

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 27-40.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024138
田丛嫣1( ), 王文强1, 杨博1, 黄文广2, 梁咏亮3, 杨君珑1, 李小伟1(
), 王文强1, 杨博1, 黄文广2, 梁咏亮3, 杨君珑1, 李小伟1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-23
修回日期:2024-06-05
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2024-11-27
通讯作者:
李小伟
作者简介:E-mail: lxwbq@126.com基金资助:
Cong-yan TIAN1( ), Wen-qiang WANG1, Bo YANG1, Wen-guang HUANG2, Yong-liang LIANG3, Jun-long YANG1, Xiao-wei LI1(
), Wen-qiang WANG1, Bo YANG1, Wen-guang HUANG2, Yong-liang LIANG3, Jun-long YANG1, Xiao-wei LI1( )
)
Received:2024-04-23
Revised:2024-06-05
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2024-11-27
Contact:
Xiao-wei LI
摘要:
沙芦草是我国二级重点保护植物,具有极强的耐旱性和适应性,在荒漠草地植被恢复和小麦遗传育种方面有重要价值。沙芦草对环境变化敏感,探究沙芦草栖息地的适宜特征,预测不同气候情境下沙芦草的潜在适生区,对保护沙芦草有重要指导意义。本研究基于119条有效分布记录和39个自然环境变量,利用最大熵模型和ArcGIS软件对自然环境下沙芦草当前和未来两种不同气候情境(SSP1-2.6和SSP5-5.8)的适生区进行预测。结果显示最湿月降水量、气温季节性变动系数和土壤酸碱度是影响沙芦草分布的主导自然因子。当前沙芦草的适生区主要集中在中国北部干旱地带,高适生区在内蒙古、陕西和宁夏的交界地带;在未来两种气候情境下,沙芦草的栖息地均有不同程度的西移。 在未来气候条件下,沙芦草潜在分布区的总体分布格局与现在相似,但适生等级变化幅度大,高适生区在未来气候条件下有向北迁移聚集的趋势,主要集中分布在内蒙古中部地区。因此,对沙芦草的保护应该着眼于当前时期沙芦草群落集中的地区,并关注内蒙古中部地区的沙芦草潜在栖息地。
田丛嫣, 王文强, 杨博, 黄文广, 梁咏亮, 杨君珑, 李小伟. 沙芦草的分布及潜在适生区预测[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 27-40.
Cong-yan TIAN, Wen-qiang WANG, Bo YANG, Wen-guang HUANG, Yong-liang LIANG, Jun-long YANG, Xiao-wei LI. Prediction of potentially suitable areas for Agropyron mongolicum to enhance its distribution[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(2): 27-40.
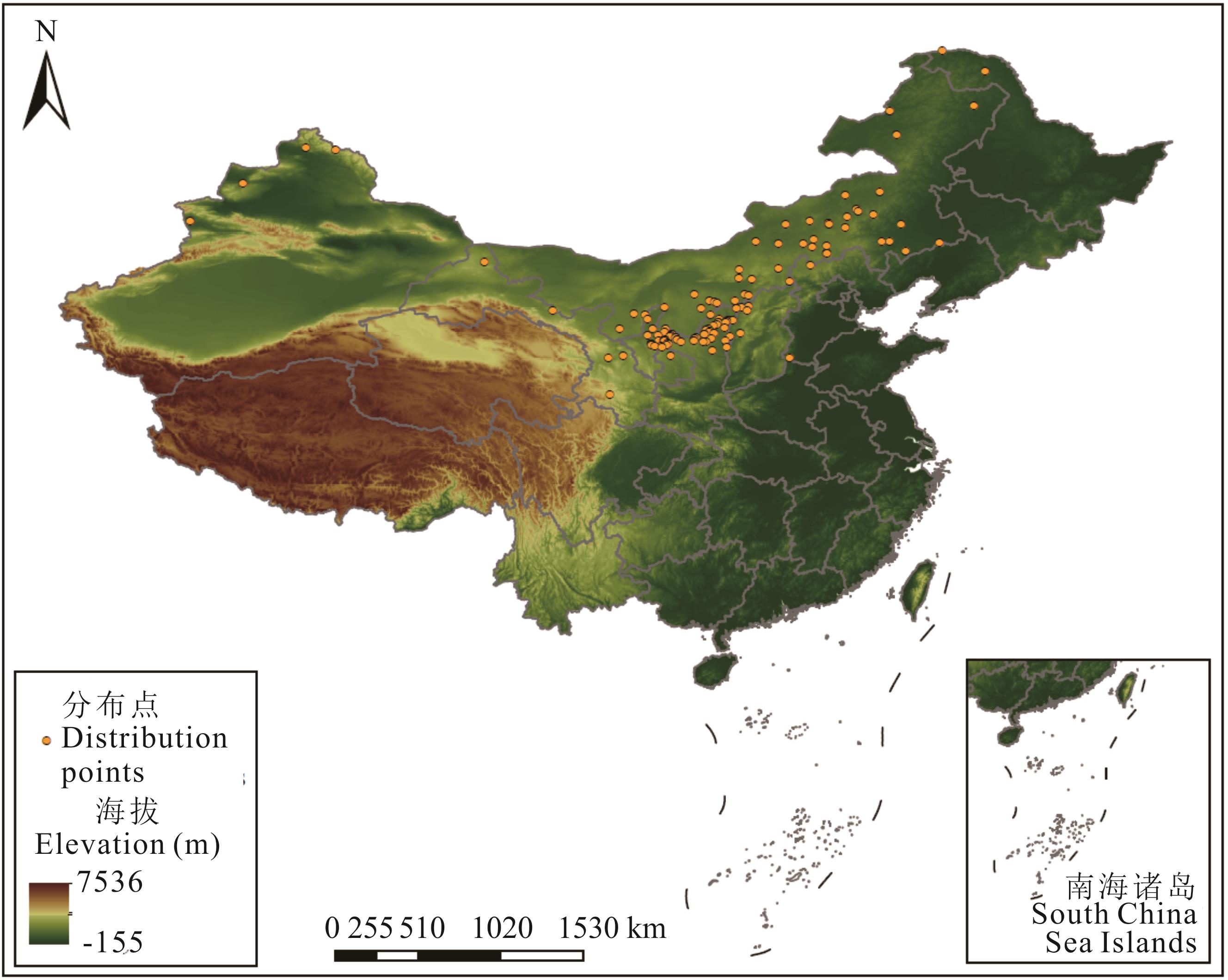
图1 沙芦草在我国的分布点基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2023)2767号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map of the Ministry of Natural Resources GS (2023) No. 2767, the boundaries of the base map have not been modified.
Fig.1 Distribution points of reed grass in China
| 变量Variable | 描述Description | 单位Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Bio1 | 年平均温度 Average annual temperature | ℃ |
| Bio2 | 昼夜温差月均值 Monthly mean temperature difference between day and night | ℃ |
| Bio3 | 昼夜温差与年温差比值Temperature difference between day and night/annual temperature difference | % |
| Bio4 | 气温季节性变动系数 Seasonal variation coefficient of temperature | |
| Bio5 | 最热月最高温 Max temperature of warmest month | ℃ |
| Bio6 | 最冷月最低温 Min temperature of coldest month | ℃ |
| Bio7 | 年温度变化范围 Temperature annual range | ℃ |
| Bio8 | 最湿季均温 Mean temperature of wettest quarter | ℃ |
| Bio9 | 最干季均温 Mean temperature of driest quarter | ℃ |
| Bio10 | 最暖季均温 Mean temperature of warmest quarter | ℃ |
| Bio11 | 最冷季均温 Mean temperature of coldest quarter | ℃ |
| Bio12 | 年均降水量 Annual precipitation | mm |
| Bio13 | 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month | mm |
| Bio14 | 最干月降水量 Precipitation of driest month | mm |
| Bio15 | 季节性降水量 Precipitation seasonality | mm |
| Bio16 | 最湿季降水量 Precipitation of wettest quarter | mm |
| Bio17 | 最干季降水量 Precipitation of driest quarter | mm |
| Bio18 | 最暖季平均降水量 Mean precipitation of warmest quarter | mm |
| Bio19 | 最冷季平均降水量 Mean precipitation of coldest quarter | mm |
| aws_class | 土壤有效水含量 Available water content of soil (AWC) | % |
| s_clay | 亚表层土壤黏粒组分 Subsoil clay fraction | 重量百分比 (wt.%) |
| t_bs | 盐基饱和度 Topsoil base saturation | % |
| t_cacos3 | 碳酸盐或石灰含量 Topsoil calcium carbonate | 重量百分比(wt.%) |
| t_cacos4 | 硫酸盐含量 Topsoil gypsum | 重量百分比 (wt.%) |
| t_cec_clay | 黏性层土壤的阳离子交换能力Topsoil cation exchange capacity (CEC)(clay) | comL·kg-1 |
| t_cec_soil | 表层土壤阳离子交换量Topsoil cation exchange capacity (CEC)(soil) | comL·kg-1 |
| t_ece | 电导率Soil conductivity (Elco) | ds·m-1 |
| t_esp | 可交换钠盐Soil exchangeable sodium (ESP) | % |
| t_gravel | 表层土壤砾石含量Topsoil gravel content | 体积百分比(vol.%) |
| t_oc | 有机碳含量Topsoil organic carbon | 重量百分比(wt.%) |
| t_ph_h2o | 酸碱度Topsoil pH (H2O) | |
| t_ref_bulk | 土壤容重Topsoil reference bulk density | g·cm-3 |
| t_sand | 沙含量Topsoil sand fraction | 重量百分比(wt.%) |
| t_silt | 表层土壤粉粒组分Topsoil silt fraction | 重量百分比(wt.%) |
| t_teb | 交换性盐基Topsoil exchange base (TEB) | comL·kg-1 |
| t_usda_tex | USDA土壤质地分类Topsoil USDA texture classification | |
| elev | 海拔 Elevation | m |
| slope | 坡度 Slope | ° |
| aspect | 坡向 Aspect | ° |
表1 39个独立的自然环境变量
Table 1 39 independent natural environment variables
| 变量Variable | 描述Description | 单位Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Bio1 | 年平均温度 Average annual temperature | ℃ |
| Bio2 | 昼夜温差月均值 Monthly mean temperature difference between day and night | ℃ |
| Bio3 | 昼夜温差与年温差比值Temperature difference between day and night/annual temperature difference | % |
| Bio4 | 气温季节性变动系数 Seasonal variation coefficient of temperature | |
| Bio5 | 最热月最高温 Max temperature of warmest month | ℃ |
| Bio6 | 最冷月最低温 Min temperature of coldest month | ℃ |
| Bio7 | 年温度变化范围 Temperature annual range | ℃ |
| Bio8 | 最湿季均温 Mean temperature of wettest quarter | ℃ |
| Bio9 | 最干季均温 Mean temperature of driest quarter | ℃ |
| Bio10 | 最暖季均温 Mean temperature of warmest quarter | ℃ |
| Bio11 | 最冷季均温 Mean temperature of coldest quarter | ℃ |
| Bio12 | 年均降水量 Annual precipitation | mm |
| Bio13 | 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month | mm |
| Bio14 | 最干月降水量 Precipitation of driest month | mm |
| Bio15 | 季节性降水量 Precipitation seasonality | mm |
| Bio16 | 最湿季降水量 Precipitation of wettest quarter | mm |
| Bio17 | 最干季降水量 Precipitation of driest quarter | mm |
| Bio18 | 最暖季平均降水量 Mean precipitation of warmest quarter | mm |
| Bio19 | 最冷季平均降水量 Mean precipitation of coldest quarter | mm |
| aws_class | 土壤有效水含量 Available water content of soil (AWC) | % |
| s_clay | 亚表层土壤黏粒组分 Subsoil clay fraction | 重量百分比 (wt.%) |
| t_bs | 盐基饱和度 Topsoil base saturation | % |
| t_cacos3 | 碳酸盐或石灰含量 Topsoil calcium carbonate | 重量百分比(wt.%) |
| t_cacos4 | 硫酸盐含量 Topsoil gypsum | 重量百分比 (wt.%) |
| t_cec_clay | 黏性层土壤的阳离子交换能力Topsoil cation exchange capacity (CEC)(clay) | comL·kg-1 |
| t_cec_soil | 表层土壤阳离子交换量Topsoil cation exchange capacity (CEC)(soil) | comL·kg-1 |
| t_ece | 电导率Soil conductivity (Elco) | ds·m-1 |
| t_esp | 可交换钠盐Soil exchangeable sodium (ESP) | % |
| t_gravel | 表层土壤砾石含量Topsoil gravel content | 体积百分比(vol.%) |
| t_oc | 有机碳含量Topsoil organic carbon | 重量百分比(wt.%) |
| t_ph_h2o | 酸碱度Topsoil pH (H2O) | |
| t_ref_bulk | 土壤容重Topsoil reference bulk density | g·cm-3 |
| t_sand | 沙含量Topsoil sand fraction | 重量百分比(wt.%) |
| t_silt | 表层土壤粉粒组分Topsoil silt fraction | 重量百分比(wt.%) |
| t_teb | 交换性盐基Topsoil exchange base (TEB) | comL·kg-1 |
| t_usda_tex | USDA土壤质地分类Topsoil USDA texture classification | |
| elev | 海拔 Elevation | m |
| slope | 坡度 Slope | ° |
| aspect | 坡向 Aspect | ° |
分布概率 Distributed probability | 评价等级 Evaluation level |
|---|---|
| P<0.16 | 非适生区 Uninhabitable area |
| 0.16≤P<0.30 | 低适生区 Low suitable area |
| 0.30≤P<0.60 | 中适生区 Medium suitable area |
| 0.60≤P<1.00 | 高适生区 High suitable area |
表2 适生区等级划分
Table 2 Classification of suitable areas
分布概率 Distributed probability | 评价等级 Evaluation level |
|---|---|
| P<0.16 | 非适生区 Uninhabitable area |
| 0.16≤P<0.30 | 低适生区 Low suitable area |
| 0.30≤P<0.60 | 中适生区 Medium suitable area |
| 0.60≤P<1.00 | 高适生区 High suitable area |
变量 Variable | 贡献率 Percent contribution (%) | 重要值 Permutation importance |
|---|---|---|
| Bio13 最湿月降水量Precipitation of wettest month | 46.8 | 41.8 |
| Bio4气温季节性变动系数Seasonal variation coefficient of temperature | 33.9 | 41.0 |
| t_ph_h2o 酸碱度Topsoil pH (H2O) | 7.4 | 2.6 |
| Bio1 年平均温度Average annual temperature | 5.3 | 6.8 |
| t_sand 沙含量Topsoil sand fraction | 2.9 | 0.7 |
| elev 海拔Elevation | 2.7 | 6.1 |
| Bio15 季节性降水量Precipitation seasonality | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Bio3 昼夜温差与年温差比值 Isothermality | 0.3 | 0.5 |
表3 8个自然环境变量及其贡献率和重要值
Table 3 8 natural environment variables and their contribution rates and important values
变量 Variable | 贡献率 Percent contribution (%) | 重要值 Permutation importance |
|---|---|---|
| Bio13 最湿月降水量Precipitation of wettest month | 46.8 | 41.8 |
| Bio4气温季节性变动系数Seasonal variation coefficient of temperature | 33.9 | 41.0 |
| t_ph_h2o 酸碱度Topsoil pH (H2O) | 7.4 | 2.6 |
| Bio1 年平均温度Average annual temperature | 5.3 | 6.8 |
| t_sand 沙含量Topsoil sand fraction | 2.9 | 0.7 |
| elev 海拔Elevation | 2.7 | 6.1 |
| Bio15 季节性降水量Precipitation seasonality | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Bio3 昼夜温差与年温差比值 Isothermality | 0.3 | 0.5 |
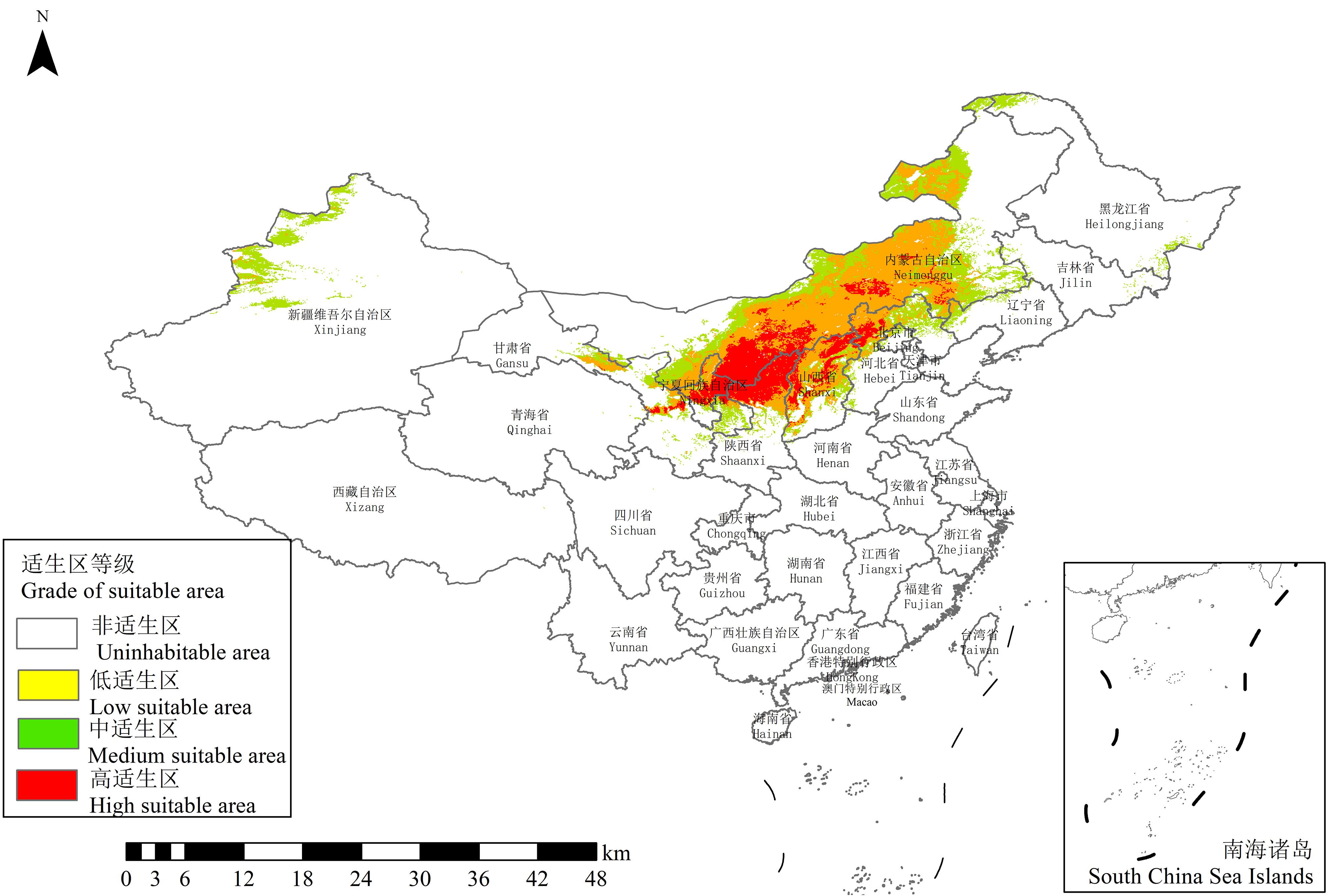
图7 当前自然条件下沙芦草潜在适生区分布基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2023)2767号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map of the Ministry of Natural Resources GS (2023) No. 2767, the boundaries of the base map have not been modified.
Fig.7 Distribution of potential suitable areas under current natural conditions
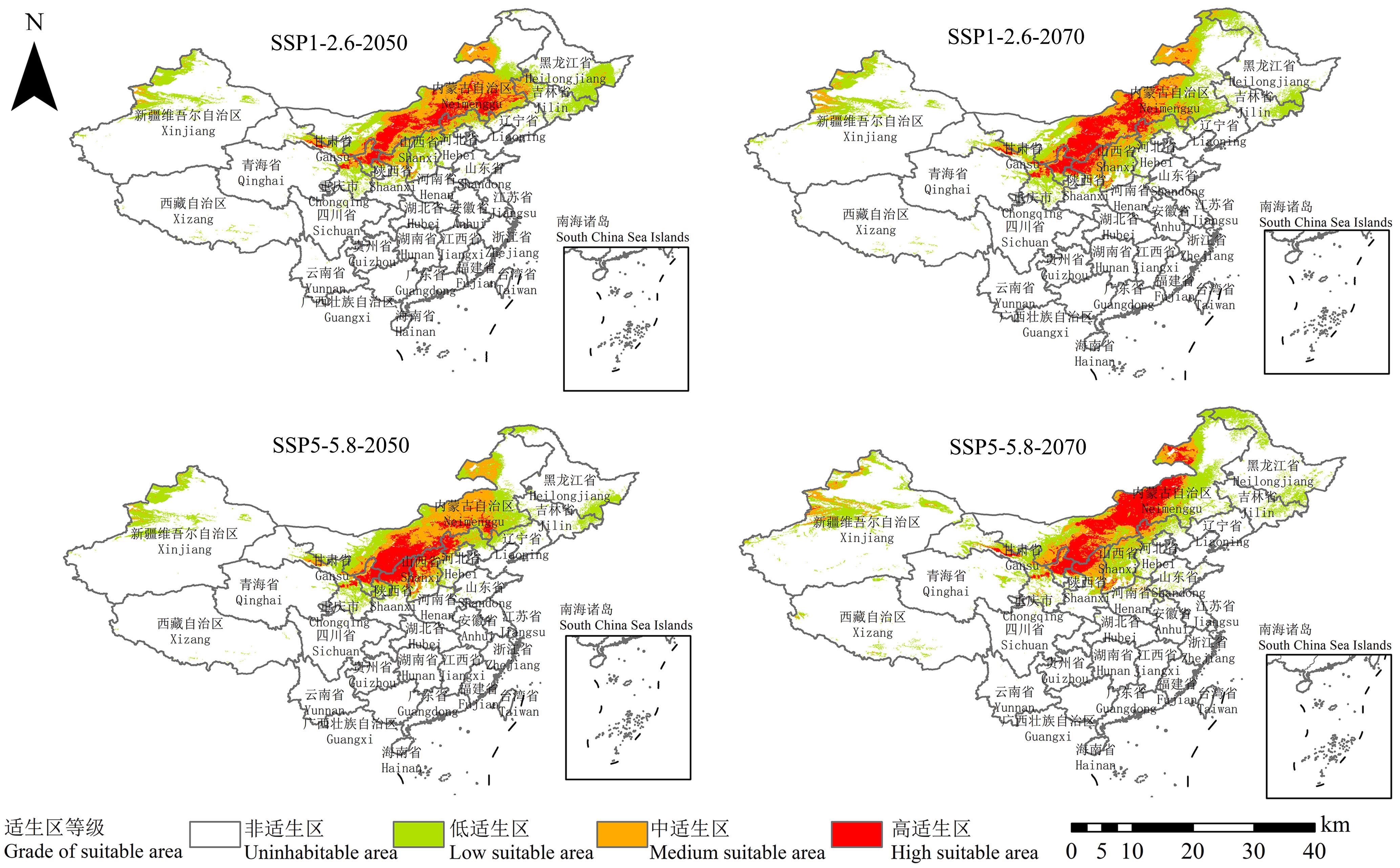
图8 两种未来环境下2050和2070年沙芦草潜在适生区分布基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2023)2767号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map of the Ministry of Natural Resources GS (2023) No. 2767, the boundaries of the base map have not been modified.
Fig.8 Distribution of potential habitat areas of reed grass in 2050 and 2070 under two future environments

图9 高适生区质心转移基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2023)2767号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。Based on the standard map of the Ministry of Natural Resources GS (2023) No. 2767, the boundaries of the base map have not been modified.
Fig.9 Centroid transfer in high suitability area
| 1 | Min F, Hideaki S, Li C. Environmental and economic risks assessment under climate changes for three land uses scenarios analysis across Teshio watershed, northernmost of Japan. The Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 599/600: 451-463. |
| 2 | Gong L, Tian B, Li Y, et al. Phenological changes of soybean in response to climate conditions in frigid region in China over the past decades. International Journal of Plant Production, 2021, 15: 363-375. |
| 3 | Novikova L Y, Bulakh P P, Nekrasov A Y, et al. Soybean response to weather and climate conditions in the Krasnodar and Primorye territories of Russia over the past decades. Agronomy, 2020, 10(9): 1278. |
| 4 | Oban H O, Orucu O K, Arslan E S. MaxEnt modeling for predicting the current and future potential geographical distribution of Quercus libani Olivier. Sustainability, 2020, 12(7): 1-17. |
| 5 | Cetin M, Sevik H, Koc I, et al. The change in biocomfort zones in the area of Mu˘gla province in near future due to the global climate change scenarios. Journal of Thermal Biology, 2023, 112: 103434. |
| 6 | Lıcıte I, Popluga D, Rivza P, et al. Nutrient-rich organic soil management patterns in light of climate change policy. Civil Engineering Journal, 2022, 8(10): 2290-2304. |
| 7 | Al-Ghussain L. Global warming: Review on driving forces and mitigation. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 2019, 38(1): 13-21. |
| 8 | Prakash S. Impact of climate change on aquatic ecosystem and its biodiversity: An overview. International Journal of Biological Innovations, 2021, 3(2): 312-317. |
| 9 | Sun S X, Zhang Y, Huang D Z, et al. The effect of climate change on the richness distribution pattern of oaks (Quercus L.) in China. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 744: 140786. |
| 10 | Wang R H, Ru X Y, Jiang T C, et al. Based on the phenological model to study the possible changes of apple flowering dates under future climate scenarios in Shaanxi Province. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2021, 42(9): 729-745. |
| 王润红, 茹晓雅, 蒋腾聪, 等. 基于物候模型研究未来气候情景下陕西苹果花期的可能变化. 中国农业气象, 2021, 42(9): 729-745. | |
| 11 | Ye X Z, Zhang M Z, Lai W F, et al. Prediction of potential suitable distribution of Phoebe bournei based on MaxEnt optimization model. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(20): 8135-8144. |
| 叶兴状, 张明珠, 赖文峰, 等. 基于MaxEnt优化模型的闽楠潜在适宜分布预测. 生态学报, 2021, 41(20): 8135-8144. | |
| 12 | Jia X, Wang C, Jin H, et al. Assessing the suitable distribution area of Pinus koraiensis based on an optimized MaxEnt model. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 38(8): 2570-2576. |
| 贾翔, 王超, 金慧, 等. 基于优化的MaxEnt模型评价红松适宜分布区. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(8): 2570-2576. | |
| 13 | Sayit H, Nurbay A, Xu Z L, et al. Simulation of potential distribution patterns of the invasive plant species Xanthium spinosum L. (Bathurst burr) in Xinjiang under climate change. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(5): 1551-1559. |
| 塞依丁·海米提, 努尔巴依·阿布都沙力克, 许仲林, 等. 气候变化情景下外来入侵植物刺苍耳在新疆的潜在分布格局模拟. 生态学报, 2019, 39(5): 1551-1559. | |
| 14 | Zhang A H, Tang C Y, Hu N, et al. Investigation on the development of the Litsea cubeba (Lour.) Pers. industry in China. Biomass Chemical Engineering, 2020, 54(6): 25-32. |
| 张爱华, 唐春艳, 胡楠, 等. 我国山苍子产业发展现状及对策. 生物质化学工程, 2020, 54(6): 25-32. | |
| 15 | Gong Z N, Su S, Du B, et al. Habitat selection and dispersal of red-crowned cranes during breeding period in Zhalong Wetland National Nature Reserve. Journal of Natural Resources, 2021, 36(8): 1964-1975. |
| 宫兆宁, 苏朔, 杜博, 等. 扎龙湿地丹顶鹤繁殖栖息地的选择及扩散. 自然资源学报, 2021, 36(8): 1964-1975. | |
| 16 | Lai W F, Ye X Z, Wen G W, et al. Analysis of potential suitable regions for the precious Tibetan medicine Sinopodophyllum hexandrum based on the optimized MaxEnt model. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 51(1): 112-120. |
| 赖文峰, 叶兴状, 文国卫, 等. 基于优化后的MaxEnt模型对珍贵藏药桃儿七潜在适生区分析. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 51(1): 112-120. | |
| 17 | Ji L T, Zheng T Y, Chen Q, et al. Responses of potential suitable area of Paris verticillata to climate change and its dominant climate factors. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(1): 89-96. |
| 姬柳婷, 郑天义, 陈倩, 等. 北重楼潜在适生区对气候变化的响应及其主导气候因子. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(1): 89-96. | |
| 18 | Coro G. A global-scale ecological niche model to predict SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus infection rate. Ecological Modelling, 2020, 431: 109187. |
| 19 | Raffini F, Bertorelle G, Biello R, et al. From nucleotides to satellite imagery: Approaches to identify and manage the invasive pathogen Xylella fastidiosa and its insect vectors in Europe. Sustainability, 2020, 12(11): 4508. |
| 20 | Yu H Y, Sun C K, Huo X, et al. Predicting the transmission risk of H7N9 using ecological niche modeling. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2019, 46(2): 206-210. |
| 21 | Lan B X, Li L H, Wang H. Genetic diversity of Agropyron mongolicum Keng populations. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2005, 38(3): 468-473. |
| 兰宝祥, 李立会, 王辉. 蒙古冰草居群遗传多样性研究. 中国农业科学, 2005, 38(3): 468-473. | |
| 22 | Li X Q, Gao Y H, Liu Y, et al. The genetic diversity of 9 populations of dry-desert Agropyron mongolicum collected in northern China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(3): 77-85. |
| 李晓全, 高有汉, 刘扬, 等. 我国北方9份旱生-沙生植物蒙古冰草遗传多样性研究. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 77-85. | |
| 23 | Liu W L, Xu D M, Shi J M, et al. Plant cluster structure and leaf functional characters of Agropyron mongolicum populations in different plant species associations. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(8): 72-80. |
| 刘万龙, 许冬梅, 史佳梅, 等. 不同群落生境蒙古冰草种群株丛结构和叶片功能性状的变化. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 72-80. | |
| 24 | Shi J M. Study on phenotypic traits and ecophysiological adaptation strategies of Agropyron mongolicum under heterogeneous habitats. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2022. |
| 史佳梅. 异质生境下蒙古冰草表型性状及生理生态适应策略研究. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2022. | |
| 25 | Li Y K, Liu J L, Xu D M, et al. Resource allocation characteristics of Agropyron mongolicum in the desert steppe in Ningxia. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(4): 1125-1133. |
| 李永康, 刘金龙, 许冬梅, 等. 宁夏荒漠草原蒙古冰草资源分配特征. 草地学报, 2023, 31(4): 1125-1133. | |
| 26 | Liu M G, Shi J M, Xu D M, et al. Physiological and ecological characteristics of Agropyron mongolicum in desert steppe under heterogeneous habitats. Grassland and Turf, 2023, 43(6): 94-100. |
| 刘梦鸽, 史佳梅, 许冬梅, 等. 异质生境条件下荒漠草原蒙古冰草生理生态特征的研究. 草原与草坪, 2023, 43(6): 94-100. | |
| 27 | Li Y F, Zhang X, Liu Z X, et al. Response of functional traits and rhizosphere effects of Agropyron mongolicum to soil properties in desert of Ningxia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(21): 8683-8691. |
| 李云飞, 张雪, 刘智贤, 等. 宁夏荒漠草原蒙古冰草功能性状和根际效应对土壤性状的响应. 生态学报, 2023, 43(21): 8683-8691. | |
| 28 | Zhang X T, Liu X T, Ma Y H, et al. Construction of expression vector and prediction of target genes of drought-responsive amo-miR5 in Agropyron mongolicum. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2018, 37(3): 1302-1307. |
| 张旭婷, 刘旭婷, 马艳红, 等. 蒙古冰草抗旱相关amo-miR5靶基因预测及表达载体构建. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2018, 37(3): 1302-1307. | |
| 29 | Zhao Y, Han H J, Zhang R, et al. Functional identification of MwMYB4 gene from Agropyron mongolicum Keng. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2020, 40(4): 565-571. |
| 赵彦, 韩慧杰, 张锐, 等. 蒙古冰草MwMYB4基因功能鉴定. 西北植物学报, 2020, 40(4): 565-571. | |
| 30 | Ma Y H, Zhang X T, Yu X X, et al. Differential expression analysis of drought-responsive microRNA and prediction of their target genes in Agropyron mongolicum at seedling stage. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2017, 37(9): 1168-1174. |
| 马艳红, 张旭婷, 于肖夏, 等. 蒙古冰草苗期抗旱相关microRNA的差异表达分析及靶基因预测. 麦类作物学报, 2017, 37(9): 1168-1174. | |
| 31 | Chen Y D, Zhang G J, Huang S. Analysis of rumen degradation characteristics and feeding value of psammophytes in desert area of Northwest China. Feed Research, 2021, 44(1): 1-5. |
| 陈毅东, 张桂杰, 黄帅. 西北荒漠区沙生植物瘤胃降解特性及饲用价值分析. 饲料研究, 2021, 44(1): 1-5. | |
| 32 | Ma Z Y, Qian Z H, Ma H B, et al. Evaluation of drought resistance of native plants in Ningxia desert steppe. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(4): 67-75. |
| 马子元, 钱志豪, 马红彬, 等. 宁夏荒漠草原乡土植物的抗旱性评价. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(4): 67-75. | |
| 33 | Zhang J Y, Li X W, Liu W D, et al. A study on the Agropyron mongolicum community classification and the relationship between that community characteristics and the environment in Ningxia. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(2): 498-509. |
| 张嘉玉, 李小伟, 刘万弟, 等. 宁夏沙芦草群落分类及群落特征与环境关系的研究. 草地学报, 2023, 31(2): 498-509. | |
| 34 | Cobos M E, Peterson A T, Barve N, et al. Kuenm: an R package for detailed development of ecological niche models using Maxent. PeerJ, 2019, 7: 6281. |
| 35 | Phillips S J, Anderson R P, Dudík M, et al. Opening the black box: an open-source release of MaxEnt. Ecography, 2017, 40(7): 887-893. |
| 36 | Anderson R P, Martínez-Meyer E, Nakamura M, et al. Ecological niches and geographic distributions (MPB-49). Monographs in Population Biology: Princeton University Press, 2011, 49: 173. |
| 37 | Swets J A. Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems. Science, 1988, 240(4857): 1285-1293. |
| 38 | Hu Q, Lin H Q, Dai Q, et al. Niche differentiation among three middle-sized carnivores in Wolong Nature Reserve. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 2020, 55(6): 685-691. |
| 胡强, 林红强, 戴强, 等. 卧龙保护区三种中型食肉动物的生态位差异. 动物学杂志, 2020, 55(6): 685-691. | |
| 39 | Swanti S, Kusum A, Dhruval B, et al. Modeling habitat suitability of Perilla frutescens with MaxEnt in Uttarakhand-A conservation approach. Journal of Applied Research on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants, 2018, 10: 99-105. |
| 40 | Morales N S, Fernández I C, Baca-González V. MaxEnt’s parameter configuration and small samples: are we paying attention to recommendations? A systematic review. PeerJ, 2017, 5: 3093. |
| 41 | Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, et al. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2011, 28(10): 2731-2739. |
| 42 | Hou C Z, Huang D Q, Gui D W, et al. Spatiotemporal variations of climate extremes and influential factors in deserts and sandy fields of northern China from 1961 to 2019. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2023, 43(8): 1495-1505. |
| 侯承志, 黄丹青, 桂东伟, 等. 1961-2019年中国北方沙漠沙地极端气候变化特征及其影响因素. 地理科学, 2023, 43(8): 1495-1505. | |
| 43 | Gao X Q, Fu B Z, Wu X J, et al. Salt tolerance of Agropyron mongolicum at seedling stage. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 53(11): 2602-2606. |
| 高雪芹, 伏兵哲, 吴晓娟, 等. 宁夏野生沙芦草苗期耐盐性研究.湖北农业科学, 2014, 53(11): 2602-2606. | |
| 44 | Tian Z P, Jiang D. Enhanced seasonality of surface air temperature over China during the mid-holocene. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2023, 16(5): 100393. |
| 45 | Zhang Z Y. Development of EST-SSR markers and identification of germplasm resources of Agropyron mongolicum Keng based on transcriptome sequencing. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2021. |
| 张则宇. 基于转录组测序的沙芦草EST-SSR分子标记开发及种质资源鉴定. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2021. | |
| 46 | Gao W D, Wang Y, Li Z X, et al. Analysis on the characteristics of climate change in the endorheic area in alpine region based on extreme precipitation index. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2021, 43(6): 1693-1703. |
| 高文德, 王昱, 李宗省, 等. 高寒内流区极端降水的气候变化特征分析. 冰川冻土, 2021, 43(6): 1693-1703. | |
| 47 | Ren X M, Yang G H, Zhu Y, et al. Effect of environmental variables on species composition and richness of alpine vegetation in Taibai Mountain. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(23): 6993-7003. |
| 任学敏, 杨改河, 朱雅, 等. 环境因子对太白山高山植被物种组成和丰富度的影响. 生态学报, 2014, 34(23): 6993-7003. | |
| 48 | Editorial Committee of Flora of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Flora of China. Beijing: Science Press, 1987. |
| 中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会. 中国植物志.北京: 科学出版社, 1987. | |
| 49 | Niu Y Y, Li C L, Wang J, et al. Performance evaluation of ERA5 reanalysis precipitation data and spatiotemporal characteristics of extreme precipitation in Inner Mongolia. Arid Land Geography, 2023, 46(9): 1418-1431. |
| 牛怡莹, 李春兰, 王军, 等. 内蒙古ERA5再分析降水数据性能评估与极端降水时空特征分析. 干旱区地理, 2023, 46(9): 1418-1431. | |
| 50 | Bu H, Ulan T Y, Siqin C T, et al. Reaponse of vegetation fraction cover change to meteorological drought in Inner Mongolia from 1982 to 2099. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2023, 38(5): 1-9. |
| 布和, 乌兰图雅, 斯琴朝克图, 等. 1982-2099年内蒙古地区植被覆盖变化对气象干旱的响应. 西北林学院学报, 2023, 38(5): 1-9. | |
| 51 | Meng Y J. Simulation assessment and projection of climate change based on CMIP5 and RegCM4 models under RCPs scenarios in Inner Mongolia. Meteorology Journal of Inner Mongolia, 2021(2): 3-8. |
| 孟玉婧. 基于 CMIP5和 RegCM4模式的内蒙古气候变化模拟评估及未来RCPs情景预估. 内蒙古气象, 2021(2): 3-8. | |
| 52 | Yang Y D, Ma J L, Ma H B, et al. Effects of grazing exclusion on root trait characteristics of dominant plants in the desert steppe. Pratacultural Science, 2023, 40(6): 1507-1517. |
| 杨彦东, 马静利, 马红彬, 等. 封育对荒漠草原优势植物根系性状特征的影响. 草业科学, 2023, 40(6): 1507-1517. |
| [1] | 王鹏, 金正, 余婷, 秦康强, 桑新亚, 陶建平, 罗唯学. 预测姜黄属植物在中国当前和未来气候情景下的潜在分布区变化[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 14-27. |
| [2] | 凤紫棋, 孙文义, 穆兴民, 高鹏, 赵广举, 陈帅. 南方山区杉木人工林林下草本植物多样性的影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 17-26. |
| [3] | 于金田, 王晶, 伏兵哲, 高雪芹. 沙芦草种子发芽抑制物的初步探究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 92-102. |
| [4] | 马倩倩, 刘彤, 董合干, 王寒月, 赵文轩, 王瑞丽, 刘延, 陈乐. 气候变化下三裂叶豚草在新疆的潜在地理分布[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 73-85. |
| [5] | 王百竹, 朱媛君, 刘艳书, 马风云, 张晓, 时忠杰, 杨晓晖. 典型草原建群种长芒草(Stipa bungeana)在中国的潜在分布范围预测及主要影响因子分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 3-13. |
| [6] | 李国旗, 赵盼盼, 邵文山, 靳长青. 围封条件下荒漠草原两种植物群落土壤理化性状与酶活性的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 49-59. |
| [7] | 赵盼盼, 李国旗, 邵文山, 靳长青. 围封对荒漠草原区沙芦草群落土壤种子库及地上植被的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(1): 42-52. |
| [8] | 王翀,林慧龙,何兰,曹坳程. 紫茎泽兰潜在分布对气候变化响应的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(4): 20-30. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||