Leng H Q, Zhang Z M, et al. Plant pathogenic mycology. Chengdu: Sichuan Science and Technology Press, 1988. |
| 张中义, 冷怀琼, 张志铭, 等. 植物病原真菌学. 成都: 成都科学技术出版社, 1988. | |
| 19 | Kerry O, Abdullah M, Takayuki A, et al. No to Neocosmospora: Phylogenomic and practical reasons for continued inclusion of the Fusarium solani species complex in the genus Fusarium. Ecological and EvolutionaryScience, 2020, 5(5): e00810-20. |
| 20 | Miettinen O, Vlasák J, Rivoire B, et al. Neocosmospora perseae sp. nov. causing trunk cankers on avocado in Italy. Fungal Systematics and Evolution, 2018, 1(1): 131-140. |
| 21 | Semeniuk G. Association of Trematosphaeria circinans with crown and root rot of alfalfa in South Dakota. Mycologia, 2018, 75(4): 744-747. |
| 22 | Yi M, Liang J J, Shi J, et al. Identification of Fusaruim acuminatum isolated from Medicago sativa root using the EF-1α sequence analysis method. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(2): 61-68. |
| 易铭, 梁嘉俊, 史建, 等. 采用EF-1α序列分析法对苜蓿根腐病病原菌—锐顶镰刀菌的鉴定. 草业学报, 2017, 26(2): 61-68. | |
| 23 | Li S, Wang Z, Tang B, et al. A pathogenesis-related protein-like gene is involved in the Panax notoginseng defense response to the root rot pathogen.Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 11: 1-13. |
| 24 | Wang W W. Microbial physiology. Beijing: Science Press, 2008: 271. |
| 王卫卫. 微生物生理学. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008: 271. | |
| 25 | Zhao J, Wang J, Li N H, et al. A study on the pathogenic crude toxin of the tobacco root rot extracted from Fusarium sp. Plant Protection, 2013, 39(3): 61-66. |
| 赵杰, 王静, 李乃会, 等. 烟草镰刀菌根腐病病菌致病粗毒素的研究. 植物保护, 2013, 39(3): 61-66. | |
| 26 | Dong Z Y, Luo M, Xiang M M. Comparison of cell wall degrading enzymes from three different Fusarium oxysporum formae speciales of Solanaceae. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 44(5): 112-117. |
| 董章勇, 罗梅, 向梅梅. 茄科尖孢镰刀菌3个专化型细胞壁降解酶的比较. 广东农业科学, 2017, 44(5): 112-117. | |
| 27 | Shen Q Q, Liu F, Hu Y. Research progress of pathogens of root rot disease on medicinal plants. Northern Horticulture, 2014(11): 187-190. |
| 沈清清, 刘芳, 胡彦. 药用植物根腐病病原菌研究进展. 北方园艺, 2014(11): 187-190. | |
| 28 | Qian H W, Xu P C, Chi M Y, et al. Mixed infection by Fusarium oxysporum and Alternaria tenuissima on sweet potato Fusarium wilt. Journal of Plant Protection, 2017, 44(5): 867-868. |
| 钱恒伟, 徐鹏程, 迟梦宇, 等. 尖孢镰刀菌与极细链格孢复合侵染引起甘薯茎枯病. 植物保护学报, 2017, 44(5): 867-868. |
| [1] | 侯金伟, 陈焘, 南志标. 不同埋藏方式及杀菌剂处理对黄土高原3种植物种子存活的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 129-136. |
| [2] | 杨凯, 史娟, 袁玉涛, 王立婷. 白三叶草叶片感染白粉病的细胞生理变化及其病原鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 92-104. |
| [3] | 王春明, 元维伟, 张小杰, 周天旺, 郭成, 金社林. 二月兰叶斑病病原甘蓝链格孢的分离鉴定及生物学特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 88-97. |
| [4] | 孙海荣, 车昭碧, 陈乙实, 鲁为华, 王树林, 李娜娜, 辛怀璐. 荒漠植物囊果草生物学特性及其种群分布格局的生态适应意义[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 198-207. |
| [5] | 李建宏, 李雪萍, 李昌宁, 韩冰, 徐万里, 姚拓. 一株植物根际促生菌Gnyt1的特性研究及分类地位的确定[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(5): 55-67. |
| [6] | 丁爱强, 徐先英, 张雯, 刘江, 富丽, 付贵全. 不同退化程度柽柳灌丛的土壤理化和生物学特性[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 1-11. |
| [7] | 富贵, 李军乔, 包锦渊, 白世俊, 韦梅琴. 磁珠富集法开发蕨麻SSR标记引物[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 123-134. |
| [8] | 杨成德, 卞静, 陈泰祥, 陈秀蓉, 王涵琦, 杨小利, 王艳. 当归炭疽病菌的生物学特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(6): 139-144. |
| [9] | 胡进玲, 汪治刚, 徐娜, 党淑钟, 李彦忠. 防治紫花苜蓿真菌病害的生防菌筛选[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(6): 145-152. |
| [10] | 贺春贵, 何振富, 王斐. 光敏型高丹草复种穴播高效栽培模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(5): 70-80. |
| [11] | 李健, 李美, 高兴祥, 房锋, 董连红. 菟丝子生防菌“鲁保一号”生物学特性及T-DNA插入突变体库的构建[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(1): 142-148. |
| [12] | 李健, 李美, 高兴祥, 房锋, 董连红. 稗草生防菌BC-1的分离及生物学特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(8): 164-171. |
| [13] | 贾辉, 陈秀蓉, 芦光新, 孔雅丽, 杨成德. 纤维素降解细菌的筛选,生物学特性及降解效果[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 60-66. |
| [14] | 李健, 李岩, 高兴祥, 房锋, 李美. 马唐生防菌厚垣孢镰刀菌ZC201301的生物学特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 234-239. |
| [15] | 章武, 胡美姣, 高兆银, 李敏, 刘国道, 南志标. 草坪草红丝病与粉斑病病原菌生物学特性研究与杀菌剂室内毒力测定[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(12): 140-149. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||