

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 94-105.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020448
祁鹤兴1( ), 芦光新1(
), 芦光新1( ), 李宗仁1, 徐成体2, 德科加2, 周孝娟1, 王英成1, 马桂花1
), 李宗仁1, 徐成体2, 德科加2, 周孝娟1, 王英成1, 马桂花1
收稿日期:2020-10-13
修回日期:2020-12-28
出版日期:2021-05-21
发布日期:2021-05-21
通讯作者:
芦光新
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: lugx74@qq.com基金资助:
He-xing QI1( ), Guang-xin LU1(
), Guang-xin LU1( ), Zong-ren LI1, Cheng-ti XU2, Ke-jia DE2, Xiao-juan ZHOU1, Ying-cheng WANG1, Gui-hua MA1
), Zong-ren LI1, Cheng-ti XU2, Ke-jia DE2, Xiao-juan ZHOU1, Ying-cheng WANG1, Gui-hua MA1
Received:2020-10-13
Revised:2020-12-28
Online:2021-05-21
Published:2021-05-21
Contact:
Guang-xin LU
摘要:
青贮玉米是青海省玉米发展的优势产业,但是链格孢叶枯病的发生对青贮玉米的品质和产量造成了影响。为了对青贮玉米链格孢叶枯病病原菌进行鉴定及对其致病力进行分析,本研究从青海省不同海拔高度青贮玉米种植区采集病叶,从中分离得到177株病原菌,根据菌落和孢子等的形态特征和rDNA-ITS序列分析对病原菌进行鉴定;根据对金皇828、铁研53号和中单2号青贮玉米的接种结果计算病情指数,对155株菌株致病力进行分析。结果表明交链格孢(Alternariaalternata)、极细链格孢(A. tenuissima)、致密链格孢(A. compacta)和Alternaria sp,分别占病原菌总数的28.2%、17.5%、15.2%和21.5%,为优势病原菌。155株病原菌都能侵染3种青贮玉米,接种铁研53号后强致病力菌株、中等致病力菌株和弱致病力菌株分别有68、56和31株;接种金皇828后强、中等和弱致病力菌株分别有69、60和26株;接种中单2号后强、中等和弱致病力菌株分别有64、58和33株。本研究结果表明青贮玉米链格孢叶枯病是由多种链格孢属真菌共同侵染造成的,且病原菌存在致病力分化。
祁鹤兴, 芦光新, 李宗仁, 徐成体, 德科加, 周孝娟, 王英成, 马桂花. 青海省青贮玉米链格孢叶枯病病原菌鉴定及其致病力分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 94-105.
He-xing QI, Guang-xin LU, Zong-ren LI, Cheng-ti XU, Ke-jia DE, Xiao-juan ZHOU, Ying-cheng WANG, Gui-hua MA. Identification and pathogenicity of Alternaria leaf blight strains in silage maize in Qinghai Province[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(6): 94-105.
采样地 Smple sites | 经纬度 Longitude and latitude | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 土壤类型 Agrotype | 年均气温 Mean annual temperature (℃) | 年均降水量 Mean annual mean precipitation(mm) | 前茬作物 Preceding crop |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 西宁市大通县景阳镇甘树湾村Ganshuwan Village, Jingyang Town, Datong County, Xining City | 101°37′14.07″ E, 36°48′45.73″ N | 2637 | 栗钙土 Chestnut soil | 4.9 | 403.4 | 马铃薯Solanum tuberosum |
| 海东市民和县马场垣乡团结村Tuanjie Village, Machangyuan Town, Minhe County, Haidong City | 102°52′56.92″ E, 36°18′51.90″ N | 1795 | 砂壤土 Sandy soil | 7.9 | 360.7 | 小麦Triticum aestivum |
| 西宁市湟中县田家寨李家台村Lijiatai Village, Tianjiazhai Town, Huangzhong County, Xining City | 101°84′16.13″ E, 36°50′71.81″ N | 2083 | 红黏土 Red clay | 4.0 | 425.0 | 玉米Z. mays |
| 黄南藏族自治州尖扎县河滩村Hetan Village, Jianzha County, Huangnan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture | 101°95′70.69″ E, 36°06′20.89″ N | 2032 | 栗钙土 Chestnut soil | 7.9 | 308.4 | 小麦T. aestivum |
表1 采样地信息
Table 1 Information of sample sites
采样地 Smple sites | 经纬度 Longitude and latitude | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 土壤类型 Agrotype | 年均气温 Mean annual temperature (℃) | 年均降水量 Mean annual mean precipitation(mm) | 前茬作物 Preceding crop |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 西宁市大通县景阳镇甘树湾村Ganshuwan Village, Jingyang Town, Datong County, Xining City | 101°37′14.07″ E, 36°48′45.73″ N | 2637 | 栗钙土 Chestnut soil | 4.9 | 403.4 | 马铃薯Solanum tuberosum |
| 海东市民和县马场垣乡团结村Tuanjie Village, Machangyuan Town, Minhe County, Haidong City | 102°52′56.92″ E, 36°18′51.90″ N | 1795 | 砂壤土 Sandy soil | 7.9 | 360.7 | 小麦Triticum aestivum |
| 西宁市湟中县田家寨李家台村Lijiatai Village, Tianjiazhai Town, Huangzhong County, Xining City | 101°84′16.13″ E, 36°50′71.81″ N | 2083 | 红黏土 Red clay | 4.0 | 425.0 | 玉米Z. mays |
| 黄南藏族自治州尖扎县河滩村Hetan Village, Jianzha County, Huangnan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture | 101°95′70.69″ E, 36°06′20.89″ N | 2032 | 栗钙土 Chestnut soil | 7.9 | 308.4 | 小麦T. aestivum |
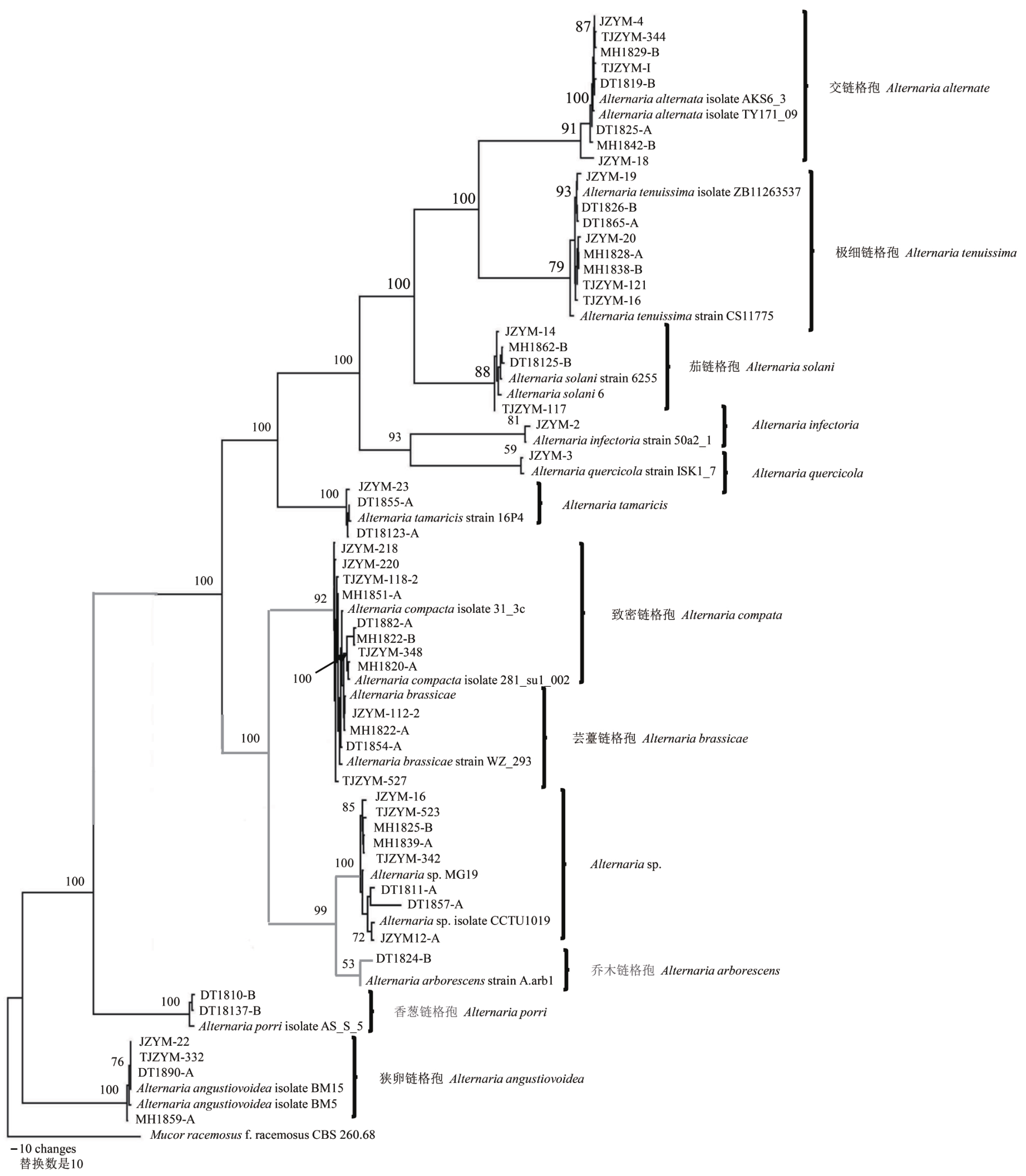
图3 52株青贮玉米链格孢叶枯病病原菌代表菌株基于rDNA-ITS序列构建的系统发育树
Fig.3 The plylogenetic tree of represent pathogens associated with Alternaria leaf blight in silage maize was inferred from rDNA-ITS sequences

图4青贮玉米链格孢叶枯病病原菌科赫氏法则验证(A)接种后病斑表面分生孢子和菌丝形态;(B)野生型菌株菌落形态;(C)从室内发病病斑分离得到菌株的菌落形态。(A) Conidiation and hypha structure of TJZYM-120 and DT1824-A, on disease lesions of their host leaves;(B) Colony morphology of wild-type isolates;(C) Colony morphology of TJZYM-120-Y and DT1824-A-Y isolated from disease lesions of their host leaves.
Fig. 4 Verification of Koch’s postulate of the pathogens associated with Alternaria leaf blight in silage maize
菌株 Isolates | 铁研53号 Tieyan 53 | 金皇828 Jinhuang 828 | 中单2号 Zhongdan 2 | 菌株 Isolates | 铁研53号 Tieyan 53 | 金皇828 Jinhuang 828 | 中单2号 Zhongdan 2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病情指数 | 致病力 | 病情指数 | 致病力 | 病情指数 | 致病力 | 病情指数 | 致病力 | 病情指数 | 致病力 | 病情指数 | 致病力 | ||
| JZYM-2 | 77.78 | 强 | 74.60 | 中 | 73.33 | 中 | MH1827-A | 85.19 | 强 | 65.43 | 中 | 82.72 | 强 |
| JZYM-3 | 36.51 | 弱 | 55.56 | 中 | 31.48 | 弱 | MH1827-ModerateB | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| JZYM-4 | 23.81 | 弱 | 64.44 | 中 | 27.78 | 弱 | MH1829-A | 62.96 | 中 | 48.15 | 中 | 34.44 | 弱 |
| JZYM-5 | 85.19 | 强 | 64.44 | 中 | 41.36 | 弱 | MH1829-B | 82.72 | 强 | 67.90 | 中 | 37.78 | 弱 |
| JZYM-9 | 85.19 | 强 | 97.53 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | MH1830-A | 62.96 | 中 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| JZYM-12 | 62.96 | 中 | 90.12 | 强 | 68.89 | 中 | MH1832-B | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 |
| JZYM-13 | 85.19 | 强 | 97.53 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | MH1834-A | 62.96 | 中 | 80.25 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 |
| JZYM-14 | 85.19 | 强 | 90.12 | 强 | 68.89 | 中 | MH1837-A | 62.96 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| JZYM-16 | 62.96 | 中 | 45.68 | 中 | 82.72 | 强 | MH1837-B | 62.96 | 中 | 45.68 | 中 | 63.89 | 中 |
| JZYM-18 | 62.96 | 中 | 80.25 | 强 | 68.89 | 中 | MH1838-B | 85.19 | 强 | 85.19 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| JZYM-19 | 85.19 | 强 | 90.12 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | MH1839-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 48.15 | 中 | 36.11 | 弱 |
| JZYM-20 | 85.19 | 强 | 97.53 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | MH1841-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 25.93 | 弱 | 38.89 | 弱 |
| JZYM-22 | 62.96 | 中 | 25.93 | 弱 | 82.72 | 强 | MH1842-B | 62.96 | 中 | 70.37 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 |
| JZYM-23 | 85.19 | 强 | 90.12 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | MH1843-A | 18.52 | 弱 | 33.33 | 弱 | 36.11 | 弱 |
| JZYM-111-1 | 85.19 | 强 | 67.90 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | MH1843-C | 62.96 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| JZYM-112-2 | 62.96 | 中 | 80.25 | 强 | 68.89 | 中 | MH1846-A | 62.96 | 中 | 87.65 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 |
| JZYM-218 | 40.74 | 弱 | 23.46 | 弱 | 24.07 | 弱 | MH1847-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 33.33 | 弱 | 34.44 | 弱 |
| JZYM-219 | 40.74 | 弱 | 25.93 | 弱 | 24.07 | 弱 | MH1851-A | 85.19 | 强 | 67.90 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 |
| JZYM-220 | 62.96 | 中 | 70.37 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | MH1854-1-A | 85.19 | 强 | 53.09 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 |
| TJZYM-I | 18.52 | 弱 | 25.93 | 弱 | 24.07 | 弱 | MH1857-A | 85.19 | 强 | 72.84 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 |
| TJZYM-6 | 62.96 | 中 | 20.99 | 弱 | 34.44 | 弱 | MH1857-1-A | 62.96 | 中 | 58.02 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 |
| TJZYM-9 | 62.96 | 中 | 67.90 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | MH1857-1-B | 18.52 | 弱 | 43.21 | 弱 | 36.11 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-10 | 18.52 | 弱 | 13.58 | 弱 | 34.44 | 弱 | MH1858-A | 62.96 | 中 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-24-1 | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 87.30 | 强 | MH1857-1-B | 62.96 | 中 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-111 | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 90.48 | 强 | MH1859-A | 62.96 | 中 | 58.02 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 |
| TJZYM-117 | 85.19 | 强 | 65.43 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | MH1862-B | 62.96 | 中 | 65.43 | 中 | 63.10 | 中 |
| TJZYM-118-2 | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | MH1863-B | 18.52 | 弱 | 43.21 | 弱 | 38.75 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-120 | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | DT1801-A | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 |
| TJZYM-121 | 40.74 | 弱 | 13.58 | 弱 | 24.07 | 弱 | DT1803-B | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-123 | 40.74 | 弱 | 20.99 | 弱 | 34.44 | 弱 | DT1805-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 58.02 | 中 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-125-1 | 85.19 | 强 | 35.80 | 弱 | 55.95 | 中 | DT1809-A | 85.19 | 强 | 65.43 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 |
| TJZYM-127-1 | 85.19 | 强 | 45.68 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 | DT1810-B | 62.96 | 中 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-130 | 40.74 | 弱 | 25.93 | 弱 | 38.89 | 弱 | DT1811-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 45.68 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 |
| TJZYM-131 | 85.19 | 强 | 45.68 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 | DT1816-A | 18.52 | 弱 | 25.93 | 弱 | 36.11 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-134 | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | DT1817-A | 85.19 | 强 | 58.02 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 |
| TJZYM-138 | 85.19 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | 87.30 | 强 | DT1819-B | 62.96 | 中 | 33.33 | 弱 | 38.89 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-138-1 | 62.96 | 中 | 25.93 | 弱 | 34.44 | 弱 | DT1824-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 75.31 | 强 | 58.33 | 中 |
| TJZYM-141 | 62.96 | 中 | 55.56 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1824-B | 85.19 | 强 | 75.31 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-146 | 85.19 | 强 | 58.02 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1825-A | 85.19 | 强 | 97.53 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 |
| TJZYM-307 | 85.19 | 强 | 55.56 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 | DT1825-B | 85.19 | 强 | 53.09 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 |
| TJZYM-310 | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | DT1827-A | 85.19 | 强 | 75.31 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-317 | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | DT1828-A | 18.52 | 弱 | 30.86 | 弱 | 24.07 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-319 | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | DT1829-A | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 53.85 | 中 |
| TJZYM-322 | 18.52 | 弱 | 25.93 | 弱 | 34.44 | 弱 | DT1835-B | 40.74 | 弱 | 30.86 | 弱 | 36.11 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-322-1 | 85.19 | 强 | 45.68 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 | DT1836-A | 62.96 | 中 | 74.41 | 中 | 63.64 | 中 |
| TJZYM-323 | 85.19 | 强 | 45.68 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1836-B | 18.52 | 弱 | 65.43 | 中 | 34.44 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-327 | 85.19 | 强 | 53.09 | 中 | 62.00 | 中 | DT1838-B | 62.96 | 中 | 53.09 | 中 | 63.64 | 中 |
| TJZYM-332 | 85.19 | 强 | 45.68 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1841-A | 62.96 | 中 | 53.09 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 |
| TJZYM-341 | 85.19 | 强 | 53.09 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1855-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 97.53 | 强 | 36.11 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-341-1 | 85.19 | 强 | 45.68 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 | DT1855-B | 62.96 | 中 | 97.53 | 强 | 36.11 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-342 | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 84.13 | 强 | DT1857-A | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-343 | 85.19 | 强 | 67.90 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 | DT1864-B | 85.19 | 强 | 75.31 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-344 | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1865-A | 85.19 | 强 | 75.31 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 |
| TJZYM-346 | 40.74 | 弱 | 33.33 | 弱 | 24.07 | 弱 | DT1882-A | 62.96 | 中 | 30.86 | 弱 | 69.23 | 中 |
| TJZYM-347 | 85.19 | 强 | 45.68 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1883-B | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 68.89 | 中 |
| TJZYM-348 | 62.96 | 中 | 45.68 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 | DT1884-B | 40.74 | 弱 | 75.31 | 强 | 36.11 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-349 | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1890-A | 62.96 | 中 | 53.09 | 中 | 53.85 | 中 |
| TJZYM-516 | 62.96 | 中 | 35.80 | 弱 | 34.44 | 弱 | DT1891-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 97.53 | 强 | 57.26 | 中 |
| TJZYM-519 | 40.74 | 弱 | 35.80 | 弱 | 36.11 | 弱 | DT1892-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 75.31 | 强 | 34.44 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-523 | 62.96 | 中 | 67.90 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1899-A | 62.96 | 中 | 97.53 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 |
| TJZYM-527 | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | DT18100-B | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 58.33 | 中 |
| TJZYM-528 | 85.19 | 强 | 65.43 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT18101-A | 85.19 | 强 | 97.53 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-533-1 | 62.96 | 中 | 58.02 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT18102-A | 85.19 | 强 | 53.09 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 |
| TJZYM-537 | 85.19 | 强 | 97.53 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | DT18102-B | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 |
| TJZYM-540 | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | DT18107-A | 62.96 | 中 | 97.53 | 强 | 62.04 | 中 |
| TJZYM-541 | 85.19 | 强 | 58.02 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT18108-A | 62.96 | 中 | 97.53 | 强 | 58.33 | 中 |
| TJZYM-542 | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | DT18113-A | 85.19 | 强 | 75.31 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-544 | 62.96 | 中 | 35.80 | 弱 | 77.78 | 强 | DT18115-A | 85.19 | 强 | 53.09 | 中 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-D | 62.96 | 中 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | DT18124-A | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 60.71 | 中 |
| TJZYM-E | 40.74 | 弱 | 58.02 | 中 | 65.48 | 中 | DT18125-B | 62.96 | 中 | 97.53 | 强 | 58.24 | 中 |
| TJZYM-J-2 | 40.74 | 弱 | 65.43 | 中 | 65.48 | 中 | DT18129-A | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| MH1820-A | 62.96 | 中 | 58.02 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 | DT18131-B | 85.19 | 强 | 97.53 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| MH1821-A | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | DT18133-A | 62.96 | 中 | 53.09 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 |
| MH1822-A | 62.96 | 中 | 80.25 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | DT18133-B | 85.19 | 强 | 53.09 | 中 | 82.72 | 强 |
| MH1822-B | 85.19 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | DT18136-B | 62.96 | 中 | 53.09 | 中 | 53.85 | 中 |
| MH1823-A | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | DT18137-B | 62.96 | 中 | 53.09 | 中 | 58.24 | 中 |
| MH1825-A | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | DT18139-A | 62.96 | 中 | 53.09 | 中 | 53.85 | 中 |
| MH1825-B | 85.19 | 强 | 70.37 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
表2 病原菌接种青贮玉米病情指数和致病力分析
Table 2 Pathogenicity analysis of pathogens associated with Alternaria leaf blight in silage maize
菌株 Isolates | 铁研53号 Tieyan 53 | 金皇828 Jinhuang 828 | 中单2号 Zhongdan 2 | 菌株 Isolates | 铁研53号 Tieyan 53 | 金皇828 Jinhuang 828 | 中单2号 Zhongdan 2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病情指数 | 致病力 | 病情指数 | 致病力 | 病情指数 | 致病力 | 病情指数 | 致病力 | 病情指数 | 致病力 | 病情指数 | 致病力 | ||
| JZYM-2 | 77.78 | 强 | 74.60 | 中 | 73.33 | 中 | MH1827-A | 85.19 | 强 | 65.43 | 中 | 82.72 | 强 |
| JZYM-3 | 36.51 | 弱 | 55.56 | 中 | 31.48 | 弱 | MH1827-ModerateB | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| JZYM-4 | 23.81 | 弱 | 64.44 | 中 | 27.78 | 弱 | MH1829-A | 62.96 | 中 | 48.15 | 中 | 34.44 | 弱 |
| JZYM-5 | 85.19 | 强 | 64.44 | 中 | 41.36 | 弱 | MH1829-B | 82.72 | 强 | 67.90 | 中 | 37.78 | 弱 |
| JZYM-9 | 85.19 | 强 | 97.53 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | MH1830-A | 62.96 | 中 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| JZYM-12 | 62.96 | 中 | 90.12 | 强 | 68.89 | 中 | MH1832-B | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 |
| JZYM-13 | 85.19 | 强 | 97.53 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | MH1834-A | 62.96 | 中 | 80.25 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 |
| JZYM-14 | 85.19 | 强 | 90.12 | 强 | 68.89 | 中 | MH1837-A | 62.96 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| JZYM-16 | 62.96 | 中 | 45.68 | 中 | 82.72 | 强 | MH1837-B | 62.96 | 中 | 45.68 | 中 | 63.89 | 中 |
| JZYM-18 | 62.96 | 中 | 80.25 | 强 | 68.89 | 中 | MH1838-B | 85.19 | 强 | 85.19 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| JZYM-19 | 85.19 | 强 | 90.12 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | MH1839-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 48.15 | 中 | 36.11 | 弱 |
| JZYM-20 | 85.19 | 强 | 97.53 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | MH1841-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 25.93 | 弱 | 38.89 | 弱 |
| JZYM-22 | 62.96 | 中 | 25.93 | 弱 | 82.72 | 强 | MH1842-B | 62.96 | 中 | 70.37 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 |
| JZYM-23 | 85.19 | 强 | 90.12 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | MH1843-A | 18.52 | 弱 | 33.33 | 弱 | 36.11 | 弱 |
| JZYM-111-1 | 85.19 | 强 | 67.90 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | MH1843-C | 62.96 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| JZYM-112-2 | 62.96 | 中 | 80.25 | 强 | 68.89 | 中 | MH1846-A | 62.96 | 中 | 87.65 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 |
| JZYM-218 | 40.74 | 弱 | 23.46 | 弱 | 24.07 | 弱 | MH1847-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 33.33 | 弱 | 34.44 | 弱 |
| JZYM-219 | 40.74 | 弱 | 25.93 | 弱 | 24.07 | 弱 | MH1851-A | 85.19 | 强 | 67.90 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 |
| JZYM-220 | 62.96 | 中 | 70.37 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | MH1854-1-A | 85.19 | 强 | 53.09 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 |
| TJZYM-I | 18.52 | 弱 | 25.93 | 弱 | 24.07 | 弱 | MH1857-A | 85.19 | 强 | 72.84 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 |
| TJZYM-6 | 62.96 | 中 | 20.99 | 弱 | 34.44 | 弱 | MH1857-1-A | 62.96 | 中 | 58.02 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 |
| TJZYM-9 | 62.96 | 中 | 67.90 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | MH1857-1-B | 18.52 | 弱 | 43.21 | 弱 | 36.11 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-10 | 18.52 | 弱 | 13.58 | 弱 | 34.44 | 弱 | MH1858-A | 62.96 | 中 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-24-1 | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 87.30 | 强 | MH1857-1-B | 62.96 | 中 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-111 | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 90.48 | 强 | MH1859-A | 62.96 | 中 | 58.02 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 |
| TJZYM-117 | 85.19 | 强 | 65.43 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | MH1862-B | 62.96 | 中 | 65.43 | 中 | 63.10 | 中 |
| TJZYM-118-2 | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | MH1863-B | 18.52 | 弱 | 43.21 | 弱 | 38.75 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-120 | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | DT1801-A | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 |
| TJZYM-121 | 40.74 | 弱 | 13.58 | 弱 | 24.07 | 弱 | DT1803-B | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-123 | 40.74 | 弱 | 20.99 | 弱 | 34.44 | 弱 | DT1805-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 58.02 | 中 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-125-1 | 85.19 | 强 | 35.80 | 弱 | 55.95 | 中 | DT1809-A | 85.19 | 强 | 65.43 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 |
| TJZYM-127-1 | 85.19 | 强 | 45.68 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 | DT1810-B | 62.96 | 中 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-130 | 40.74 | 弱 | 25.93 | 弱 | 38.89 | 弱 | DT1811-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 45.68 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 |
| TJZYM-131 | 85.19 | 强 | 45.68 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 | DT1816-A | 18.52 | 弱 | 25.93 | 弱 | 36.11 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-134 | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | DT1817-A | 85.19 | 强 | 58.02 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 |
| TJZYM-138 | 85.19 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | 87.30 | 强 | DT1819-B | 62.96 | 中 | 33.33 | 弱 | 38.89 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-138-1 | 62.96 | 中 | 25.93 | 弱 | 34.44 | 弱 | DT1824-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 75.31 | 强 | 58.33 | 中 |
| TJZYM-141 | 62.96 | 中 | 55.56 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1824-B | 85.19 | 强 | 75.31 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-146 | 85.19 | 强 | 58.02 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1825-A | 85.19 | 强 | 97.53 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 |
| TJZYM-307 | 85.19 | 强 | 55.56 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 | DT1825-B | 85.19 | 强 | 53.09 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 |
| TJZYM-310 | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | DT1827-A | 85.19 | 强 | 75.31 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-317 | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | DT1828-A | 18.52 | 弱 | 30.86 | 弱 | 24.07 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-319 | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | DT1829-A | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 53.85 | 中 |
| TJZYM-322 | 18.52 | 弱 | 25.93 | 弱 | 34.44 | 弱 | DT1835-B | 40.74 | 弱 | 30.86 | 弱 | 36.11 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-322-1 | 85.19 | 强 | 45.68 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 | DT1836-A | 62.96 | 中 | 74.41 | 中 | 63.64 | 中 |
| TJZYM-323 | 85.19 | 强 | 45.68 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1836-B | 18.52 | 弱 | 65.43 | 中 | 34.44 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-327 | 85.19 | 强 | 53.09 | 中 | 62.00 | 中 | DT1838-B | 62.96 | 中 | 53.09 | 中 | 63.64 | 中 |
| TJZYM-332 | 85.19 | 强 | 45.68 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1841-A | 62.96 | 中 | 53.09 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 |
| TJZYM-341 | 85.19 | 强 | 53.09 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1855-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 97.53 | 强 | 36.11 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-341-1 | 85.19 | 强 | 45.68 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 | DT1855-B | 62.96 | 中 | 97.53 | 强 | 36.11 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-342 | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 84.13 | 强 | DT1857-A | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-343 | 85.19 | 强 | 67.90 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 | DT1864-B | 85.19 | 强 | 75.31 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-344 | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1865-A | 85.19 | 强 | 75.31 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 |
| TJZYM-346 | 40.74 | 弱 | 33.33 | 弱 | 24.07 | 弱 | DT1882-A | 62.96 | 中 | 30.86 | 弱 | 69.23 | 中 |
| TJZYM-347 | 85.19 | 强 | 45.68 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1883-B | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 68.89 | 中 |
| TJZYM-348 | 62.96 | 中 | 45.68 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 | DT1884-B | 40.74 | 弱 | 75.31 | 强 | 36.11 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-349 | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1890-A | 62.96 | 中 | 53.09 | 中 | 53.85 | 中 |
| TJZYM-516 | 62.96 | 中 | 35.80 | 弱 | 34.44 | 弱 | DT1891-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 97.53 | 强 | 57.26 | 中 |
| TJZYM-519 | 40.74 | 弱 | 35.80 | 弱 | 36.11 | 弱 | DT1892-A | 40.74 | 弱 | 75.31 | 强 | 34.44 | 弱 |
| TJZYM-523 | 62.96 | 中 | 67.90 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT1899-A | 62.96 | 中 | 97.53 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 |
| TJZYM-527 | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | DT18100-B | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 58.33 | 中 |
| TJZYM-528 | 85.19 | 强 | 65.43 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT18101-A | 85.19 | 强 | 97.53 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-533-1 | 62.96 | 中 | 58.02 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT18102-A | 85.19 | 强 | 53.09 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 |
| TJZYM-537 | 85.19 | 强 | 97.53 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | DT18102-B | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 |
| TJZYM-540 | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | DT18107-A | 62.96 | 中 | 97.53 | 强 | 62.04 | 中 |
| TJZYM-541 | 85.19 | 强 | 58.02 | 中 | 68.89 | 中 | DT18108-A | 62.96 | 中 | 97.53 | 强 | 58.33 | 中 |
| TJZYM-542 | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | DT18113-A | 85.19 | 强 | 75.31 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-544 | 62.96 | 中 | 35.80 | 弱 | 77.78 | 强 | DT18115-A | 85.19 | 强 | 53.09 | 中 | 82.72 | 强 |
| TJZYM-D | 62.96 | 中 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | DT18124-A | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 60.71 | 中 |
| TJZYM-E | 40.74 | 弱 | 58.02 | 中 | 65.48 | 中 | DT18125-B | 62.96 | 中 | 97.53 | 强 | 58.24 | 中 |
| TJZYM-J-2 | 40.74 | 弱 | 65.43 | 中 | 65.48 | 中 | DT18129-A | 62.96 | 中 | 75.31 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| MH1820-A | 62.96 | 中 | 58.02 | 中 | 77.78 | 强 | DT18131-B | 85.19 | 强 | 97.53 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 |
| MH1821-A | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | DT18133-A | 62.96 | 中 | 53.09 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 |
| MH1822-A | 62.96 | 中 | 80.25 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | DT18133-B | 85.19 | 强 | 53.09 | 中 | 82.72 | 强 |
| MH1822-B | 85.19 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | 77.78 | 强 | DT18136-B | 62.96 | 中 | 53.09 | 中 | 53.85 | 中 |
| MH1823-A | 85.19 | 强 | 87.65 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | DT18137-B | 62.96 | 中 | 53.09 | 中 | 58.24 | 中 |
| MH1825-A | 85.19 | 强 | 80.25 | 强 | 82.72 | 强 | DT18139-A | 62.96 | 中 | 53.09 | 中 | 53.85 | 中 |
| MH1825-B | 85.19 | 强 | 70.37 | 中 | 58.33 | 中 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |

图5 青贮玉米链格孢叶枯病的代表病原菌接种菌株DT18131-B 、MH1862-B、JZYM-218和MH1829-B分别与交链格孢、茄链格孢、致密链格孢和交链格孢的相似性分别为99.81%、99.44%、99.44%和99.63%。The sequence similarity of DT18131-B, MH1862-B, JZYM-218 and MH1829-B with A. alternata, A. solani, A. compacta and A. alternata were 99.81%, 99.44%, 99.44% and 99.63%, respectively.
Fig.5 Inoculation of represent pathogens associated with Alternaria leaf blight in silage maize
| 1 | Wang L. Cultivation and processing technology of silage maize with high yield and high quality. Shandong Animal Husbandry and Veterinary, 2019, 2: 11-12. |
| 王莉. 青贮玉米优质高产种植及加工技术. 山东畜牧兽医, 2019, 2: 11-12. | |
| 2 | Zhao G B, Liu G C, Li B W. High-quality and high-yield cultivation technology regulation for silage corn in dryland of Gansu province. Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, 5: 61-65. |
| 赵贵宾, 刘广才, 李博文. 甘肃省旱地青贮玉米优质高产栽培技术规程. 甘肃农业科学, 2020, 5: 61-65. | |
| 3 | Wusiman X. Common problems and solutions of cultivation silage maize. Rural Science and Technology, 2020, 8: 109-110. |
| 希尔艾力·吾斯曼. 青贮玉米栽培常见问题及解决策略. 乡村科技, 2020, 8: 109-110. | |
| 4 | He C B, Wang M, Ye J X, et al. Identify and evaluate on maize silage varieties in Qinghai Plateau. Agriculture and Forestry Technology of Qinghai, 2016, 4: 1-4. |
| 贺晨邦, 王敏, 叶景秀, 等. 青海高原青贮饲用玉米品种鉴定评价. 青海农林科技, 2016, 4: 1-4. | |
| 5 | Fraeyman S, Croubels S, Devreese M, et al. Emerging Fusarium and Alternaria mycotoxins: Occurrence, toxicity and toxicokinetics. Toxins (Basel), 2017, 9(7): 228. |
| 6 | Romero B Á R, Reynoso C M, García L V A, et al. Alternaria toxins in Argentinean wheat, bran, and flour. Food Additives & Contaminants Part B-Surveillailce, 2019, 12(1): 24-30. |
| 7 | Pinto V E, Patriarca A. Alternaria species and their associated mycotoxins. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2017, 1542: 13-32. |
| 8 | Wenderoth M, Garganese F, Schmidt H M, et al. Alternariol as virulence and colonization factor of Alternaria alternata during plant infection. Molecular Microbiology, 2019, 112(1): 131-146. |
| 9 | Lópeza P, Venema D, Mol H, et al. Alternaria toxins and conjugates in selected foods in the Netherlands. Food Control, 2016, 69: 153-159. |
| 10 | Meena M, Gupta S K, Swapnil P, et al. Alternaria toxins: Potential virulence factors and genes related to pathogenesis. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 1451. |
| 11 | Wang H X, Zhang Q, Wang L J, et al. Advances in genetic research related to the synthesis of Alternaria alternata toxins. China Biotechnology, 2015, 35(11): 92-98. |
| 王洪秀, 张倩, 王玲杰, 等. 链格孢菌毒素合成相关基因研究进展. 中国生物工程杂志, 2015, 35(11): 92-98. | |
| 12 | Hyang B L, Andrea P, Naresh M. Alternaria in food: Ecophysiology, mycotoxin production and toxicology. Mycobiology, 2015, 43: 2, 93-106. |
| 13 | Hickert S, Bergmann M, Ersen S, et al. Survey of Alternaria toxin contamination in food from the German market, using a rapid HPLC-MS/MS approach. Mycotoxin Research, 2016, 32(1): 7-18. |
| 14 | Battilani P, Costa L G, Dossena A, et al. Scientific information on mycotoxins and natural plant toxicants. Efsa Supporting Publications, 2009, 6(9): 168-172. |
| 15 | Pero R W, Posner H, Blois M, et al. Toxicity of metabolites produced by the “Alternaria”. Environmental Health Perspectives, 1973, 4: 87–94. |
| 16 | Brugger E, Wagner J, Schumacher D M, et al. Mutagenicity of the mycotoxin alternariol in cultured mammalian cells. Toxicology Letters, 2006, 164: 221-230. |
| 17 | Pfeiffer E, Eschenbach S, Metzler M. Alternaria toxins: DNA strand-breaking activity in mammalian cells in vitro. Mycotoxin Research, 2007, 23: 152-157. |
| 18 | Yang N, Zou S Y, Qi R X, et al. Research progress on microbial preparations of silage and selection of optimum strains for silage preparing. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(2): 578-585. |
| 杨楠, 邹苏燕, 戚如鑫, 等. 青贮微生物制剂及优良青贮菌种筛选的研究进展. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(2): 578-585. | |
| 19 | Sifeeldein A, Wang S, Li J, et al. Phylogenetic identification of lactic acid bacteria isolates and their effects on the fermentation quality of sweet sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) silage. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2019, 126(3): 718-729. |
| 20 | Huang F, Zhang L, Zhou B, et al. Research process in silage microorganism and its effect on silage aerobic stability. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2019, 31(1): 82-89. |
| 黄峰, 张露, 周波, 等. 青贮微生物及其对青贮饲料有氧稳定性影响的研究进展. 动物营养学报, 2019, 31(1): 82-89. | |
| 21 | Borreani G, Piano S, Tabacco E. Aerobic stability of maize silage stored under plastic films with different oxygen permeability. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2014, 94(13): 2684-2690. |
| 22 | Cui Y Y, Tian Z M, Lu H J, et al. Bran nutritional value and its fermented feed application in animal production. China Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2019, 46(10): 2902-2915. |
| 崔艺燕, 田志梅, 鲁慧杰, 等. 糠麸营养价值及其发酵饲料在动物生产中的应用. 中国畜牧兽医, 2019, 46(10): 2902-2915. | |
| 23 | Dai S, Wang F, Dong X, et al. Effects of mixing ratio of alfalfa and sweet sorghum on nutritional quality and aerobic stability of total mixed ration silage. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(5): 2306-2315. |
| 代胜, 王飞, 董祥, 等. 紫花苜蓿与甜高粱混合比例对发酵全混合日粮营养品质及有氧稳定性的影响. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(5): 2306-2315. | |
| 24 | Liang L F, Wang F, Dong X, et al. Fermentation quality and aerobic stability of the total mixed ration after replacing alfalfa with different rations of King grass ‘Reyan No. 4’. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(3): 703-711. |
| 梁龙飞, 王飞, 董祥, 等. ‘热研4号’王草替代紫花苜蓿对TMR发酵品质及有氧稳定性的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(3): 703-711. | |
| 25 | He J Q, Zhang R. Occurrence and comprehensive control of maize Alternaria leaf blight. Yunnan Agricultural Science and Technology, 2008, 6: 46. |
| 何建群, 张润. 玉米链格孢菌叶枯病发生及综合防治技术. 云南农业科学, 2008, 6: 46. | |
| 26 | Zhou S Y, Wang C L, Qiao Z X, et al. Identification of the pathogen of maize Alternaria leaf spot. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(11): 261-263. |
| 周舒扬, 汪春蕾, 乔志新, 等. 玉米链格孢菌叶枯病病原菌的分子鉴定. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(11): 261-263. | |
| 27 | Chen G Q, Wang D C, Zhang J W, et al. Diagnosis of maize Alternaria alternata leaf spot and identification pathogen of Hexi corridor corn farming. Shannxi Agricultural Science, 2010, 1: 41, 73. |
| 陈广泉, 王多成, 张建文, 等. 河西走廊玉米制种田细链格孢菌叶斑病诊断及病原鉴定. 陕西农业科学, 2010, 1: 41, 73. | |
| 28 | Zheng X L, Zhao S, Han X W, et al. Identification and biological characteristics of pathogens associated with Alternaria leaf blight in silage maize from breeding in Hainan province. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(6): 82-87. |
| 郑肖兰, 赵爽, 韩小雯, 等. 海南省南繁区玉米链格孢叶斑病病原菌鉴定及其生物学特性. 江苏农业科学, 2018, 46(6): 82-87. | |
| 29 | Valent B, Crawford M S, Weaver C G, et al. Genetic studies of fertility and pathogenicity in Magnaporthe grisea (Pyricularia oryzae). Iowa State Journal of Research, 1986, 60: 569-594. |
| 30 | Rogers S O, Bendich A J. Extraction of DNA from milligram amount of fresh, herbarium, and mummified plant tissue. Plant Molecular Biology, 1985, 5: 69-76. |
| 31 | Stackebrandt E, Goebel B M. Taxonomic note a place for DNA-DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology, 1994, 44(4): 846-849. |
| 32 | Rajarammohan S, Paritosh K, Pental D, et al. Correction to: Comparative genomics of Alternaria species provides insights into the pathogenic lifestyle of Alternaria brassicae-a pathogen of the Brassicaceae family. BMC Genomics, 2020, 21(1): 82. |
| 33 | Hou Y J, Ma X, Wan W T, et al. Comparative genomics of pathogens causing brown spot disease of tobacco: Alternaria longipes and Alternaria alternata. PLoS One, 2016, 11(5): e0155258. |
| 34 | Ayad D, Aribi D, Hamon B, et al. Distribution of large-spored Alternaria species associated with early blight of potato and tomato in Algeria. Phytopathologia Mediterranea, 2019, 58 (1): 139-149. |
| 35 | Zheng H Y. Studies on biological characteristic and virulence differentiation of Alternaria solani causing potato early blight. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2010. |
| 郑寰宇. 马铃薯早疫病菌生物学特性及致病力分化的研究. 大庆: 黑龙江八一农垦大学, 2010. | |
| 36 | Shao X P, Zhong X G, Xue Y Y, et al. Identification and its cross protection on pathogens of apple leaf spot in Gansu province. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2014, 49(3): 78-84. |
| 邵旭平, 钟小刚, 薛应钰, 等. 甘肃省苹果叶斑病病原菌鉴定及交叉保护作用研究. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2014, 49(3): 78-84. |
| [1] | 娄芬, 李小冬, 尚以顺, 吴佳海, 张蓉, 甘小波, 熊俊, 陈光吉, 李世歌, 裴成江. 毕节地区适宜青贮玉米品种(系)筛选及营养价值评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 214-224. |
| [2] | 李亚娇, 马培杰, 吴佳海, 牟琼, 覃涛英, 王晓强, 马宁, 张蓉, 李德芳, 朗永祥, 吴有松, 田应学, 韩永芬. 不同品种青贮玉米与拉巴豆套种对青贮玉米农艺性状及产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 209-216. |
| [3] | 林语梵, 朱鸿福, 王丽慧, 张桂杰. 宁夏黄灌区专用青贮玉米品种生产性能和营养价值研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 40-48. |
| [4] | 刘晓, 王博, 朱晓艳, 郭晓洁, 王成章, 李德锋. 21个粮饲兼用型青贮玉米在河南的品种比较试验[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 49-60. |
| [5] | 孙雪丽, 李秋凤, 刘英财, 曹玉凤, 王增林, 李艺, 赵洋洋, 葛瀚聪, 刘桃桃, 赵立新. 全株青贮玉米对西门塔尔杂交牛生产性能、表观消化率及血液生化指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(9): 201-209. |
| [6] | 梁小玉, 季杨, 易军, 付茂忠, 胡远彬. 混合比例和添加剂对菊苣与青贮玉米混合青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 173-181. |
| [7] | 王旭哲, 贾舒安, 张凡凡, 鲁为华, 张前兵, 马春晖. 紧实度对青贮玉米有氧稳定期发酵品质、微生物数量的效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(9): 156-166. |
| [8] | 苗芳, 张凡凡, 唐开婷, 贾舒安, 王旭哲, 马春晖. 同/异质型乳酸菌添加对全株玉米青贮发酵特性、营养品质及有氧稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(9): 167-175. |
| [9] | T-DNA插入位点侧翼序列的克隆. 柱花草炭疽菌致病力丧失突变菌株1869的[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(8): 142-149. |
| [10] | 马磊,袁飞,朱玲玲,王忠美,戎郁萍. 氮复合肥种类及施氮量对坝上地区青贮玉米产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(6): 53-59. |
| [11] | 李洪影,焉石,孙涛,李佶恺,崔国文. 施磷对不同收获时期青贮玉米碳水化合物积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(4): 90-97. |
| [12] | 徐敏云,李建国,谢帆,曹玉凤,敖特根,于海良,李佳祥,李运起. 不同施肥处理对青贮玉米生长和产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(3): 245-250. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||