

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 81-95.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020067
郭家萌( ), 何灵芝, 闫东良, 李卓, 王泳超, 邵瑞鑫, 杨青华(
), 何灵芝, 闫东良, 李卓, 王泳超, 邵瑞鑫, 杨青华( )
)
收稿日期:2020-02-21
修回日期:2020-04-26
出版日期:2021-01-20
发布日期:2021-01-08
通讯作者:
杨青华
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: yangqh2000@163.com基金资助:
Jia-meng GUO( ), Ling-zhi HE, Dong-liang YAN, Zhuo LI, Yong-chao WANG, Rui-xin SHAO, Qing-hua YANG(
), Ling-zhi HE, Dong-liang YAN, Zhuo LI, Yong-chao WANG, Rui-xin SHAO, Qing-hua YANG( )
)
Received:2020-02-21
Revised:2020-04-26
Online:2021-01-20
Published:2021-01-08
Contact:
Qing-hua YANG
摘要:
在黄淮海夏玉米生产区,不同控释氮肥和尿素的配比下,研究不同氮效率玉米品种的产量及其花前花后干物质和氮素累积分配规律,以及相应的氮素利用效率与经济效益,为该区域夏玉米氮肥高效施用提供理论与技术依据。试验采用裂区设计,周期为两年,以施氮处理为主区,设置0、180、300 kg·hm-2 3个施氮水平,并在180 kg·hm-2水平上设置全尿素处理(U)、控释尿素处理(C),控释尿素与尿素按1∶2(C1)与2∶1(C2)配施,共6个施肥处理,分别为N0、N180U、N180C、N180C1、N180C2、N300U;品种为副区,分别为氮低效品种豫禾988(YH988)和氮高效品种郑单958(ZD958)。结果表明,在黄淮海砂质潮土条件下,氮低效品种YH988和氮高效品种ZD958均在180 kg·hm-2施氮水平下实现了最高的产量水平,其中YH988和ZD958最佳的氮肥比例分别为控释氮∶尿素氮=1∶2和2∶1,即N180C1和N180C2。YH988和ZD958分别在N180C1和N180C2处理下花后干物质和氮素累积比例较高。同时,YH988和ZD958在N180C1和N180C2处理下分别实现了氮肥偏生产力、氮肥农学效率、氮肥当季利用率和经济效益的最高。综上,在黄淮海潮土区夏玉米生产体系中,不同氮效率品种YH988和ZD958分别在180 kg·hm-2施氮量,控施氮∶尿素氮=1∶2和2∶1的条件下,实现了高产及较高的花后干物质和氮素累积,促进了其产量和氮素利用效率的协同提高。
郭家萌, 何灵芝, 闫东良, 李卓, 王泳超, 邵瑞鑫, 杨青华. 控释氮肥和尿素配比对不同品种夏玉米氮素累积、转移及其利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 81-95.
Jia-meng GUO, Ling-zhi HE, Dong-liang YAN, Zhuo LI, Yong-chao WANG, Rui-xin SHAO, Qing-hua YANG. Effects of controlled release nitrogen and urea ratio on nitrogen accumulation, transfer, and nitrogen-use efficiency of different summer maize varieties[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 81-95.
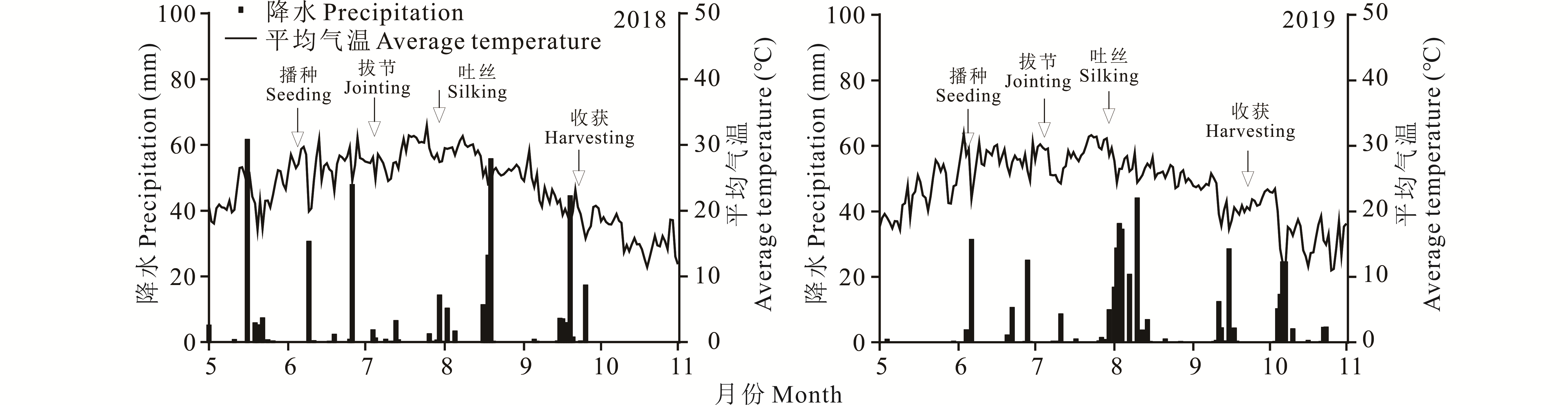
图1 2018-2019年夏玉米生育期间日平均气温和日降水量
Fig.1 The average temperature and daily precipitation of the experiment site during the growth period of maize in 2018 and 2019
年份 Year | 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 穗数 Ear number (plant·hm-2) | 穗粒数 Grain number | 百粒重 Hundred grain weight (g) | 产量 Yield (kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | YH988 | N0 | 74074ab | 481.79e | 26.30d | 6481.60e |
| N180U | 79630a | 538.94d | 27.13cd | 8873.42c | ||
| N180C | 72222b | 565.09abcd | 29.41b | 9450.72abc | ||
| N180C1 | 76389ab | 586.71a | 31.05a | 9853.15ab | ||
| N180C2 | 72222b | 567.30abc | 30.80a | 9285.72bc | ||
| N300U | 76852ab | 551.44cd | 27.61c | 7874.18d | ||
| ZD958 | N0 | 65278c | 492.40e | 29.89ab | 6700.54e | |
| N180U | 71296b | 563.13abcd | 30.02ab | 9025.29c | ||
| N180C | 72222b | 557.22bcd | 29.44b | 8886.66c | ||
| N180C1 | 75000ab | 569.24abc | 30.07ab | 9454.43abc | ||
| N180C2 | 73148b | 584.25ab | 30.59ab | 10027.62a | ||
| N300U | 65278c | 538.48d | 29.95d | 9188.97c | ||
| 2019 | YH988 | N0 | 66667a | 455.97c | 26.53ab | 7845.25e |
| N180U | 65740a | 566.27ab | 28.24ab | 10634.65ab | ||
| N180C | 64814a | 589.68a | 27.38ab | 9169.49c | ||
| N180C1 | 69444a | 576.64ab | 28.29ab | 11719.94a | ||
| N180C2 | 65740a | 583.23ab | 28.01ab | 9805.86bc | ||
| N300U | 66667a | 559.36ab | 28.42ab | 10749.58ab | ||
| ZD958 | N0 | 65740a | 509.68bc | 26.54b | 8435.69d | |
| N180U | 69444a | 568.61ab | 28.92ab | 10390.63ab | ||
| N180C | 71296a | 519.73abc | 27.50ab | 10476.21ab | ||
| N180C1 | 65740a | 535.25ab | 29.03ab | 10235.82ab | ||
| N180C2 | 65740a | 573.95ab | 29.31a | 10772.16ab | ||
| N300U | 66667a | 580.11ab | 29.39a | 10308.70ab | ||
| 品种 Variety (V) | ns | ns | *** | ns | ||
| 施氮处理Nitrogen application (N) | ns | *** | *** | *** | ||
| 年份Year (Y) | *** | ns | *** | *** | ||
| 品种×施氮处理V×N | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 品种×年份V×Y | * | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 施氮处理×年份N×Y | ns | ns | * | ns | ||
| 品种×施氮处理×年份V×N×Y | ns | ns | * | ns | ||
表1 氮肥处理对不同品种夏玉米产量及产量构成因素的影响
Table 1 Effects of nitrogen treatments on yield and yield components of different maize varieties
年份 Year | 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 穗数 Ear number (plant·hm-2) | 穗粒数 Grain number | 百粒重 Hundred grain weight (g) | 产量 Yield (kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | YH988 | N0 | 74074ab | 481.79e | 26.30d | 6481.60e |
| N180U | 79630a | 538.94d | 27.13cd | 8873.42c | ||
| N180C | 72222b | 565.09abcd | 29.41b | 9450.72abc | ||
| N180C1 | 76389ab | 586.71a | 31.05a | 9853.15ab | ||
| N180C2 | 72222b | 567.30abc | 30.80a | 9285.72bc | ||
| N300U | 76852ab | 551.44cd | 27.61c | 7874.18d | ||
| ZD958 | N0 | 65278c | 492.40e | 29.89ab | 6700.54e | |
| N180U | 71296b | 563.13abcd | 30.02ab | 9025.29c | ||
| N180C | 72222b | 557.22bcd | 29.44b | 8886.66c | ||
| N180C1 | 75000ab | 569.24abc | 30.07ab | 9454.43abc | ||
| N180C2 | 73148b | 584.25ab | 30.59ab | 10027.62a | ||
| N300U | 65278c | 538.48d | 29.95d | 9188.97c | ||
| 2019 | YH988 | N0 | 66667a | 455.97c | 26.53ab | 7845.25e |
| N180U | 65740a | 566.27ab | 28.24ab | 10634.65ab | ||
| N180C | 64814a | 589.68a | 27.38ab | 9169.49c | ||
| N180C1 | 69444a | 576.64ab | 28.29ab | 11719.94a | ||
| N180C2 | 65740a | 583.23ab | 28.01ab | 9805.86bc | ||
| N300U | 66667a | 559.36ab | 28.42ab | 10749.58ab | ||
| ZD958 | N0 | 65740a | 509.68bc | 26.54b | 8435.69d | |
| N180U | 69444a | 568.61ab | 28.92ab | 10390.63ab | ||
| N180C | 71296a | 519.73abc | 27.50ab | 10476.21ab | ||
| N180C1 | 65740a | 535.25ab | 29.03ab | 10235.82ab | ||
| N180C2 | 65740a | 573.95ab | 29.31a | 10772.16ab | ||
| N300U | 66667a | 580.11ab | 29.39a | 10308.70ab | ||
| 品种 Variety (V) | ns | ns | *** | ns | ||
| 施氮处理Nitrogen application (N) | ns | *** | *** | *** | ||
| 年份Year (Y) | *** | ns | *** | *** | ||
| 品种×施氮处理V×N | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 品种×年份V×Y | * | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 施氮处理×年份N×Y | ns | ns | * | ns | ||
| 品种×施氮处理×年份V×N×Y | ns | ns | * | ns | ||

图2 氮肥处理对不同品种夏玉米全生育期干物质累积的影响
Fig.2 Effects of nitrogen treatments on dry matter accumulation during the whole growth period of different maize varieties
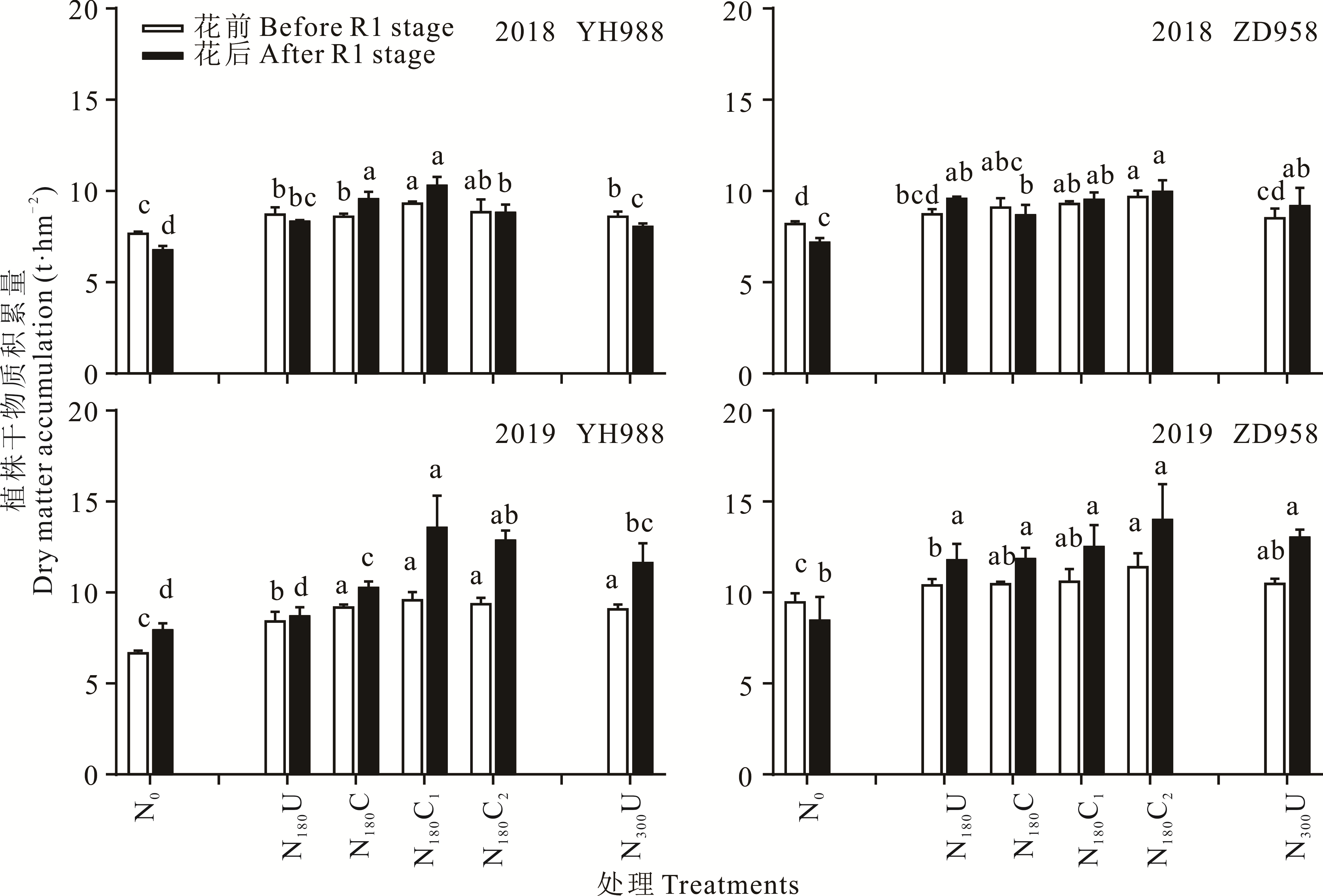
图3 氮肥处理对不同品种玉米花前花后干物质累积的影响不同字母表示同年差异达5%显著水平。下同。Different letters above the bars mean significant differences at the 5% level. The same below.
Fig.3 Effects of nitrogen treatments on dry matter accumulation during pre-and post-silking stage of different maize varieties

图4 氮肥处理对不同品种玉米花前花后干物质分配的影响
Fig.4 Effects of nitrogen treatments on dry matter distribution during pre-and post-silking stage of different maize varieties
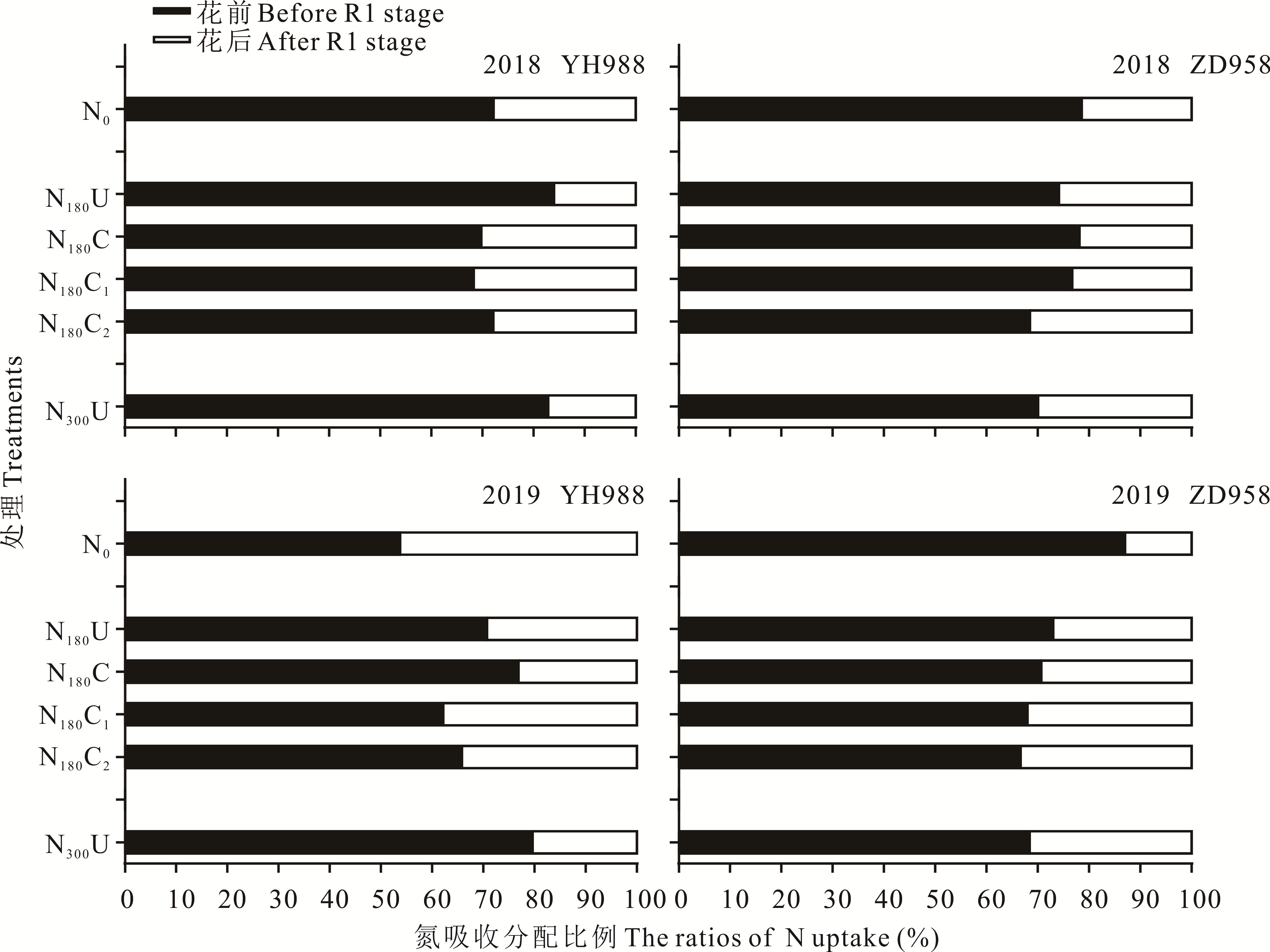
图7 氮肥处理对不同品种夏玉米花前花后植株吸氮量分配的影响
Fig.7 Effects of nitrogen treatments on nitrogen distribution at pre-and post-silking stage of different maize varieties
年份 Year | 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 吐丝期秸秆氮含量Stover N content at R1 (kg·hm-2) | 收获期秸秆氮 含量Stover N content at harvest (kg·hm-2) | 秸秆氮素表观转移量 Apparent amount of N remobilization (kg·hm-2) | 收获期籽粒氮含量Grain N content (kg·hm-2) | 花后根系氮吸收及转移量Nitrogen from root absorption and transfer after flowering (kg·hm-2) | 氮收获指数N harvest index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | YH988 | N0 | 103.49d | 59.31abc | 44.18e | 83.49c | 38.39cde | 58.73e |
| N180U | 137.09ab | 49.16c | 86.74a | 111.54ab | 24.80e | 69.47ab | ||
| N180C | 132.50ab | 67.39ab | 65.11bc | 123.47a | 46.89bcd | 64.82bcde | ||
| N180C1 | 138.96a | 75.77a | 63.19bcd | 128.77a | 65.58ab | 62.92bcde | ||
| N180C2 | 136.22ab | 48.68bc | 87.55a | 126.31ab | 38.76cde | 72.11a | ||
| N300U | 141.22a | 65.86abc | 75.35abc | 103.37b | 29.59de | 61.73cde | ||
| ZD958 | N0 | 115.80bc | 60.10abc | 55.70cd | 87.56d | 35.67de | 59.73de | |
| N180U | 128.61ab | 57.97abc | 70.65abc | 115.63c | 44.99cde | 66.54abcd | ||
| N180C | 141.88a | 58.88abc | 83.00ab | 123.16bc | 48.05abcd | 67.84abc | ||
| N180C1 | 141.83a | 60.00abc | 81.83ab | 129.93ab | 48.10abcd | 68.52abc | ||
| N180C2 | 143.33a | 72.38a | 70.96abc | 138.40a | 67.45a | 65.90abcd | ||
| N300U | 135.66ab | 60.67abc | 74.99abc | 133.04ab | 58.05abc | 68.67abc | ||
| 2019 | YH988 | N0 | 49.75d | 17.95d | 31.80c | 65.97d | 27.70abc | 78.54abc |
| N180U | 73.54c | 24.15c | 49.39abc | 81.94bcd | 32.54abc | 77.20bcd | ||
| N180C | 83.17abc | 24.41c | 58.77ab | 85.08bcd | 32.43abc | 77.47bc | ||
| N180C1 | 79.02abc | 32.96ab | 46.06bc | 94.84abc | 41.44ab | 74.15cd | ||
| N180C2 | 85.01abc | 33.75ab | 51.27ab | 87.83bcd | 36.57abc | 72.32d | ||
| N300U | 94.04ab | 29.01bc | 65.03ab | 90.65bcd | 25.62 bc | 75.46bcd | ||
| ZD958 | N0 | 77.05bc | 14.84d | 62.22ab | 74.06cd | 15.12c | 83.19a | |
| N180U | 95.44ab | 26.64c | 68.80a | 105.03ab | 36.23abc | 79.60ab | ||
| N180C | 89.27 abc | 26.66c | 62.61ab | 98.30abc | 35.69abc | 78.32bc | ||
| N180C1 | 86.98abc | 25.36c | 61.62ab | 102.25ab | 47.50ab | 80.06ab | ||
| N180C2 | 99.19a | 34.92a | 64.28ab | 115.81a | 51.54a | 76.76bcd | ||
| N300U | 98.13a | 34.81ab | 63.32ab | 106.47ab | 43.16ab | 74.31cd | ||
| 品种Variety (V) | ** | ns | ** | *** | * | ** | ||
| 施氮处理Nitrogen application (N) | *** | ** | *** | *** | ** | ns | ||
| 年份Year (Y) | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | ||
| 品种×施氮处理V×N | ns | ** | ns | ns | ** | ns | ||
| 品种×年份V×Y | * | ns | * | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 施氮处理×年份N×Y | ns | * | ns | ns | ns | *** | ||
| 品种×施氮处理×年份V×N×Y | ns | ns | * | ns | ns | * | ||
表2 不同氮肥处理下吐丝期和收获期秸秆氮含量、秸秆表观转移量、收获期籽粒氮含量、花后根系氮吸收及转移量和氮收获指数
Table 2 Differences in stover N content at silking and harvesting stage, apparent amount of N remobilization, grain N content at harvest stage, N from root absorption and transfer after flowering and N harvest index under different nitrogen treatments
年份 Year | 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 吐丝期秸秆氮含量Stover N content at R1 (kg·hm-2) | 收获期秸秆氮 含量Stover N content at harvest (kg·hm-2) | 秸秆氮素表观转移量 Apparent amount of N remobilization (kg·hm-2) | 收获期籽粒氮含量Grain N content (kg·hm-2) | 花后根系氮吸收及转移量Nitrogen from root absorption and transfer after flowering (kg·hm-2) | 氮收获指数N harvest index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | YH988 | N0 | 103.49d | 59.31abc | 44.18e | 83.49c | 38.39cde | 58.73e |
| N180U | 137.09ab | 49.16c | 86.74a | 111.54ab | 24.80e | 69.47ab | ||
| N180C | 132.50ab | 67.39ab | 65.11bc | 123.47a | 46.89bcd | 64.82bcde | ||
| N180C1 | 138.96a | 75.77a | 63.19bcd | 128.77a | 65.58ab | 62.92bcde | ||
| N180C2 | 136.22ab | 48.68bc | 87.55a | 126.31ab | 38.76cde | 72.11a | ||
| N300U | 141.22a | 65.86abc | 75.35abc | 103.37b | 29.59de | 61.73cde | ||
| ZD958 | N0 | 115.80bc | 60.10abc | 55.70cd | 87.56d | 35.67de | 59.73de | |
| N180U | 128.61ab | 57.97abc | 70.65abc | 115.63c | 44.99cde | 66.54abcd | ||
| N180C | 141.88a | 58.88abc | 83.00ab | 123.16bc | 48.05abcd | 67.84abc | ||
| N180C1 | 141.83a | 60.00abc | 81.83ab | 129.93ab | 48.10abcd | 68.52abc | ||
| N180C2 | 143.33a | 72.38a | 70.96abc | 138.40a | 67.45a | 65.90abcd | ||
| N300U | 135.66ab | 60.67abc | 74.99abc | 133.04ab | 58.05abc | 68.67abc | ||
| 2019 | YH988 | N0 | 49.75d | 17.95d | 31.80c | 65.97d | 27.70abc | 78.54abc |
| N180U | 73.54c | 24.15c | 49.39abc | 81.94bcd | 32.54abc | 77.20bcd | ||
| N180C | 83.17abc | 24.41c | 58.77ab | 85.08bcd | 32.43abc | 77.47bc | ||
| N180C1 | 79.02abc | 32.96ab | 46.06bc | 94.84abc | 41.44ab | 74.15cd | ||
| N180C2 | 85.01abc | 33.75ab | 51.27ab | 87.83bcd | 36.57abc | 72.32d | ||
| N300U | 94.04ab | 29.01bc | 65.03ab | 90.65bcd | 25.62 bc | 75.46bcd | ||
| ZD958 | N0 | 77.05bc | 14.84d | 62.22ab | 74.06cd | 15.12c | 83.19a | |
| N180U | 95.44ab | 26.64c | 68.80a | 105.03ab | 36.23abc | 79.60ab | ||
| N180C | 89.27 abc | 26.66c | 62.61ab | 98.30abc | 35.69abc | 78.32bc | ||
| N180C1 | 86.98abc | 25.36c | 61.62ab | 102.25ab | 47.50ab | 80.06ab | ||
| N180C2 | 99.19a | 34.92a | 64.28ab | 115.81a | 51.54a | 76.76bcd | ||
| N300U | 98.13a | 34.81ab | 63.32ab | 106.47ab | 43.16ab | 74.31cd | ||
| 品种Variety (V) | ** | ns | ** | *** | * | ** | ||
| 施氮处理Nitrogen application (N) | *** | ** | *** | *** | ** | ns | ||
| 年份Year (Y) | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | ||
| 品种×施氮处理V×N | ns | ** | ns | ns | ** | ns | ||
| 品种×年份V×Y | * | ns | * | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 施氮处理×年份N×Y | ns | * | ns | ns | ns | *** | ||
| 品种×施氮处理×年份V×N×Y | ns | ns | * | ns | ns | * | ||
年份 Year | 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 氮肥偏生产力 PFPN (kg·kg-1) | 氮肥农学效率 ANUE (kg·kg-1) | 氮肥回收效率 NRE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | YH988 | N0 | |||
| N180U | 48.14c | 13.29cde | 11.91e | ||
| N180C | 52.55abc | 16.50abc | 28.68abc | ||
| N180C1 | 54.74ab | 18.73a | 30.63ab | ||
| N180C2 | 49.85bc | 15.58abcd | 23.50cde | ||
| N300U | 25.36e | 4.64g | 10.52e | ||
| ZD958 | N0 | ||||
| N180U | 50.14c | 12.92de | 14.41de | ||
| N180C | 49.37c | 12.15e | 19.10cde | ||
| N180C1 | 52.52abc | 15.30bcde | 23.48bcd | ||
| N180C2 | 55.71a | 18.48ab | 35.07a | ||
| N300U | 30.63d | 8.29f | 25.58abc | ||
| 2019 | YH988 | N0 | |||
| N180U | 59.08ab | 9.58c | 12.31c | ||
| N180C | 50.94b | 19.65b | 14.20bc | ||
| N180C1 | 65.11a | 28.23a | 24.37abc | ||
| N180C2 | 54.48b | 27.05a | 19.32abc | ||
| N300U | 35.83d | 14.11bc | 19.85abc | ||
| ZD958 | N0 | ||||
| N180U | 57.73ab | 13.14bc | 23.77abc | ||
| N180C | 58.20ab | 13.03bc | 20.04abc | ||
| N180C1 | 56.87ab | 13.20bc | 21.51abc | ||
| N180C2 | 59.85ab | 18.77b | 34.35a | ||
| N300U | 34.36d | 8.65c | 30.23ab | ||
| 品种 Variety (V) | ns | ns | ** | ||
| 施氮处理Nitrogen application (N) | *** | *** | ** | ||
| 年份Year (Y) | *** | ns | ns | ||
| 品种×施氮处理V×N | ns | ns | ** | ||
| 品种×年份V×Y | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 施氮处理×年份N×Y | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 品种×施氮处理×年份V×N×Y | ns | ns | ns | ||
表3 不同氮肥处理下玉米的氮肥利用效率
Table 3 Nitrogen use efficiency of maize under different nitrogen treatments of different maize varieties
年份 Year | 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 氮肥偏生产力 PFPN (kg·kg-1) | 氮肥农学效率 ANUE (kg·kg-1) | 氮肥回收效率 NRE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | YH988 | N0 | |||
| N180U | 48.14c | 13.29cde | 11.91e | ||
| N180C | 52.55abc | 16.50abc | 28.68abc | ||
| N180C1 | 54.74ab | 18.73a | 30.63ab | ||
| N180C2 | 49.85bc | 15.58abcd | 23.50cde | ||
| N300U | 25.36e | 4.64g | 10.52e | ||
| ZD958 | N0 | ||||
| N180U | 50.14c | 12.92de | 14.41de | ||
| N180C | 49.37c | 12.15e | 19.10cde | ||
| N180C1 | 52.52abc | 15.30bcde | 23.48bcd | ||
| N180C2 | 55.71a | 18.48ab | 35.07a | ||
| N300U | 30.63d | 8.29f | 25.58abc | ||
| 2019 | YH988 | N0 | |||
| N180U | 59.08ab | 9.58c | 12.31c | ||
| N180C | 50.94b | 19.65b | 14.20bc | ||
| N180C1 | 65.11a | 28.23a | 24.37abc | ||
| N180C2 | 54.48b | 27.05a | 19.32abc | ||
| N300U | 35.83d | 14.11bc | 19.85abc | ||
| ZD958 | N0 | ||||
| N180U | 57.73ab | 13.14bc | 23.77abc | ||
| N180C | 58.20ab | 13.03bc | 20.04abc | ||
| N180C1 | 56.87ab | 13.20bc | 21.51abc | ||
| N180C2 | 59.85ab | 18.77b | 34.35a | ||
| N300U | 34.36d | 8.65c | 30.23ab | ||
| 品种 Variety (V) | ns | ns | ** | ||
| 施氮处理Nitrogen application (N) | *** | *** | ** | ||
| 年份Year (Y) | *** | ns | ns | ||
| 品种×施氮处理V×N | ns | ns | ** | ||
| 品种×年份V×Y | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 施氮处理×年份N×Y | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 品种×施氮处理×年份V×N×Y | ns | ns | ns | ||
年份 Year | 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 肥料投入Fertilizer inputs (CNY·hm-2) | 人工投入Manual input (CNY·hm-2) | 其他投入Other inputs (CNY·hm-2) | 总投入 Total input (CNY·hm-2) | 产量收入 Production of income (CNY·hm-2) | 纯收益 Net income (CNY·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | YH988 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 2811.6 | 2811.6 | 10240.9d | 7429.3de |
| N180U | 807.9 | 1500 | 2811.6 | 5119.5 | 14020.0b | 8900.5b | ||
| N180C | 3200.0 | 0 | 2811.6 | 6011.6 | 14932.1b | 8920.5b | ||
| N180C1 | 1606.9 | 0 | 2811.6 | 4418.5 | 15568.0a | 11149.5a | ||
| N180C2 | 2403.5 | 0 | 2811.6 | 5215.1 | 14671.4b | 9456.3b | ||
| N300U | 1347.3 | 1500 | 2811.6 | 5658.9 | 12441.2c | 6782.3e | ||
| ZD958 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 2895.0 | 2895.0 | 10586.9d | 7691.9de | |
| N180U | 807.9 | 1500 | 2895.0 | 5202.9 | 14260.0b | 9057.1b | ||
| N180C | 3200.0 | 0 | 2895.0 | 6095.0 | 14041.0b | 7946.0cd | ||
| N180C1 | 1606.9 | 0 | 2895.0 | 4502.0 | 14938.0b | 10436.1a | ||
| N180C2 | 2403.5 | 0 | 2895.0 | 5298.5 | 15843.6a | 10545.2a | ||
| N300U | 1347.3 | 1500 | 2895.0 | 5742.3 | 14518.6b | 8776.3bc | ||
| 2019 | YH988 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 2811.6 | 2811.6 | 12395.5d | 9583.9bc |
| N180U | 807.9 | 1500 | 2811.6 | 5119.5 | 16802.7b | 11683.2ab | ||
| N180C | 3200.0 | 0 | 2811.6 | 6011.6 | 14487.8bc | 8476.2c | ||
| N180C1 | 1606.9 | 0 | 2811.6 | 4418.5 | 18517.5a | 14099.0a | ||
| N180C2 | 2403.5 | 0 | 2811.6 | 5215.1 | 15493.3bc | 10278.1b | ||
| N300U | 1347.3 | 1500 | 2811.6 | 5658.9 | 17055.4ab | 11396.5a | ||
| ZD958 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 2895.0 | 2895.0 | 13328.4c | 10433.4b | |
| N180U | 807.9 | 1500 | 2895.0 | 5202.9 | 16417.2b | 11214.3ab | ||
| N180C | 3200.0 | 0 | 2895.0 | 6095.0 | 16552.4b | 10457.4b | ||
| N180C1 | 1606.9 | 0 | 2895.0 | 4502.0 | 16172.6b | 11670.6ab | ||
| N180C2 | 2403.5 | 0 | 2895.0 | 5298.5 | 17020.0ab | 11721.5ab | ||
| N300U | 1347.3 | 1500 | 2895.0 | 5742.3 | 16287.7b | 10545.5ab | ||
| 品种Variety (V) | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 施氮处理Nitrogen application (N) | *** | *** | ns | *** | ** | ** | ||
| 年份Year (Y) | ns | ns | ns | ns | ** | *** | ||
| 品种×施氮处理V×N | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 品种×年份V×Y | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 施氮处理×年份N×Y | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 品种×施氮处理×年份V×N×Y | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
表4 氮肥处理对不同品种夏玉米经济效益的影响
Table 4 Effects of nitrogen treatments on economic benefits of different maize varieties
年份 Year | 品种 Variety | 处理 Treatment | 肥料投入Fertilizer inputs (CNY·hm-2) | 人工投入Manual input (CNY·hm-2) | 其他投入Other inputs (CNY·hm-2) | 总投入 Total input (CNY·hm-2) | 产量收入 Production of income (CNY·hm-2) | 纯收益 Net income (CNY·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | YH988 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 2811.6 | 2811.6 | 10240.9d | 7429.3de |
| N180U | 807.9 | 1500 | 2811.6 | 5119.5 | 14020.0b | 8900.5b | ||
| N180C | 3200.0 | 0 | 2811.6 | 6011.6 | 14932.1b | 8920.5b | ||
| N180C1 | 1606.9 | 0 | 2811.6 | 4418.5 | 15568.0a | 11149.5a | ||
| N180C2 | 2403.5 | 0 | 2811.6 | 5215.1 | 14671.4b | 9456.3b | ||
| N300U | 1347.3 | 1500 | 2811.6 | 5658.9 | 12441.2c | 6782.3e | ||
| ZD958 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 2895.0 | 2895.0 | 10586.9d | 7691.9de | |
| N180U | 807.9 | 1500 | 2895.0 | 5202.9 | 14260.0b | 9057.1b | ||
| N180C | 3200.0 | 0 | 2895.0 | 6095.0 | 14041.0b | 7946.0cd | ||
| N180C1 | 1606.9 | 0 | 2895.0 | 4502.0 | 14938.0b | 10436.1a | ||
| N180C2 | 2403.5 | 0 | 2895.0 | 5298.5 | 15843.6a | 10545.2a | ||
| N300U | 1347.3 | 1500 | 2895.0 | 5742.3 | 14518.6b | 8776.3bc | ||
| 2019 | YH988 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 2811.6 | 2811.6 | 12395.5d | 9583.9bc |
| N180U | 807.9 | 1500 | 2811.6 | 5119.5 | 16802.7b | 11683.2ab | ||
| N180C | 3200.0 | 0 | 2811.6 | 6011.6 | 14487.8bc | 8476.2c | ||
| N180C1 | 1606.9 | 0 | 2811.6 | 4418.5 | 18517.5a | 14099.0a | ||
| N180C2 | 2403.5 | 0 | 2811.6 | 5215.1 | 15493.3bc | 10278.1b | ||
| N300U | 1347.3 | 1500 | 2811.6 | 5658.9 | 17055.4ab | 11396.5a | ||
| ZD958 | N0 | 0 | 0 | 2895.0 | 2895.0 | 13328.4c | 10433.4b | |
| N180U | 807.9 | 1500 | 2895.0 | 5202.9 | 16417.2b | 11214.3ab | ||
| N180C | 3200.0 | 0 | 2895.0 | 6095.0 | 16552.4b | 10457.4b | ||
| N180C1 | 1606.9 | 0 | 2895.0 | 4502.0 | 16172.6b | 11670.6ab | ||
| N180C2 | 2403.5 | 0 | 2895.0 | 5298.5 | 17020.0ab | 11721.5ab | ||
| N300U | 1347.3 | 1500 | 2895.0 | 5742.3 | 16287.7b | 10545.5ab | ||
| 品种Variety (V) | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 施氮处理Nitrogen application (N) | *** | *** | ns | *** | ** | ** | ||
| 年份Year (Y) | ns | ns | ns | ns | ** | *** | ||
| 品种×施氮处理V×N | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 品种×年份V×Y | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 施氮处理×年份N×Y | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 品种×施氮处理×年份V×N×Y | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| 1 | Zhang Z Y, Mao X F, Yang J. Maize at the crossroads: Staple food grain or feed grain. Chinese Rural Economy, 2019(6): 38-53. |
| 张在一, 毛学峰, 杨军. 站在变革十字路口的玉米: 主粮还是饲料粮之论. 中国农村经济, 2019(6): 38-53. | |
| 2 | 中华人民共和国统计局. 中国统计年鉴. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2019. |
| The Statistical Bureau of the People’s Republic of China. China statistical yearbook. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2019. | |
| 3 | Liu W R, Zheng J Y, Luo Y, et al. Research advance on physiological changes respond to level of N application. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2010, 25(Supple1): 239-242. |
| 刘武仁, 郑金玉, 罗洋, 等. 概述氮肥水平对玉米生理及产量性状的影响. 华北农学报, 2010, 25(增刊1): 239-242. | |
| 4 | Sun H, Zhang J W, Jin L B. Problems and approaches of achieving high yield and high nitrogen use efficiency in maize production. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2014, 22(1): 143-148. |
| 孙浒, 张吉旺, 靳立斌. 玉米高产与氮肥高效协同实现存在的问题及其途径. 玉米科学, 2014, 22(1): 143-148. | |
| 5 | Wang D, Ji D Z, Ma L, et al. Effects of corn yield and nitrogen application on nitrogen use efficiency. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2013(6): 42-46. |
| 王端, 纪德智, 马琳, 等. 春玉米产量和施氮量对氮素利用率的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2013(6): 42-46. | |
| 6 | Guo P, Zhu C H, Zha L, et al. Effects of the combined application of slow-release urea and urea on activities of key enzymes related to nitrogen metabolism and nitrogen utilization of maize. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2016(6): 99-105. |
| 郭萍, 朱从桦, 査丽, 等. 缓释尿素与普通尿素不同配比对玉米氮代谢酶和氮素利用的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2016(6): 99-105. | |
| 7 | Tian X J. Research on the cost of foodstuff production in China. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2005. |
| 田新建. 中国粮食生产成本研究. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2005. | |
| 8 | Shoji S, Delgado J, Mosier A, et al. Use of controlled release fertilizers and nitrification inhibitors to increase nitrogen use efficiency and to conserve air and water quality. Communications in Soil Science & Plant Analysis, 2001, 32(7): 1051-1070. |
| 9 | Li M, Wu J, Han S, et al. Effect of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer as jointing fertilizer on yield, dry matter and nitrogen accumulation and distribution in winter wheat. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2017, 37(7): 955-962. |
| 李敏, 武际, 韩上, 等. 控释氮肥拔节期施用对冬小麦产量及干物质、氮素累积与分配的影响. 麦类作物学报, 2017, 37(7): 955-962. | |
| 10 | Gao X, Li C, Zhang M, et al. Controlled release urea improved the nitrogen use efficiency, yield and quality of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) on silt loamy soil. Field Crops Research, 2015, 181: 60-68. |
| 11 | Yang Y C, Zhang M, Li Y C, et al. Controlled release urea improved nitrogen use efficiency, activities of leaf enzymes, and rice yield. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2012, 76(6): 2307-2317. |
| 12 | Feng X J, Zhan X M, Wang X X, et al. Effects of soil inorganic nitrogen and nitrogen absorbing by maize under the reduced application of coated urea at different proportions. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2019, 52(10): 1733-1745. |
| 冯小杰, 战秀梅, 王雪鑫, 等. 包膜尿素不同配比减施对土壤无机氮含量及玉米氮素吸收的影响. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(10): 1733-1745. | |
| 13 | Ji Y, Yu H Y, Xu H. Effect of controlled-release fertilizer and its combined application with urea on CH4 and N2O emissions in rice soil. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017, 26(9): 1494-1500. |
| 纪洋, 于海洋, 徐华. 控释肥与尿素配合施用对稻季土壤CH4和N2O排放的影响. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(9): 1494-1500. | |
| 14 | Jin R, Li L, Guo P, et al. Effect of the mixed ratios of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer on soil nitrogen content and its uptake and utilization of maize. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 32(6): 214-221. |
| 金容, 李兰, 郭萍, 等. 控释氮肥比例对土壤氮含量和玉米氮素吸收利用的影响. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(6): 214-221. | |
| 15 | Ji J H, Li Y Y, Liu S Q, et al. Effect of different mixing rates of controlled-release urea and common urea on grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of spring maize. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2015, 46(3): 669-675. |
| 姬景红, 李玉影, 刘双全, 等. 控释掺混肥对春玉米产量、光合特性及氮肥利用率的影响. 土壤通报, 2015, 46(3): 669-675. | |
| 16 | Li W, Li X H, Li H Y, et al. Effects of different mixing rates of controlled-release urea and common urea on grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of summer maize. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2012, 38(4): 699-706. |
| 李伟, 李絮花, 李海燕, 等. 控释尿素与普通尿素混施对夏玉米产量和氮肥效率的影响. 作物学报, 2012, 38(4): 699-706. | |
| 17 | Guo J J, Zhang F C, Yan S C, et al. Effects of blending of slow-release nitrogen fertilizer and urea on maize physiological characteristics and nitrogen uptake. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2018, 24(5): 1194-1204. |
| 郭金金, 张富仓, 闫世程, 等. 缓释氮肥与尿素掺混对玉米生理特性和氮素吸收的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2018, 24(5): 1194-1204. | |
| 18 | Guo J J, Zhang F C, Wang H D, et al. Effects of slow-release nitrogen fertilizer and urea blending on maize growth and nitrogen uptake under different nitrogen application rates. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50(20): 3930-3943. |
| 郭金金, 张富仓, 王海东, 等. 不同施氮量下缓释氮肥与尿素掺混对玉米生长与氮素吸收利用的影响. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(20): 3930-3943. | |
| 19 | Wang L M, Ye Y L, Chen F J, et al. Effect of nitrogen fertilization on maize yield and nitrogen efficiency of different maize varieties. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2012, 20(5): 529-535. |
| 王玲敏, 叶优良, 陈范骏, 等. 施氮对不同品种玉米产量、氮效率的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2012, 20(5): 529-535. | |
| 20 | Li Q, Kong F L, Yuan J C. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer operation on dry matter production and yield of maize cultivars with contrasting nitrogen efficiency. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2018, 33(6): 174-182. |
| 李强, 孔凡磊, 袁继超. 氮肥运筹对不同氮效率玉米品种干物质生产及产量的影响. 华北农学报, 2018, 33(6): 174-182. | |
| 21 | Chen D. Pilot study on coated slow/controlled release fertilizer and the determination of slow/controlled fertilizer. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2016. |
| 陈迪. 包膜缓/控释肥中试研究及缓/控释肥规律测定. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2016. | |
| 22 | Wu L Q, Wu L, Cui Z L, et al. Basic NPK fertilizer recommendation and fertilizer formula for maize production regions in China. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2015, 52(4): 802-817. |
| 吴良泉, 武良, 崔振岭, 等. 中国玉米区域氮磷钾肥推荐用量及肥料配方研究. 土壤学报, 2015, 52(4): 802-817. | |
| 23 | Zhang F S, Wang J Q, Zhang W F, et al. Nutrient use efficiencies of major cereal crops in China and measures for improvement. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2008, 45(5): 915-924. |
| 张福锁, 王激清, 张卫峰, 等. 中国主要粮食作物肥料利用率现状与提高途径. 土壤学报, 2008, 45(5): 915-924. | |
| 24 | Yan P. The mechanisms of root-zone N management regulates maize canopy development with high yield and high N use efficiency. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2015. |
| 颜鹏. 支撑夏玉米高产高效群体的根层氮素调控机制与途径. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2015. | |
| 25 | Li W J, He P, Gao Q, et al. Dry matter formation and nitrogen uptake in two maize cultivars differing in nitrogen use efficiency. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2010, 16(1): 51-57. |
| 李文娟, 何萍, 高强, 等. 不同氮效率玉米干物质形成及氮素营养特性差异研究. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(1): 51-57. | |
| 26 | Li Z S, Tan D S, Wang W, et al. Effects of different controlled release fertilizers on agronomic characters and yield of summer maize. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 46(9): 85-88. |
| 李子双, 谭德水, 王薇, 等. 不同控释肥对夏玉米农艺性状及产量的影响. 山东农业科学, 2014, 46(9): 85-88. | |
| 27 | Yi W P, Zhu G L, Wu L, et al. Application of different release duration controlled-release coated urea combined with conventional urea on summer maize. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2010, 16(6): 1497-1502. |
| 衣文平, 朱国梁, 武良, 等. 不同量的包膜控释尿素与普通尿素配施在夏玉米上的应用研究. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(6): 1497-1502. | |
| 28 | Zheng W, Liu Z, Zhang M, et al. Improving crop yields, nitrogen use efficiencies, and profits by using mixtures of coated controlled-released and uncoated urea in a wheat-maize system. Field Crops Research, 2017, 205: 106-115. |
| 29 | Zheng W, Zhang M, Liu Z, et al. Combining controlled-release urea and normal urea to improve the nitrogen use efficiency and yield under wheat-maize double cropping system. Field Crops Research, 2016, 197: 52-62. |
| 30 | Chen G P. Production and distribution of dry matter in maize. Journal of Maize Sciences, 1994, 2(1): 48-53. |
| 陈国平. 玉米的干物质生产与分配. 玉米科学, 1994, 2(1): 48-53. | |
| 31 | Zhang F S, Cui Z L, Chen X P, et al. Integrated nutrient management for food security and environmental quality in China. Advances in Agronomy, 2012, 116: 1-40. |
| 32 | Meng Q F, Yue S C, Hou P, et al. Improving yield and nitrogen use efficiency simultaneously for maize and wheat in China: A review. Pedosphere, 2016, 26(2): 137-147. |
| 33 | Bertin P, Gallais A. Genetic variation for nitrogen use efficiency in a set of recombinant maize inbred lines. I. Agrophysiological results. Maydica, 2000, 45(1): 53-66. |
| 34 | Gallais A, Coque M. Genetic variation and selection for nitrogen use efficiency in maize: A synthesis. Maydica, 2005, 50(3): 531-547. |
| 35 | He P, Jin J Y, Lin B, et al. Dynamics of biomass and its componentis and models of nutrients absorption by spring maize under different nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium application rates. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 1998(2): 123-130. |
| 何萍, 金继运, 林葆, 等. 不同氮磷钾用量下春玉米生物产量及其组分动态与养分吸收模式研究. 植物营养与肥料学报, 1998(2): 123-130. | |
| 36 | Chen X P, Cui Z L, Meng Q F, et al. Producing more grain with lower environmental costs. Nature, 2014, 514(7523): 486-489. |
| 37 | Cassman K G, Dobermann A, Walters D T. Agroecosystems, nitrogen-use efficiency, and nitrogen management. AMBIO: A Journal of the Human Environment, 2002, 31(2): 132-140. |
| 38 | Farmaha B S, Sims A L. The influence of polymer-coated urea and urea fertilizer mixtures on spring wheat protein concentrations and economic returns. Agronomy Journal, 2013, 105(5): 1328-1334. |
| [1] | 谢开云, 王玉祥, 万江春, 张树振, 隋晓青, 赵云, 张博. 混播草地中豆科/禾本科牧草氮转移机理及其影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 157-170. |
| [2] | 朱亚琼, 于辉, 郑伟, 黎松松, 娜尔克孜, 刘岳含, 郝帅, 艾丽菲热. 燕麦+箭筈豌豆混播草地混播优势的测度与影响因素分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 74-85. |
| [3] | 朱亚琼, 关正翾, 郑伟, 王祥. 混播种类和群体结构对豆禾牧草混播系统氮素利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 1-14. |
| [4] | 戢林,杨欢,李廷轩,张锡洲,余海英. 氮高效利用基因型水稻干物质生产和氮素积累特性[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(6): 327-335. |
| [5] | 谢开云,赵云,李向林,何峰,万里强,王丹,韩冬梅. 豆-禾混播草地种间关系研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(3): 284-. |
| [6] | 王平,周道玮,姜世成. 半干旱地区禾-豆混播草地生物固氮作用研究[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(6): 276-280. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||