

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 64-72.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020245
马英1( ), 许志豪1, 曾巧红1, 孟建龙2, 胡亚虎1(
), 许志豪1, 曾巧红1, 孟建龙2, 胡亚虎1( ), 苏洁琼3
), 苏洁琼3
收稿日期:2020-05-26
修回日期:2020-07-16
出版日期:2021-05-21
发布日期:2021-05-21
通讯作者:
胡亚虎
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: huyh@lzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Ying MA1( ), Zhi-hao XU1, Qiao-hong ZENG1, Jian-long MENG2, Ya-hu HU1(
), Zhi-hao XU1, Qiao-hong ZENG1, Jian-long MENG2, Ya-hu HU1( ), Jie-qiong SU3
), Jie-qiong SU3
Received:2020-05-26
Revised:2020-07-16
Online:2021-05-21
Published:2021-05-21
Contact:
Ya-hu HU
摘要:
为研究氮(N)沉降增加后荒漠草本植物的养分利用策略及碳(C)同化能力和分配格局的变化,以腾格里沙漠东南缘的典型荒漠化草原为研究区,分析了N素添加下不同功能型草本植物根部和地上部化学计量比的变化。结果表明:N素添加会导致土壤中总N、铵态N以及植物体内N含量的显著增加,同时会促进多年生植物尤其是非禾本科植物对磷(P)的吸收,但会显著降低一年生植物根部P的含量。一年生和多年生非禾本科植物的C含量在N素添加下显著降低,多年生禾本科植物的C含量则表现出显著的器官差异,其中地上部的C含量显著降低,而根部显著增加。不同功能型植物体内的C/N和C/P(除一年生植物根部的C/P)在N素添加后显著降低,且二者均表现出根部大于地上部的趋势。植物的N/P在N素添加下显著增加,尤其是一年生植物的变化趋势随施肥水平的变化更加显著。可见,在N素受限的荒漠化草原,外源N素输入导致的土壤N素有效性提升后会凸显P素对植物生长的限制性作用,同时会降低草本植物的C同化能力并加强C向植物根部的分配。
马英, 许志豪, 曾巧红, 孟建龙, 胡亚虎, 苏洁琼. 氮素添加对荒漠化草原草本植物养分化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 64-72.
Ying MA, Zhi-hao XU, Qiao-hong ZENG, Jian-long MENG, Ya-hu HU, Jie-qiong SU. Impact of nitrogen addition on stoichiometric characteristics of herbaceous species in desert steppe[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(6): 64-72.
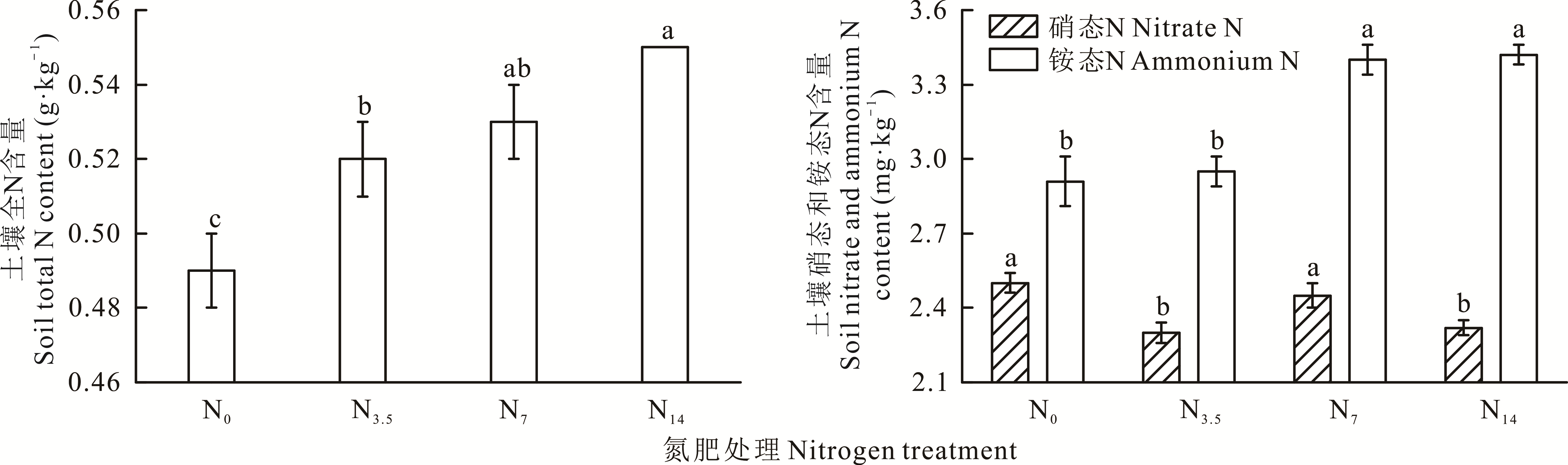
图1 不同N素添加处理下土壤全N和有效态N素含量的变化不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments at the P<0.05 level.
Fig.1 Changes of soil total N and available N content under different N addition treatments
试验因素 Experimental factors | 碳C | 氮N | 磷P | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| 氮肥处理 Nitrogen treatment (N) | 10.292 | <0.001 | 367.064 | <0.001 | 41.045 | <0.001 |
| 植物类型 Plant type (PT) | 320.504 | <0.001 | 64.697 | <0.001 | 282.462 | <0.001 |
| 植物器官 Plant organ (PO) | 4.091 | <0.050 | 2505.708 | <0.001 | 3126.423 | <0.001 |
| N×PT | 24.538 | <0.001 | 20.713 | <0.001 | 78.397 | <0.001 |
| N×PO | 51.786 | <0.001 | 67.221 | <0.001 | 19.794 | <0.001 |
| PT×PO | 126.714 | <0.001 | 171.746 | <0.001 | 372.315 | <0.001 |
| N×PT×PO | 29.831 | <0.001 | 9.669 | <0.001 | 27.573 | <0.001 |
表1 植物C、N、P含量的多因素方差分析
Table 1 Results of the univariate multi-factor ANOVA on the content of C, N, and P in the plant
试验因素 Experimental factors | 碳C | 氮N | 磷P | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| 氮肥处理 Nitrogen treatment (N) | 10.292 | <0.001 | 367.064 | <0.001 | 41.045 | <0.001 |
| 植物类型 Plant type (PT) | 320.504 | <0.001 | 64.697 | <0.001 | 282.462 | <0.001 |
| 植物器官 Plant organ (PO) | 4.091 | <0.050 | 2505.708 | <0.001 | 3126.423 | <0.001 |
| N×PT | 24.538 | <0.001 | 20.713 | <0.001 | 78.397 | <0.001 |
| N×PO | 51.786 | <0.001 | 67.221 | <0.001 | 19.794 | <0.001 |
| PT×PO | 126.714 | <0.001 | 171.746 | <0.001 | 372.315 | <0.001 |
| N×PT×PO | 29.831 | <0.001 | 9.669 | <0.001 | 27.573 | <0.001 |

图2 不同N素添加处理下植物根部和地上部C、N、P含量的变化不同大写和小写字母分别表示植物根部和地上部C、N和P含量在不同处理间差异显著,P<0.05。下同。Different capital letters and lowercase letters indicate significant differences of C, N, and P contents in plant roots and shoots among different N addition treatments at the 0.05 level, respectively. The same below.
Fig.2 Changes of C, N and P contents in roots and shoots of plants under different N addition treatments

图3 不同N素添加处理下植物体内C、N、P生态化学计量比的变化
Fig.3 Changes of ecological stoichiometry of C, N, and P in plant roots and shoots under different N addition treatments
| 1 | Yue K, Fornara D A, Yang W, et al. Effects of three global change drivers on terrestrial C∶N∶P stoichiometry: A global synthesis. Global Change Biology, 2017, 23(6): 2450-2463. |
| 2 | Tang K W, Dam H G. Limitation of zooplankton production: Beyond stoichiometry. Oikos, 1999, 84(3): 537-542. |
| 3 | An H, Tang Z, Keesstra S, et al. Impact of desertification on soil and plant nutrient stoichiometry in a desert grassland. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 9422. |
| 4 | Yan X, An H. Fractal features of soil particle size in the process of desertification in desert grassland of Ningxia, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2017, 28(10): 3243-3250. |
| 阎欣, 安慧. 宁夏荒漠草原沙漠化过程中土壤粒径分形特征. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(10): 3243-3250. | |
| 5 | Zhang K, He M Z, Li X R, et al. Foliar carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry of typical desert plants across the Alashan Desert. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(22): 6538-6547. |
| 张珂, 何明珠, 李新荣, 等. 阿拉善荒漠典型植物叶片碳、氮、磷化学计量特征. 生态学报, 2014, 34(22): 6538-6547. | |
| 6 | Guo H, Zhuang W W, Li J. Characteristics of biomass and stoichiometry of four desert herbaceous plants in the Gurbantunggut Desert. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(3): 421-430. |
| 郭浩, 庄伟伟, 李进. 古尔班通古特沙漠中4种荒漠草本植物的生物量与化学计量特征. 植物研究, 2019, 39(3): 421-430. | |
| 7 | Lu Y, Wang B L, Shen Y. C, N, and P stoichiometric characteristics of plant communities and dominant plants from different vegetation restoration periods in typical Ningxia grasslands. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(5): 1200-1206. |
| 陆颖, 王保林, 沈艳. 宁夏典型草原区不同退耕年限草地植物群落及优势植物C、N、P化学计量特征. 草业科学, 2019, 36(5): 1200-1206. | |
| 8 | Zhang B, Gao X, Li L, et al. Groundwater depth affects phosphorus but not carbon and nitrogen concentrations of a desert phreatophyte in Northwest China. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 338. |
| 9 | Li L, Liu B, Gao X, et al. Nitrogen and phosphorus addition differentially affect plant ecological stoichiometry in desert grassland. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 18673. |
| 10 | Schimel D S. All life is chemical. Bioscience, 2003, 53(5): 521-524. |
| 11 | Su J Q, Li X R, Yang H T. Effects of fertilization on population density and productivity of herbaceous plants in desert steppe. Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions, 2014, 6(3): 219-225. |
| 12 | Chen J B, Dong C C, Yao X D, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition on plant biomass and tissue elemental content in different degradation stages of temperate steppe in Northern China. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2018, 11(5): 730-739. |
| 13 | Wang P, Zhu W W, Niu Y B, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition on plant community composition and microbial biomass ecological stoichiometry in a desert steppe in China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2019, 43(5): 427-436. |
| 王攀, 朱湾湾, 牛玉斌, 等. 氮添加对荒漠草原植物群落组成与微生物生物量生态化学计量特征的影响. 植物生态学报, 2019, 43(5): 427-436. | |
| 14 | Huang J, Wang P, Niu Y, et al. Changes in C∶N∶P stoichiometry modify N and P conservation strategies of a desert steppe species Glycyrrhiza uralensis. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 12668. |
| 15 | Huang J, Yu H, Liu J, et al. Phosphorus addition changes belowground biomass and C∶N∶P stoichiometry of two desert steppe plants under simulated N deposition. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 3400. |
| 16 | Gao Z B, Wang H Y, Lv X T, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on C∶N∶P stoichiometry in roots and leaves of four dominant plant species in a meadow steppe of Hulunbuir. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(1): 80-88. |
| 高宗宝, 王洪义, 吕晓涛, 等. 氮磷添加对呼伦贝尔草甸草原4种优势植物根系和叶片C∶N∶P化学计量特征的影响. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(1): 80-88. | |
| 17 | Zhang G D, Zhao C Y, Rong Z L, et al. Ecological stoichiometry of soils with different vegetation types in the middle part of the Qilian Mountains. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2019, 55(4): 533-540. |
| 张光德, 赵传燕, 戎战磊, 等. 祁连山中部不同植被类型土壤生态化学计量特征研究. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(4): 533-540. | |
| 18 | Yang D, Song L, Jin G. The soil C∶N∶P stoichiometry is more sensitive than the leaf C∶N∶P stoichiometry to nitrogen addition: A four-year nitrogen addition experiment in a Pinus koraiensis plantation. Plant and Soil, 2019, 442(1/2): 183-198. |
| 19 | Peng Y, Chen Q B, Wang C Y. Determination of organic carbon in different organs of rubber trees by using oven-heating method. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2009, 29(10): 13-16. |
| 彭懿, 陈秋波, 王春燕. 烘箱加热法测定橡胶树不同器官有机碳含量. 热带农业科学, 2009, 29(10): 13-16. | |
| 20 | Su J, Li X, Li X, et al. Effects of additional N on herbaceous species of desertified steppe in arid regions of China: A four-year field study. Ecological Research, 2013, 28(1): 21-28. |
| 21 | Shareef M, Gui D W, Zeng F J, et al. Nitrogen leaching, recovery efficiency, and cotton productivity assessments on desert-sandy soil under various application methods. Agricultural Water Management, 2019, 223: 105716. |
| 22 | Chen L, Liu L, Qin S, et al. Regulation of priming effect by soil organic matter stability over a broad geographic scale. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 5112. |
| 23 | Stevens C J, David T Ι, Storkey J. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition in terrestrial ecosystems: Its impact on plant communities and consequences across trophic levels. Functional Ecology, 2018, 32(7): 1757-1769. |
| 24 | Zhao H, He N, Xu L, et al. Variation in the nitrogen concentration of the leaf, branch, trunk, and root in vegetation in China. Ecological Indicators, 2019, 96: 496-504. |
| 25 | Han H G. Effecs of nitrogen deposition on nutrient use strategies and their responses to soil water availability. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2015. |
| 韩会阁. 氮沉降背景下植物养分利用策略及其对水分的响应. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2015. | |
| 26 | Guo Y, Du Q, Li G, et al. Soil phosphorus fractions and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi diversity following long-term grazing exclusion on semi-arid steppes in Inner Mongolia. Geoderma, 2016, 269: 79-90. |
| 27 | Su J Q, Li X R, Bao J T. Effects of nitrogen addition on soil physico-chemical properties and enzyme activities in desertified steppe. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(3): 664-670. |
| 苏洁琼, 李新荣, 鲍婧婷. 施氮对荒漠化草原土壤理化性质及酶活性的影响. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(3): 664-670. | |
| 28 | Su J Q, Li X R, Feng L, et al. Response of herbaceous vegetation to phosphorus fertilizer in steppe desert. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(1): 93-100. |
| 苏洁琼, 李新荣, 冯丽, 等. 草原化荒漠草本植物对人工施加磷素的响应. 生态学报, 2012, 32(1): 93-100. | |
| 29 | Li L, Gao X, Gui D, et al. Stoichiometry in aboveground and fine roots of Seriphidium koroviniiin in desert grassland in response to artificial nitrogen addition. Journal of Plant Research, 2017, 130(4): 689-697. |
| 30 | González-Paleo L, Pastor-Pastor A, Rajnoch G, et al. Mechanisms of nitrogen conservation at the leaf-level in annual and perennial desert forbs: Implications for perennial crops domestication. Flora, 2019, 252: 62-68. |
| 31 | Shi M, Fisher J B, Brzostek E R, et al. Carbon cost of plant nitrogen acquisition: Global carbon cycle impact from an improved plant nitrogen cycle in the Community Land Model. Global Change Biology, 2016, 22(3): 1299-1314. |
| 32 | Guo M L, Yao B Q, Shi G X, et al. Phylogenetic relationships of leaf carbon content and plasticity in alpine meadow plants. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(6): 1841-1848. |
| 郭美玲, 姚步青, 石国玺, 等. 高寒草甸植物叶片碳含量及其可塑性与系统发育的关系. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(6): 1841-1848. | |
| 33 | Dovrat G, Meron E, Shachak M, et al. Plant size is related to biomass partitioning and stress resistance in water-limited annual plant communities. Journal of Arid Environments, 2019, 165: 1-9. |
| 34 | Wang B, Gong J, Zhang Z, et al. Nitrogen addition alters photosynthetic carbon fixation, allocation of photoassimilates, and carbon partitioning of Leymus chinensis in a temperate grassland of Inner Mongolia. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2019, 279: 107743. |
| 35 | Pastor-Pastor A, González-Paleo L, Vilela A, et al. Age-related changes in nitrogen resorption and use efficiency in the perennial new crop Physaria mendocina (Brassicaceae). Industrial Crops and Products, 2015, 65: 227-232. |
| 36 | Pastor-Pastor A, Vilela A E, González-Paleo L. The root of the problem of perennials domestication: Is selection for yield changing key root system traits required for ecological sustainability? Plant and Soil, 2019, 435(1/2): 161-174. |
| 37 | Sistla S A, Appling A P, Lewandowska A M, et al. Stoichiometric flexibility in response to fertilization along gradients of environmental and organismal nutrient richness. Oikos, 2015, 124(7): 949-959. |
| 38 | Koerselman W, Meuleman A F M. The vegetation N∶P ratio: A new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation. The Journal of Applied Ecology, 1996, 33(6): 1441-1450. |
| 39 | Xu X Y, Cao J J, Yang L, et al. Effects of grazing and enclosure on foliar and soil stoichiometry of grassland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(5): 1349-1355. |
| 许雪贇, 曹建军, 杨淋, 等. 放牧与围封对青藏高原草地土壤和植物叶片化学计量学特征的影响. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(5): 1349-1355. | |
| 40 | Jin Y, Liang C Z, Cui L J. Effects of different nutrient additions on the stoichiometric characteristics of leaves of dominant plants in grassland communities. Journal of Northern Agriculture, 2019, 47(2): 59-65. |
| 金月, 梁存柱, 崔利剑. 不同养分添加对草地群落优势植物叶片化学计量特征的影响. 北方农业学报, 2019, 47(2): 59-65. | |
| 41 | Menge D N L, Field C B. Simulated global changes alter phosphorus demand in annual grassland. Global Change Biology, 2007, 13(12): 2582-2591. |
| 42 | Vitousek P M, Porder S, Houlton B Z, et al. Terrestrial phosphorus limitation: Mechanisms, implications and nitrogen-phosphorus interactions. Ecological Applications, 2010, 20(1): 5-15. |
| 43 | Phoenix G K, Booth R E, Leake J R, et al. Effects of enhanced nitrogen deposition and phosphorus limitation on nitrogen budgets of semi-natural grasslands. Global Change Biology, 2003, 9(9): 1309-1321. |
| 44 | Lv X T, Kong D L, Pan Q M, et al. Nitrogen and water availability interact to affect leaf stoichiometry in a semi-arid grassland. Oecologia, 2012, 168(2): 301-310. |
| [1] | 李静, 红梅, 闫瑾, 张宇晨, 梁志伟, 叶贺, 高海燕, 赵巴音那木拉. 短花针茅荒漠草原植被群落结构及生物量对水氮变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 38-48. |
| [2] | 杨乃瑞, 胡玉福, 舒向阳, 曾建, 张祥林, 申屠瑜程, 何佳, 程琪, 李杰, 李智, 余颖. 草地土壤C∶N∶P化学计量及微生物呼吸对氮沉降响应的Meta分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 1-12. |
| [3] | 雷玮倩, 胡玉福, 杨泽鹏, 何剑锋, 肖海华, 舒向阳, 阳帆, 李正青. 垦殖对川西北高寒草地土壤中不同磷组分含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(5): 36-45. |
| [4] | 李明, 秦洁, 红雨, 杨殿林, 周广帆, 王宇, 王丽娟. 氮素添加对贝加尔针茅草原土壤团聚体碳、氮和磷生态化学计量学特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 29-40. |
| [5] | 李东, 罗旭鹏, 曹广民, 吴琴, 卓玛措, 李惠梅, 杨永梅, 庞炳坤. 高寒草甸土壤异养呼吸对气候变化和氮沉降响应的模拟[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(7): 1-11. |
| [6] | 张峰,南志标,闫飞扬,李芳,段廷玉. AM真菌在草地生态系统碳汇中的重要作用[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(4): 191-200. |
| [7] | 于雯超,宋晓龙,修伟明,张贵龙,赵建宁,杨殿林. 氮素添加对贝加尔针茅草原凋落物分解的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(5): 49-60. |
| [8] | 曹丛丛,齐玉春,董云社,彭琴,刘欣超,孙良杰,贾军强,郭树芳,闫钟清. 氮沉降对陆地生态系统关键有机碳组分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(2): 323-332. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||