

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 210-222.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025117
收稿日期:2025-04-07
修回日期:2025-06-25
出版日期:2026-03-20
发布日期:2026-01-19
通讯作者:
朱林
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: zhulinscience@126.com基金资助:
Gang ZHANG1,2( ), Xing XU3, Lin ZHU1,2(
), Xing XU3, Lin ZHU1,2( )
)
Received:2025-04-07
Revised:2025-06-25
Online:2026-03-20
Published:2026-01-19
Contact:
Lin ZHU
摘要:
抽穗期是影响作物产量形成和环境适应性的关键阶段,解析其分子调控机制对牧草种质资源创新和新品种培育具有重要意义。很多稗属植物是优良的耐盐碱牧草,然而目前稗属牧草抽穗期的分子调控机制尚不明确,制约了不同生态区适生品种的分子设计育种和盐碱地的可持续利用。为了系统解析稗草抽穗期的遗传调控网络,本研究以稗的基因组作为参考基因组,采用BSA-Seq(bulked segregant analysis sequencing)技术对湖南稷子和宁夏无芒稗及其杂交F2:3群体(共62份样本)进行分析。基于R 4.2.2,采用Index算法定位抽穗期相关QTL(quantitative trait locus),通过String数据库构建蛋白质互作网络筛选候选基因,并利用GO和KEGG数据库对候选基因进行功能注释。研究结果表明:共鉴定出11347个SNP和1992个Indel有效变异位点;定位到两个候选QTL:qHD-16-1(193.14 kb,包含17个基因)和qHD-6-1(11.05 kb,包含2个基因);筛选出EcRCS3、EcCYSK(错义突变)、EcP0710H01.9、EcAPG、EcCFAT、EcNBA1共6个关键候选基因。功能注释表明,这些基因主要通过调控硫代谢、半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸等代谢途径影响开花基因表达或直接影响花芽分化,从而调控稗草的抽穗期。本研究为稗草分子标记辅助育种提供了重要的基因资源和潜在的分子靶点,并为盐碱地适生牧草品种的精准选育奠定了理论基础,具有重要的科学价值和应用前景。
张刚, 许兴, 朱林. 基于BSA技术的稗属牧草抽穗期QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(3): 210-222.
Gang ZHANG, Xing XU, Lin ZHU. QTL mapping and analysis candidate genes for heading stage in Echinochloa based on bulked segregant analysis[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(3): 210-222.
项目 Item | 亲本均值Parental mean (d) | F2:3群体F2:3 population | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
湖南稷子 E. crusgalli var. frumentacea | 宁夏无芒稗 E. crusgalli var. mitis | 标准差 Standard deviation | 平均值Mean (d) | 变异范围 Range of variation (d) | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation (%) | 峰度 Kurtosis | 偏度 Skewness | |
| 抽穗期Heading stage | 109±9.35a | 96±10.80b | 19.17 | 94.00 | 66.00~130.00 | 20.39 | -1.20 | 0.00 |
表1 亲本和F2:3代群体抽穗期天数分布特征
Table 1 Distribution characteristics of the heading stage days of the F2:3 generation population and parental
项目 Item | 亲本均值Parental mean (d) | F2:3群体F2:3 population | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
湖南稷子 E. crusgalli var. frumentacea | 宁夏无芒稗 E. crusgalli var. mitis | 标准差 Standard deviation | 平均值Mean (d) | 变异范围 Range of variation (d) | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation (%) | 峰度 Kurtosis | 偏度 Skewness | |
| 抽穗期Heading stage | 109±9.35a | 96±10.80b | 19.17 | 94.00 | 66.00~130.00 | 20.39 | -1.20 | 0.00 |
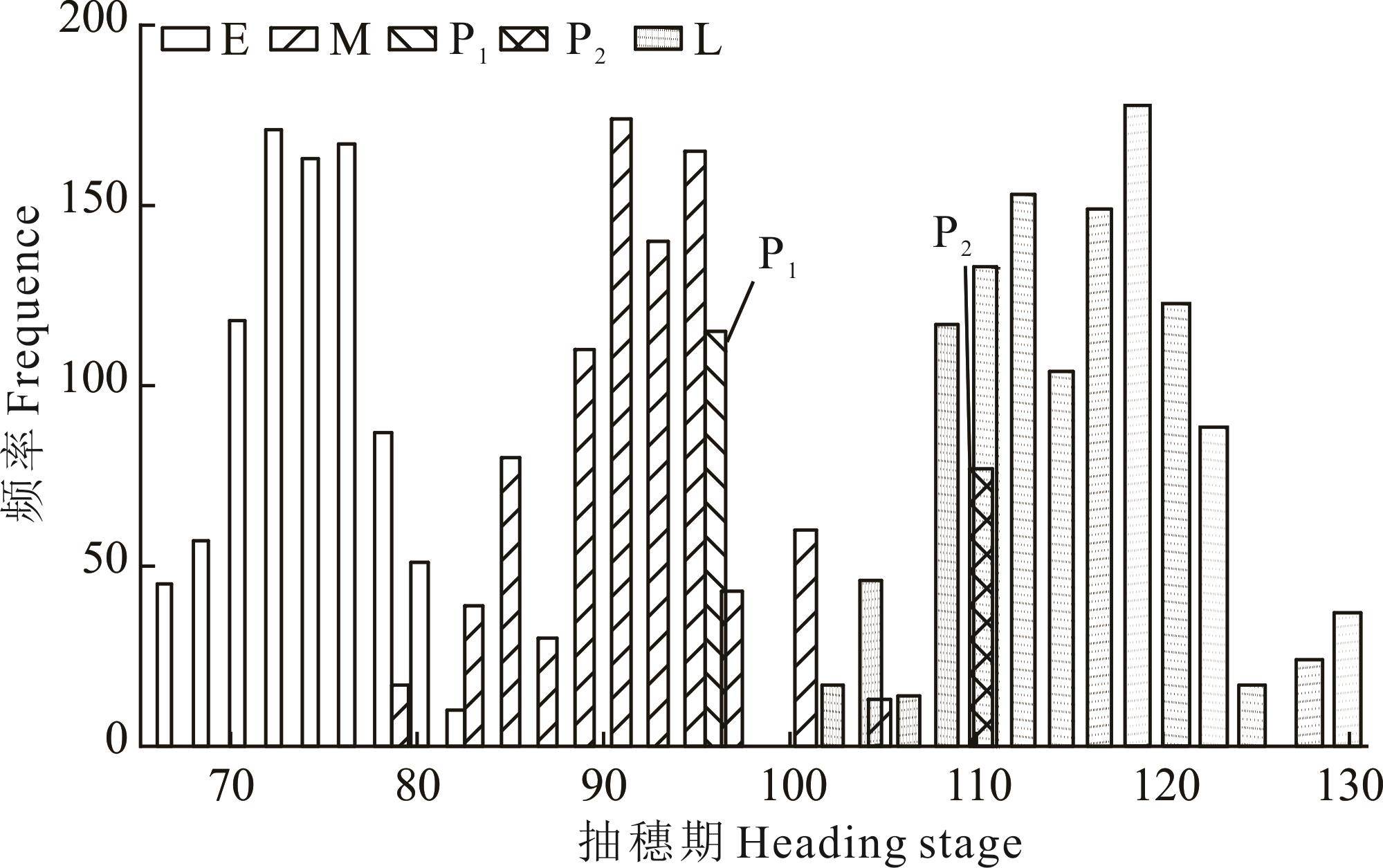
图1 亲本和F2:3群体抽穗期性状频率分布E: 早抽穗群体Early heading population; M: 中间型群体Intermediate population; L: 晚抽穗群体Late heading population; P2: 湖南稷子(母本)E. crusgalli var.frumentacea (Female); P1: 宁夏无芒稗(父本)E. crusgalli var. mitis (Male).
Fig.1 Frequency distribution of heading stage in parents and F2:3 population
样本名 Sample ID | 宁夏无芒稗 E. crusgalli var. mitis | 湖南稷子 E. crusgalli var.frumentacea | 早抽穗混合池 Early heading pool | 晚抽穗混合池 Late heading pool |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 原始序列数Raw reads | 110698444 | 97387918 | 293041906 | 296602604 |
| 原始碱基数Raw bases (bp) | 16715465044 | 14705575618 | 44249327806 | 44786993204 |
| 过滤序列数Clean reads | 108936494 | 95849704 | 287622304 | 291064822 |
| 过滤碱基数Clean bases (bp) | 16249584281 | 14308880560 | 42973291907 | 43460506570 |
| GC含量GC content (%) | 48.35 | 46.63 | 45.73 | 46.13 |
| Q30含量Q30 content (%) | 94.82 | 94.96 | 94.97 | 95.06 |
| 比对率Mapped ratio (%) | 99.72 | 99.75 | 98.97 | 99.48 |
| 优质比对率Proper ratio (%) | 96.38 | 96.61 | 96.07 | 96.60 |
| 插入片段长度Insert fregment length (bp) | 338 | 345 | 323 | 310 |
| 平均测序深度Average sequencing depth | 13.20 | 11.58 | 33.81 | 34.42 |
| 覆盖度(≥1×) Coverage (≥1×) (%) | 91.57 | 91.93 | 93.84 | 93.69 |
| 覆盖度(≥4×) Coverage (≥4×) (%) | 81.55 | 84.93 | 91.36 | 91.35 |
表2 原始测序和质控后测序数据与参考基因组比对结果统计分析
Table 2 Quality statistics of raw data and matching of quality control data with reference genome
样本名 Sample ID | 宁夏无芒稗 E. crusgalli var. mitis | 湖南稷子 E. crusgalli var.frumentacea | 早抽穗混合池 Early heading pool | 晚抽穗混合池 Late heading pool |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 原始序列数Raw reads | 110698444 | 97387918 | 293041906 | 296602604 |
| 原始碱基数Raw bases (bp) | 16715465044 | 14705575618 | 44249327806 | 44786993204 |
| 过滤序列数Clean reads | 108936494 | 95849704 | 287622304 | 291064822 |
| 过滤碱基数Clean bases (bp) | 16249584281 | 14308880560 | 42973291907 | 43460506570 |
| GC含量GC content (%) | 48.35 | 46.63 | 45.73 | 46.13 |
| Q30含量Q30 content (%) | 94.82 | 94.96 | 94.97 | 95.06 |
| 比对率Mapped ratio (%) | 99.72 | 99.75 | 98.97 | 99.48 |
| 优质比对率Proper ratio (%) | 96.38 | 96.61 | 96.07 | 96.60 |
| 插入片段长度Insert fregment length (bp) | 338 | 345 | 323 | 310 |
| 平均测序深度Average sequencing depth | 13.20 | 11.58 | 33.81 | 34.42 |
| 覆盖度(≥1×) Coverage (≥1×) (%) | 91.57 | 91.93 | 93.84 | 93.69 |
| 覆盖度(≥4×) Coverage (≥4×) (%) | 81.55 | 84.93 | 91.36 | 91.35 |
SNP变异位点信息 SNP variation sites information | 宁夏无芒稗 E. crusgalli var. mitis | 湖南稷子 E. crusgalli var.frumentacea | 早抽穗混合池Early heading pool | 晚抽穗混合池Late heading pool | Indel变异位点信息 Indel variation sites information | 宁夏无芒稗 E. crusgalli var. mitis | 湖南稷子 E. crusgalli var.frumentacea | 早抽穗混合池Early heading pool | 晚抽穗混合池 Late heading pool |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 起始密码子丢失Start lost | 538 | 521 | 550 | 557 | 起始密码子丢失Start lost | 176 | 177 | 198 | 188 |
| 终止密码子丢失Stop lost | 539 | 536 | 586 | 553 | 终止密码子丢失Stop lost | 167 | 165 | 184 | 188 |
| 终止密码子获得Stop gained | 2874 | 2934 | 3252 | 3030 | 终止密码子获得Stop gained | 454 | 452 | 528 | 509 |
| 非同义突变Nonsynonymous mutation | 118535 | 120467 | 129985 | 124244 | 基因区间Intragenic region | 411710 | 418151 | 469267 | 448800 |
| 同义突变Synonymous mutation | 67254 | 68338 | 73371 | 70561 | 移码突变Frameshift mutation | 16809 | 16500 | 18908 | 18208 |
| 基因区间Intragenic region | 2420168 | 2436130 | 2621923 | 2544620 | 非编码转录突变Non coding transcript mutation | 15 | 12 | 13 | 17 |
| 终止子编码突变Stop retained mutation | 104 | 111 | 118 | 113 | 外显子缺失突变Exon loss mutation | 5 | 4 | 6 | 3 |
| SNP和Sum SNP | 2610012 | 2629037 | 2829785 | 2743678 | Indel和Sum Indel | 429336 | 435461 | 489104 | 467913 |
| SNP总数Total SNP | 2882936 | 2919872 | 3139343 | 3039142 | Indel总数Total Indel | 511925 | 523408 | 582001 | 558165 |
表3 多态性位点注释统计
Table 3 Annotation of polymorphism sites
SNP变异位点信息 SNP variation sites information | 宁夏无芒稗 E. crusgalli var. mitis | 湖南稷子 E. crusgalli var.frumentacea | 早抽穗混合池Early heading pool | 晚抽穗混合池Late heading pool | Indel变异位点信息 Indel variation sites information | 宁夏无芒稗 E. crusgalli var. mitis | 湖南稷子 E. crusgalli var.frumentacea | 早抽穗混合池Early heading pool | 晚抽穗混合池 Late heading pool |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 起始密码子丢失Start lost | 538 | 521 | 550 | 557 | 起始密码子丢失Start lost | 176 | 177 | 198 | 188 |
| 终止密码子丢失Stop lost | 539 | 536 | 586 | 553 | 终止密码子丢失Stop lost | 167 | 165 | 184 | 188 |
| 终止密码子获得Stop gained | 2874 | 2934 | 3252 | 3030 | 终止密码子获得Stop gained | 454 | 452 | 528 | 509 |
| 非同义突变Nonsynonymous mutation | 118535 | 120467 | 129985 | 124244 | 基因区间Intragenic region | 411710 | 418151 | 469267 | 448800 |
| 同义突变Synonymous mutation | 67254 | 68338 | 73371 | 70561 | 移码突变Frameshift mutation | 16809 | 16500 | 18908 | 18208 |
| 基因区间Intragenic region | 2420168 | 2436130 | 2621923 | 2544620 | 非编码转录突变Non coding transcript mutation | 15 | 12 | 13 | 17 |
| 终止子编码突变Stop retained mutation | 104 | 111 | 118 | 113 | 外显子缺失突变Exon loss mutation | 5 | 4 | 6 | 3 |
| SNP和Sum SNP | 2610012 | 2629037 | 2829785 | 2743678 | Indel和Sum Indel | 429336 | 435461 | 489104 | 467913 |
| SNP总数Total SNP | 2882936 | 2919872 | 3139343 | 3039142 | Indel总数Total Indel | 511925 | 523408 | 582001 | 558165 |
| Loess拟合Loess fitting | 滑窗策略Sliding window strategy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 染色体Chromosome | 开始位置Start position | 结束位置End position | 染色体Chromosome | 开始位置Start position | 结束位置End position |
| 2 | 17062211 | 51531094 | 1 | 4108439 | 9491129 |
| 6 | 6601800 | 16813256 | 13 | 9003411 | 9044483 |
| 7 | 6840956 | 9180095 | 14 | 40414541 | 49041093 |
| 21 | 10182932 | 41322793 | 16 | 1612839 | 2819921 |
| 24 | 28707547 | 28722744 | 17 | 32032451 | 32989414 |
| 26 | 15686452 | 36334572 | 26 | 15686452 | 36334572 |
| 4 | 5777936 | 5787128 | 6 | 16802203 | 16813256 |
| 7 | 3110078 | 8649515 | |||
| 8 | 19854393 | 24310847 | |||
| 2 | 17062211 | 51531094 | |||
| 4 | 5777936 | 5787128 | |||
表4 Indel-index 算法关联的区间
Table 4 Indel-index correlation interval
| Loess拟合Loess fitting | 滑窗策略Sliding window strategy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 染色体Chromosome | 开始位置Start position | 结束位置End position | 染色体Chromosome | 开始位置Start position | 结束位置End position |
| 2 | 17062211 | 51531094 | 1 | 4108439 | 9491129 |
| 6 | 6601800 | 16813256 | 13 | 9003411 | 9044483 |
| 7 | 6840956 | 9180095 | 14 | 40414541 | 49041093 |
| 21 | 10182932 | 41322793 | 16 | 1612839 | 2819921 |
| 24 | 28707547 | 28722744 | 17 | 32032451 | 32989414 |
| 26 | 15686452 | 36334572 | 26 | 15686452 | 36334572 |
| 4 | 5777936 | 5787128 | 6 | 16802203 | 16813256 |
| 7 | 3110078 | 8649515 | |||
| 8 | 19854393 | 24310847 | |||
| 2 | 17062211 | 51531094 | |||
| 4 | 5777936 | 5787128 | |||
染色体 Chromosome | 基因名 Gene name | 基因位置起始Start site of the gene | 基因位置结束End site of the gene | 功能 Function | 变异注释 Variant annotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | EcRCS3 | 2363209 | 2369975 | 半胱氨酸合酶Cysteine synthase | 内含子变异Intron_variant |
| 16 | EcCYSK | 2375433 | 2377934 | 半胱氨酸合酶Cysteine synthase | 非同义突变Nonsynonymous mutation |
| 16 | EcP0710H01.9 | 2372051 | 2374659 | 半胱氨酸合酶Cysteine synthase | 下游基因变异Downstream_gene_variant |
| 16 | EcAPG | 2320024 | 2321505 | GDSL酯酶/脂肪酶GDSL esterase/lipase | 基因区间Intergenic_region |
| 16 | EcCFAT | 2455168 | 2456550 | 松柏醇酰基转移酶Coniferyl alcohol acyltransferase | 下游基因变异Downstream_gene_variant |
| 16 | EcNBA1 | 2382266 | 2384322 | BRISC复合体BRISC complex | 下游基因变异/内含子变异Downstream_gene_varian/Intron_variant |
表5 候选基因功能分析
Table 5 Functional analysis of candidate genes
染色体 Chromosome | 基因名 Gene name | 基因位置起始Start site of the gene | 基因位置结束End site of the gene | 功能 Function | 变异注释 Variant annotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | EcRCS3 | 2363209 | 2369975 | 半胱氨酸合酶Cysteine synthase | 内含子变异Intron_variant |
| 16 | EcCYSK | 2375433 | 2377934 | 半胱氨酸合酶Cysteine synthase | 非同义突变Nonsynonymous mutation |
| 16 | EcP0710H01.9 | 2372051 | 2374659 | 半胱氨酸合酶Cysteine synthase | 下游基因变异Downstream_gene_variant |
| 16 | EcAPG | 2320024 | 2321505 | GDSL酯酶/脂肪酶GDSL esterase/lipase | 基因区间Intergenic_region |
| 16 | EcCFAT | 2455168 | 2456550 | 松柏醇酰基转移酶Coniferyl alcohol acyltransferase | 下游基因变异Downstream_gene_variant |
| 16 | EcNBA1 | 2382266 | 2384322 | BRISC复合体BRISC complex | 下游基因变异/内含子变异Downstream_gene_varian/Intron_variant |
| [1] | Bhatt D, Rasane P, Singh J, et al. Nutritional advantages of barnyard millet and opportunities for its processing as value-added foods. Journal of Food Science and Technology-Mysore, 2023, 60(11): 2748-2760. |
| [2] | Renganathan V G, Vanniarajan C, Karthikeyan A, et al. Barnyard millet for food and nutritional security: current status and future research direction. Frontiers in Genetics, 2020, 11: 500. |
| [3] | Wang Y L, Lin S, Zhao L Z, et al. The trial cultivation of Hunan millet in saline-alkali wasteland showed good results. Grass and Forage Journal, 1992(1): 22. |
| 王玉兰, 林森, 赵莱章, 等. 盐碱荒地试种湖南稷子情况良好. 草与畜杂志, 1992(1): 22. | |
| [4] | Wang F, Li S C, Kong F J, et al. Altered regulation of flowering expands growth ranges and maximizes yields in major crops. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 14: 1094411. |
| [5] | Kippes N, Debernardi J M, Vasquez-Gross H A, et al. Identification of the VERNALIZATION 4 gene reveals the origin of spring growth habit in ancient wheats from South Asia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(39): 5401-5410. |
| [6] | Wilhelm E P, Turner A S, Laurie D A. Photoperiod insensitive Ppd-A1a mutations in tetraploid wheat (Triticum durum Desf.). Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2009, 118(2): 285-294. |
| [7] | Beales J, Turner A, Griffiths S, et al. A pseudo-response regulator is misexpressed in the photoperiod insensitive Ppd-D1a mutant of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2007, 115(5): 721-733. |
| [8] | Yu X L, Li X, Yao X H, et al. Genetic mapping and candidate gene analysis of the major QTL cqHD2H-2 for early heading in barley (Hordeum vulare L.). Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2022, 48(10): 2463-2474. |
| 余鑫莲, 李新, 姚晓华, 等. 青稞早抽穗主效QTL cqHD2H-2的遗传定位及候选基因分析. 作物学报, 2022, 48(10): 2463-2474. | |
| [9] | Michelmore R W, Paran I, Kesseli R V. Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1991, 88(21): 9828-9832. |
| [10] | Zhang G, Zhu L, Nie H J, et al. Application and prospect of BSA method based on bibliometrics in crop breeding. Hereditas, 2024, 46(5): 360-372. |
| 张刚, 朱林, 聂豪杰, 等. 基于文献计量学BSA在作物育种领域的应用现状与展望. 遗传, 2024, 46(5): 360-372. | |
| [11] | Takagi H, Tamiru M, Abe A, et al. MutMap accelerates breeding of a salt-tolerant rice cultivar. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(5): 445-449. |
| [12] | Gao Y B, Yuan Y H, Zhang X Y, et al. Conuping BSA-Seq and RNA-Seq reveal the molecular pathway and genes associated with the plant height of foxtail millet (Setaria italica). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(19): 11824. |
| [13] | Zhao W G, Ta N, Wang H, et al. Analysis of significantly associated regions and candidate genes for dwarf stem trait in Brassica napus based on BSA-seq. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2024, 44(12): 1890-1899. |
| 赵卫国, 塔娜, 王灏, 等. 基于BSA-seq技术对甘蓝型油菜矮秆性状的显著关联区域和候选基因分析. 西北植物学报, 2024, 44(12): 1890-1899. | |
| [14] | Wu D Y, Shen E H, Jiang B W, et al. Genomic insights into the evolution of Echinochloa species as weed and orphan crop. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 689. |
| [15] | Wan L S, Geng B R, Shao S R, et al. A promising forage and food crop-Echinochloa frumentacea. Journal of Ningxia Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology, 1984(1): 37-38. |
| 万力生, 耿本仁, 邵生荣, 等. 一种很有前途的草料兼用作物——湖南稷子. 宁夏农业科技, 1984(1): 37-38. | |
| [16] | Wu S Q, Yang P, Fan Z J, et al. Study on Echinochloa crusgalli (L.) Beauv. var. mitis (Pursh) Peter. Pratacultural Science, 2002, 19(2): 33-36. |
| 吴素琴, 杨平, 樊振军, 等. 宁夏无芒稗的研究. 草业科学, 2002, 19(2): 33-36. | |
| [17] | Li D X, Yang J, Sun K, et al. Mapping new rice heading date QTLs based on high-density genetic map. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(8): 43-49. |
| 李冬秀, 杨靖, 孙凯, 等. 基于高密度遗传图谱定位新的水稻抽穗期QTLs. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 48(8): 43-49. | |
| [18] | Doyle J J T, Doyle J L. Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus (san Francisco, California.), 1990, 12(1): 13-15. |
| [19] | Chen S F, Zhou Y Q, Chen Y R, et al. Fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, 2018, 34(17): 884-890. |
| [20] | Jung Y, Han D S. BWA-MEME: BWA-MEM emulated with a machine learning approach. Bioinformatics, 2022, 38(9): 2404-2413. |
| [21] | McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, et al. The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Research, 2010, 20(9): 1297-1303. |
| [22] | Cingolani P, Platts A, Wang L L, et al. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly (Austin), 2012, 6(2): 80-92. |
| [23] | Takagi H, Abe A, Yoshida K, et al. QTL-seq: rapid mapping of quantitative trait loci in rice by whole genome resequencing of DNA from two bulked populations. The Plant Journal: For Cell and Molecular Biology, 2013, 74(1): 174-183. |
| [24] | Li Z Q, Xu Y H. Bulk segregation analysis in the NGS era: a review of its teenage years. The Plant Journal: For Cell and Molecular Biology, 2022, 109(6): 1355-1374. |
| [25] | Jaiswal V, Gupta S, Gahlaut V, et al. Genome-wide association study of major agronomic traits in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.) using ddRAD sequencing. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 5020. |
| [26] | Sobieszczuk-Nowicka E, Arasimowicz-Jelonek M, Tanwar U K, et al. Plant homocysteine, a methionine precursor and plant’s hallmark of metabolic disorders. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 1044944. |
| [27] | Wang H, Niu Q W, Wu H W, et al. Analysis of non-coding transcriptome in rice and maize uncovers roles of conserved lncRNAs associated with agriculture traits. Plant Journal, 2015, 84(2): 404-416. |
| [28] | Huang X Z, Chen S D, Li W P, et al. ROS regulated reversible protein phase separation synchronizes plant flowering. Nature Chemical Biology, 2021, 17(5): 549-557. |
| [29] | Kopriva S, Mugford S G, Matthewman C, et al. Plant sulfate assimilation genes: redundancy versus specialization. Plant Cell Reports, 2009, 28(12): 1769-1780. |
| [30] | Kopriva S. Regulation of sulfate assimilation in Arabidopsis and beyond. Annals of Botany, 2006, 97(4): 479-495. |
| [31] | Hage H, Rosso M N, Tarrago L. Distribution of methionine sulfoxide reductases in fungi and conservation of the free-methionine-R-sulfoxide reductase in multicellular eukaryotes. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2021, 169: 187-215. |
| [32] | Ravanel S, Gakière B, Job D, et al. The specific features of methionine biosynthesis and metabolism in plants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1998, 95(13): 7805-7812. |
| [33] | Chen D D, Shao Q S, Yin L H, et al. Polyamine function in plants: metabolism, regulation on development, and roles in abiotic stress responses. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 9: 1945. |
| [34] | Zhao H, Yin C C, Ma B, et al. Ethylene signaling in rice and Arabidopsis: new regulators and mechanisms. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(1): 102-125. |
| [35] | Iqbal N, Khan N A, Ferrante A, et al. Ethylene role in plant growth, development and senescence: interaction with other phytohormones. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 475. |
| [36] | Xu M T, Li X X, Xie W, et al. Correction to: ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3/EIN3-LIKE1 modulate FLOWERING LOCUS C expression via histone demethylase interaction. Plant Physiology, 2024, 196(2): 1712. |
| [37] | Chen Y L, Zhang L P, Zhang H Y, et al. ERF1 delays flowering through direct inhibition of FLOWERING LOCUS T expression in Arabidopsis. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(10): 1712-1723. |
| [38] | Sun Y R, McCorvie T J, Yates L A, et al. Structural basis of homologous recombination. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2020, 77(1): 3-18. |
| [39] | Liu S J, Hua Y, Wang J N, et al. RNA polymerase III is required for the repair of DNA double-strand breaks by homologous recombination. Cell, 2021, 184(5): 1314. |
| [40] | Li F M, Xie J Y, Zhu X Y, et al. Genetic basis underlying correlations among growth duration and yield traits revealed by GWAS in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 650. |
| [1] | 王延翠, 于伟丽, 王树楷, 葛春霞, 张国斌, 陈翠霞. 芒属植物分蘖数性状的QTL定位[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 52-59. |
| [2] | 何飞, 张帆, 张铁军, 康俊梅, 龙瑞才, 杨青川, 马春晖. 紫花苜蓿开花性状的遗传特性分析与QTL定位[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 112-120. |
| [3] | 唐露, 黄琳凯, 赵欣欣, 张旭, 聂刚, 张新全, 马啸. 四倍体鸭茅产量及其构成因素的QTL定位[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(11): 67-76. |
| [4] | 崔阔澍, 于肖夏, 于卓, 姜超, 石悦. 四倍体彩色马铃薯花青素含量及产量性状的QTL定位[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(5): 116-124. |
| [5] | 姬奇武,韩汝旦,董宽虎,马雪豪. 山西不同居群白羊草的营养成分及瘤胃降解规律[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(9): 53-62. |
| [6] | 胡亮亮, 叶亚琼, 吕婷婷, 栗孟飞, 刘媛, 常磊, 柴守玺, 杨德龙. 不同水分环境下小麦粒重QTL定位及遗传分析[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(8): 118-129. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||