

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (6): 163-177.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021165
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
沈江龙1( ), 陈吉军2, 阿布都瓦里 ·伊玛木2, 杨坤2, 郭雅婷2, 郑江华1(
), 陈吉军2, 阿布都瓦里 ·伊玛木2, 杨坤2, 郭雅婷2, 郑江华1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-04-28
修回日期:2021-09-22
出版日期:2022-06-20
发布日期:2022-05-11
通讯作者:
郑江华
作者简介:E-mail: zheng_jianghua@126.com基金资助:
Jiang-long SHEN1( ), Ji-jun CHEN2, Abuduwali IMAM2, Kun YANG2, Ya-ting GUO2, Jiang-hua ZHENG1(
), Ji-jun CHEN2, Abuduwali IMAM2, Kun YANG2, Ya-ting GUO2, Jiang-hua ZHENG1( )
)
Received:2021-04-28
Revised:2021-09-22
Online:2022-06-20
Published:2022-05-11
Contact:
Jiang-hua ZHENG
摘要:
探索亮柔伪步甲虫害发生与草地退化的耦合关系,定量分析虫害发生对草地植被的影响,为草原部门科学有效地防治虫害提供理论依据。本研究基于环境一号遥感影像、土地覆盖产品数据、气象数据分别反演草地植被覆盖度、土地利用状态、气候要素等环境变量,结合野外调查数据,使用线性趋势分析、叠加分析、土地利用状态转移矩阵、相关分析、方差分析等方法,分析亮柔伪步甲发生水平与草地植被覆盖度、气候等环境因素相互作用关系,总结亮柔伪步甲虫害的发生机制。结果表明:亮柔伪步甲虫口密度与归一化植被指数(NDVI)呈显著负相关性,NDVI随虫害发生程度的加重呈降低趋势:level 3(重度发生)<level 2(中度发生)<level 0(对照)<level 1(轻度发生);亮柔伪步甲虫口密度与年际间的植被覆盖变化无相关性,且各危害水平之间也无显著性差异。河床、河漫滩、农牧交错区等裸露地表是亮柔伪步甲虫害的高爆发区,而草地内部的发生水平较低。虫口密度高的实测点与草地退化区域并无空间关系。荒漠草地生态系统脆弱且敏感,植被覆盖度低,草地破碎。草地退化是气候干旱、过度放牧等因素综合作用的结果,并非直接由亮柔伪步甲虫害造成。
沈江龙, 陈吉军, 阿布都瓦里 ·伊玛木, 杨坤, 郭雅婷, 郑江华. 新疆荒漠草地亮柔伪步甲虫害与草地变化关系研究—以昌吉州南山草场为例[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 163-177.
Jiang-long SHEN, Ji-jun CHEN, Abuduwali IMAM, Kun YANG, Ya-ting GUO, Jiang-hua ZHENG. The relationship between attack by Prosodes dilaticollis and desert grassland changes in Xinjiang: A case study of southern mountain grassland in Changji[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(6): 163-177.

图1 研究区概况a:研究区区位图、b:野外调查工作照、c:亮柔伪步甲危害景观、d:研究区概况图。a:Position map of study, b:Field work photo, c:Landscape of pests, d:Overview of study area.
Fig.1 Overview of the study area
| 时间Time | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
日期Date (月-日Month-day) | 4-24 5-31 6-30 | 4-25 5-30 6-25 | 4-26 5-28 6-23 | 4-25 6-04 6-26 | 4-21 6-05 6-22 | 4-30 5-28 6-30 | 4-21 5-23 6-30 | 5-05 5-30 | 5-12 5-28 | 5-15 6-01 | 4-28 5-15 5-28 |
表1 遥感影像时间
Table 1 Remote sensing image date
| 时间Time | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
日期Date (月-日Month-day) | 4-24 5-31 6-30 | 4-25 5-30 6-25 | 4-26 5-28 6-23 | 4-25 6-04 6-26 | 4-21 6-05 6-22 | 4-30 5-28 6-30 | 4-21 5-23 6-30 | 5-05 5-30 | 5-12 5-28 | 5-15 6-01 | 4-28 5-15 5-28 |

图2 虫口密度与NDVI的空间关系a:高分一号遥感影像,b:NDVI,c:土地覆盖类型。a: Image data of GF1-WFV,b: NDVI,c: Land coverage.
Fig. 2 The spatial relationship between insect density and NDVI
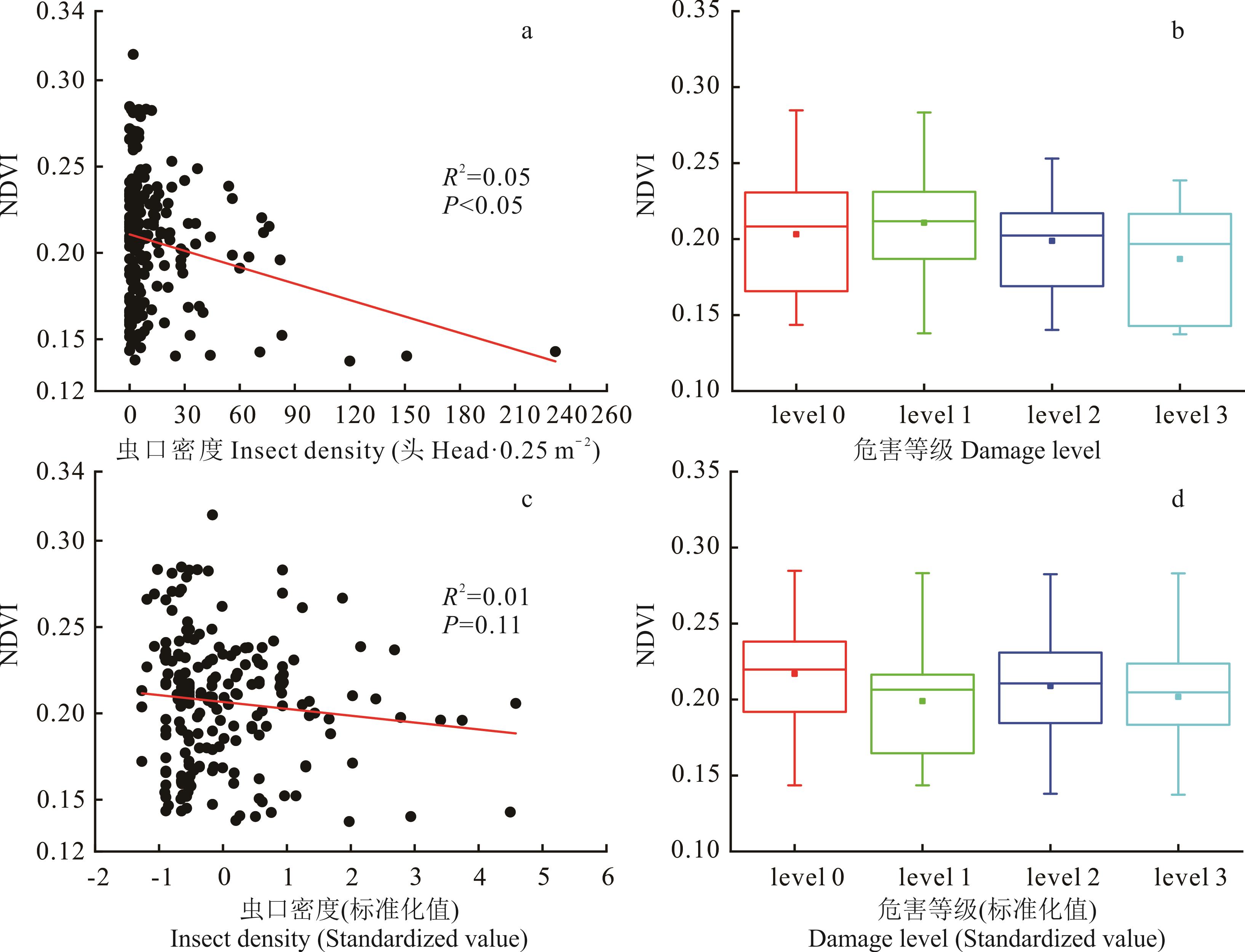
图3 虫口密度与NDVI的相关性和方差分析*代表相关系数通过0.05置信水平下的显著性检验。 a:原始数据的相关分析;b:原始数据的方差分析;c:标准化数据的相关分析;d:标准化数据的方差分析。下同。*represents correlation coefficient passing the significance test at the 0.05 confidence level. a:Correlation analysis of raw data; b:Variance analysis of raw data; c:Correlation analysis of standardized data; d:Variance analysis of standardized data. The same below.
Fig.3 Correlation and variance analysis of insect density and NDVI
项目 Item | 降水量 Precipitation | 平均温度 Mean annual temperature | 平均相对湿度 Average relative humidity | 日照时数 Duration of sunshine | 归一化植被指数 NDVI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均温度Mean annual temperature | -0.70* | ||||
| 平均相对湿度Average relative humidity | 0.68* | -0.76* | |||
| 日照时数Duration of sunshine | -0.09 | 0.20 | -0.66* | ||
| 归一化植被指数NDVI | 0.78* | -0.56 | 0.88* | -0.49 | |
| 虫口密度Insect density | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.04 | -0.05 |
表2 自然环境因素、虫口密度相关系数矩阵
Table 2 Correlation coefficient matrix of environment factors and insect density
项目 Item | 降水量 Precipitation | 平均温度 Mean annual temperature | 平均相对湿度 Average relative humidity | 日照时数 Duration of sunshine | 归一化植被指数 NDVI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均温度Mean annual temperature | -0.70* | ||||
| 平均相对湿度Average relative humidity | 0.68* | -0.76* | |||
| 日照时数Duration of sunshine | -0.09 | 0.20 | -0.66* | ||
| 归一化植被指数NDVI | 0.78* | -0.56 | 0.88* | -0.49 | |
| 虫口密度Insect density | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.04 | -0.05 |
地类 Land type | 草地 Grassland | 村庄 Village | 裸地 Bareland | 农田 Farmland | 水体 Water | 2010年合计 Total 2010 | 流出总计 Total outflow |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 草地Grassland | 10833.33 | 433.33 | 12940.00 | 1240.00 | 33.33 | 25480.00 | 14646.66 |
| 村庄Village | 1766.67 | 180.00 | 2553.33 | 346.67 | 6.67 | 4853.33 | 4673.34 |
| 裸地Bareland | 15380.00 | 973.33 | 39393.33 | 2706.67 | 886.67 | 59340.00 | 19946.67 |
| 农田Farmland | 2100.00 | 153.33 | 3320.00 | 453.33 | 13.33 | 6040.00 | 5586.66 |
| 水体Water | 6.67 | 20.00 | 226.67 | 60.00 | 400.00 | 713.33 | 313.34 |
| 2017年总计Total 2017 | 30086.67 | 1753.33 | 58440.00 | 4800.00 | 1340.00 | ||
| 流入总计Total inflow | 19253.34 | 1579.99 | 19040.00 | 4353.34 | 940.00 |
表3 2010-2017年土地利用状态转移矩阵
Table 3 Land cover state transfer matrix of 2010-2017 (hm2)
地类 Land type | 草地 Grassland | 村庄 Village | 裸地 Bareland | 农田 Farmland | 水体 Water | 2010年合计 Total 2010 | 流出总计 Total outflow |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 草地Grassland | 10833.33 | 433.33 | 12940.00 | 1240.00 | 33.33 | 25480.00 | 14646.66 |
| 村庄Village | 1766.67 | 180.00 | 2553.33 | 346.67 | 6.67 | 4853.33 | 4673.34 |
| 裸地Bareland | 15380.00 | 973.33 | 39393.33 | 2706.67 | 886.67 | 59340.00 | 19946.67 |
| 农田Farmland | 2100.00 | 153.33 | 3320.00 | 453.33 | 13.33 | 6040.00 | 5586.66 |
| 水体Water | 6.67 | 20.00 | 226.67 | 60.00 | 400.00 | 713.33 | 313.34 |
| 2017年总计Total 2017 | 30086.67 | 1753.33 | 58440.00 | 4800.00 | 1340.00 | ||
| 流入总计Total inflow | 19253.34 | 1579.99 | 19040.00 | 4353.34 | 940.00 |

图10 2010-2017年南山草场草地变化与虫口密度的叠加分析A:未叠加样点; B:叠加样点; a: 旱卡子滩; b:黑羊沟; c:加崂; d:阿克齐。A: No overlying samples; B: Overlying samples; a: Hanqiazitan; b: Heiyanggou; c: Jialao; d: Akeqi.
Fig.10 2010-2017 overlap analysis of land cover change and insect density
| 1 | Li P X, Zheng J H, Ni Y F, et al. Estimating area of grassland rodent damage rangeland and rat wastelands based on remote sensing in Altun Mountain, China. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 53(7): 1346-1355. |
| 李培先, 郑江华, 倪亦非, 等. 阿尔金山草地鼠害发生区及鼠荒地面积遥感估算. 新疆农业科学, 2016, 53(7): 1346-1355. | |
| 2 | Wu X L. Studies on remote sensing and spatial distribution of Prosodes dilaticollis Motsch disaster: A case study of Manasi and Hutubi county grassland in Xinjiang. Urumqi: Xinjiang University, 2015. |
| 吴秀兰. 亮柔伪步甲灾害遥感监测与空间分布特征研究—以玛纳斯、呼图壁草场为例. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2015. | |
| 3 | Zhang S Y, Li J W, Zhang S C. A study on distribution feature of Prosodes dilaticollis Motsch disaster of grassland in Nilek county. Xinjiang Animal Husbandry, 2016(S1): 58-59. |
| 张生楹, 李建伟, 张生翠. 尼勒克县草原地下害虫伪步甲分布规律研究. 新疆畜牧业, 2016(增刊1): 58-59. | |
| 4 | Eklundh L, Johansson T, Solberg S. Mapping insect defoliation in Scots pine with MODIS time-series data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2009, 113(7): 1566-1573. |
| 5 | Thayn J B. Using a remotely sensed optimized disturbance index to detect insect defoliation in the Apostle islands, Wisconsin, USA. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2013, 136(2): 210-217. |
| 6 | Renier C, Waldner F, Jacques D C, et al. A dynamic vegetation senescence indicator for near-real-time desert locust habitat monitoring with MODIS. Remote Sensing, 2015, 7(6): 7545-7570. |
| 7 | Waldner F, Ebbe M A B, Cressman K, et al. Operational monitoring of the desert locust habitat with earth observation: An assessment. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2015, 4(4): 2379-2400. |
| 8 | Tian H D, Ji R, Xie B Y, et al. Using multi-temporal Landsat ETM+ data to monitor the plague of oriental migratory locust. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2008, 29(6): 1685-1692. |
| 9 | Wang J Y. The countermeasures of Prosodes dilaticollis Motsch disaster. Xinjiang Animal Husbandry, 2009(S1): 59-61. |
| 王吉云. 伪步甲发生危害及治理对策. 新疆畜牧业, 2009(增刊1): 59-61. | |
| 10 | Liu F Z, Zhao L, Zhang M X. Study on the experimental ecology of Prosodes dilaticollis Motsch. Journal of August 1st Agricultural College, 1986, 9(2): 34-38. |
| 刘芳政, 赵莉, 张茂新. 亮柔伪步甲实验生态学的研究. 八一农学院学报, 1986, 9(2): 34-38. | |
| 11 | Zhao L, Liu F Z. Methods of rearing the darkling beetles Prosodes dilaticollis Motsch in laboratory. Journal of August 1st Agricultural College, 1989, 12(2): 76-78. |
| 赵莉, 刘芳政. 亮柔伪步甲室内饲养方法. 八一农学院学报, 1989, 12(2): 76-78. | |
| 12 | Xiao H W, Ma W P. Study on occurrence dynamics and control of Prosodes dilaticollis Motsch pests of Changji. Xinjiang Animal Husbandry, 2013(6): 60-61. |
| 肖宏伟, 马卫平. 昌吉州草原伪步甲发生动态及防治的研究. 新疆畜牧业, 2013(6): 60-61. | |
| 13 | Chen X Q. Prevention and control of Prosodes dilaticollis Motsch in the northern foot of Tianshan Mountain in Xinjiang. Xinjiang Animal Husbandry, 2016(12): 61-63. |
| 陈新乔. 浅析新疆天山北麓草原伪步甲的防治. 新疆畜牧业, 2016(12): 61-63. | |
| 14 | Li P X, Zheng J H, Lin J, et al. Prediction of potential geographic distribution and analysis of the major driving factors for Prosodes (Lioprosodes) dilaticollis Motschulsky in Xinjiang by using MaxEnt model. Journal of Plant Protection, 2017, 44(3): 445-452. |
| 李培先, 郑江华, 林峻, 等. 基于MaxEnt模型的突颊侧琵甲潜新疆潜在地理分布预测和主要影响因子分析. 植物保护学报, 2017, 44(3): 445-452. | |
| 15 | Wu X L, Zheng J H, Abuduwali·yimamu, et al. Remote sensing monitoring of Prosodes dilaticollis Motsch hazards for grassland based on domestic ZY1-02C satellite’s P/MS data. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 52(3): 551-559. |
| 吴秀兰, 郑江华, 阿不都瓦里·伊玛木, 等. 基于ZY1-02C卫星P/MS数据的草原伪步甲灾害遥感监测. 新疆农业科学, 2015, 52(3): 551-559. | |
| 16 | Wu X L, Zheng J H, Zheng S D, et al. Spatial distribution of Prosodes dilaticollis Motsch hazards based on terrain gradient in Xinjiang grassland. Ecological Science, 2015, 34(2): 16-21. |
| 吴秀兰, 郑江华, 郑淑丹, 等. 伪步甲危害在新疆草原不同地形梯度的空间分布特征. 生态科学, 2015, 34(2): 16-21. | |
| 17 | Wu X L, Zheng J H, Li S, et al. RS-based analysis on hazards of Prosodes dilaticollis and topographic factors: A case study in grasslands in Manas and Hutubi counties. Arid Zone Research, 2017, 34(2): 437-444. |
| 吴秀兰, 郑江华, 李帅, 等. 伪步甲危害遥感监测及地形分析——以新疆玛纳斯-呼图壁县草场为例. 干旱区研究, 2017, 34(2): 437-444. | |
| 18 | Liu R T, Zhu F, Steinberger Y. Effectiveness of afforested shrub plantation on ground-active arthropod communities and trophic structure in desertified regions. Catena, 2015, 125(3): 1-9. |
| 19 | Rosas Y M, Peri P L, Carrara R, et al. Potential biodiversity map of darkling beetles (Tenebrionidae): Environmental characterization, land-uses and analyses of protection areas in Southern Patagonia. Journal of Insect Conservation, 2019, 23(5/6): 885-897. |
| 20 | Lescano M N, Elizalde L, Werenkraut V, et al. Ant and tenebrionid beetle assemblages in arid lands: Their associations with vegetation types in the Patagonian steppe. Journal of Arid Environments, 2017, 138(1): 51-57. |
| 21 | Abuduwali·yimamu, Xiao H W. Control effect of several new pesticides on Prosodes dilaticollis Motsch. Xinjiang Animal Husbandry, 2012(9): 38. |
| 阿不都瓦里·伊玛木, 肖宏伟. 几种新农药防治草原伪步甲的药效试验. 新疆畜牧业, 2012(9): 38. | |
| 22 | Gong P, Li X C, Wang J, et al. Annual maps of global artificial impervious area (GAIA) between 1985 and 2018. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2020, 236: 1-12. |
| 23 | Gong P, Chen B, Li X C, et al. Mapping essential urban land use categories in China (EULUC-China): Preliminary results for 2018. Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(3): 182-187. |
| 24 | Zha Y, Gao J, Ni S, et al. Temporal filtering of successive MODIS data in monitoring a locust outbreak. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2005, 26(24): 5665-5674. |
| 25 | Carlson T N, Ripley D A. On the relation between NDVI, fractional vegetation cover, and leaf area index. Remote Sensing of Environment, 1997, 62(3): 241-252. |
| 26 | Wang H, Zhong Y, Pu R L, et al. Dynamic analysis of Robinia pseudoacacia forest health levels from 1995 to 2013 in the Yellow River Delta, China using multitemporal Landsat imagery. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2018, 39(12): 4232-4253. |
| 27 | Kim Y, Jackson T, Bindlish R, et al. Retrieval of wheat growth parameters with radar vegetation indices. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(4): 808-812. |
| 28 | Eckert S, Hüsler F, Liniger H, et al. Trend analysis of MODIS NDVI time series for detecting land degradation and regeneration in Mongolia. Journal of Arid Environments, 2015, 113(4): 16-28. |
| 29 | Gu Z J, Duan X W, Shi Y D, et al. Spatio-temporal variation in vegetation coverage and its response to climatic factors in the Red River Basin, China. Ecological Indicators, 2018, 93(3): 54-64. |
| 30 | Cui B C, Zheng J H, Hasimu·tuerxun, et al. Spatio-temporal characteristics of grassland net primary productivity (NPP) in the Tarim river basin. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(6): 1-13. |
| 崔博超, 郑江华, 吐尔逊·哈斯木, 等. 塔里木河流域草地净初级生产力时空分异特征研究. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 1-13. | |
| 31 | Chen Y N, Chen Y P, Zhu C G, et al. The concept and mode of ecosystem sustainable management in arid desert areas in northwest China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(20): 7410-7417. |
| 陈亚宁, 陈亚鹏, 朱成刚, 等. 西北干旱荒漠区生态系统可持续管理理念与模式. 生态学报, 2019, 39(20): 7410-7417. | |
| 32 | Chen Y N. Impacts of climate change on the water cycle mechanism and water resources security in the arid region of Northwest China. China Basic Science, 2015, 17(2): 15-21. |
| 陈亚宁. 气候变化对西北干旱区水循环影响机理与水资源安全研究. 中国基础科学, 2015, 17(2): 15-21. | |
| 33 | Yaacobi G, Ziv Y, Rosenzweig M L. Habitat fragmentation may not matter to species diversity. Proceedings: Biology Science, 2007, 274: 2409-2412. |
| 34 | Office of Local Chronicles Compilation Committee of Manas County. Manas Statistical Yearbook. Manas: Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps Press, 2006-2016. |
| 玛纳斯县地方志编纂委员会办公室. 玛纳斯统计年鉴. 玛纳斯: 新疆生产建设兵团出版社, 2006-2016. | |
| 35 | Wei S H, Ma L J, Bai L, et al. Preliminary studies on species diversity of beetles in temperate grassland and their value as bioindicators. Journal of Environmental Entomology, 2017, 39(6): 1287-1298. |
| 魏淑花, 马林杰, 白玲, 等. 宁夏温性草原甲虫多样性及其对环境指示作用的初步研究. 环境昆虫学报, 2017, 39(6): 1287-1298. | |
| 36 | Yang G J, He H M, Wang X P. The time structure and population dynamics of the desert-steppe darkling beetle community in Yanchi, Ningxia, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 2012, 49(6): 1610-1617. |
| 杨贵军, 贺海明, 王新谱. 盐池荒漠草地拟步甲昆虫群落时间结构和动态. 应用昆虫学报, 2012, 49(6): 1610-1617. | |
| 37 | Liu J L, Zhao W Z, Li F R, et al. Effects of microtopography variation on the distribution of ground darkling beetles in a sandy desert ecosystem. Arid Zone Research, 2017, 34(6): 1388-1394. |
| 刘继亮, 赵文智, 李锋瑞, 等. 微地形变化对沙质荒漠拟步甲科昆虫分布的影响. 干旱区研究, 2017, 34(6): 1388-1394. |
| [1] | 张茹, 李建平, 彭文栋, 王芳, 李志刚. 柠条枝条覆盖对宁夏荒漠草原土壤水热及补播牧草生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 58-67. |
| [2] | 陈宸, 井长青, 邢文渊, 邓小进, 付皓宇, 郭文章. 近20年新疆荒漠草地动态变化及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 1-14. |
| [3] | 刘慧霞, 董乙强, 崔雨萱, 刘星宏, 何盘星, 孙强, 孙宗玖. 新疆阿勒泰地区荒漠草地土壤有机碳特征及其环境影响因素分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 41-52. |
| [4] | 陆丰帅, 阿的鲁骥, 程云湘, 侯扶江. 祁连山高寒草原土壤水分与植被盖度的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 23-32. |
| [5] | 田梦, 孙宗玖, 李莹, 李培英, 谢开云. 蒿类荒漠草地土壤种子库特征及其萌发植物多样性对降水增加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 17-28. |
| [6] | 郭春秀, 马俊梅, 何芳兰, 王理德, 李金辉, 安富博, 袁宏波, 刘开琳. 石羊河下游不同类型荒漠草地黑果枸杞群落结构特征及土壤特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(9): 14-24. |
| [7] | 阎欣, 刘任涛, 安慧. 土壤易氧化有机碳与溶解性有机碳对荒漠草地沙漠化过程中土壤碳库变异的表征[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(11): 15-25. |
| [8] | 井长青, 安沙舟. CoLM陆面模式对中亚干旱荒漠草地生态系统陆面过程的数值模拟[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(3): 13-32. |
| [9] | 刘文亭, 卫智军, 吕世杰, 王天乐, 张爽, 海松. 放牧调控对短花针茅种群年龄及叶性状的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(1): 63-71. |
| [10] | 许玉凤, 杨井, 李卫红, 方功焕, 张淑花, 邓海军, 董杰. 1982-2013年新疆不同植被生长时空变化[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(1): 47-63. |
| [11] | 赵凤杰,王正浩,王慧萍,吴惠惠,刘航玮,王广君,张泽华. 不同密度短星翅蝗危害后羊草的高光谱变化及对产草量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(3): 195-203. |
| [12] | 花立民. 玛曲草原植被NDVI与气候和载畜量变化的关系分析[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(4): 224-235. |
| [13] | 宋春桥,游松财,刘高焕,柯灵红,钟新科. 那曲地区草地植被时空格局与变化及其人文因素影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(3): 1-10. |
| [14] | 杨智明,李建龙2*,杜广明,李国良,刘香萍,王宁3. 宁夏滩羊放牧系统草地利用率及草畜平衡性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(1): 35-41. |
| [15] | 刘永红,陈菊兰,张洪荣,肖金玉,傅华. 阿拉善荒漠草地牧草氨基酸组成特点与营养价值研究[J]. 草业学报, 2008, 17(6): 25-33. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||