

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (12): 1-12.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024050
• 研究论文 •
于泽航1,2,3( ), 俞旸1,2,3, 曹铨1,2,3, 刘玉祯1,2,3, 冯斌1,2,3, 张小芳1,2,3, 董全民1,2,3(
), 俞旸1,2,3, 曹铨1,2,3, 刘玉祯1,2,3, 冯斌1,2,3, 张小芳1,2,3, 董全民1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2024-02-05
修回日期:2024-04-08
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2024-10-09
通讯作者:
董全民
作者简介:E-mail: qmdong@qhu.edu.cn基金资助:
Ze-hang YU1,2,3( ), Yang YU1,2,3, Quan CAO1,2,3, Yu-zhen LIU1,2,3, Bin FENG1,2,3, Xiao-fang ZHANG1,2,3, Quan-min DONG1,2,3(
), Yang YU1,2,3, Quan CAO1,2,3, Yu-zhen LIU1,2,3, Bin FENG1,2,3, Xiao-fang ZHANG1,2,3, Quan-min DONG1,2,3( )
)
Received:2024-02-05
Revised:2024-04-08
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-10-09
Contact:
Quan-min DONG
摘要:
植被-土壤系统的协同耦合度是衡量草地生态系统一致性和协调度的综合评价指标,是实现对草地量化管理的重要标志。以青海省祁连县野牛沟乡为研究区域,以冬季完全放牧、冬季放牧+补饲、冬季围封(不放牧)等3种不同放牧管理的植被-土壤系统为研究对象,通过构建植被因子与土壤因子组成的评价体系,采用熵权法确定各指标权重,获取协同耦合度模型,用于评价植被-土壤系统的协调关系。结果表明:不同放牧管理下植被群落Shannon-Wiener指数和Patrick丰富度指数存在显著差异,放牧+补饲草地的植被系统评分最高,完全放牧草地评分最低。不同放牧管理的土壤全碳、全氮、全磷、铵态氮、硝态氮、速效钾、速效磷含量均存在显著差异,围封草地的土壤系统评分最高,完全放牧草地评分最低。不同放牧管理下协同耦合度依次为围封(0.510)>放牧+补饲(0.482)>完全放牧(0.397),其中围封草地属于勉强协调土壤滞后发展型,放牧+补饲草地属于濒临失调土壤滞后发展型,完全放牧草地属于轻度失调同步衰退发展型。综上,祁连山区冬季围封草地更有利于生态系统的健康稳定,但未达到最佳协调模式。
于泽航, 俞旸, 曹铨, 刘玉祯, 冯斌, 张小芳, 董全民. 不同放牧管理下祁连山区冬季牧场植被-土壤协同耦合效应评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 1-12.
Ze-hang YU, Yang YU, Quan CAO, Yu-zhen LIU, Bin FENG, Xiao-fang ZHANG, Quan-min DONG. Evaluation of vegetation-soil synergistic coupling in winter rangeland of the Qilian Mountains under different winter grazing management systems[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(12): 1-12.
目标层 Objective level | 子目标层 Subgoal layer | 指标层 Index level | 权重 Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
植被-土壤 耦合系统 Vegetation-soil coupling system | 植被系统 Vegetation system | Shannon-Wiener指数H′ | 0.058 |
| Pielou均匀度指数J | 0.101 | ||
| Simpson多样性指数C | 0.086 | ||
| Patrick丰富度指数R | 0.070 | ||
土壤系统 Soil system | 全碳TC | 0.114 | |
| 全氮TN | 0.135 | ||
| 全磷TP | 0.060 | ||
| 全钾TK | 0.049 | ||
| 铵态氮NH4+-N | 0.046 | ||
| 硝态氮NO3--N | 0.061 | ||
| 速效磷AP | 0.105 | ||
| 速效钾AK | 0.116 |
表1 植被-土壤系统耦合度评价指标及权重
Table 1 Evaluation indexes and weights of vegetation-soil system coupling degree
目标层 Objective level | 子目标层 Subgoal layer | 指标层 Index level | 权重 Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
植被-土壤 耦合系统 Vegetation-soil coupling system | 植被系统 Vegetation system | Shannon-Wiener指数H′ | 0.058 |
| Pielou均匀度指数J | 0.101 | ||
| Simpson多样性指数C | 0.086 | ||
| Patrick丰富度指数R | 0.070 | ||
土壤系统 Soil system | 全碳TC | 0.114 | |
| 全氮TN | 0.135 | ||
| 全磷TP | 0.060 | ||
| 全钾TK | 0.049 | ||
| 铵态氮NH4+-N | 0.046 | ||
| 硝态氮NO3--N | 0.061 | ||
| 速效磷AP | 0.105 | ||
| 速效钾AK | 0.116 |
类型 Type | 协同耦合度 Synergetic coupling degree (Sc ) | 等级 Level | 植被-土壤系统综合对比关系Comprehensive correlation of vegetation-soil system (SEy/VEx) | 协同耦合模型 Cooperative coupling model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
失调型 Disordered type | 0<Sc ≤0.1 | 极度失调Extreme disorder | ||
| 0.1<Sc ≤0.2 | 严重失调Severe disorder | 0<SEy/VEx<0.8 | 植被滞后型Vegetation lag type | |
| 0.2<Sc ≤0.3 | 中度失调Moderate disorder | 0.8≤SEy/VEx≤1.2 | 同步衰退型Synchronous decay pattern | |
| 0.3<Sc ≤0.4 | 轻度失调Mild disorder | SEy/VEx>1.2 | 土壤滞后型Soil lag type | |
| 0.4<Sc ≤0.5 | 濒临失调Borderline disorder | |||
协调型 Coordinated type | 0.5<Sc ≤0.6 | 勉强协调Forced coordination | ||
| 0.6<Sc ≤0.7 | 初级协调Primary coordination | 0<SEy/VEx<0.8 | 植被滞后型Vegetation lag type | |
| 0.7<Sc ≤0.8 | 中级协调Moderate coordination | 0.8≤SEy/VEx≤1.2 | 同步发展型Synchronous development pattern | |
| 0.8<Sc ≤0.9 | 良好协调Good coordination | SEy/VEx>1.2 | 土壤滞后型Soil lag type | |
| 0.9<Sc ≤1.0 | 优质协调Quality coordination |
表2 植被-土壤系统协同耦合度划分标准
Table 2 Classification standard of vegetation-soil coupling cooperation degree
类型 Type | 协同耦合度 Synergetic coupling degree (Sc ) | 等级 Level | 植被-土壤系统综合对比关系Comprehensive correlation of vegetation-soil system (SEy/VEx) | 协同耦合模型 Cooperative coupling model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
失调型 Disordered type | 0<Sc ≤0.1 | 极度失调Extreme disorder | ||
| 0.1<Sc ≤0.2 | 严重失调Severe disorder | 0<SEy/VEx<0.8 | 植被滞后型Vegetation lag type | |
| 0.2<Sc ≤0.3 | 中度失调Moderate disorder | 0.8≤SEy/VEx≤1.2 | 同步衰退型Synchronous decay pattern | |
| 0.3<Sc ≤0.4 | 轻度失调Mild disorder | SEy/VEx>1.2 | 土壤滞后型Soil lag type | |
| 0.4<Sc ≤0.5 | 濒临失调Borderline disorder | |||
协调型 Coordinated type | 0.5<Sc ≤0.6 | 勉强协调Forced coordination | ||
| 0.6<Sc ≤0.7 | 初级协调Primary coordination | 0<SEy/VEx<0.8 | 植被滞后型Vegetation lag type | |
| 0.7<Sc ≤0.8 | 中级协调Moderate coordination | 0.8≤SEy/VEx≤1.2 | 同步发展型Synchronous development pattern | |
| 0.8<Sc ≤0.9 | 良好协调Good coordination | SEy/VEx>1.2 | 土壤滞后型Soil lag type | |
| 0.9<Sc ≤1.0 | 优质协调Quality coordination |
| 项目Item | GM1 | GM2 | GM3 | 项目Item | GM1 | GM2 | GM3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甘肃羊茅F. kansuensis | 0.1201 | 0.3249 | 0.3565 | 火绒草Leontopodium leontopodioides | 0.0384 | 0.1013 | 0.0298 |
| 高山嵩草C. parvula | 0.3975 | 0.1514 | 0.1983 | 肉果草L. tibetica | 0.0014 | - | 0.0230 |
| 干生薹草Carex aridula | 0.0056 | 0.0858 | 0.0250 | 白花棘豆Oxytropis coerulea | 0.0032 | 0.0037 | 0.0234 |
| 斜茎黄芪A. laxmannii | 0.0201 | 0.0062 | 0.0046 | 狗娃花Aster hispidus | - | 0.0134 | - |
| 鸡冠茶S. bifurca | 0.1179 | 0.0427 | 0.0622 | 洽草Koeleria macrantha | - | 0.0377 | - |
| 多茎委陵菜Potentilla multicaulis | 0.0257 | 0.0346 | 0.0694 | 赖草Leymus secalinus | - | 0.0529 | 0.0767 |
| 翻白草Potentilla discolor | 0.0269 | 0.0431 | 0.0306 | 早熟禾Poa annua | - | 0.0084 | - |
| 蒲公英Taraxacum mongolicum | 0.0466 | 0.0057 | 0.0148 | 臭蒿Artemisia hedinii | - | 0.0037 | - |
| 毛莓草S. adpressa | 0.0111 | 0.0023 | 0.0059 | 藜Chenopodium album | - | - | 0.0151 |
| 秦艽Gentiana macrophylla | 0.0199 | 0.0106 | - | 西藏大戟Euphorbia tibetica | - | - | 0.0145 |
| 珠芽蓼B. vivipara | 0.1225 | 0.0716 | 0.0416 | 多刺绿绒蒿Meconopsis horridula | - | - | 0.0080 |
表3 不同放牧管理下物种组成及其重要值
Table 3 Species composition and its important value under different grazing management
| 项目Item | GM1 | GM2 | GM3 | 项目Item | GM1 | GM2 | GM3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甘肃羊茅F. kansuensis | 0.1201 | 0.3249 | 0.3565 | 火绒草Leontopodium leontopodioides | 0.0384 | 0.1013 | 0.0298 |
| 高山嵩草C. parvula | 0.3975 | 0.1514 | 0.1983 | 肉果草L. tibetica | 0.0014 | - | 0.0230 |
| 干生薹草Carex aridula | 0.0056 | 0.0858 | 0.0250 | 白花棘豆Oxytropis coerulea | 0.0032 | 0.0037 | 0.0234 |
| 斜茎黄芪A. laxmannii | 0.0201 | 0.0062 | 0.0046 | 狗娃花Aster hispidus | - | 0.0134 | - |
| 鸡冠茶S. bifurca | 0.1179 | 0.0427 | 0.0622 | 洽草Koeleria macrantha | - | 0.0377 | - |
| 多茎委陵菜Potentilla multicaulis | 0.0257 | 0.0346 | 0.0694 | 赖草Leymus secalinus | - | 0.0529 | 0.0767 |
| 翻白草Potentilla discolor | 0.0269 | 0.0431 | 0.0306 | 早熟禾Poa annua | - | 0.0084 | - |
| 蒲公英Taraxacum mongolicum | 0.0466 | 0.0057 | 0.0148 | 臭蒿Artemisia hedinii | - | 0.0037 | - |
| 毛莓草S. adpressa | 0.0111 | 0.0023 | 0.0059 | 藜Chenopodium album | - | - | 0.0151 |
| 秦艽Gentiana macrophylla | 0.0199 | 0.0106 | - | 西藏大戟Euphorbia tibetica | - | - | 0.0145 |
| 珠芽蓼B. vivipara | 0.1225 | 0.0716 | 0.0416 | 多刺绿绒蒿Meconopsis horridula | - | - | 0.0080 |
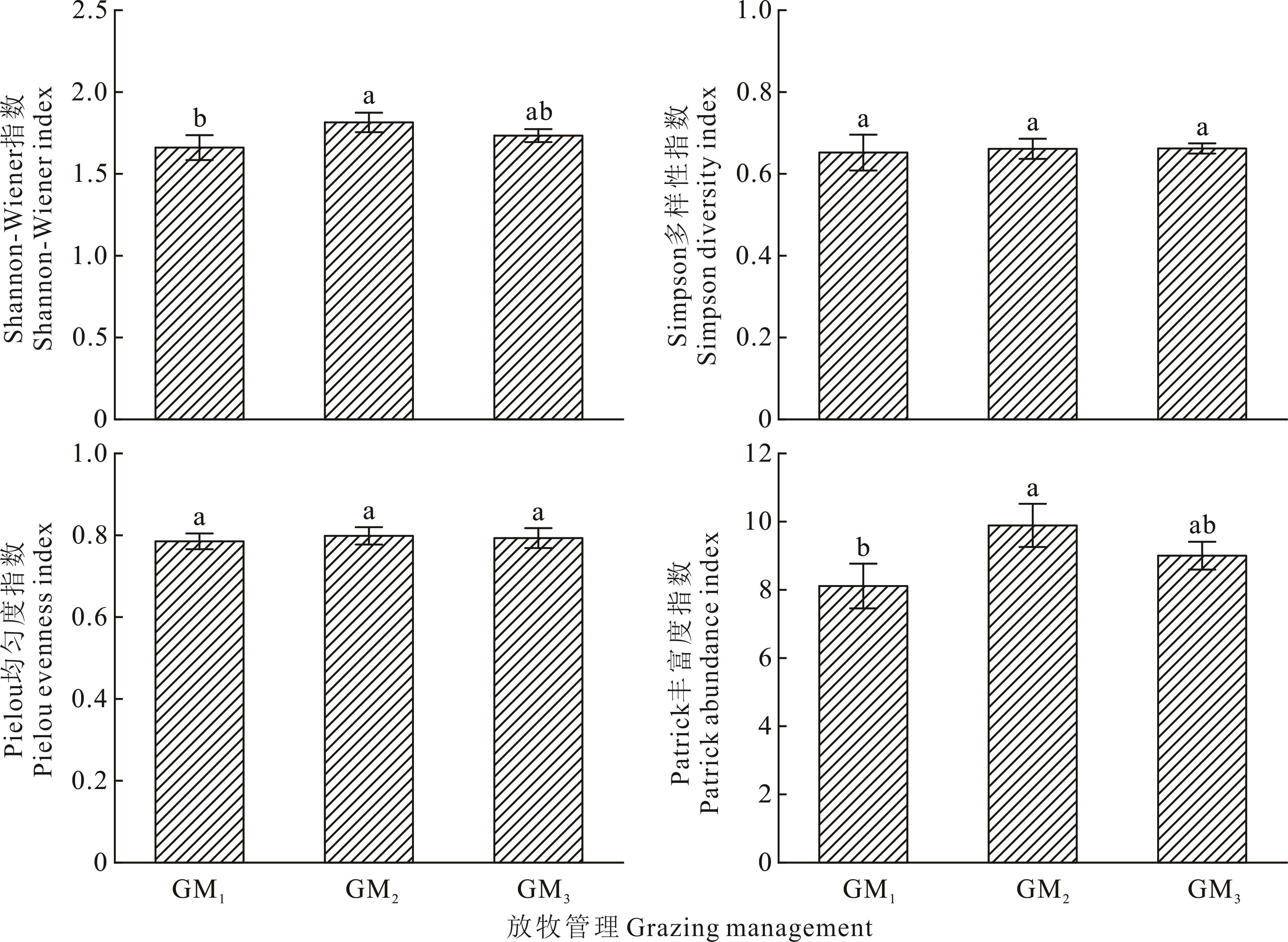
图1 不同放牧管理下植物多样性特征不同小写字母代表处理间存在显著差异(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters represent significant differences among treatments (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.1 Characteristics of plant diversity under different grazing management
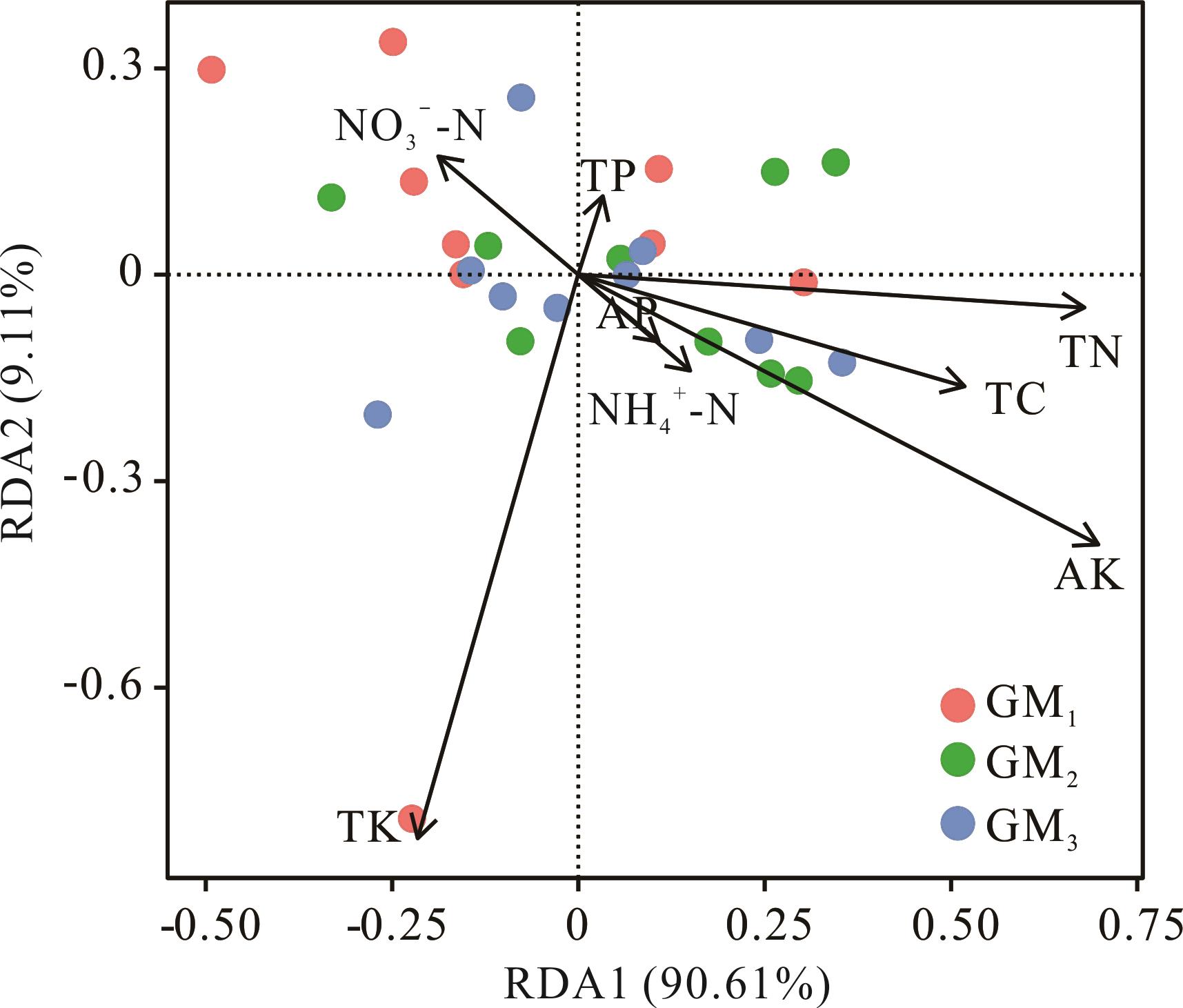
图3 不同放牧管理下植被-土壤因子RDA分析TC: 土壤全碳 Soil total carbon; TN: 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen; TP: 土壤全磷 Soil total phosphorus; TK: 土壤全钾 Soil total potassium; AP: 土壤速效磷 Soil available phosphorus; AK: 土壤速效钾 Soil available potassium; NH4+-N: 土壤铵态氮 Soil ammonia nitrogen; NO3--N: 土壤硝态氮 Soil nitrate nitrogen.
Fig.3 Redundancy analysis of vegetation-soil factors under different grazing management
处理 Treatment | 植被指数 VEx | 土壤指数 SEy | 植被-土壤系统对比关系 SEy/VEx | 植被-土壤系统耦合度Sc | 植被-土壤系统耦合模式 Vegetation-soil system coupling model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GM1 | 0.137 | 0.199 | 1.171 | 0.397 | 轻度失调同步衰退发展型Mild dyssynchrony decline developmental type |
| GM2 | 0.177 | 0.319 | 1.802 | 0.482 | 濒临失调土壤滞后发展型Borderline disordered soil lagging development type |
| GM3 | 0.158 | 0.424 | 2.684 | 0.510 | 勉强协调土壤滞后发展型Barely coordinated with soil lagging development type |
表4 植被-土壤生态系统耦合协同效应评价
Table 4 Evaluation of vegetation-soil ecosystem coupling synergistic effect
处理 Treatment | 植被指数 VEx | 土壤指数 SEy | 植被-土壤系统对比关系 SEy/VEx | 植被-土壤系统耦合度Sc | 植被-土壤系统耦合模式 Vegetation-soil system coupling model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GM1 | 0.137 | 0.199 | 1.171 | 0.397 | 轻度失调同步衰退发展型Mild dyssynchrony decline developmental type |
| GM2 | 0.177 | 0.319 | 1.802 | 0.482 | 濒临失调土壤滞后发展型Borderline disordered soil lagging development type |
| GM3 | 0.158 | 0.424 | 2.684 | 0.510 | 勉强协调土壤滞后发展型Barely coordinated with soil lagging development type |
| 1 | Gibson D J. Grasses and grassland ecology. New York: Oxford University Press, 2009. |
| 2 | Fang J Y, Bai Y F, Li L H, et al. Scientific basis and practical ways for sustainable development of China’s pasture regions. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(2): 155-164. |
| 方精云, 白永飞, 李凌浩, 等. 我国草原牧区可持续发展的科学基础与实践. 科学通报, 2016, 61(2): 155-164. | |
| 3 | Schils R L M, Bufe C, Rhymer C M, et al. Permanent grasslands in Europe: Land use change and intensification decrease their multifunctionality. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2022, 330(1): 107891. |
| 4 | Xu M M, Meng C, Wang X, et al. Study on the effect of grazing and enclosure on the preferential flow of soil in desert grassland and shrub grassland. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2023, 37(3): 81-86. |
| 徐苗苗, 孟晨, 王兴, 等. 围栏封育对荒漠草原灌丛草地土壤优先流的影响研究. 水土保持学报, 2023, 37(3): 81-86. | |
| 5 | Dong Q M, Ma Y S, Xu C J, et al. Study of classification and gradation, restoration of black-soil beach degraded grassland in the headwaters of Three Rivers. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2015, 23(3): 441-447. |
| 董全民, 马玉寿, 许长军, 等. 三江源区黑土滩退化草地分类分级体系及分类恢复研究. 草地学报, 2015, 23(3): 441-447. | |
| 6 | Zhang Z H, Zhou H K, Zhao X Q, et al. Relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in alpine meadows of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 2018, 26(2): 111-129. |
| 张中华, 周华坤, 赵新全, 等. 青藏高原高寒草地生物多样性与生态系统功能的关系. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(2): 111-129. | |
| 7 | Metera E, Sakowski T, Słoniewski K, et al. Grazing as a tool to maintain biodiversity of grassland-A review. Animal Science Papers and Reports, 2010, 28(4): 315-334. |
| 8 | Bond W J. Large parts of the world are brown or black: A different view on the ‘Green World’ hypothesis. Journal of Vegetation Science, 2005, 16(3): 261-266. |
| 9 | Kimble J M. Soil carbon management economic, environmental and societal benefits. Leighton: CRC Press, 2007. |
| 10 | Fei X, Zhu S, Peng Y H, et al. Linking plant functional trait diversity and community structure characteristics in a seasonal grazing alpine meadow on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2024, 30(3): 449-457. |
| 费璇, 朱莎, 彭幼红, 等. 青藏高原东缘季节性放牧高寒草甸植物功能性状多样性与群落结构特征的联系. 应用与环境生物学报, 2024, 30(3): 449-457. | |
| 11 | Shi Y, Hu T H, Gao H J, et al. The community vegetation composition and stability characteristics of alpine meadow under two grazing modes. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(9): 1-10. |
| 施颖, 胡廷花, 高红娟, 等. 两种放牧模式下高寒草甸群落植被构成及稳定性特征. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 1-10. | |
| 12 | Zhou H K, Zhao X Q, Zhou L, et al. A study on correlations between vegetation degradation and soil degradation in the ‘Alpine Meadow’ of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2005, 14(3): 31-40. |
| 周华坤, 赵新全, 周立, 等. 青藏高原高寒草甸的植被退化与土壤退化特征研究. 草业学报, 2005, 14(3): 31-40. | |
| 13 | Yang Y H, Rao S, Hu H F, et al. Plant species richness of alpine grasslands in relation to environmental factors and biomass on the Tibetan Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 2004, 12(1): 200-205. |
| 杨元合, 饶胜, 胡会峰, 等. 青藏高原高寒草地植物物种丰富度及其与环境因子和生物量的关系. 生物多样性, 2004, 12(1): 200-205. | |
| 14 | Shi F Y, Wang Y, Fu X Y, et al. Metrological characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in grassland ecosystem under different grazing intensity in east of Qilian Mountain. Journal of Domestic Animal Ecology, 2017, 38(3): 61-66. |
| 石福于, 王毅, 付晓悦, 等. 不同放牧强度下祁连山东段草地生态系统氮磷计量特征. 家畜生态学报, 2017, 38(3): 61-66. | |
| 15 | Qian S, Mao L X, Hou Y Y, et al. Livestock carrying capacity and balance between carrying capacity of grass land with added forage and actual livestock in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Natural Resources, 2007, 22(3): 389-397, 498. |
| 钱拴, 毛留喜, 侯英雨, 等. 青藏高原载畜能力及草畜平衡状况研究. 自然资源学报, 2007, 22(3): 389-397, 498. | |
| 16 | Yu Z H, Dong Q M, Cao Q, et al. Effects of different grazing patterns on plant community characteristics of alpine meadows in Qilian Mountains. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(9): 2621-2627. |
| 于泽航, 董全民, 曹铨, 等. 不同放牧模式对祁连山高寒草甸植物群落特征的影响. 草地学报, 2023, 31(9): 2621-2627. | |
| 17 | Dong Q M, Zhao X Q, Shi J J, et al. Effect of dietary composition on the digestive and energy metabolisms of yak calves. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(3): 281-286. |
| 董全民, 赵新全, 施建军, 等. 日粮组成对牦犊牛消化和能量代谢的影响. 草业学报, 2012, 21(3): 281-286. | |
| 18 | Zhang X P, Sun G Z. Current situation and model selection in the construction of national parks administration. Journal of Beijing Forestry University (Social Sciences), 2021, 20(1): 76-83. |
| 张小鹏, 孙国政. 国家公园管理单位机构的设置现状及模式选择. 北京林业大学学报(社会科学版), 2021, 20(1): 76-83. | |
| 19 | Bao S D. Analysis of agri-chemical soil (third edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2005. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2005. | |
| 20 | Zhang Y Y. Investigation and analysis of plant community species diversity and landscape structure. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2023, 21(22): 7566-7570. |
| 张岩岩. 植物群落物种多样性与景观结构调查与分析. 分子植物育种, 2023, 21(22): 7566-7570. | |
| 21 | Guo W F, Li X, Chen Y M, et al. Evaluation of the coupling relationship between vegetation and soil system under different management measures in Taihang Mountains. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(15): 6170-6181. |
| 郭文芳, 李鑫, 陈艳梅, 等. 太行山坡地不同管理措施植被-土壤系统耦合关系. 生态学报, 2023, 43(15): 6170-6181. | |
| 22 | Peng W X, Song T Q, Zeng F P, et al. Models of vegetation and soil coupling coordinative degree in grain for green project in depressions between karst hills. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2011, 27(9): 305-310. |
| 彭晚霞, 宋同清, 曾馥平, 等. 喀斯特峰丛洼地退耕还林还草工程的植被土壤耦合协调度模型. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(9):305-310. | |
| 23 | Nan G W, Zhao M X, Wang Y Y, et al. Evaluation of coupling coordination relationship between soil and vegetation systems in different afforestation types. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2021, 35(5): 157-162. |
| 南国卫, 赵满兴, 王月月, 等. 不同退耕类型土壤-植被系统耦合协调关系评价. 干旱区资源与环境, 2021, 35(5): 157-162. | |
| 24 | Wang C, Tang N. Spatio-temporal characteristics and evolution of rural production-living-ecological space function coupling coordination in Chongqing Municipality. Geographical Research, 2018, 37(6): 1100-1114. |
| 王成, 唐宁. 重庆市乡村三生空间功能耦合协调的时空特征与格局演化. 地理研究, 2018, 37(6): 1100-1114. | |
| 25 | Liu Y B, Li R D, Song X F. Analysis of coupling degrees of urbanization and ecological environment in China. Journal of Natural Resources, 2005, 20(1): 105-112. |
| 刘耀彬, 李仁东, 宋学锋. 中国城市化与生态环境耦合度分析. 自然资源学报, 2005, 20(1): 105-112. | |
| 26 | Olff H, Ritchie M E. Effects of herbivores on grassland plant diversity. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 1998, 13(7): 261-265. |
| 27 | Belsky A J. Effects of grazing, competition, disturbance and fire on species composition and diversity in grassland communities. Journal of Vegetation Science, 1992, 3(2): 187-200. |
| 28 | McNaughton S J. Ecology of a grazing ecosystem: The serengeti. Ecological Monographs, 1985, 55(3): 259-294. |
| 29 | Fang J. The interactions between foraging of large herbivore with different body size and Songnen grassland vegetation characteristics. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2013. |
| 房健. 不同体尺大型草食动物采食对松嫩草地植被特征的响应及作用研究. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2013. | |
| 30 | Borer E T, Seabloom E W, Gruner D S, et al. Herbivores and nutrients control grassland plant diversity via light limitation. Nature, 2014, 508(7497): 517-520. |
| 31 | Wang J, Xu M X, Sun H, et al. Effects of grazing on community characteristics of Robinia pseudoacacia forest in the Hilly Loess Plateau region of northern Shaanxi Province. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(6): 1826-1833. |
| 王菊, 许明祥, 孙会, 等. 放牧对陕北黄土丘陵区刺槐林群落特征的影响. 草地学报, 2023, 31(6): 1826-1833. | |
| 32 | Wang P. The coupling effects of ecological-economic-social systems with different grazing intensity on the Loess Plateau. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2023. |
| 王鹏. 黄土高原不同放牧强度生态经济社会系统耦合效应研究. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2023. | |
| 33 | Fan F, Liang C, Tang Y, et al. Effects and relationships of grazing intensity on multiple ecosystem services in the Inner Mongolian steppe. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 675(4): 642-650. |
| 34 | Dadkhah M, Gifford G F. Influence of vegetation, rock cover, and trampling on infiltration rates and sediment production. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 1980, 16(6): 979-986. |
| 35 | An H, Li G Q. Effects of grazing on carbon and nitrogen in plants and soils in a semiarid desert grassland, China. Journal of Arid Land, 2015, 7: 341-349. |
| 36 | Su Y Z, Li Y L, Cui J Y, et al. Influences of continuous grazing and livestock exclusion on soil properties in a degraded sandy grassland, Inner Mongolia, northern China. Catena, 2005, 59(3): 267-278. |
| 37 | Zhou Z H, Wang C K. Changes of the relationships between soil and microbes in carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry during ecosystem succession. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2016, 40(12): 1257-1266. |
| 周正虎, 王传宽. 生态系统演替过程中土壤与微生物碳氮磷化学计量关系的变化. 植物生态学报, 2016, 40(12): 1257-1266. | |
| 38 | Dong Q, Li Q Q, Wang C Q, et al. Effects of different land use patterns on soil potassium distribution in Chengdu Plain, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(4): 1389-1396. |
| 董琴, 李启权, 王昌全, 等. 成都平原不同土地利用方式对土壤剖面钾素分布的影响. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(4): 1389-1396. | |
| 39 | Liu S Q, Gao L L, Pu Y L, et al. Status of soil P and K nutrient and their influencing factors in Tibet. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2005, 19(1): 75-78, 88. |
| 刘世全, 高丽丽, 蒲玉琳, 等. 西藏土壤磷素和钾素养分状况及其影响因素. 水土保持学报, 2005, 19(1): 75-78, 88. | |
| 40 | Delgado-Baquerizo M, Powell J R, Hamonts K, et al. Circular linkages between soil biodiversity, fertility and plant productivity are limited to topsoil at the continental scale. New Phytologist, 2017, 215(3): 1186-1196. |
| 41 | Zeng X H, Zhang W J, Song Y G, et al. Species diversity and soil nutrient dynamics along a chronosequence of vegetation restoration in Taihang Mountains hilly region, Hebei Province of North China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2013, 32(4): 852-858. |
| 曾歆花, 张万军, 宋以刚, 等. 河北太行山低山丘陵区植被恢复过程中物种多样性与土壤养分变化. 生态学杂志, 2013, 32(4): 852-858. | |
| 42 | Cao Y L, Zhang X L, Lv G, et al. Study on potassium release characteristics of aeolian sandy soil under different land use patterns in Zhanggutai, Liaoning Province. Forest Resources Management, 2023(4): 161-168. |
| 曹怡立, 张学利, 吕刚, 等. 辽宁章古台不同土地利用方式风沙土钾素释放特征研究. 林业资源管理, 2023(4): 161-168. | |
| 43 | Jiao J Y, Ma X H, Bai W J, et al. Correspondence analysis of vegetation communities and soil environmental factors on abandoned cropland on hilly-gullied loess plateau. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2005, 42(5): 42-50. |
| 焦菊英, 马祥华, 白文娟, 等. 黄土丘陵沟壑区退耕地植物群落与土壤环境因子的对应分析. 土壤学报, 2005, 42(5): 42-50. | |
| 44 | Ge J, Wang S, Fan J, et al. Soil nutrients of different land-use types and topographic positions in the water-wind erosion crisscross region of China’s Loess Plateau. Catena, 2020, 184(8): 104243. |
| 45 | Zheng X, Li Z Z, Zheng L Y, et al. Distribution pattern and correlation of soil available potassium and plant total potassium at different altitudes in Wugong Mountain. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(4): 211-214. |
| 郑翔, 李真真, 郑利亚, 等. 武功山不同海拔高度土壤速效钾与植物全钾分布格局及相关性. 江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(4): 211-214. | |
| 46 | Xu J Y, Zhang Z B, Wang Y K, et al. Effects of different cover crops on nitrate dynamics in Shajiang black soil profile. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2023, 42(10): 2281-2290. |
| 徐静怡, 张中彬, 王玥凯, 等. 不同覆盖作物对砂姜黑土剖面硝态氮动态的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2023, 42(10): 2281-2290. | |
| 47 | Hu X, Wei J J, Ma L, et al. Effects of removal of the plant functional groups on vegetation biomass and soil properties in Carex tibetikobresia meadow. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(11): 3240-3250. |
| 胡雪, 魏晶晶, 马丽, 等. 西藏嵩草草甸植物功能群去除影响群落生物量及土壤理化性质. 草地学报, 2023, 31(11): 3240-3250. | |
| 48 | Liu S L, Lin L, Zhang F W, et al. Effects of grazing season and degradation degree on the soil organic carbon in alpine meadow. Pratacultural Science, 2016, 33(1): 11-18. |
| 刘淑丽, 林丽, 张法伟, 等. 放牧季节及退化程度对高寒草甸土壤有机碳的影响. 草业科学, 2016, 33(1): 11-18. | |
| 49 | Zhao Z W, Guo X M, Niu D K, et al. Variations of N content in soil of upland meadow in different seasons and degradation degrees. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2015, 46(8): 1401-1405. |
| 赵自稳, 郭晓敏, 牛德奎, 等. 不同季节和退化程度下山地草甸土壤氮素含量的变化. 南方农业学报, 2015, 46(8): 1401-1405. | |
| 50 | Lin H L, Hou F J. Research progress and trends in system coupling and discordance for grassland agroecosystems. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004, 24(6): 1252-1258. |
| 林慧龙, 侯扶江. 草地农业生态系统中的系统耦合与系统相悖研究动态. 生态学报, 2004, 24(6): 1252-1258. | |
| 51 | Zhao F, Xie Y Z, Ma H B, et al. Effects of enclosure on species diversity and soil organic matter of typical steppe. Pratacultural Science, 2011, 28(6): 887-891. |
| 赵菲, 谢应忠, 马红彬, 等. 封育对典型草原植物群落物种多样性及土壤有机质的影响. 草业科学, 2011, 28(6): 887-891. | |
| 52 | Ma Y S, Lang B N, Li Q Y, et al. Study on rehabilitating and rebuilding technologies for degenerated alpine meadow in the Changjiang and Yellow River source region. Pratacultural Science, 2002, 19(9): 1-5. |
| 马玉寿, 郎百宁, 李青云, 等. 江河源区高寒草甸退化草地恢复与重建技术研究. 草业科学, 2002, 19(9): 1-5. | |
| 53 | He G Y, Sun H Z, Shi X M, et al. Soil properties of Tibetan Plateau alpine wetland affected by grazing and season. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(4): 12-20. |
| 何贵永, 孙浩智, 史小明, 等. 青藏高原高寒湿地不同季节土壤理化性质对放牧模式的响应. 草业学报, 2015, 24(4): 12-20. |
| [1] | 刘继亮, 赵文智, 王永珍, 冯怡琳, 祁进贤, 李永元. 禁牧和放牧对祁连山高寒草原秋季大型和中型土壤节肢动物多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 214-221. |
| [2] | 李紫晶, 高翠萍, 王忠武, 韩国栋. 中国草地固碳减排研究现状及其建议[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 191-200. |
| [3] | 王德利, 王岭, 韩国栋. 草地精准放牧管理:概念、理论、技术及范式[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 191-199. |
| [4] | 赛宁刚, 祁娟, 贾燕伟, 车美美, 杨娟弟, 王晓娟, 徐长林. 东祁连山不同土地利用方式下土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 99-109. |
| [5] | 贺翔, 白梅梅, 徐长林, 宋美娟, 汪鹏斌, 鱼小军. 东祁连山小叶金露梅+杯腺柳灌丛草地植被和土壤对其自然恢复演替的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 12-24. |
| [6] | 赵文, 尹亚丽, 李世雄, 刘燕, 刘晶晶, 董怡玲, 苏世锋, 吉凌鹤. 祁连山不同类型草地土壤细菌群落特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 161-171. |
| [7] | 贺国宝. 祁连山北坡植物群落空间分布格局与多样性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 194-201. |
| [8] | 高亚敏, 罗慧琴, 姚拓, 张建贵, 李海云, 杨琰珊, 兰晓君. 高寒退化草地委陵菜根围丛枝菌根菌(AMF)分离鉴定及促生效应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 145-154. |
| [9] | 李海云, 姚拓, 马亚春, 张慧荣, 路晓雯, 杨晓蕾, 夏东慧, 张建贵, 高亚敏. 祁连山中段退化高寒草地土壤细菌群落分布特征[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 170-179. |
| [10] | 张建贵, 王理德, 姚拓, 李海云, 高亚敏, 杨晓玫, 李昌宁, 李琦, 冯影, 胡彦婷. 祁连山高寒草地不同退化程度植物群落结构与物种多样性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(5): 15-25. |
| [11] | 刘玉祯, 曹文侠, 王金兰, 李文, 辛雨琼, 王世林, 王小军. 祁连山东段不同类型灌丛斑块土壤特征对围封的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(11): 32-45. |
| [12] | 景美玲, 马玉寿, 李世雄, 王彦龙. 大通河上游16种多年生禾草引种试验研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(6): 76-88. |
| [13] | 李文, 曹文侠, 师尚礼, 李小龙, 陈建刚, 徐长林. 放牧管理模式对高寒草甸生态系统有机碳、氮储量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(11): 25-33. |
| [14] | 朱平, 陈仁升, 宋耀选, 刘光琇, 陈拓, 张威. 祁连山不同植被类型土壤微生物群落多样性差异[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(6): 75-84. |
| [15] | 李文, 曹文侠, 刘皓栋, 李小龙, 徐长林, 师尚礼, 冯今, 周传猛. 不同放牧管理模式对高寒草甸草原土壤呼吸特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(10): 22-32. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||