

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (10): 147-158.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023431
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
赵文军1,2( ), 刘蕊3(
), 刘蕊3( ), 王正旭1, 冯瑜4, 薛开政1, 刘魁1, 徐梓荷1, 曹卫东5, 付利波6, 尹梅6, 陈华6(
), 王正旭1, 冯瑜4, 薛开政1, 刘魁1, 徐梓荷1, 曹卫东5, 付利波6, 尹梅6, 陈华6( )
)
收稿日期:2023-11-15
修回日期:2023-12-22
出版日期:2024-10-20
发布日期:2024-07-15
通讯作者:
陈华
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: chenhua19792003@126.com基金资助:
Wen-jun ZHAO1,2( ), Rui LIU3(
), Rui LIU3( ), Zheng-xu WANG1, Yu FENG4, Kai-zheng XUE1, Kui LIU1, Zi-he XU1, Wei-dong CAO5, Li-bo FU6, Mei YIN6, Hua CHEN6(
), Zheng-xu WANG1, Yu FENG4, Kai-zheng XUE1, Kui LIU1, Zi-he XU1, Wei-dong CAO5, Li-bo FU6, Mei YIN6, Hua CHEN6( )
)
Received:2023-11-15
Revised:2023-12-22
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-07-15
Contact:
Hua CHEN
摘要:
本研究旨在探讨烤烟轮作绿肥对烤烟产量、土壤质量和微生物养分限制的影响,为云南烟区筛选适宜与烤烟轮作的绿肥种类提供理论与技术支撑。于2017年布置田间定位试验,研究轮作绿肥对烤烟产量、土壤质量、养分循环相关水解酶活性和微生物养分限制的影响。试验设冬闲-烤烟(WF)、肥田萝卜-烤烟(RD)、光叶苕子-烤烟(SV)、黑麦草-烤烟(RG)4个处理。相比WF处理,2019年SV处理烟叶产量增加了6.8%,2022年RD和SV处理烟叶产量分别增加了6.4%和8.4%。2022年较2019年,各处理土壤有机质、全氮、有效磷、速效钾含量增加,pH值、全磷含量降低。在2022年,相比WF处理,SV处理土壤全磷含量降低了22.9%,RG处理土壤有机质和速效钾含量增加了9.7%和73.6%,RD、SV和RG处理土壤硝态氮含量分别增加了97.1%、75.9%和26.0%、可溶性有机氮含量增加了228.8%、85.0%和96.7%。总体上,RD、RG处理土壤质量面积指数显著增加了27.0%和15.6%。相比WF处理,轮作绿肥处理碳(α-葡萄糖苷酶、β-葡萄糖苷酶、β-木糖苷酶)、氮(亮氨酸氨基肽酶)、磷(碱性磷酸酶)相关水解酶活性分别增加了48.8%~262.1%、59.3%~125.0%和312.0%~435.9%。轮作不同绿肥处理较WF处理降低了微生物碳限制,却增加了微生物磷限制。综上,轮作光叶苕子和肥田萝卜可增加烤烟产量、提高烟田土壤质量,是实现云南烟区清洁烟叶生产和可持续土壤管理的有效途径。
赵文军, 刘蕊, 王正旭, 冯瑜, 薛开政, 刘魁, 徐梓荷, 曹卫东, 付利波, 尹梅, 陈华. 烤烟-绿肥轮作对云南烟田土壤质量与微生物养分限制的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 147-158.
Wen-jun ZHAO, Rui LIU, Zheng-xu WANG, Yu FENG, Kai-zheng XUE, Kui LIU, Zi-he XU, Wei-dong CAO, Li-bo FU, Mei YIN, Hua CHEN. Effects of rotation with a green manure crop on soil quality and microbial nutrient limitation in a tobacco field in Yunnan[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(10): 147-158.
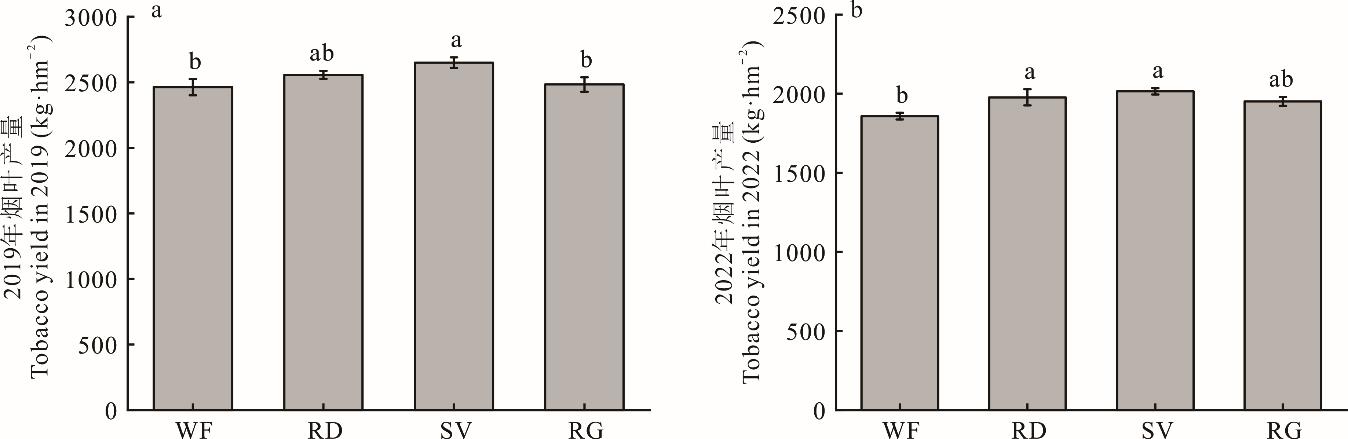
图1 不同处理烟叶产量WF: 冬闲-烤烟轮作; RD: 肥田萝卜-烤烟轮作;SV: 光叶苕子-烤烟轮作;RG: 黑麦草-烤烟轮作,不同字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。WF: Winter follow-tobacco rotation; RD: Radish-tobacco rotation; SV: Smooth vetch-tobacco rotation; RG: Ryegrass-tobacco rotation, different letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.1 Tobacco yield in different treatments
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | pH 值 pH value | 有机质 Organic matter (SOM, g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (TN, g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (TP, g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium (TK, g·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus (AP, mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (AK, mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | WF | 6.79±0.06a | 17.61±1.61a | 1.27±0.16a | 1.64±0.19a | 9.64±0.35a | 32.84±2.12a | 144.5±13.7a |
| RD | 6.79±0.14a | 17.03±0.46a | 1.25±0.05a | 1.59±0.06a | 9.52±0.31a | 36.16±2.43a | 128.2±8.8a | |
| SV | 6.94±0.10a | 17.32±2.36a | 1.26±0.14a | 1.56±0.06a | 9.01±0.64a | 32.56±2.76a | 152.2±12.8a | |
| RG | 6.93±0.07a | 18.20±3.26a | 1.15±0.13a | 1.54±0.04a | 9.51±0.62a | 33.42±3.03a | 144.0±9.2a | |
| 2022 | WF | 6.06±0.05a | 20.21±0.11b | 1.43±0.01a | 1.66±0.03a | 9.83±0.37a | 42.79±5.56ab | 265.0±33.4b |
| RD | 6.26±0.08a | 20.66±0.40b | 1.47±0.05a | 1.57±0.05a | 9.95±1.51a | 43.08±2.30ab | 320.0±40.8b | |
| SV | 6.29±0.24a | 21.52±0.26ab | 1.47±0.01a | 1.28±0.01b | 10.07±2.08a | 39.79±2.39b | 326.7±73.6b | |
| RG | 6.17±0.04a | 22.17±0.91a | 1.41±0.01a | 1.44±0.05a | 8.47±0.15a | 52.98±8.26a | 460.0±46.4a | |
增幅 Increase (%) | WF | -10.7±0.8a | 14.8±0.6b | 12.6±0.5b | 1.3±1.9a | 1.9±3.8a | 30.3±16.9b | 83.4±23.1b |
| RD | -7.9±1.2a | 21.3±2.4a | 17.6±3.6b | -1.2±3.0a | 4.4±15.9a | 19.1±6.4b | 149.6±31.9ab | |
| SV | -9.5±3.5a | 24.2±1.5a | 16.7±1.1b | -17.7±0.8c | 11.7±23.1a | 22.2±7.3b | 114.6±48.4b | |
| RG | -11.0±0.6a | 21.8±5.0ab | 22.6±1.3a | -6.6±3.3b | -11.0±1.5b | 58.5±24.7a | 219.5±32.2a |
表1 不同处理下耕层土壤化学性状
Table 1 Soil chemical properties in different treatments
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | pH 值 pH value | 有机质 Organic matter (SOM, g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (TN, g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (TP, g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium (TK, g·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus (AP, mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (AK, mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | WF | 6.79±0.06a | 17.61±1.61a | 1.27±0.16a | 1.64±0.19a | 9.64±0.35a | 32.84±2.12a | 144.5±13.7a |
| RD | 6.79±0.14a | 17.03±0.46a | 1.25±0.05a | 1.59±0.06a | 9.52±0.31a | 36.16±2.43a | 128.2±8.8a | |
| SV | 6.94±0.10a | 17.32±2.36a | 1.26±0.14a | 1.56±0.06a | 9.01±0.64a | 32.56±2.76a | 152.2±12.8a | |
| RG | 6.93±0.07a | 18.20±3.26a | 1.15±0.13a | 1.54±0.04a | 9.51±0.62a | 33.42±3.03a | 144.0±9.2a | |
| 2022 | WF | 6.06±0.05a | 20.21±0.11b | 1.43±0.01a | 1.66±0.03a | 9.83±0.37a | 42.79±5.56ab | 265.0±33.4b |
| RD | 6.26±0.08a | 20.66±0.40b | 1.47±0.05a | 1.57±0.05a | 9.95±1.51a | 43.08±2.30ab | 320.0±40.8b | |
| SV | 6.29±0.24a | 21.52±0.26ab | 1.47±0.01a | 1.28±0.01b | 10.07±2.08a | 39.79±2.39b | 326.7±73.6b | |
| RG | 6.17±0.04a | 22.17±0.91a | 1.41±0.01a | 1.44±0.05a | 8.47±0.15a | 52.98±8.26a | 460.0±46.4a | |
增幅 Increase (%) | WF | -10.7±0.8a | 14.8±0.6b | 12.6±0.5b | 1.3±1.9a | 1.9±3.8a | 30.3±16.9b | 83.4±23.1b |
| RD | -7.9±1.2a | 21.3±2.4a | 17.6±3.6b | -1.2±3.0a | 4.4±15.9a | 19.1±6.4b | 149.6±31.9ab | |
| SV | -9.5±3.5a | 24.2±1.5a | 16.7±1.1b | -17.7±0.8c | 11.7±23.1a | 22.2±7.3b | 114.6±48.4b | |
| RG | -11.0±0.6a | 21.8±5.0ab | 22.6±1.3a | -6.6±3.3b | -11.0±1.5b | 58.5±24.7a | 219.5±32.2a |
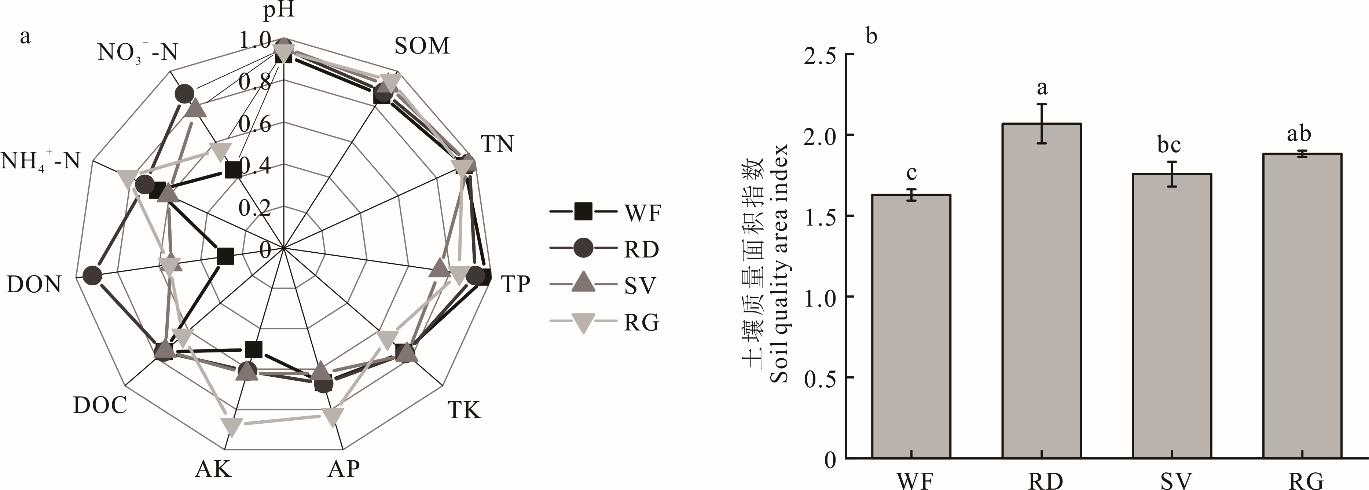
图2 土壤化学性状及土壤质量面积指数pH: pH值; SOM: 有机质;TN: 全氮;TP: 全磷;TK: 全钾;AP: 有效磷;AK: 速效钾;DOC: 可溶性有机碳;DON: 可溶性有机氮;NH4+-N: 铵态氮;NO3--N: 硝态氮。下同。pH: pH value; SOM: Soil organic matter; TN: Total nitrogen; TP: Total phosphorus; TK: Total potassium; AP: Available phosphorus; AK: Available potassium; DOC: Dissolved organic carbon; DON: Dissolved organic nitrogen; NH4+-N: Ammonium nitrogen; NO3--N: Nitrate nitrogen. The same below.
Fig.2 Soil chemical properties and soil quality area index in different treatments
处理 Treat-ment | 碳相关酶活性 C-related enzyme activities | 氮相关酶活性 N-related enzyme activities | 磷相关酶活性P-related enzyme activities | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
β-葡萄糖苷酶 β-glucosidase (BG) | β-纤维二糖苷酶 β-cellobiosidase (CB) | β-木糖苷酶 β-xylosidase (XYL) | α-葡萄糖苷酶 α-glucosidase (AG) | 乙酰氨基葡萄糖苷酶 N-acetylglucosaminidase (NAG) | 亮氨酸氨基肽酶 L-leucine-7-amido-4-methyl coumarin (LAP) | 碱性磷酸酶 Alkaline phosphatase (AKP) | |
| WF | 25.95±1.39b | 4.37±1.30a | 11.80±2.46c | 1.23±0.15c | 14.58±1.73a | 10.30±1.44c | 40.19±5.74c |
| RD | 47.78±7.15a | 3.71±0.62a | 14.22±0.83bc | 1.47±0.16c | 16.15±0.35a | 16.41±1.82b | 165.60±5.06b |
| SV | 44.90±2.01a | 4.33±1.62a | 28.62±0.62a | 2.89±0.64b | 13.92±2.61a | 23.18±0.37a | 189.40±26.61ab |
| RG | 43.24±7.37a | 4.37±0.62a | 17.57±2.10b | 4.45±0.53a | 12.83±2.24a | 20.17±0.48ab | 215.39±36.32a |
表2 不同轮作处理土壤水解酶活性
Table 2 Hydrolase enzyme activities in soils under different treatments (nmol·h-1·g-1)
处理 Treat-ment | 碳相关酶活性 C-related enzyme activities | 氮相关酶活性 N-related enzyme activities | 磷相关酶活性P-related enzyme activities | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
β-葡萄糖苷酶 β-glucosidase (BG) | β-纤维二糖苷酶 β-cellobiosidase (CB) | β-木糖苷酶 β-xylosidase (XYL) | α-葡萄糖苷酶 α-glucosidase (AG) | 乙酰氨基葡萄糖苷酶 N-acetylglucosaminidase (NAG) | 亮氨酸氨基肽酶 L-leucine-7-amido-4-methyl coumarin (LAP) | 碱性磷酸酶 Alkaline phosphatase (AKP) | |
| WF | 25.95±1.39b | 4.37±1.30a | 11.80±2.46c | 1.23±0.15c | 14.58±1.73a | 10.30±1.44c | 40.19±5.74c |
| RD | 47.78±7.15a | 3.71±0.62a | 14.22±0.83bc | 1.47±0.16c | 16.15±0.35a | 16.41±1.82b | 165.60±5.06b |
| SV | 44.90±2.01a | 4.33±1.62a | 28.62±0.62a | 2.89±0.64b | 13.92±2.61a | 23.18±0.37a | 189.40±26.61ab |
| RG | 43.24±7.37a | 4.37±0.62a | 17.57±2.10b | 4.45±0.53a | 12.83±2.24a | 20.17±0.48ab | 215.39±36.32a |

图5 土壤化学性状与酶活性间相关性分析pH: pH值; SOM: 有机质;TN: 全氮;TP: 全磷;TK: 全钾;C/N: 有机碳/全氮含量比值;C/P: 有机碳/全磷含量比值;N/P: 全氮/全磷含量比值;AP: 有效磷;AK: 速效钾;DOC: 可溶性有机碳;DON: 可溶性有机氮;NH4+-N: 铵态氮;NO3--N: 硝态氮; BG: β-葡萄糖苷酶; CB: β-纤维二糖苷酶; XYL: β-木糖苷酶; AG: α-葡萄糖苷酶; NAG: 乙酰氨基葡萄糖苷酶; LAP: 亮氨酸氨基肽酶; AKP: 碱性磷酸酶;Length:矢量长度;Angle:矢量角度。下同。pH: pH value; SOM: Soil organic matter; TN: Total nitrogen; TP: Total phosphorus; TK: Total potassium; C/N: The ratio of soil organic carbon/total nitrogen; C/P: The ratio of soil organic carbon/total phosphorus; N/P: The ratio of total nitrogen/total phosphorus; AP: available phosphorus; AK: Available potassium; DOC: Dissolved organic carbon; DON: Dissolved organic nitrogen; NH4+-N: Ammonium; NO3--N: Nitrate, BG: β-glucosidase; CB: β- cellobiosidase; XYL: β-xylosidase; AG: α-glucosidase; NAG: N-acetylglucosaminidase; LAP: L-leucine-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin; AKP: Alkaline phosphatase; Length: Vector length; Angle: Vector angle. The same below.
Fig.5 The correlation analysis between soil chemical properties and enzyme activities

图6 矢量长度、矢量角度、土壤化学性状和烟草产量间Mantel分析Yield: 烟草产量Tobacco yield.
Fig.6 Mantel analysis between vector length, vector angle, soil chemical properties and tobacco yield
| 1 | Deng X H, Huang J, Yang L L, et al. The synergistic effect of lime, green manure and bio-organic fertilizer on restoration of acid field and improvement of tobacco production efficiency. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2019, 25(9): 1577-1587. |
| 邓小华, 黄杰, 杨丽丽, 等. 石灰、绿肥和生物有机肥协同改良酸性土壤并提高烟草生产效益. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(9): 1577-1587. | |
| 2 | Chavez M D, Berentsen P B M, Oude Lansink A G J M. Analyzing diversification possibilities on specialized tobacco farms in Argentina using a bio-economic farm model. Agricultural Systems, 2014, 128(3): 35-43. |
| 3 | Su Y, Zi H, Wei X, et al. Application of manure rather than plant-origin organic fertilizers alters the fungal community in continuous cropping tobacco soil. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2022, 13: 818956. |
| 4 | Li S J, Zhu Q F, Pei Z Y, et al. Reasons and countermeasures of tobacco successive cropping obstacle. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018(4): 54-56, 58. |
| 李世金, 朱启法, 裴洲洋, 等. 烟草种植连作障碍产生的原因及防治对策.现代农业科技, 2018(4): 54-56, 58. | |
| 5 | Wang Z, Zhang Y, Bo G, et al. Ralstonia solanacearum infection disturbed the microbiome structure throughout the whole tobacco crop niche as well as the nitrogen metabolism in soil. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2022, 10: 903555. |
| 6 | Zhang J G, Shen G M, Zhang J Q, et al. Advance in continuous cropping problems of tobacco. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2011, 32(3): 95-99. |
| 张继光, 申国明, 张久权, 等. 烟草连作障碍研究进展. 中国烟草科学, 2011, 32(3): 95-99. | |
| 7 | Cao W D, Bao X G, Xu C X, et al. Reviews and prospects on science and technology of green manure in China. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2017, 23(6): 1450-1461. |
| 曹卫东, 包兴国, 徐昌旭, 等. 中国绿肥科研60年回顾与未来展望. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(6): 1450-1461. | |
| 8 | Gao S J, Zhou G P, Cao W D. Effects of milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus) as winter green manure on rice yield and rate of fertilizer application in rice paddies in south China. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(12): 2115-2126. |
| 高嵩涓, 周国朋, 曹卫东. 南方稻田紫云英作冬绿肥的增产节肥效应与机制. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(12): 2115-2126. | |
| 9 | Ning S Q, Jiang R, Li Z M, et al. Effects of three kinds of green manure on the yield and quality of flue-cured tobacco, soil nutrients and enzyme activities. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2023: 1-10. (2023-8-29) [2024-3-27] https: //link.cnki.net/urlid/11.5498.S.20230828.1557.002. |
| 宁诗琪, 蒋如, 李治模, 等. 三种绿肥对烤烟产质量及土壤养分和酶活性的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2023: 1-10. (2023-8-29) [2024-3-27] https: //link.cnki.net/urlid/11.5498.S.20230828.1557.002. | |
| 10 | Sinsabaugh R L, Follstad Shah J J. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and ecological theory. Annual Review of Ecology Evolution and Systematics, 2012, 43(1): 313-343. |
| 11 | Curtright A J, Tiemann L K. Intercropping increases soil extracellular enzyme activity: A meta-analysis. Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment, 2021, 319(2): 107489. |
| 12 | Xu M, Li W, Wang J, et al. Soil ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals microbial phosphorus limitation after vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau, China. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 815: 152918. |
| 13 | Yu J, Bing H, Chang R, et al. Microbial metabolic limitation response to experimental warming along an altitudinal gradient in alpine grasslands, eastern Tibetan Plateau. Catena, 2022, 214: 106243. |
| 14 | Jia R, Zhou J, Chu J, et al. Insights into the associations between soil quality and ecosystem multifunctionality driven by fertilization management: A case study from the North China Plain. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 362: 132265. |
| 15 | Zheng W, Gong Q, Zhao Z, et al. Changes in the soil bacterial community structure and enzyme activities after intercrop mulch with cover crop for eight years in an orchard. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2018, 86(1): 34-41. |
| 16 | Wang H, Zhou G P, Chang D N, et al.Nitrogen reduction effects in double rice by planting and returning Chinese milk vetch to the field in Northern Hunan Province. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(1): 33-44. |
| 王慧, 周国朋, 常单娜, 等. 湘北双季稻区种植翻压紫云英的氮肥减施效应. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(1): 33-44. | |
| 17 | Zheng W, Gong Q, Lv F, et al. Tree-scale spatial responses of extracellular enzyme activities and stoichiometry to different types of fertilization and cover crop in an apple orchard. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2020, 99(1): 103207. |
| 18 | Fang Y T, Zhang L M, Jiao Y G, et al. Corrigendum: Tobacco rotated with rapeseed for soil-borne Phytophthora pathogen biocontrol: mediated by rapeseed root exudates. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 372. |
| 19 | Liu Y X, Zhang H, Yao Y J, et al. Study on the mechanism of biological control of tobacco bacterial wilt with different green manures. Pratacultural Science, 2022, 39(11): 2326-2337. |
| 刘艳霞, 张恒, 姚云静, 等. 不同绿肥防控烟草青枯病的机理. 草业科学, 2022, 39(11): 2326-2337. | |
| 20 | Zhao W J, Xue K Z, Yang J Z, et al. Effect of various amounts of smooth vetch on tobacco yield and quality under reduced nitrogen fertilizer application. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 50(16): 73-78. |
| 赵文军, 薛开政, 杨继周, 等. 氮肥减施下光叶紫花苕不同翻压量对烟草产量和品质的影响. 江苏农业科学, 2022, 50(16): 73-78. | |
| 21 | Zha H B, Zhao F, Tao Y P, et al. Effects on the agronomic traits, economic characters and chemical composition of flue-cured tobacco by green manures application. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 58(6): 101-103. |
| 查宏波, 赵芳, 陶永萍, 等. 绿肥翻压还田对连作烟地烤烟农艺性状、经济性状和化学成分的影响. 湖北农业科学, 2019, 58(6): 101-103. | |
| 22 | Bao S D. Soil agrochemical analysis (the third edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第3版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 23 | Ai C. Carbon and nitrogen transformations and microbial diversity in the rhizosphere soil under long-term fertilization practices. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2015. |
| 艾超. 长期施肥下根际碳氮转化与微生物多样性研究. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2015. | |
| 24 | Kuzyakov Y, Gunina K, Zamanian K, et al. New approaches for evaluation of soil health, sensitivity and resistance to degradation. Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering, 2020, 7(3): 282-288. |
| 25 | Wang P H, Zhang Q W, Shi Y L, et al. Effects of straw mulching and organic fertilizer on the stoichiometry of soil extracellular enzymes in eroded slope farmland. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(3): 459-471. |
| 王珮环, 张晴雯, 石玉龙, 等. 秸秆覆盖和配施有机肥对侵蚀坡耕地土壤胞外酶化学计量特征的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(3): 459-471. | |
| 26 | Moorhead D L, Sinsabaugh R L, Hill B H, et al. Vector analysis of ecoenzyme activities reveal constraints on coupled C, N and P dynamics. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2016, 93(10): 1-7. |
| 27 | Wang J L, Sun C F, Cheng Y G, et al. Effects of different green manures on chemical properties and enzyme activities of reclaimed soil. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2022(9): 85-93. |
| 王晋龙, 孙崇凤, 程永钢, 等. 不同绿肥对复垦地土壤化学性状及酶活性的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022(9): 85-93. | |
| 28 | Thorup-Kristensen K, Magid J, Jensen L S. Catch crops and green manures as biological tools in nitrogen management in temperate zones. Advances in Agronomy, 2003, 79(2): 227-302. |
| 29 | Zhou G, Gao S, Xu C, et al. Rational utilization of leguminous green manure to mitigate methane emissions by influencing methanogenic and methanotrophic communities. Geoderma, 2020, 361(6): 114071. |
| 30 | Huang Z, Cui C, Cao Y, et al. Tea plant-legume intercropping simultaneously improves soil fertility and tea quality by changing Bacillus species composition. Horticulture Research, 2022, 9: uhac046 |
| 31 | Wang L, Guan Y X, Chen Z, et al. Comparison of nutrient accumulation of different green manures and the effects on rice yield. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 36(5): 1139-1143. |
| 王琳, 管永祥, 陈震, 等. 不同种类绿肥养分积累比较及其对水稻产量的影响. 江苏农业学报, 2020, 36(5): 1139-1143. | |
| 32 | Zhao X, Liu B Y, Liu S L, et al. Sustaining crop production in China’s cropland by crop residue retention: A meta-analysis. Land Degradation and Development, 2020, 31(6): 694-709. |
| 33 | Zhou G, Gao S, Lu Y, et al. Co-incorporation of green manure and rice straw improves rice production, soil chemical, biochemical and microbiological properties in a typical paddy field in southern China. Soil and Tillage Research, 2020, 197: 104499. |
| 34 | Ni M Y, Zhang Q F, Gao J T, et al. Seasonal response of extracellular enzyme activity to precipitation exclusion in a subtropical Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(6): 2119-2127. |
| 倪梦颖, 张秋芳, 高金涛, 等. 亚热带杉木人工林土壤胞外酶活性对隔离降雨的季节响应. 生态学报, 2018, 38(6): 2119-2127. | |
| 35 | Guo Z M, Zhang X Y, Green S M, et al. Soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry along a gradient of vegetation restoration at the Karst Critical Zone Observatory in Southwest China. Land Degradation and Development, 2019, 30(16): 1916-1927. |
| 36 | Liu S, Xu G X, Chen M, et al. Effects of slope aspect on soil enzyme activity and microbial nutrient limitation in subalpine region of western Sichuan, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2023, 34(11): 2993-3002. |
| 刘顺, 许格希, 陈淼, 等. 坡向对川西亚高山土壤酶活性和微生物养分限制的影响. 应用生态学报, 2023, 34(11): 2993-3002. | |
| 37 | Burns R G, DeForest J L, Marxsen J, et al. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: Current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2013, 58(11): 216-234. |
| 38 | Xu Z W, Yu G R, Zhang X Y, et al. Soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry in forest ecosystems along the North-South Transect in eastern China (NSTEC). Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2017, 104(10): 152-163. |
| [1] | 张丽星, 海春兴, 常耀文, 高晓媚, 高文邦, 解云虎. 羊草及芨芨草草原和西北针茅草原土壤质量评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 68-79. |
| [2] | 刘江, 吕涛, 张立欣, 叶丽娜, 刘向阳, 代香荣, 王伟伟, 丁茹. 基于主成分分析的不同种植年限甘草地土壤质量评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 162-171. |
| [3] | 宿婷婷, 马红彬, 周瑶, 贾希洋, 张蕊, 张双乔, 胡艳莉. 黄土丘陵典型草原土壤理化性质对生态恢复措施的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(4): 34-46. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||