

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (12): 73-84.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025024
收稿日期:2025-01-20
修回日期:2025-03-10
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-10-20
通讯作者:
韩其飞
作者简介:E-mail: hanqifei@nuist.edu.cn基金资助:
Long YIN1( ), Qi-fei HAN1(
), Qi-fei HAN1( ), Yang ZHAO2,3, Wen-xin LIU2,3
), Yang ZHAO2,3, Wen-xin LIU2,3
Received:2025-01-20
Revised:2025-03-10
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-10-20
Contact:
Qi-fei HAN
摘要:
毒杂草型草地退化没有表现出地表裸露、植物生物量减少等特征,对其大尺度的遥感识别较为困难,纹理特征、时相作为遥感影像的重要衍生,能够在影像上提供更多的地物细节,降低了“同物异谱”“同谱异物”的现象,能够很好地提高分类的准确性和可靠性。本研究以伊犁河谷托乎拉苏草原为研究区,利用Sentinel-2卫星数据,对该区主要的毒杂草白喉乌头进行特征提取;基于像元尺度识别白喉乌头分布范围并计算其在混合像元中的占比;最后,通过计算剔除白喉乌头后的植被覆盖度,分析2018-2024年托乎拉苏草原草地退化趋势。结果表明:1) 特征优选有效减少信息冗余,光谱与纹理特征结合有效提高分类精度(总体精度91.67%,Kappa系数0.83)。2) 白喉乌头主要分布于阳坡中海拔平坦区及河谷地带,占研究区40%以上的面积,以稀疏覆盖(0%~0.25%)为主,2018-2024年间各密度等级分布变化为0.67%~1.17%。3) 经校正后草地退化指数2018与2024年均由轻度转为中度,但未退化面积占比提升1.17%,中度与重度退化面积分别下降1.15%与0.70%。本研究为基于多光谱数据进行大区域有毒杂草识别和草原退化监测提供重要方法支撑。
尹龙, 韩其飞, 赵阳, 刘文新. 基于多特征融合的新疆托乎拉苏草原白喉乌头分布区识别及草地退化监测[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(12): 73-84.
Long YIN, Qi-fei HAN, Yang ZHAO, Wen-xin LIU. Identification of areas of Aconitum leucostomum incursion and monitoring of grassland degradation in the Tuohulasu grassland of Xinjiang based on multi feature fusion[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(12): 73-84.
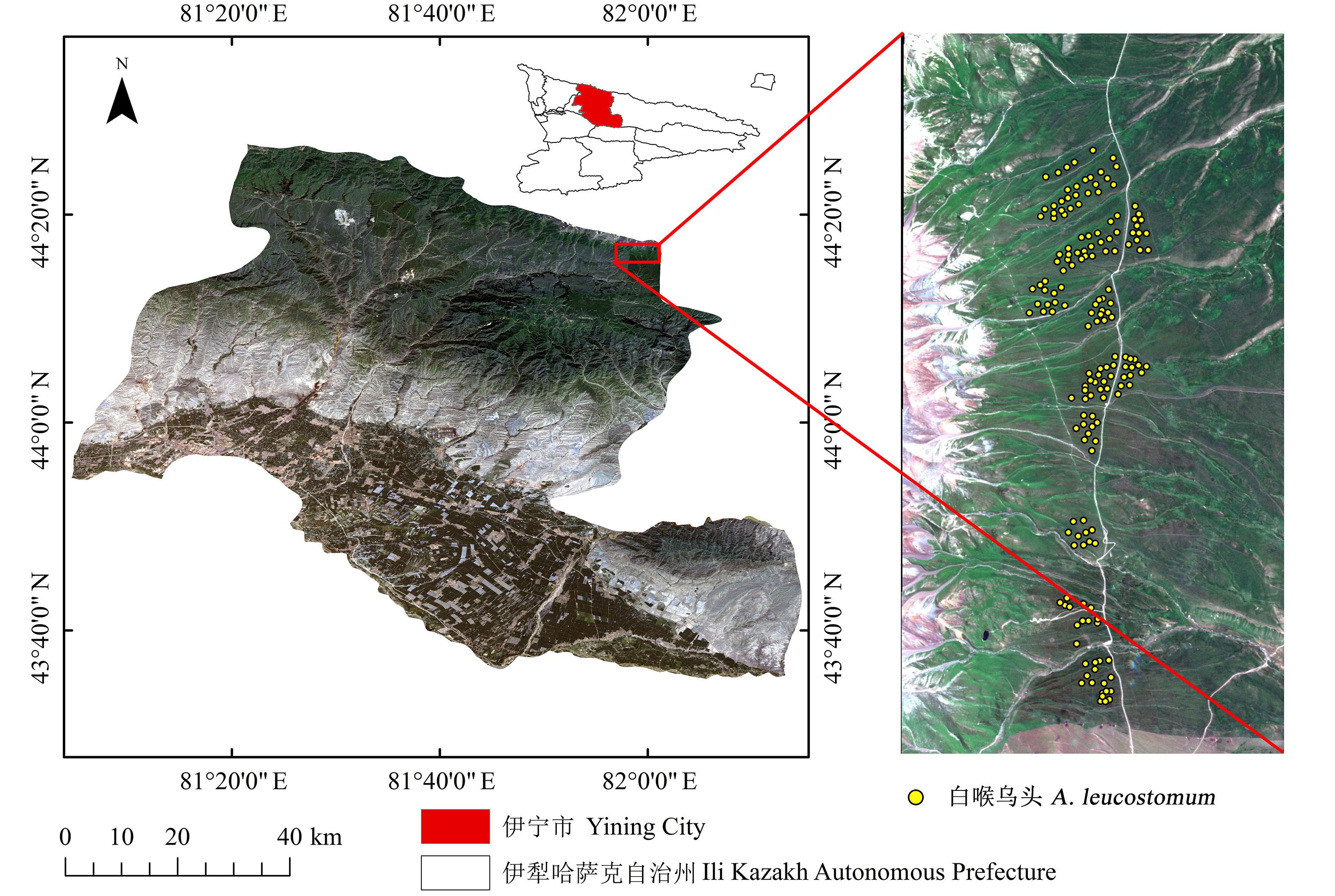
图1 研究区位置基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS (2024) 0650号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map service website GS (2024) 0650 of the Ministry of Natural Resources, the boundary of the base map is not modified.
Fig. 1 Location of research area
| 特征变量Characteristic variable | 特征因子 Characteristic factors | 公式 Formula |
|---|---|---|
光谱特征 Band feature | Band2 (B2) | 蓝Blue |
| Band3 (B3) | 绿Green | |
| Band4 (B4) | 红Red | |
| Band5 (B5) | 红边1 Red edge1 | |
| Band6 (B6) | 红边2 Red edge 2 | |
| Band7 (B7) | 红边3 Red edge 3 | |
| Band8 (B8) | 近红外1 Near-infrared 1 | |
| Band8A (B8A) | 近红外2 Near-infrared 2 | |
| 无红边植被指数Vegetation index without red edge | 归一化植被指数Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | (B8-B4)/(B8+B4) |
| 比值植被指数Relative vegetation index (RVI) | B8/B4 | |
| 差值植被指数Difference vegetation index (DVI) | B8-B4 | |
| 改良土壤调整植被指数Modified soil adjusted vegetation index (MSAVI) | ||
| 绿光归一化差值植被指数Green normalized difference vegetation index (GNDVI) | (B8-B3)/(B8+B3) | |
| 土壤调整植被指数Soil adjusted vegetation index (SAVI) | ||
| 增强植被指数Enhanced vegetation index (EVI) | ||
| 红边差异植被指数Red edge normalized difference vegetation index (RENDVI) | ||
红边植被指数 Red edge vegetation index | 改良红边土壤调整植被指数Modified soil adjusted red edge vegetation index (MSAre) | |
| 红边比值植被指数1 Modified red edge simple ratio index 1 (mSR1) | B8/B5 | |
| 红边比值植被指数2 Modified red edge simple ratio index 2 (mSR2) | B5/B4 | |
| 红边近红外归一化植被指数Red edge near-infrared normalized difference vegetation index (NDVIreni ) | (B8-B5)/(B8+B5) | |
| 红边叶绿素指数Red edge chlorophyll index (CIre) | B8/B5-1 | |
| 红边归一化植被指数Red edge normalized difference vegetation index (NDVIre) | (B5-B4)/(B5+B4) | |
| 三角植被指数Triangular vegetation index (TVI) | 0.5×{[120(B5-B3)]-[200(B4-B3)]} | |
| 纹理特征Texture features | 均值、方差、同质性、对比度、相异性、熵、角二阶矩和相关性Mean, variance, homogeneity, contrast, dissimilarity, entropy, angular second moment, correlation | 基于灰度共生矩阵, 3×3窗口计算 Based on the Gray-Level Co-occurrence Matrix, (GLCM), calculated with a window size of 3×3 |
表1 特征变量
Table 1 Characteristic variable
| 特征变量Characteristic variable | 特征因子 Characteristic factors | 公式 Formula |
|---|---|---|
光谱特征 Band feature | Band2 (B2) | 蓝Blue |
| Band3 (B3) | 绿Green | |
| Band4 (B4) | 红Red | |
| Band5 (B5) | 红边1 Red edge1 | |
| Band6 (B6) | 红边2 Red edge 2 | |
| Band7 (B7) | 红边3 Red edge 3 | |
| Band8 (B8) | 近红外1 Near-infrared 1 | |
| Band8A (B8A) | 近红外2 Near-infrared 2 | |
| 无红边植被指数Vegetation index without red edge | 归一化植被指数Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | (B8-B4)/(B8+B4) |
| 比值植被指数Relative vegetation index (RVI) | B8/B4 | |
| 差值植被指数Difference vegetation index (DVI) | B8-B4 | |
| 改良土壤调整植被指数Modified soil adjusted vegetation index (MSAVI) | ||
| 绿光归一化差值植被指数Green normalized difference vegetation index (GNDVI) | (B8-B3)/(B8+B3) | |
| 土壤调整植被指数Soil adjusted vegetation index (SAVI) | ||
| 增强植被指数Enhanced vegetation index (EVI) | ||
| 红边差异植被指数Red edge normalized difference vegetation index (RENDVI) | ||
红边植被指数 Red edge vegetation index | 改良红边土壤调整植被指数Modified soil adjusted red edge vegetation index (MSAre) | |
| 红边比值植被指数1 Modified red edge simple ratio index 1 (mSR1) | B8/B5 | |
| 红边比值植被指数2 Modified red edge simple ratio index 2 (mSR2) | B5/B4 | |
| 红边近红外归一化植被指数Red edge near-infrared normalized difference vegetation index (NDVIreni ) | (B8-B5)/(B8+B5) | |
| 红边叶绿素指数Red edge chlorophyll index (CIre) | B8/B5-1 | |
| 红边归一化植被指数Red edge normalized difference vegetation index (NDVIre) | (B5-B4)/(B5+B4) | |
| 三角植被指数Triangular vegetation index (TVI) | 0.5×{[120(B5-B3)]-[200(B4-B3)]} | |
| 纹理特征Texture features | 均值、方差、同质性、对比度、相异性、熵、角二阶矩和相关性Mean, variance, homogeneity, contrast, dissimilarity, entropy, angular second moment, correlation | 基于灰度共生矩阵, 3×3窗口计算 Based on the Gray-Level Co-occurrence Matrix, (GLCM), calculated with a window size of 3×3 |
退化等级 Degradation level | 草地退化等级划分标准 Classification criteria for grassland degradation levels | 评分Grade |
|---|---|---|
| 未退化Undegraded | 草地覆盖度达未退化草地的80%以上Grassland coverage reaches over 80% of the undegraded grassland | 1 |
| 轻度退化Mild degradation | 草地覆盖度达未退化草地的60%~80% Grassland coverage reaches 60% to 80% of the undegraded grassland | 2 |
| 中度退化Moderate degradation | 草地覆盖度达未退化草地的40%~60% Grassland coverage reaches 40% to 60% of the undegraded grassland | 3 |
| 重度退化Severe degradation | 草地覆盖度达未退化草地的40%以下Grassland coverage is less than 40% of the undegraded grassland | 4 |
表2 研究区草地退化等级划分方法及评分
Table 2 Classification method and scoring of grassland degradation levels in the research area
退化等级 Degradation level | 草地退化等级划分标准 Classification criteria for grassland degradation levels | 评分Grade |
|---|---|---|
| 未退化Undegraded | 草地覆盖度达未退化草地的80%以上Grassland coverage reaches over 80% of the undegraded grassland | 1 |
| 轻度退化Mild degradation | 草地覆盖度达未退化草地的60%~80% Grassland coverage reaches 60% to 80% of the undegraded grassland | 2 |
| 中度退化Moderate degradation | 草地覆盖度达未退化草地的40%~60% Grassland coverage reaches 40% to 60% of the undegraded grassland | 3 |
| 重度退化Severe degradation | 草地覆盖度达未退化草地的40%以下Grassland coverage is less than 40% of the undegraded grassland | 4 |

图2 白喉乌头分布区各特征相关系数矩阵a: 光谱特征Band feature; b: 无红边植被指数Vegetation index without red edge; c: 红边植被指数Red edge vegetation index; d: 纹理特征Texture features; NDVI: 归一化植被指数Normalized difference vegetation index; RVI: 比值植被指数Relative vegetation index; DVI: 差值植被指数Difference vegetation index; MSAVI: 改良土壤调整植被指数Modified soil adjusted vegetation index; GNDVI: 绿光归一化差值植被指数Green normalized difference vegetation index; SAVI: 土壤调整植被指数 Soil adjusted vegetation index; EVI: 增强植被指数Enhanced vegetation index; RENDVI: 红边差异植被指数Red edge normalized difference vegetation index; MSAre: 改良红边土壤调整植被指数Modified soil adjusted red edge vegetation index; mSR1: 红边比值植被指数1Modified red edge simple ratio index 1; mSR2: 红边比值植被指数2 Modified red edge simple ratio index 2; NDVIreni: 红边近红外归一化植被指数Red edge near-infrared normalized difference vegetation index; CIre: 红边叶绿素指数Red edge chlorophyll index; NDVIre: 红边归一化植被指数Red edge normalized difference vegetation index; TVI: 三角植被指数Triangular vegetation index; Contrast: 对比度; Correlation: 相关度; Dissimilarity: 相异性; Entropy: 熵; Homogeneity: 同质性; Mean: 均值; Angular second moment: 角二阶距; Variance: 方差.
Fig.2 Correlation coefficient matrix of each feature of A.leucostomum distribution
特征分量 Principal component | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 占比 Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 第1主成分Principal component 1 (PC1) | 0.13774 | 45.4521 |
| 第2主成分Principal component 2 (PC2) | 0.05692 | 64.2347 |
| 第3主成分Principal component 3 (PC3) | 0.04714 | 79.7890 |
| 第4主成分Principal component 4 (PC4) | 0.04157 | 93.5066 |
| 第5主成分Principal component 5 (PC5) | 0.01968 | 100.0000 |
表3 纹理特征主成分分析
Table 3 Principal component analysis (PCA) of texture feature
特征分量 Principal component | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 占比 Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 第1主成分Principal component 1 (PC1) | 0.13774 | 45.4521 |
| 第2主成分Principal component 2 (PC2) | 0.05692 | 64.2347 |
| 第3主成分Principal component 3 (PC3) | 0.04714 | 79.7890 |
| 第4主成分Principal component 4 (PC4) | 0.04157 | 93.5066 |
| 第5主成分Principal component 5 (PC5) | 0.01968 | 100.0000 |
方案 Scheme | 光谱 特征 Spectral signature | 光谱+纹理特征Spectral signature+texture feature | 变化 Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| 总体精度Overall accuracy (OA, %) | 89.22 | 91.67 | 2.45 |
| Kappa系数Kappa coefficient | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.05 |
表4 2018年白喉乌头分类精度对比
Table 4 Accuracy comparison of A. leucostomum in 2018
方案 Scheme | 光谱 特征 Spectral signature | 光谱+纹理特征Spectral signature+texture feature | 变化 Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| 总体精度Overall accuracy (OA, %) | 89.22 | 91.67 | 2.45 |
| Kappa系数Kappa coefficient | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.05 |
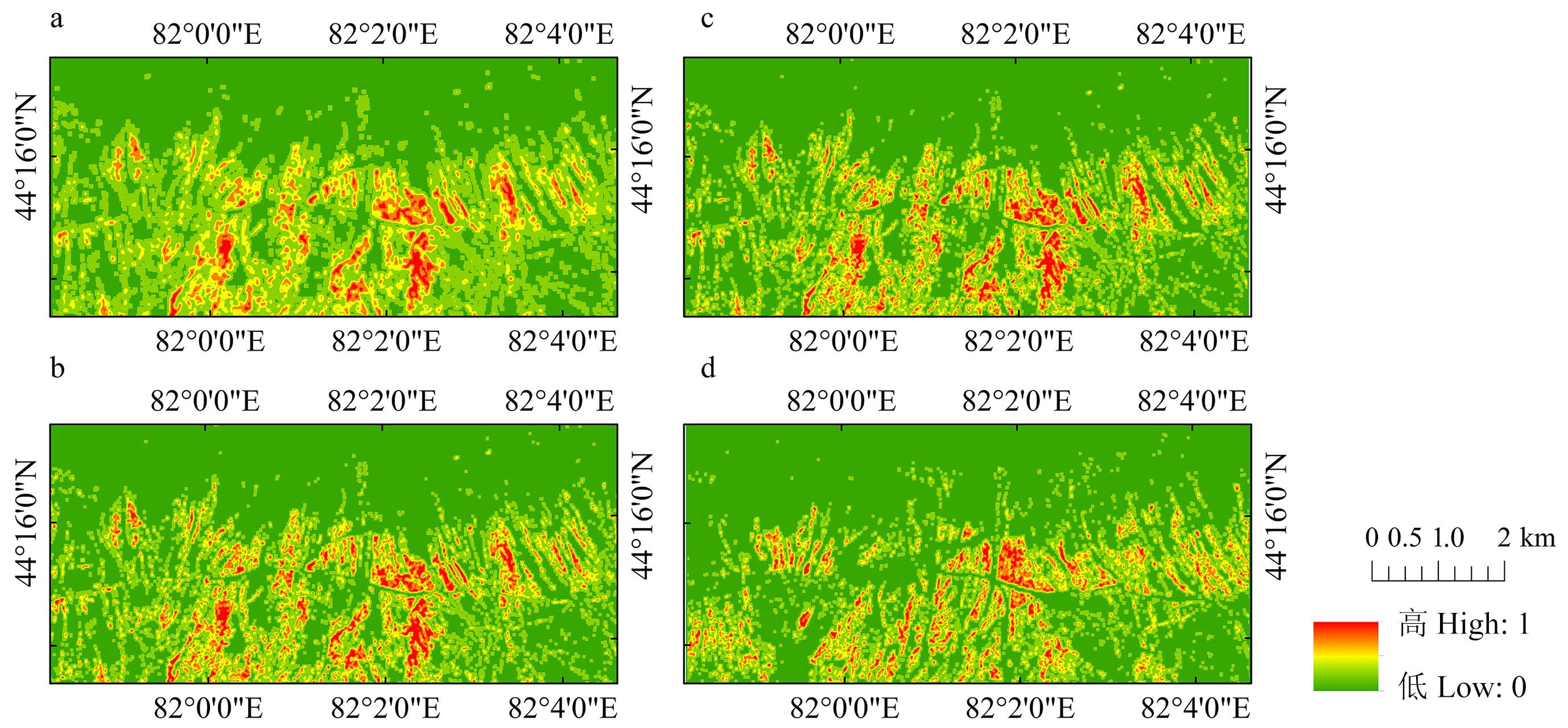
图3 不同特征组合白喉乌头分类a: 光谱特征分类Classification of spectral signature; b: 光谱+纹理特征分类Classification of spectral signature and texture feature; c: 2018年粗化结果Coarsening results in 2018; d: 2024年粗化结果Coarsening results in 2024.
Fig.3 Classification of A.leucostomum with different feature combinations
像元类别 Pixel category | 像元个数 Number of pixels | 占比变化Percentage change (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2024 | ||
| 无毒草Non-toxic grass | 4938701 | 5328710 | 4.62 |
| 稀疏分布Sparse distribution | 2153158 | 1923890 | -2.72 |
| 较稀疏分布Slightly sparse distribution | 789568 | 728267 | -0.73 |
| 较密集分布Slightly densely distribution | 404119 | 358436 | -0.54 |
| 密集分布Densely distribution | 150334 | 96577 | -0.64 |
| 总和All | 8435880 | 8435880 | 0.00 |
表5 2018-2024年白喉乌头盖度变化情况
Table 5 The proportion of pixels with varying degrees of poisoning from 2018 to 2024
像元类别 Pixel category | 像元个数 Number of pixels | 占比变化Percentage change (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2024 | ||
| 无毒草Non-toxic grass | 4938701 | 5328710 | 4.62 |
| 稀疏分布Sparse distribution | 2153158 | 1923890 | -2.72 |
| 较稀疏分布Slightly sparse distribution | 789568 | 728267 | -0.73 |
| 较密集分布Slightly densely distribution | 404119 | 358436 | -0.54 |
| 密集分布Densely distribution | 150334 | 96577 | -0.64 |
| 总和All | 8435880 | 8435880 | 0.00 |
| [1] | Tian X C. Causes of grassland degradation in Xinjiang and its impact on soil ecology and biodiversity. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022(5): 181-184. |
| 田新春. 新疆草地退化原因及对土壤生态和生物多样性的影响. 现代农业科技, 2022(5): 181-184. | |
| [2] | Lang Y B. The characteristics of natural grassland resource and types of grassland deterioration in Sunan County of Gansu Province. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2008, 30(3): 100-105. |
| 郎永斌. 甘肃省肃南县天然草地资源特征及退化类型. 中国草地学报, 2008, 30(3): 100-105. | |
| [3] | Yu H Y, Yu L P, Yang L P, et al. Analysis on the change of the yield and nutrient content of the edible forage and the grassland grazing capacity in the alpine grassland of Maqu County. China Herbivore Science, 2020, 40(3): 40-46. |
| 俞慧云, 俞联平, 杨林平, 等. 玛曲县高寒草地可食牧草产量和养分含量变化及草地承载力分析. 中国草食动物科学, 2020, 40(3): 40-46. | |
| [4] | Gusman H W, Menges R M, Escobar D E, et al. Pubescence affects spectra and imagery of silverleaf sunflower (Helianthus argophyllus). Weed Science, 1977, 25(5): 437-440. |
| [5] | An R, Jiang D P, Li X X, et al. Using hyperspectral data to determine spectral characteristics of grassland vegetation in central and eastern parts of Three-River Source. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2014, 29 (2): 202-211. |
| 安如, 姜丹萍, 李晓雪, 等. 基于地面实测高光谱数据的三江源中东部草地植被光谱特征研究. 遥感技术与应用, 2014, 29(2): 202-211. | |
| [6] | Hu Y N, An R, Ai Z T, et al. Researches on grass species fine identification based on UAV hyperspectral images in Three-River Source region. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2021, 36(4): 926-935. |
| 胡宜娜, 安如, 艾泽天, 等. 基于无人机高光谱影像的三江源草种精细识别研究. 遥感技术与应用, 2021, 36(4): 926-935. | |
| [7] | Li H R. Classification and degradation index extraction of grassland vegetation based on hyperspectral remote sensing. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2022. |
| 李浩然. 基于高光谱遥感的草地植被分类与退化指标提取研究. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2022. | |
| [8] | Li Y F, Sun B, Gao Z H, et al. Farmland shelterbelt information extraction based on multispectral image of the ZY1-02E satellite. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2024, 28(3): 624-634. |
| 李毅夫, 孙斌, 高志海, 等. 5米光学02星多光谱影像农田防护林信息提取. 遥感学报, 2024, 28(3): 624-634. | |
| [9] | Li H. Technical manual for prevention and control of biological disasters in Yili grassland. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press Co.,Ltd, 2012. |
| 李宏. 伊犁草原生物灾害防治技术手册. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2012. | |
| [10] | Qinghai Provincial Administration for Market Regulation. DB63/T 241-2021. Technical specification for comprehensive management of poisonous grass in grassland. Xining: Qinghai Provincial Administration for Market Regulation. 2021. |
| 青海省市场监督管理局. DB63/T 241-2021. 草地毒害草综合治理技术规范. 西宁: 青海省市场监督管理局, 2021. | |
| [11] | Su D X, Zhang Z H, Chen Z Z, et al. Discussion on grading indicators for degradation, desertification, and salinization of natural grasslands in China// Research on desertification control and sand industry in China-celebrating the 10th anniversary of the establishment of the Chinese society for desertification control and sand industry (1993-2003). Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press Academic Papers Collection, 2003. |
| 苏大学, 张自和, 陈佐忠, 等. 中国天然草地退化、沙化、盐渍化分级指标的商榷// 中国治沙暨沙产业研究——庆贺中国治沙暨沙业学会成立10周年(1993-2003)学术论文集. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2003. | |
| [12] | Abdureheman·Wusiman, Yusufujiang R, Zhang F, et al. Temporal and spatial characteristics of grassland degradation in Xinjiang section of Tianshan Mountains based on remote sensing monitoring and its relationship with climate factors. Pratacultural Science, 2023, 40(7): 1779-1792. |
| 阿卜杜热合曼·吾斯曼, 玉素甫江·如素力, 张发, 等. 基于遥感监测的天山新疆段草地退化时空特征及其与气候因子的关系. 草业科学, 2023, 40(7): 1779-1792. | |
| [13] | Tian C H, Li M Y, Li T, et al. Estimation of forest net primary productivity based on sentinel active and passive remote sensing data and canopy height. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2024, 48(4): 132-140. |
| 田春红, 李明阳, 李陶, 等. 基于Sentinel 1&2主被动遥感数据和冠层高度的森林净初级生产力估测. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48(4): 132-140. | |
| [14] | Cao Y J, Dai J G, Zhang G S, et al. Remote sensing monitoring of non-agriculturalization in typical areas of the Northern Xinjiang of China based on feature optimization. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2024, 40(5): 275-286. |
| 曹宇娟, 戴建国, 张国顺, 等. 基于特征优选的北疆典型区域非农化遥感监测. 农业工程学报, 2024, 40(5): 275-286. | |
| [15] | Xu D. Research on typical crop classification based on multiple features. Changchun: Jilin University, 2023. |
| 徐达. 基于多种特征的典型农作物分类研究. 长春: 吉林大学, 2023. | |
| [16] | She J, Shen A H, Shi Y, et al. Vegetation classification of UAV remote sensing in desert steppe based on object-oriented technology. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(7): 1-14. |
| 佘洁, 沈爱红, 石云, 等. 基于无人机遥感影像和面向对象技术的荒漠草原植被分类. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 1-14. | |
| [17] | Zhou X C, Zheng L, Huang H Y. Classification of forest stand based on multi-feature optimization of UAV visible light remote sensing. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2021, 57(6): 24-36. |
| 周小成, 郑磊, 黄洪宇. 基于多特征优选的无人机可见光遥感林分类型分类. 林业科学, 2021, 57(6): 24-36. | |
| [18] | Wang J L. Research on species diversity and integrated control technology of poisonous weeds in Xinjiang grazing grassland. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2020. |
| 王军亮. 新疆放牧草地毒害草种属多样性与综合防控措施研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2020. | |
| [19] | Chen N, Zhang Y J, Zhu J T, et al. Nonlinear responses of productivity and diversity of alpine meadow communities to degradation. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2018, 42(1): 50-65. |
| 陈宁, 张扬建, 朱军涛, 等. 高寒草甸退化过程中群落生产力和物种多样性的非线性响应机制研究. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(1): 50-65. | |
| [20] | Tuo W H, Liu Z H, Zhang R L, et al. Research progress on the causes and restoration of degraded grassland of black soil land in Qinghai Province. Qinghai Prataculture, 2024, 33(4): 43-49. |
| 妥万花, 刘泽华, 张润琳, 等. 青海省黑土滩退化草地的成因及恢复治理研究进展. 青海草业, 2024, 33(4): 43-49. | |
| [21] | Ren H, Zhao C Z, An L J. Spatial point patterns of Stellera chamaejasme and Stipa krylovii populations in degraded grassland of noxious and miscellaneous types based on Ripley’s K(r) function. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2015, 29(1): 59-64. |
| 任珩, 赵成章, 安丽涓. 基于Ripley的K(r)函数的"毒杂草"型退化草地狼毒与西北针茅种群空间分布格局. 干旱区资源与环境, 2015, 29(1): 59-64. | |
| [22] | Ren H, Zhao C Z, An L J. Niche characteristics of ‘noxious and miscellaneous grass type’ degraded grassland on northern slope of Qilian Mountains, China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2013, 32(10): 2711-2715. |
| 任珩, 赵成章, 安丽涓. 祁连山北坡“毒杂草”型退化草地群落生态位特征. 生态学杂志, 2013, 32(10): 2711-2715. | |
| [23] | Deng T T, Li C B, Sun H S, et al. Degradation and vegetation characteristics of Kovresia tibeica swamp meadow in the Sanjiangyuan area. Grassland and Turf, 2024, 44(6): 199-207. |
| 邓彤彤, 李长斌, 孙海松, 等. 青藏高原三江源地区藏嵩草沼泽化草地退化与植被特征的变化. 草原与草坪, 2024, 44(6): 199-207. | |
| [24] | Zhao C Z, Fan S Y, Yin C Q, et al. Study on vegetation community’s structure of degraded grassland of noxious and miscellaneous grass type. Journal of Desert Research, 2004, 24(4): 129-134. |
| 赵成章, 樊胜岳, 殷翠琴, 等. 毒杂草型退化草地植被群落特征的研究. 中国沙漠, 2004, 24(4): 129-134. | |
| [25] | Huang B, Wang Y, Deng X B, et al. Study on the effects of different degradation types on plant diversity and interspecific relationship in alpine grassland: a case study in Lixian County. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 2024, 45(5): 85-91. |
| 黄波, 王悦, 邓小兵, 等. 高寒草地不同退化类型对植物多样性与种间关系的影响研究——以理县为例. 四川林业科技, 2024, 45(5): 85-91. | |
| [26] | Cheng C F. Causes and countermeasures of grassland degradation of Altai mountains. Protection Forest Science and Technology, 2022(2): 57-59. |
| 程传飞. 阿尔泰山草地退化原因及治理对策. 防护林科技, 2022(2): 57-59. | |
| [27] | Sun X F, Tang H J, Yang H W, et al. The causes of grassland degradation and countermeasures in China. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 52(9): 39-44, 50. |
| 孙小富, 唐华江, 杨红文, 等. 我国草地退化原因及治理对策. 安徽农业科学, 2024, 52(9): 39-44, 50. | |
| [28] | Li M M, Wu B F, Yan C Z, et al. Estimation of vegetation fraction in the Upper Basin of Miyun Reservoir by remote sensing. Resources Science, 2004, 26(4): 153-159. |
| 李苗苗, 吴炳方, 颜长珍, 等. 密云水库上游植被覆盖度的遥感估算. 资源科学, 2004, 26(4): 153-159. | |
| [29] | Pang G W, Yang Q K, Wang C M. et al. Influence of parameter determination methods of the pixel dichotomy model on the estimation accuracy of fractional vegetation cover by GF-1 PMS data. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2019, 35(4): 27-33. |
| 庞国伟, 杨勤科, 王春梅, 等. 像元二分模型参数确定方法对高分一号PMS数据估算植被覆盖度精度的影响. 地理与地理信息科学, 2019, 35(4): 27-33. | |
| [30] | Yang J Y, Li X G, Yan K, et al. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics of grassland vegetation coverage in Hejing of Xinjiang based on remote sensing and Dimidiate pixel model. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2017, 32(1): 210-217. |
| 杨静雅, 李新国, 闫凯, 等. 基于遥感与像元二分模型的新疆和静县草地植被覆盖度时空变化特征研究. 西北林学院学报, 2017, 32(1): 210-217. | |
| [31] | Liu X B. Experimental study on estimation of grassland coverage by the pixel dichotomy model using remotely sensed data. Huhhot: Inner Mongolia Normal University, 2020. |
| 刘晓波. 基于像元二分模型的草地覆盖度遥感估算实验研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古师范大学, 2020. | |
| [32] | Wang J Q, Li J F, Wang Z Y, et al. Analysis of vegetation coverage change in typical oasis area in recent 20 years based on Dimidiate Pixel model. Water Saving Irrigation, 2019(1): 96-101. |
| 王金强, 李俊峰, 王昭阳, 等. 基于像元二分模型的典型绿洲区近20年植被覆盖变化及分析. 节水灌溉, 2019(1): 96-101. |
| [1] | 冉健民, 宋小艳, 王丹, 王长庭. 退化高寒草甸土壤有机碳组分变化与增汇潜力研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 38-52. |
| [2] | 佘洁, 沈爱红, 石云, 赵娜, 张风红, 何洪源, 吴涛, 李红霞, 马益婷, 朱晓雯. 基于无人机遥感影像和面向对象技术的荒漠草原植被分类[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 1-14. |
| [3] | 马源, 王晓丽, 马玉寿, 张德罡. 高寒草甸退化程度对优势物种根际土壤真菌群落和生态网络的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 125-137. |
| [4] | 韩枫, 张志涛, 张鑫, 王建浩, 王浩. 美国公共牧草地法治管理进程的经验借鉴与若干启示[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 220-232. |
| [5] | 李成一, 李希来, 杨元武, 李宏林, 梁德飞. 氮添加对不同坡度退化高寒草甸土壤细菌多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 161-170. |
| [6] | 王学霞, 董世魁, 高清竹, 张勇, 胡国铮, 罗文蓉. 青藏高原退化高寒草地土壤氮矿化特征以及影响因素研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(6): 1-9. |
| [7] | 李亚娟, 刘静, 徐长林, 曹文侠. 不同退化程度对高寒草甸土壤无机氮及脲酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 45-53. |
| [8] | 刘昌义, 胡夏嵩, 窦增宁, 李希来, 徐志闻. 黄河源区高寒草地植被根-土复合体抗剪强度试验及退化程度阈值确定[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(9): 14-26. |
| [9] | 曹旭娟, 干珠扎布, 梁艳, 高清竹, 张勇, 李玉娥, 万运帆, 旦久罗布. 基于NDVI的藏北地区草地退化时空分布特征分析[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 1-8. |
| [10] | 张永超, 袁晓波, 牛得草, 吴淑娟, 张典业, 宗文杰, 傅华. 玛曲高寒草甸高原鼠兔种群数量对植被调控措施的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2): 87-94. |
| [11] | 郭承录,李宗礼,陈年来,刘蕾. 石羊河流域下游民勤绿洲草地退化问题分析[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(6): 62-71. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||