

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 204-215.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023265
• 研究简报 • 上一篇
席驳鑫1( ), 崔晓宁2(
), 崔晓宁2( ), 尚素琴1, 胡桂馨2, 王彦1, 李昌宁2, 彭斌2, 史薛强2
), 尚素琴1, 胡桂馨2, 王彦1, 李昌宁2, 彭斌2, 史薛强2
收稿日期:2023-07-25
修回日期:2023-10-08
出版日期:2024-05-20
发布日期:2024-02-03
通讯作者:
崔晓宁
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: cxn213@qq.com基金资助:
Bo-xin XI1( ), Xiao-ning CUI2(
), Xiao-ning CUI2( ), Su-qin SHANG1, Gui-xin HU2, Yan WANG1, Chang-ning LI2, Bin PENG2, Xue-qiang SHI2
), Su-qin SHANG1, Gui-xin HU2, Yan WANG1, Chang-ning LI2, Bin PENG2, Xue-qiang SHI2
Received:2023-07-25
Revised:2023-10-08
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-02-03
Contact:
Xiao-ning CUI
摘要:
白刺粗角叶甲是我国西北荒漠草原危害防风固沙先锋植物白刺的重要害虫之一,开发和利用基于性信息素或寄主挥发物介导的昆虫化学通讯手段是防治该害虫的新途径。本研究以白刺粗角叶甲为对象,通过分子克隆技术获得白刺粗角叶甲成虫触角的非典型气味受体(atypical odorant receptor co-receptor,Orco)基因序列;利用同源建模方法预测蛋白三级结构,并构建系统发育树;借助荧光定量PCR技术检测DrybOrco基因在叶甲成虫各组织中的表达量差异。结果显示:克隆获得的白刺粗角叶甲非典型气味受体基因DrybOrco的cDNA全长为1918 bp,其中开放阅读框为1440 bp,编码479个氨基酸,蛋白分子量为53.94 kD,含有7个跨膜结构域,为疏水性膜蛋白。系统发育表明,Orco基因在6目68种昆虫间保守性较高(相似度大于68%),聚类分为3个分支,相同目的昆虫聚集到同一支。白刺粗角叶甲与其他鞘翅目昆虫聚为一支,其中与玉米根萤叶甲的Orco基因亲缘关系最近,核酸相似度高达92.28%。荧光定量表明,白刺粗角叶甲DrybOrco基因在成虫触角中特异性表达,且雄虫显著高于雌虫,表达量比值为2.27;此外,该基因在雄虫足和雌虫翅中少量表达,其他组织中几乎不表达。本研究明确了白刺粗角叶甲非典型气味受体基因DrybOrco的序列特征、蛋白结构和组织表达情况,这为阐明DrybOrco在该害虫化学通讯过程中的生理功能,以及探究白刺粗角叶甲寄主专化的嗅觉分子机制研究提供重要依据。
席驳鑫, 崔晓宁, 尚素琴, 胡桂馨, 王彦, 李昌宁, 彭斌, 史薛强. 荒漠草地白刺粗角叶甲非典型气味受体基因克隆及组织表达谱[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 204-215.
Bo-xin XI, Xiao-ning CUI, Su-qin SHANG, Gui-xin HU, Yan WANG, Chang-ning LI, Bin PENG, Xue-qiang SHI. Cloning and tissue-specific expression patterns of a gene encoding an atypical odorant receptor co-receptor in the leaf beetle Diorhabda rybakowi (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae)[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(5): 204-215.
引物名称 Primer name | 5′→3′引物序列 5′→3′ primer sequence | 产物大小 Product size (bp) | 试验用途 Use of experiment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Orco-F | GATTAGTGAGTTTAAGATGTCGCA | 1918 | 克隆Cloning |
| Orco-R | TGGTGTTGATGGAAGTTGG | ||
| RPLS18-F | GACAAACGTGCGGGAGAA | 102 | 荧光定量PCR Rreal-time PCR |
| RPLS18-R | CTGTTCAAAAACCAGTCGGG | ||
| RPL13A-F | CCGTTCCATTTTAGAGCTCCCT | 158 | 荧光定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| RPL13A-R | CCAGGTACAACAACACGTTTCC | ||
| DOrco-F | GGATCCTGAAAACGAGAACG | 157 | 荧光定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| DOrco-R | CAGATTCGCGTGCATTAGAG |
表1 白刺粗角叶甲DrybOrco基因的克隆和荧光定量PCR引物
Table 1 Primers used for cloning and real-time PCR of DrybOrco gene in D. rybakowi
引物名称 Primer name | 5′→3′引物序列 5′→3′ primer sequence | 产物大小 Product size (bp) | 试验用途 Use of experiment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Orco-F | GATTAGTGAGTTTAAGATGTCGCA | 1918 | 克隆Cloning |
| Orco-R | TGGTGTTGATGGAAGTTGG | ||
| RPLS18-F | GACAAACGTGCGGGAGAA | 102 | 荧光定量PCR Rreal-time PCR |
| RPLS18-R | CTGTTCAAAAACCAGTCGGG | ||
| RPL13A-F | CCGTTCCATTTTAGAGCTCCCT | 158 | 荧光定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| RPL13A-R | CCAGGTACAACAACACGTTTCC | ||
| DOrco-F | GGATCCTGAAAACGAGAACG | 157 | 荧光定量PCR Real-time PCR |
| DOrco-R | CAGATTCGCGTGCATTAGAG |

图1 白刺粗角叶甲DrybOrco蛋白的二级结构蓝色:α螺旋;绿色:β转角;紫色:无规则卷曲;红色:延伸链。Blue: Alpha helix; Green: Beta turn; Purple: Random curl; Red: Extension chains. 标尺数值表示DrybOrco氨基酸位置。The scale numbers represent the position of DrybOrco amino acid.
Fig.1 Secondary structure of DrybOrco protein in D. rybakowi
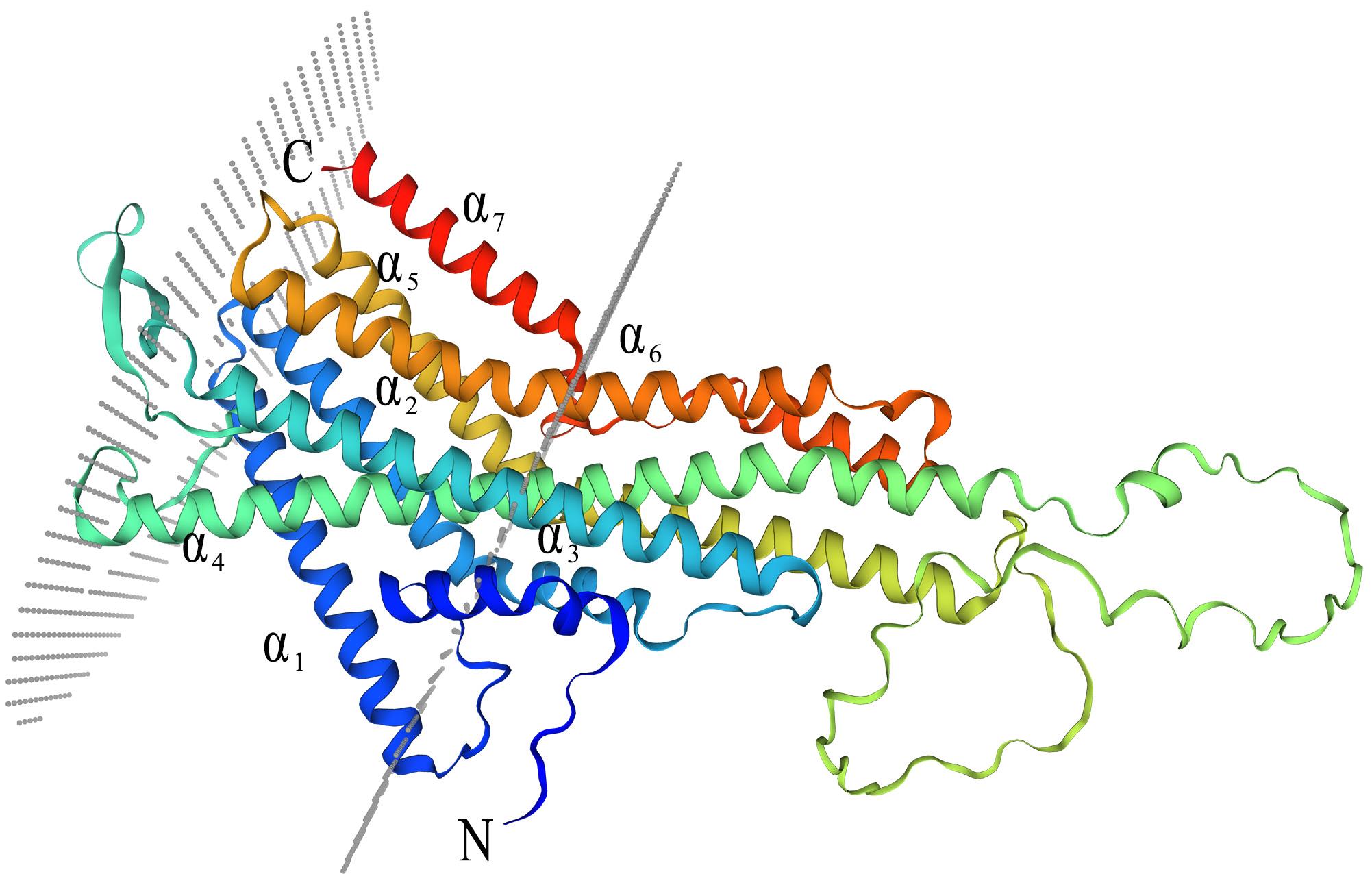
图2 白刺粗角叶甲DrybOrco蛋白的三级结构α1~α7分别代表α1~α7螺旋,N、C分别代表该蛋白的N端和C端。α1-α7 represented α1-α7 helix, N and C represented N-terminal and C-terminal of DrybOrco protein, respectively.
Fig.2 Tertiary structure ofDrybOrco proteinin D. rybakowi
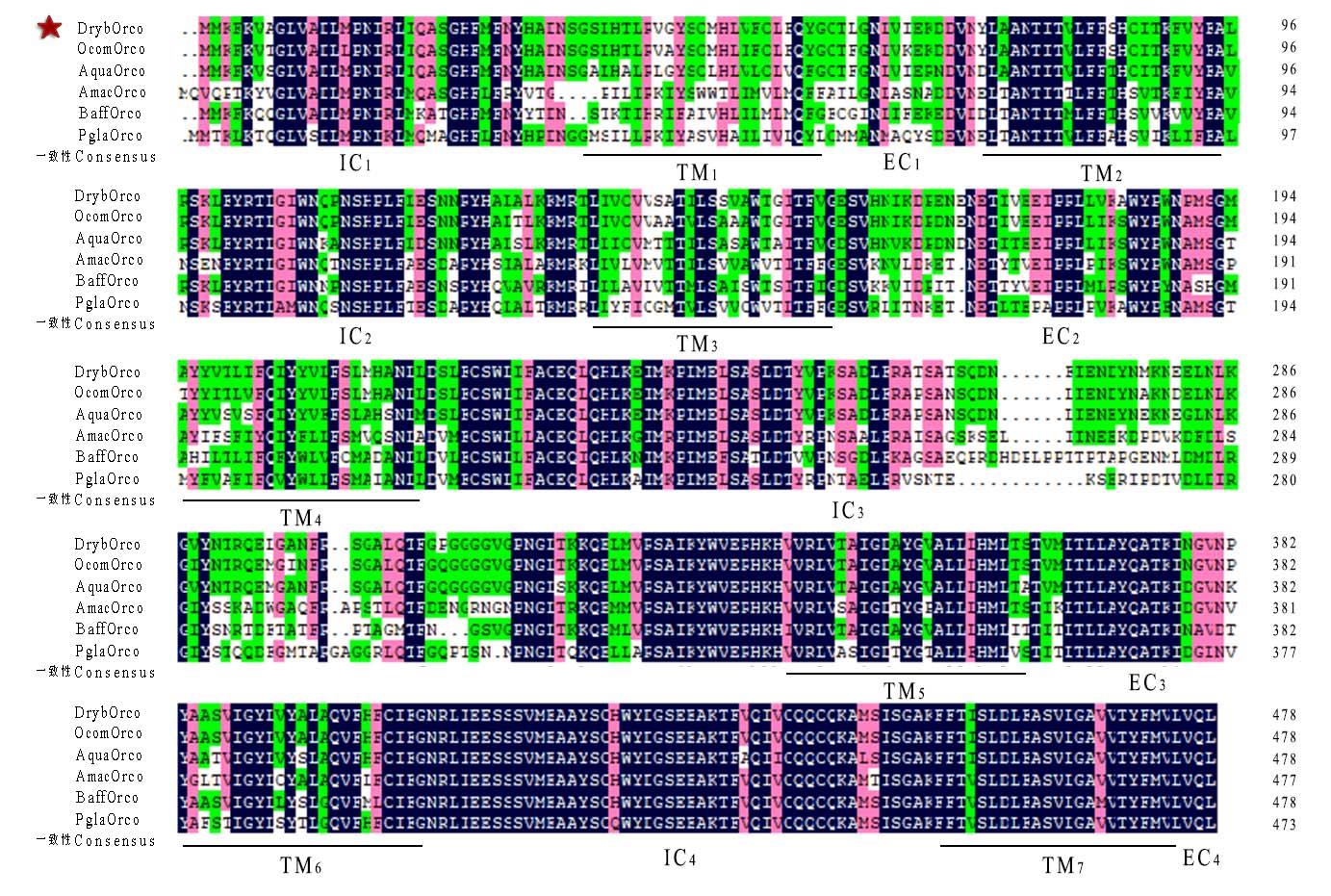
图3 白刺粗角叶甲与其他昆虫的Orco蛋白的氨基酸序列比对DrybOrco以红色五角星标记。下同。图中蓝色、粉红色和绿色分别代表相似度大于100%、75%、50%的区域;TM表示跨膜区;IC表示膜内区域;EC表示膜外区域。DrybOrcowas marked by red five-pointed star. The same below. Blue, pink, and green color areas indicated similarities greater than 100%, 75%, and 50%, respectively. TM: Transmembrane domains; IC: Intracellular domains; EC: Extracellular domains.OcomOrco: 广聚萤叶甲的Orco Orcoof O. communa (QEE83332.1);AquaOrco: 榆紫叶甲的Orco Orcoof A. quadriimpressum (AJF94638.2);AmacOrco: 斑须按蚊的Orco Orco of A. maculipalpis (XP_050069771.1);BaffOrco: 锈斑熊蜂的Orco Orcoof B. affinis (XP_050577029.1);PglaOrco: 东方虎凤蝶的Orco Orcoof P. glaucus (WCC57399.1).
Fig.3 Alignment of Orco amino acid sequences in D. rybakowi with other insect species
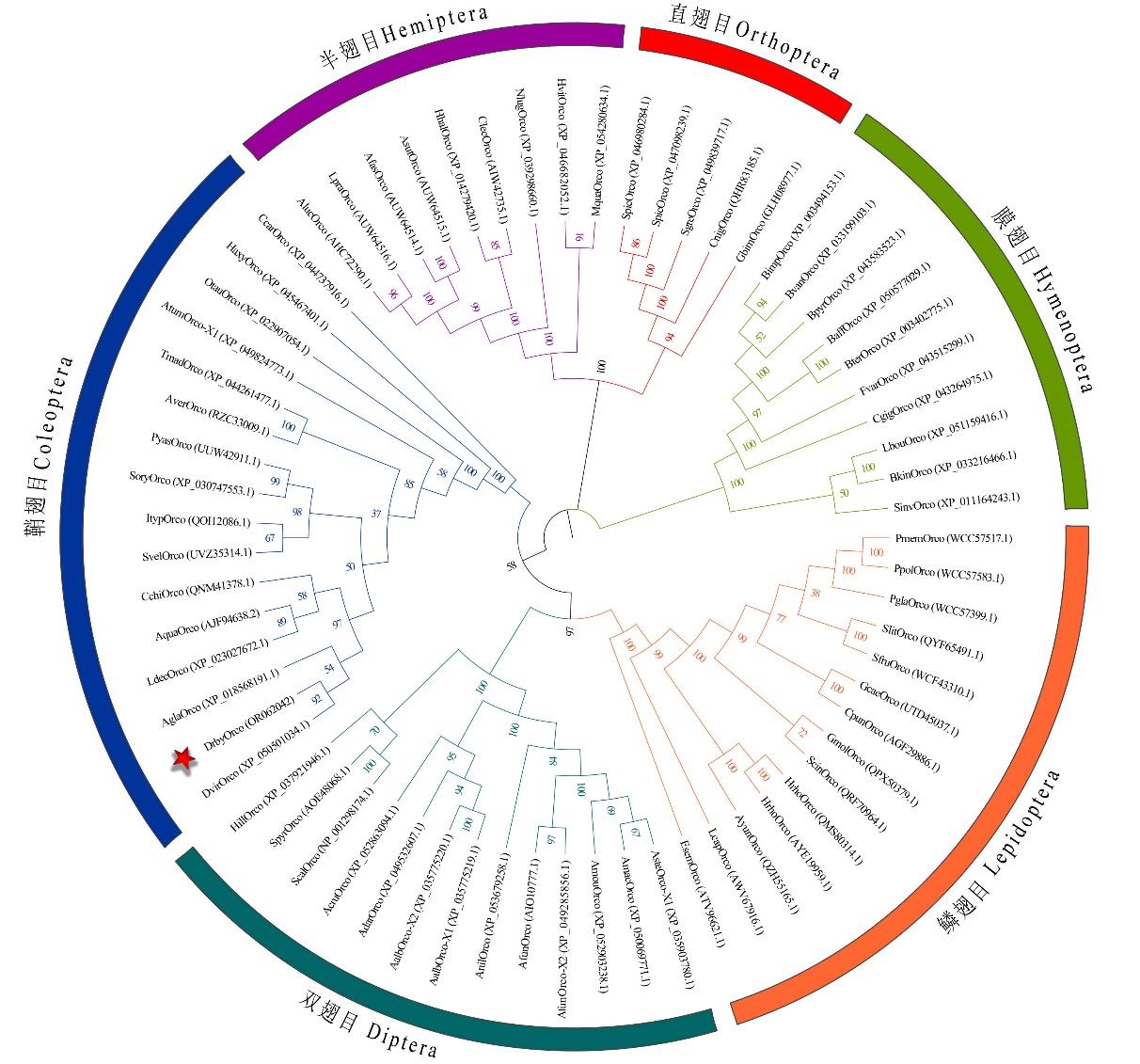
图4 基于DrybOrco与其他昆虫氨基酸序列构建的系统发育树不同物种均标示Orco氨基酸序列的缩写和GenBank登录号。The different species were marked with Orco amino acid abbreviation and GenBank accession number. ClecOrco: 温带臭虫的Orco Orco of Cimex lectularius; LpraOrco: 牧草盲蝽的Orco Orco of Lygus pratensis; AsutOrco: 中黑苜蓿盲蝽的Orco Orco of Adelphocoris suturalis; AfasOrco: 三点苜蓿盲蝽的Orco Orco of Adelphocoris fasciaticollis; MquaOrco: 四线二叉叶蝉的Orco Orco of Macrosteles quadrilineatus; SgreOrco: 沙漠蝗的Orco Orco of Schistocerca gregaria; NlugOrco: 褐飞虱的Orco Orco of Nilaparvata lugens; SinvOrco: 红火蚁的Orco Orco of Solenopsis invicta; CnigOrco: 青脊竹蝗的Orco Orco of Ceracris nigricornis; HhalOrco: 茶翅蝽的Orco Orco of Halyomorpha halys; HrhoOrco: 重阳木锦斑蛾的Orco Orco of Histia rhodope; SfruOrco: 草地贪夜蛾的Orco Orco of Spodoptera frugiperda; AyunOrco: 云南锦斑蛾的Orco Orco of Achelura yunnanensis; CpunOrco: 桃蛀螟的Orco Orco of Conogethes punctiferalis; PpolOrco: 玉带凤蝶的Orco Orco of Papilio polytes; PmemOrco: 美凤蝶的Orco Orco of Papilio memnon; PglaOrco: 美洲虎纹凤蝶的Orco Orco of Papilio glaucus; SlitOrco: 斜纹夜蛾的Orco Orco of Spodoptera litura; GcaeOrco: 黄翅绢丝野螟的Orco Orco of Glyphodes caesalis; ScinOrco: 槐尺蛾的Orco Orco of Semiothisa cinerearia; GmolOrco: 梨小食心虫的Orco Orco of Grapholitha molesta; DvirOrco: 玉米根萤叶甲的Orco Orco of D. virgifera; AquaOrco: 紫榆叶甲的Orco Orco of A. quadriimpressum; TmadOrco: 黑拟谷盗的Orco Orco of Tribolium madens; AverOrco: 沙漠铁包甲虫的Orco Orco of Asbolus verrucosus; PyasOrco: 枣食芽象甲的Orco Orco of Pachyrhinus yasumatsui; SoryOrco: 米象的Orco Orco of Sitophilus oryzae; ItypOrco: 云杉八齿小蠹的Orco Orco of Ips typographus; SvelOrco: 大灰象的Orco Orco of Sympiezomias velatus; LdecOrco: 马铃薯叶甲的Orco Orco of L. decemlineata; CchiOrco: 绿豆象的Orco Orco of Callosobruchus chinensis; EsemOrco: 波纹毛顶蛾的Orco Orco of Eriocrania semipurpurella; AmouOrco: 毛捷蒂按蚊的Orco Orco of Anopheles moucheti; SpyrOrco: 斜斑鼓额蚜蝇的Orco Orco of Scaeva pyrastri; AmacOrco: 斑须按蚊的Orco Orco of A. maculipalpis; AsteOrco: 斯氏按蚊的Orco Orco of Anopheles stephensi; AdarOrco: 达氏按蚊的Orco Orco of Anopheles darlingi; AfunOrco: 致死按蚊的Orco Orco of Anopheles funestus; BpyrOrco: 火红熊蜂的Orco Orco of Bombus pyrosoma; AalbOrco: 淡色按蚊的Orco Orco of Anopheles albimanus; BterOrco: 欧洲熊蜂的Orco Orco of Bombus terrestris; BaffOrco: 锈斑熊蜂的Orco Orco of B. affinis; LcapOrco: 红醋栗穿孔蛾的Orco Orco of Lampronia capitella; BvanOrco: 温哥华熊峰的Orco Orco of Bombus vancouverensis nearcticus; AnilOrco: 乌有按蚊的Orco Orco of Anopheles nili; BkinOrco: 瘿蜂的Orco Orco of Belonocnema kinseyi; CgigOrco: 大分舌蜂的Orco Orco of Colletes gigas; ScalOrco: 厩螫蝇的Orco Orco of Stomoxys calcitrans; BimpOrco: 熊蜂的Orco Orco of Bombus impatiens; AcruOrco: 按蚊的Orco Orco of Anopheles cruzii; FvarOrco: 巴西无刺蜜蜂的Orco Orco of Frieseomelitta varia; HillOrco: 亮斑扁角水虻的Orco Orco of Hermetia illucens; LbouOrco: 环腹瘿蜂的Orco Orco of Leptopilina boulardi; HvitOrco: 透茎扁头叶蝉的Orco Orco of Homalodisca vitripennis; AlucOrco: 绿后丽盲蝽的Orco Orco of Apolygus lucorum; AtumOrco: 蜂箱小甲虫的Orco Orco of Aethina tumida; AglaOrco: 光肩星天牛的Orco Orco of Anoplophora glabripennis; HaxyOrco: 异色瓢虫的Orco Orco of Harmonia axyridis; OtauOrco: 食粪金龟的Orco Orco of Onthophagus taurus; CcarOrco: 普通草蛉的Orco Orco of Chrysoperla carnea; SpicOrco: 中美洲蝗虫的Orco Orco of Schistocerca piceifrons; GbimOrco: 双斑蟋的Orco Orco of Gryllus bimaculatus.
Fig.4 Phylogenetic tree of DrybOrco with other insect species based on amino acid sequences
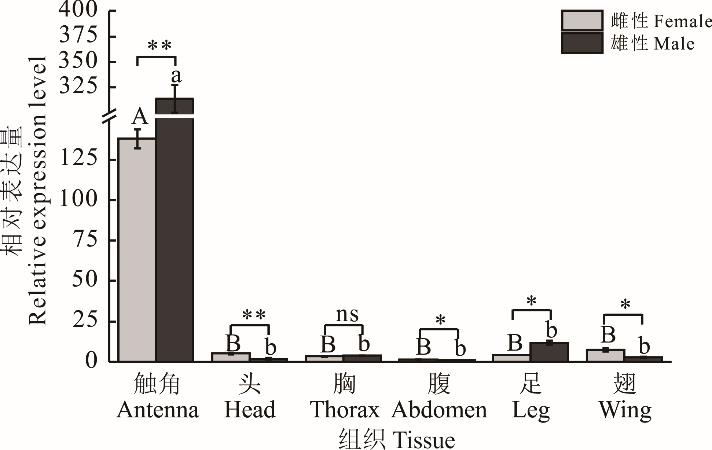
图5 白刺粗角叶甲DrybOrco基因在成虫不同组织中的表达量星号表示DrybOrco基因在同一组织雌雄之间存在显著性差异(*: P<0.05, **: P<0.01, ns: P>0.05)。不同大、小写字母分别表示DrybOrco基因在雌虫或雄虫不同组织间的显著性差异。Asterisk indicate significant difference of DrybOrco between female and male (*: P<0.05, **: P<0.01, ns: P>0.05). Different uppercase or lowercase indicate significant differences of DrybOrco gene in different adult tissues for same sexes.
Fig.5 The relative expression of DrybOrco gene in different tissues of D. rybakowi adult
| 1 | He D H, Tian C, Jin G L, et al. On some biological paramenters and simulation models of natural population dynamics of Diorhabda rybakowi Weise. Journal of Ningxia Agricultural College, 1989(1): 37-42. |
| 贺答汉, 田畴, 金桂兰, 等. 白茨一条萤叶甲自然种群动态的生物学参数及模拟模型. 宁夏农学院学报, 1989(1): 37-42. | |
| 2 | Li J Y, Tian C. A preliminary study on the spatial pattern and sequential sampling technique of Diorhabda rybakowi Weise. Journal of Ningxia Agricultural College, 1988(2): 73-78. |
| 李进跃, 田畴. 白茨一条萤叶甲的空间格局及序贯抽样技术的初步研究. 宁夏农学院学报, 1988(2): 73-78. | |
| 3 | Guan M Z, Li G X, Zhen C S, et al. Study on the behavior of Diorhabda rybakowi and its control. Grassland of China, 1991(1): 41-44. |
| 关明卓, 李国霞, 甄常生, 等. 白刺萤叶甲生活规律及防治研究. 中国草地, 1991(1): 41-44. | |
| 4 | Chen S K, Bao P, Yang H M. Damage of certain prominent insect pests on deserted grassland in Alshan and their control. Pratacultural Science, 2000, 17(3): 44-46, 50. |
| 陈善科, 保平, 杨惠民. 阿拉善荒漠几种主要害虫对草地的危害及其防治. 草业科学, 2000, 17(3): 44-46, 50. | |
| 5 | Chen Y W, Chen Q X, Yang H T. Diversity and fauna of terrestrial wild vertebrates in the Tengger Desert. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 216-222. |
| 陈应武, 陈庆霄, 杨昊天. 腾格里沙漠昆虫多样性及区系特征. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(4): 216-222. | |
| 6 | Tian C, He D H, Zhao L Q. Studies on the biology and control of a new pest in desert steppe Diorhabda rybakowi. Entomological Knowledge, 1990(2): 102-104. |
| 田畴, 贺达汉, 赵立群. 荒漠草原新害虫—白茨粗角萤叶甲生物学及防治的研究. 昆虫知识, 1990(2): 102-104. | |
| 7 | Xu G X, Zhao P, Chen S H, et al. Interspecific association and niche of Calligonum mongolicum community in Minqin oasis-desert transition zone. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2023, 38(1): 25-33. |
| 徐高兴, 赵鹏, 陈思航, 等. 民勤绿洲荒漠过渡带沙拐枣群落种间关联及生态位研究. 西北林学院学报, 2023, 38(1): 25-33. | |
| 8 | Zhao P, Xu X Y, Qu J J, et al. Spatial distribution of Nitraria tangutorum communities and its environmental interpretations in the Minqin oasis-desert ecotone. Arid Zone Research, 2016, 33(5): 1003-1011. |
| 赵鹏, 徐先英, 屈建军, 等. 民勤绿洲-荒漠过渡带白刺群落空间分布及其环境解释. 干旱区研究, 2016, 33(5): 1003-1011. | |
| 9 | Zhang H L, Wan G D. The Nitraria pasture resource and its protection and utilization in Wuwei of the Gansu Province. Pratacultural Science, 2003, 20(9): 63-65. |
| 张惠玲, 万国栋. 武威市白刺草地资源及其保护利用. 草业科学, 2003, 20(9): 63-65. | |
| 10 | Li H R, Wang J H, Jiang Z R, et al. Relationship between soil moisture and root biomass during developmental process of Nitraria tangutorum Nebkha. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2010, 45(6): 133-138. |
| 李鸿儒, 王继和, 蒋志荣, 等. 白刺沙包发育过程的土壤水分与根系生物量的关系. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2010, 45(6): 133-138. | |
| 11 | Wang J R, Sun T, Han F G, et al. Variation characteristics of soil temperature, water and nutrient in Nitraria tangutorum shrub-growing sand pile in arid desert area. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2023, 38(2): 45-52. |
| 王景瑞, 孙涛, 韩福贵, 等. 干旱荒漠区白刺灌丛沙堆土壤温度及水分养分变化特征. 西北林学院学报, 2023, 38(2): 45-52. | |
| 12 | Yan Q, Li J Y, Yin Z D, et al. Numerical simulation of the influence of typical shrub types on wind-sand flow field. Arid Zone Research, 2023, 40(5): 785-797. |
| 闫晴, 李菊艳, 尹忠东, 等. 典型株型沙生灌丛对风沙流场影响的数值模拟. 干旱区研究, 2023, 40(5): 785-797. | |
| 13 | Liu N Y, Gou W S, Ma W X, et al. Effects of temperature on the growth, development and reproduction of Diorhabda rybakowi (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Plant Protection, 2023, 49(2): 220-226. |
| 刘宁云, 勾文山, 马维新, 等. 温度对白茨粗角萤叶甲生长发育及繁殖的影响. 植物保护, 2023, 49(2): 220-226. | |
| 14 | Dai S M, Qiu G Y, Zhao M. Study on land desertification and its prevention and control measures in the Minqin oasis in Gansu Province. Arid Zone Research, 2008, 25(3): 319-324. |
| 戴晟懋, 邱国玉, 赵明. 甘肃民勤绿洲荒漠化防治研究. 干旱区研究, 2008, 25(3): 319-324. | |
| 15 | Li N L. Occurrence characteristics of grassland insect pest in Gulang county and suggestions for its control. Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology, 2011(2): 37-39. |
| 李能丽. 古浪县草原虫害发生特点及防治建议. 甘肃农业科技, 2011(2): 37-39. | |
| 16 | Schneider D. Insect antennae. Annual Review of Entomology, 1964, 9(1): 103-122. |
| 17 | Chapman R F. Contact chemoreception in feeding by phytophagous insects. Annual Review of Entomology, 2003, 48(1): 455-484. |
| 18 | Gomez D C, Bargeton B, Abuin L, et al. A CD36 ectodomain mediates insect pheromone detection via a putative tunnelling mechanism. Nature Communications, 2016, 7(1): 11866. |
| 19 | Wu F, Zhang L, Qiu Y L, et al. Research progress of olfactory binding proteins in insects. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 2021, 64(4): 523-535. |
| 吴帆, 张莉, 邱一蕾, 等. 昆虫嗅觉结合蛋白研究进展. 昆虫学报, 2021, 64(4): 523-535. | |
| 20 | Ha T S, Smith D P. Recent insights into insect olfactory receptors and odorant-binding proteins. Insects, 2022, 13(10): 926. |
| 21 | Del Marmol J, Yedlin M A, Ruta V. The structural basis of odorant recognition in insect olfactory receptors. Nature, 2021, 597(7874): 126-131. |
| 22 | Khadka R, Carraher C, Hamiaux C, et al. Synergistic improvement in the performance of insect odorant receptor based biosensors in the presence of Orco. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2020, 153: 112040. |
| 23 | Cheema J A, Carraher C, Plank N O V, et al. Insect odorant receptor-based biosensors: current status and prospects. Biotechnology Advances, 2021, 53: 107840. |
| 24 | Venthur H, Zhou J J. Odorant receptors and odorant-binding proteins as insect pest control targes: A comparative analysis. Frontiers in Physiology, 2018, 9: 1163. |
| 25 | Larsson M C, Domingos A I, Jones W D, et al. Or83b encodes a broadly expressed odorant receptor essential for drosophila olfaction. Neuron, 2004, 43(5): 703-714. |
| 26 | Fleischer J, Pregitzer P, Breer H, et al. Access to the odor world: Olfactory receptors and their role for signal transduction in insects. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences: CMLS, 2018, 75(3): 485-508. |
| 27 | Zhang R R, Gao G Q, Chen H. Silencing of the olfactory co-receptor gene in Dendroctonus armandi leads to EAG response declining to major host volatile. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 23136. |
| 28 | Li X M, Zhu X Y, Wang Z Q, et al. Candidate chemosensory genes identified in Colaphellus bowringi by antennal transcriptome analysis. BMC Genomics, 2015, 16(1): 1028. |
| 29 | Tang Q, Zhang Y, Shen C, et al. Identification and expression profiling of odorant receptor protein genes in Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Curculionoidea) using RT-qPCR. Neotropical Entomology, 2019, 48(4): 538-551. |
| 30 | Soffan A, Antony B, Abdelazim M, et al. Silencing the olfactory co-receptor RferOrco reduces the response to pheromones in the red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus. PLoS One, 11(9): e0162203. |
| 31 | Engsontia P, Sanderson A P, Cobb M, et al. The red flour beetle’s large nose: an expanded odorant receptor gene family in Tribolium castaneum. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2008, 38(4): 387-397. |
| 32 | He D H, Tian C. Life tables of Diorhabda rybakowi Weise at different temperature and thermoperiod. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 1990, 33(4): 437-443. |
| 贺达汉, 田畴. 不同温度和温周期下白茨粗角萤叶甲的实验生命表. 昆虫学报, 1990, 33(4): 437-443. | |
| 33 | He D H, Tian C, Jin G L. Studies on the life-table and the shift matrix model of natural population dynamic of Diorhabda rybakowi Weise. Journal of Ningxia Agricultural College, 1990, 11(1): 24-31,101-102. |
| 贺达汉, 田畴, 金桂兰. 白茨粗角萤叶甲自然种群生命表及转移矩阵模型的研究. 宁夏农学院学报, 1990, 11(1): 24-31,101-102. | |
| 34 | He D H, Tian C, Ma W, et al. An evaluation of the effects of natural enemies preying upon a forage grass pest insect Diorhabda rybakowi Weise. Grassland of China, 1991(4): 73-78. |
| 贺达汉, 田畴, 马武, 等. 白茨粗角萤叶甲天敌作用力的评估. 中国草地, 1991(4): 73-78. | |
| 35 | Jumper J, Evans R, Pritzel A, et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature, 2021, 596(7873): 583-589. |
| 36 | Varadi M, Anyango S, Deshpande M, et al. AlphaFold protein structure database: massively expanding the structural coverage of protein-sequence space with high-accuracy models. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 50(D1): D439-D444. |
| 37 | Paritala V. Comparative modeling for saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD56 using SWISS-MODEL, I-TASSER, and Phyre2. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2022, 14(3): 28-33. |
| 38 | Katoh K, Standley D M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2013, 30(4): 772-780. |
| 39 | Gascuel O. BIONJ: An improved version of the NJ algorithm based on a simple model of sequence data. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 1997, 14(7): 685-695. |
| 40 | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-410. |
| 41 | Bai P H, Wang B, Zhang X H, et al. Research methods and advances of odorant receptors in insects. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 2022, 65(3): 364-385. |
| 白鹏华, 王冰, 张仙红, 等. 昆虫气味受体的研究方法与进展. 昆虫学报, 2022, 65(3): 364-385. | |
| 42 | Zhang X X, Wang X, Zhao S W, et al. Response of odorant receptors with phenylacetaldehyde and the effects on the behavior of the rice water weevil (Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2023, 71(17): 6541-6551. |
| 43 | Wang B, Yin J, Li K B, et al. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the odorant receptor gene OrCo in Holotrichia oblita. Plant Protection, 2012, 38(4): 14-20. |
| 王冰, 尹姣, 李克斌, 等. 华北大黑鳃金龟气味受体OrCo基因的克隆及序列分析. 植物保护, 2012, 38(4): 14-20. | |
| 44 | Hong B, Chang Q, Zhai Y Y, et al. Cloning and tissue expression profiling of the odorant receptor co-receptor gene in jujube bud weevil Pachyrhinus yasumatsui (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Journal of Plant Protection, 2022, 49(4): 1143-1152. |
| 洪波, 常青, 翟颖妍, 等. 枣食芽象甲非典型气味受体基因的克隆及组织表达谱分析. 植物保护学报, 2022, 49(4): 1143-1152. | |
| 45 | Song Y Q, Li W L, Liu S T, et al. Cloning, molecular characteristics and expression pattern of the olfactory receptor co-receptor gene of Athetis dissimilis. Journal of Plant Protection, 2015, 42(6): 997-1003. |
| 宋月芹, 李文亮, 刘顺通, 等. 双委夜蛾非典型嗅觉受体Orco的克隆、分子特征及表达. 植物保护学报, 2015, 42(6): 997-1003. | |
| 46 | Krieger J, Klink O, Mohl C, et al. A candidate olfactory receptor subtype highly conserved across different insect orders. Journal of Comparative Physiology A: Neuroethology Sensory, Neural and Behavioral Physiology, 2003, 189(7): 519-526. |
| 47 | Brand P, Robertson H M, Lin W, et al. The origin of the odorant receptor gene family in insects. Elife, 2018, 7: e38340. |
| 48 | Benton R, Sachse S, Michnick S W, et al. A typical membrane topology and heteromeric function of Drosophila odorant receptors in vivo. PLoS Biology, 2006, 4(2): e20. |
| 49 | Zhang J H, Li L, Li N, et al. Expression profiling and functional analysis of candidate odorant receptors in Galeruca daurica. Insects, 2022, 13(7): 563. |
| 50 | Tian C H, Liu X G, Huang J R, et al. cDNA cloning, prokaryotic expression and polyclonal antibody preparation of the olfactory receptor co-receptor AlepOrco from Athetis lepigone (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Acta Entomologica Sinica, 2020, 63(6): 667-678. |
| 田彩红, 刘晓光, 黄建荣, 等. 二点委夜蛾非典型嗅觉受体AlepOrco的基因克隆、原核表达及多克隆抗体制备. 昆虫学报, 2020, 63(6): 667-678. | |
| 51 | Dong J F, Song Y Q, Sun J G, et al. Cloning and tissue expression profiling of the olfactory receptor gene CchlOrco in Campoletis chlorideae (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae). Acta Entomologica Sinica, 2015, 58(6): 603-609. |
| 董钧锋, 宋月芹, 孙九光, 等. 棉铃虫齿唇姬蜂嗅觉受体基因CchlOrco的克隆及组织表达谱分析. 昆虫学报, 2015, 58(6): 603-609. | |
| 52 | Zhang X F, Liu P J, Qin Q J, et al. Characterizing the role of Orco gene in detecting aggregation pheromone and food resources in Protaetia brevitarsis Leiws (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Frontiers in Physiology, 2021, 12: 649590. |
| 53 | Sun H, Bu L A, Su S, et al. Knockout of the odorant receptor co-receptor, orco, impairs feeding, mating and egg-laying behavior in the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2023, 152: 103889. |
| 54 | Alejandra G B, James I, Eunice M D, et al. Identification and analysis of odorant receptors expressed in the two main olfactory organs, antennae and palps, of Schistocerca americana. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 22628. |
| 55 | Hansen A I, Rodriguez D S, Drake L L, et al. The odorant receptor co-receptor from the bed bug, Cimex lectularius L. PLoS One, 2017, 9(11): e113692. |
| 56 | Chen H H, Dewer Y, Wang Y, et al. Interference with Orco gene expression affects host recognition in Diorhabda tarsalis. Frontiers in Physiology, 2022, 13: 1069391. |
| 57 | Zhao H T, Gao P F, Zhang G X, et al. Expression and localization analysis of the odorant receptor gene Orco in drones antennae of Apis cerana. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(4): 796-803. |
| 赵慧婷, 高鹏飞, 张桂贤, 等. 气味受体基因Orco在中华蜜蜂雄蜂触角中的表达及定位分析. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(4): 796-803. | |
| 58 | Yang Y, Krieger J, Zhang L, et al. The olfactory co-receptor Orco from the migratory locust (Locusta migratoria) and the desert locust (Schistocerca gregaria): Identification and expression pattern. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 2012, 8(2): 159-170. |
| 59 | Xi B X, Shang S Q, Hu G X, et al. Ultrastructural morphology on antennal sensilla of the adult Diorhabda rybakowi on grassland. Pratacultural Science, 2023, 40(7): 1920-1931. |
| 席驳鑫, 尚素琴, 胡桂馨, 等. 草地白刺粗角叶甲成虫触角感器的超微形态学. 草业科学, 2023, 40(7): 1920-1931. | |
| 60 | Franco T A, Oliveira D S, Moreira M F, et al. Silencing the odorant receptor co-receptor RproOrco affects the physiology and behavior of the chagas disease vector Rhodnius prolixus. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2015, 69: 82-90. |
| 61 | Dennis J E, Goldman V O, Vosshall B L. Aedes aegypti mosquitoes use their legs to sense DEET on contact. Current Biology, 2019, 29(9): 1551-1556. |
| 62 | Kepchia D, Xu P X, Terryn R, et al. Use of machine learning to identify novel behaviorally active antagonists of the insect odorant receptor coreceptor Orco subunit. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 4055. |
| 63 | Li X, Jiang H B, Tang K Y, et al. CRISPR-mediated mutagenesis of the odorant receptor co-receptor (Orco) gene disrupts olfaction-mediated behaviors in Bactrocera dorsalis. Insect Science, 2022, 29(5): 1275-1286. |
| 64 | Liu X M, Zhang B X, Li S G, et al. Knockdown of the olfactory co-receptor Orco impairs mate recognition in Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 2016, 19(2): 503-508. |
| 65 | Ning X Y, Huang C, Dong C H, et al. RNAi verifications on olfactory defects of an essential biocontrol agent Agasicles hygrophila (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) regarding mating and host allocation. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 2023, 11: 1104962. |
| 66 | Chen S S, Luetje C W. Trace amines inhibit insect odorant receptor function through antagonism of the co-receptor subunit. F1000Research, 2014, 3: 84. |
| [1] | 胡尚钦, 汪军成, 姚立蓉, 司二静, 马小乐, 杨轲, 张宏, 孟亚雄, 王化俊, 李葆春. 盐生草根系基因HgAKR6C的克隆与初步功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 61-74. |
| [2] | 刘增辉, 卢素锦, 王雨欣, 张春辉, 尹鑫. 三江源地区人工克隆植物群落生物多样性对初级生产力的影响及机制[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 27-38. |
| [3] | 王园, 王晶, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿MsBBX24基因的克隆及耐盐性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 107-117. |
| [4] | 刘福, 陈诚, 张凯旋, 周美亮, 张新全. 日本百脉根LjbHLH34基因克隆及耐旱功能鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 178-191. |
| [5] | 巴超群, 马群, 汪海洋, 刘志民. 根茎克隆植物研究面临的挑战[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 200-207. |
| [6] | 王玲玲, 库努都孜阿依·吐鲁洪null, 孟广飞, 郭正刚. 土壤水分和植株密度互作对垂穗披碱草地下营养繁殖及生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 52-61. |
| [7] | 侯洁茹, 段晓玥, 李州, 彭燕. 白三叶TrSAMDC1克隆及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 170-178. |
| [8] | 罗维, 舒健虹, 刘晓霞, 王子苑, 牟琼, 王小利, 吴佳海. 高羊茅FaRVE8基因的克隆、亚细胞定位及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 60-69. |
| [9] | 杨婷, 张建平, 刘自刚, 齐燕妮, 李闻娟, 谢亚萍. 胡麻异质型ACCase亚基基因的克隆与表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 111-120. |
| [10] | 白乌云, 侯向阳, 武自念, 田春育, 丁勇. 羊草不同地理种群表型变异及其对根茎克隆繁殖的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 86-94. |
| [11] | 夏曾润, 王文颖, 刘亚琪, 王锁民. 罗布麻K+通道编码基因AvAKT1的克隆与表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 180-189. |
| [12] | 徐晓霞, 刘金平, 游明鸿, 张小晶, 谢瑞娟. 遮阴和干旱对荩草克隆生长和有性繁殖及权衡关系的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 121-132. |
| [13] | 汪王, 田忠平, 苏小霞, 杨柳慧, 周蕴薇. 细叶百合LpAGD14基因的克隆与表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 117-123. |
| [14] | 王艳, 马亚茹, 万学瑞, 王川, 吴润, 刘桂林, 刘原子, 吴自祥. 多粘类芽孢杆菌β-葡萄糖苷酶bglA、bglB和bgl基因在大肠杆菌中的表达[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(5): 189-196. |
| [15] | 董笛, 滕珂, 于安东, 檀鹏辉, 梁小红, 韩烈保. 沟叶结缕草八氢番茄红素基因ZmPSY的克隆、亚细胞定位及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(11): 69-76. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||