

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (1): 33-49.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023074
赵吉美1,2( ), 胡夏嵩3(
), 胡夏嵩3( ), 付江涛4, 刘昌义3, 邢光延1, 杨馥铖3, 张培豪3, 周喆3
), 付江涛4, 刘昌义3, 邢光延1, 杨馥铖3, 张培豪3, 周喆3
收稿日期:2023-03-07
修回日期:2023-05-31
出版日期:2024-01-20
发布日期:2023-11-23
通讯作者:
胡夏嵩
作者简介:E-mail: huxiasong@tsinghua.org.cn基金资助:
Ji-mei ZHAO1,2( ), Xia-song HU3(
), Xia-song HU3( ), Jiang-tao FU4, Chang-yi LIU3, Guang-yan XING1, Fu-cheng YANG3, Pei-hao ZHANG3, Zhe ZHOU3
), Jiang-tao FU4, Chang-yi LIU3, Guang-yan XING1, Fu-cheng YANG3, Pei-hao ZHANG3, Zhe ZHOU3
Received:2023-03-07
Revised:2023-05-31
Online:2024-01-20
Published:2023-11-23
Contact:
Xia-song HU
摘要:
为研究黄河上游巨型滑坡区植被分布类型及其根系力学强度特征,以位于黄河上游席芨滩巨型滑坡区为研究区,通过野外植被样方调查、制取根系和土体试样以及室内开展单根拉伸试验等方法,探讨了区内3种优势草本植物醉马草、异针茅、冷地早熟禾的单根抗拉力学特征,以及植物生长区土体营养元素特征对植物分布的影响。结果表明:席芨滩滑坡区以草本植物为主,灌木零星分布,物种数呈“驼峰状分布”;通过采用冗余分析得到,草本植物生长区土壤含水量(P<0.01,F=12.7)、pH值(P<0.05,F=8.0)和全氮(P<0.05,F=4.5)对植物群落生长和分布特征影响较为显著。进一步研究表明,同种植物生长位置不同,则其单根抗拉力学强度亦不同,而相同位置处的不同种植物,相应地其单根力学强度亦表现出不同的特征。这种特征表现在分布于滑坡中部的冷地早熟禾的平均单根抗拉力和平均抗拉强度均显著高于生长在滑坡前缘和后壁位置的;分布在滑坡中部位置处的3种优势草本植物,其平均单根抗拉力和平均单根抗拉强度由大至小依次为异针茅(9.10 N,80.29 MPa)、冷地早熟禾(7.51 N,49.78 MPa)、醉马草(6.69 N,34.82 MPa)。本研究结果可为科学防治席芨滩滑坡分布区边坡水土流失、浅层滑坡等坡面水土灾害提供理论依据和实际指导。
赵吉美, 胡夏嵩, 付江涛, 刘昌义, 邢光延, 杨馥铖, 张培豪, 周喆. 黄河上游巨型滑坡区植被分布及其根系力学强度特征[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 33-49.
Ji-mei ZHAO, Xia-song HU, Jiang-tao FU, Chang-yi LIU, Guang-yan XING, Fu-cheng YANG, Pei-hao ZHANG, Zhe ZHOU. Vegetation distribution patterns and root mechanical properties of selected plant species on the Xijitan giant landslide in the upper reaches of the Yellow River[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(1): 33-49.
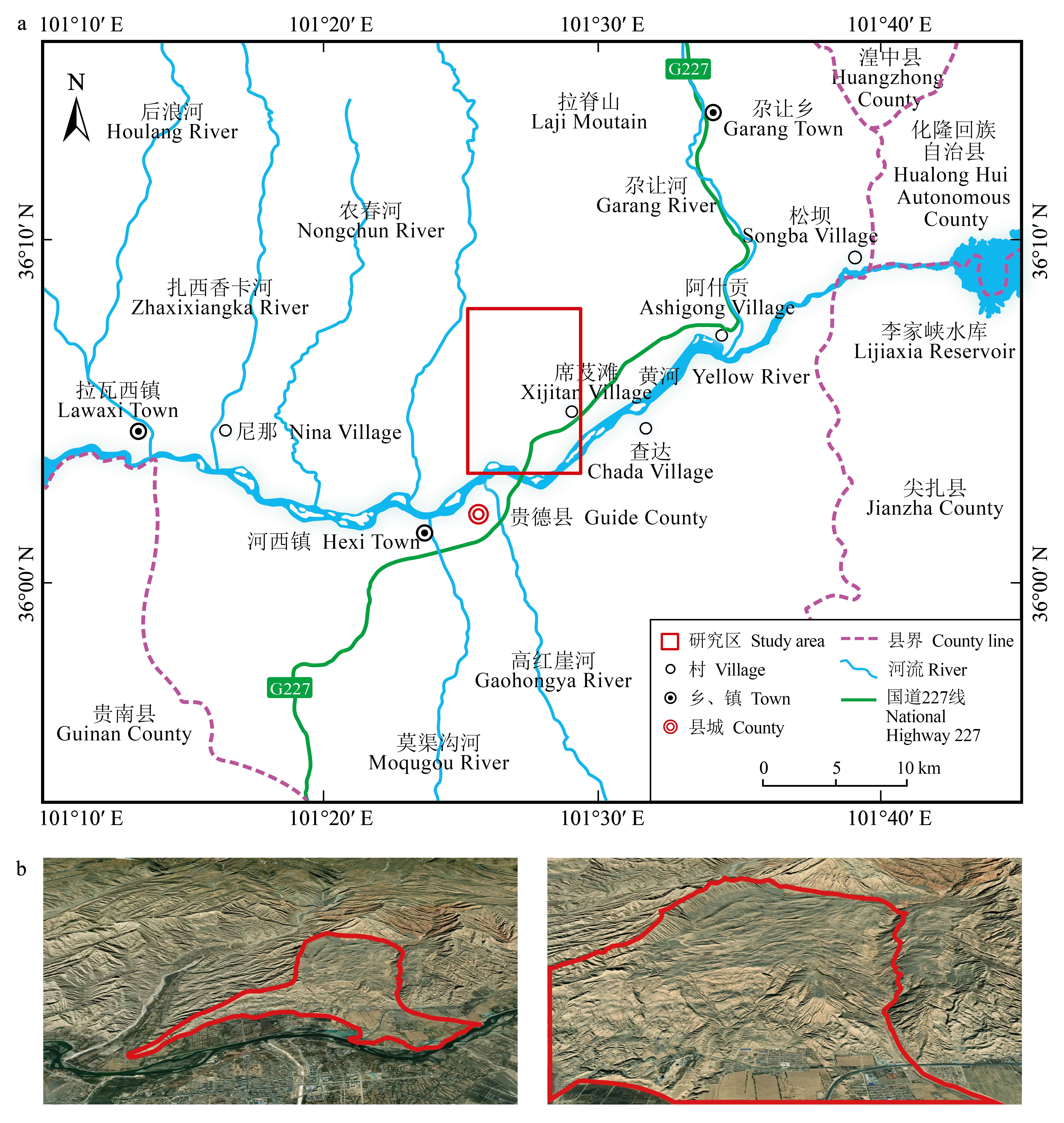
图1 研究区位置及席芨滩滑坡分布区a: 研究区及席芨滩滑坡位置Location of study area and Xijitan landslide; b: 席芨滩滑坡分布区Xijitan landslide distribution area.
Fig.1 The study area location and Xijitan landslide distribution area
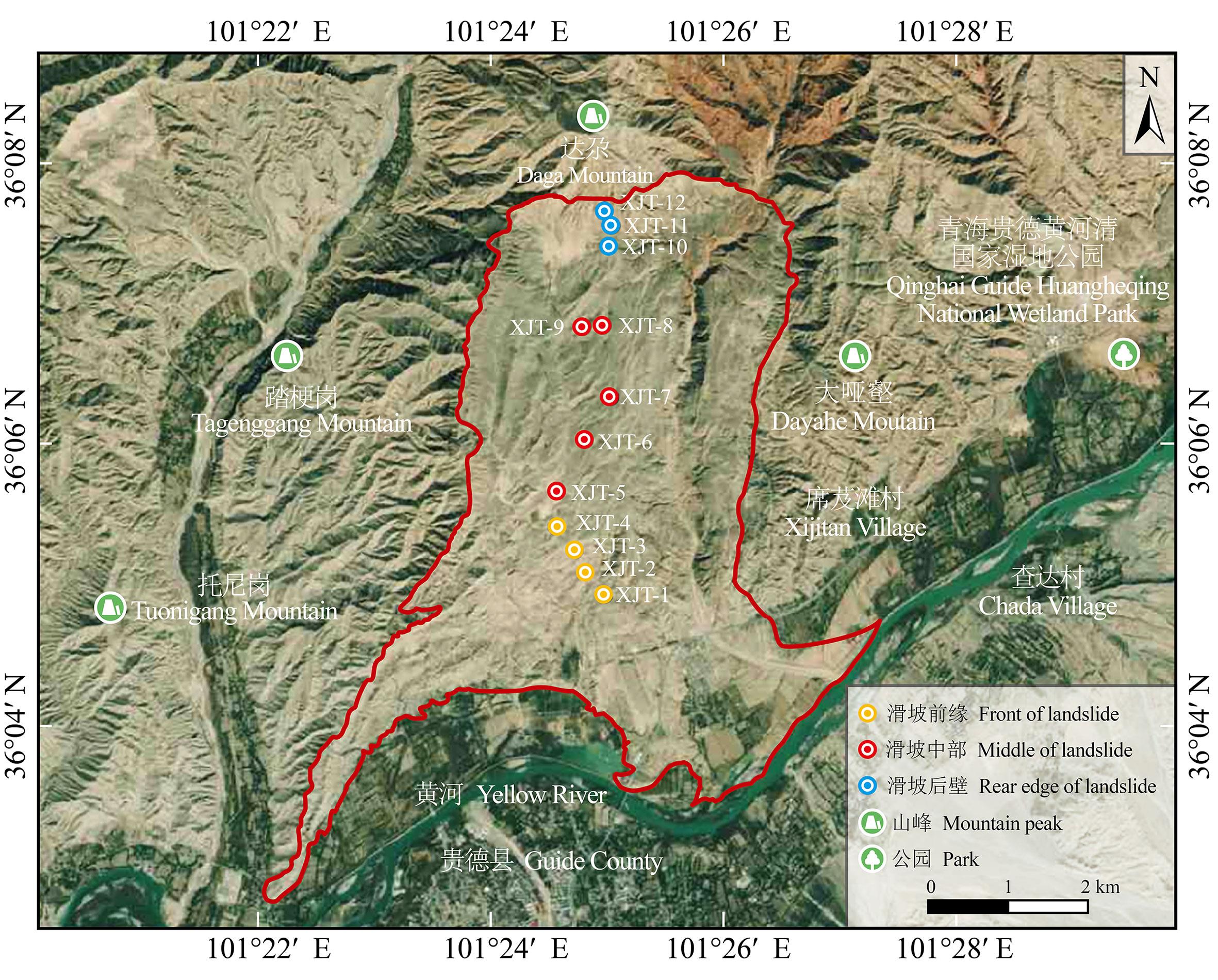
图4 研究区采样点位置布设情况XJT-1~XJT-12为采样点编号,下同。XJT-1-XJT-12 are the sampling point numbers, the same below.
Fig.4 Location and distribution of sampling points in the study area
科名 Families | 属数 Genera | 种数 Species | 占总种百分比 Percentage in total species (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 菊科Asteraceae | 8 | 11 | 21.6 |
| 禾本科Poaceae | 9 | 12 | 23.5 |
| 豆科Fabaceae | 3 | 5 | 9.8 |
| 藜科Chenopodiaceae | 4 | 4 | 7.8 |
| 蔷薇科Rosaceae | 1 | 3 | 5.8 |
| 莎草科Cyperaceae | 2 | 3 | 5.8 |
| 蒺藜科Zygophyllaceae | 3 | 3 | 5.8 |
| 十字花科Brassicaceae | 2 | 2 | 3.9 |
| 蓼科Polygonacea | 1 | 1 | 2.0 |
| 百合科Liliaceae | 1 | 1 | 2.0 |
| 柽柳科Tamaricaceae | 1 | 1 | 2.0 |
| 旋花科Convolvulaceae | 1 | 1 | 2.0 |
| 车前科Plantaginaceae | 1 | 1 | 2.0 |
| 瑞香科Thymelaeaceae | 1 | 1 | 2.0 |
| 亚麻科Linaceae | 1 | 1 | 2.0 |
| 茄科Solanaceae | 1 | 1 | 2.0 |
| 总计Total | 40 | 51 | 100.0 |
表1 席芨滩滑坡区域植物物种组成分布结果
Table 1 Results of plant species composition distribution in Xijitan landslide area
科名 Families | 属数 Genera | 种数 Species | 占总种百分比 Percentage in total species (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 菊科Asteraceae | 8 | 11 | 21.6 |
| 禾本科Poaceae | 9 | 12 | 23.5 |
| 豆科Fabaceae | 3 | 5 | 9.8 |
| 藜科Chenopodiaceae | 4 | 4 | 7.8 |
| 蔷薇科Rosaceae | 1 | 3 | 5.8 |
| 莎草科Cyperaceae | 2 | 3 | 5.8 |
| 蒺藜科Zygophyllaceae | 3 | 3 | 5.8 |
| 十字花科Brassicaceae | 2 | 2 | 3.9 |
| 蓼科Polygonacea | 1 | 1 | 2.0 |
| 百合科Liliaceae | 1 | 1 | 2.0 |
| 柽柳科Tamaricaceae | 1 | 1 | 2.0 |
| 旋花科Convolvulaceae | 1 | 1 | 2.0 |
| 车前科Plantaginaceae | 1 | 1 | 2.0 |
| 瑞香科Thymelaeaceae | 1 | 1 | 2.0 |
| 亚麻科Linaceae | 1 | 1 | 2.0 |
| 茄科Solanaceae | 1 | 1 | 2.0 |
| 总计Total | 40 | 51 | 100.0 |
植物生长位置 Plant growth position | 土体平均密度 Average density of soil mass (g·cm-3) | 土体平均含水量 Average moisture content of soil mass (%) | d60 (mm) | d30 (mm) | d10 (mm) | 不均匀系数 Uniformity coefficient (Cu) | 曲率系数 Curvature coefficient (Cc) | 土体分类 Soil classification | 土体类型 Soil type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
滑坡前缘 Front of landslide | 1.47±0.11 | 5.95±2.20 | 2.17 | 0.33 | 0.07 | 29.70 | 0.68 | 不良级配 Poor grading | 砂类土 Sandy soil |
滑坡中部 Middle of landslide | 1.37±0.15 | 10.57±3.80 | 0.63 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 7.58 | 0.78 | 不良级配 Poor grading | 砂类土 Sandy soil |
滑坡后壁 Rear edge of landslide | 1.59±0.14 | 8.47±1.68 | 0.78 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 13.03 | 0.53 | 不良级配 Poor grading | 砂类土 Sandy soil |
表2 研究区土体物理性质指标试验测试结果
Table 2 Test results of soil physical properties indexes in the study area
植物生长位置 Plant growth position | 土体平均密度 Average density of soil mass (g·cm-3) | 土体平均含水量 Average moisture content of soil mass (%) | d60 (mm) | d30 (mm) | d10 (mm) | 不均匀系数 Uniformity coefficient (Cu) | 曲率系数 Curvature coefficient (Cc) | 土体分类 Soil classification | 土体类型 Soil type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
滑坡前缘 Front of landslide | 1.47±0.11 | 5.95±2.20 | 2.17 | 0.33 | 0.07 | 29.70 | 0.68 | 不良级配 Poor grading | 砂类土 Sandy soil |
滑坡中部 Middle of landslide | 1.37±0.15 | 10.57±3.80 | 0.63 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 7.58 | 0.78 | 不良级配 Poor grading | 砂类土 Sandy soil |
滑坡后壁 Rear edge of landslide | 1.59±0.14 | 8.47±1.68 | 0.78 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 13.03 | 0.53 | 不良级配 Poor grading | 砂类土 Sandy soil |
滑坡位置 Landslide location | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Rapid available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Rapid available potassium (mg·kg-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
滑坡前缘 Front of landslide | 0.69±0.45b | 1.62±0.08b | 20.57±1.77a | 7.64±7.21b | 41.50±32.46b | 3.68±2.07a | 74.00±62.74b | 8.90±0.57a |
滑坡中部 Middle of landslide | 2.21±0.60a | 1.84±0.16a | 21.78±2.33a | 30.56±7.94a | 131.18±62.92a | 7.27±5.22a | 243.00±138.73a | 8.34±0.37a |
滑坡后壁 Rear edge of landslide | 1.50±0.52a | 1.69±0.09ab | 22.50±1.94a | 20.61±9.61a | 93.33±47.43ab | 4.83±2.25a | 198.33±69.17ab | 8.41±0.18a |
表3 研究区滑坡体不同位置土壤营养元素含量试验测试结果
Table 3 Test results of soil nutrient element content in different locations of the study area
滑坡位置 Landslide location | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Rapid available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Rapid available potassium (mg·kg-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
滑坡前缘 Front of landslide | 0.69±0.45b | 1.62±0.08b | 20.57±1.77a | 7.64±7.21b | 41.50±32.46b | 3.68±2.07a | 74.00±62.74b | 8.90±0.57a |
滑坡中部 Middle of landslide | 2.21±0.60a | 1.84±0.16a | 21.78±2.33a | 30.56±7.94a | 131.18±62.92a | 7.27±5.22a | 243.00±138.73a | 8.34±0.37a |
滑坡后壁 Rear edge of landslide | 1.50±0.52a | 1.69±0.09ab | 22.50±1.94a | 20.61±9.61a | 93.33±47.43ab | 4.83±2.25a | 198.33±69.17ab | 8.41±0.18a |
参数 Statistic | 排序轴1 Axis 1 | 排序轴2 Axis 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 特征值Eigenvalues | 0.910 | 0.019 |
| 植物群落累积解释量Plant communities cumulative explained variation (%) | 90.99 | 92.88 |
植物群落分布与环境因子相关性 Plant community distribution and environmental factors correlation | 0.9784 | 0.8511 |
| 植物群落分布与环境因子累积解释量Plant community distribution and environmental factors cumulative explained fitted variation (%) | 96.64 | 98.65 |
| 所有特征值All eigenvalue | 1.000 | |
| 标准特征值Standard eigenvalue | 0.941 | |
| 第一典范轴P值P-value of the first canonical axis | 0.002 | |
| 所有典范轴P值P-value of all canonical axis | 0.002 | |
表4 研究区植物群落分布与环境因子RDA排序结果
Table 4 RDA ranking of plant communities and environmental factors
参数 Statistic | 排序轴1 Axis 1 | 排序轴2 Axis 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 特征值Eigenvalues | 0.910 | 0.019 |
| 植物群落累积解释量Plant communities cumulative explained variation (%) | 90.99 | 92.88 |
植物群落分布与环境因子相关性 Plant community distribution and environmental factors correlation | 0.9784 | 0.8511 |
| 植物群落分布与环境因子累积解释量Plant community distribution and environmental factors cumulative explained fitted variation (%) | 96.64 | 98.65 |
| 所有特征值All eigenvalue | 1.000 | |
| 标准特征值Standard eigenvalue | 0.941 | |
| 第一典范轴P值P-value of the first canonical axis | 0.002 | |
| 所有典范轴P值P-value of all canonical axis | 0.002 | |
环境因子 Environmental factor | 解释率 Explains (%) | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | F | P | 环境因子 Environmental factor | 解释率 Explains (%) | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含水量Moisture content | 44.3 | 47.1 | 12.7 | 0.004 | 有机质Organic matter | 5.1 | 5.4 | 2.7 | 0.120 |
| pH | 6.7 | 7.1 | 8.0 | 0.020 | 全钾Total potassium | 3.3 | 3.5 | 2.0 | 0.170 |
| 全氮Total nitrogen | 9.5 | 10.1 | 4.5 | 0.044 | 海拔Elevation | 2.4 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 0.230 |
| 全磷Total phosphorus | 9.4 | 10.0 | 3.5 | 0.094 | 速效钾Rapid available potassium | 2.4 | 2.5 | 1.3 | 0.264 |
| 速效磷Rapid available phosphorus | 8.3 | 8.9 | 2.6 | 0.116 | 碱解氮Available nitrogen | 2.7 | 2.9 | 1.0 | 0.332 |
表5 研究区植被群落与环境因子的冗余分析向前选择结果
Table 5 Forward selection results of redundancy analysis between vegetation communities and environmental factors in the study area
环境因子 Environmental factor | 解释率 Explains (%) | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | F | P | 环境因子 Environmental factor | 解释率 Explains (%) | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含水量Moisture content | 44.3 | 47.1 | 12.7 | 0.004 | 有机质Organic matter | 5.1 | 5.4 | 2.7 | 0.120 |
| pH | 6.7 | 7.1 | 8.0 | 0.020 | 全钾Total potassium | 3.3 | 3.5 | 2.0 | 0.170 |
| 全氮Total nitrogen | 9.5 | 10.1 | 4.5 | 0.044 | 海拔Elevation | 2.4 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 0.230 |
| 全磷Total phosphorus | 9.4 | 10.0 | 3.5 | 0.094 | 速效钾Rapid available potassium | 2.4 | 2.5 | 1.3 | 0.264 |
| 速效磷Rapid available phosphorus | 8.3 | 8.9 | 2.6 | 0.116 | 碱解氮Available nitrogen | 2.7 | 2.9 | 1.0 | 0.332 |
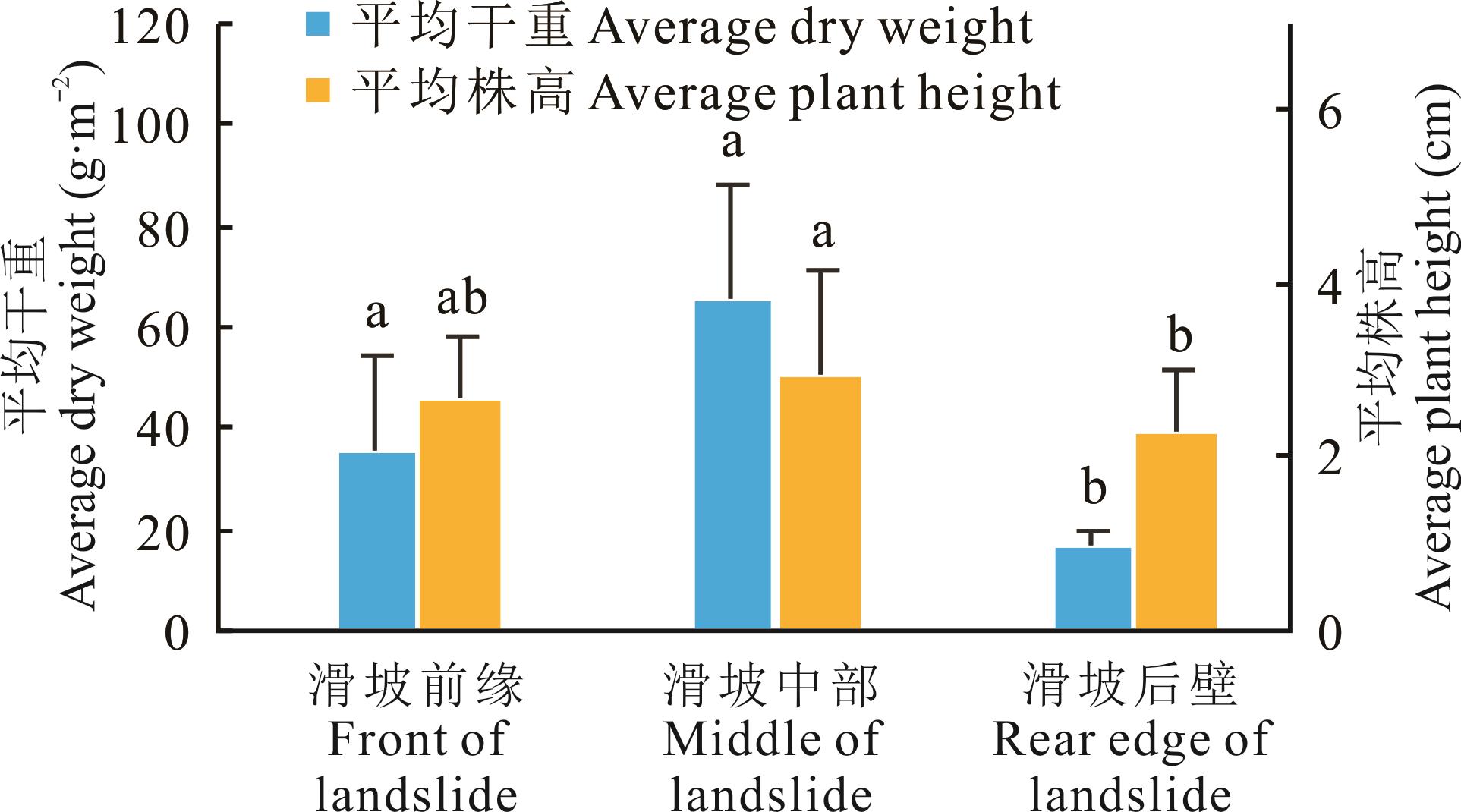
图10 不同位置处冷地早熟禾生物量对比特征不同小写字母表示不同位置间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different locations (P<0.05).
Fig.10 Comparative characteristics of P. crymophila biomass at different locations
植物生长位置 Plant growth position | 平均根径 Average root diameter (mm) | 平均单根抗拉力 Average tensile resistance of single root (N) | 平均单根抗拉强度 Average tensile strength of single root (MPa) | 样本数量 Samples number (No.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 滑坡前缘Front of landslide | 0.42±0.12a | 3.58±1.41c | 28.86±11.90c | 60 |
| 滑坡中部Middle of landslide | 0.46±0.10a | 7.51±1.78a | 49.78±12.58a | 60 |
| 滑坡后壁Rear edge of landslide | 0.44±0.11a | 4.62±1.36b | 34.00±13.56b | 60 |
表6 研究区不同生长位置处冷地早熟禾单根拉伸试验结果
Table 6 Single root tensile test results of P. crymophila at different locations in the study area
植物生长位置 Plant growth position | 平均根径 Average root diameter (mm) | 平均单根抗拉力 Average tensile resistance of single root (N) | 平均单根抗拉强度 Average tensile strength of single root (MPa) | 样本数量 Samples number (No.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 滑坡前缘Front of landslide | 0.42±0.12a | 3.58±1.41c | 28.86±11.90c | 60 |
| 滑坡中部Middle of landslide | 0.46±0.10a | 7.51±1.78a | 49.78±12.58a | 60 |
| 滑坡后壁Rear edge of landslide | 0.44±0.11a | 4.62±1.36b | 34.00±13.56b | 60 |
植物生长位置 Plant growth position | 单根抗拉力与根径拟合方程Fitting equation of single root tensile resistance and root diameter | 拟合优度 Goodness of fit (R2) | 显著性水平 Significance level | 单根抗拉强度与根径拟合方程Fitting equation of single root tensile strength and root diameter | 拟合优度 Goodness of fit (R2) | 显著性水平 Significance level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 滑坡前缘Front of landslide | y=0.9455e2.9971x | 0.7159 | 0.845** | y=11.206x-0.951 | 0.7031 | -0.861** |
| 滑坡中部Middle of landslide | y=2.7684e2.1251x | 0.7035 | 0.941** | y=20.273x-1.071 | 0.7036 | -0.941** |
| 滑坡后壁Rear edge of landslide | y=1.5432e2.414x | 0.7006 | 0.908** | y=12.682x-1.059 | 0.7014 | -0.868** |
表7 不同生长位置冷地早熟禾单根抗拉力和抗拉强度与根径之间的拟合关系式
Table 7 The fitting relationship between the single root tensile resistance, tensile strength and root diameter of P. crymophila at different locations
植物生长位置 Plant growth position | 单根抗拉力与根径拟合方程Fitting equation of single root tensile resistance and root diameter | 拟合优度 Goodness of fit (R2) | 显著性水平 Significance level | 单根抗拉强度与根径拟合方程Fitting equation of single root tensile strength and root diameter | 拟合优度 Goodness of fit (R2) | 显著性水平 Significance level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 滑坡前缘Front of landslide | y=0.9455e2.9971x | 0.7159 | 0.845** | y=11.206x-0.951 | 0.7031 | -0.861** |
| 滑坡中部Middle of landslide | y=2.7684e2.1251x | 0.7035 | 0.941** | y=20.273x-1.071 | 0.7036 | -0.941** |
| 滑坡后壁Rear edge of landslide | y=1.5432e2.414x | 0.7006 | 0.908** | y=12.682x-1.059 | 0.7014 | -0.868** |
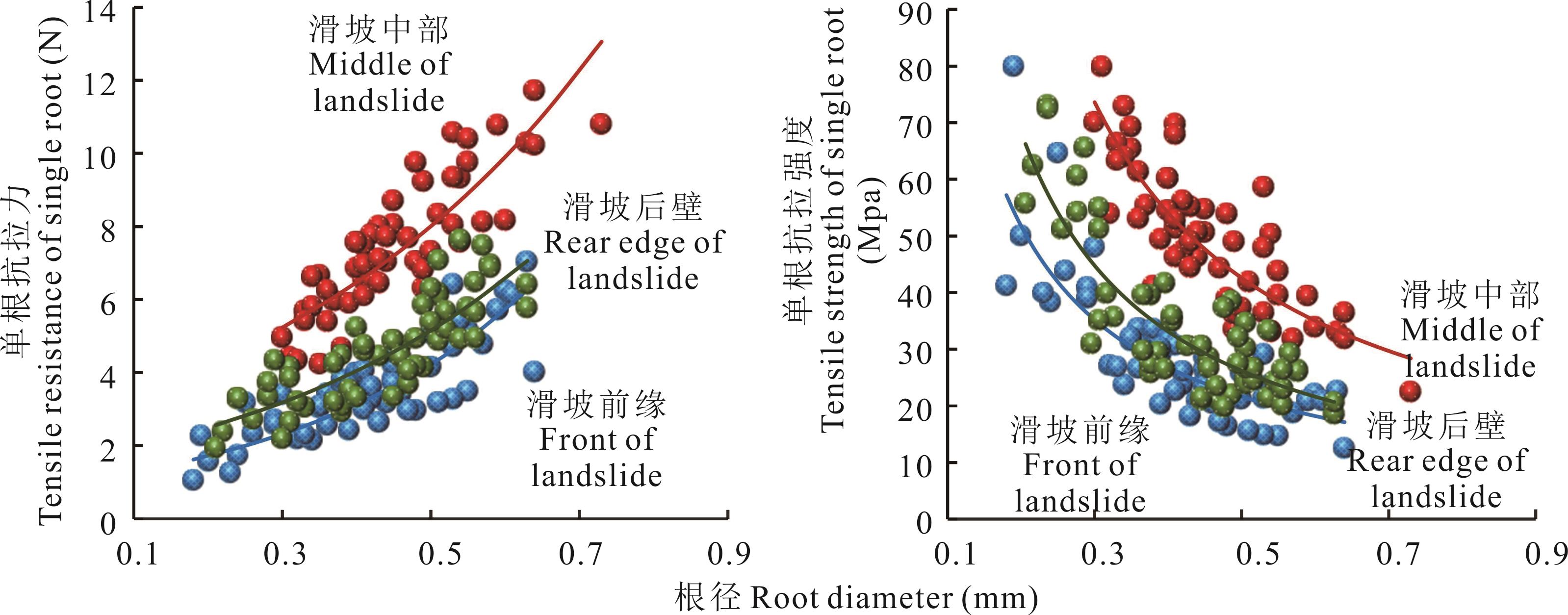
图11 不同位置处冷地早熟禾单根抗拉力、抗拉强度与根径之间的关系
Fig.11 Relationship between the single root tensile resistance, tensile strength and root diameter of P. crymophila at different locations
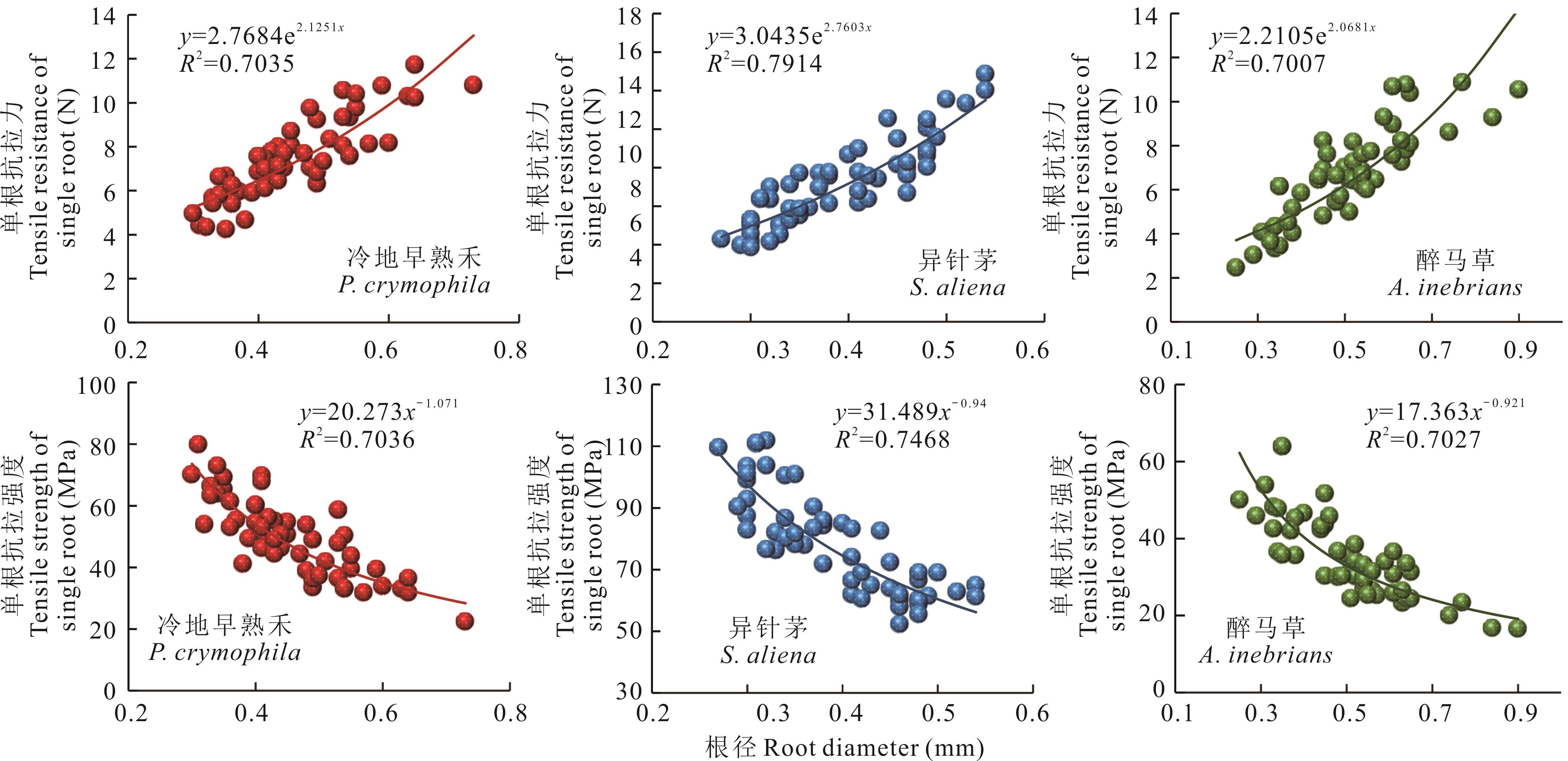
图12 滑坡中部3种草本植物单根抗拉力、抗拉强度与根径之间的关系
Fig.12 Relationship between the single root tensile resistance, tensile strength and root diameter of three herbaceous plant in the middle of landslide
植物名称 Plant name | 平均根径 Average root diameter (mm) | 平均单根抗拉力 Average tensile resistance of single root (N) | 平均单根抗拉强度 Average tensile strength of single root (MPa) | 样本数量 Number of samples (No.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 异针茅S. aliena | 0.39±0.08c | 9.10±2.20a | 80.29±17.73a | 60 |
| 冷地早熟禾P. crymophila | 0.46±0.10b | 7.51±1.78b | 49.78±12.58b | 60 |
| 醉马草A. inebrians | 0.51±0.14a | 6.69±2.04c | 34.82±11.25c | 60 |
表8 滑坡中部3种草本植物单根拉伸试验结果
Table 8 Single root tensile test results of three herbaceous plant in the middle of landslide
植物名称 Plant name | 平均根径 Average root diameter (mm) | 平均单根抗拉力 Average tensile resistance of single root (N) | 平均单根抗拉强度 Average tensile strength of single root (MPa) | 样本数量 Number of samples (No.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 异针茅S. aliena | 0.39±0.08c | 9.10±2.20a | 80.29±17.73a | 60 |
| 冷地早熟禾P. crymophila | 0.46±0.10b | 7.51±1.78b | 49.78±12.58b | 60 |
| 醉马草A. inebrians | 0.51±0.14a | 6.69±2.04c | 34.82±11.25c | 60 |
| 1 | Wei G. Study on the distribution characteristics and risk assessment of super large scale landslides from Longyang Gorge to Sigou Gorge in the upper reaches of Yellow River. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2013. |
| 魏刚. 黄河上游龙羊峡至寺沟峡段巨型滑坡分布特征及风险评价研究. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2013. | |
| 2 | Yin Z Q, Wei G, Qin X G, et al. Research progress on landslides and dammed lakes in the upper reaches of the Yellow River, northeastern Tibetan plateau. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(2): 46-57. |
| 殷志强, 魏刚, 秦小光, 等. 青藏高原东北缘黄河上游滑坡与堰塞湖研究进展. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(2): 46-57. | |
| 3 | Li X L, Ma J Q, Hu G S. Genetic analysis on huge landslides along the section from Longyang Gorge to Liujia Gorge of the Yellow River. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2007, 18(1): 28-32. |
| 李小林, 马建青, 胡贵寿. 黄河龙羊峡-刘家峡河段特大型滑坡成因分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2007, 18(1): 28-32. | |
| 4 | Zhao W J, Yin Z Q, Ma J F, et al. Multi-stage development characteristics and geomorphic evolution process of the Xijitan super large landslide in the Guide Basin, upper reaches of Yellow River. Gelogical Review, 2016, 62(3): 709-721. |
| 赵无忌, 殷志强, 马吉福, 等. 黄河上游贵德盆地席芨滩巨型滑坡发育特征及地貌演化. 地质评论, 2016, 62(3): 709-721. | |
| 5 | Zhao W J. The formation characteristics and geomorphical evolution of the landslides and debris flow fans in Guide Basin, the upper reaches of the Yellow River. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2015. |
| 赵无忌. 黄河上游贵德盆地滑坡泥石流扇发育特征及地貌演化过程. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2015. | |
| 6 | Ye P L, Zhang Q, Wang Y, et al. Climate change in the upper Yellow River Basin and its impact on ecological vegetation and runoff from 1980 to 2018. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2020, 43(6): 967-979. |
| 叶培龙, 张强, 王莺, 等. 1980-2018年黄河上游气候变化及其对生态植被和径流量的影响. 大气科学学报, 2020, 43(6): 967-979. | |
| 7 | Zhang P D, Jie X B. Current situation of grassland degradation and its mechanism in the upstream of Yellow River in Gansu. Pratacultural Science, 2007(9): 1-4. |
| 张培栋, 介小兵. 黄河上游甘肃段草地退化的现状及机理研究. 草业科学, 2007(9): 1-4. | |
| 8 | Zhang X Y, Liu K, Wang S D, et al. Spatiotemporal evolution of ecological vulnerability in the Yellow River Basin under ecological restoration initiatives. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 135: 108586. |
| 9 | Wu Y H, Wu R H. The seed plant flora of valley in upper reaches of Yellow River in east Qinghai, China. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 2006, 28(1): 1-12. |
| 吴玉虎, 吴瑞华. 青海东部黄河上游谷地种子植物区系. 云南植物研究, 2006, 28(1): 1-12. | |
| 10 | Wang Z L, Zhu C Y, Yang Z W, et al. Character of vegetation distribution on the upper reaches of the Yellow River between Guide and Minhe. Science and Technology of Qinghai Agriculture and Forestry, 2006(1): 17-18, 46. |
| 王占林, 朱春云, 杨占武, 等. 黄河上游贵德——民和段两岸植被分布特征. 青海农林科技, 2006(1): 17-18, 46. | |
| 11 | Wei T T. Desertification assessment and landscape dynamics of Gonghe Basin in Qinghai Province. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2011. |
| 魏婷婷. 青海共和盆地荒漠化评价与景观动态研究. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2011. | |
| 12 | Wang H Z, Xu D Q, Chen H, et al. Effect of surface runoff reduction by slope protection plants. Soil and Water Conservation in China, 2013(9): 46-48, 74, 77. |
| 王慧子, 徐得潜, 陈慧, 等. 护坡植物减缓地表径流效果研究. 中国水土保持, 2013(9): 46-48, 74, 77. | |
| 13 | Zhou Y Y. Study on mechanism of soil reinforcement by roots and slope protection technology. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2010. |
| 周云艳. 植物根系固土机理与护坡技术研究. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2010. | |
| 14 | Liu C Y, Dou Z N, Hu X S, et al. Research on the effect of plant combination types on the shear strength of the root-soil composition system of alpine grassland in the source region of the Yellow River. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(1): 43-52. |
| 刘昌义, 窦增宁, 胡夏嵩, 等. 黄河源区高寒草地植物组合对根-土复合体抗剪强度的影响. 草地学报, 2019, 27(1): 43-52. | |
| 15 | Xu T, Liu C Y, Hu X S, et al. Study on the mechanical properties of roots and the shear strengths of four halophytic plants in Qaidam Basin. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 28(3): 101-110. |
| 许桐, 刘昌义, 胡夏嵩, 等. 柴达木盆地4种盐生植物根系力学特性及根-土复合体抗剪强度研究. 水土保持研究, 2021, 28(3): 101-110. | |
| 16 | Osman N, Dorairaj D, Halim A, et al. Dynamics of plant ecology and soil conservation: Implications for cut-slope protection. Acta Oecologica, 2021, 111: 103744. |
| 17 | Wu P, Xie P C, Song W L, et al. Morphology-based plant root mechanics and function mechanism for slope stabilization. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2014, 42(5): 139-142. |
| 吴鹏, 谢朋成, 宋文龙, 等. 基于根系形态的植物根系力学与固土护坡作用机理. 东北林业大学学报, 2014, 42(5): 139-142. | |
| 18 | Feng S, Liu H W, Ng C W W. Analytical analysis of the mechanical and hydrological effects of vegetation on shallow slope stability. Computer and Geotechnics, 2020, 118: 103335. |
| 19 | Guide County Local Records Compilation Committee. Guide yearbook (2021). Xi’an: Sanqin Press, 2021: 12. |
| 贵德县地方志编纂委员会. 贵德年鉴(2021). 西安: 三秦出版社, 2021: 12. | |
| 20 | Zhou B. Research on development characteristic and mass mechanism of super larger landslide in the upper Yellow River. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2010. |
| 周保. 黄河上游(拉干峡-寺沟峡段)特大型滑坡发育特征与群发机理研究. 西安: 长安大学, 2010. | |
| 21 | Zhou H K, Ren F, Huo Q, et al. Map of vascular plants in Hainan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Qinghai Province. Beijing: Science Press, 2020. |
| 周华坤, 任飞, 霍青, 等. 青海省海南藏族自治州维管植物图谱. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020. | |
| 22 | Hu X S, Mao X Q, Zhu H L, et al. Vegetation slope protection Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Beijing: Geology Press, 2011. |
| 胡夏嵩, 毛小青, 朱海丽, 等. 青藏高原植被护坡. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011. | |
| 23 | Bao S D. Agrochemical analysis of soil. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2007. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2007. | |
| 24 | Yang F C, Liu C Y, Hu X S, et al. Study on physical and chemical properties and shear strength characteristics of root-soil composite system with different degradation degrees of alpine grassland in the source region of the Yellow River. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(2): 560-571. |
| 杨馥铖, 刘昌义, 胡夏嵩, 等. 黄河源区不同退化程度高寒草地理化性质及复合体抗剪强度研究. 干旱区研究, 2022, 39(2): 560-571. | |
| 25 | Liu C Y, Hu X S, Li X L, et al. Relationship between shear strength of root-soil composite systems of alpine grassland and distribution of soil nutrient elements in the source region of the Yellow River, China. Mountain Research, 2020, 38(3): 349-359. |
| 刘昌义, 胡夏嵩, 李希来, 等. 黄河源区高寒草地根-土复合体抗剪强度与土壤营养元素分布关系. 山地学报, 2020, 38(3): 349-359. | |
| 26 | Li D B, Zhu L. Comparative study on soil fixation mechanical characteristics of slope vegetation root in desert-crossing highway. Subgrade Engineering, 2022(1): 8-13. |
| 李东彪, 朱磊. 穿沙公路边坡植被根系固土力学特征比较研究. 路基工程, 2022(1): 8-13. | |
| 27 | Chen L, Zeng G H, Cheng X Y, et al. Application and development of vegetation slope protection. Yangtze River, 2007, 38(9): 127-129. |
| 陈莉, 曾光辉, 程心意, 等. 浅议植被护坡的应用及发展. 人民长江, 2007, 38(9): 127-129. | |
| 28 | Zhao C R. Study on the effect of vegetation protection on the stability of railroad embankment slopes. Journal of Gansu Sciences, 2022, 34(4): 125-129. |
| 赵呈冉. 植物防护对路堤边坡稳定性的影响研究. 甘肃科学学报, 2022, 34(4): 125-129. | |
| 29 | Zhao Y K, Zhang W S, Wang Y N, et al. Research progress in physiology and molecular biology of plant responses to high pH. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2008, 16(3): 783-787. |
| 赵彦坤, 张文胜, 王幼宁, 等. 高pH对植物生长发育的影响及其分子生物学研究进展. 中国生态农业学报, 2008, 16(3): 783-787. | |
| 30 | Lu H, Cong J, Liu X, et al. Plant diversity patterns along altitudinal gradients in alpine meadows in the Three River Headwater Region, China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(7): 197-204. |
| 卢慧, 丛静, 刘晓, 等. 三江源区高寒草甸植物多样性的海拔分布格局. 草业学报, 2015, 24(7): 197-204. | |
| 31 | Bai H B. Effects of nitrogen application on plant communities in abandoned lands and soil nutrient in hilly and gully regions on the Loess Plateau. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University, 2013. |
| 白宏兵. 施氮对黄土高原丘陵沟壑区不同退耕年限植被群落以及土壤养分的影响. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2013. | |
| 32 | Fu J T, Yang Y Q, Zhao J M, et al. Impact of sampling sites, slope aspects and growth periods on the tensile mechanical behavior of roots in high-altitude alpine pasture. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(9): 2449-2459. |
| 付江涛, 杨幼清, 赵吉美, 等. 高寒矿区采样位置和生长期及坡向对草本植物根系力学特性影响. 草地学报, 2022, 30(9): 2449-2459. | |
| 33 | Liu Y B, Li S X, Yu D M, et al. Experiment on single root tensile mechanical properties of typical herb species in loess region of Xining Basin. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(15): 157-166. |
| 刘亚斌, 李淑霞, 余冬梅, 等. 西宁盆地黄土区典型草本植物单根抗拉力学特性试验. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(15): 157-166. | |
| 34 | Liu Y F, Meng L C, Huang Z, et al. Contribution of fine roots mechanical property of Poaceae grasses to soil erosion resistance on the Loess Plateau. Geoderma, 2022, 426: 116122. |
| 35 | Zhou L H, Liu C Y, Hu X S, et al. Experimental study on the mechanical properties of four herbs roots in cold-arid area. Yellow River, 2019, 41(5): 90-95. |
| 周林虎, 刘昌义, 胡夏嵩, 等. 寒旱区4种草本根系力学特性试验研究. 人民黄河, 2019, 41(5): 90-95. | |
| 36 | He W P, Liu C Y, Zhou G Y, et al. A study of the mechanical properties of herbaceous roots and root-soil composite systems in the degraded alpine pasture artificially restored grassland. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(2): 207-218. |
| 何伟鹏, 刘昌义, 周国英, 等. 退化高寒草原人工恢复植被根系及根-土复合体力学特性研究. 水文地质工程地质, 2022, 49(2): 207-218. | |
| 37 | Guo F, Liang Z Z, Gong B, et al. Tensile failure in stability analysis of rock and soil slopes. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(S1): 3192-3205. |
| 郭芳, 梁正召, 龚斌, 等. 岩土工程边坡稳定性分析中的拉伸破坏问题. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(S1): 3192-3205. | |
| 38 | Wang J W. Study on properties of landslide soil and formation mechanism of loess-bedrock-The Erzhuangke landslide in Yan’an as an example. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2016. |
| 王建伟. 黄土-基岩滑坡滑带土特性及形成机理研究-以延安二庄科滑坡为例. 西安: 长安大学, 2016. |
| [1] | 何伟鹏, 胡夏嵩, 刘昌义, 李璇, 李希来, 付江涛, 卢海静, 杨馥铖, 李国荣. 黄河源区不同禁牧年限对垂穗披碱草单根及其根-土复合体力学强度特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 106-117. |
| [2] | 焦菊英,王宁,杜华栋,王东丽. 土壤侵蚀对植被发育演替的干扰与植物的抗侵蚀特性研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(5): 311-318. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||