

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 131-139.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022065
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2022-02-14
修回日期:2022-04-20
出版日期:2023-02-20
发布日期:2022-12-01
通讯作者:
毛胜勇
作者简介:E-mail: maoshengyong@njau.edu.cn基金资助:
Tao ZHANG( ), Ying-yu MU, Wang-pan QI, Ji-you ZHANG, Sheng-yong MAO(
), Ying-yu MU, Wang-pan QI, Ji-you ZHANG, Sheng-yong MAO( )
)
Received:2022-02-14
Revised:2022-04-20
Online:2023-02-20
Published:2022-12-01
Contact:
Sheng-yong MAO
摘要:
本试验旨在探究SARA(亚急性瘤胃酸中毒)耐受性不同奶牛的瘤胃上皮形态及其功能差异。选取12头装有永久性瘤胃瘘管的泌乳中期荷斯坦奶牛,饲喂精粗比为4∶6的日粮,并根据瘤胃pH值的高低,分为SARA易感组(SUS,n=4)和SARA耐受组(TOL,n=4)。瘤胃上皮形态及功能分析结果显示,与TOL组比较,SUS组奶牛瘤胃上皮的棘突层和基底层厚度明显增厚(P<0.05),SUS组奶牛瘤胃上皮组织中参与挥发性脂肪酸(VFA)吸收的PAT1、MCT4和DRA基因表达量较TOL组显著下调(P<0.05),而H+转运载体NHE1、NHE2、NHE3和调节胞内pH的vH+ ATPase和Na+/K+ ATPase的表达量显著升高(P<0.05);对参与调控瘤胃VFA代谢的基因定量结果表明,SUS组PDHA1和SREBP2的表达量显著高于TOL组(P<0.05),而HMGCL-2的表达量显著降低(P<0.05);此外, SUS组CDK2、CDK6和Cyclin D1、Bad及Caspase-9等参与瘤胃上皮细胞增殖与凋亡的基因表达量显著高于TOL组(P<0.05)。结果说明,在相同日粮条件下,SUS组奶牛瘤胃上皮细胞调控游离脂肪酸吸收的基因表达量下调,造成瘤胃上皮对VFA的吸收能力下降,使得瘤胃内VFA累积和pH下降,并导致SUS组奶牛SARA的患病风险增高。
张涛, 牟英玉, 亓王盼, 张继友, 毛胜勇. 亚急性瘤胃酸中毒耐受性不同的奶牛瘤胃上皮形态及功能差异研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 131-139.
Tao ZHANG, Ying-yu MU, Wang-pan QI, Ji-you ZHANG, Sheng-yong MAO. Comparison of rumen epithelium morphology and function in dairy cows with differences in susceptibility for subacute ruminal acidosis[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(2): 131-139.
基因名称 Gene name | 引物片段 Primer sequence (5’-3’) | 基因登录号 Gene ID |
|---|---|---|
| 甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶 GAPDH | F: TGCCGCCTGGAGAAACC; R: CGCCTGCTTCACCACCTT | NM_001034034 |
| 钠-氢离子交换蛋白1 NHE1 | F: GAAAGACAAGCTCAACCGGTTT; R: GGAGCGCTCACCGGCTAT | NM_174833 |
| 钠-氢离子交换蛋白2 NHE2 | F: TTGTGCGATGACCATGAATAAGT; R: TGATGGTCGTGTAGGATTTCTGA | XM_604493 |
| 钠-氢离子交换蛋白3 NHE3 | F: AGCCTTCGTGCTCCTGACA; R: TGACCCCTATGGCCCTGTAC | AJ131764.1 |
| 氢离子ATP酶 vH + ATPase | F: TTTTATTGAACAAGAAGCCAATGA; R: GATTCATCAAATTGGACATCTGAA | NM_001076798 |
| 钠/钾离子ATP酶 Na+/K+ ATPase | F: CATCTTCCTCATCGGCATCA; R: ACGGTGGCCAGCAAACC | NM_001076798 |
| 钠/氢离子逆转运体 Na+/H+ antiporter | F: GAAAGACAAGCTCAACCGGTTT; R: GGAGCGCTCACCGGCTAT | U49432 |
| G蛋白偶联受体41 GPR41 | F: TTCCTCTCCTGCCTCTACACCATC; R: GCCGCTGCCAGGTTGATGAAG | NM_005304 |
| G蛋白偶联受体43 GPR43 | F: CCACAGACTGAACCAGACCA; R: CCAGGAACATCCCTAGTCCA | NP_001157256.1 |
| 单羧酸转运蛋白1 MCT1 | F: CGCGGGATTCTTTGGATTT; R: GTCCATCAGCGTTTCAAACAGTAC | NM_001037319 |
| 氨基酸转运蛋白 1 PAT1 | F: GGGCACTTCTTCGATGCTTCT; R: GTCGTGGACCGAGGCAAA | BC_123616 |
| 腺瘤下调蛋白 DRA | F: TGCACAAAGGGCCAAGAAA; R: GCTGGCAACCAAGATGCTATG | NM_001083676.1 |
| 单羧酸转运蛋白4 MCT4 | F: ATCTACGCGGGATTCTTTGGAT; R: AAGGTCCATCAGCGTTTCAAAC | NM_001109980 |
| 阴离子交换蛋白2 AE2 | F: AGCAGCAACAACCTGGAGT; R: GGTGAAACGGGAGACGAA | NM_001205664.1 |
| 酰基辅酶A合成酶 Acyl-CoA synthetase | F: CCGATCAGGTCCTGGTAGTGA; R: GCCTCCGCATGACTTTTCC | BC114698.1 |
丙酰基辅酶A羧化酶 Propionyl-CoA carboxylase | F: AGAATGGAAGATGCCCTGGAT; R: CCTCTCGAAGCAATGCGATAT | BC123876 |
丁酰基辅酶A合成酶 Butyrl-CoA synthetase | F: ACCCTTTGACATTCAGATCATTGAT; R: CCAATGTTTCCTTCCGTGTTG | BC109602 |
| 乳酸脱氢酶a LDHa | F: CCAACCCAGTGGATATTCTCACA; R: TCACACGGTGCTTGGGTAATC | BC142006 |
| 丙酮酸脱氢酶1 PDHA1 | F: CAGTTTGCTACTGCTGATCCTGAA; R: AGGTGGATCGTTGCAGTAAATGT | NM_001101046 |
| 三羟基三甲基辅酶A合成酶1 HMGCS-1 | F: AGGATACTCATCACTTGGCCAACT; R: CATGTTCCTTCGAAGAGGGAAT | AY581197 |
| 三羟基三甲基辅酶A合成酶2 HMGCS-2 | F: CCT GCTGCAATCACTGTCATG; R: TCTGTCCCGCCACCTCTTC | NM_001045883 |
| 3羟甲基3甲基戊二酰辅酶A裂合酶 HMGCL-2 | F: TGCAGATGGGAGTGAGTGTCA; R: GACGCCCCCTGTGCATAG | NM_001075132 |
| 胆固醇调节元件结合蛋白1 SREBP1 | F: CCAGCTGACAGCTCCATTGA; R: TGCGCGCCACAAGGA | NM_001113302.1 |
| 胆固醇调节元件结合蛋白2 SREBP2 | F: CTGGCTCCAGGGAGATGAC; R: GCTCTGCAGGTGTGGAAGAC | XM_002687950.1 |
| 3-羟基丁酸脱氢酶1 BDH1 | F: GACTGCCACCACTCCCTACAC; R: TCCGCAGCCACCAGTAGTAGT | NM_001034600 |
| 周期蛋白依赖性激酶2 CDK 2 | F: CTCACTGATCTTGTCTGGTT; R: TAAGCAACGACTAAGAGGAG | NM_001014934 |
| 周期蛋白依赖性激酶4 CDK 4 | F: ACTCTGGTATCGTGCTCCAGAAG; R: CAGAAGAGAGGCTTTCGACGAA | NM_001037594 |
| 周期蛋白依赖性激酶6 CDK 6 | F: TTCGTGGAAGTTCAGATGTC; R: TGCCTTGTTCATCAATGTCT | NM_001192301 |
| 细胞周期蛋白E1 Cyclin E1 | F: TTGACAGGACTGTGAGAAGC; R: TTCAGTACAGGCAGTGGCGA | XM_612960 |
| 细胞周期蛋白D1 Cyclin D1 | F: GCACTTCCTCTCCAAGATGC; R: GTCAGGCGGTGATAGGAGAG | NM_001046273 |
| B淋巴细胞瘤-2基因相关启动子 Bad | F: GCAGGCCTTATGCAAAACGA; R: CTTTGGGTCAGACCTCAGTCTTC | BC 103323.1 |
| B淋巴细胞瘤-2基因关联蛋白 Bax | F: GCTGTGGACACAGACTCTC; R: CTGATCAACTGGGCACCTT | NM_173894.1 |
| B淋巴细胞瘤-2基因 Bcl-2 | F: AGGTTGGTAACCGGACCCTA; R: TTCCTGCCTGTCCTCGAATG | NM_001075417-2 |
| 半胱氨酸蛋白酶3 Caspase-3 | F: CAGCGTCGTAGCTGAACGTAA; R: ATCGACAGGCCATGCCAGTAT | NM_001077840.1 |
| 半胱氨酸蛋白酶9 Caspase-9 | F: AGCAAATGGTCCAGGCTTTG; R: ATTCTCTCGACGGACACAGG | NM_001205504.1 |
表1 瘤胃上皮细胞功能基因实时定量PCR引物序列
Table 1 The primer sequences of rumen epithelium cell for qRT-PCR
基因名称 Gene name | 引物片段 Primer sequence (5’-3’) | 基因登录号 Gene ID |
|---|---|---|
| 甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶 GAPDH | F: TGCCGCCTGGAGAAACC; R: CGCCTGCTTCACCACCTT | NM_001034034 |
| 钠-氢离子交换蛋白1 NHE1 | F: GAAAGACAAGCTCAACCGGTTT; R: GGAGCGCTCACCGGCTAT | NM_174833 |
| 钠-氢离子交换蛋白2 NHE2 | F: TTGTGCGATGACCATGAATAAGT; R: TGATGGTCGTGTAGGATTTCTGA | XM_604493 |
| 钠-氢离子交换蛋白3 NHE3 | F: AGCCTTCGTGCTCCTGACA; R: TGACCCCTATGGCCCTGTAC | AJ131764.1 |
| 氢离子ATP酶 vH + ATPase | F: TTTTATTGAACAAGAAGCCAATGA; R: GATTCATCAAATTGGACATCTGAA | NM_001076798 |
| 钠/钾离子ATP酶 Na+/K+ ATPase | F: CATCTTCCTCATCGGCATCA; R: ACGGTGGCCAGCAAACC | NM_001076798 |
| 钠/氢离子逆转运体 Na+/H+ antiporter | F: GAAAGACAAGCTCAACCGGTTT; R: GGAGCGCTCACCGGCTAT | U49432 |
| G蛋白偶联受体41 GPR41 | F: TTCCTCTCCTGCCTCTACACCATC; R: GCCGCTGCCAGGTTGATGAAG | NM_005304 |
| G蛋白偶联受体43 GPR43 | F: CCACAGACTGAACCAGACCA; R: CCAGGAACATCCCTAGTCCA | NP_001157256.1 |
| 单羧酸转运蛋白1 MCT1 | F: CGCGGGATTCTTTGGATTT; R: GTCCATCAGCGTTTCAAACAGTAC | NM_001037319 |
| 氨基酸转运蛋白 1 PAT1 | F: GGGCACTTCTTCGATGCTTCT; R: GTCGTGGACCGAGGCAAA | BC_123616 |
| 腺瘤下调蛋白 DRA | F: TGCACAAAGGGCCAAGAAA; R: GCTGGCAACCAAGATGCTATG | NM_001083676.1 |
| 单羧酸转运蛋白4 MCT4 | F: ATCTACGCGGGATTCTTTGGAT; R: AAGGTCCATCAGCGTTTCAAAC | NM_001109980 |
| 阴离子交换蛋白2 AE2 | F: AGCAGCAACAACCTGGAGT; R: GGTGAAACGGGAGACGAA | NM_001205664.1 |
| 酰基辅酶A合成酶 Acyl-CoA synthetase | F: CCGATCAGGTCCTGGTAGTGA; R: GCCTCCGCATGACTTTTCC | BC114698.1 |
丙酰基辅酶A羧化酶 Propionyl-CoA carboxylase | F: AGAATGGAAGATGCCCTGGAT; R: CCTCTCGAAGCAATGCGATAT | BC123876 |
丁酰基辅酶A合成酶 Butyrl-CoA synthetase | F: ACCCTTTGACATTCAGATCATTGAT; R: CCAATGTTTCCTTCCGTGTTG | BC109602 |
| 乳酸脱氢酶a LDHa | F: CCAACCCAGTGGATATTCTCACA; R: TCACACGGTGCTTGGGTAATC | BC142006 |
| 丙酮酸脱氢酶1 PDHA1 | F: CAGTTTGCTACTGCTGATCCTGAA; R: AGGTGGATCGTTGCAGTAAATGT | NM_001101046 |
| 三羟基三甲基辅酶A合成酶1 HMGCS-1 | F: AGGATACTCATCACTTGGCCAACT; R: CATGTTCCTTCGAAGAGGGAAT | AY581197 |
| 三羟基三甲基辅酶A合成酶2 HMGCS-2 | F: CCT GCTGCAATCACTGTCATG; R: TCTGTCCCGCCACCTCTTC | NM_001045883 |
| 3羟甲基3甲基戊二酰辅酶A裂合酶 HMGCL-2 | F: TGCAGATGGGAGTGAGTGTCA; R: GACGCCCCCTGTGCATAG | NM_001075132 |
| 胆固醇调节元件结合蛋白1 SREBP1 | F: CCAGCTGACAGCTCCATTGA; R: TGCGCGCCACAAGGA | NM_001113302.1 |
| 胆固醇调节元件结合蛋白2 SREBP2 | F: CTGGCTCCAGGGAGATGAC; R: GCTCTGCAGGTGTGGAAGAC | XM_002687950.1 |
| 3-羟基丁酸脱氢酶1 BDH1 | F: GACTGCCACCACTCCCTACAC; R: TCCGCAGCCACCAGTAGTAGT | NM_001034600 |
| 周期蛋白依赖性激酶2 CDK 2 | F: CTCACTGATCTTGTCTGGTT; R: TAAGCAACGACTAAGAGGAG | NM_001014934 |
| 周期蛋白依赖性激酶4 CDK 4 | F: ACTCTGGTATCGTGCTCCAGAAG; R: CAGAAGAGAGGCTTTCGACGAA | NM_001037594 |
| 周期蛋白依赖性激酶6 CDK 6 | F: TTCGTGGAAGTTCAGATGTC; R: TGCCTTGTTCATCAATGTCT | NM_001192301 |
| 细胞周期蛋白E1 Cyclin E1 | F: TTGACAGGACTGTGAGAAGC; R: TTCAGTACAGGCAGTGGCGA | XM_612960 |
| 细胞周期蛋白D1 Cyclin D1 | F: GCACTTCCTCTCCAAGATGC; R: GTCAGGCGGTGATAGGAGAG | NM_001046273 |
| B淋巴细胞瘤-2基因相关启动子 Bad | F: GCAGGCCTTATGCAAAACGA; R: CTTTGGGTCAGACCTCAGTCTTC | BC 103323.1 |
| B淋巴细胞瘤-2基因关联蛋白 Bax | F: GCTGTGGACACAGACTCTC; R: CTGATCAACTGGGCACCTT | NM_173894.1 |
| B淋巴细胞瘤-2基因 Bcl-2 | F: AGGTTGGTAACCGGACCCTA; R: TTCCTGCCTGTCCTCGAATG | NM_001075417-2 |
| 半胱氨酸蛋白酶3 Caspase-3 | F: CAGCGTCGTAGCTGAACGTAA; R: ATCGACAGGCCATGCCAGTAT | NM_001077840.1 |
| 半胱氨酸蛋白酶9 Caspase-9 | F: AGCAAATGGTCCAGGCTTTG; R: ATTCTCTCGACGGACACAGG | NM_001205504.1 |
项目 Item | 均值Mean | 标准误差 SEM | P 值 P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 易感组SUS | 耐受组TOL | |||
| 角质层 Corneum | 20.19 | 19.24 | 1.64 | 0.568 |
| 颗粒层 Stratum | 15.23 | 14.42 | 0.88 | 0.360 |
| 棘突层和基底层 Spinous and basale | 137.04 | 93.13 | 11.06 | 0.001 |
| 总厚度 Total thickness | 172.46 | 126.79 | 12.60 | 0.001 |
表2 SUS和TOL组奶牛瘤胃上皮厚度变化
Table 2 The changes in rumen epithelial thickness between the SUS (susceptible) and TOL (tolerant) groups (μm)
项目 Item | 均值Mean | 标准误差 SEM | P 值 P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 易感组SUS | 耐受组TOL | |||
| 角质层 Corneum | 20.19 | 19.24 | 1.64 | 0.568 |
| 颗粒层 Stratum | 15.23 | 14.42 | 0.88 | 0.360 |
| 棘突层和基底层 Spinous and basale | 137.04 | 93.13 | 11.06 | 0.001 |
| 总厚度 Total thickness | 172.46 | 126.79 | 12.60 | 0.001 |

图2 瘤胃上皮细胞参与离子交换及VFA吸收相关基因相对表达量*P<0.05, **P<0.01.下同The same below.
Fig.2 The relative expression levels of ion exchange and VFA absorption-related gene in rumen epithelial cells
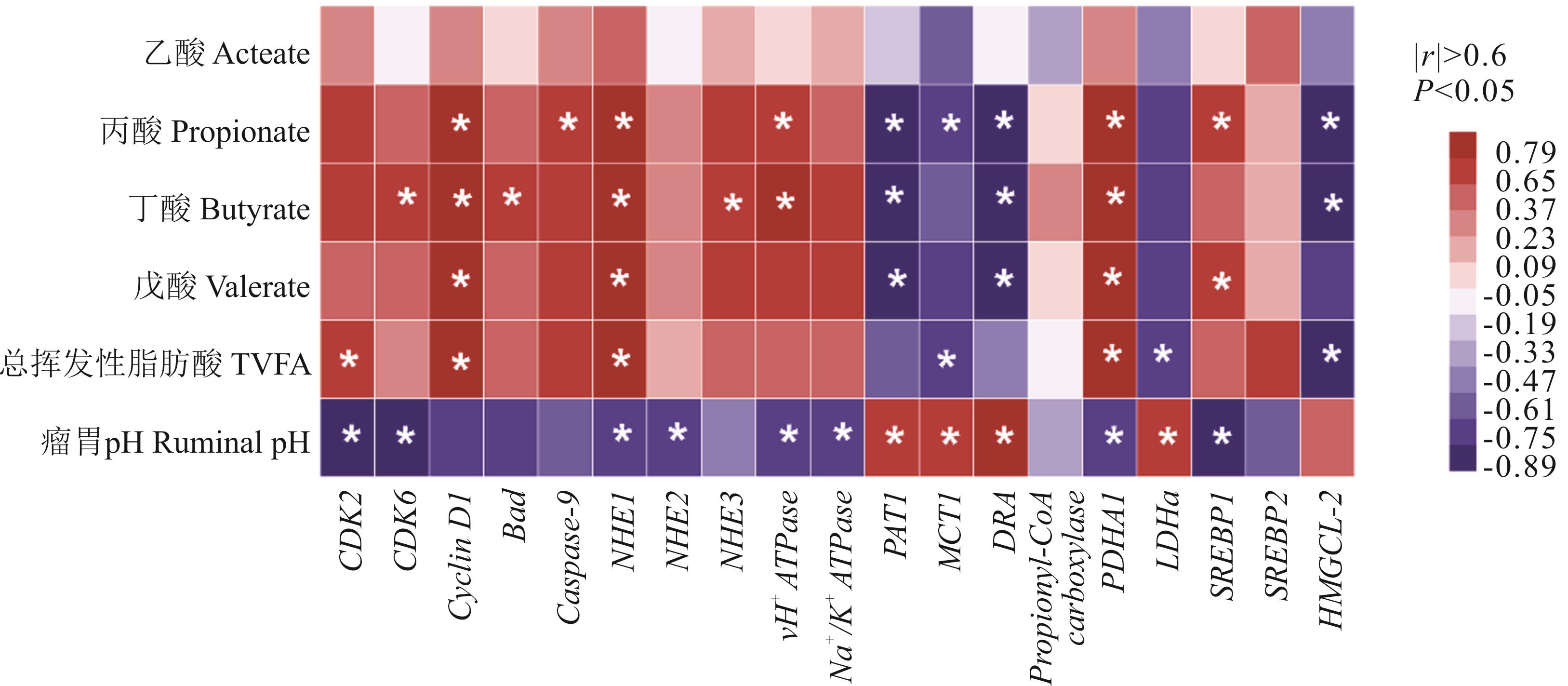
图5 瘤胃发酵参数与瘤胃上皮功能基因相对表达量的相关性红色表示正相关,蓝色表示负相关,*: |r|>0.6, P<0.05。Red means positive correlation, blue means negative correlation.
Fig.5 Correlation between rumen fermentation parameters and relative expression of epithelial functional genes
| 1 | Wang H R. Mechanism analysis and nutritional strategies for prevention of sub-acute ruminal acidosis in ruminants. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2014, 26(10): 3140-3148. |
| 王洪荣. 反刍动物瘤胃酸中毒机制解析及其营养调控措施. 动物营养学报, 2014, 26(10): 3140-3148. | |
| 2 | Oetzel G R. Diagnosis and management of subacute ruminal acidosis in dairy herds. Veterinary Clinics of North America: Food Animal Practice, 2017, 33(3): 463-480. |
| 3 | Plaizier J C, Li S, Danscher A M, et al. Changes in microbiota in rumen digesta and feces due to a grain-based subacute ruminal acidosis (SARA) challenge. Microbial Ecology, 2017, 74(2): 485-495. |
| 4 | Plaizier J C, Li S, Tun H M, et al. Nutritional models of experimentally-induced subacute ruminal acidosis (SARA) differ in their impact on rumen and hindgut bacterial communities in dairy cows. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2016, 7: 2128. |
| 5 | Pourazad P, Khiaosa-Ard R, Qumar M, et al. Transient feeding of a concentrate-rich diet increases the severity of subacute ruminal acidosis in dairy cattle. Journal of Animal Science, 2016, 94(2): 726-738. |
| 6 | Humer E, Ghareeb K, Harder H, et al. Peripartal changes in reticuloruminal pH and temperature in dairy cows differing in the susceptibility to subacute rumen acidosis. Journal of Dairy Science, 2015, 98(12): 8788-8799. |
| 7 | Jing L, Dewanckele L, Vlaeminck B, et al. Susceptibility of dairy cows to subacute ruminal acidosis is reflected in milk fatty acid proportions, with C18:1 trans-10 as primary and C15:0 and C18:1 trans-11 as secondary indicators. Journal of Dairy Science, 2018, 101(11): 9827-9840. |
| 8 | Khiaosa-ard R, Pourazad P, Aditya S, et al. Factors related to variation in the susceptibility to subacute ruminal acidosis in early lactating Simmental cows fed the same grain-rich diet. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2018, 238: 111-122. |
| 9 | Yan L, Zhang B, Shen Z. Dietary modulation of the expression of genes involved in short-chain fatty acid absorption in the rumen epithelium is related to short-chain fatty acid concentration and pH in the rumen of goats. Journal of Dairy Science, 2014, 97(9): 5668-5675. |
| 10 | Gao X, Oba M. Characteristics of dairy cows with a greater or lower risk of subacute ruminal acidosis: Volatile fatty acid absorption, rumen digestion, and expression of genes in rumen epithelial cells. Journal of Dairy Science, 2016, 99(11): 8733-8745. |
| 11 | Zhang T, Mu Y Y, Qi W P, et al. Analysis of plasma and milk fatty acid and metabolite composition in lactating dairy cows with differing tolerance to subacute ruminal acidosis. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(7): 101-110. |
| 张涛, 牟英玉, 亓王盼,等. 亚急性瘤胃酸中毒耐受性不同的奶牛血浆和乳中脂肪酸及代谢物组成分析. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 101-110. | |
| 12 | Steele M A, Croom J, Kahler M, et al. Bovine rumen epithelium undergoes rapid structural adaptations during grain-induced subacute ruminal acidosis. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 2011, 300(6): 1515-1523. |
| 13 | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-△△CT method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| 14 | Zhang T, Mu Y Y, Zhang R Y, et al. Responsive changes of rumen microbiome and metabolome in dairy cows with different susceptibility to subacute ruminal acidosis. Animal Nutrition, 2021, 8(1): 331-340. |
| 15 | Zhao C X, Liu G W, Li X B, et al. Inflammatory mechanism of rumenitis in dairy cows with subacute ruminal acidosis. BMC Veterinary Research, 2018, 14(1): 135-143. |
| 16 | Humer E, Aditya S, Zebeli Q. Innate immunity and metabolomic responses in dairy cows challenged intramammarily with lipopolysaccharide after subacute ruminal acidosis. Animal, 2018, 12(12): 2551-2560. |
| 17 | Penner G B, Aschenbach J R, Gabel G, et al. Epithelial capacity for apical uptake of short chain fatty acids is a key determinant for intraruminal pH and the susceptibility to subacute ruminal acidosis in sheep. Journal of Nutrition, 2009, 139(9): 1714-1720. |
| 18 | Gao X, Oba M. Relationship of severity of subacute ruminal acidosis to rumen fermentation, chewing activities, sorting behavior, and milk production in lactating dairy cows fed a high-grain diet. Journal of Dairy Science, 2014, 97(5): 3006-3016. |
| 19 | Nasrollahi S M, Zali A, Ghorbani G R, et al. Variability in susceptibility to acidosis among high producing mid-lactation dairy cows is associated with rumen pH, fermentation, feed intake, sorting activity, and milk fat percentage. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2017, 228: 72-82. |
| 20 | Graham C, Simmons N L. Functional organization of the bovine rumen epithelium. The American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 2005, 288(1): 173-181. |
| 21 | Gao J, Qi Z L. Absorption and metabolism of short chain fatty acids in ruminal epithelium. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2018, 30(4): 1271-1278. |
| 高景, 齐智利. 瘤胃上皮短链脂肪酸的吸收和代谢. 动物营养学报, 2018, 30(4): 1271-1278. | |
| 22 | Petri R M, Wetzels S U, Qumar M, et al. Adaptive responses in short-chain fatty acid absorption, gene expression, and bacterial community of the bovine rumen epithelium recovered from a continuous or transient high-grain feeding. Journal of Dairy Science, 2019, 102(6): 5361-5378. |
| 23 | Mirzaei-Alamouti H, Moradi S, Shahalizadeh Z, et al. Both monensin and plant extract alter ruminal fermentation in sheep but only monensin affects the expression of genes involved in acid-base transport of the ruminal epithelium. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2016, 219: 132-143. |
| 24 | Graham C, Gatherar I, Haslam I, et al. Expression and localization of monocarboxylate transporters and sodium/proton exchangers in bovine rumen epithelium. The American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 2007, 292(2): 997-1007. |
| 25 | Schurmann B. Functional adaptation of the ruminal epithelium. Saskatioon: University of Saskatchewan, 2013. |
| 26 | Sehested J, Diernaes L, Moller P D, et al. Ruminal transport and metabolism of short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) in vitro: Effect of SCFA chain length and pH. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 1999, 123(4): 359-368. |
| 27 | Ash R, Baird G D. Activation of volatile fatty acids in bovine liver and rumen epithelium. Evidence for control by autoregulation. Biochemical Journal, 1973, 136(2): 311-319. |
| 28 | Martinez-Outschoorn U E, Lin Z, Whitaker-Menezes D, et al. Ketone bodies and two-compartment tumor metabolism: Stromal ketone production fuels mitochondrial biogenesis in epithelial cancer cells. Cell Cycle, 2012, 11(21): 3956-3963. |
| [1] | 张涛, 牟英玉, 亓王盼, 郭长征, 张继友, 毛胜勇. 亚急性瘤胃酸中毒耐受性不同的奶牛血浆和乳中脂肪酸及代谢物组成分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 101-110. |
| [2] | 亓王盼, 牟英玉, 张涛, 张继友, 毛胜勇. 亚急性瘤胃酸中毒对泌乳奶牛血浆生化指标及代谢组的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 141-150. |
| [3] | 刘祥圣, 邓波波, 王阔鹏, 封丽梅, 赵国琦, 林淼. 常规与非常规粗饲料在奶牛瘤胃中的降解特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 190-197. |
| [4] | 董文科, 陈春艳, 马晖玲. 转OvBAN/bar双价基因的紫花苜蓿对虫蚀及除草剂的耐受性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 159-167. |
| [5] | 任伟忠, 高艳霞, 李秋凤, 曹玉凤, 李建国. 全株玉米青贮、谷草和羊草组合全混合日粮饲喂干奶前期奶牛对其围产期生产性能和血液生化及免疫指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 124-136. |
| [6] | 孙大明, 李弘伟, 毛胜勇, 刘军花. 断奶前补饲不同直/支链淀粉比开食料对羔羊瘤胃上皮发育的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 197-203. |
| [7] | 陈雅坤,王建平,卜登攀,刘宁,刘威. 复合酶制剂对瘤胃发酵及泌乳早期奶牛生产性能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 170-177. |
| [8] | 占今舜, 陈小连, 詹康, 苏效双, 赵国琦. 苜蓿黄酮对脂多糖诱导下奶牛乳腺上皮细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(1): 187-194. |
| [9] | 占今舜, 邬彩霞, 刘明美, 苏效双, 詹康, 赵国琦. 饲粮添加苜蓿黄酮对奶牛瘤胃菌群的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(7): 82-89. |
| [10] | 刘军花, 朱伟云, 毛胜勇. 高谷物日粮促进山羊瘤胃上皮单羧酸转运蛋白1及钠钾ATP酶mRNA的表达[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(2): 95-101. |
| [11] | 耿雅丽, 田平, 罗燕文, 华灿枫, 陶诗煜, 田靖, 倪迎冬. 高精料对泌乳奶山羊瘤胃上皮氧化应激和胆固醇代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(11): 94-103. |
| [12] | 张春刚, 苏效双, 刘光磊, 吴天佑, 占今舜, 赵国琦. 复方中草药添加剂对荷斯坦奶牛免疫和泌乳性能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(11): 104-112. |
| [13] | 李媛, 刁其玉, 孔路欣, 张婷婷, 张博, 周朝龙, 屠焰. 辣木在奶牛瘤胃中的降解特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(10): 140-148. |
| [14] | 殷雨洋, 刘玉洁, 张瑞阳, 朱伟云, 毛胜勇. 高精料日粮下添加阿卡波糖对奶牛瘤胃及后肠发酵的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(6): 198-203. |
| [15] | 朱晓艳, 赵诚, 史莹华, 王成章, 姚国磊, 吕先召, 韩康康, 李栋栋. 苜蓿青贮料替代苜蓿青干草对奶牛生产性能及乳品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(5): 156-164. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||