

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (7): 172-181.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023294
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
符勇耀1( ), 蔡莉1, 李丰耀1, 杨文俊1, 徐文姬1, 姜思佳2(
), 蔡莉1, 李丰耀1, 杨文俊1, 徐文姬1, 姜思佳2( ), 杨利平1(
), 杨利平1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-08-29
修回日期:2023-10-26
出版日期:2024-07-20
发布日期:2024-04-08
通讯作者:
姜思佳,杨利平
作者简介:yangliping1962@126.com基金资助:
Yong-yao FU1( ), Li CAI1, Feng-yao LI1, Wen-jun YANG1, Wen-ji XU1, Si-jia JIANG2(
), Li CAI1, Feng-yao LI1, Wen-jun YANG1, Wen-ji XU1, Si-jia JIANG2( ), Li-ping YANG1(
), Li-ping YANG1( )
)
Received:2023-08-29
Revised:2023-10-26
Online:2024-07-20
Published:2024-04-08
Contact:
Si-jia JIANG,Li-ping YANG
摘要:
兰州百合是我国最重要的可食用甜百合。为培育优质的百合新种质,用不同浓度的秋水仙素离体诱变兰州百合小鳞茎,通过不定芽诱导获得变异幼苗。利用染色体倍性分析、幼苗早期形态观察及ISSR分子标记对其进行鉴定。结果表明,用0.15%秋水仙素处理小鳞茎48 h诱导效果最好,变异率为58.06%。选择2个形态变异且生长较快的幼苗进行流式细胞仪分析和根尖压片计数,发现其中1个变异株系含36条染色体的细胞数比例达到了80%,接近纯合三倍体。形态学观察显示,2个变异幼苗的叶片、鳞茎及根系与对照相比存在显著差异,且气孔保卫细胞大于对照,气孔密度降低。ISSR标记检测表明,2个诱变株系与对照相比均发生遗传变异,变异率分别为19.64%和20.91%。研究结果可为获得兰州百合三倍体新种质及秋水仙素诱变育种提供重要参考依据。
符勇耀, 蔡莉, 李丰耀, 杨文俊, 徐文姬, 姜思佳, 杨利平. 兰州百合多倍体离体诱导及其分子细胞鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 172-181.
Yong-yao FU, Li CAI, Feng-yao LI, Wen-jun YANG, Wen-ji XU, Si-jia JIANG, Li-ping YANG. Induction and molecular and cellular identification of polyploid Lilium davidii var. unicolor[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(7): 172-181.
秋水仙素浓度 Colchicine concentration (%) | 处理时间 Treated time (h) | 处理数 Treated number (No.) | 成活数 Survived number (No.) | 成活率 Survival rate (%) | 变异数 Varied number (No.) | 变异率 Mutation rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.10 | 24 | 119 | 111 | 93.18 | 65 | 54.62 |
| 48 | 27 | 27 | 100.00 | 9 | 33.33 | |
| 72 | 38 | 15 | 39.47 | 0 | 0 | |
| 96 | 42 | 7 | 16.67 | 3 | 7.14 | |
| 0.15 | 24 | 28 | 25 | 89.29 | 12 | 42.86 |
| 48 | 31 | 29 | 93.55 | 18 | 58.06 | |
| 72 | 54 | 44 | 81.48 | 3 | 5.56 | |
| 96 | 30 | 22 | 73.33 | 1 | 3.33 | |
| 0.20 | 24 | 30 | 24 | 80.00 | 11 | 36.67 |
| 48 | 28 | 27 | 96.43 | 4 | 14.29 | |
| 72 | 47 | 31 | 65.96 | 1 | 2.13 | |
| 96 | 90 | 80 | 88.89 | 4 | 4.44 | |
| 0.30 | 24 | 36 | 24 | 66.67 | 3 | 8.33 |
| 48 | 41 | 25 | 60.98 | 5 | 12.20 | |
| 72 | 27 | 2 | 7.41 | 0 | 0 | |
| 96 | 35 | 4 | 11.43 | 3 | 8.57 | |
| 0.35 | 24 | 106 | 91 | 85.85 | 27 | 25.47 |
| 48 | 37 | 11 | 29.73 | 1 | 2.70 | |
| 72 | 27 | 14 | 51.85 | 3 | 11.11 | |
| 96 | 31 | 2 | 6.45 | 2 | 6.45 |
表1 不同浓度秋水仙素处理不同时间对兰州百合的影响
Table 1 Effects of colchicine concentration and treatment time on L. davidii var. unicolor
秋水仙素浓度 Colchicine concentration (%) | 处理时间 Treated time (h) | 处理数 Treated number (No.) | 成活数 Survived number (No.) | 成活率 Survival rate (%) | 变异数 Varied number (No.) | 变异率 Mutation rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.10 | 24 | 119 | 111 | 93.18 | 65 | 54.62 |
| 48 | 27 | 27 | 100.00 | 9 | 33.33 | |
| 72 | 38 | 15 | 39.47 | 0 | 0 | |
| 96 | 42 | 7 | 16.67 | 3 | 7.14 | |
| 0.15 | 24 | 28 | 25 | 89.29 | 12 | 42.86 |
| 48 | 31 | 29 | 93.55 | 18 | 58.06 | |
| 72 | 54 | 44 | 81.48 | 3 | 5.56 | |
| 96 | 30 | 22 | 73.33 | 1 | 3.33 | |
| 0.20 | 24 | 30 | 24 | 80.00 | 11 | 36.67 |
| 48 | 28 | 27 | 96.43 | 4 | 14.29 | |
| 72 | 47 | 31 | 65.96 | 1 | 2.13 | |
| 96 | 90 | 80 | 88.89 | 4 | 4.44 | |
| 0.30 | 24 | 36 | 24 | 66.67 | 3 | 8.33 |
| 48 | 41 | 25 | 60.98 | 5 | 12.20 | |
| 72 | 27 | 2 | 7.41 | 0 | 0 | |
| 96 | 35 | 4 | 11.43 | 3 | 8.57 | |
| 0.35 | 24 | 106 | 91 | 85.85 | 27 | 25.47 |
| 48 | 37 | 11 | 29.73 | 1 | 2.70 | |
| 72 | 27 | 14 | 51.85 | 3 | 11.11 | |
| 96 | 31 | 2 | 6.45 | 2 | 6.45 |

图1 兰州百合多倍体诱导过程植株形态A:未改变的小鳞茎;B,C:发生形态变异的小鳞茎;D,E:培育发生形态变异的器官;F:变异器官继代再生长出芽;G:对照植株幼苗;H:诱变株系LZ-1;I:诱变株系LZ-2。A: Induced but unchanged bulblets; B, C: Bulblets undergoing morphological variation; D, E: Cutting organs undergoing morphological variation; F: The subculture buds from mutated organs; G: The control seedlings; H: Induced line LZ-1; I: Induced line LZ-2.
Fig.1 Plant morphology during polyploid induction of L. davidii var. unicolor

图2 兰州百合染色体倍性测试A~C:流式细胞仪分析染色体倍性,A为对照植株,B为诱变株系LZ-1,C为诱变株系LZ-2;D~F:根尖压片分析染色体数目,D为对照植株,E为诱变株系LZ-1,F为诱变株系LZ-2。A-C: Analysis of the chromosome ploidy by flow cytometry, A is control plants, B is mutant lines LZ-1, C is mutant lines LZ-2; D-F: Chromosome tableting using by root tips, D is control plants, E is mutant lines LZ-1, F is mutant lines LZ-2.
Fig.2 Chromosome ploidy analysis of L.davidii var. unicolor
样本 Sample | 细胞总数Total of cells | 含24条染色体的细胞数Number of cells with 24 chromosomes | 含36条染色体的细胞数Number of cells with 36 chromosomes | 其他染色体数量Cell of other chromosomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 Control | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| 兰州-1 LZ-1 | 17 | 0 | 5 | 12 |
| 兰州-2 LZ-2 | 20 | 0 | 16 | 4 |
表2 兰州百合染色体数目观察
Table 2 Chromosome number analysis in L.davidii var. unicolor
样本 Sample | 细胞总数Total of cells | 含24条染色体的细胞数Number of cells with 24 chromosomes | 含36条染色体的细胞数Number of cells with 36 chromosomes | 其他染色体数量Cell of other chromosomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 Control | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| 兰州-1 LZ-1 | 17 | 0 | 5 | 12 |
| 兰州-2 LZ-2 | 20 | 0 | 16 | 4 |
样本 Sample | 株高 Plant height (mm) | 叶片长度 Leaf length (mm) | 叶片宽度 Leaf width (mm) | 叶长宽比 Leaf length-width ratio | 鳞茎直径 Bulblet diameter (mm) | 鳞片长 Scale length (mm) | 鳞片宽 Scale width (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 Control | 84.78±1.46b | 82.83±1.72b | 1.69±0.11c | 54.47±3.15a | 4.25±0.16c | 5.11±0.34b | 3.29±0.21c |
| 兰州-1 LZ-1 | 105.68±2.39a | 99.65±2.47a | 6.01±0.18a | 17.01±0.63b | 8.96±0.21b | 11.16±0.36a | 5.84±0.22b |
| 兰州-2 LZ-2 | 81.73±1.53b | 72.09±1.72c | 4.76±0.16b | 15.63±0.70b | 10.70±0.26a | 11.35±2.67a | 6.82±0.15a |
表3 兰州百合对照和变异植株的形态学特征比较
Table 3 Comparison of morphological characterization in control and mutagenic plants
样本 Sample | 株高 Plant height (mm) | 叶片长度 Leaf length (mm) | 叶片宽度 Leaf width (mm) | 叶长宽比 Leaf length-width ratio | 鳞茎直径 Bulblet diameter (mm) | 鳞片长 Scale length (mm) | 鳞片宽 Scale width (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 Control | 84.78±1.46b | 82.83±1.72b | 1.69±0.11c | 54.47±3.15a | 4.25±0.16c | 5.11±0.34b | 3.29±0.21c |
| 兰州-1 LZ-1 | 105.68±2.39a | 99.65±2.47a | 6.01±0.18a | 17.01±0.63b | 8.96±0.21b | 11.16±0.36a | 5.84±0.22b |
| 兰州-2 LZ-2 | 81.73±1.53b | 72.09±1.72c | 4.76±0.16b | 15.63±0.70b | 10.70±0.26a | 11.35±2.67a | 6.82±0.15a |
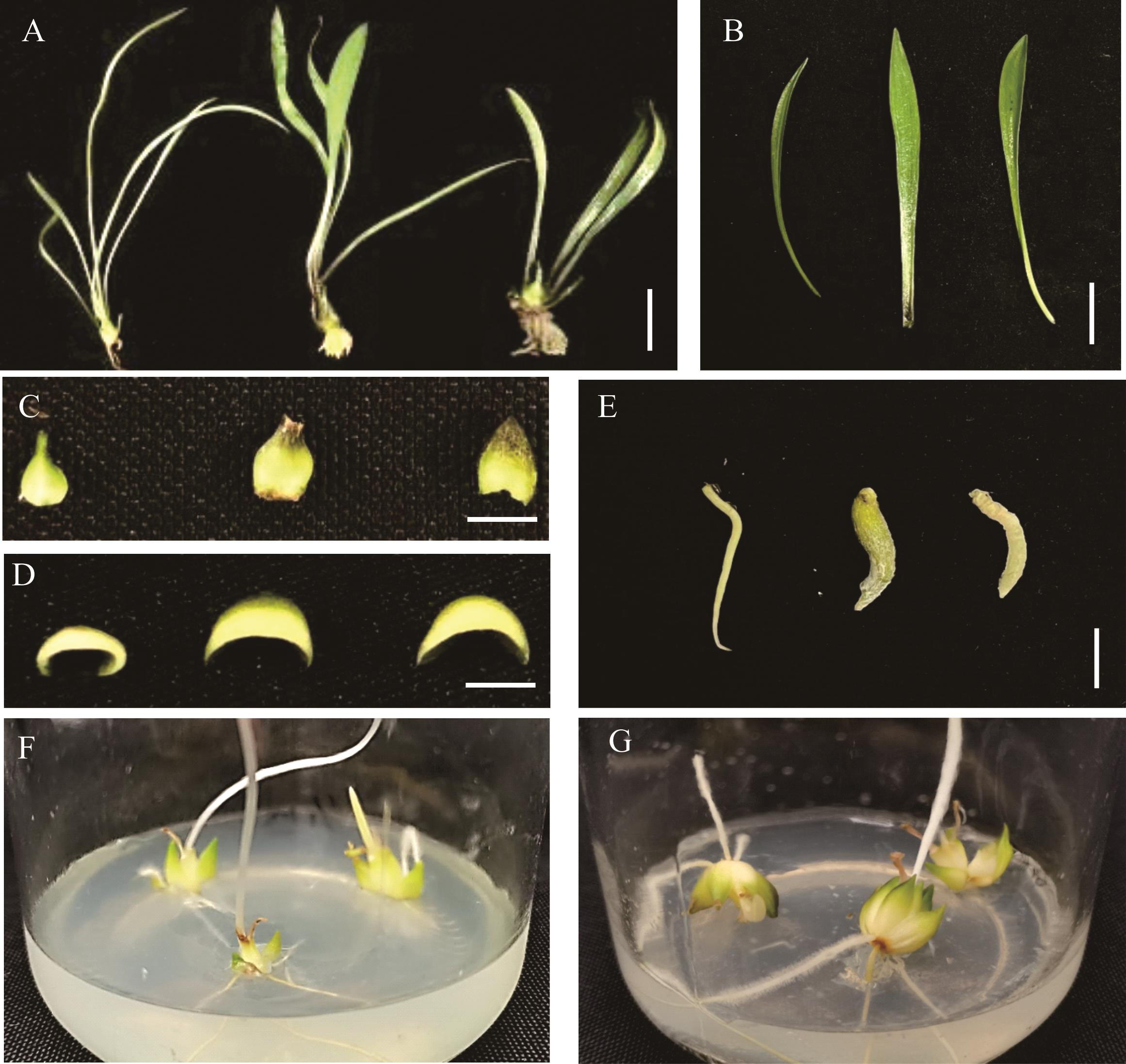
图3 兰州百合变异幼苗植株形态的比较A:从左到右分别是兰州百合对照和2个诱变株系(LZ-1和LZ-2)幼苗植株形态,标尺为1.8 cm;B:从左到右分别是对照和2个诱变株系叶片形态,标尺为1.5 cm; C,D:从左到右分别是对照和2个诱变株系外层鳞片及其横切面,标尺为0.8和0.5 cm;E:从左到右分别是对照和2个诱变株系不定根,标尺为 1.0 cm;F,G:对照和LZ-2接种1个月的小鳞茎比较。A: The plant morphology of the control and two induced lines of the L. davidii var. unicolor seedling from left to right, the bar represents 1.8 cm; B: The leaf morphology of the control and two induced lines of the L. davidii var. unicolor from left to right, the bar represents 1.5 cm; C, D: The outer scales and its transverse section of the control and two induced lines of the L. davidii var. unicolor from left to right, the bars represent 0.8 and 0.5 cm; E: The roots of the control and two induced lines of the L. davidii var. unicolor from left to right, the bar represents 1.0 cm; F, G: The comparison of the bulblets of the control and LZ-2 grown for one month.
Fig.3 The comparison of morphology in mutant seedling plants of L. davidii var. unicolor
样本 Sample | 上表皮细胞长 Adaxial epidermal cell length (μm) | 上表皮细胞宽 Adaxial epidermal cell width (μm) | 上表皮细胞长宽比 Adaxial epidermal cell length-width ratio | 气孔密度 Stomatal frequency (No.·mm-2) | 保卫细胞长 Guard cell length (μm) | 保卫细胞宽 Guard cell width (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照Control | 256.94±5.15c | 30.30±0.61c | 8.76±0.29c | 42.07±2.27a | 19.86±0.40c | 15.62±0.20c |
| 兰州-1 LZ-1 | 406.85±8.49b | 41.04±0.84a | 10.10±0.26b | 24.51±1.54c | 32.33±0.21a | 27.39±0.27a |
| 兰州-2 LZ-2 | 448.89±13.55a | 37.62±0.76b | 12.28±0.49a | 30.49±1.66b | 27.31±0.34b | 18.38±0.22b |
表4 兰州百合对照和变异植株上表皮细胞、保卫细胞和气孔的比较
Table 4 Comparison of adaxial epidermis cell, guard cell and stomata in control and mutagenic plants
样本 Sample | 上表皮细胞长 Adaxial epidermal cell length (μm) | 上表皮细胞宽 Adaxial epidermal cell width (μm) | 上表皮细胞长宽比 Adaxial epidermal cell length-width ratio | 气孔密度 Stomatal frequency (No.·mm-2) | 保卫细胞长 Guard cell length (μm) | 保卫细胞宽 Guard cell width (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照Control | 256.94±5.15c | 30.30±0.61c | 8.76±0.29c | 42.07±2.27a | 19.86±0.40c | 15.62±0.20c |
| 兰州-1 LZ-1 | 406.85±8.49b | 41.04±0.84a | 10.10±0.26b | 24.51±1.54c | 32.33±0.21a | 27.39±0.27a |
| 兰州-2 LZ-2 | 448.89±13.55a | 37.62±0.76b | 12.28±0.49a | 30.49±1.66b | 27.31±0.34b | 18.38±0.22b |

图4 兰州百合变异幼苗的上表皮和气孔观察A~C:兰州百合对照、诱变株系LZ-1和LZ-2上表皮细胞形态,标尺为20 μm;D~F:对照、诱变株系LZ-1和LZ-2叶片气孔,标尺为20 μm;G~I:对照、诱变株系LZ-1和LZ-2叶片气孔,标尺为10 μm。A-C: The adaxial epidermal cells in the control of L. davidii var. unicolor and mutant lines LZ-1, LZ-2 respectively, scales represent 20 μm; D-F: The leaf blade stomas in the control of L. davidii var. unicolor and mutant lines LZ-1, LZ-2 respectively, scales represent 20 μm; G-I: The leaf blade stomas in the control of L. davidii var. unicolor and mutant lines LZ-1, LZ-2 respectively, scales represent 10 μm.
Fig.4 The observation of adaxial epidermal cells and leaf blade stomas in mutant seedlings of L.davidii var. unicolor
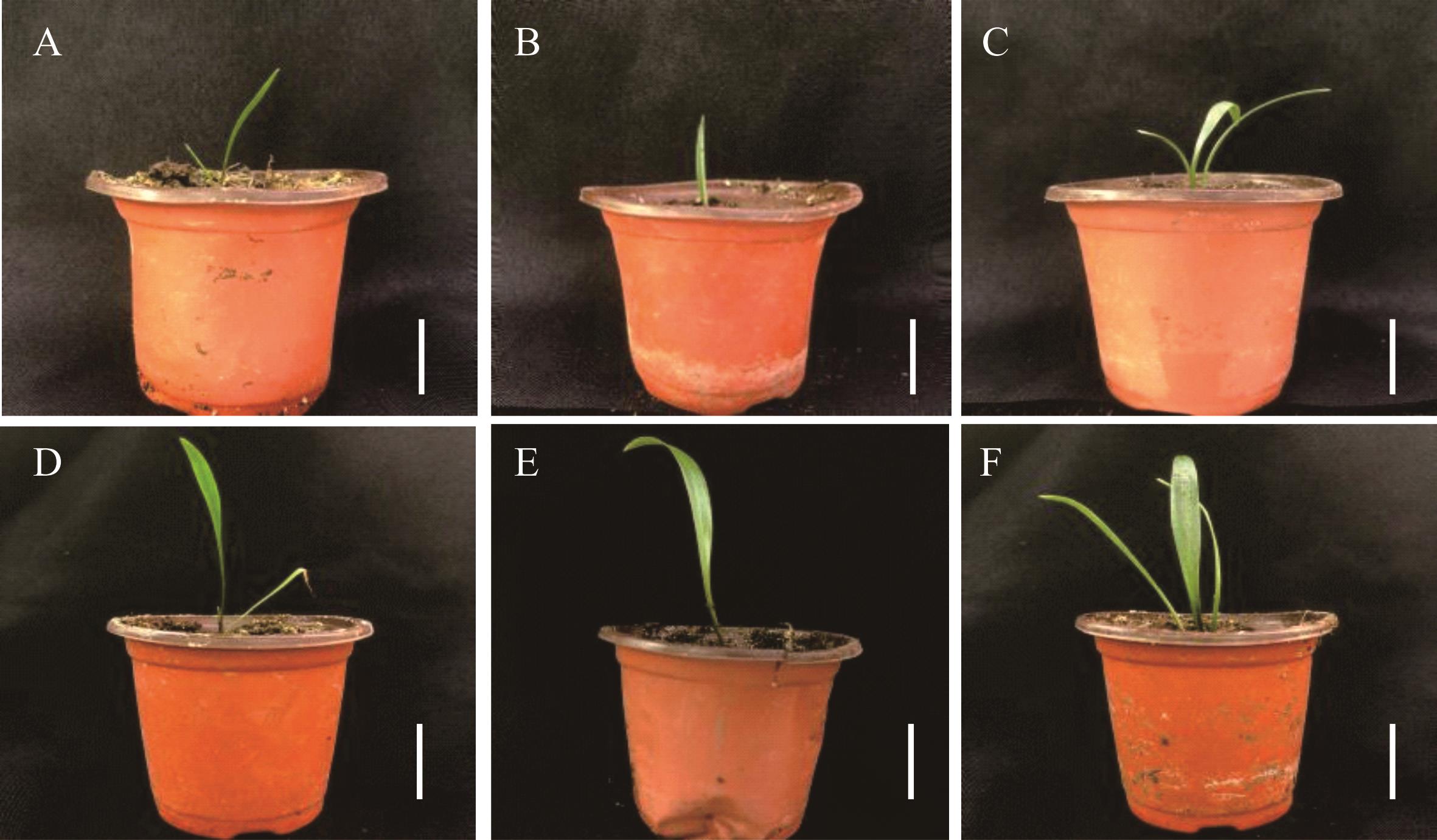
图5 兰州百合变异幼苗移栽生长比较A~C:兰州百合对照、诱变株系LZ-1和LZ-2幼苗移栽当天形态;D~F:兰州百合对照、诱变株系LZ-1和LZ-2幼苗移栽30 d形态,标尺为3 cm。A-C: The morphology of the control, induced lines LZ-1 and LZ-2 of L. davidii var. unicolor for 0 day; D-F: The morphology of the control, induced lines LZ-1 and LZ-2 of L. davidii var. unicolor for 30 days, the bars represent 3 cm.
Fig.5 The growth of transplanting seedlings in mutant L. davidii var. unicolor plants

图6 兰州百合变异植株的ISSR检测A:引物3A30;B:引物3A50;C:引物UBC811;D:引物UBC814;E:引物UBC815; F:引物UBC835;G:引物UBC842;H:引物UBC843;I:引物UBC844;J:引物UBC845;K:引物UBC857;1~3为3个独立的LZ-2样本,4~6为3个独立的LZ-1样本,7~9为3个独立的对照样本,M为Marker 2000。A: Primer 3A30; B: Primer 3A50; C: Primer UBC811; D: Primer UBC814; E: Primer UBC815; F: Primer UBC835; G: Primer UBC842; H: Primer UBC843; I: Primer UBC844; J: Primer UBC845; K: Primer UBC857; 1-3: Three independent LZ-2 samples; 4-6: Three independent LZ-1 samples; 7-9: Three independent control samples; M: Marker 2000.
Fig.6 ISSR detection for mutant plants of L. davidii var. unicolor
| 1 | Liang Z X, Zhang J Z, Xin C, et al. Analysis of edible characteristics, antioxidant capacities, and phenolic pigment monomers in Lilium bulbs native to China. Food Research International, 2022, 151: 110854. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110854. |
| 2 | Zhao X Y, Wang W H. Status and development proposals of lily industry in China//Ming J, Yuan S X. Papers (abstracts) of the 12th Symposium of Chinese Society of Flower Bulbs. Beijing: Beijing Zhonglyu Garden Science Research Institute, 2017: 61-69. |
| 赵祥云, 王文和. 我国百合产业的现状及存在问题和发展建议//明军, 袁素霞. 第12届中国球宿根花卉研讨会论文(摘要)集. 北京: 北京中绿园林科学研究院, 2017: 61-69. | |
| 3 | Mi L, Wang K W, Zhu X M, et al. The identification of phytochemical components in Lilium davidii var. unicolor using UHPLC-QTOF-MS. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(2): 48-58. |
| 米璐, 王珂雯, 祝秀梅, 等. 基于 UHPLC-QTOF-MS的兰州百合植物化学成分鉴定. 食品工业科技, 2024, 45(2): 48-58. | |
| 4 | He J Q, Chen Y Q, Zhi S, et al. The evaluation of nutritional components and safety in the lily of alpine area. Tropical Agricultural Science & Technology, 2022, 45(2): 41-46. |
| 和继泉, 陈玉芹, 知史, 等. 高寒区百合鳞茎营养成分及安全性评价. 热带农业科技, 2022, 45(2): 41-46. | |
| 5 | Li W M, Wang Y J, Wei H L, et al. Structural characterization of Lanzhou lily (Lilium davidii var. unicolor) polysaccharides and determination of their associated antioxidant activity. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2020,100(15): 5603-5616. |
| 6 | Lin Y H, Guo F X, Luo J J, et al. Effect of different N rates on nutrient accumulation and nitrogen use efficiency in rainfed land Lanzhou lily. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2011, 20(2): 101-108. |
| 林玉红, 郭凤霞, 罗俊杰, 等. 不同施氮水平对旱地兰州百合养分累积与氮肥利用的影响. 草业学报, 2011, 20(2): 101-108. | |
| 7 | Wang H M, Wang L G, Liu X X, et al. Establishment and application of virus detection technology of Lilium davidii var. unicolor. Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology, 2021, 52(3): 38-42. |
| 王红梅, 王立光, 刘新星, 等. 兰州百合病毒 RT-PCR 检测技术建立及应用. 甘肃农业科技, 2021, 52(3): 38-42. | |
| 8 | Li D, Luo Y R, Han G W, et al. Studies on polyploidy induction of wild Lilium nepalense D. Don. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 32(4): 678-684. |
| 李旦, 罗一然, 韩国伟, 等. 野生紫斑百合多倍体诱导研究. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 32(4): 678-684. | |
| 9 | Zhang X Q, Wang L J, Cao Q Z, et al. Polyploidy induction and identification in Lilium concolor var. pulchellum. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2017, 39(7): 96-102. |
| 张锡庆, 汪莲娟, 曹钦政, 等. 有斑百合多倍体诱导及鉴定. 北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(7): 96-102. | |
| 10 | Sun H M, Fu L L, Wang Z P, et al. Polyploidy induction and identification of Lilium pumilum and Lilium davidii var. unicolor based on somatic embryogenesis. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2018, 45(6): 1136-1146. |
| 孙红梅, 付麟岚, 王志平, 等. 基于体细胞胚发生的细叶百合和兰州百合多倍体诱导及鉴定. 园艺学报, 2018, 45(6): 1136-1146. | |
| 11 | Lian X B. Polyploid induction test reports of Lilium davidii var. unicolor. Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology, 1995(6): 14-15. |
| 连雪斌. 兰州百合多倍体诱导试验报告. 甘肃农业科技, 1995(6): 14-15. | |
| 12 | Wang Z Y, Gao S L, Yu B Y, et al. Rapid propagation and polyploidy induction of Lilium davidii var. unicolor. Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, 2013, 20(1): 26-28. |
| 王姿云, 高山林, 余伯阳, 等. 兰州百合的快速繁殖及多倍体诱导. 药物生物技术, 2013, 20(1): 26-28. | |
| 13 | Kang X Y. Research progress and prospect of triploid breeding of forest trees. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 2020, 50(2): 136-143. |
| 康向阳. 林木三倍体育种研究进展及展望. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2020, 50(2): 136-143. | |
| 14 | Barba-Gonzalez R, Lim K B, Ramanna M S, et al. Occurrence of 2n gametes in the F1 hybrids of Oriental×Asiatic lilies (Lilium): Relevance to intergenomic recombination and backcrossing. Euphytica, 2005, 143(1): 67-73. |
| 15 | Fu Y Y, Yi D Y, Yang X M, et al. Analysis of morphological characteristics and genetic variation in a new germplasm Lilium lancifolium JD-h-15. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2022, 38(11): 140-150. |
| 符勇耀, 易德燕, 杨先茂, 等. 卷丹新种质 JD-h-15的形态特征与遗传变异分析. 生物技术通报, 2022, 38(11): 140-150. | |
| 16 | Ou Z Y. Polyploid induction, identification, and ISSR analysis of a new lily germplasm ‘Light Pink Beauty’. Chongqing: Yangtze Normal University, 2022. |
| 欧正应. 百合新种质‘淡粉佳人’的多倍体诱导、鉴定及ISSR分析. 重庆: 长江师范学院, 2022. | |
| 17 | Chen A, Yang L P, Tan Y, et al. Study on polyploid induction of Lilium lancifolium in vitro with colchicine treatment. Journal of Plant Genetic Resource, 2014, 15(6): 1385-1389. |
| 陈艾, 杨利平, 谭艳, 等. 秋水仙素诱变离体卷丹多倍体的研究. 植物遗传资源学报, 2014, 15(6): 1385-1389. | |
| 18 | Liu Y, Yang L P. Polyploid induction of Lilium amabile in vitro. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University, 2015, 38(3): 30-33. |
| 刘洋, 杨利平. 朝鲜百合离体多倍体诱导. 河北农业大学学报, 2015, 38(3): 30-33. | |
| 19 | Wu X J, Yang L P, Chen M. In vitro polyploid induction of Lilium callosum. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(8): 84-86. |
| 吴雪娟, 杨利平, 陈敏. 条叶百合的离体多倍体诱导. 贵州农业科学, 2016, 44(8): 84-86. | |
| 20 | Li M Q, Shi G Y, Ye S H, et al. Optimization of ISSR-PCR reaction system for Lanzhou lily. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2014, 49(6): 76-81. |
| 李谋强, 师桂英, 叶树辉, 等. ‘兰州百合’ISSR-PCR体系的优化. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2014, 49(6): 76-81. | |
| 21 | Liu J, Zhao Q F, Ding L. Polyploid induction and indentification of Lilium davidii var. unicolor (Hoog) Cotton. Northern Horticulture, 2011(18): 138-141. |
| 刘静, 赵庆芳, 丁兰. 兰州百合多倍体诱导及鉴定. 北方园艺, 2011(18): 138-141. | |
| 22 | Wang L Y, Jing R Y. Tetraploid induction of Lilium davidii var. unicolor through colchicine treatment. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2008, 22(5): 581-584. |
| 王丽艳, 荆瑞勇. 秋水仙碱诱导兰州百合四倍体. 核农学报, 2008, 22(5): 581-584. | |
| 23 | Li M X, Zhang X F. Research of plant chromosome technology. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University Press, 1991. |
| 李懋学, 张敩芳. 植物染色体研究技术. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学出版社, 1991. | |
| 24 | Yang Y J, Ge B B, Wei Q, et al. Colchicines-induced polyploid plants and identification in Lilium pumilum DC. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2013, 18(1): 128-133. |
| 杨英杰, 葛蓓孛, 魏倩, 等. 秋水仙素诱导细叶百合多倍体研究. 中国农业大学学报, 2013, 18(1): 128-133. | |
| 25 | Chen M M, Zhou Y, Sun Y J, et al. Polyploidy induction of Lilium spp. by colchicine and ploidy identification by flow cytometry. Acta Agriculturae Shanghai, 2018, 34(2): 81-87. |
| 陈敏敏, 周音, 孙亿敬, 等. 秋水仙素诱导百合多倍体及流式细胞仪倍性鉴定研究. 上海农业学报, 2018, 34(2): 81-87. | |
| 26 | Wang M L, Li X T, Wang W H, et al. Ploidy identification of 100 lily accessions based on stomatal characteristics. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2021, 33(12): 27-33. |
| 王美玲, 李兴桃, 王文和, 等. 用气孔性状鉴定 100 份百合倍性的研究. 江西农业学报, 2021, 33(12): 27-33. | |
| 27 | Mallick P, Chattaraj S, Sikdar S R. Molecular characterizations of somatic hybrids developed between Pleurotus florida and Lentinus squarrosulus through inter-simple sequence repeat markers and sequencing of ribosomal RNA-ITS gene. Biotechnology, 2017, 7(5): 298. |
| 28 | Zhang Z L, Zheng Z W, Zheng S X, et al. The cultivation and identification of allotriploid lily. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2022, 20(19): 6424-6432. |
| 张震林, 郑梓唯, 郑思乡, 等. 异源三倍体百合的培育及鉴定. 分子植物育种, 2022, 20(19): 6424-6432. | |
| 29 | Luo Q, Yang Z J, Peng Z S, et al. Evaluation of genetic diversity in synthetic hexaploid wheats using ISSR markers. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2016, 31(4): 119-125. |
| 罗琴, 杨在君, 彭正松, 等. 人工合成六倍体小麦的ISSR位点遗传多样性分析. 华北农学报, 2016, 31(4): 119-125. | |
| 30 | Mcgregor C E, Lambert C A, Greyling M M, et al. A comparative assessment of DNA fingerprinting techniques (RAPD, ISSR, AFLP and SSR) in tetraploid potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) germplasm. Euphytica, 2000, 113(2): 135-144. |
| [1] | 张金青, 牛奎举, 李玉珠, 马晖玲. 植物无融合生殖发生因素解析及其在草地早熟禾育种中的应用前景展望[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 205-217. |
| [2] | 李淑洁, 张金文, 裴怀弟, 王红梅, 罗俊杰, 林玉红. 兰州百合同源四倍体诱导及其基因组大小估算[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 190-196. |
| [3] | 黄钰芳, 张恩和, 张新慧, 王惠珍, 王琦, 刘青林, 石雨仟. 兰州百合连作障碍效应及机制研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 146-155. |
| [4] | 黄钰芳, 张恩和, 张新慧, 王惠珍, 王琦, 刘青林, 石雨仟. 兰州百合根及鳞茎水浸液自毒作用的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 93-103. |
| [5] | 李悦, 师尚礼. 秋水仙素处理清水苜蓿胚根对染色体倍性与叶表皮细胞的诱变效应[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2): 141-149. |
| [6] | 钟小仙,刘智微,常盼盼,吴娟子,张建丽. 秋水仙素诱导获得自交结实的海滨雀稗体细胞突变体[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(6): 205-212. |
| [7] | 曾亮,袁庆华,王方,王瑜. 冰草属植物种质资源遗传多样性的ISSR分析[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(1): 260-267. |
| [8] | 曾亮,李敏权,杨晓明. 豌豆属种质资源遗传多样性的ISSR分析[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(3): 125-131. |
| [9] | 林玉红. 钾肥施用量对兰州百合生长、养分吸收及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(1): 141-148. |
| [10] | 林玉红,罗俊杰. 氮素对兰州百合产量、养分累积和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(5): 223-230. |
| [11] | 杨雨华,李文龙,黄鹏,宗建伟,李自珍. 钾肥与覆膜调控对兰州百合生长及个体大小不整齐性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(5): 217-222. |
| [12] | 林玉红,郭凤霞,罗俊杰,孙建好,张运晖. 不同施氮水平对旱地兰州百合养分累积与氮肥利用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(2): 101-108. |
| [13] | 崔广荣,张子学,张从宇,胡能兵,隋益虎,李杰勤. 文心兰多倍体诱导及其鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(1): 184-190. |
| [14] | 王丽艳,荆瑞勇,肖莉杰,方淑梅,张红梅,王北艳,殷奎德. 扁茎黄芪离体快繁及多倍体诱导[J]. 草业学报, 2009, 18(1): 94-99. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||