

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 195-209.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2025132
收稿日期:2025-04-17
修回日期:2025-06-16
出版日期:2026-03-20
发布日期:2026-01-19
通讯作者:
宋敏丽
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: smlcc@126.com基金资助:
Peng-yu TIAN1( ), Yi-ru ZHANG1, Xu-kai LI2, Min-li SONG1(
), Yi-ru ZHANG1, Xu-kai LI2, Min-li SONG1( )
)
Received:2025-04-17
Revised:2025-06-16
Online:2026-03-20
Published:2026-01-19
Contact:
Min-li SONG
摘要:
CCoAOMT蛋白家族属于S-腺苷-L-甲硫氨酸(SAM)依赖性甲基转移酶,在植物木质素合成和生长发育中具有关键作用,但在谷子中的功能尚未被系统研究。本研究以谷子基因组数据为基础,鉴定SiCCoAOMT家族成员,并进行生物信息学分析及非生物胁迫响应验证。结果表明:在谷子SiCCoAOMT基因家族中鉴定出5个SiCCoAOMT基因:Si2g25370、Si4g06670、Si6g06400、Si6g19790和Si6g19800,定位于第2、4和6号染色体,编码蛋白的理化性质差异明显。通过系统发育分析,将谷子SiCCoAOMT基因与拟南芥、水稻和狗尾草的同源基因划分为两个亚族,且同一亚族内的成员保守序列和基因结构高度相似。CCoAOMT基因家族成员均包含相同的蛋白保守结构域(motif 1、motif 2、motif 4、motif 5和motif 6),同一亚族的成员具有相似的motif。顺式作用元件预测中,SiCCoAOMT2和SiCCoAOMT4中含有大量关于光响应(Sp1)、植物激素(ABRE、CGTCA-motif和TGACG-motif)和非生物胁迫(ARE)的作用元件。谷子与水稻、狗尾草共线性基因对分析发现,谷子和狗尾草CCoAOMT受到中性选择的同时,还存在纯化选择;谷子与水稻CCoAOMT之间存在正选择效应。加权基因共表达网络分析(WGCNA)发现,SiCCoAOMT2和SiCCoAOMT4被划分在yellowgreen模块中。对‘晋谷21’幼苗进行干旱和低温胁迫处理,利用qRT-PCR对SiCCoAOMT家族基因进行表达模式分析发现,SiCCoAOMT2和SiCCoAOMT4表达量明显上调。基于360份谷子和38份狗尾草种质资源的单核苷酸多态性(SNPs)和插入/缺失变异(InDels)基因型信息分析发现,SiCCoAOMT5有利于谷子籽粒的生长发育,对谷子的产量提高和抵抗胁迫有一定的作用。综上所述,本研究对谷子SiCCoAOMT基因家族进行了系统地分析,鉴定出SiCCoAOMT2和SiCCoAOMT4是谷子响应干旱及寒冷胁迫的关键基因,为谷子抗逆境胁迫和生长调控机制的深入研究提供了一定的依据。
田鹏宇, 张义茹, 李旭凯, 宋敏丽. 谷子SiCCoAOMT基因家族的鉴定及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(3): 195-209.
Peng-yu TIAN, Yi-ru ZHANG, Xu-kai LI, Min-li SONG. Identification and expression analysis of the SiCCoAOMT gene family in Setaria italica[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2026, 35(3): 195-209.
| 基因名称Gene name | 上游引物Forward primer (5'-3') | 下游引物Reverse primer (3'-5') |
|---|---|---|
| SiActin7 | AGGGCTGTCTTCCCGAGTAT | ATGGCTCACACCATCACCAG |
| SiCCoAOMT1 | TGATCCATCCGAATCGCCAG | CACCGAGCACGGAGATTGAT |
| SiCCoAOMT2 | TCGGGTTCGACTTGGAATGG | TCCACAGCGTGTTGTCGTAG |
| SiCCoAOMT3 | GGCAGCCCTGCTTCACATTA | TGAATCGCAATGCGGCAATC |
| SiCCoAOMT4 | GCGAGTACTACGAGATCGGC | GACGTCCAGACGGAATGGAA |
| SiCCoAOMT5 | GGTGCGCCAAGCCTAAACTG | GGCGTTCAAGGGACGGTACT |
表1 qRT-PCR 引物序列
Table 1 qRT-PCR primer sequences
| 基因名称Gene name | 上游引物Forward primer (5'-3') | 下游引物Reverse primer (3'-5') |
|---|---|---|
| SiActin7 | AGGGCTGTCTTCCCGAGTAT | ATGGCTCACACCATCACCAG |
| SiCCoAOMT1 | TGATCCATCCGAATCGCCAG | CACCGAGCACGGAGATTGAT |
| SiCCoAOMT2 | TCGGGTTCGACTTGGAATGG | TCCACAGCGTGTTGTCGTAG |
| SiCCoAOMT3 | GGCAGCCCTGCTTCACATTA | TGAATCGCAATGCGGCAATC |
| SiCCoAOMT4 | GCGAGTACTACGAGATCGGC | GACGTCCAGACGGAATGGAA |
| SiCCoAOMT5 | GGTGCGCCAAGCCTAAACTG | GGCGTTCAAGGGACGGTACT |
基因名称 Gene name | 基因号 Gene ID | 蛋白长度 Protein length (aa) | 分子量 Molecular weight (Da) | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 不稳定指数 Instability index | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiCCoAOMT1 | Si2g25370 | 242 | 25798.61 | 5.04 | 33.80 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| SiCCoAOMT2 | Si4g06670 | 265 | 29517.68 | 5.24 | 26.54 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| SiCCoAOMT3 | Si6g06400 | 295 | 32293.69 | 9.01 | 50.34 | 叶绿体Chloroplast, 线粒体Mitochondrion |
| SiCCoAOMT4 | Si6g19790 | 202 | 22591.96 | 5.26 | 26.21 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| SiCCoAOMT5 | Si6g19800 | 544 | 58335.97 | 4.93 | 48.70 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic, 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| AtCCoAOMT1 | AT1G24735 | 291 | 33157.44 | 6.89 | 31.20 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| AtCCoAOMT2 | AT1G67980 | 232 | 26114.06 | 5.16 | 20.45 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| AtCCoAOMT3 | AT1G67990 | 233 | 26350.49 | 5.25 | 19.47 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| AtCCoAOMT4 | AT3G61990 | 290 | 32168.92 | 5.23 | 41.90 | 叶绿体Chloroplast, 细胞核Nucleus |
| AtCCoAOMT5 | AT3G62000 | 352 | 39671.76 | 9.05 | 38.35 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| AtCCoAOMT6 | AT4G26220 | 232 | 25945.79 | 5.37 | 36.58 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| AtCCoAOMT7 | AT4G34050 | 286 | 32473.04 | 5.81 | 39.11 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| OsCCoAOMT1 | LOC_Os06g06980 | 260 | 28847.77 | 5.21 | 27.11 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| OsCCoAOMT2 | LOC_Os08g05790 | 317 | 34307.55 | 9.08 | 36.74 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| OsCCoAOMT3 | LOC_Os08g38900 | 252 | 27771.74 | 5.11 | 29.60 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| OsCCoAOMT4 | LOC_Os08g38910 | 292 | 31897.36 | 5.34 | 43.26 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| OsCCoAOMT5 | LOC_Os08g38920 | 234 | 25883.49 | 5.57 | 29.56 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic, 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| OsCCoAOMT6 | LOC_Os09g30360 | 258 | 27132.08 | 5.09 | 34.32 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic, 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| SevirCCoAOMT1 | Sevir.2G259200 | 242 | 25798.61 | 5.04 | 33.80 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| SevirCCoAOMT2 | Sevir.4G059400 | 265 | 29544.71 | 5.24 | 25.82 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| SevirCCoAOMT3 | Sevir.6G056900 | 297 | 32568.99 | 9.01 | 49.82 | 叶绿体Chloroplast, 线粒体Mitochondrion |
| SevirCCoAOMT4 | Sevir.6G204900 | 246 | 27324.29 | 5.09 | 31.64 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| SevirCCoAOMT5 | Sevir.6G205000 | 245 | 26808.57 | 5.17 | 29.79 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| SevirCCoAOMT6 | Sevir.6G205100 | 309 | 33724.22 | 6.27 | 47.54 | 叶绿体Chloroplast, 线粒体Mitochondrion |
表2 4种植物CCoAOMT基因家族编码蛋白理化性质
Table 2 Physicochemical properties of CCoAOMT family proteins encoded by the genes of four plant species
基因名称 Gene name | 基因号 Gene ID | 蛋白长度 Protein length (aa) | 分子量 Molecular weight (Da) | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 不稳定指数 Instability index | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiCCoAOMT1 | Si2g25370 | 242 | 25798.61 | 5.04 | 33.80 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| SiCCoAOMT2 | Si4g06670 | 265 | 29517.68 | 5.24 | 26.54 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| SiCCoAOMT3 | Si6g06400 | 295 | 32293.69 | 9.01 | 50.34 | 叶绿体Chloroplast, 线粒体Mitochondrion |
| SiCCoAOMT4 | Si6g19790 | 202 | 22591.96 | 5.26 | 26.21 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| SiCCoAOMT5 | Si6g19800 | 544 | 58335.97 | 4.93 | 48.70 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic, 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| AtCCoAOMT1 | AT1G24735 | 291 | 33157.44 | 6.89 | 31.20 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| AtCCoAOMT2 | AT1G67980 | 232 | 26114.06 | 5.16 | 20.45 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| AtCCoAOMT3 | AT1G67990 | 233 | 26350.49 | 5.25 | 19.47 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| AtCCoAOMT4 | AT3G61990 | 290 | 32168.92 | 5.23 | 41.90 | 叶绿体Chloroplast, 细胞核Nucleus |
| AtCCoAOMT5 | AT3G62000 | 352 | 39671.76 | 9.05 | 38.35 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| AtCCoAOMT6 | AT4G26220 | 232 | 25945.79 | 5.37 | 36.58 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| AtCCoAOMT7 | AT4G34050 | 286 | 32473.04 | 5.81 | 39.11 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| OsCCoAOMT1 | LOC_Os06g06980 | 260 | 28847.77 | 5.21 | 27.11 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| OsCCoAOMT2 | LOC_Os08g05790 | 317 | 34307.55 | 9.08 | 36.74 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| OsCCoAOMT3 | LOC_Os08g38900 | 252 | 27771.74 | 5.11 | 29.60 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| OsCCoAOMT4 | LOC_Os08g38910 | 292 | 31897.36 | 5.34 | 43.26 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| OsCCoAOMT5 | LOC_Os08g38920 | 234 | 25883.49 | 5.57 | 29.56 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic, 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| OsCCoAOMT6 | LOC_Os09g30360 | 258 | 27132.08 | 5.09 | 34.32 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic, 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| SevirCCoAOMT1 | Sevir.2G259200 | 242 | 25798.61 | 5.04 | 33.80 | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| SevirCCoAOMT2 | Sevir.4G059400 | 265 | 29544.71 | 5.24 | 25.82 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| SevirCCoAOMT3 | Sevir.6G056900 | 297 | 32568.99 | 9.01 | 49.82 | 叶绿体Chloroplast, 线粒体Mitochondrion |
| SevirCCoAOMT4 | Sevir.6G204900 | 246 | 27324.29 | 5.09 | 31.64 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| SevirCCoAOMT5 | Sevir.6G205000 | 245 | 26808.57 | 5.17 | 29.79 | 细胞质Cytoplasmic |
| SevirCCoAOMT6 | Sevir.6G205100 | 309 | 33724.22 | 6.27 | 47.54 | 叶绿体Chloroplast, 线粒体Mitochondrion |
同源基因 Homologous gene | 同义替 换率 (Ks ) | 非同义替换率 (Ka ) | 非同义替换/同义替换 (Ka/Ks ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiCCoAOMT1-LOC_Os08g38900 | 0.3068 | 0.3415 | 1.113103 |
| SiCCoAOMT1-LOC_Os09g30360 | 0.0515 | 0.1322 | 2.566990 |
| SiCCoAOMT1-Sevir.2G259200 | 1.3027 | 1.3657 | 1.048361 |
| SiCCoAOMT1-Sevir.6G204900 | 1.4866 | 1.6951 | 1.140253 |
| SiCCoAOMT2-LOC_Os06g06980 | 0.0585 | 0.1486 | 2.540171 |
| SiCCoAOMT2-Sevir.4G059400 | 1.3714 | 1.3570 | 0.989500 |
| SiCCoAOMT3-LOC_Os08g05790 | 0.1405 | 0.1639 | 1.166548 |
| SiCCoAOMT3-Sevir.6G056900 | 2.1684 | 1.5731 | 0.725466 |
| SiCCoAOMT4-LOC_Os08g38900 | 0.1196 | 0.2554 | 2.135452 |
| SiCCoAOMT4-LOC_Os09g30360 | 0.2908 | 0.3400 | 1.169188 |
| SiCCoAOMT4-Sevir.2G259200 | 1.1080 | 1.2859 | 1.160560 |
| SiCCoAOMT4-Sevir.6G204900 | 1.7213 | 1.6205 | 0.941440 |
表3 谷子、水稻、狗尾草CCoAOMT共线性基因对Ka/Ks 值
Table 3 Ka/Ks values of syntenic gene pairs for CCoAOMT in millet, rice, and foxtail millet calculated
同源基因 Homologous gene | 同义替 换率 (Ks ) | 非同义替换率 (Ka ) | 非同义替换/同义替换 (Ka/Ks ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiCCoAOMT1-LOC_Os08g38900 | 0.3068 | 0.3415 | 1.113103 |
| SiCCoAOMT1-LOC_Os09g30360 | 0.0515 | 0.1322 | 2.566990 |
| SiCCoAOMT1-Sevir.2G259200 | 1.3027 | 1.3657 | 1.048361 |
| SiCCoAOMT1-Sevir.6G204900 | 1.4866 | 1.6951 | 1.140253 |
| SiCCoAOMT2-LOC_Os06g06980 | 0.0585 | 0.1486 | 2.540171 |
| SiCCoAOMT2-Sevir.4G059400 | 1.3714 | 1.3570 | 0.989500 |
| SiCCoAOMT3-LOC_Os08g05790 | 0.1405 | 0.1639 | 1.166548 |
| SiCCoAOMT3-Sevir.6G056900 | 2.1684 | 1.5731 | 0.725466 |
| SiCCoAOMT4-LOC_Os08g38900 | 0.1196 | 0.2554 | 2.135452 |
| SiCCoAOMT4-LOC_Os09g30360 | 0.2908 | 0.3400 | 1.169188 |
| SiCCoAOMT4-Sevir.2G259200 | 1.1080 | 1.2859 | 1.160560 |
| SiCCoAOMT4-Sevir.6G204900 | 1.7213 | 1.6205 | 0.941440 |
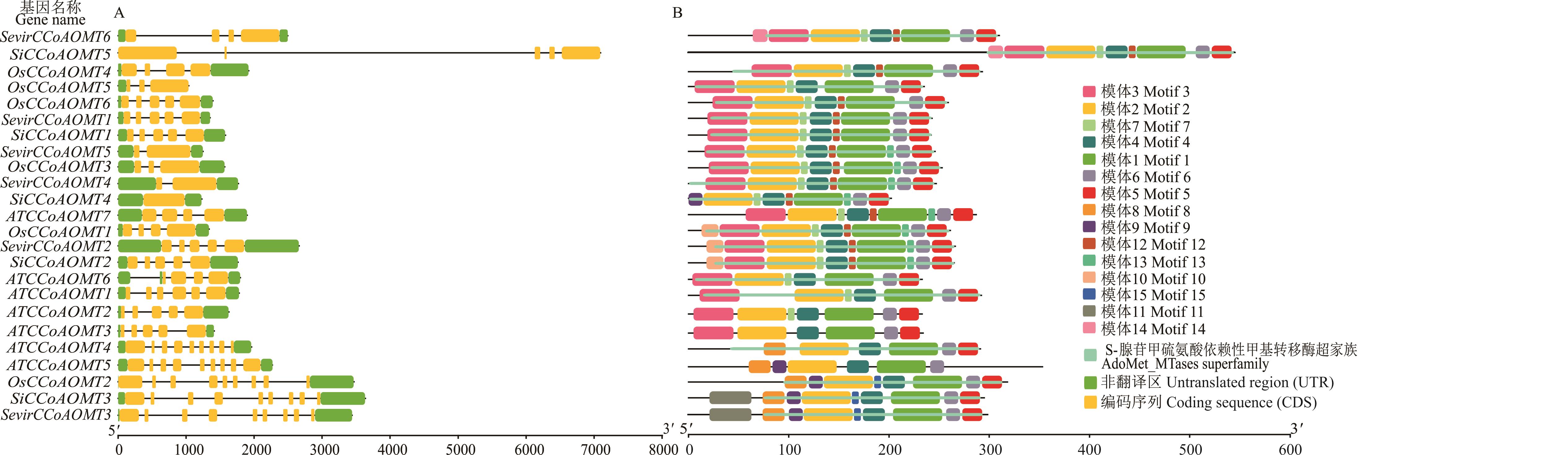
图3 谷子、拟南芥、水稻和狗尾草CCoAOMT家族基因结构A: 拟南芥、水稻、狗尾草、谷子CCoAOMT家族基因结构Gene structures of the CCoAOMT family in arabidopsis, rice, foxtail millet, and millet; B: 拟南芥、水稻、狗尾草、谷子CCoAOMT家族基因保守序列及结构域Conserved motifs and domains of the CCoAOMT family genes across arabidopsis, rice, foxtail millet, and millet.
Fig.3 Structural of the CCoAOMT family genes in millet, arabidopsis, rice, and foxtail millet

图4 谷子、拟南芥、水稻和狗尾草CCoAOMT家族启动子顺式作用元件分析ACE: 光响应元件Cis-acting element involved in light responsiveness; Box 4: 保守光响应模块Part of a conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness; G-box: 光响应G盒Cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness; GATA-motif: 光调控GATA基序Light-responsive GATA transcription factor binding site; Sp1: 光响应Sp1结合位点Light-responsive Sp1 transcription factor binding site; TCCC-motif: 光响应TCCC基序Cis-acting element involved in light responsiveness; A-box/I-box: 光调控A/I盒Light-responsive A-box/I-box binding factor recognition site; CAT-box: 光响应CAT盒Cis-acting regulatory element related to light response; ATCT-motif: 光响应ATCT基序Cis-acting element involved in light responsiveness; AE-box: 光调控AE盒Light-responsive AE-box binding factor recognition site; GT1-motif: 光响应GT1基序Light-responsive GT1 transcription factor binding site; RY-element: 种子特异性调控元件Seed-specific regulatory element; TCT-motif: 韧皮部调控元件Phloem-specific regulatory element; ABRE: 脱落酸响应相关作用元件Cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness; CGTCA-motif: 茉莉酸甲酯响应元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in methyl jasmonate-responsiveness; TGACG-motif: 茉莉酸甲酯响应元件Cis-acting regulatory element involved in MeJA-responsiveness; GARE-motif: 赤霉素响应元件Gibberellin-responsive element; TGA-element: 生长素响应元件Auxin-responsive element; AuxRR-core: 生长素响应核心元件Core sequence of auxin response element; TCA-element: 水杨酸响应元件Cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness; LTR: 低温响应元件Low-temperature responsive element; ARE: 厌氧响应元件Anaerobic induction responsive element; MBS: 干旱诱导MYB结合位点MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility; TC-rich repeats: 防御与胁迫响应元件Defense and stress responsive element. chs-CMA1a: 查耳酮合酶基因调控模块Cis-acting element involved in light responsiveness for chalcone synthase expression; GA-motif: 赤霉素响应元件Gibberellin-responsive element; MRE: 金属离子响应元件Metal ion responsive element; P-box: 赤霉素响应元件Gibberellin-responsive element; WUN-motif: 损伤响应元件Wound-responsive element.
Fig.4 Cis-acting element analysis of CCoAOMT family gene promoters in millet, arabidopsis, rice, and foxtail millet

图5 谷子CCoAOMT家族相关基因局部网络图A: yellowgreen模块SiCCoAOMT相关基因网络图Gene network diagram of millet CCoAOMT family genes in the yellowgreen module; B: yellow模块SiCCoAOMT相关基因网络图Gene network diagram of millet CCoAOMT family genes in the yellow module; C: blue模块SiCCoAOMT相关基因网络图Gene network diagram of millet CCoAOMT family genes in the blue module. 红色表示核心基因,橙色表示转录因子,绿色表示候选基因,蓝色表示其他连通度较高的共表达基因。Red nodes represent core genes, orange nodes represent transcription factors, green nodes represent candidate genes, and blue nodes indicate other highly co-expressed genes.
Fig.5 Local network diagrams of millet CCoAOMT family-related genes

图6 谷子SiCCoAOMT家族成员在不同组织和发育时期的表达图谱A: SiCCoAOMT家族成员在‘晋谷21’(JG21)和‘xiaomi’(XM)不同组织和发育时期的表达谱(JG21和XM分别包括23和6个组织时期)。The expression profiles of SiCCoAOMT gene family members in different tissues and developmental stages of ‘Jingu 21’ (JG21) and ‘xiaomi’ (XM) (JG21 and XM included 23 and 6 tissue stages, respectively). JG21.G3: 种子萌发3 d Seed germination 3-days; JG21.T1L2: 两叶一心期幼苗One-tip-two-leaf stage seedlings; JG21.Ah2: 抽穗2 d后2~3片顶叶2-3 top leaves after 2 days of heading; JG21.N: 灌浆期穗颈Panicle necks at filling stage; JG21.F: 灌浆期旗叶Flag leaves at filling stage; JG21.Fsh: 灌浆期旗叶叶鞘Flag leaf sheaths at filling stage; JG21.J2: 灌浆期S3的倒二节茎秆The second stems from the top of S3 at the filling stage; JG21.D4Y: 灌浆期倒四叶Leaf-top-fourth at filling stage; JG21.D4sh: 灌浆期倒四叶叶鞘Leaf-sheath-top-fourth at filling stage; JG21.R: 灌浆期根Roots at filling stage; JG21.P1: 初生分枝分化期小穗Spikelets at primary branch differentiation stage; JG21.P3: 第3级分枝分化期小穗Spikelets at the third branch differentiation stage; JG21.PS2: 灌浆期S2小穗Spikelets of S2 at filling stage; JG21.PS4: 灌浆期S4小穗Spikelets of S4 at filling stage; JG21.S1~JG21.S5: 灌浆期S1~S5籽粒Grains of S1-S5 at filling stage; JG21.AM30: 成熟30 d籽粒Grains of 30-days-after-maturation; JG21.AM60: 成熟60 d籽粒Seeds of 60-days-after-maturation; JG21.LV: S3期叶脉Leaf veins of S3; JG21.M: S3期叶肉Mesophyll of S3; XM.LW3: 3周的叶片3-week leaves; XM.L2: 抽穗期倒二叶The second leaves from the top at heading stage; XM.Ah2: 抽穗2 d后的穗Panicles 2 days after heading; XM.PP: 授粉期的穗Panicles at pollination stage; XM.P: 灌浆期穗Spikes at filling stage; XM.S: 灌浆期茎Stems at filling stage. B: SiCCoAOMT基因籽粒灌浆S3时期的qRT-PCR验证。qRT-PCR validation of SiCCoAOMT gene at S3 stage of grain filling.
Fig.6 Expression profiles of SiCCoAOMT family members in millet across different developmental stages and tissues
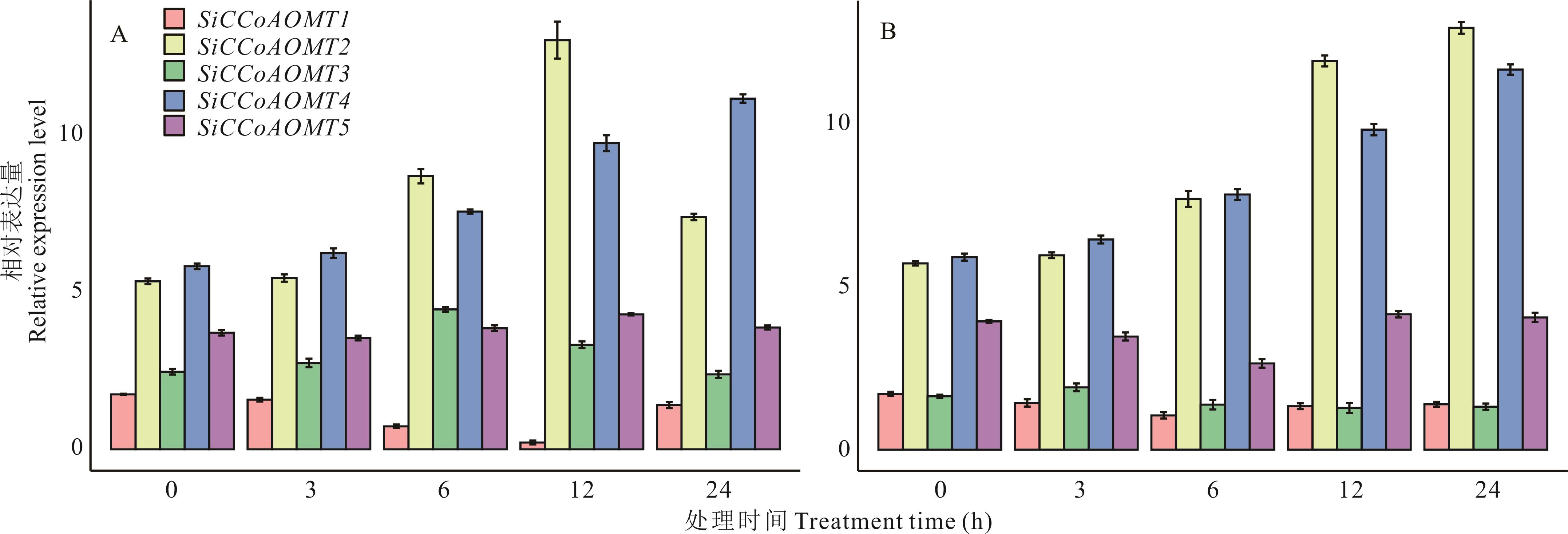
图7 非生物胁迫下谷子SiCCoAOMT家族成员的表达模式A: 干旱胁迫下SiCCoAOMT家族成员的表达模式Expression patterns of SiCCoAOMT gene family under drought stress; B: 低温胁迫下SiCCoAOMT家族成员的表达模式Expression patterns of SiCCoAOMT gene family under low temperature stress.
Fig.7 Expression patterns of SiCCoAOMT gene family in response to abiotic stress
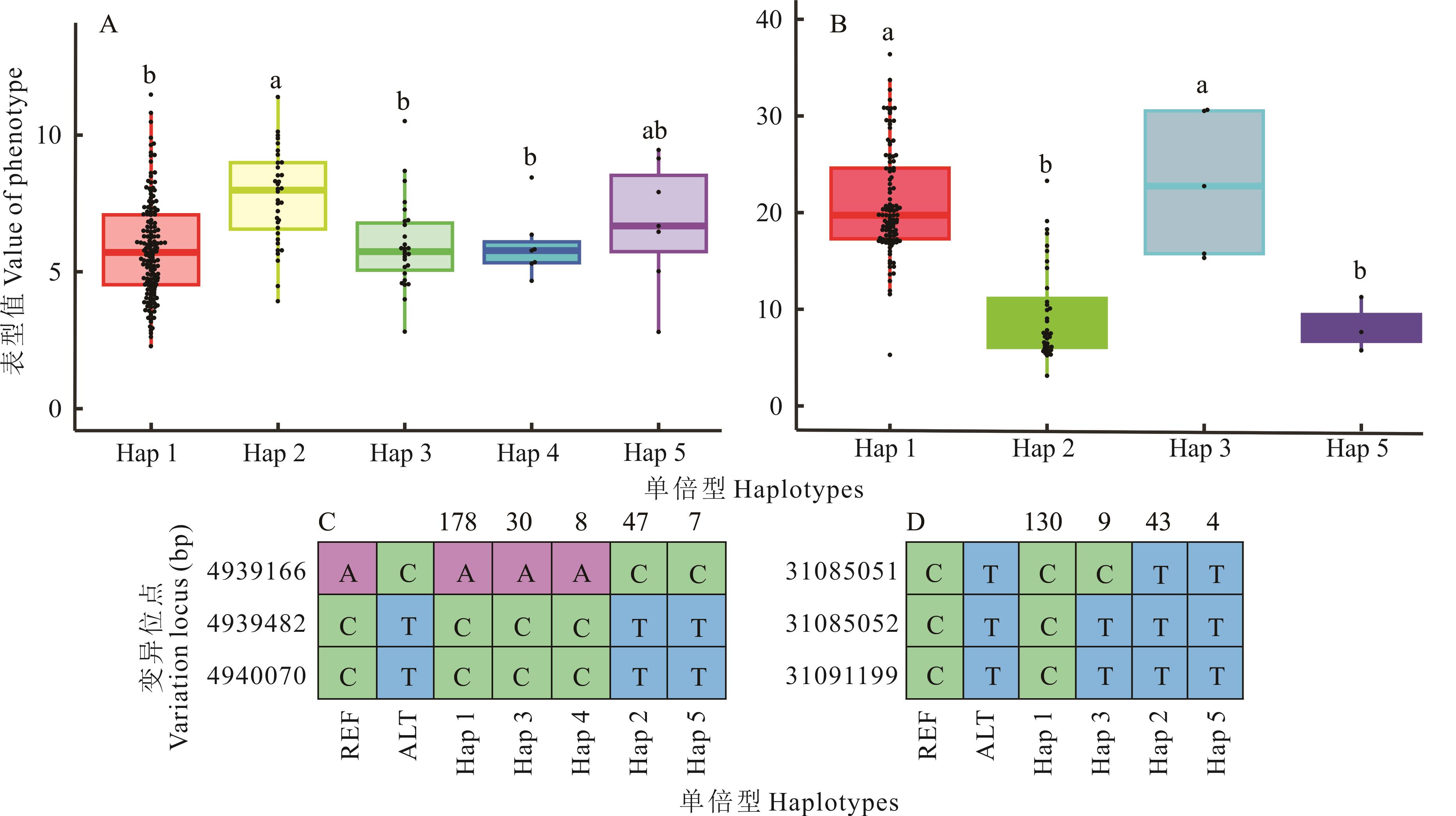
图8 SiCCoAOMT单倍型分析A: SiCCoAOMT3基因单倍型箱线图Boxplot of SiCCoAOMT3 gene’s haplotype; B: SiCCoAOMT5基因单倍型箱线图Boxplot of SiCCoAOMT5 gene’s haplotype; C: SiCCoAOMT3基因单倍型位点(上面是单倍型包含样本数量)Haplotype sites of the SiCCoAOMT3 gene (the data on the top side were the number of samples haplotype contained); D: SiCCoAOMT5基因单倍型位点Haplotype sites of the SiCCoAOMT5 gene. 不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05) Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05).
Fig.8 SiCCoAOMT gene dominant haplotype
| [1] | Kahie M A, Wang Y, Fang P, et al. Evolution and expression analysis of the caffeoyl-CoA 3-O-methyltransferase (CCoAOMT) gene family in jute (Corchorus L.). BMC Genomics, 2023, 24: 204. |
| [2] | Liu Q, Luo L, Zheng L Q. Lignins: biosynthesis and biological functions in plants.International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19: 335. |
| [3] | Hongo S, Sato K, Yokoyama R, et al. Demethylesterification of the primary wall by PECTIN METHYLESTERASE35 provides mechanical support to the Arabidopsis stem. Plant Cell, 2012, 24: 2624-2634. |
| [4] | Zhao H Y, Sheng Q X, Lv S Y, et al. Characterization of three rice CCoAOMT genes. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49: 1602-1606. |
| [5] | Shan C R, Chen X H, Ding Y F, et al. Functional analysis of FmCCoAOMT gene in Fraxinus mandshurica during lignin synthesis and abiotic stress. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(5): 768-778. |
| 单超然, 陈晓慧, 丁云飞, 等. 水曲柳FmCCoAOMT基因在木质素合成及非生物胁迫中的功能分析. 植物研究, 2023, 43(5): 768-778. | |
| [6] | Kühnl T, Koch U, Heller W, et al. Elicitor induced S-adenosyl-l-methionine: caffeoyl-CoA 3-O-methyltransferase from carrot cell suspension cultures. Plant Science, 1989, 60: 21-25. |
| [7] | Schmitt D, Pakusch A E, Matern U. Molecular cloning, induction and taxonomic distribution of caffeoyl-CoA 3-O-methyltransferase, an enzyme involved in disease resistance. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1991, 266: 17416-17423. |
| [8] | Ye Z H, Kneusel R E, Matern U, et al. Multiple cDNAs for caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase in plant tissues. Plant Journal, 1994, 6: 211-219. |
| [9] | Ibrahim R K, Bruneau A, Bantignies B. Plant O-methyltransferases: molecular analysis, common signature and classification. Plant Molecular Biology, 1998, 36: 1-10. |
| [10] | Zhang G Y, Zhang Y J, Xu J T, et al. The CCoAOMT1 gene from jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) is involved in lignin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene,2014, 546: 398-402. |
| [11] | Zhao H Y, Shen Q X, Lv S Y, et al. Expression analysis of caffeoyl-CoA-O-methyltransferase gene (CCoAOMT) in rice. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(14): 1390-1394. |
| 赵华燕, 沈庆喜, 吕世友, 等. 水稻咖啡酰辅酶A-O-甲基转移酶基因(CCoAOMT)表达特性分析. 科学通报, 2004, 49(14): 1390-1394. | |
| [12] | Brutnell T P, Wang L, Swartwood K, et al. Setaria viridis: a model for C4 photosynthesis. Plant Cell,2010, 22: 2537-2544. |
| [13] | Wang Y G, Lyu X Y, Ji M C, et al. Stress tolerance improvement by BvM14-CCoAOMT gene in sugar beet M14 strain. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2018, 34(34): 30-35. |
| 王宇光, 吕笑言, 季美超, 等. 甜菜M14品系咖啡酰辅酶A-O-甲基转移酶提高植物抗逆性功能分析. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(34): 30-35. | |
| [14] | Riccardi F, Gazeau P, de Vienne D, et al. Protein changes in response to progressive water deficit in maize: quantitative variation and polypeptide identification. Plant and Cell Physiology,1998, 117: 1253-1263. |
| [15] | Salekdeh G H, Siopongco J, Wade L J, et al. A proteomic approach to analyzing drought- and salt-responsiveness in rice. Field Crops Research, 2002, 76: 199-219. |
| [16] | Wang C, Chen J F, Zhi H, et al. Population genetics of foxtail millet and its wild ancestor. BMC Genetics, 2010, 11: 1-13. |
| [17] | Yan W M. The origin of agriculture and Chinese civilization. Chinese Rural Discovery, 2016, 8(5): 38-45. |
| 严文明. 农业起源与中华文明. 中国乡村发现, 2016, 8(5): 38-45. | |
| [18] | Diao X M. Breeding innovation creates new development of millet seed industry. China Seed Industry, 2022, 4(4): 4-7. |
| 刁现民. 育种创新造就谷子种业新发展. 中国种业, 2022, 4(4): 4-7. | |
| [19] | Liu Q. We should attach great importance to the strategic value of “planting belt moving north”. Farmers Daily, 2021-11-27(004). |
| 刘强.应高度重视“种植带北移”的战略价值. 农民日报, 2021-11-27(004). | |
| [20] | Yang Z R, Zhang H S, Li X K, et al. A mini foxtail millet with an Arabidopsis-like life cycle as a C4 model system. Nature Plants, 2020, 6: 1167-1178. |
| [21] | Song L N, Zhang Y M, Hu C S, et al. Comprehensive analysis of emissions and global warming effects of greenhouse gases in winter-wheat fields in the high-yield agro-region of north China Plain. Chinese Journal of Ecological Agriculture, 2013, 21(3): 297-307. |
| 宋利娜, 张玉铭, 胡春胜, 等. 华北平原高产农区冬小麦农田土壤温室气体排放及其综合温室效应.中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(3): 297-307. | |
| [22] | Ferreira S S, Simões M S, Carvalho G G, et al. The lignin toolbox of the model grass Setaria viridis. Plant Molecular Biology,2019, 101: 235-255. |
| [23] | Chen C J, Wu Y, Li J W, et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Molecular Plant, 2023, 16: 1733-1742. |
| [24] | Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S. MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2021, 38: 3022-3027. |
| [25] | Bailey T L, Johnson J, Grant C E, et al. The MEME suite. Nucleic Acids Research, 2015, 43: W39-W49. |
| [26] | Yu C S, Lin C J, Hwang J K. Predicting subcellular localization of proteins for Gram-negative bacteria by support vector machines based on n-peptide compositions.Protein Science, 2004, 13: 1402-1406. |
| [27] | Sun R, Yang Y Y, Li Y J, et al. Genome-wide identification and analysis of PLATZ transcription factor gene family in foxtail millet. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 548-559. |
| 孙蓉, 杨宇琭, 李亚军, 等. 谷子PLATZ转录因子基因家族的鉴定和分析. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 548-559. | |
| [28] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔ C T method. Methods, 2001, 25: 402-408. |
| [29] | Li X K, Gao J, Song J, et al. Multi-omics analyses of 398 foxtail millet accessions reveal genomic regions associated with domestication, metabolite traits, and anti-inflammatory effects. Molecular Plant, 2022, 15: 1367-1383. |
| [30] | Li X K, Shi Z, Gao J, et al. CandiHap: a haplotype analysis toolkit for natural variation study. Molecular Breeding, 2023, 43: 21. |
| [31] | Lee Y J, Kim B G, Chong Y, et al. Cation dependent O-methyltransferases from rice. Planta, 2008, 227: 641-647. |
| [32] | Kim J S, Mizoi J, Yoshida T, et al. An ABRE promoter sequence is involved in osmotic stress-responsive expression of the DREB2A gene, which encodes a transcription factor regulating drought-inducible genes in Arabidopsis. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2011, 52: 2136-2146. |
| [33] | Hu J, Liu T, Huo H, et al. Genome-wide characterization, evolutionary analysis, and expression pattern analysis of the trihelix transcription factor family and gene expression analysis under MeJA treatment in Panax ginseng. BMC Plant Biology, 2023, 23: 376. |
| [34] | Jalmi S K, Bhagat P K, Verma D, et al. Traversing the links between heavy metal stress and plant signaling. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 12. |
| [35] | Yao T, Zhang J, Xie M, et al. Transcriptional regulation of drought response in Arabidopsis and woody plants.Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 11: 572137. |
| [36] | Guo B, Qin J F, Li N, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of SHMT gene family in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.). Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2025, 51(3): 586-597. |
| 郭冰, 秦家范, 李娜, 等. 谷子SHMT基因家族全基因组鉴定与表达分析. 作物学报, 2025, 51(3): 586-597. | |
| [37] | Guo Z W, Si X Y, Jiao L P, et al. Cloning and bioinformatics of CCoAOMT relating to resistance of soybean to cyst nematodes. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 38(5): 616-623. |
| 郭子雯, 司修洋, 焦莉苹, 等. 大豆咖啡酰辅酶A-O-甲基转移酶(CCoAOMT)基因克隆及结构分析. 福建农业学报, 2023, 38(5): 616-623. | |
| [38] | Lu C, Zhang X Y, Lu M, et al. Identification and bioinformatics analysis of RrCCoAOMT gene family in Rosa roxburghii. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2023, 21(3): 764-771. |
| 卢晨, 张小英, 鲁敏, 等. 刺梨RrCCoAOMT基因家族的鉴定与生物信息学分析. 分子植物育种, 2023, 21(3): 764-771. | |
| [39] | Ma Q, Yan Q, Zhang Z S, et al. Identification, evolution and expression analysis of the CCoAOMT family genes in Medicago sativa. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(11): 144-156. |
| 马倩, 闫启, 张正社, 等. 紫花苜蓿CCoAOMT基因家族的鉴定、进化及表达分析. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 144-156. | |
| [40] | Peng S N, Li Y K, Luo D D, et al. Identification and expression analysis of flavonoid O-methyltransferase gene family in Artemisia argyi. Acta Pharmaceutical Sinica, 2023, 58(4): 1069-1078. |
| 彭赛男, 李宇琨, 罗丹丹, 等. 艾叶类黄酮O-甲基转移酶基因家族的鉴定及表达分析. 药学学报, 2023, 58(4): 1069-1078. | |
| [41] | Suo Q Q, Wu N, Yang H, et al. Prokaryotic expression, antibody preparation and application of rice caffeoyl-CoA-O-methyltransferase gene. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2022, 38(8): 135-141. |
| 索青青, 吴楠, 杨慧, 等. 水稻咖啡酰辅酶A-O-甲基转移酶基因的原核表达、抗体制备和应用. 生物技术通报, 2022, 38(8): 135-141. | |
| [42] | Rakoczy M, Femiak I, Alejska M, et al. Sorghum CCoAOMT and CCoAOMT-like gene evolution, structure, expression and the role of conserved amino acids in protein activity. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2018, 293: 1077-1089. |
| [43] | Yang Q, He Y, Kabahuma M, et al. A gene encoding maize caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase confers quantitative resistance to multiple pathogens. Nature Genetics, 2017, 49: 1364-1372. |
| [44] | Luo T R, Ma J Z, Du M Y, et al. Identification and expression analysis of LACS gene family members in Medicago sativa. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(4): 124-136. |
| 罗天蓉, 马健芝, 杜明阳, 等. 紫花苜蓿LACS基因家族成员鉴定及表达分析. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 124-136. |
| [1] | 柳家乐, 祁娟, 李文亮, 路欣, 袁琪, 李明洁, 张奥龙, 杜旺毅. 老芒麦EsJRL基因家族鉴定与表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2026, 35(1): 206-222. |
| [2] | 邹苇鹏, 刘怡, 翟佳兴, 周思懿, 宫祉祎, 岑慧芳, 朱慧森, 许涛. 紫花苜蓿MsNAC053基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 121-133. |
| [3] | 鲜燃, 邓雨, 付秋月, 蒋晶霞, 陶佳丽, 许涛, 朱慧森, 岑慧芳. 紫花苜蓿MsMYB86基因克隆及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(9): 162-172. |
| [4] | 左志芳, 李永龙, 魏雨佳, 周生辉, 李岩, 杨国锋. 结缕草DREB基因家族的鉴定及非生物胁迫下的表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 74-88. |
| [5] | 周昕越, 王丽萍, 蒋庆雪, 马晓冉, 仪登霞, 王学敏. 紫花苜蓿低温诱导蛋白MsLTI65的分离及其对不同逆境的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 89-104. |
| [6] | 罗天蓉, 马健芝, 杜明阳, 多杰措, 熊辉岩, 段瑞君. 紫花苜蓿LACS基因家族成员鉴定及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 124-136. |
| [7] | 王晓彤, 李小红, 麻旭霞, 蔡文祺, 冯学丽, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿FBA基因家族成员的鉴定与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 81-93. |
| [8] | 马圆, 刘欢, 赵桂琴, 王敬龙, 张然, 姚瑞瑞. 燕麦sHSP基因家族的鉴定及其响应高温及老化的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 145-158. |
| [9] | 伍国强, 于祖隆, 魏明. PGPR调控植物响应逆境胁迫的作用机制[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 203-218. |
| [10] | 刘昊, 李显炀, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 紫花苜蓿SAUR基因家族的鉴定及其在非生物胁迫中的表达模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 135-153. |
| [11] | 李显炀, 刘昊, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿WRKY转录因子家族鉴定与表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 154-170. |
| [12] | 黎泽斌, 邱永争, 刘延杰, 喻金秋, 王柏吉, 刘千宁, 王月, 崔国文. 紫花苜蓿BZR基因家族鉴定及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 106-122. |
| [13] | 张鑫苗, 伍国强, 魏明. MAPK在植物响应逆境胁迫中的作用[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 182-197. |
| [14] | 者玉琦, 武志娟, 王吉坤, 钟金城, 柴志欣, 信金伟. 基于mtDNA COX3基因对西藏特色牦牛群体遗传结构的分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 231-240. |
| [15] | 史先飞, 高宇, 黄旭升, 周雅莉, 蔡桂萍, 李昕儒, 李润植, 薛金爱. 油莎豆CeWRKY转录因子响应非生物胁迫的功能表征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 186-201. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||