

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (12): 194-201.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020463
• 研究简报 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2020-10-14
修回日期:2020-11-11
出版日期:2021-11-11
发布日期:2021-11-11
作者简介:贺国宝(1967-),男,甘肃肃南人,畜牧师。E-mail: hebaoguo1967@163.com
基金资助:Received:2020-10-14
Revised:2020-11-11
Online:2021-11-11
Published:2021-11-11
摘要:
干旱区山地植物群落的空间分布格局和多样性特征对海拔梯度的响应分析,有助于探究山地植物的生态适应性策略。采用TWINSPAN和DCA排序等方法,研究了祁连山北坡植物群落分布格局和多样性特征。结果表明:祁连山北坡植物群落可以分为9个类群,随着海拔的升高,植被类型由荒漠-荒漠草原-典型草原逐渐转变为草甸草原,植物群落由斑块状分布的盐爪爪+珍珠群丛至灌木亚菊+珍珠群丛和合头草+珍珠群丛过渡为甘蒙锦鸡儿+芨芨草群丛、扁穗冰草+西北针茅群丛和西北针茅+赖草群丛,最后逐渐演化为呈镶嵌分布的鬼箭锦鸡儿+高山柳群丛和苔草+嵩草群丛;草地群落的Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H')和物种丰富度指数(R)呈“双峰”变化趋势,Pielou均匀度指数(J)在中海拔有最大值,而Simpson优势度指数(C)在中海拔有最小值。祁连山植被类型由低海拔荒漠至高海拔草甸草原演化过程中伴随着植物群落分布格局和种类组成的改变,体现了山地环境对植物群落构建的过滤作用。
贺国宝. 祁连山北坡植物群落空间分布格局与多样性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 194-201.
Guo-bao HE. Distribution characteristics and plant community diversity on the north slopes of the Qilian Mountains[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(12): 194-201.
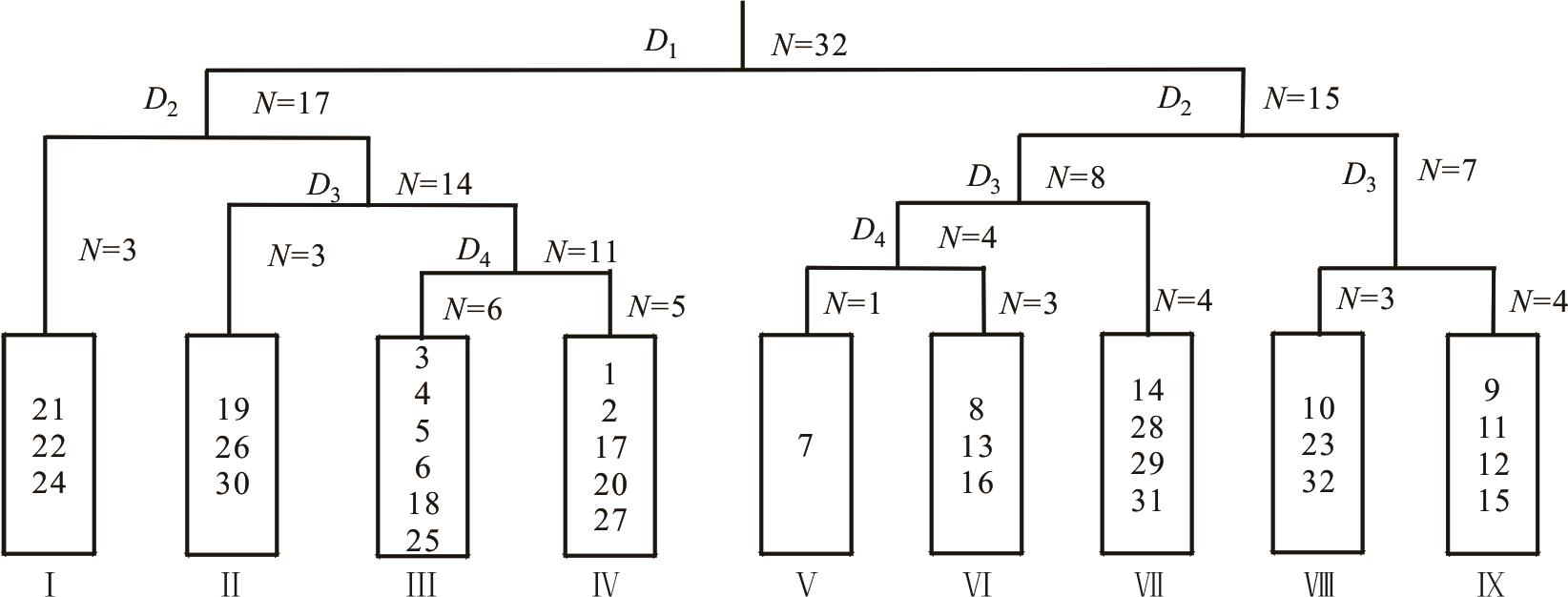
图1 祁连山北坡植物群落32个样方的TWINSPAN分类Dn: 分类级别The classification level; N: 样方个数The number of plots.
Fig.1 TWINSPAN taxonomic tree of 32 plots of community on the north slope of Qilian Mountain
| 组Group | 样方编号 Plots number | 群丛类型 Association types | 盖度 Cover (%) | 海拔 Elevation (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 21, 22, 24 | 盐爪爪+珍珠-灌木亚菊+多根葱群丛Assoc. K. foliatum+Phyllanthus urinaria-A.fruticulosa+Allium polyrhizum | 20~30 | 1670~1690 |
| Ⅱ | 19, 26, 30 | 灌木亚菊+珍珠-合头草+茵陈蒿群丛Assoc.A. fruticulosa+P. urinaria-S. regelii+Artemisia capillaris | 20~30 | 1710~1750 |
| Ⅲ | 3, 4, 5, 6, 18, 25 | 合头草+珍珠-多根葱+茵陈蒿群丛Assoc. S. regelii+P. urinaria-A. polyrhizum+A. capillaris | 30~50 | 1820~2480 |
| Ⅳ | 1, 2, 17, 20, 27 | 合头草+珍珠-多根葱+铁杆蒿群丛Assoc. S. regelii+P.urinaria-A. polyrhizum+Artemisia gmelinii | 30~50 | 2170~2480 |
| Ⅴ | 7 | 甘蒙锦鸡儿+芨芨草-针茅+醉马草群丛Assoc. Caragana opulens+Achnatherum splendens-Stipa capillata+Achnatherum inebrians | 60~80 | 2470 |
| Ⅵ | 8, 13, 16 | 扁穗冰草+西北针茅-棘豆群丛Assoc. A. cristatum+S. sareptana-Oxytropis caerulea | 70~90 | 2630~2790 |
| Ⅶ | 14, 28, 29, 31 | 西北针茅+赖草-委陵菜+阿尔泰狗娃花Assoc. S. sareptana+Leymus secalinus-Potentilla chinensis+Heteropappus altaicus | 85~100 | 2760~2900 |
| Ⅷ | 10, 23, 32 | 鬼箭锦鸡儿+高山柳-绣线菊+珠芽蓼群丛Assoc. C. jubata+S.cupularis -Spiraea salicifolia+Polygonum viviparum | 95 | 3120~3410 |
| Ⅸ | 9, 11, 12, 15 | 苔草+嵩草-火绒草+灯心草+唐松草群丛Assoc. C. tristachya+K. myosuroides-Leontopodium hayachinense+Juncus effuses+Thalictrum aquilegiifolium | 90~100 | 2910~3440 |
表1 祁连山北坡9个植物群丛类型的群落特征及其主要物种成分
Table 1 Community characteristics and main species components of nine plant association types on the north slope of Qilian Mountains
| 组Group | 样方编号 Plots number | 群丛类型 Association types | 盖度 Cover (%) | 海拔 Elevation (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 21, 22, 24 | 盐爪爪+珍珠-灌木亚菊+多根葱群丛Assoc. K. foliatum+Phyllanthus urinaria-A.fruticulosa+Allium polyrhizum | 20~30 | 1670~1690 |
| Ⅱ | 19, 26, 30 | 灌木亚菊+珍珠-合头草+茵陈蒿群丛Assoc.A. fruticulosa+P. urinaria-S. regelii+Artemisia capillaris | 20~30 | 1710~1750 |
| Ⅲ | 3, 4, 5, 6, 18, 25 | 合头草+珍珠-多根葱+茵陈蒿群丛Assoc. S. regelii+P. urinaria-A. polyrhizum+A. capillaris | 30~50 | 1820~2480 |
| Ⅳ | 1, 2, 17, 20, 27 | 合头草+珍珠-多根葱+铁杆蒿群丛Assoc. S. regelii+P.urinaria-A. polyrhizum+Artemisia gmelinii | 30~50 | 2170~2480 |
| Ⅴ | 7 | 甘蒙锦鸡儿+芨芨草-针茅+醉马草群丛Assoc. Caragana opulens+Achnatherum splendens-Stipa capillata+Achnatherum inebrians | 60~80 | 2470 |
| Ⅵ | 8, 13, 16 | 扁穗冰草+西北针茅-棘豆群丛Assoc. A. cristatum+S. sareptana-Oxytropis caerulea | 70~90 | 2630~2790 |
| Ⅶ | 14, 28, 29, 31 | 西北针茅+赖草-委陵菜+阿尔泰狗娃花Assoc. S. sareptana+Leymus secalinus-Potentilla chinensis+Heteropappus altaicus | 85~100 | 2760~2900 |
| Ⅷ | 10, 23, 32 | 鬼箭锦鸡儿+高山柳-绣线菊+珠芽蓼群丛Assoc. C. jubata+S.cupularis -Spiraea salicifolia+Polygonum viviparum | 95 | 3120~3410 |
| Ⅸ | 9, 11, 12, 15 | 苔草+嵩草-火绒草+灯心草+唐松草群丛Assoc. C. tristachya+K. myosuroides-Leontopodium hayachinense+Juncus effuses+Thalictrum aquilegiifolium | 90~100 | 2910~3440 |
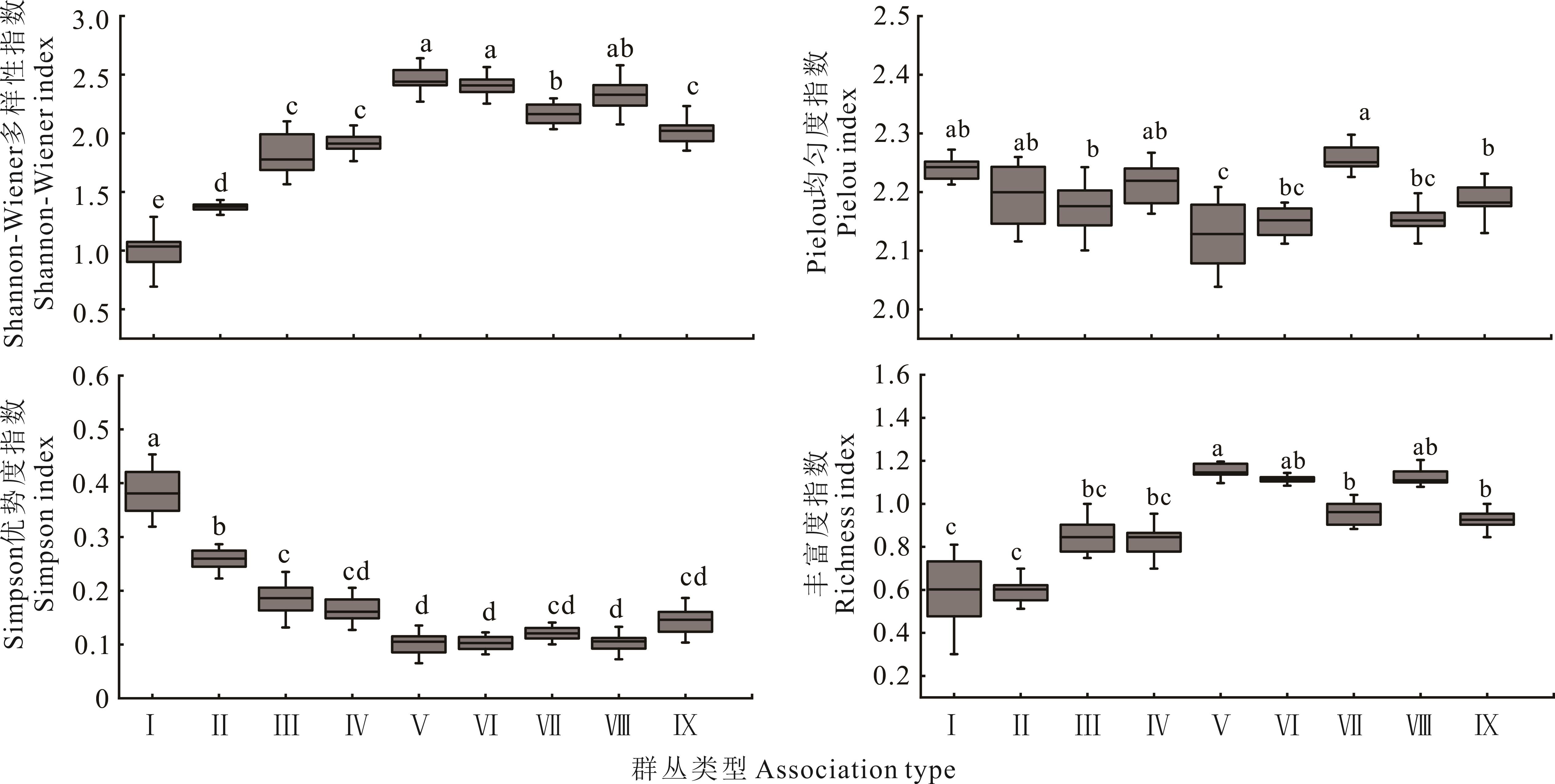
图3 祁连山北坡9个植物群丛类型多样性指数不同小写字母表示群落间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among communities (P<0.05).
Fig.3 Diversity index of 9 plant association types on the north slope of Qilian Mountain
| 1 | Zhang Q, Niu J M, Buyantuyev A, et al. Ecological analysis and classification of Stipa breviflora communities in the Inner Mongolia region: The role of environmental factors. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(1): 83-92. |
| 张庆, 牛建明, Buyantuyev A, 等. 内蒙古短花针茅群落数量分类及环境解释. 草业学报, 2012, 21(1): 83-92. | |
| 2 | Li S Y, Zhang J, Yao L A, et al. The community structure of phytoplankton and its relationship with environmental factors in Xizhijiang River. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(6): 1939-1947. |
| 李思阳, 张娟, 姚玲爱, 等. 西枝江流域浮游植物群落结构特征与主要环境因子的关系研究. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(6): 1939-1947. | |
| 3 | Qin P Y, Yang H J, Jiang F L, et al. Quantitative classification of natural plant communities in the Saihanba National Nature Reserve, Hebei Province, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(5): 1383-1392. |
| 秦朋遥, 杨会娟, 蒋凤玲, 等. 河北省塞罕坝保护区天然植物群落数量分类. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(5): 1383-1392. | |
| 4 | Zhou X, Zuo X A, Zhao X Y, et al. Comparison analyses of DCA, CCA and DCCA on relationships between plant community distribution and soil properties of Horqin sandy land. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2015, 34(4): 947-954. |
| 周欣, 左小安, 赵学勇, 等. 科尔沁沙地植物群落分布与土壤特性关系的DCA、CCA及DCCA分析. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(4): 947-954. | |
| 5 | Ermakov N, Makhatkov I. Classification and ordination of north boreal light-coniferous forests of the West Siberian Plain. Plant Biosystems, 2011, 145(S): 199-207. |
| 6 | Ahmad S S, Quratulann. Vegetation classification in Ayubia National Park, Pakistan using ordination methods. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 2011, 43(5): 2315-2321. |
| 7 | Xu X, Zhang H Y, Xie T, et al. Elevational pattern of seed plant diversity in Xishuangbanna and its mechanisms. Biodiversity Science, 2018, 26(7): 678-689. |
| 徐翔, 张化永, 谢婷, 等. 西双版纳种子植物物种多样性的垂直格局及机制. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(7): 678-689. | |
| 8 | Liu Z, Li Q, Chen D D, et al. Patterns of plant species diversity along an altitudinal gradient and its effect on above ground biomass in alpine meadows in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 2015, 23(4): 451-462. |
| 刘哲, 李奇, 陈懂懂, 等. 青藏高原高寒草甸物种多样性的海拔梯度分布格局及对地上生物量的影响. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(4): 451-462. | |
| 9 | Sun M, Su T, Zhang S, et al. Variations in leaf morphological traits of Quercus guyavifolia (Fagaceae) were minly influenced by water and ultraviolet irradiation at high elevations on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 2016, 18: 266-273. |
| 10 | Dunbar-Co S, Sporck M J, Sack L. Leaf trait diversification and design in seven rare taxa of the Hawaiian Plantago radiation. International Journal of Plant Sciences, 2009, 170(1): 61-75. |
| 11 | Gui D W, Lei J Q, Zeng F J, et al. Effect of ecological factors on plant communities of the Cele River basin on the north slope of the middle Kunlun Mountains. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2010, 19(3): 38-46. |
| 桂东伟, 雷加强, 曾凡江, 等. 中昆仑山北坡策勒河流域生态因素对植物群落的影响. 草业学报, 2010, 19(3): 38-46. | |
| 12 | Zhao C Z, Gao F Y, Shi F X, et al. Melica przewalskyi population spatial pattern and response to soil moisture in degraded alpine grassland. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(22): 6688-6695. |
| 赵成章, 高福元, 石福习, 等. 高寒退化草地甘肃臭草种群分布格局及其对土壤水分的响应. 生态学报, 2011, 31(22): 6688-6695. | |
| 13 | Ma R, Zhao J M. Relationship between the grassland and soil conditions in the Eastern Qilian Mountains. Arid Zone Research, 2020, 37(2): 1-9. |
| 马瑞, 赵锦梅. 东祁连山河谷高寒草地植被群落特征及其与土壤性状的关系. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(2): 1-9. | |
| 14 | Tang Z H, Yu Q S, Liu H J, et al. Characteristics of alpine vegetation community and its relationship to topographic climate factors in the Eastern Qilian Mountain. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(1): 223-232. |
| 唐志红, 尉秋实, 刘虎俊, 等. 祁连山东段高寒植被群落特征及其与地形气候因子关系研究. 生态学报, 2020, 40(1): 223-232. | |
| 15 | Rong Z L. Effects of climate change on distribution of dominant species and pattern of vegetation in Qilian Mountains. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019. |
| 戎战磊. 气候变化对祁连山优势物种分布和植被格局的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2019. | |
| 16 | Zhang Q, Sun X M, Yang J, et al. Effect of slope aspect on species functional groups and species diversity in alpine meadow of the East of Qilian Mountains. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2019, 39(8): 1480-1490. |
| 张倩, 孙小妹, 杨晶, 等. 坡向对东祁连山高寒草甸群落物种功能群及其多样性的影响. 西北植物学报, 2019, 39(8): 1480-1490. | |
| 17 | Ren J Z. Scientific research methods of grass industry. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 1998: 1-19. |
| 任继周. 草业科学研究方法. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1998: 1-19. | |
| 18 | Zhang L J, Yue M, Zhang Y D, et al. Characteristics of plant community species diversity of oasis desert ecotone in Fukang, Xinjiang. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2003, 23(3): 329-334. |
| 张林静, 岳明, 张远东, 等. 新疆阜康绿洲-荒漠过渡带植物群落物种多样性特征. 地理科学, 2003, 23(3): 329-334. | |
| 19 | Zhang J T. Quantitative ecology. 3nd. Beijing: Science Press, 2004. |
| 张金屯. 数量生态学. 第三版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004. | |
| 20 | Zhang L, Guo W, Li S Q, et al. Distribution pattern and species diversity of artificial vegetation communities in sandy-hilly region of Northwest Shanxi Province, China. Forest Resources Management, 2017(6): 60-66. |
| 张鸾, 郭伟, 李素清, 等. 晋西北丘陵风沙区人工植被群落分布格局与多样性. 林业资源管理, 2017(6): 60-66. | |
| 21 | Ma K P, Huang J H, Yu S L, et al. Plant community diversity in Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1995, 15: 268-277. |
| 马克平, 黄建辉, 于顺利, 等. 北京东灵山地区植物群落多样性的研究. 生态学报, 1995, 15: 268-277. | |
| 22 | Gallardo-Cruz J A, Pérez-García E A, Meave J A. β-diversity and vegetation structure as influenced by slope aspect and altitude in a seasonally dry tropical landscape. Landscape Ecology, 2009, 24: 473-482. |
| 23 | Zheng J K, Wei T X, Zheng L K, et al. Effects of landforms on α biodiversity in slope scale. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2009, 18(6): 2254-2259. |
| 郑江坤, 魏天兴, 郑路坤, 等. 坡面尺度上地貌对α生物多样性的影响. 生态环境学报, 2009, 18(6): 2254-2259. | |
| 24 | Ren Q W, Wang X, Li L D, et al. Vertical variation of physical and chemical properties of soil at different elevations in Xiaowutai Mountain. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(1): 241-247. |
| 任启文, 王鑫, 李联地, 等. 小五台山不同海拔土壤理化性质垂直变化规律. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(1): 241-247. | |
| 25 | Wu J H, Zhang S, Jiang Y, et al. Phytogeography. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2004: 284. |
| 武吉华, 张绅, 江源, 等. 植物地理学. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2004: 284. | |
| 26 | Ma G F, Mansour S, Zhang X Q, et al. Physical and chemical properties of shrub soils at different elevations in the upper reaches of the Teran River in the Tomur Peak Nature Reserve. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2017, 48(6): 1288-1295. |
| 马国飞, 满苏尔·沙比提, 张雪琪, 等. 托木尔峰自然保护区台兰河上游不同海拔灌木土壤理化性质研究. 土壤通报, 2017, 48(6): 1288-1295. | |
| 27 | Feng G, Zhang J L, Pei N C, et al. Comparison of phylobeta diversity indices based on community data from Gutian Mountain plot. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(34): 2857-2864. |
| 冯刚, 张金龙, 裴男才, 等. 系统发育α多样性指数的比较: 以古田山样地为例. 科学通报, 2011, 56(34): 2857-2864. |
| [1] | 贺翔, 白梅梅, 徐长林, 宋美娟, 汪鹏斌, 鱼小军. 东祁连山小叶金露梅+杯腺柳灌丛草地植被和土壤对其自然恢复演替的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 12-24. |
| [2] | 马婧婧, 刘耘华, 盛建东, 李宁, 武红旗, 贾宏涛, 孙宗玖, 程军回. 新疆草地优势种植物相对生物量沿海拔梯度变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 25-35. |
| [3] | 罗巧玉, 王彦龙, 杜雷, 刘念, 李丽, 马玉寿. 黄河源区发草适生地植物群落特征及其土壤因子解释[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 80-89. |
| [4] | 赵文, 尹亚丽, 李世雄, 刘燕, 刘晶晶, 董怡玲, 苏世锋, 吉凌鹤. 祁连山不同类型草地土壤细菌群落特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 161-171. |
| [5] | 聂莹莹, 陈金强, 辛晓平, 徐丽君, 杨桂霞, 王旭. 呼伦贝尔草甸草原区主要植物种群生态位特征与物种多样性对封育年限响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 15-25. |
| [6] | 韩福贵, 满多清, 郑庆钟, 赵艳丽, 张裕年, 肖斌, 付贵全, 杜娟. 青土湖典型湿地白刺灌丛沙堆群落物种多样性及土壤养分变化特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 36-45. |
| [7] | 杨勤, 官久强, 柴志欣, 李华德, 曹诗晓, 张翔飞, 柏琴, 钟金城, 罗晓林. 低海拔舍饲对牦牛肌肉品质的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 33-42. |
| [8] | 车力木格, 刘新平, 何玉惠, 孙姗姗, 王明明. 半干旱沙地草本植物群落特征对短期降水变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 19-28. |
| [9] | 吴昊, 张辰, 代文魁. 气候变暖和物种多样性交互效应对空心莲子草入侵的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 38-48. |
| [10] | 杨鼎, 齐昊昊, 王倩, 徐海鹏, 张静, 张红艳, 郭正刚. 青藏高原高原鼢鼠鼠丘植被恢复过程中植物群落特征的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 114-122. |
| [11] | 崔雨萱, 孙宗玖, 刘慧霞, 董乙强. 短期封育对蒿类荒漠草地现存生物量及植物群落多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 17-26. |
| [12] | 聂莹莹, 徐丽君, 辛晓平, 陈宝瑞, 张保辉. 围栏封育对温性草甸草原植物群落构成及生态位特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 11-22. |
| [13] | 高亚敏, 罗慧琴, 姚拓, 张建贵, 李海云, 杨琰珊, 兰晓君. 高寒退化草地委陵菜根围丛枝菌根菌(AMF)分离鉴定及促生效应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 145-154. |
| [14] | 官惠玲, 樊江文, 李愈哲. 不同人工草地对青藏高原温性草原群落生物量组成及物种多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 192-201. |
| [15] | 王鑫, 罗雪萍, 字洪标, 杨文高, 胡雷, 王长庭. 青海森林凋落物生态化学计量特征及其影响因子[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 1-14. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
