

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 54-63.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020246
收稿日期:2020-05-26
修回日期:2020-07-06
出版日期:2021-05-21
发布日期:2021-05-21
通讯作者:
肖波
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail:xiaobo@cau.edu.cn基金资助:
Fu-hai SUN1( ), Bo XIAO1,2(
), Bo XIAO1,2( ), Sheng-long LI1, Fang-fang WANG1
), Sheng-long LI1, Fang-fang WANG1
Received:2020-05-26
Revised:2020-07-06
Online:2021-05-21
Published:2021-05-21
Contact:
Bo XIAO
摘要:
为探明黄土高原不同发育阶段生物结皮对土壤导水和持水特性的影响,以裸沙和不同发育阶段生物结皮(藻结皮、藻-藓混生结皮、藓结皮)为研究对象, 分别采用定水头法和威尔科克斯法对其导水和持水特性进行了测定。结果表明, 在0~10 cm土层, 生物结皮显著降低了土壤饱和导水率, 藻结皮、藻-藓混生结皮和藓结皮土壤的饱和导水率较裸沙分别平均下降了59.3%,62.9%和27.6%;同时, 其水分入渗参数(初始入渗速率、稳定入渗速率、平均入渗速率和累积入渗量)较裸沙分别平均降低了37.7%、54.3%和18.4%, 延缓了土壤水分入渗过程;此外, 3种发育阶段生物结皮的田间持水量(体积含水量)较裸沙分别增加了0.97、1.10和0.70倍, 退水过程(0~120 h)的平均土壤体积含水量分别增加了1.14、1.40和0.74倍。与裸沙相比, 不同发育阶段的生物结皮均显著降低了土壤导水率, 同时提高了土壤持水性;其中藻-藓混生结皮对土壤导水和持水性能的影响大于藻结皮和藓结皮, 其主要原因可能是不同发育阶段生物结皮中非维管束植物和微生物的群落结构存在差异。综上, 随着生物结皮由藻向藓的发育演替, 其土壤导水性呈现先降低后增加的趋势, 而土壤持水性表现为先增加后降低的变化规律。
孙福海, 肖波, 李胜龙, 王芳芳. 黄土高原不同发育阶段生物结皮的导水和持水特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 54-63.
Fu-hai SUN, Bo XIAO, Sheng-long LI, Fang-fang WANG. Effects of biological soil crusts in different developmental stages on soil water permeability and water holding capacity in the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(6): 54-63.
土壤深度 Soil depth (cm) | 处理 Treatments | 结皮厚度 Biocrust thickness (mm) | 生物量 Biomass (g·cm-2) | 容重 Soil bulk density (g·cm-3) | 孔隙度 Soil porosity (%) | 砂粒含量 Sand content (%) | 粉粒含量 Silt content (%) | 黏粒含量 Clay content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~5 | CK | - | - | 1.57±0.03a | 40.87±1.08b | 95.52±0.40a | 4.48±0.40c | 0.00±0.00d |
| A | 3.24±0.72c | 0.08±0.03b | 1.52±0.05b | 42.70±1.76a | 79.57±0.45b | 20.32±0.45b | 0.11±0.00c | |
| B | 5.88±1.37b | 0.10±0.03b | 1.50±0.01b | 43.49±0.43a | 77.95±0.74c | 21.89±0.70a | 0.16±0.04b | |
| C | 8.06±0.74a | 0.15±0.05a | 1.48±0.05b | 44.27±1.83a | 77.39±0.31c | 22.03±0.30a | 0.58±0.01a | |
| 5~10 | CK | - | - | 1.61±0.04a | 39.24±1.45b | 95.57±1.85a | 4.42±1.86c | 0.01±0.01c |
| A | - | - | 1.54±0.02b | 42.08±0.79a | 89.78±0.58b | 10.20±0.58b | 0.02±0.01c | |
| B | - | - | 1.55±0.02b | 41.54±0.81a | 86.63±2.57c | 13.26±2.69a | 0.11±0.10a | |
| C | - | - | 1.61±0.01a | 39.39±0.25b | 96.14±0.98a | 3.76±0.95c | 0.10±0.03ab |
表1 不同发育阶段生物结皮和无结皮的土壤样品理化性质
Table 1 Soil physicochemical properties of the biocrusts in different developmental stages and bare soil
土壤深度 Soil depth (cm) | 处理 Treatments | 结皮厚度 Biocrust thickness (mm) | 生物量 Biomass (g·cm-2) | 容重 Soil bulk density (g·cm-3) | 孔隙度 Soil porosity (%) | 砂粒含量 Sand content (%) | 粉粒含量 Silt content (%) | 黏粒含量 Clay content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~5 | CK | - | - | 1.57±0.03a | 40.87±1.08b | 95.52±0.40a | 4.48±0.40c | 0.00±0.00d |
| A | 3.24±0.72c | 0.08±0.03b | 1.52±0.05b | 42.70±1.76a | 79.57±0.45b | 20.32±0.45b | 0.11±0.00c | |
| B | 5.88±1.37b | 0.10±0.03b | 1.50±0.01b | 43.49±0.43a | 77.95±0.74c | 21.89±0.70a | 0.16±0.04b | |
| C | 8.06±0.74a | 0.15±0.05a | 1.48±0.05b | 44.27±1.83a | 77.39±0.31c | 22.03±0.30a | 0.58±0.01a | |
| 5~10 | CK | - | - | 1.61±0.04a | 39.24±1.45b | 95.57±1.85a | 4.42±1.86c | 0.01±0.01c |
| A | - | - | 1.54±0.02b | 42.08±0.79a | 89.78±0.58b | 10.20±0.58b | 0.02±0.01c | |
| B | - | - | 1.55±0.02b | 41.54±0.81a | 86.63±2.57c | 13.26±2.69a | 0.11±0.10a | |
| C | - | - | 1.61±0.01a | 39.39±0.25b | 96.14±0.98a | 3.76±0.95c | 0.10±0.03ab |
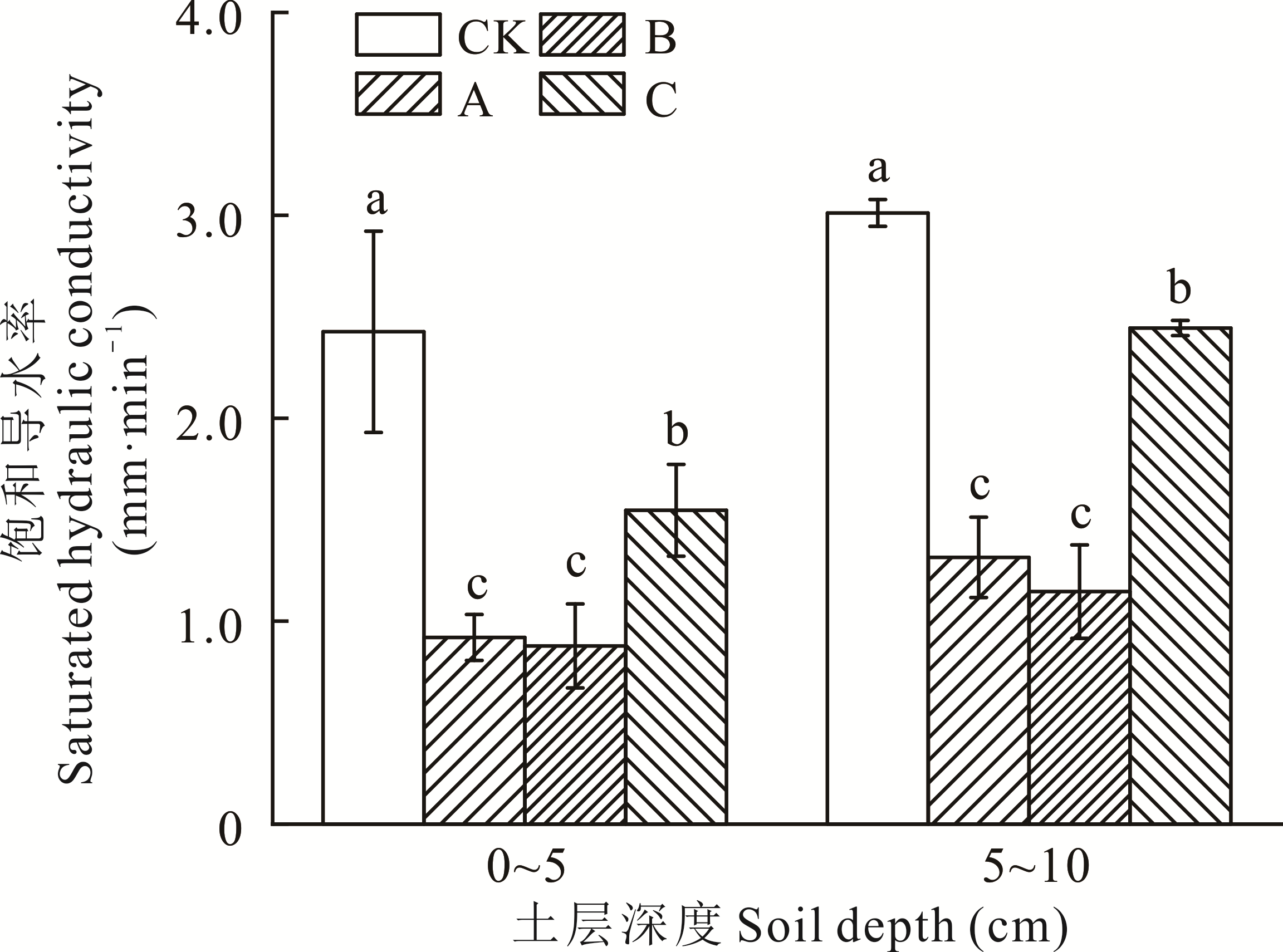
图1 不同发育阶段生物结皮和无结皮覆盖下不同深度土层的饱和导水率不同小写字母表示同一土层不同处理之间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments at the same soil depth (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 Saturated hydraulic conductivity of the biocrusts in different developmental stages and bare soil at different depths
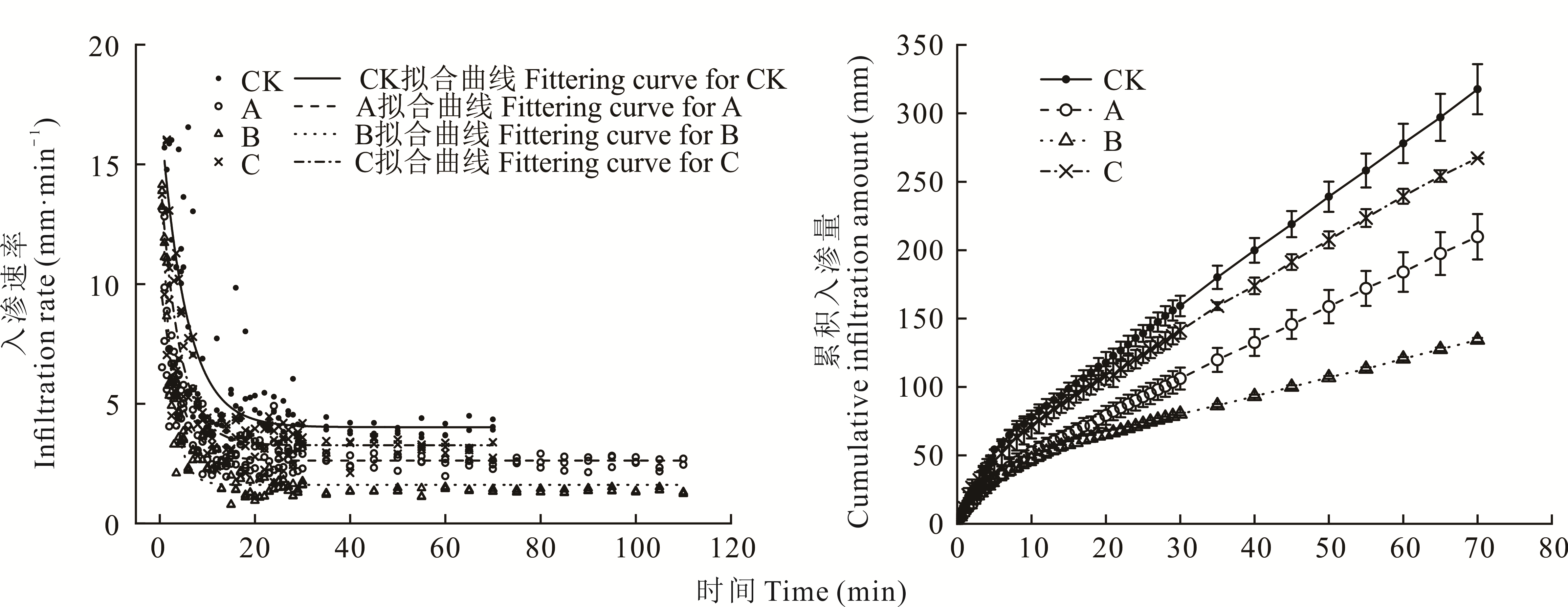
图2 不同发育阶段生物结皮和无结皮覆盖土壤的水分入渗过程与累积入渗量
Fig.2 Infiltration process and cumulative infiltration amount of the biocrusts in different developmental stages and bare soil
处理 Treatments | 初始入渗速率 Initial infiltration rate (mm·min-1) | 稳定入渗速率 Stable infiltration rate (mm·min-1) | 平均入渗速率 Average infiltration rate (mm·min-1) | 累积入渗量 Cumulative infiltration amount (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 12.65±2.10a | 4.02±0.40a | 4.53±0.26a | 277.96±14.37a |
| A | 7.10±1.15c | 2.58±0.13c | 2.84±0.21c | 184.01±14.50c |
| B | 8.56±0.70bc | 1.35±0.03d | 1.72±0.03d | 120.64±1.18d |
| C | 9.87±1.23b | 3.09±0.18b | 3.87±0.09b | 239.36±5.42b |
表2 不同发育阶段生物结皮覆盖土壤和无结皮的水分入渗参数
Table 2 Infiltration parameters of the biocrusts in different developmental stages and bare soil
处理 Treatments | 初始入渗速率 Initial infiltration rate (mm·min-1) | 稳定入渗速率 Stable infiltration rate (mm·min-1) | 平均入渗速率 Average infiltration rate (mm·min-1) | 累积入渗量 Cumulative infiltration amount (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 12.65±2.10a | 4.02±0.40a | 4.53±0.26a | 277.96±14.37a |
| A | 7.10±1.15c | 2.58±0.13c | 2.84±0.21c | 184.01±14.50c |
| B | 8.56±0.70bc | 1.35±0.03d | 1.72±0.03d | 120.64±1.18d |
| C | 9.87±1.23b | 3.09±0.18b | 3.87±0.09b | 239.36±5.42b |
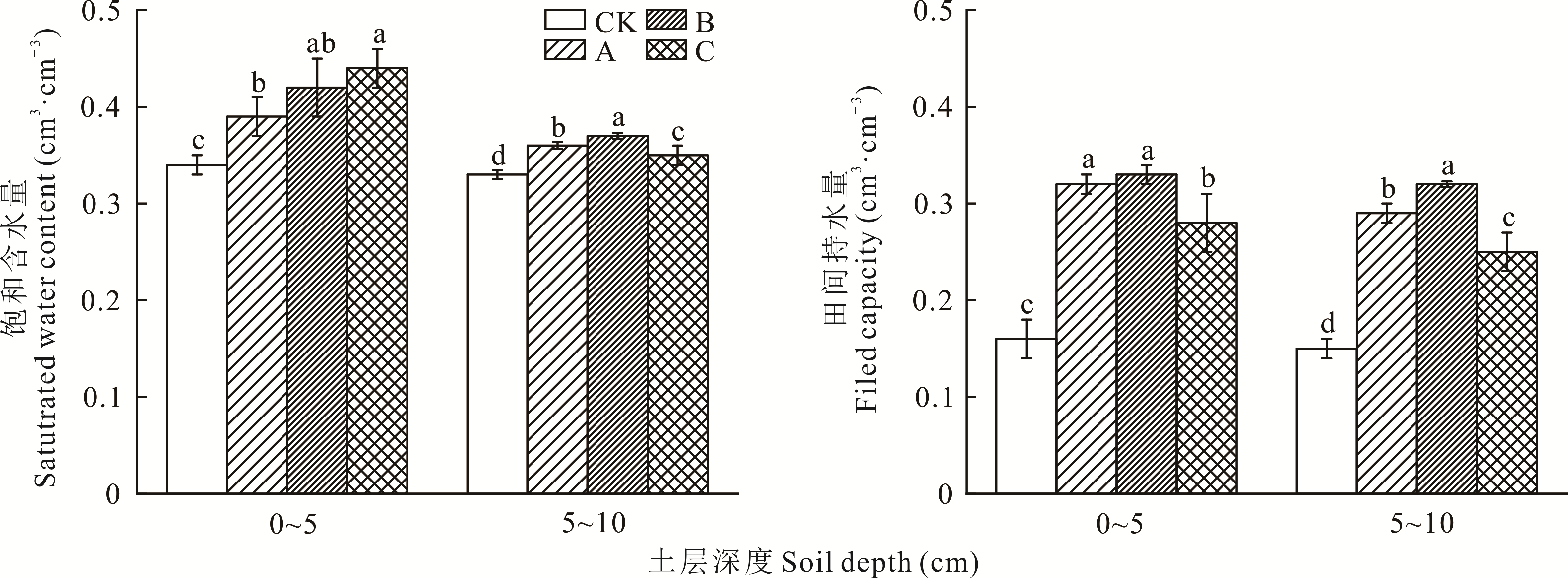
图4 不同发育阶段生物结皮和无结皮覆盖下0~10 cm土层的饱和含水量和田间持水量
Fig.4 Saturated water content and field capacity of the biocrusts in different developmental stages and bare soil at 0-10 cm depth
| 1 | Zhang Q D, Wei W, Chen L D, et al. Spatial variation of soil moisture species diversity patterns along a precipitation gradient in the grasslands of the Loess Plateau. Journal of Natural Resources, 2018, 33(8): 1351-1362. |
| 张钦弟, 卫伟, 陈利顶, 等. 黄土高原草地土壤水分和物种多样性沿降水梯度的分布格局. 自然资源学报, 2018, 33(8): 1351-1362. | |
| 2 | Li X Y. Mechanism of coupling, response and adaptation between soil, vegetation and hydrology in arid and semiarid regions. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2011, 41(12): 1721-1730. |
| 李小雁. 干旱地区土壤-植被-水文耦合、响应与适应机制. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 41(12): 1721-1730. | |
| 3 | Zhang Y W, Deng L, Yan W M, et al. Interaction of soil water storage dynamics and long-term natural vegetation succession on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena, 2016, 137: 52-60. |
| 4 | You S C, Di S C, Yuan Y. Study on soil field capacity estimation in the Loess Plateau region. Journal of Natural Resources, 2009, 24(3): 545-552. |
| 游松财, 邸苏闯, 袁晔. 黄土高原地区土壤田间持水量的计算. 自然资源学报, 2009, 24(3): 545-552. | |
| 5 | Kidron G J. The dual effect of sand-covered biocrusts on annual plants: Increasing cover but reducing individual plant biomass and fecundity. Catena, 2019, 182: 104120. |
| 6 | Yao X M, Xiao B, Kidron G J, et al. Respiration rate of moss-dominated biocrusts and their relationships with temperature and moisture in a semiarid ecosystem. Catena, 2019, 183: 104195. |
| 7 | Xiao B, Zhao Y G, Shao M A. Effects of biological soil crust on soil physicochemical properties in water-wind erosion crisscross region, northern Shannxi Province, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(11): 4664-4670. |
| 肖波, 赵允格, 邵明安. 陕北水蚀风蚀交错区两种生物结皮对土壤理化性质的影响. 生态学报, 2007, 27(11): 4664-4670. | |
| 8 | Chen N, Wang X P, Zhang Y F, et al. Ecohydrological effects of biological soil crust on the vegetation dynamics of restoration in a dryland ecosystem. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 563: 1068-1077. |
| 9 | Wang H, Zhang G H, Liu F, et al. Temporal variations in infiltration properties of biological crusts covered soils on the Loess Plateau of China. Catena, 2017, 159: 115-125. |
| 10 | Xiao B, Sun F H, Hu K L, et al. Biocrusts reduce surface soil infiltrability and impede soil water infiltration under tension and ponding conditions in dryland ecosystem. Journal of Hydrology, 2019, 568: 792-802. |
| 11 | Liu X, Zhou H F, Liu H, et al. Characteristic and numerical simulation of sandy soil infiltration under the different types of biological soil crusts. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(18): 5820-5826. |
| 刘翔, 周宏飞, 刘昊, 等. 不同类型生物土壤结皮覆盖下风沙土的入渗特征及模拟. 生态学报, 2016, 36(18): 5820-5826. | |
| 12 | Jiang Z Y, Li X Y, Wei J Q, et al. Contrasting surface soil hydrology regulated by biological and physical soil crusts for patchy grass in the high-altitude alpine steppe ecosystem. Geoderma, 2018, 326: 201-209. |
| 13 | Wang X P, Li X R, Xiao H L, et al. Effects of surface characteristics on infiltration patterns in an arid shrub desert. Hydrological Processes, 2010, 21(1): 72-79. |
| 14 | Williams J D, Dobrowolski J P, West N E. Microbiotic crust influence on unsaturated hydraulic conductivity. Arid Soil Research and Rehabilitation, 1999, 13(1): 145-154. |
| 15 | Wu L, Chen X G, Zhang G K, et al. Development and succession of artificial biological soil crusts and water holding characteristics of topsoil. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(3): 1138-1143. |
| 吴丽, 陈晓国, 张高科, 等. 人工生物结皮的发育演替及表土持水特性研究. 环境科学, 2014, 35(3): 1138-1143. | |
| 16 | Wang X P, Xiao H L, Zhang J G, et al. Hydrophysical characteristics of biological soil crust in an arid desert area. Advances in Water Science, 2006, 17(5): 592-598. |
| 王新平, 肖洪浪, 张景光, 等. 荒漠地区生物土壤结皮的水文物理特征分析. 水科学进展, 2006, 17(5): 592-598. | |
| 17 | Gypser S, Veste M, Fisher T, et al. Infiltration and water retention of biological soil crusts on reclaimed soils of former open-cast lignite mining in Brandenburg, north-east Germany. Journal of Hydrology and Hydromechanics, 2016, 64(1): 1-11. |
| 18 | Huang T T, Shi Y Z, Cao Q, et al. Soil erosion evaluation of Liudaogou catchment in the Loess Plateau during the past 30 years. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 18(1): 8-17. |
| 黄婷婷, 史扬子, 曹琦, 等. 黄土高原六道沟小流域近30年来土壤侵蚀变化评价. 中国水土保持科学, 2020, 18(1): 8-17. | |
| 19 | Li S L, Xiao B, Sun F H. Characteristics of water vapor sorption and condensation in biocrusts covered surface soil in arid and semiarid areas of the Loess Plateau, China. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(15): 111-119. |
| 李胜龙, 肖波, 孙福海. 黄土高原干旱半干旱区生物结皮覆盖土壤水汽吸附与凝结特征. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(15): 111-119. | |
| 20 | Li Y B, Li S L, Xiao B, et al. Study on soil water permeability and water flow characteristics under moss crusts covering in Loess Plateau. Arid Zone Research, 2020, 37(2): 390-399. |
| 李渊博, 李胜龙, 肖波, 等. 黄土高原藓结皮覆盖土壤导水性能和水流特征. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(2): 390-399. | |
| 21 | Xiao H, Liu G, Liu P L. Response of detachment rate of loess slope to hydrodynamic characteristic under concentrate flow condition. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(17): 106-111. |
| 肖海, 刘刚, 刘普灵. 集中流作用下黄土坡面剥蚀率对侵蚀动力学参数的响应. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(17): 106-111. | |
| 22 | Hu S J, Tian C Y, Song Y. Determination and calculation of soil permeability coefficient. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2011, 27(5): 68-72. |
| 胡顺军, 田长彦, 宋郁. 土壤渗透系数测定与计算方法的探讨. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(5): 68-72. | |
| 23 | Wang H, Zhang G H, Liu F, et al. Impact of biological crust on soil infiltration in hilly areas of Loess Plateau. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 29(5): 117-123. |
| 王浩, 张光辉, 刘法, 等. 黄土丘陵区生物结皮对土壤入渗的影响. 水土保持学报, 2015, 29(5): 117-123. | |
| 24 | Li X R, Tan H J, Hui R, et al. Researches in biological soil crust of China: A review. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(23): 2320-2334. |
| 李新荣, 谭会娟, 回嵘, 等. 中国荒漠与沙地生物土壤结皮研究. 科学通报, 2018, 63(23): 2320-2334. | |
| 25 | Pereira S, Zille A, Micheletti E, et al. Complexity of cyanobacterial exopolysaccharides: Composition, structures, inducing factors and putative genes involved in their biosynthesis and assembly. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2009, 33(5): 917-941. |
| 26 | Xiao B, Zhao Y G, Shao M A. Effects of biological soil crust on saturated hydraulic conductivity in water-wind erosion crisscross region, North of Shaanxi Province, China. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2007, 23(12): 35-40. |
| 肖波, 赵允格, 邵明安. 陕北水蚀风蚀交错区两种生物结皮对土壤饱和导水率的影响. 农业工程学报, 2007, 23(12): 35-40. | |
| 27 | Zhang J, Zhang Y M, Zhou X B, et al. The influence of biological soil crusts on dew deposition and characteristics of soil surface in Gurbantunggut desert. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(12): 6600-6608. |
| 张静, 张元明, 周晓兵, 等. 生物结皮影响下沙漠土壤表面凝结水的形成与变化特征. 生态学报, 2009, 29(12): 6600-6608. | |
| 28 | Rao B Q, Wu Y W, Li H, et al. Comparison studies on dew condensation of different development artificial crusts in Hopq desert. Journal of Soil and Water conservation, 2011, 25(6): 159-164. |
| 饶本强, 吴易雯, 李华, 等. 库布齐沙漠不同发育类型人工结皮对露水凝结作用的比较研究. 水土保持学报, 2011, 25(6): 159-164. | |
| 29 | Hu C X, Liu Y D. Extracellular carbohydrate polymers from five desert soil algae with different cohesion in the stabilization of fine sand grain. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2003, 54: 33-42. |
| 30 | De Philippis R, Vincenzini M. Outermost polysaccharidic investments of cyanobacteria: Nature, significance and possible applications. Recent Research Developments in Microbiology, 2003, 7: 13-22. |
| 31 | Wang G P, Xiao B, Li S L, et al. Surface roughness of biological soil crusts and its influencing factors in the water-wind erosion crisscross region on the Loess Plateau of China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(10): 3050-3056. |
| 王国鹏, 肖波, 李胜龙, 等. 黄土高原水蚀风蚀交错区生物结皮的地表粗糙度特征及其影响因素. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(10): 3050-3056. | |
| 32 | Ma H X, Zhang D G, Chen J, et al. Change in factors influencing soil water holding capacity at microsites along a slope transect in alpine meadow in the eastern Qilian Mountains. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(1): 28-37. |
| 马海霞, 张德罡, 陈瑾, 等. 祁连山东段高寒草甸土壤持水能力在小尺度不同坡面位置的分异特征. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 28-37. | |
| 33 | Gao L Q, Zhao Y G, Qin N Q, et al. Impact of biological soil crust on soil physical properties in the hilly Loess Plateau region, China. Journal of Natural Resources, 2012, 27(8): 1316-1326. |
| 高丽倩, 赵允格, 秦宁强, 等. 黄土丘陵区生物结皮对土壤物理属性的影响. 自然资源学报, 2012, 27(8): 1316-1326. | |
| 34 | Wu L, Zhang G K, Chen X G, et al. Development and succession of biological soil crusts and the changes of microbial biomasses. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(4): 1479-1485. |
| 吴丽, 张高科, 陈晓国, 等. 生物结皮的发育演替与微生物生物量变化. 环境科学, 2014, 35(4): 1479-1485. | |
| 35 | Raddadi N, Giacomucci L, Marasco R, et al. Bacterial polyextremotolerant bioemulsifiers from arid soils improve water retention capacity and humidity uptake in sandy soil. Microbial Cell Factories, 2018, 17: 83. |
| 36 | Mazor G, Kidron G J, Vonshak A, et al. The role of cyanobacterial expolysaccharides in structuring desert microbial crusts. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 1996, 21: 121-130. |
| 37 | Lan S B, Wu L, Zhang D L, et al. Successional stages of biological soil crusts and their microstructure variability in Shapotou region (China). Environmental Earth Sciences, 2012, 65(1): 77-88. |
| [1] | 马海霞, 张德罡, 陈瑾, 郭春秀, 董永平, 马源, 康玉坤, 陈璐, 杜凯, 陈建纲. 祁连山东段高寒草甸土壤持水能力在小尺度不同坡面位置的分异特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 28-37. |
| [2] | 吉雪花, 王露洁, 庞胜群. 蛇麻黄浸提液对苔藓结皮生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 187-193. |
| [3] | 宋丽萍, 罗珠珠, 李玲玲, 蔡立群, 张仁陟, 牛伊宁. 陇中黄土高原半干旱区苜蓿-作物轮作对土壤物理性质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(7): 12-20. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||