

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 149-162.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024110
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
麦晶晶1( ), 冯琦胜1(
), 冯琦胜1( ), 王瑞泾2, 封森耀3, 金哲人4, 张忠雪1, 梁天刚1, 金加明5
), 王瑞泾2, 封森耀3, 金哲人4, 张忠雪1, 梁天刚1, 金加明5
收稿日期:2024-04-09
修回日期:2024-06-20
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2024-11-27
通讯作者:
冯琦胜
作者简介:E-mail: fengqsh@lzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Jing-jing MAI1( ), Qi-sheng FENG1(
), Qi-sheng FENG1( ), Rui-jing WANG2, Sen-yao FENG3, Zhe-ren JIN4, Zhong-xue ZHANG1, Tian-gang LIANG1, Jia-ming JIN5
), Rui-jing WANG2, Sen-yao FENG3, Zhe-ren JIN4, Zhong-xue ZHANG1, Tian-gang LIANG1, Jia-ming JIN5
Received:2024-04-09
Revised:2024-06-20
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2024-11-27
Contact:
Qi-sheng FENG
摘要:
耕地是农业生产和保障粮食安全问题重要的物质基础,耕地的准确识别对耕地资源的保护和农业生产可持续发展有着重要意义。为了构建高精度的耕地识别模型,本研究基于空间云计算平台使用Sentinel-1/2数据,构建不同特征类型组合,通过特征重要性分析对耕地识别特征进行筛选,形成最优特征集合,使用随机森林(random forest,RF)、支持向量机(support vector machine,SVM)和分类回归树(classification and regression tree,CART)模型对甘肃省张掖市2021年度的耕地进行识别,同时对比分析了各分类器的分类精度。结果表明,使用植被指数特征、雷达特征和地形特征的特征类型组合能够把分类精度提升到91.32%;在研究区耕地识别中表现较好的特征有海拔(elevation)、雷达VH极化通道及归一化水指数(normalized difference water index, NDWI)等;在张掖市耕地识别中,RF算法优势明显,总精度达90.04%,Kappa系数为0.79,基于RF模型得到的张掖市耕地面积为58.5万hm2,面积占比为15.4%。本研究实现了张掖市耕地的精确识别,可为该地区耕地制图提供参考。
麦晶晶, 冯琦胜, 王瑞泾, 封森耀, 金哲人, 张忠雪, 梁天刚, 金加明. 基于机器学习的高精度耕地识别模型构建——以甘肃省张掖市为例[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 149-162.
Jing-jing MAI, Qi-sheng FENG, Rui-jing WANG, Sen-yao FENG, Zhe-ren JIN, Zhong-xue ZHANG, Tian-gang LIANG, Jia-ming JIN. Construction of a high-precision cultivated land identification model based on machine learning-using Zhangye City, Gansu Province as an example[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(2): 149-162.
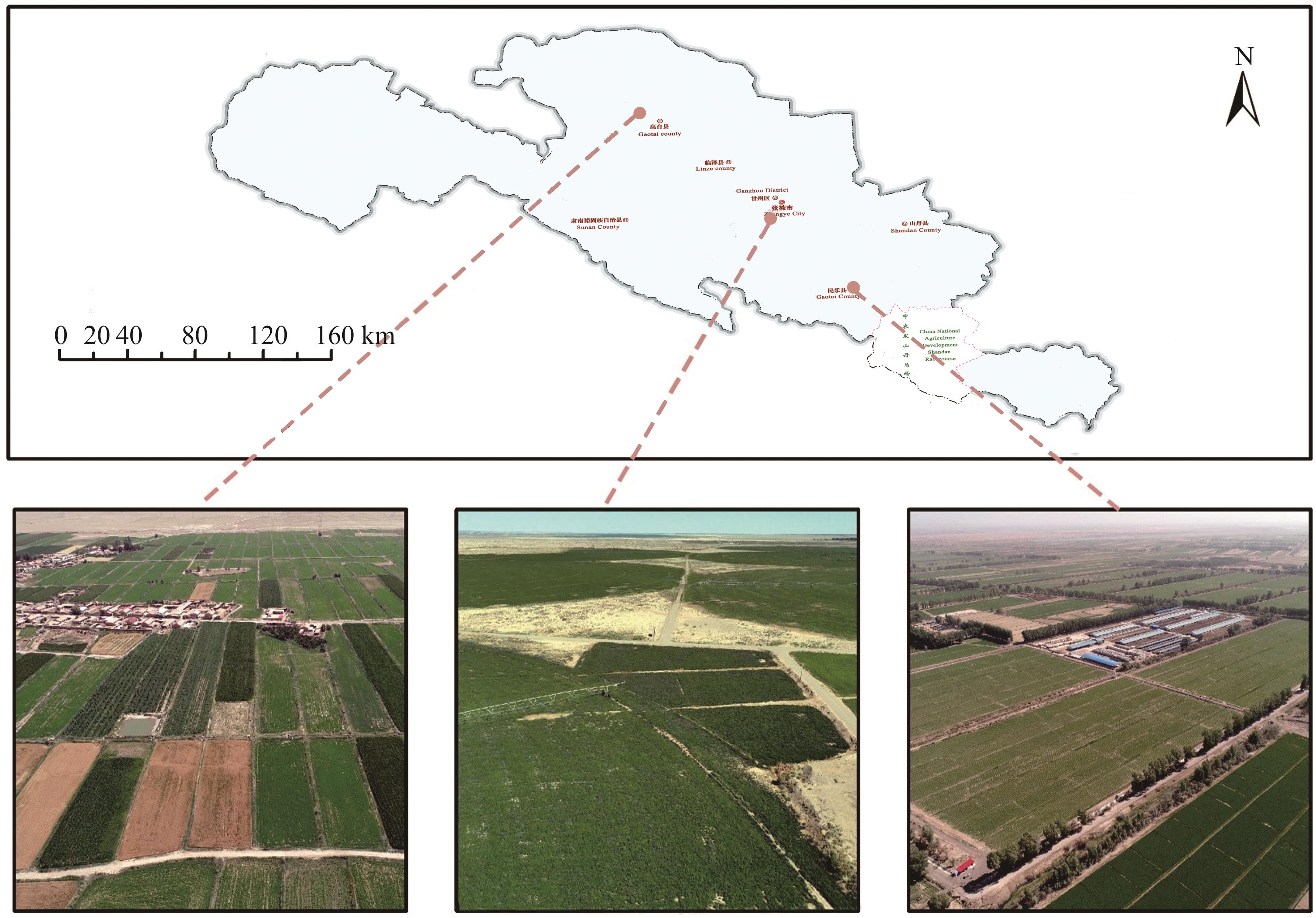
图1 研究区概况基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站甘S(2023)91号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。The map was based on the standard map service website of the Ministry of Nature Resources with the drawing review No. gan S(2021)91, and the base map borders were not modified.
Fig.1 Overview of the study area
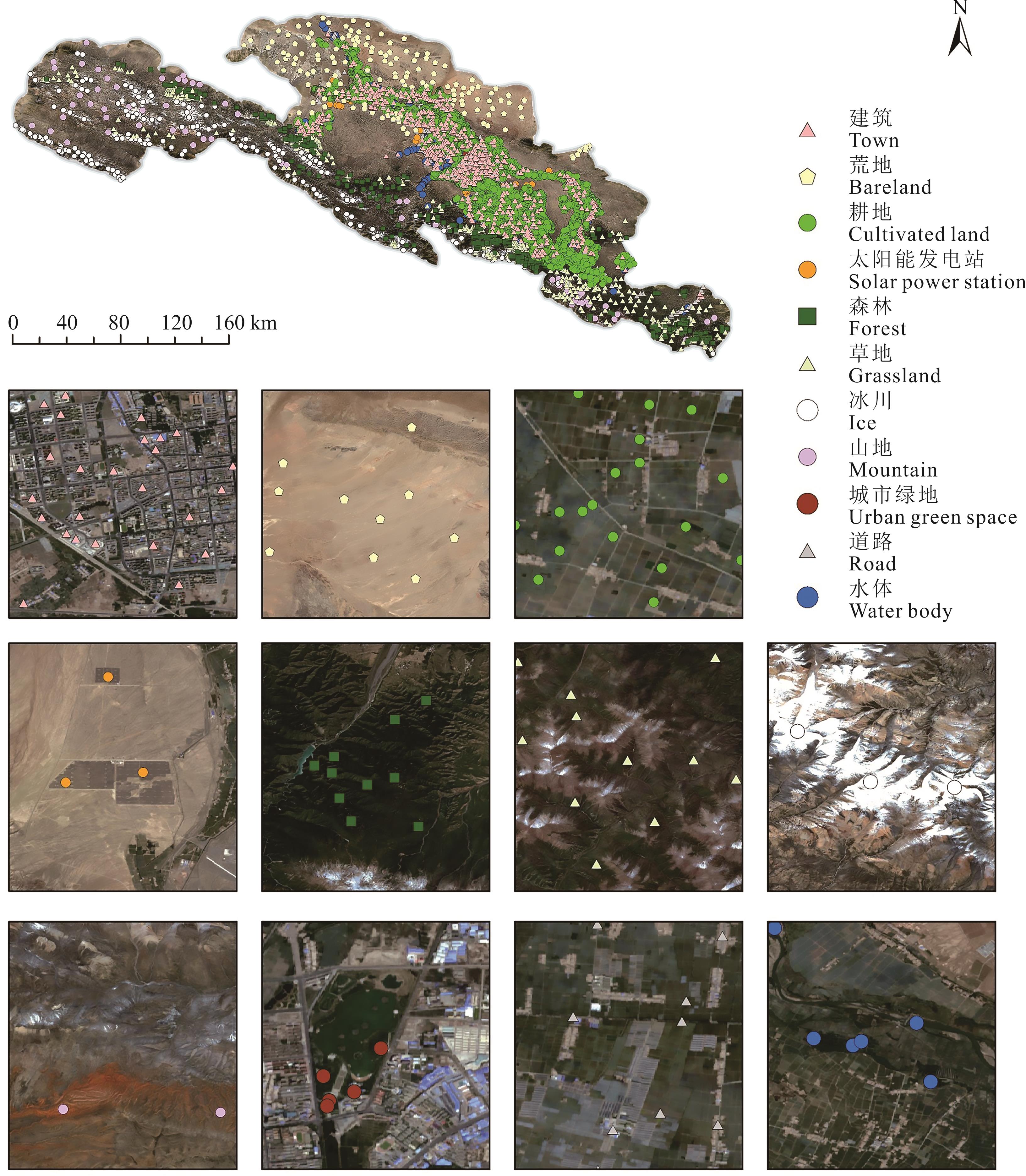
图2 研究区样本点分布基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站甘S(2023)60号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。The map was based on the standard map service website of the Ministry of Nature Resources with the drawing review No.gan S(2023)60, and the base map borders were not modified.
Fig.2 Samples distribution of study area

图3 工作流程RF: 随机森林Random forest; SVM: 支持向量机Support vector machine; CART: 分类回归树Classification and regression tree; RFE: 递归特征消除Recursive feature elimination; Kappa: 卡帕系数.
Fig.3 Workflow of the cultivated land identification in Zhangye City
| 编号Number | 特征类型组合Feature type combinations |
|---|---|
| 1 | 光谱Spectrum |
| 2 | 光谱+雷达Spectrum+synthetic aperture radar (SAR) |
| 3 | 光谱+植被指数Spectrum+vegetation index |
| 4 | 植被指数+雷达Vegetation index+SAR |
| 5 | 光谱+植被指数+雷达Spectrum+vegetation index+SAR |
| 6 | 植被指数+雷达+土壤Vegetation index+SAR+soil |
| 7 | 植被指数+雷达+地形Vegetation index+SAR+topography |
| 8 | 植被指数+雷达+地形+土壤Vegetation index+SAR+topography+soil |
| 9 | 全部特征类型组合All feature types |
表1 9组不同特征类型组合
Table 1 9 groups of different feature type combinations
| 编号Number | 特征类型组合Feature type combinations |
|---|---|
| 1 | 光谱Spectrum |
| 2 | 光谱+雷达Spectrum+synthetic aperture radar (SAR) |
| 3 | 光谱+植被指数Spectrum+vegetation index |
| 4 | 植被指数+雷达Vegetation index+SAR |
| 5 | 光谱+植被指数+雷达Spectrum+vegetation index+SAR |
| 6 | 植被指数+雷达+土壤Vegetation index+SAR+soil |
| 7 | 植被指数+雷达+地形Vegetation index+SAR+topography |
| 8 | 植被指数+雷达+地形+土壤Vegetation index+SAR+topography+soil |
| 9 | 全部特征类型组合All feature types |
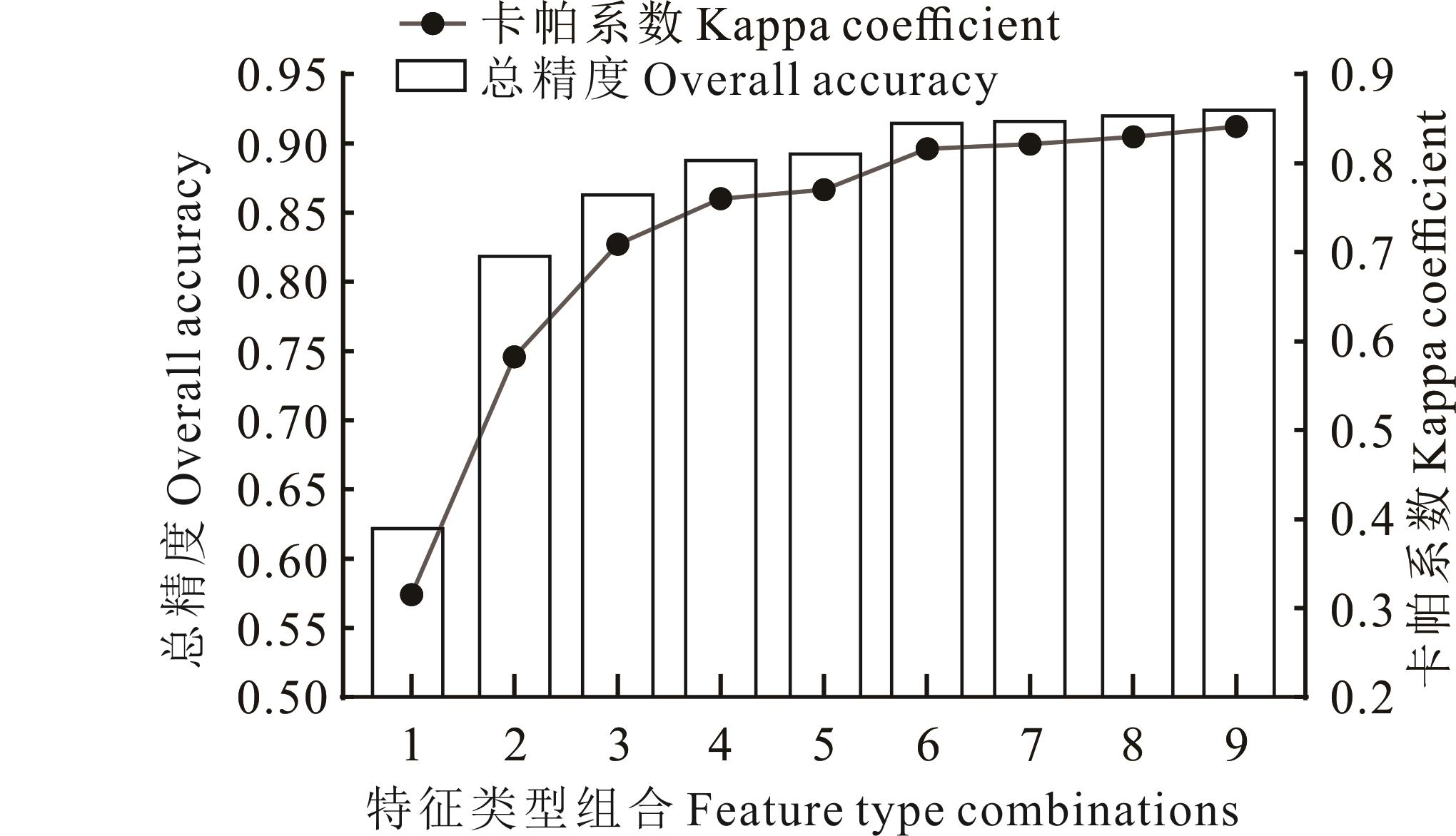
图4 9种特征类型组合的分类精度和Kappa系数比较图中特征类型组合1为光谱特征,组合2为光谱和雷达特征组合,组合3为光谱和植被指数的特征组合,组合4为植被指数和雷达的特征组合,组合5为光谱、植被指数及雷达的特征组合,组合6为植被指数、雷达及土壤的特征组合,组合7为植被指数、雷达及地形的特征组合,组合8为植被指数、雷达、地形及土壤的特征组合,组合9为全特征组合。The combinations of feature types in the figure are as follows: Combination 1 consists of spectral features; Combination 2 consists of a combination of spectral and synthetic aperture radar features; Combination 3 consists of a combination of spectral features and vegetation indices; Combination 4 consists of a combination of vegetation indices and synthetic aperture radar features; Combination 5 consists of a combination of spectral, vegetation indices, and synthetic aperture radar features; Combination 6 consists of a combination of vegetation indices, synthetic aperture radar features, and soil features; Combination 7 consists of a combination of vegetation indices, synthetic aperture radar features, and topography features; Combination 8 consists of a combination of vegetation indices, synthetic aperture radar features, topography features, and soil features; Combination 9 consists of all features.
Fig.4 Accuracy and Kappa coefficient comparison of 9 feature type combinations
| 识别特征Feature | 特征重要性Feature importance |
|---|---|
| 海拔Elevation | 8771.81 |
| VH, 雷达特征中的VH极化Synthetic aperture radar features VH polarization | 8210.86 |
| 归一化水指数Normalized difference water index, NDWI | 8128.18 |
| 简单比值Sample ratio, SR | 7979.18 |
| VV, 雷达特征中的VV极化Synthetic aperture radar features VV polarization | 7978.85 |
| 归一化物候指数Normalized difference phenology index, NDPI | 7947.32 |
| 土壤调整植被指数Soil adjusted vegetation index, SAVI | 7896.25 |
表2 不同识别特征的重要性排名
Table 2 Rank of feature importance
| 识别特征Feature | 特征重要性Feature importance |
|---|---|
| 海拔Elevation | 8771.81 |
| VH, 雷达特征中的VH极化Synthetic aperture radar features VH polarization | 8210.86 |
| 归一化水指数Normalized difference water index, NDWI | 8128.18 |
| 简单比值Sample ratio, SR | 7979.18 |
| VV, 雷达特征中的VV极化Synthetic aperture radar features VV polarization | 7978.85 |
| 归一化物候指数Normalized difference phenology index, NDPI | 7947.32 |
| 土壤调整植被指数Soil adjusted vegetation index, SAVI | 7896.25 |

图5 不同模型的耕地识别结果基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站甘S(2023)58号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。The map was based on the standard map service website of the Ministry of Nature Resources with the drawing review No.gan S(2023)58, and the base map borders were not modified.
Fig.5 Cultivated land identification result of random forest, support vector machine and classification and regression tree respectively
模型 Model | 总精度 Overall accuracy | 用户精度 User’s accuracy | 生产者精度 Producer’s accuracy | 卡帕系数 Kappa coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 随机森林Random forest, RF | 0.9004 | 0.9540 | 0.9747 | 0.7944 |
| 支持向量机Support vector machine, SVM | 0.8868 | 0.9466 | 0.9694 | 0.7660 |
| 分类回归树Classification and regression trees, CART | 0.8547 | 0.9467 | 0.9494 | 0.7054 |
表3 RF、SVM、CART模型分类精度比较
Table 3 Comparison of accuracy of random forest, support vector machine, and classification and regression tree
模型 Model | 总精度 Overall accuracy | 用户精度 User’s accuracy | 生产者精度 Producer’s accuracy | 卡帕系数 Kappa coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 随机森林Random forest, RF | 0.9004 | 0.9540 | 0.9747 | 0.7944 |
| 支持向量机Support vector machine, SVM | 0.8868 | 0.9466 | 0.9694 | 0.7660 |
| 分类回归树Classification and regression trees, CART | 0.8547 | 0.9467 | 0.9494 | 0.7054 |
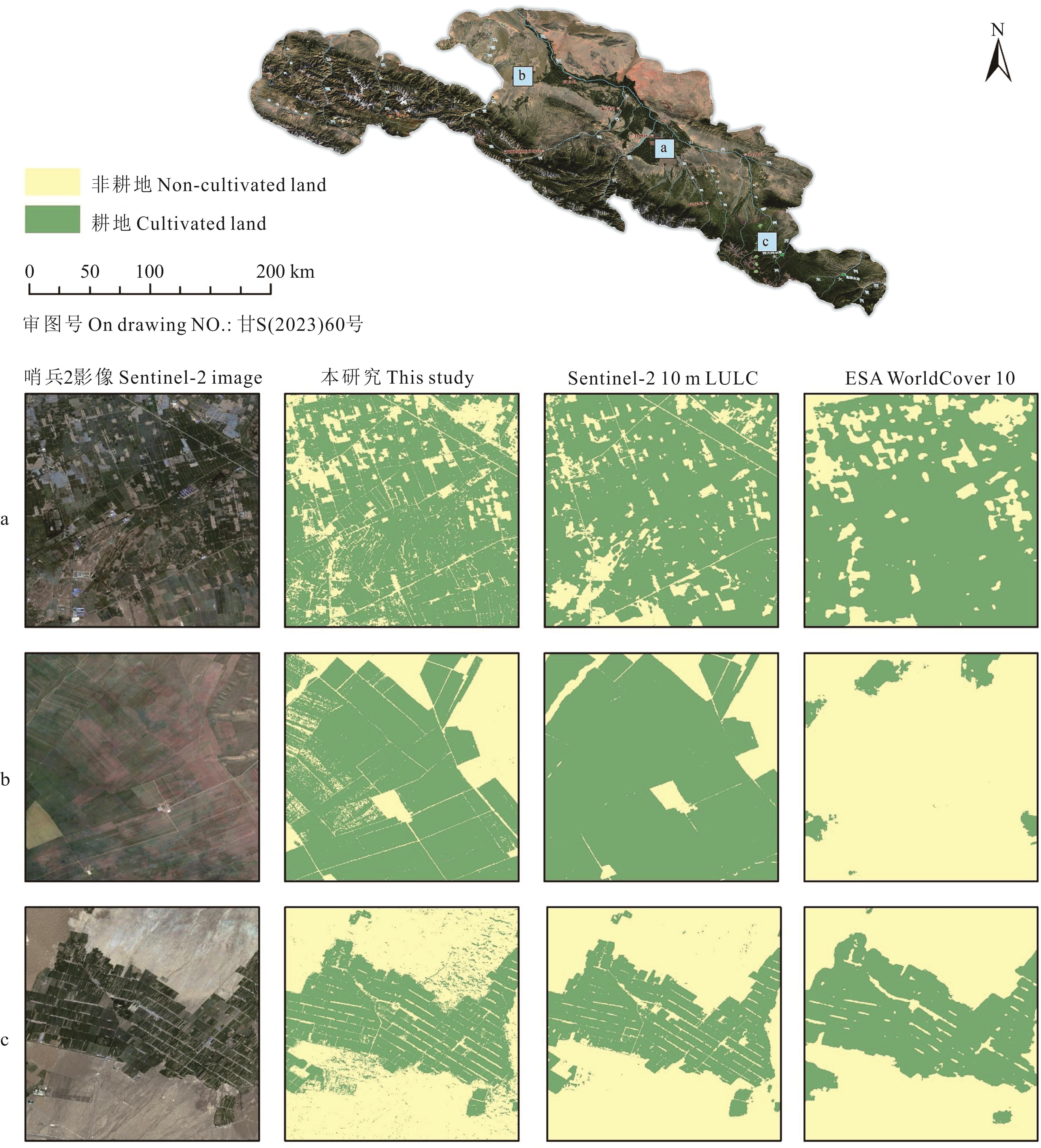
图6 本研究与Sentinel-2 10 m LULC和ESA WorldCover 10产品耕地识别结果比较基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站甘S(2023)60号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。The map was based on the standard map service website of the Ministry of Nature Resources with the drawing review No.gan S(2023)60, and the base map borders were not modified. a、b、c分别代表图中三个展示区域a, b and c represent the three display areas in the figure respectively.
Fig.6 Comparison of this study, Sentinel-2 10 m LULC and ESA WorldCover 10
| 1 | Wardlow B D, Egbert S L. Large-area crop mapping using time-series MODIS 250 m NDVI data: An assessment for the U.S. Central Great Plains. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2008, 112(3): 1096-1116. |
| 2 | Clark M L, Aide T M, Grau H R, et al. A scalable approach to mapping annual land cover at 250 m using MODIS time series data: A case study in the Dry Chaco ecoregion of South America. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2010, 114(11): 2816-2832. |
| 3 | Johnson D M. Using the Landsat archive to map crop cover history across the United States. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2019, 232: 111286. |
| 4 | Gong P, Wang J, Yu L, et al. Finer resolution observation and monitoring of global land cover: first mapping results with Landsat TM and ETM+ data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2013, 34(7): 2607-2654. |
| 5 | Du B J, Zhang J, Wang Z M, et al. Crop mapping based on Sentinel-2A NDVI time series using object-oriented classification and decision tree model. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2019, 21(5): 740-751. |
| 杜保佳, 张晶, 王宗明, 等. 应用Sentinel-2A NDVI时间序列和面向对象决策树方法的农作物分类. 地球信息科学学报, 2019, 21(5): 740-751. | |
| 6 | Valero S, Morin D, Inglada J, et al. Processing Sentinel-2 image time series for developing a real-time cropland mask//2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). Milan, Italy: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, 2015: 2731-2734. |
| 7 | Xiong J, Thenkabail P, Tilton J, et al. Nominal 30-m cropland extent map of continental Africa by integrating pixel-based and object-based algorithms using Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 data on Google Earth Engine. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(10): 1065. |
| 8 | Xiong X L, Hu Y M, Wen N, et al. Progress and prospect of cultivated land extraction research using remote sensing. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2020, 37(6): 856-865. |
| 熊曦柳, 胡月明, 文宁, 等. 耕地遥感识别研究进展与展望. 农业资源与环境学报, 2020, 37(6): 856-865. | |
| 9 | Wu B, Zhang M, Zeng H, et al. Challenges and opportunities in remote sensing-based crop monitoring: a review. National Science Review, 2023, 10(4): nwac290. https://academic.oup.com/nsr/article/10/4/nwac290/6939854. |
| 10 | Liu C, Chen Z, Shao Y, et al. Research advances of SAR remote sensing for agriculture applications: A review. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2019, 18(3): 506-525. |
| 11 | Song Q, Zhou Q B, Wu W B, et al. Recent progresses in research of integrating multi-source remote sensing data for crop mapping. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(6): 1122-1135. |
| 宋茜, 周清波, 吴文斌, 等. 农作物遥感识别中的多源数据融合研究进展. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(6): 1122-1135. | |
| 12 | Orynbaikyzy A, Gessner U, Conrad C. Crop type classification using a combination of optical and radar remote sensing data: a review. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2019, 40(17): 6553-6595. |
| 13 | Sun C, Bian Y, Zhou T, et al. Using of multi-source and multi-temporal remote sensing data improves crop-type mapping in the subtropical agriculture region. Sensors, 2019, 19(10): 2401. |
| 14 | Guo J, Zhu L, Jin B, et al. Crop classification based on data fusion of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(4): 192-198. |
| 郭交, 朱琳, 靳标, 等. 基于Sentinel-1和Sentinel-2数据融合的农作物分类. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(4): 192-198. | |
| 15 | Lin C J, Liu Z H, Hu Y M, et al. Cultivated land extraction based on Google Earth Engine multisource data. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 35(10): 2372-2378. |
| 林陈捷, 刘振华, 胡月明, 等. 基于Google Earth Engine多源数据的耕地提取研究. 西南农业学报, 2022, 35(10): 2372-2378. | |
| 16 | Maxwell A E. Implementation of machine-learning classification in remote sensing: an applied review. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2018, 39(9): 2784-2817. |
| 17 | Pazúr R, Huber N, Weber D, et al. A national extent map of cropland and grassland for Switzerland based on Sentinel-2 data. Earth System Science Data, 2022, 14(1): 295-305. |
| 18 | Rawat S, Saini R. Cropland mapping using single date Sentinel-2 imagery using machine learning classifiers//2022 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication and Materials (ICACCM). Dehradun, India: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, 2022: 1-7. |
| 19 | Savitha C, Talari R. Mapping cropland extent using Sentinel-2 datasets and machine learning algorithms for an agriculture watershed. Smart Agricultural Technology, 2023(4): 100193. |
| 20 | Wang R, Feng Q, Jin Z, et al. Identification and area information extraction of oat pasture based on GEE-A case study in the Shandan racecourse (China). Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(17): 4358. |
| 21 | Zhang J, Zhang X, Tian L, et al. The support vector machine method for RS images’ classification in northwest arid area. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2017, 42(1): 49-52, 58. |
| 张静, 张翔, 田龙, 等. 西北旱区遥感影像分类的支持向量机法. 测绘科学, 2017, 42(1): 49-52, 58. | |
| 22 | Fu D J, Xiao H, Su F Z, et al. Remote sensing cloud computing platform development and earth science application. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2021, 25(1): 220-230. |
| 付东杰, 肖寒, 苏奋振, 等. 遥感云计算平台发展及地球科学应用. 遥感学报, 2021, 25(1): 220-230. | |
| 23 | Tamiminia H, Salehi B, Mahdianpari M, et al. Google Earth Engine for geo-big data applications: A meta-analysis and systematic review. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 164: 152-170. |
| 24 | Teluguntla P, Thenkabail P S, Oliphant A, et al. A 30-m Landsat-derived cropland extent product of Australia and China using random forest machine learning algorithm on Google Earth Engine cloud computing platform. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2018, 144: 325-340. |
| 25 | Pan L, Xia H M, Wang R M, et al. Mapping of the winter crop planting areas in Huaihe river basin based on Google Earth Engine. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2021, 37(18): 211-218. |
| 潘力, 夏浩铭, 王瑞萌, 等. 基于Google Earth Engine的淮河流域越冬作物种植面积制图. 农业工程学报, 2021, 37(18): 211-218. | |
| 26 | Han J, Zhang Z, Cao J, et al. Prediction of winter wheat yield based on multi-source data and machine learning in China. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(2): 236. |
| 27 | Chen X Y, Zhang H P, Hu J L. Current status and promotion measures of Zhangye City’s grain-forage transformation work. China Dairy Cattle, 2022(1): 40-42. |
| 陈晓燕, 张和平, 胡江林. 张掖市粮改饲工作现状及推进措施. 中国奶牛, 2022(1): 40-42. | |
| 28 | Farr T G, Rosen P A, Caro E, et al. The shuttle radar topography mission. Reviews of Geophysics, 2007, 45(2): RG2004.doi:10.1029/2005RG000183. |
| 29 | Poggio L, de Sousa L M, Batjes N H, et al. SoilGrids 2.0: producing soil information for the globe with quantified spatial uncertainty. Soil, 2021,7(1): 217-240. |
| 30 | Cao X, Chen X H, Zhang W W, et al. Global cultivated land mapping at 30 m spatial resolution. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2016, 46(11): 1426-1435. |
| 曹鑫, 陈学泓, 张委伟, 等. 全球30 m空间分辨率耕地遥感制图研究. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2016, 46(11): 1426-1435. | |
| 31 | Dong J, Xiao X, Menarguez M A, et al. Mapping paddy rice planting area in northeastern Asia with Landsat 8 images, phenology-based algorithm and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2016, 185: 142-154. |
| 32 | Breiman L. Random forests. Machine Learning, 2001, 45: 5-32. |
| 33 | Fang K N, Wu J B, Zhu J P, et al. A review of technologies on random forests. Journal of Statistics and Information, 2011, 26(3): 32-38. |
| 方匡南, 吴见彬, 朱建平, 等. 随机森林方法研究综述. 统计与信息论坛, 2011, 26(3): 32-38. | |
| 34 | Zhang B H, Zhang Y L, Gu C J, et al. Land cover classification based on random forest and feature optimism in the Southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2023, 43(3): 388-397. |
| 张炳华, 张镱锂, 谷昌军, 等. 基于随机森林与特征选择的藏东南土地覆被分类方法及精度评价. 地理科学, 2023, 43(3): 388-397. | |
| 35 | Cortes C, Vapnik V. Support-vector networks. Machine Learning, 1995, 20(3): 273-297. |
| 36 | Yang X F, Tureniguli·Amuti. Study of SVM classification method optimized by artificial bee colony algorithm: A case study of the Ancient Manasi Lake Basin. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2018, 34(4): 40-45. |
| 杨雪峰, 吐热尼古丽·阿木提. 基于人工蜂群算法优化的SVM遥感分类方法——以玛纳斯湖古湖盆为例. 地理与地理信息科学, 2018, 34(4): 40-45. | |
| 37 | Breiman L, Friedman J, Olshen R A, et al. Classification and regression trees. Monterey, California, U.S.A.: Wadsworth International Group, 1984. |
| 38 | Congalton R G. A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 1991, 37(1): 35-46. |
| 39 | Karra K, Kontgis C, Statman-Weil Z, et al. Global land use/land cover with Sentinel 2 and deep learning//2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS. Brussels, Belgium: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, 2021: 4704-4707. |
| 40 | Zanaga D, Van De Kerchove R, Daems D, et al. ESA WorldCover 10 m 2021 v200. Zenodo. 2022, https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7254221. |
| 41 | Feng S, Li W, Xu J, et al. Land use/land cover mapping based on GEE for the monitoring of changes in ecosystem types in the upper Yellow River Basin over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(21): 5361. |
| 42 | Palanisamy P A, Jain K, Bonafoni S. Machine learning classifier evaluation for different input combinations: A case study with Landsat 9 and Sentinel-2 data. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(13): 3241. |
| 43 | Qian X, Li P X, Xie H Q, et al. Crop information extraction and water demand analysis based on Sentinel-2 remote sensing image. Water Saving Irrigation, 2022(5): 33-38, 46. |
| 钱鑫, 李培显, 谢宏全, 等. 基于Sentinel-2遥感影像的作物信息提取与需水量分析研究. 节水灌溉, 2022(5): 33-38, 46. | |
| 44 | Li H Y, He R B, Xie M D, et al. Influence of natural and anthropogenic factors on soil organic matter content in farmland. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2023, 54(5): 1050-1059. |
| 李洪义, 贺任彬, 谢模典, 等. 自然和人为因素对耕地土壤有机质含量影响的研究. 土壤通报, 2023, 54(5): 1050-1059. | |
| 45 | Chakhar A, Hernández-López D, Ballesteros R, et al. Improving the accuracy of multiple algorithms for crop classification by integrating Sentinel-1 observations with Sentinel-2 data. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(2): 243. |
| 46 | Blickensdörfer L, Schwieder M, Pflugmacher D, et al. Mapping of crop types and crop sequences with combined time series of Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 data for Germany. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2022, 269: 112831. |
| 47 | Mu Y X, Wu M Q, Niu Z, et al. Method of remote sensing extraction of cultivated land area under complex conditions in southern region. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2020, 35(5): 1127-1135. |
| 牟昱璇, 邬明权, 牛铮, 等. 南方地区复杂条件下的耕地面积遥感提取方法. 遥感技术与应用, 2020, 35(5): 1127-1135. | |
| 48 | Xie D, Xu H, Xiong X, et al. Cropland extraction in southern China from very high-resolution images based on deep learning. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(9): 2231. |
| 49 | Wang M, Zhang X C, Wang J Y, et al. Forest resource classification based on random forest and object-oriented method. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2020, 49(2): 235-244. |
| 王猛, 张新长, 王家耀, 等. 结合随机森林面向对象的森林资源分类. 测绘学报, 2020, 49(2): 235-244. | |
| 50 | Gu H Y, Yan L, Li H T, et al. An object-based automatic interpretation method for geographic features based on random forest machine learning. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2016, 41(2): 228-234. |
| 顾海燕, 闫利, 李海涛, 等. 基于随机森林的地理要素面向对象自动解译方法. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2016, 41(2): 228-234. |
| [1] | 杨志贵, 张建国, 李锦荣, 于红妍, 常丽, 宜树华, 吕燕燕, 张玉琢, 孟宝平. 内蒙古温性草原草地类型近20年时空动态变化研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 1-16. |
| [2] | 张慧龙, 杨秀春, 杨东, 陈昂, 张敏. 2000-2020年内蒙古草地植被覆盖度时空变化及趋势预测[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 1-13. |
| [3] | 郭芮, 伏帅, 侯蒙京, 刘洁, 苗春丽, 孟新月, 冯琦胜, 贺金生, 钱大文, 梁天刚. 基于Sentinel-2数据的青海门源县天然草地生物量遥感反演研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 15-29. |
| [4] | 苗春丽, 李仲贤, 赵志成, 伏帅, 高金龙, 刘洁, 冯琦胜, 梁天刚. 栽培苜蓿草地智能感知系统关键生物物理指标实时监测及分析算法研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 90-103. |
| [5] | 厉方桢, 钟华平, 欧阳克蕙, 赵小敏, 李愈哲. 基于机器学习的阿勒泰地区草地地下生物量估测与数字制图[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 13-23. |
| [6] | 赵翊含, 侯蒙京, 冯琦胜, 高宏元, 梁天刚, 贺金生, 钱大文. 基于Landsat 8和随机森林的青海门源天然草地地上生物量遥感估算[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 1-14. |
| [7] | 秦格霞, 吴静, 李纯斌, 吉珍霞, 邱政超, 李颖. 基于机器学习算法的天祝藏族自治县草地地上生物量反演[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 177-188. |
| [8] | 金哲人, 冯琦胜, 王瑞泾, 梁天刚. 基于MODIS数据与机器学习的青藏高原草地地上生物量研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 1-17. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||