

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (8): 1-13.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022370
• 研究论文 •
收稿日期:2022-09-15
修回日期:2022-10-10
出版日期:2023-08-20
发布日期:2023-06-16
通讯作者:
杨秀春
作者简介:E-mail: Yangxiuchun@bjfu.edu.cn基金资助:
Hui-long ZHANG( ), Xiu-chun YANG(
), Xiu-chun YANG( ), Dong YANG, Ang CHEN, Min ZHANG
), Dong YANG, Ang CHEN, Min ZHANG
Received:2022-09-15
Revised:2022-10-10
Online:2023-08-20
Published:2023-06-16
Contact:
Xiu-chun YANG
摘要:
草地植被覆盖度(FVC)是反映草地生态状况最直接的指标之一。目前在大区域内构建准确的FVC估算模型,进行长时间序列的动态分析,仍是一个挑战。基于大量地面调查样本,使用2000-2020年MODIS遥感数据、气象数据,通过随机森林模型进行FVC分区建模与结果估算。利用Sen+Mann-Kendall趋势分析法、Hurst指数法等,分析FVC时空变化特征和未来变化情况。研究表明:1)内蒙古草地FVC随机森林模型精度表现为分区优于全区,有效地降低了空间异质性的影响。2)内蒙古草地FVC总体上呈东高西低的分布格局,空间差异明显。3)近21年,内蒙古草地FVC总体呈波动上升趋势,年增长率为0.2%·a-1;增长区域面积占比(79.5%)大于减少区域面积占比(20.5%),并且极显著增长和显著增长占比(28.3%)远大于极显著减少和显著减少(1.6%)。4)未来内蒙古草地FVC总体为正持续性发展。预测增长区域(57.6%)多于减少区域(42.4%),其中极显著增长和显著增长占比较高(25.9%),未来草地FVC整体向好发展。
张慧龙, 杨秀春, 杨东, 陈昂, 张敏. 2000-2020年内蒙古草地植被覆盖度时空变化及趋势预测[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 1-13.
Hui-long ZHANG, Xiu-chun YANG, Dong YANG, Ang CHEN, Min ZHANG. Spatio-temporal changes in grassland fractional vegetation cover in Inner Mongolia from 2000 to 2020 and a future forecast[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(8): 1-13.

图1 研究区草地类型分布(a)、海拔分布(b)、调查样地分布(c)以及草地分区(d)
Fig.1 Grassland type distribution (a), altitude distribution (b), survey plots distribution (c) and grassland zoning map (d) in the study area
| 植被指数Vegetation index | 计算公式Formula |
|---|---|
| 归一化植被指数Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | |
| 增强植被指数Enhanced vegetation index (EVI) | |
| 差值环境植被指数Difference vegetation index (DVI) | |
| 比值植被指数Ratio vegetation index (RVI) | |
| 土壤调节植被指数Soil adjusted vegetation index (SAVI) |
表 1 植被指数计算方法
Table 1 Calculation formula of vegetation index
| 植被指数Vegetation index | 计算公式Formula |
|---|---|
| 归一化植被指数Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | |
| 增强植被指数Enhanced vegetation index (EVI) | |
| 差值环境植被指数Difference vegetation index (DVI) | |
| 比值植被指数Ratio vegetation index (RVI) | |
| 土壤调节植被指数Soil adjusted vegetation index (SAVI) |
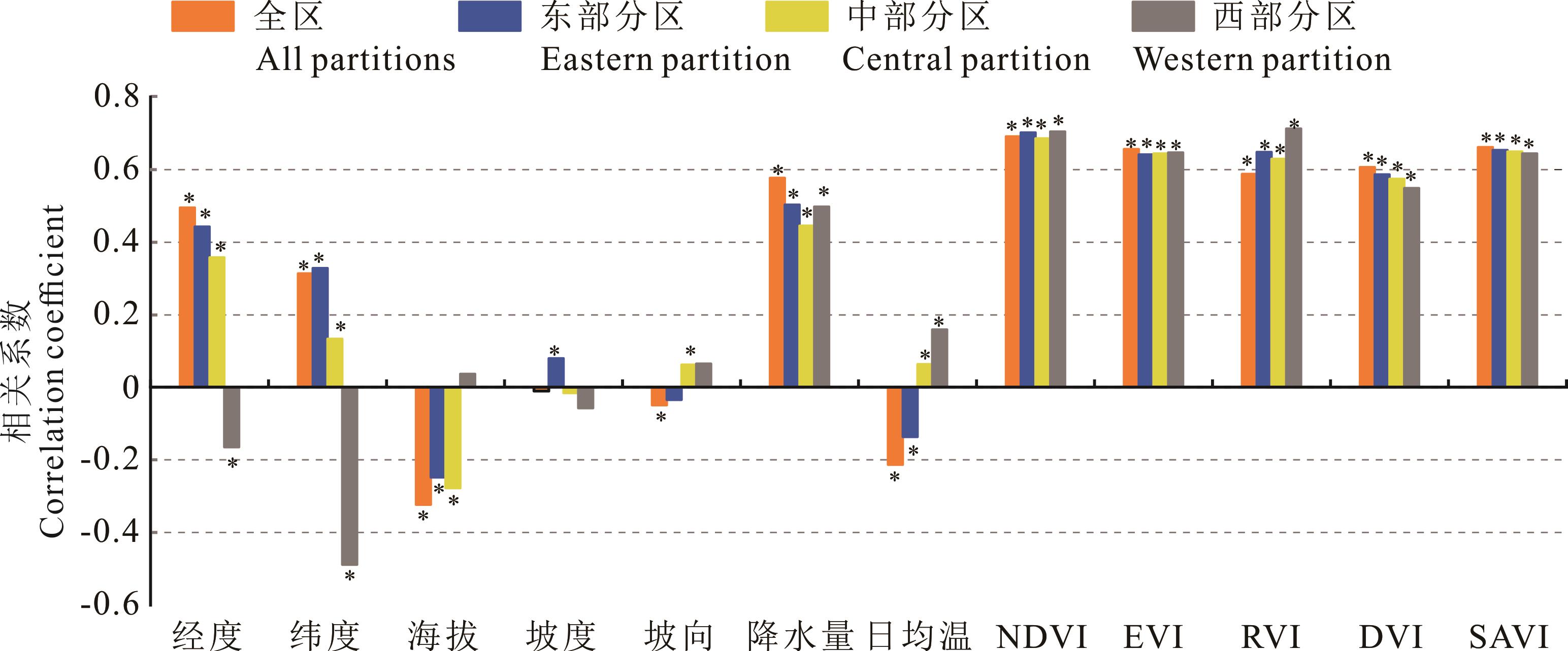
图2 解释变量相关性分析及显著性检验经度: Latitude; 纬度: Longitude; 海拔: Altitude; 坡度: Slope; 坡向: Aspect; 降水量: Precipitation; 日均温: Daily mean temperature; NDVI: 归一化植被指数; EVI: 增强植被指数; RVI: 比值植被指数; DVI: 差值环境植被指数; SAVI: 土壤调节植被指数; * : P<0.01.
Fig.2 Correlation analysis and significance test results of explanatory variables
分区 Partition | 训练集Training set | 测试集Test set | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE (%) | R2 | MAE (%) | RMSE (%) | R2 | MAE (%) | |
| 全区All partitions | 7.3 | 0.9 | 5.6 | 15.2 | 0.6 | 11.8 |
| 东部分区Eastern partition | 5.8 | 0.9 | 4.8 | 9.2 | 0.7 | 7.6 |
| 中部分区Central partition | 5.8 | 0.9 | 4.4 | 10.5 | 0.7 | 8.6 |
| 西部分区Western partition | 4.1 | 0.9 | 3.0 | 6.8 | 0.8 | 5.3 |
表 2 训练集及测试集模型精度评价
Table 2 Accuracy evaluation of training set and test set model
分区 Partition | 训练集Training set | 测试集Test set | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE (%) | R2 | MAE (%) | RMSE (%) | R2 | MAE (%) | |
| 全区All partitions | 7.3 | 0.9 | 5.6 | 15.2 | 0.6 | 11.8 |
| 东部分区Eastern partition | 5.8 | 0.9 | 4.8 | 9.2 | 0.7 | 7.6 |
| 中部分区Central partition | 5.8 | 0.9 | 4.4 | 10.5 | 0.7 | 8.6 |
| 西部分区Western partition | 4.1 | 0.9 | 3.0 | 6.8 | 0.8 | 5.3 |

图4 2000-2020年内蒙古草地植被覆盖度变化率空间分布(a)、变化趋势分级统计结果(b)、空间分布(c)以及平均植被覆盖度逐年变化(d)
Fig.4 Spatial distribution of change rate of grassland vegetation coverage (a), statistical results of change trend (b) and spatial distribution (c) and annual change of average vegetation coverage (d) in Inner Mongolia from 2000 to 2020

图 5 2000-2020年内蒙古草地植被覆盖度Hurst指数空间分布(a)、分段统计(b)以及未来变化趋势空间分布(c)和分级统计(d)
Fig.5 Spatial distribution (a) and segmentation statistical results (b) of Hurst index and future trend spatial distribution (c) and classification statistical results (d) of grassland vegetation coverage in Inner Mongolia during 2000-2020
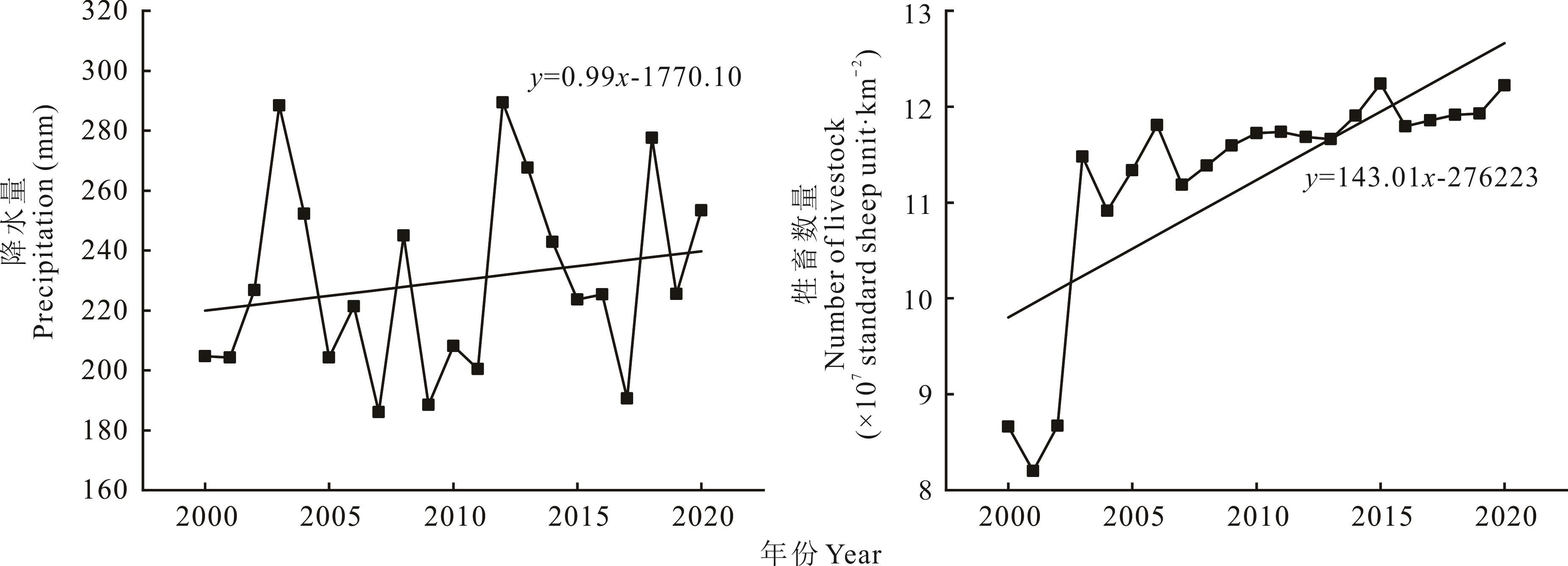
图6 2000-2020年内蒙古草地生长季降水量和牲畜数量年际变化
Fig.6 Annual change of precipitation in the growing season and number of livestock of grassland in Inner Mongolia from 2000 to 2020
| 1 | Shen H H, Zhu Y K, Zhao X, et al. Analysis of current grassland resources in China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(2): 139-154. |
| 沈海花, 朱言坤, 赵霞, 等. 中国草地资源的现状分析. 科学通报, 2016, 61(2): 139-154. | |
| 2 | Mu S J, Li J L, Chen Y Z, et al. Spatial differences of variations of vegetation coverage in Inner Mongolia during 2001-2010. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2012, 67(9): 1255-1268. |
| 穆少杰, 李建龙, 陈奕兆, 等. 2001-2010年内蒙古植被覆盖度时空变化特征. 地理学报, 2012, 67(9): 1255-1268. | |
| 3 | Mu S J, Zhu C, Zhou K X, et al. The preventive strategies of degradation and the approaches to enhance carbon sequestration ability in Inner Mongolia grassland. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2017, 25(2): 217-225. |
| 穆少杰, 朱超, 周可新, 等. 内蒙古草地退化防治对策及碳增汇途径研究. 草地学报, 2017, 25(2): 217-225. | |
| 4 | Wen Q K, Zhang Z X, Liu B, et al.Research progress in grassland fractional coverage estimation methods. Pratacultural Science, 2009, 26(12): 30-36. |
| 温庆可, 张增祥, 刘斌, 等. 草地覆盖度测算方法研究进展.草业科学, 2009, 26(12): 30-36. | |
| 5 | Ma Z G, Sun H, Wang G X, et al . Modeling percentage vegetation cover of a desert area using Landsat 8-OLI image. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2016, 36(9): 12-18. |
| 马中刚, 孙华, 王广兴, 等. 基于Landsat 8-OLI的荒漠化地区植被覆盖度反演模型研究. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2016, 36(9): 12-18. | |
| 6 | Zhang Y, Yang Z H, Guo S J, et al. Ecological changes in the Minqin oasis belt over the past 20 years. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(7): 14-24. |
| 张永, 杨自辉, 郭树江, 等. 基于遥感分析20年来民勤绿洲防护林带植被变化研究. 草业学报, 2018, 27(7): 14-24. | |
| 7 | Wu D, Wu H, Zhao X, et al. Evaluation of spatiotemporal variations of global fractional vegetation cover based on GIMMS NDVI data from 1982 to 2011. Remote Sensing, 2014, 6(5): 4217-4239. |
| 8 | Jia K, Liang S, Gu X, et al. Fractional vegetation cover estimation algorithm for Chinese GF-1 wide field view data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2016, 177: 184-191. |
| 9 | Chen Q, Li X S, Xiu X M, et al. Large scale shrub coverage mapping of sandy land at 30 m resolution based on Google Earth Engine and machine learning. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(11): 4056-4069. |
| 陈黔, 李晓松, 修晓敏, 等. 基于Google Earth Engine与机器学习的大尺度30 m分辨率沙地灌木覆盖度估算.生态学报, 2019, 39(11): 4056-4069. | |
| 10 | Cheng J Y, Zhang X F, Sun M, et al. Random forest model for the estimation of fractional vegetation coverage based on a UAV-ground co-sampling strategy.Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2020, 56(1): 143-154. |
| 程俊毅, 张显峰, 孙敏, 等. 基于空地协同采样的植被覆盖度随机森林估算方法. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(1): 143-154. | |
| 11 | Wu T, Luo J, Gao L, et al. Geoparcel-based spatial prediction method for grassland fractional vegetation cover mapping. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 9241-9253. |
| 12 | Chen Y, Song Y Q, Wang W. Grassland vegetation cover inversion model based on random forest regression: A case study in Burqin County, Altay, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(7): 2384-2394. |
| 陈妍, 宋豫秦, 王伟. 基于随机森林回归的草场植被盖度反演模型研究-以新疆阿勒泰地区布尔津县为例. 生态学报, 2018, 38(7): 2384-2394. | |
| 13 | Zhang Y R, Liu T X, Tong X, et al. Inversion of vegetation coverage based on multi-source remote sensing data and machine learning method in the Horqin Sandy Land, China. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(3): 187-195. |
| 张亦然, 刘廷玺, 童新, 等. 基于多源遥感和机器学习方法的科尔沁沙地植被覆盖度反演. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(3): 187-195. | |
| 14 | Zhang L, Qun L, Bao L S, et al. Opportunities and challenges of grassland ecological restoration in Inner Mongolia. Inner Mongolia Forestry, 2022(7): 33-34. |
| 张雷, 群力, 包龙山, 等. 内蒙古草地生态修复的机遇和挑战. 内蒙古林业, 2022(7): 33-34. | |
| 15 | Department of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary, General Station of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary of Ministry of Agriculture of China. Rangeland resources of China. Beijing: China Science & Technology Press, 1996. |
| 中华人民共和国农业部畜牧兽医司, 全国畜牧兽医总站. 中国草地资源. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 1996. | |
| 16 | Tian Q J, Min X J. Advances in study on vegetation indices.Advance in Earth Sciences, 1998,13(4): 10-16. |
| 田庆久, 闵祥军. 植被指数研究进展. 地球科学进展, 1998,13(4): 10-16. | |
| 17 | Jiang Z, Huete A R, Didan K, et al. Development of a two-band enhanced vegetation index without a blue band. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2008, 112(10): 3833-3845. |
| 18 | Hua Y C, Gao R H, Ao D.Temporal lag of desert steppe vegetation growth response to climate factors in Inner Mongolia. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2021, 36(4): 1-10. |
| 滑永春, 高润宏, 敖敦. 内蒙古荒漠草原植被对气候响应的滞后性研究. 西北林学院学报, 2021, 36(4): 1-10. | |
| 19 | Chen K, Yang C C, Bai L G, et al. Effects of natural and human factors on vegetation normalized difference vegetation index based on geographical detectors in Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(12): 4963-4975. |
| 陈宽, 杨晨晨, 白力嘎, 等. 基于地理探测器的内蒙古自然和人为因素对植被NDVI变化的影响. 生态学报, 2021, 41(12): 4963-4975. | |
| 20 | Xing X Y, Yang X C, Xu B, et al. Remote sensing estimation of grassland aboveground biomass based on random forest. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2021, 23(7): 1312-1324. |
| 邢晓语, 杨秀春, 徐斌, 等. 基于随机森林算法的草原地上生物量遥感估算方法研究. 地球信息科学学报, 2021, 23(7): 1312-1324. | |
| 21 | Cavadias G, Yue S, Pilon P. Power of the Mann-Kendall and Spearman’s rho tests for detecting monotonic trends in hydrological series. Journal of Hydrology, 2002, 259(1): 254-271. |
| 22 | Kang Y, Guo E L, Wang Y F, et al. Application of temperature vegetation dryness index for drought monitoring in Mongolian Plateau. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(7): 2534-2544. |
| 康尧, 郭恩亮, 王永芳, 等. 温度植被干旱指数在蒙古高原干旱监测中的应用. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(7): 2534-2544. | |
| 23 | Li Y W, Jia K, Wei X Q, et al. Fractional vegetation cover estimation in Northern China and its change analysis.Remote Sensing for Land and Resources, 2015, 27(2): 112-117. |
| 李钰溦, 贾坤, 魏香琴, 等. 中国北方地区植被覆盖度遥感估算及其变化分析. 国土资源遥感, 2015, 27(2): 112-117. | |
| 24 | Li F, Chen W, Zeng Y, et al. Improving estimates of grassland fractional vegetation cover based on a pixel dichotomy model: A case study in Inner Mongolia, China. Remote Sensing, 2014, 6(6): 4705-4722. |
| 25 | Dong S K, Tang F L, Ping X Y, et al. Zoning and functions of China’s grassland in the New Era of ecological civilization. Journal of Natural Resources, 2022, 37(3): 568-581. |
| 董世魁, 唐芳林, 平晓燕, 等. 新时代生态文明背景下中国草原分区与功能辨析. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(3): 568-581. | |
| 26 | Mu X, Zhao T, Ruan G, et al. High spatial resolution and high temporal frequency(30 m/15 day) fractional vegetation cover estimation over China using multiple remote sensing datasets: Method development and validation. Journal of Meteorological Research, 2021, 35(1): 128-147. |
| 27 | Ge J, Hou M, Liang T, et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of grassland aboveground biomass and its driving factors in North China over the past 20 years. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 826: 154226. |
| 28 | Tong S, Zhang J, Ha S, et al. Dynamics of fractional vegetation coverage and its relationship with climate and human activities in Inner Mongolia, China. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(9): 776. |
| 29 | Wang J F, He L, Lu S J, et al. Photosynthetic vegetation cover response to precipitation on the Inner Mongolian steppe. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(16): 5620-5629. |
| 王举凤, 何亮, 陆绍娟, 等. 内蒙古不同类型草原光合植被覆盖度对降水变化的响应. 生态学报, 2020, 40(16): 5620-5629. | |
| 30 | Tong S, Zhang J, Bao Y, et al. Analyzing vegetation dynamic trend on the Mongolian Plateau based on the Hurst exponent and influencing factors from 1982-2013. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2018, 28(5): 595-610. |
| 31 | Sa Q R L, Ao D G W. Analysis on the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of grassland degradation in Alukorqin Banner, Inner Mongolia.Western Resources, 2017(3): 181-183. |
| 萨其日拉, 敖登高娃. 内蒙古阿鲁科尔沁旗草地退化时空分布特征分析. 西部资源, 2017(3): 181-183. | |
| 32 | Zhao C W, Guo W, Yan Y G, et al. Analysis of vegetation cover change and driving forces in typical resource-based cities: A case study of Ordos. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2022, 37(2): 389-398. |
| 赵传武, 郭伟, 阎跃观, 等. 典型资源型城市的植被覆盖变化及驱动力分析-以鄂尔多斯市为例. 遥感技术与应用, 2022, 37(2): 389-398. | |
| 33 | Chen Q, Yang J Y, Yan R L, et al. Analysis of NDVI variation characteristics of different vegetation types in desert areas—A case study of Alxa League, Inner Mongolia. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(3): 17-28. |
| 陈琪, 杨九艳, 闫瑞玲, 等. 荒漠区不同植被类型NDVI变化特征分析—以内蒙古阿拉善盟为例. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(3): 17-28. | |
| 34 | Liu M, Dries L, Heijman W, et al. The impact of ecological construction programs on grassland conservation in Inner Mongolia, China. Land Degradation & Development, 2018, 29(2): 326-336. |
| 35 | Qu Y B, Zhao Y Y, Ding G D, et al. Effects of climate and human activities on vegetation cover changes in Xilingol steppe. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(3): 802-811. |
| 屈莹波, 赵媛媛, 丁国栋, 等. 气候变化和人类活动对锡林郭勒草原植被覆盖度的影响. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(3): 802-811. | |
| 36 | Zhou X, Yamaguchi Y, Arjasakusuma S. Distinguishing the vegetation dynamics induced by anthropogenic factors using vegetation optical depth and AVHRR NDVI: A cross-border study on the Mongolian Plateau. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 616: 730-743. |
| 37 | Meng X Y. Regulations of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region on the balance of grass and livestock and the prohibition of grazing. Inner Mongolia Forestry, 2021(9): 12-14. |
| 孟宪毅. 内蒙古自治区草畜平衡和禁牧休牧条例. 内蒙古林业, 2021(9): 12-14. | |
| 38 | Zhang M, Wang J M, Li S. Tempo-spatial changes and main anthropogenic influence factors of vegetation fractional coverage in a large-scale opencast coal mine area from 1992 to 2015. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 232(20): 940-952. |
| [1] | 修炀景, 侯蒙京, 田骄阳, 梁天刚, 冯琦胜. 基于土地利用/覆盖的甘肃省景观生态风险时空变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 1-15. |
| [2] | 赵翊含, 侯蒙京, 冯琦胜, 高宏元, 梁天刚, 贺金生, 钱大文. 基于Landsat 8和随机森林的青海门源天然草地地上生物量遥感估算[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 1-14. |
| [3] | 李颖, 吴静, 李纯斌, 秦格霞. 2003-2018年青藏高原草地的地表层土壤热通量时空变化[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 1-14. |
| [4] | 张仁平, 郭靖, 马晓芳, 郭伟勇. 基于MODIS数据的新疆草地物候提取方法及变化趋势分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 1-12. |
| [5] | 崔博超, 郑江华, 吐尔逊·哈斯木, 段素素, 杜梦洁. 塔里木河流域草地净初级生产力时空分异特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 1-13. |
| [6] | 普雪可, 吴春花, 周永瑾, 勉有明, 苗芳芳, 侯贤清, 李荣. 宁南旱区地膜秸秆沟垄双覆盖对土壤水分时空变化及马铃薯产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 149-160. |
| [7] | 张永, 杨自辉, 郭树江, 王强强, 詹科杰, 张剑挥, 魏怀东. 基于遥感分析20年来民勤绿洲防护林带植被变化研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(7): 14-24. |
| [8] | 张仁平, 郭靖, 冯琦胜, 梁天刚. 新疆地区草地植被物候时空变化[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 66-75. |
| [9] | 马晓芳, 陈思宇, 邓婕, 冯琦胜, 黄晓东. 青藏高原植被物候监测及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(1): 13-21. |
| [10] | 王勇, 于信芳, 庄大方. 近30年北京市高尔夫球场时空变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(8): 188-198. |
| [11] | 马琳雅,崔霞,冯琦胜,梁天刚. 2001-2011年甘南草地植被覆盖度动态变化分析[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(4): 1-9. |
| [12] | 陈思宇,于惠,冯琦胜,梁天刚. 2002-2010年青藏高原植被含水量微波遥感动态监测[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(5): 1-10. |
| [13] | 穆少杰,李建龙,杨红飞,刚成诚,陈奕兆. 内蒙古草地生态系统近10年NPP时空变化及其与气候的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(3): 6-. |
| [14] | 王浩,李文龙,杜国祯,朱晓丽. 基于3S技术的甘南草地覆盖度动态变化研究[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(3): 26-37. |
| [15] | 宋春桥,游松财,刘高焕,柯灵红,钟新科. 那曲地区草地植被时空格局与变化及其人文因素影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(3): 1-10. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||