

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 189-199.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022081
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2022-02-18
修回日期:2022-03-31
出版日期:2023-03-20
发布日期:2022-12-30
通讯作者:
张前兵
作者简介:E-mail: qbz102@163.com基金资助:
Xuan-shuai LIU( ), Yan-liang SUN, Xiao-xia AN, Chun-hui MA, Qian-bing ZHANG(
), Yan-liang SUN, Xiao-xia AN, Chun-hui MA, Qian-bing ZHANG( )
)
Received:2022-02-18
Revised:2022-03-31
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2022-12-30
Contact:
Qian-bing ZHANG
摘要:
为探讨不同施磷水平下接种丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)和解磷细菌(PSB)对紫花苜蓿光合特性及生物量的影响,提高紫花苜蓿的磷肥利用效率及优质高产研究、制定科学合理的施肥制度提供理论依据。采用随机区组设计进行盆栽试验,设置4个接菌处理[未接菌对照组(CK,J0)、单接巨大芽孢杆菌(Bm,J1)、单接摩西管柄囊霉(Fm,J2)和双接菌(Bm×Fm,J3)]和4个施磷(P2O5)水平[0 (P0)、50 (P1)、100 (P2)和150 mg·kg-1 (P3)],共计16个处理。通过对紫花苜蓿的叶片净光合速率(Pn)、蒸腾速率(Tr)、气孔导度(Gs)、胞间CO2浓度(Ci)、光能利用效率(LUE)、水分利用效率(WUE)、叶绿素[Chl (a+b)]含量和生物量进行测定,并通过相关性分析明确紫花苜蓿各光合指标与生物量之间的关系,通过隶属函数分析筛选出有利于促进紫花苜蓿生物量形成的最佳菌磷耦合模式,明确施磷和接种解磷菌对紫花苜蓿光合特性及生物量的影响。结果表明:相同接菌处理下,紫花苜蓿叶片Pn、Tr、Gs、LUE、WUE、Chl (a+b)和生物量均随施磷水平的提高而呈先升高后降低的趋势,在P2处理达到最大值,且施磷处理均显著大于未施磷处理(P<0.05),而Ci则随施磷水平的提高呈逐渐降低的趋势,且施磷处理均显著低于未施磷处理(P<0.05);相同施磷处理下,紫花苜蓿叶片的Pn、Tr、Gs、LUE、WUE、Chl (a+b)和生物量均为接菌处理显著大于未接菌处理(P<0.05),且除Chl (a+b)外,Pn 、Tr、Gs、LUE、WUE、Chl和生物量均为在J3处理达到最大值,而Ci显著低于未接菌处理(P<0.05),在J3处理达到最小值。相关性分析表明,Ci与Pn、Tr、Gs、LUE、WUE、Chl (a+b)和生物量均呈显著负相关(P<0.05),其余各指标间均两两呈显著正相关(P<0.05)。根据隶属函数值大小排序,排名前3位的分别为J3P2、J2P2和J3P1。双接种丛枝菌根真菌与解磷细菌,并施磷100 mg·kg-1的菌磷耦合模式,能够显著提高紫花苜蓿叶片的光合特性并增加叶绿素含量,进而有利于促进紫花苜蓿生物量的形成。
刘选帅, 孙延亮, 安晓霞, 马春晖, 张前兵. 施磷和接种解磷菌对紫花苜蓿光合特性及生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 189-199.
Xuan-shuai LIU, Yan-liang SUN, Xiao-xia AN, Chun-hui MA, Qian-bing ZHANG. Effects of phosphorus application and inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria on the photosynthetic characteristics and biomass of alfalfa[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 189-199.
全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | 容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.53 | 68.30 | 0.22 | 15.70 | 132.60 | 1.46 | 24.20 |
表1 供试土壤基本理化性质
Table 1 The basic physical and chemical properties of the tested soil
全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkaline nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) | 容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.53 | 68.30 | 0.22 | 15.70 | 132.60 | 1.46 | 24.20 |
因素 Factor | 项目 Item | 净光合 速率 Pn | 蒸腾 速率 Tr | 气孔 导度 Gs | 胞间CO2 浓度 Ci | 光能利用 效率 LUE | 水分利用 效率 WUE | 叶绿素a 含量Chl a content | 叶绿素b 含量Chl b content | 叶绿素总含量Chl (a+b) content | 生物量Biomass |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F值F value | 27.019 | 328.403 | 14973.605 | 3725.991 | 1636.166 | 573.374 | 23.100 | 1108.286 | 33.038 | 4.797 |
| P值P value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.037 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.029 | |
| P | F值F value | 10.801 | 189.577 | 1401.009 | 1930.936 | 494.982 | 204.594 | 9.155 | 315.671 | 12.065 | 24.769 |
| P值P value | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.004 | <0.001 | 0.002 | <0.001 | |
| J×P | F值F value | 121.347 | 6.234 | 157.332 | 31.519 | 40.454 | 32.397 | 159.307 | 38.547 | 30.442 | 1846.891 |
| P值P value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.015 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
表2 接菌和施磷对苜蓿光合相关参数及生物量影响的两因素方差分析
Table 2 Two-way ANOVA of the effect of rhizobium, P application on photosynthetic related parameters and biomass of alfalfa
因素 Factor | 项目 Item | 净光合 速率 Pn | 蒸腾 速率 Tr | 气孔 导度 Gs | 胞间CO2 浓度 Ci | 光能利用 效率 LUE | 水分利用 效率 WUE | 叶绿素a 含量Chl a content | 叶绿素b 含量Chl b content | 叶绿素总含量Chl (a+b) content | 生物量Biomass |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F值F value | 27.019 | 328.403 | 14973.605 | 3725.991 | 1636.166 | 573.374 | 23.100 | 1108.286 | 33.038 | 4.797 |
| P值P value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.037 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.029 | |
| P | F值F value | 10.801 | 189.577 | 1401.009 | 1930.936 | 494.982 | 204.594 | 9.155 | 315.671 | 12.065 | 24.769 |
| P值P value | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.004 | <0.001 | 0.002 | <0.001 | |
| J×P | F值F value | 121.347 | 6.234 | 157.332 | 31.519 | 40.454 | 32.397 | 159.307 | 38.547 | 30.442 | 1846.891 |
| P值P value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.015 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
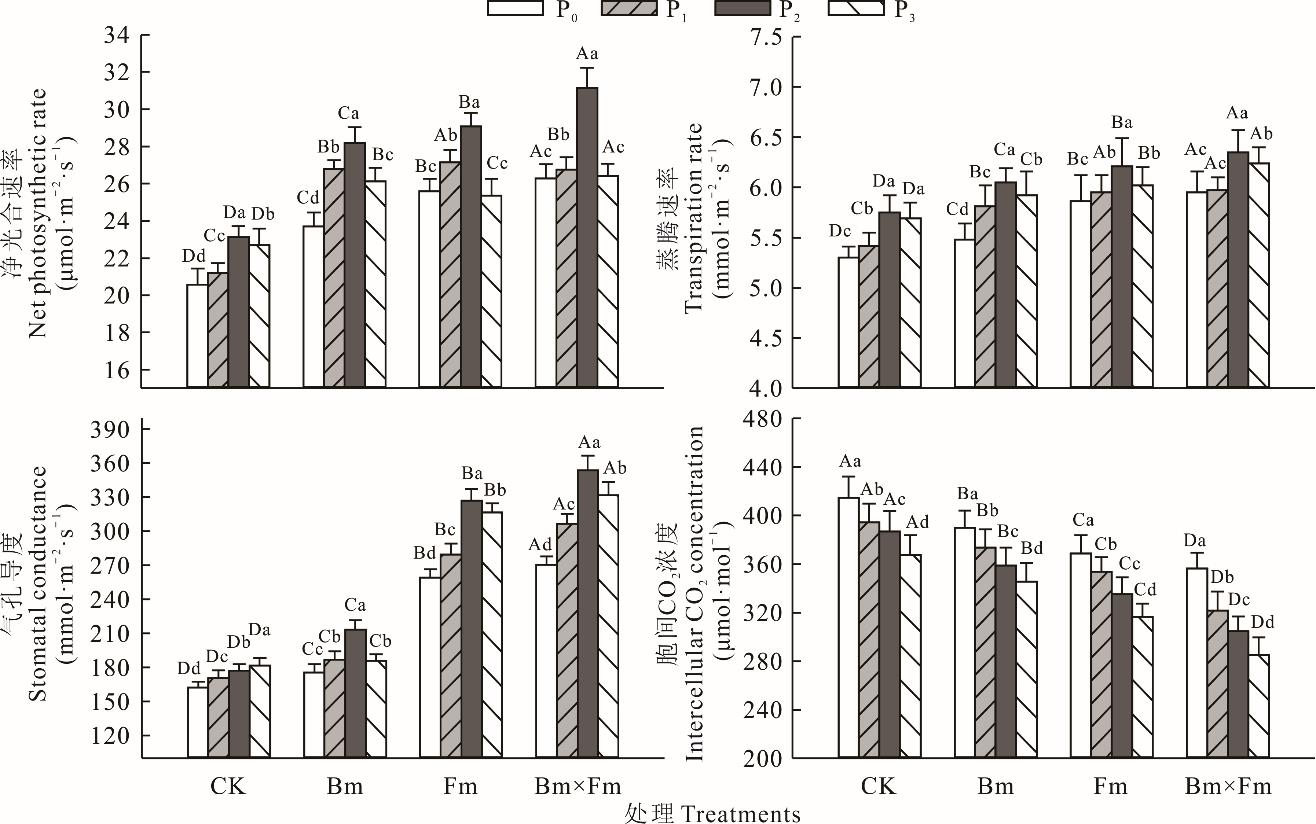
图1 不同处理下紫花苜蓿叶片的净光合速率、蒸腾速率、气孔导度和胞间CO2浓度不同大写字母表示在相同施磷处理下,不同接菌处理之间差异显著(P<0.05),不同小写字母表示相同接菌条件下,不同磷肥水平之间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Different capital letters indicate significant differences among different bacteria treatments under the same phosphorus application treatment (P<0.05), differences lowercase letters indicate significant different among different phosphorus application treatments under the same bacteria application treatment (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 Net photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, stomatal conductance and intercellular CO2 concentration of alfalfa leaves under different treatments
指标 Index | 净光合速率 Pn | 蒸腾速率 Tr | 气孔导度 Gs | 胞间CO2 浓度Ci | 光能利用 效率LUE | 水分利用 效率WUE | 叶绿素总含量Chl (a+b) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蒸腾速率Transpiration rate (Tr) | 0.905** | ||||||
| 气孔导度Stomatal conductance (Gs) | 0.734** | 0.846** | |||||
| 胞间CO2浓度Intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) | -0.716** | -0.893** | -0.874** | ||||
| 光能利用效率Light use efficiency (LUE) | 0.988** | 0.924** | 0.764** | -0.769** | |||
| 水分利用效率Water use efficiency (WUE) | 0.954** | 0.740** | 0.568* | -0.513* | 0.925** | ||
| 叶绿素总含量Chlorophyll content [Chl (a+b)] | 0.854** | 0.778** | 0.662** | -0.731** | 0.854** | 0.814** | |
| 生物量Biomass | 0.714** | 0.728** | 0.585* | -0.610** | 0.704** | 0.605* | 0.746** |
表3 不同处理下各指标相关性分析
Table 3 The correlation analysis of each index under different treatments
指标 Index | 净光合速率 Pn | 蒸腾速率 Tr | 气孔导度 Gs | 胞间CO2 浓度Ci | 光能利用 效率LUE | 水分利用 效率WUE | 叶绿素总含量Chl (a+b) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蒸腾速率Transpiration rate (Tr) | 0.905** | ||||||
| 气孔导度Stomatal conductance (Gs) | 0.734** | 0.846** | |||||
| 胞间CO2浓度Intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) | -0.716** | -0.893** | -0.874** | ||||
| 光能利用效率Light use efficiency (LUE) | 0.988** | 0.924** | 0.764** | -0.769** | |||
| 水分利用效率Water use efficiency (WUE) | 0.954** | 0.740** | 0.568* | -0.513* | 0.925** | ||
| 叶绿素总含量Chlorophyll content [Chl (a+b)] | 0.854** | 0.778** | 0.662** | -0.731** | 0.854** | 0.814** | |
| 生物量Biomass | 0.714** | 0.728** | 0.585* | -0.610** | 0.704** | 0.605* | 0.746** |
处理 Treatment | 净光合速率 Pn | 蒸腾速率 Tr | 气孔导度 Gs | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci | 光能利用效率 LUE | 水分利用效率 WUE | 叶绿素总含量 Chl (a+b) | 生物量 Biomass | 平均值 Average | 排序Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J0P0 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 16 |
| J0P1 | 0.060 | 0.114 | 0.043 | 0.157 | 0.036 | 0.029 | 0.192 | 0.295 | 0.116 | 15 |
| J0P2 | 0.241 | 0.429 | 0.077 | 0.214 | 0.202 | 0.137 | 0.288 | 0.538 | 0.266 | 12 |
| J0P3 | 0.202 | 0.371 | 0.102 | 0.365 | 0.179 | 0.108 | 0.164 | 0.099 | 0.199 | 14 |
| J1P0 | 0.296 | 0.171 | 0.070 | 0.191 | 0.298 | 0.431 | 0.521 | 0.033 | 0.251 | 13 |
| J1P1 | 0.589 | 0.486 | 0.128 | 0.317 | 0.536 | 0.716 | 0.630 | 0.267 | 0.459 | 10 |
| J1P2 | 0.720 | 0.714 | 0.267 | 0.432 | 0.786 | 0.765 | 0.781 | 0.803 | 0.659 | 5 |
| J1P3 | 0.525 | 0.590 | 0.123 | 0.534 | 0.595 | 0.520 | 0.548 | 0.407 | 0.480 | 9 |
| J2P0 | 0.475 | 0.533 | 0.506 | 0.354 | 0.536 | 0.480 | 0.178 | 0.053 | 0.389 | 11 |
| J2P1 | 0.623 | 0.619 | 0.613 | 0.471 | 0.643 | 0.667 | 0.534 | 0.294 | 0.558 | 7 |
| J2P2 | 0.804 | 0.867 | 0.861 | 0.613 | 0.810 | 0.784 | 0.836 | 0.937 | 0.814 | 2 |
| J2P3 | 0.452 | 0.686 | 0.805 | 0.757 | 0.512 | 0.324 | 0.452 | 0.527 | 0.564 | 6 |
| J3P0 | 0.539 | 0.619 | 0.564 | 0.449 | 0.536 | 0.529 | 0.575 | 0.114 | 0.491 | 8 |
| J3P1 | 0.585 | 0.638 | 0.754 | 0.719 | 0.643 | 0.588 | 1.000 | 0.720 | 0.706 | 3 |
| J3P2 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.849 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.932 | 1.000 | 0.973 | 1 |
| J3P3 | 0.553 | 0.895 | 0.885 | 1.000 | 0.655 | 0.343 | 0.753 | 0.424 | 0.689 | 4 |
表4 各指标隶属函数分析
Table 4 Membership function analysis of each index
处理 Treatment | 净光合速率 Pn | 蒸腾速率 Tr | 气孔导度 Gs | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci | 光能利用效率 LUE | 水分利用效率 WUE | 叶绿素总含量 Chl (a+b) | 生物量 Biomass | 平均值 Average | 排序Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J0P0 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 16 |
| J0P1 | 0.060 | 0.114 | 0.043 | 0.157 | 0.036 | 0.029 | 0.192 | 0.295 | 0.116 | 15 |
| J0P2 | 0.241 | 0.429 | 0.077 | 0.214 | 0.202 | 0.137 | 0.288 | 0.538 | 0.266 | 12 |
| J0P3 | 0.202 | 0.371 | 0.102 | 0.365 | 0.179 | 0.108 | 0.164 | 0.099 | 0.199 | 14 |
| J1P0 | 0.296 | 0.171 | 0.070 | 0.191 | 0.298 | 0.431 | 0.521 | 0.033 | 0.251 | 13 |
| J1P1 | 0.589 | 0.486 | 0.128 | 0.317 | 0.536 | 0.716 | 0.630 | 0.267 | 0.459 | 10 |
| J1P2 | 0.720 | 0.714 | 0.267 | 0.432 | 0.786 | 0.765 | 0.781 | 0.803 | 0.659 | 5 |
| J1P3 | 0.525 | 0.590 | 0.123 | 0.534 | 0.595 | 0.520 | 0.548 | 0.407 | 0.480 | 9 |
| J2P0 | 0.475 | 0.533 | 0.506 | 0.354 | 0.536 | 0.480 | 0.178 | 0.053 | 0.389 | 11 |
| J2P1 | 0.623 | 0.619 | 0.613 | 0.471 | 0.643 | 0.667 | 0.534 | 0.294 | 0.558 | 7 |
| J2P2 | 0.804 | 0.867 | 0.861 | 0.613 | 0.810 | 0.784 | 0.836 | 0.937 | 0.814 | 2 |
| J2P3 | 0.452 | 0.686 | 0.805 | 0.757 | 0.512 | 0.324 | 0.452 | 0.527 | 0.564 | 6 |
| J3P0 | 0.539 | 0.619 | 0.564 | 0.449 | 0.536 | 0.529 | 0.575 | 0.114 | 0.491 | 8 |
| J3P1 | 0.585 | 0.638 | 0.754 | 0.719 | 0.643 | 0.588 | 1.000 | 0.720 | 0.706 | 3 |
| J3P2 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.849 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.932 | 1.000 | 0.973 | 1 |
| J3P3 | 0.553 | 0.895 | 0.885 | 1.000 | 0.655 | 0.343 | 0.753 | 0.424 | 0.689 | 4 |
| 1 | Vassilev N, Vassileva M, Nikolaeva I. Simultaneous P-solubilizing and biocontrol activity of microorganisms: Potentials and future trends. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 71(2): 137-144. |
| 2 | Li H S. Modern plant physiology (3rd Edition). Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2012. |
| 李合生. 现代植物生理学(第3版). 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2012. | |
| 3 | Jia Y, Li F M, Wang X L, et al. Dynamics of soil organic carbon and soil fertility affected by alfalfa productivity in a semiarid agro-ecosystem. Biogeochemistry, 2006, 80(3): 233-243. |
| 4 | Zhao C, Feng Z, Chen G. Soil water balance simulation of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) in the semiarid Chinese Loess Plateau. Agricultural Water Management, 2004, 69(2): 101-114. |
| 5 | Wang H Z, Han L, Xu Y L, et al. Photosynthetic responses of the heteromorphic leaves in Populus euphratica to light intensity and CO2 concentration. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38(10): 1099-1109. |
| 王海珍, 韩路, 徐雅丽, 等. 胡杨异形叶光合作用对光强与CO2浓度的响应. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(10): 1099-1109. | |
| 6 | Qi M X, Liu X J, Zhang X L, et al. Effects of different phosphorus levels on photosynthesis and root nodule nitrogen-fixing characteristic of alfalfa. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2013, 21(3): 512-516. |
| 齐敏兴, 刘晓静, 张晓磊, 等. 不同磷水平对紫花苜蓿光合作用和根瘤固氮特性的影响. 草地学报, 2013, 21(3): 512-516. | |
| 7 | Liu J Y, Liu X S, Zhang Q B, et al. Response of alfalfa growth to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria under different phosphorus application levels. AMB Express, 2020, 10(1): 1-13. |
| 8 | Friesen M L, Porter S S, Stark S C, et al. Microbially mediated plant functional traits. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 2011, 42(8): 23-46. |
| 9 | Liu R J, Chen Y L. Mycorrhizology. Beijing: Science Press, 2007. |
| 刘润进, 陈应龙. 菌根学. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007. | |
| 10 | Willmann M, Gerlach N, Buer B, et al. Mycorrhizal phosphate uptake pathway in maize: Vital for growth and cob development on nutrient poor agricultural and greenhouse soils. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2013, 4(12): 533. |
| 11 | Smith S E, Smith F A. Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizas in plant nutrition and growth: New paradigms from cellular to ecosystem scales. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2011, 62(6): 227-250. |
| 12 | Shan L W, Zhang Q, Zhu R F, et al. Effects of AMF on growth and photosynthetic physiological characteristics of Leymus chinensis and Medicago sativa with and without nitrogen and phosphorus application. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(8): 46-57. |
| 单立文, 张强, 朱瑞芬, 等. 氮、磷添加下AMF对羊草和苜蓿生长与光合生理特性的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 46-57. | |
| 13 | Tilak K, Ranganayaki N, Manoharachari C. Synergistic effects of plant-growth promoting rhizobacteria and rhizobium on nodulation and nitrogen fixation by pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan). European Journal of Soil Science, 2006, 57(1): 67-71. |
| 14 | Qin L J, Yang Y Z, Yang X Y. Research progress in mechanism of soil phosphorus solubilizing microorganisms. Life Sciences Research, 2019, 23(1): 59-64, 86. |
| 秦利均, 杨永柱, 杨星勇. 土壤溶磷微生物溶磷、解磷机制研究进展. 生命科学研究, 2019, 23(1): 59-64, 86. | |
| 15 | Han H W, Sun L N, Yao T, et al. Effects of bio-fertilizers with different PGPR strain combinations on yield and quality of alfalfa. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(5): 104-112. |
| 韩华雯, 孙丽娜, 姚拓, 等. 不同促生菌株组合对紫花苜蓿产量和品质的影响. 草业学报, 2013, 22(5): 104-112. | |
| 16 | Qin F L, Tian Z M. Effect of co-inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and four different phosphate-solubilizing bacteria on nutrients uptake of red clover in a low phosphorus soil. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 37(6): 151-157. |
| 秦芳玲, 田中民. 同时接种解磷细菌与丛枝菌根真菌对低磷土壤红三叶草养分利用的影响. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 37(6): 151-157. | |
| 17 | Li H Y, Wei X, Xu Q X. Photosynthetic functions and anatomical structure variations of Fraxinus mandshurica seedling leaf after AMF inoculation. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2019, 47(10): 49-54. |
| 李虹谕, 卫星, 徐庆祥. 接种丛枝菌根真菌对水曲柳实生苗光合特性和叶片解剖结构的影响. 东北林业大学学报, 2019, 47(10): 49-54. | |
| 18 | Yao R B, Wu X Q. Interaction between high effective phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and mycorrhizal fungi and its effect on poplar growth. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 36(5): 170-173. |
| 姚如斌, 吴小芹. 高效解磷细菌与菌根真菌菌剂交互作用对杨树的促生效应. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 36(5): 170-173. | |
| 19 | Xue Z M, Xue Q, Gao J H. The relationship of stomatal movement and photosynthetic characteristics of alfalfa seedlings under osmotic stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(2): 420-426. |
| 薛泽民, 薛琪, 高景慧. 渗透胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗气孔运动与光合作用的关系. 草地学报, 2018, 26(2): 420-426. | |
| 20 | Hu S L, Wan S M, Jia Z K, et al. A study on photosynthetic characteristics of alfalfas grown for different lengths of time in the semi-humid region of the Loess Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2008, 17(5): 60-67. |
| 胡守林, 万素梅, 贾志宽, 等. 黄土高原半湿润区不同生长年限苜蓿叶片光合性能研究. 草业学报, 2008, 17(5): 60-67. | |
| 21 | Behn O. Influence of Pseudomonas fluorescens and arbuscular mycorrhiza on the growth, yield, quality and resistance of wheat infected with Gaeumannomyces graminis. Journal of Plant Diseases and Protection, 2008, 115(1): 4-8. |
| 22 | Zhang D Y, Wang X H, Chen Y, et al. Determinant of photosynthetic capacity in rice leaves under ambient air conditions. Photosynthetica, 2005, 43(2): 273-276. |
| 23 | Zhao C D, Liu Y C, Yang Z, et al. Effects of different gradient phosphorus additions on photosynthetic characteristics of Vitex negundo seedlings. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2020, 49(6): 94-99. |
| 赵琛迪, 刘雅辰, 杨子, 等. 不同磷添加梯度对荆条幼苗光合特性的影响. 西部林业科学, 2020, 49(6): 94-99. | |
| 24 | Elkoca E, Kantar F, Sahin F. Influence of nitrogen fixing and phosphorus solubilizing bacteria on the nodulation, plant growth, and yield of chickpea. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2007, 31(1): 157-171. |
| 25 | Hinsinger P. Bioavailability of soil inorganic P in the rhizosphere as affected by root-induced chemical changes: A review. Plant and Soil, 2001, 237(2): 173-195. |
| 26 | Xue Y L, Li C Y, Wang C R, et al. Mechanisms of phosphorus uptake from soils by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(6): 10-20. |
| 薛英龙, 李春越, 王苁蓉, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌促进植物摄取土壤磷的作用机制. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(6): 10-20. | |
| 27 | Liu J Y, Hui J F, Sun M Y, et al. Effects of phosphorus application and inoculation arbuscular mycorrhizae fungi (AMF) and phosphate solubilizing bacteria on dry matter yield and phosphorus use efficiency of alfalfa. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(19): 142-149. |
| 刘俊英, 回金峰, 孙梦瑶, 等. 施磷水平和接种AMF与解磷细菌对苜蓿产量及磷素利用效率的影响. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(19): 142-149. | |
| 28 | Hinsinger P, Herrmann L, Lesueur D, et al. Impact of roots, microorganisms and microfauna on the fate of soil phosphorus in the rhizosphere. Annual Plant Reviews, 2015, 48(3): 377-408. |
| 29 | Raliya R, Tarafdar J C, Biswas P. Enhancing the mobilization of native phosphorus in the mung bean rhizosphere using ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by soil fungi. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2016, 64(16): 3111-3118. |
| 30 | Jones D L, Dennis P G, Owen A G, et al. Organic acid behavior in soils-misconceptions and knowledge gaps. Plant and Soil, 2003, 248(1): 31-41. |
| 31 | Toro M, Azcón R, Barea J M. The use of isotopic dilution techniques to evaluate the interactive effects of rhizobium genotype, mycorrhizal fungi, phosphate-solubilizing rhizobacteria and rock phosphate on nitrogen and phosphorus acquisition by Medicago sativa. The New Phytologist, 1998, 138(2): 265-273. |
| [1] | 王园, 王晶, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿MsBBX24基因的克隆及耐盐性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 107-117. |
| [2] | 田政, 杨正禹, 陆忠杰, 罗奔, 张茂, 董瑞. 44个紫花苜蓿品种的酸铝适应性与耐受性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 142-151. |
| [3] | 孙守江, 唐艺涵, 马馼, 李曼莉, 毛培胜. 紫花苜蓿种子吸胀期胚根线粒体AsA-GSH循环对低温胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 152-162. |
| [4] | 赵艳兰, 曾鑫奕, 弓晋超, 李香君, 李旭旭, 刘珊, 张新全, 周冀琼. 丛枝菌根真菌接种对白车轴草耐盐性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 179-188. |
| [5] | 郭丽珠, 孟慧珍, 范希峰, 滕珂, 滕文军, 温海峰, 岳跃森, 张辉, 武菊英. 野牛草雌雄株对不同形态氮素的生理响应差异[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 65-74. |
| [6] | 钱文武, 郭鹏, 朱慧森, 张士敏, 李德颖. 草地早熟禾叶片表皮特征、解剖结构及光合特性对不同施氮量的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 131-143. |
| [7] | 王晓龙, 杨曌, 来永才, 李红, 钟鹏, 徐艳霞, 柴华, 李莎莎, 吴玥, 宋敏超, 周景明. 不同秋眠等级苜蓿根系性状对越冬的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 144-153. |
| [8] | 戎荣, 孙斌, 武志涛, 高志海, 杜自强, 滕思翰. 灌丛化草原小叶锦鸡儿灌丛地上生物量测量方法研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 36-47. |
| [9] | 孙延亮, 赵俊威, 刘选帅, 李生仪, 马春晖, 王旭哲, 张前兵. 施氮对苜蓿初花期光合日变化、叶片形态及干物质产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 63-75. |
| [10] | 王星, 黄薇, 余淑艳, 李小云, 高雪芹, 伏兵哲. 宁夏地区地下滴灌水肥耦合对紫花苜蓿种子产量及构成因素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 76-85. |
| [11] | 厉方桢, 钟华平, 欧阳克蕙, 赵小敏, 李愈哲. 基于机器学习的阿勒泰地区草地地下生物量估测与数字制图[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 13-23. |
| [12] | 赵建涛, 岳亚飞, 张前兵, 马春晖. 不同秋眠级紫花苜蓿品种抗寒性对新疆北疆地区覆雪厚度的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 24-34. |
| [13] | 周泽东, 马晖玲, 韩煦, 李元恒, 李西良, 李坤娜. 温性典型草原羊草光合特性对模拟放牧因素分解的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 81-89. |
| [14] | 赵翊含, 侯蒙京, 冯琦胜, 高宏元, 梁天刚, 贺金生, 钱大文. 基于Landsat 8和随机森林的青海门源天然草地地上生物量遥感估算[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 1-14. |
| [15] | 刘彩婷, 毛丽萍, 阿依谢木, 于应文, 沈禹颖. 紫花苜蓿与垂穗披碱草混播比例对其抗寒生长生理特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 133-143. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||